C++进阶--哈希表模拟实现unordered_set和unordered_map
哈希表模拟实现unordered_set和unordered_map
- 一、定义哈希表的结点结构
- 二、定义哈希表的迭代器
- 三、定义哈希表的结构
- 3.1 begin()和end()的实现
- 3.2 默认成员函数的实现
- 3.2.1 构造函数的实现
- 3.2.2 拷贝构造函数的实现(深拷贝)
- 3.2.3 赋值运算符重载函数的实现(现代写法)
- 3.2.4 析构函数的实现
- 四、实现哈希表的相关接口
- 4.1 查找结点
- 4.2 插入结点
- 4.3 删除结点
- 五、针对除留余数法的取模问题
- 六、unordered_set的模拟实现
- 七、unordered_map的模拟实现
- 八、完整代码
- 8.1 HashTable.h
- 8.2 UnorderedSet.h
- 8.3 UnorderedMap.h
- 8.4 test.cpp
一、定义哈希表的结点结构
这里直接拿自己写的开散列(原先是KV模型)改造下,使其既可兼容K模型,也可兼容KV模型:
哈希表里面具体存的是什么类型的元素,是由模板参数T来决定:
- 如果是unordered_set,传给T就是Key
- 如果是unordered_map,传给T的就是pair<const Key, V>
哈希表结点结构:
template<class T>struct HashNode{HashNode<T>* _next;T _data;HashNode(const T& data):_next(nullptr),_data(data){}};
二、定义哈希表的迭代器
迭代器的结构:
注意:哈希表迭代器封装的是结点指针和哈希表指针,因为要在哈希表中找下一个桶,所以要用到哈希表指针
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash >class HashTable;template<class K, class T,class Ref,class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash >struct __HashIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;/*template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class HashTable*/typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash> HT;typedef __HashIterator < K, T,Ref,Ptr,KeyOfT, Hash> Self;typedef __HashIterator < K, T,T&,T*,KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator;Node* _node;const HT* _ht;
};
在构造正向迭代器时,我们不仅需要对应哈希结点的指针,还需要该哈希结点所在哈希表的地址。
__HashIterator(Node* node,const HT* ht):_node(node),_ht(ht)
{}__HashIterator(const Iterator& it):_node(it._node), _ht(it._ht)
{}
当对正向迭代器进行解引用操作时,我们直接返回对应结点数据的引用即可
Ref operator*()
{return _node->_data;
}
当对正向迭代器进行->操作时,我们直接返回对应结点数据的地址即可
Ptr operator->()
{return &_node->_data;
}
当我们需要比较两个迭代器是否相等时,只需要判断这两个迭代器所封装的结点是否是同一个即可。
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{return _node!=s._node;
}
++运算符重载函数的实现逻辑并不是很难,我们只需要知道如何找到当前结点的下一个结点即可。
- 若当前结点不是当前哈希桶中的最后一个结点,则++后走到当前哈希桶的下一个结点。
- 若当前结点是当前哈希桶的最后一个结点,则++后走到下一个非空哈希桶的第一个结点。
Self& operator++(){if (_node->_next != nullptr){_node = _node->_next;}else{//找下一个不为空的桶KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;//算出我当前的桶位置size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();++hashi;while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size()){if (_ht->_tables[hashi]){_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];break;}else{++hashi;}}//没有找到不为空的桶if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size()){_node = nullptr;}}return *this;}
三、定义哈希表的结构
一个数组,数组中存储着各个链表头结点的地址。
注意:
这里有一个私有成员访问的问题,我们在哈希表迭代器中封装了一个哈希表指针,当一个桶遍历完成时,用来在哈希表中找下一个桶,但哈希表_tables是私有成员,无法访问,所以需要将迭代器类模板声明为友元
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>class HashTable{template<class K,class T,class Ref,class Ptr,class KeyOfT,class Hash>friend struct __HashIterator;typedef HashNode<T> Node;public:typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&,T*,KeyOfT, Hash> iterator;typedef __HashIterator<K, T, const T&,const T*,KeyOfT, Hash> const_iterator;private:vector<Node*> _tables; //指针数组size_t _n=0; //存储有效数据个数};
3.1 begin()和end()的实现
注意:this指针指向当前调用begin()成员函数的哈希表对象
- begin函数:返回哈希表中第一个非空哈希桶中的第一个结点的正向迭代器。
- end函数:返回空指针的正向迭代器。
iterator begin(){Node* cur = nullptr;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i){cur = _tables[i];if (cur){break;}}return iterator(cur, this);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = nullptr;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i){cur = _tables[i];if (cur){break;}}return const_iterator(cur, this);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr, this);}
3.2 默认成员函数的实现
3.2.1 构造函数的实现
哈希表中有两个成员变量,当我们实例化一个对象时:
- _table会自动调用vector的默认构造函数进行初始化
- _n会根据我们所给的缺省值被设置为0
vector<Node*> _table; //哈希表
size_t _n = 0; //哈希表中的有效元素个数
因此我们不需要编写构造函数,使用默认生成的构造函数就足够了,但是由于我们后面需要编写拷贝构造函数,编写了拷贝构造函数后,默认的构造函数就不会生成了,此时我们需要使用default关键字显示指定生成默认构造函数。
//构造函数
HashTable() = default; //显示指定生成默认构造函数
3.2.2 拷贝构造函数的实现(深拷贝)
哈希表在拷贝时需要进行深拷贝,否则拷贝出来的哈希表和原哈希表中存储的都是同一批结点。
哈希表的拷贝函数实现逻辑如下:
1.将哈希表的大小调整为ht._table的大小
2.将ht._table每个桶当中的结点一个个拷贝到自己的哈希表中
3.更改哈希表当中的有效数据个数
//拷贝构造函数
HashTable(const HashTable& ht)
{//1、将哈希表的大小调整为ht._table的大小_table.resize(ht._table.size());//2、将ht._table每个桶当中的结点一个个拷贝到自己的哈希表中(深拷贝)for (size_t i = 0; i < ht._table.size(); i++){if (ht._table[i]) //桶不为空{Node* cur = ht._table[i];while (cur) //将该桶的结点取完为止{Node* copy = new Node(cur->_data); //创建拷贝结点//将拷贝结点头插到当前桶copy->_next = _table[i];_table[i] = copy;cur = cur->_next; //取下一个待拷贝结点}}}//3、更改哈希表当中的有效数据个数_n = ht._n;
}
3.2.3 赋值运算符重载函数的实现(现代写法)
实现赋值运算符重载函数时,可以通过参数间接调用拷贝构造函数,之后将拷贝构造出来的哈希表和当前哈希表的两个成员变量分别进行交换即可,当赋值运算符重载函数调用结束后,拷贝构造出来的哈希表会因为出了作用域而被自动析构,此时原哈希表之前的数据也就顺势被释放了。
//赋值运算符重载函数
HashTable& operator=(HashTable ht)
{//交换哈希表中两个成员变量的数据_table.swap(ht._table);swap(_n, ht._n);return *this; //支持连续赋值
}
3.2.4 析构函数的实现
因为哈希表当中存储的结点都是new出来的,因此在哈希表被析构时必须进行结点的释放。在析构哈希表时我们只需要一次取出非空的哈希桶,遍历哈希桶当中的结点并进行释放即可。
~HashTable(){for (auto& cur : _tables){while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}cur = nullptr;}}
四、实现哈希表的相关接口
4.1 查找结点
查找结点接口中,需要获取不同类型元素的关键码key,因为元素间的比较是通过key值来比较的,以及通过元素关键码key取模计算出哈希位置。
所以需要借助两个仿函数类:
- 仿函数类KeyOfT,获取不同类型的data中的关键码key值(如果data是key就取key,如果是pair就取first)
