容器库(4)-std::forward_list
std::forward_list是可以从任何位置快速插入和移除元素的容器,不支持快速随机访问,只支持正向迭代。
本文章的代码库:
https://gitee.com/gamestorm577/CppStd
成员函数
构造、析构和赋值
构造函数
可以用元素、元素列表、迭代器或者另一个forward_list来构造forward_list。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::vector<float> vec(10, 1.2f);std::forward_list<float> f1(4, 3.2f);
std::forward_list<float> f2(4);
std::forward_list<float> f3(vec.begin(), vec.end());
std::forward_list<float> f4(f1);
std::forward_list<float> tmp(f1);
std::forward_list<float> f5(std::move(tmp));
std::forward_list<float> f6{1.f, 2.f, 3.f};print_func(f1);
print_func(f2);
print_func(f3);
print_func(f4);
print_func(f5);
print_func(f6);输出结果:
3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2
0 0 0 0
1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2
3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2
3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2
1 2 3 析构函数
forward_list析构时,会按照正向顺序依次删除元素。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{MyStruct(int i): Index(i){}~MyStruct(){std::cout << "destruct, Index = " << Index << std::endl;}int Index = 0;
};std::forward_list<MyStruct> f;
f.emplace_front(1);
f.emplace_front(3);
f.emplace_front(5);输出结果:
destruct, Index = 5
destruct, Index = 3
destruct, Index = 1赋值函数
可以用元素列表或者另一个forward_list赋值给forward_list。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::forward_list<float> tmp = {1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f};
std::forward_list<float> f1;
std::forward_list<float> f2;f1 = tmp;
f2 = {2.1f, 2.2f, 2.3f, 2.4f};
print_func(f1);
print_func(f2);输出结果:
1.1 2.1 3.1
2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 assign
将值赋值给forward_list,可以是元素、元素列表或者迭代器。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::vector<float> vec(10, 1.2f);
std::forward_list<float> f;f.assign(5, 1.2);
print_func(f);
f.assign(vec.begin(), vec.end());
print_func(f);
f.assign({1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f});
print_func(f);输出结果:
1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2
1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2
1.1 2.1 3.1 元素访问
front
返回首个元素的引用。示例代码:
std::forward_list<float> f = {1.f, 2.f, 3.f};
f.front() = 4.1f;
std::cout << "f front is: " << f.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
f front is: 4.1迭代器
before_begin和cbefore_begin返回forward_list开头之前的迭代器,begin和cbegin返回forward_list起始的迭代器,end和cend返回forward_list末尾的迭代器。代码示例:
std::forward_list<float> f = {1.f, 2.f, 3.f};
for (auto iter = f.begin(); iter != f.end(); ++iter)
{*iter += 1.1f;
}for (auto iter = f.cbegin(); iter != f.cend(); ++iter)
{std::cout << "num is: " << *iter << std::endl;
}输出结果:
num is: 2.1
num is: 3.1
num is: 4.1容量
empty
检查forward_list是否为空。代码示例:
std::forward_list<float> f1;
std::forward_list<float> f2 = {1.f, 2.f, 3.f};
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "f1 empty: " << f1.empty() << std::endl;
std::cout << "f2 empty: " << f2.empty() << std::endl;输出结果:
f1 empty: true
f2 empty: falsemax_size
返回可以容纳的最大元素个数。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{double num1;double num2;double num3;double num4;
};std::forward_list<float> f1;
std::forward_list<double> f2;
std::forward_list<MyStruct> f3;
std::cout << "f1 max size = " << f1.max_size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "f2 max size = " << f2.max_size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "f3 max size = " << f3.max_size() << std::endl;输出结果:
f1 max size = 1152921504606846975
f2 max size = 1152921504606846975
f3 max size = 461168601842738790修改器
clear
清除所有的元素。代码示例:
std::forward_list<float> f(3, 1.f);
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "f empty: " << f.empty() << std::endl;
f.clear();
std::cout << "f empty: " << f.empty() << std::endl;输出结果:
f empty: false
f empty: trueinsert_after
在指定位置后面插入元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::vector<float> tmp = {11.1f, 11.2f, 11.3f};
std::forward_list<float> f = {1.1f};
auto pos = f.insert_after(f.begin(), 2.1f);
print_func(f);
f.insert_after(pos, 3, 3.1f);
print_func(f);
pos = f.insert_after(f.begin(), tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
print_func(f);
f.insert_after(pos, {25.1f, 25.2f});
print_func(