- 仿函数类Hash,有些元素关键码key的类型不能直接取模,需要将其转换成可以取模的size_t类型
iterator Find(const K& key){if (_tables.size() == 0)return end();KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return iterator(cur,this);}cur = cur->_next;}return end();}
4.2 插入结点
插入结点接口中,需要获取不同类型元素的关键码key,因为元素间的比较是通过key值来比较的,以及通过元素关键码key取模计算出哈希位置。
所以需要借助两个仿函数类:
- 仿函数类KeyOfT,获取不同类型的data中的关键码key值(如果data是key就取key,如果是pair就取first)
- 仿函数类Hash,有些元素关键码key的类型不能直接取模,需要将其转换成可以取模的size_t类型
函数的返回值为pair<iterator,bool>类型对象:
- 目的是为了在unordered_set和unordered_map中模拟实现operator[]运算符重载函数
插入元素接口功能:插入元素前,会通过该元素的关键码key检查该元素是否已在哈希表中(不允许冗余):
- 如果在,返回:pair<指向该元素的迭代器,false>
- 如果不在,先插入结点,再返回:pair<指向该元素的迭代器,true>
pair < iterator, bool > Insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;iterator it = Find(kot(data));if (it!=end()){return make_pair(it,false);}Hash hash;//负载因子==1时扩容if (_n == _tables.size()){/*size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;HashTable<K, V> newht;newht.resize(newsize);for (auto cur : _tables){while (cur){newht.Insert(cur->_kv);cur = cur->_next;}}_tables.swap(newht._tables);*/size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newtables(newsize, nullptr);//for(Node*& cur:_tables)for (auto& cur : _tables){/*for (size_t i=0;i<_tables.size();++i){Node*& cur = _tables[i];*/while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;size_t hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newtables.size();//头插到新表cur->_next = newtables[hashi];newtables[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}}_tables.swap(newtables);}size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();//头插Node* newnode = new Node(data);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;++_n;return make_pair(iterator(newnode,this),false);}
4.3 删除结点
删除结点接口中,需要获取不同类型元素的关键码key,因为元素间的比较是通过key值来比较的,以及通过元素关键码key取模计算出哈希位置。
所以需要借助两个仿函数类:
- 仿函数类KeyOfT,获取不同类型的data中的关键码key值(如果data是key就取key,如果是pair就取first)
- 仿函数类Hash,有些元素关键码key的类型不能直接取模,需要将其转换成可以取模的size_t类型
bool Erase(const K& key){Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* prev = nullptr;Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) ==key){if (prev == nullptr){_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;}else{prev->_next = cur->_next;}delete cur;return true;}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}}return false;}
五、针对除留余数法的取模问题
实现哈希表,计算元素关键码对应哈希位置的哈希函数采用的是除留余数法,需要传仿函数将不能取模的类型转换成可以取模的size_t类型。
这里给出针对普通类型取模和string类型取模的仿函数,放到全局域中,方便模拟unordered_set和unordered_map时使用。
template<class K>struct HashFunc{size_t operator()(const K& key){return key;}};//特化template<>struct HashFunc<string>{//BKDRsize_t operator()(const string & s){//return s[0];size_t hash = 0;for (auto ch : s){hash += ch;hash *= 31;}return hash;}};
六、unordered_set的模拟实现
实现unordered_set的各个接口时,就只需要调用底层哈希表对应的接口就行了
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"namespace set
{template<class K>class unordered_set{public:struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair < iterator, bool > insert(const K& key){return _ht.Insert(key);}iterator find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _ht;};void print(const unordered_set<int>& s){unordered_set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){//*it = 1;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test_unordered_set(){int a[] = { 3,33,2,13,5,12,1002 };unordered_set<int> s;for (auto e : a){s.insert(e);}s.insert(103);unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;print(s);}
}
七、unordered_map的模拟实现
实现unordered_map的各个接口时,也是调用底层哈希表对应的接口就行了,此外还需要实现[ ]运算符的重载
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"namespace map
{template<class K,class V>class unordered_map{public:struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair < iterator, bool > insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}iterator find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K,V>, MapKeyOfT> _ht;};void test_unordered_map1(){unordered_map<int,int> m;m.insert(make_pair(1,1));m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));m.insert(make_pair(2, 2));unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();while (it != m.end()){/*it->first = 1;it->second = 1;*/cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}void test_unordered_map2(){string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜","苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };unordered_map<string, int> countMap;for (auto& e : arr){countMap[e]++;}for (auto& kv : countMap){cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;}}
}
八、完整代码
8.1 HashTable.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>namespace OpenAddress
{enum State{EMPTY,EXIST,DELETE};template <class K, class V>struct HashData{pair<K, V> _kv;State _state = EMPTY;};template<class K, class V>class HashTable{public:bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (Find(kv.first))return false;//负载因子超过0.7就扩容//if((double)_n/(double)_tables.size()>=0.7)//if (_tables.size()==0 || _n * 10 / _tables.size() >= 7)//{// 1、表为空,扩不上去// 2、光扩容无法访问,size没变// //_tables.reserve(_tables.capacity() * 2); //不能这么做// size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size()*2;// //_tables.resize(newsize); //有问题// vector<HashData> newtables(newsize);// //遍历旧表,重新映射到新表// for (auto& data : _tables)// {// if (data._state==EXIST)// {// //重新算在新表的位置// size_t i = 1;// size_t index = hashi;// while (newtables[hashi]._state == EXIST)// {// index = hashi + i;// index %= newtables.size();// ++i;// }// newtables[index]._kv = data._kv;// newtables[index]._state = EXIST;// }// }// _tables.swap(newtables);if (_tables.size() == 0 || _n * 10 / _tables.size() >= 7){size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;HashTable<K, V> newht;newht._tables.resize(newsize);//遍历旧表,重新映射到新表for (auto& data : _tables){if (data._state == EXIST){newht.Insert(data._kv);}}_tables.swap(newht._tables);}size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();//线性探测size_t i = 1;size_t index = hashi;while (_tables[index]._state == EXIST){index = hashi + i;index %= _tables.size();++i;}_tables[index]._kv = kv;_tables[index]._state = EXIST;_n++;return true;}HashData<K, V>* Find(const K& key){if (_tables.size() == 0){return nullptr;}size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();//线性探测size_t i = 1;size_t index = hashi;while (_tables[index]._state != EMPTY){if (_tables[index]._state == EXIST &&_tables[index]._kv.first == key){return &_tables[index];}index = hashi + i;index %= _tables.size();++i;//如果已经查找一圈,那么说明全是存在+删除if (index == hashi){break;}}return nullptr;}bool Erase(const K& key){HashData<K, V>* ret = Find(key);if (ret){ret->_state = DELETE;--_n;return true;}else{return false;}}private:vector<HashData<K, V>> _tables;size_t _n = 0; //存储的数据个数/*HashData* tables;size_t size;size_t _capacity;*/};void TestHashTable1(){int a[] = { 3,33,2,13,5,12,1002 };HashTable<int, int> ht;for (auto e : a){ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));}ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));if (ht.Find(13)){cout << "13在" << endl;}else{cout << "13不在" << endl;}ht.Erase(13);if (ht.Find(13)){cout << "13在" << endl;}else{cout << "13不在" << endl;}}
}namespace HashBucket
{template<class T>struct HashNode{HashNode<T>* _next;T _data;HashNode(const T& data):_next(nullptr),_data(data){}};template<class K>struct HashFunc{size_t operator()(const K& key){return key;}};//特化template<>struct HashFunc<string>{//BKDRsize_t operator()(const string & s){//return s[0];size_t hash = 0;for (auto ch : s){hash += ch;hash *= 31;}return hash;}};//前置声明template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash >class HashTable;template<class K, class T,class Ref,class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash >struct __HashIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;/*template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class HashTable*/typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash> HT;typedef __HashIterator < K, T,Ref,Ptr,KeyOfT, Hash> Self;typedef __HashIterator < K, T,T&,T*,KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator;Node* _node;const HT* _ht;__HashIterator(Node* node,const HT* ht):_node(node),_ht(ht){}__HashIterator(const Iterator& it):_node(it._node), _ht(it._ht){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node!=s._node;}//itSelf& operator++(){if (_node->_next != nullptr){_node = _node->_next;}else{//找下一个不为空的桶KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;//算出我当前的桶位置size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();++hashi;while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size()){if (_ht->_tables[hashi]){_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];break;}else{++hashi;}}//没有找到不为空的桶if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size()){_node = nullptr;}}return *this;}};template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>class HashTable{template<class K,class T,class Ref,class Ptr,class KeyOfT,class Hash>friend struct __HashIterator;typedef HashNode<T> Node;public:typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&,T*,KeyOfT, Hash> iterator;typedef __HashIterator<K, T, const T&,const T*,KeyOfT, Hash> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = nullptr;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i){cur = _tables[i];if (cur){break;}}return iterator(cur, this);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = nullptr;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i){cur = _tables[i];if (cur){break;}}return const_iterator(cur, this);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr, this);}~HashTable(){for (auto& cur : _tables){while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}cur = nullptr;}}iterator Find(const K& key){if (_tables.size() == 0)return end();KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return iterator(cur,this);}cur = cur->_next;}return end();}bool Erase(const K& key){Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* prev = nullptr;Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) ==key){if (prev == nullptr){_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;}else{prev->_next = cur->_next;}delete cur;return true;}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}}return false;}pair < iterator, bool > Insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;iterator it = Find(kot(data));if (it!=end()){return make_pair(it,false);}Hash hash;//负载因子==1时扩容if (_n == _tables.size()){/*size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;HashTable<K, V> newht;newht.resize(newsize);for (auto cur : _tables){while (cur){newht.Insert(cur->_kv);cur = cur->_next;}}_tables.swap(newht._tables);*/size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newtables(newsize, nullptr);//for(Node*& cur:_tables)for (auto& cur : _tables){/*for (size_t i=0;i<_tables.size();++i){Node*& cur = _tables[i];*/while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;size_t hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newtables.size();//头插到新表cur->_next = newtables[hashi];newtables[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}}_tables.swap(newtables);}size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();//头插Node* newnode = new Node(data);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;++_n;return make_pair(iterator(newnode,this),false);}size_t MaxBucketSize(){size_t max = 0;for (size_t i=0;i<_tables.size();++i){auto cur = _tables[i];size_t size = 0;while (cur){++size;cur = cur->_next;}printf("[%d]->%d\n", i,size);if (size > max){max = size;}}return max;}private:vector<Node*> _tables; //指针数组size_t _n=0; //存储有效数据个数};//void TestHashTable1()//{// int a[] = { 3,33,2,13,5,12,1002 };// HashTable<int, int> ht;// for (auto e : a)// {// ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));// }// ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));// ht.Insert(make_pair(25, 25));// ht.Insert(make_pair(35, 35));// ht.Insert(make_pair(45, 45));//}//void TestHashTable2()//{// int a[] = { 3,33,2,13,5,12,1002 };// HashTable<int, int> ht;// for (auto e : a)// {// ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));// }// ht.Erase(12);// ht.Erase(3);// ht.Erase(33);//}//struct HashStr//{// //BKDR// size_t operator()(const string& s)// {// //return s[0];// size_t hash = 0;// for (auto ch : s)// {// hash += ch;// hash *= 31;// }// return hash;// }//};//void TestHashTable3()//{// //HashTable<string, string, HashStr> ht;// HashTable<string, string> ht;// ht.Insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));// ht.Insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));// ht.Insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));// ht.Insert(make_pair("right", "右边"));// ht.Insert(make_pair("", "右边"));// HashStr hashstr;// cout << hashstr("abcd") << endl;// cout << hashstr("bcda") << endl;// cout << hashstr("aadd") << endl;// cout << hashstr("eat") << endl;// cout << hashstr("ate") << endl;//}//void TestHashTable4()//{// size_t N = 10000;// HashTable<int, int> ht;// srand(time(0));// for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)// {// size_t x = rand();// ht.Insert(make_pair(x, x));// }// cout << ht.MaxBucketSize() << endl;//}增删改查的时间复杂度:O(1)1.负载因子控制1.单个桶超过一定长度,这个桶改成挂红黑树}
8.2 UnorderedSet.h
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"namespace set
{template<class K>class unordered_set{public:struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair < iterator, bool > insert(const K& key){return _ht.Insert(key);}iterator find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _ht;};void print(const unordered_set<int>& s){unordered_set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){//*it = 1;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test_unordered_set(){int a[] = { 3,33,2,13,5,12,1002 };unordered_set<int> s;for (auto e : a){s.insert(e);}s.insert(103);unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;print(s);}
}
8.3 UnorderedMap.h
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"namespace map
{template<class K,class V>class unordered_map{public:struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair < iterator, bool > insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}iterator find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K,V>, MapKeyOfT> _ht;};void test_unordered_map1(){unordered_map<int,int> m;m.insert(make_pair(1,1));m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));m.insert(make_pair(2, 2));unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();while (it != m.end()){/*it->first = 1;it->second = 1;*/cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}void test_unordered_map2(){string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜","苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };unordered_map<string, int> countMap;for (auto& e : arr){countMap[e]++;}for (auto& kv : countMap){cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;}}
}
8.4 test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include <iostream>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;#include "UnorderedMap.h"
#include "UnorderedSet.h"int main()
{//set::test_unordered_set();map::test_unordered_map1();return 0;
}
相关文章:

C++进阶--哈希表模拟实现unordered_set和unordered_map
哈希表模拟实现unordered_set和unordered_map 一、定义哈希表的结点结构二、定义哈希表的迭代器三、定义哈希表的结构3.1 begin()和end()的实现3.2 默认成员函数的实现3.2.1 构造函数的实现3.2.2 拷贝构造函数的实现(深拷贝)3.2.3 赋值运算符重载函数的实…...
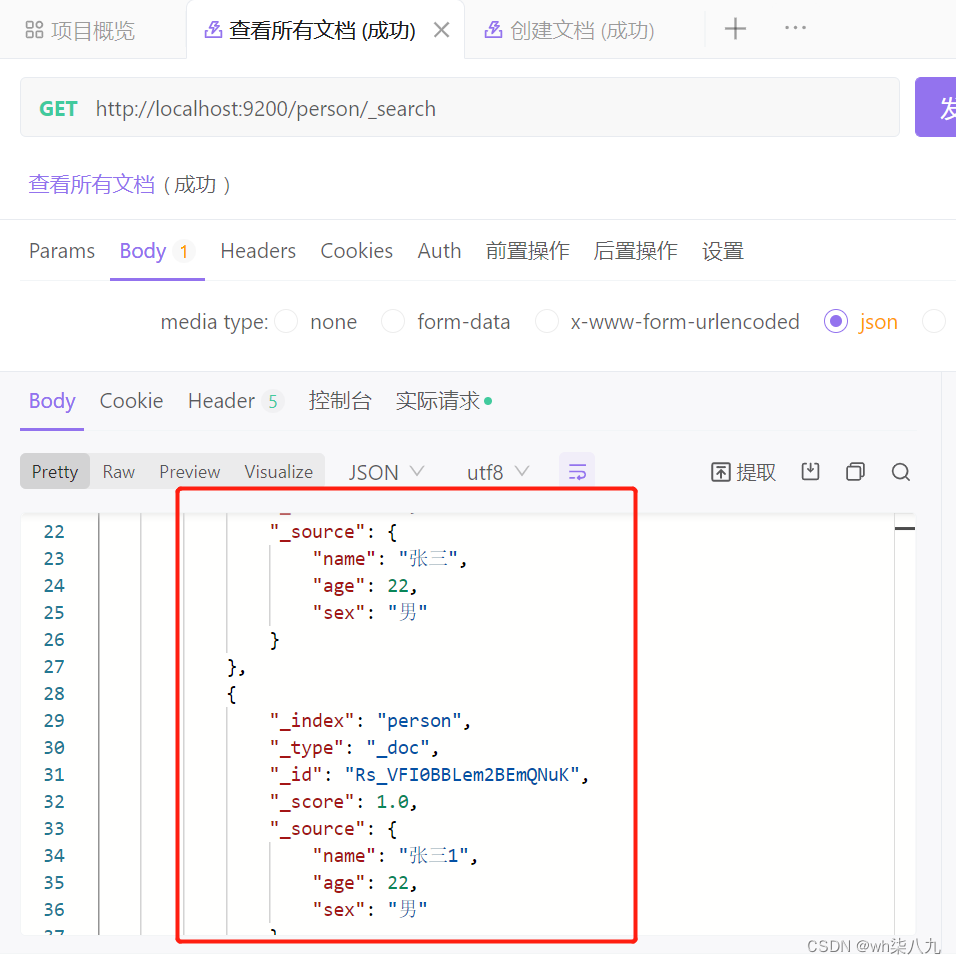
Elasticsearch各种高级文档操作
本文来记录下Elasticsearch各种文档操作 文章目录 初始化文档数据查询所有文档匹配查询文档关键字精确查询文档多关键字精确查询文档字段匹配查询文档指定查询字段查询文档过滤字段查询文档概述指定想要显示的字段示例指定不想要显示的字段示例 组合查询文档范围查询文档概述使…...
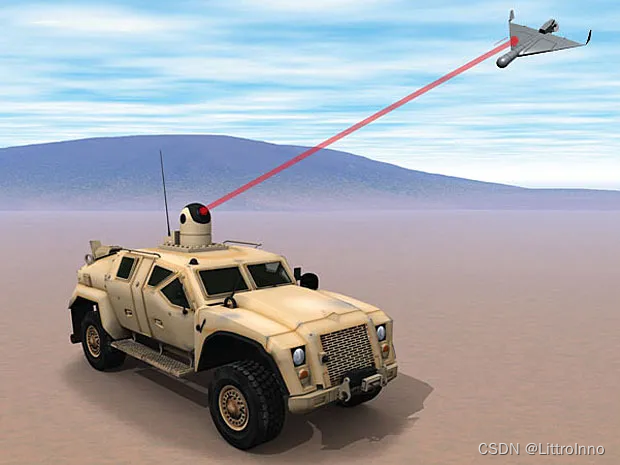

激光无人机打击系统——光束控制和指向系统
激光无人机(UAV)打击系统中的光束控制和指向系统通常包括以下几个关键组件和技术: 激光发射器:这是系统的核心,负责生成高能量的激光束。常用的激光类型包括固体激光器、化学激光器、光纤激光器等,选择取决…...

pycharm import torch
目录 1 安装 2 conda环境配置 3 测试 开始学习Pytorch! 1 安装 我的电脑 Windows 11 Python 3.11 Anaconda3-2023.09-0-Windows-x86_64.exe cuda_11.8.0_522.06_windows.exe pytorch (管理员命令行安装) pycharm-community-2023.3.2.exe 2 c…...

flask 与小程序 购物车删除和编辑库存功能
编辑 : 数量加减 价格汇总 数据清空 mina/pages/cart/index.wxml <!--index.wxml--> <view class"container"><view class"title-box" wx:if"{{ !list.length }}">购物车空空如也~</view>…...

蓝桥杯真题(Python)每日练Day3
题目 题目分析 为了找到满足条件的放置方法,可以带入总盘数为2和3的情景,用递归做法实现。 2. A中存在1 2两个盘,为了实现最少次数放入C且上小下大,先将1放入B,再将2放入C,最后将1放入C即可。同理当A中存在…...
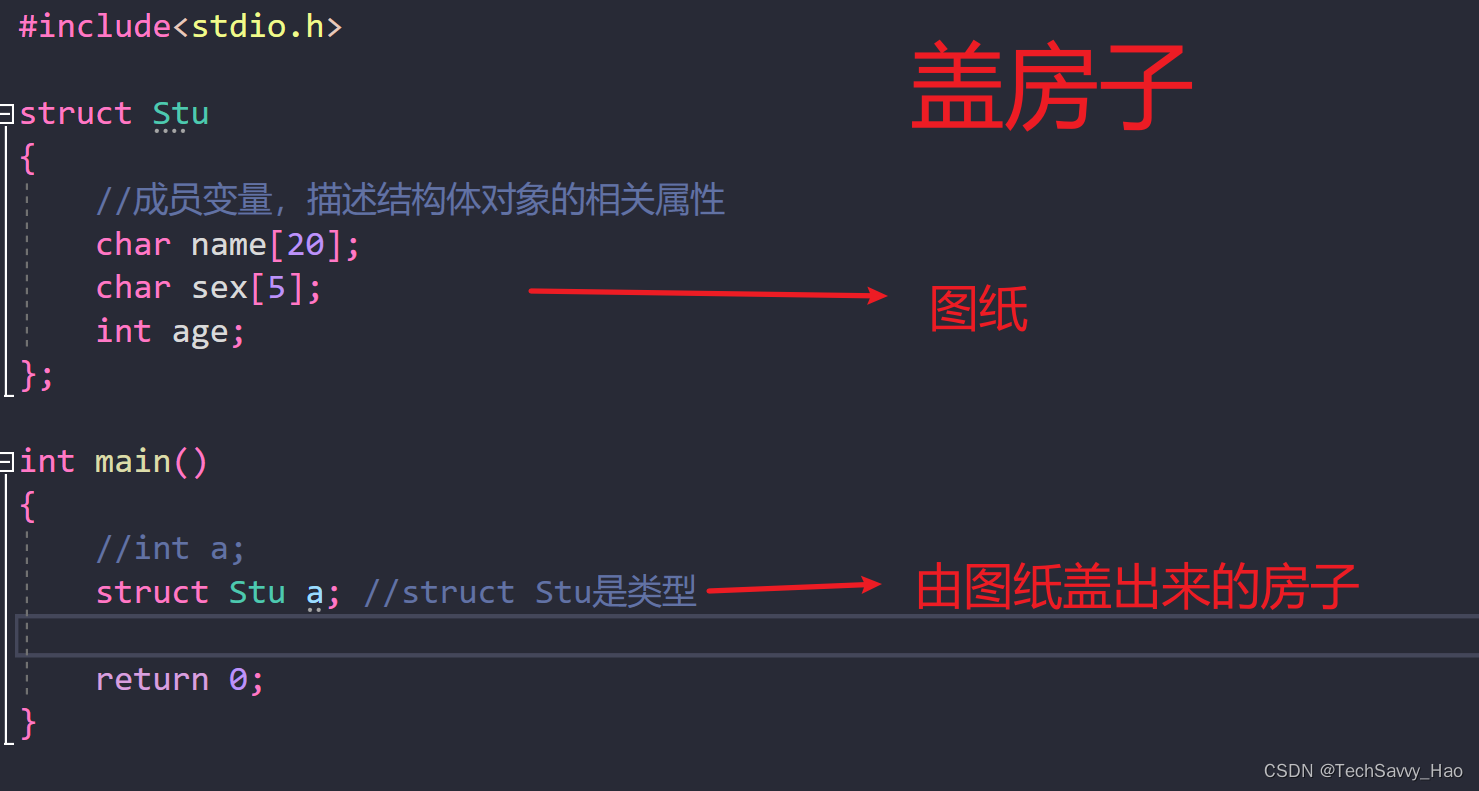
结构体大揭秘:代码中的时尚之选(上)
目录 结构结构的声明结构成员的类型结构体变量的定义和初始化结构体成员的访问结构体传参 结构 结构是一些值的集合,这些值被称为成员变量。之前说过数组是相同类型元素的集合。结构的每个成员可以是不同类型的变量,当然也可以是相同类型的。 我们在生活…...
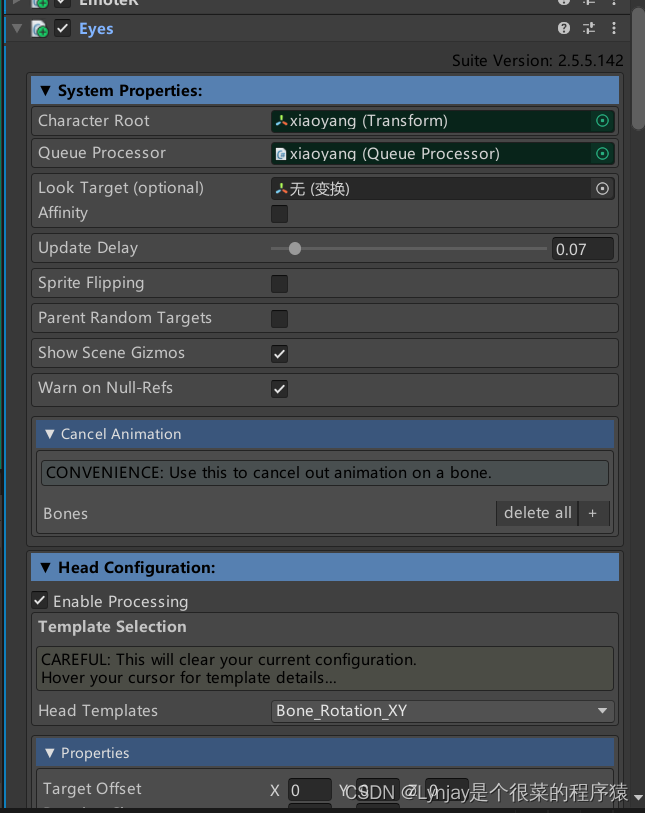
【unity学习笔记】语音驱动blendershape
1.导入插件 https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/tools/animation/salsa-lipsync-suite-148442 1.选择小人,点击添加组件 分别加入组件: SALSA EmoteR Eyes Queue Processor(必须加此脚本):控制前三个组件的脚本。…...
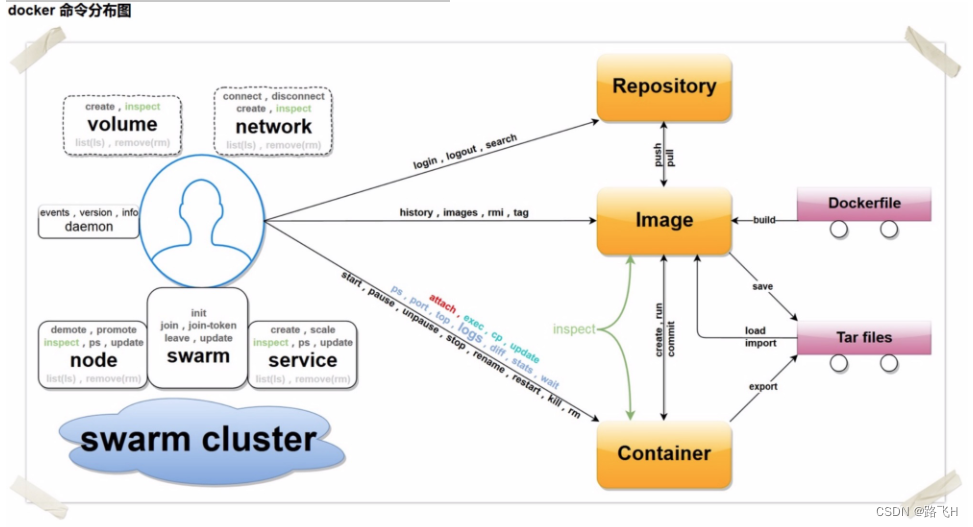
docker常用基础命令
文章目录 1、Docker 环境信息命令1.1、docker info1.2、docker version 2、系统日志信息常用命令2.1、docker events2.2、docker logs2.3、docker history 3、容器的生命周期管理命令3.1、docker create3.2、docker run 总结 1、Docker 环境信息命令 1.1、docker info 显示 D…...

自动驾驶中的坐标系
自动驾驶中的坐标系 自动驾驶中的坐标系 0.引言1.相机传感器坐标系2.激光雷达坐标系3.车体坐标系4.世界坐标系4.1.地理坐标系4.2.投影坐标系4.2.1.投影方式4.2.2.墨卡托(Mercator)投影4.2.3.高斯-克吕格(Gauss-Kruger)投影4.2.4.通用横轴墨卡托UTM(UniversalTransve…...

js数组的截取和合并
在JavaScript中,你可以使用slice()方法来截取数组,使用concat()方法来合并数组。 截取数组 slice()方法返回一个新的数组对象,这个对象是一个由原数组的一部分浅复制而来。它接受两个参数,第一个参数是开始截取的位置(…...

2024美赛数学建模思路 - 案例:感知机原理剖析及实现
文章目录 1 感知机的直观理解2 感知机的数学角度3 代码实现 4 建模资料 # 0 赛题思路 (赛题出来以后第一时间在CSDN分享) https://blog.csdn.net/dc_sinor?typeblog 1 感知机的直观理解 感知机应该属于机器学习算法中最简单的一种算法,其…...

大中台,小前台:打造快速响应市场的企业竞争力
2015年,大家都听过“大中台、小前台”战略,听上去很牛。“大中台、小前台”背后完成了一件事情:把阿里巴巴和支付宝所有的基础技术全部统一到阿里云上,这是个重大的技术变革。为了完成这个技术变革,阿里巴巴做了非常好…...

SpringCloud Alibaba 深入源码 - Nacos 和 Eureka 的区别(健康检测、服务的拉取和订阅)
目录 一、Nacos 和 Eureka 的区别 1.1、以 Nacos 注册流程来解析区别 一、Nacos 和 Eureka 的区别 1.1、以 Nacos 注册流程来解析区别 a)首先,我们的服务启动时。都会把自己的信息提交给注册中心,然后注册中心就会把信息保存下来. 注册的…...

Java复习_3
填空题 课程推荐的 jdk 下载网址为 jdk.java.net 使用命令行编译程序:javac -d bin stc*.java 使用命令行运行程序: java -cp bin 类名 java 语言标识符:字母、数字、下划线和美元符号,数字不能做首字母 java 语言中标识符区…...
分类预测 | Matlab实现KPCA-EBWO-SVM分类预测,基于核主成分分析和改进的白鲸优化算法优化支持向量机分类预测
分类预测 | Matlab实现KPCA-EBWO-SVM分类预测,基于核主成分分析和改进的白鲸优化算法优化支持向量机分类预测 目录 分类预测 | Matlab实现KPCA-EBWO-SVM分类预测,基于核主成分分析和改进的白鲸优化算法优化支持向量机分类预测分类效果基本描述程序设计参…...

力扣hot100 找到字符串中所有字母异位词 滑动窗口 双指针 一题双解
Problem: 438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词 文章目录 思路滑动窗口 数组滑动窗口 双指针 思路 👩🏫 参考题解 滑动窗口 数组 ⏰ 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 🌎 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) class Solution { // 滑动窗口 …...

PG DBA培训21:PostgreSQL性能优化之基准测试
本课程由风哥发布的基于PostgreSQL数据库的系列课程,本课程属于PostgreSQL Performance Benchmarking,学完本课程可以掌握PostgreSQL性能基准测试基础知识,基准测试介绍,基准测试相关指标,TPCC基准测试基础,PostgreSQL测试工具介绍,PostgreSQL性能基准测…...

使用excel从1-2048中随机选择1个整数,并展示与其对应的单词
在Excel中,你可以使用以下指令来从1到2048之间随机选择一个整数,并展示其对应的单词: 1. 首先,在一个空白单元格中输入以下公式: INDEX(单词列表范围, RANDBETWEEN(1, 2048)) 这里的"单词列表范围"是一个包…...

c++可调用对象、function类模板与std::bind
函数调用与函数调用运算符 先写一个简单的函数,如下: /*函数的定义*/ int func(int i) {cout<<"这是一个函数\t"<<i<<endl; }void test() {func(1);//函数的调用 } 通过这个普通的函数可以看到,调用一个函数很…...

利用最小二乘法找圆心和半径
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <Eigen/Dense> // 需安装Eigen库用于矩阵运算 // 定义点结构 struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x_, double y_) : x(x_), y(y_) {} }; // 最小二乘法求圆心和半径 …...

2021-03-15 iview一些问题
1.iview 在使用tree组件时,发现没有set类的方法,只有get,那么要改变tree值,只能遍历treeData,递归修改treeData的checked,发现无法更改,原因在于check模式下,子元素的勾选状态跟父节…...
:滤镜命令)
ffmpeg(四):滤镜命令
FFmpeg 的滤镜命令是用于音视频处理中的强大工具,可以完成剪裁、缩放、加水印、调色、合成、旋转、模糊、叠加字幕等复杂的操作。其核心语法格式一般如下: ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf "滤镜参数" output.mp4或者带音频滤镜: ffmpeg…...
)
python爬虫:Newspaper3k 的详细使用(好用的新闻网站文章抓取和解析的Python库)
更多内容请见: 爬虫和逆向教程-专栏介绍和目录 文章目录 一、Newspaper3k 概述1.1 Newspaper3k 介绍1.2 主要功能1.3 典型应用场景1.4 安装二、基本用法2.2 提取单篇文章的内容2.2 处理多篇文档三、高级选项3.1 自定义配置3.2 分析文章情感四、实战案例4.1 构建新闻摘要聚合器…...

Matlab | matlab常用命令总结
常用命令 一、 基础操作与环境二、 矩阵与数组操作(核心)三、 绘图与可视化四、 编程与控制流五、 符号计算 (Symbolic Math Toolbox)六、 文件与数据 I/O七、 常用函数类别重要提示这是一份 MATLAB 常用命令和功能的总结,涵盖了基础操作、矩阵运算、绘图、编程和文件处理等…...

HTML前端开发:JavaScript 常用事件详解
作为前端开发的核心,JavaScript 事件是用户与网页交互的基础。以下是常见事件的详细说明和用法示例: 1. onclick - 点击事件 当元素被单击时触发(左键点击) button.onclick function() {alert("按钮被点击了!&…...

QT: `long long` 类型转换为 `QString` 2025.6.5
在 Qt 中,将 long long 类型转换为 QString 可以通过以下两种常用方法实现: 方法 1:使用 QString::number() 直接调用 QString 的静态方法 number(),将数值转换为字符串: long long value 1234567890123456789LL; …...

ios苹果系统,js 滑动屏幕、锚定无效
现象:window.addEventListener监听touch无效,划不动屏幕,但是代码逻辑都有执行到。 scrollIntoView也无效。 原因:这是因为 iOS 的触摸事件处理机制和 touch-action: none 的设置有关。ios有太多得交互动作,从而会影响…...

学习STC51单片机32(芯片为STC89C52RCRC)OLED显示屏2
每日一言 今天的每一份坚持,都是在为未来积攒底气。 案例:OLED显示一个A 这边观察到一个点,怎么雪花了就是都是乱七八糟的占满了屏幕。。 解释 : 如果代码里信号切换太快(比如 SDA 刚变,SCL 立刻变&#…...
中的KV缓存压缩与动态稀疏注意力机制设计)
大语言模型(LLM)中的KV缓存压缩与动态稀疏注意力机制设计
随着大语言模型(LLM)参数规模的增长,推理阶段的内存占用和计算复杂度成为核心挑战。传统注意力机制的计算复杂度随序列长度呈二次方增长,而KV缓存的内存消耗可能高达数十GB(例如Llama2-7B处理100K token时需50GB内存&a…...
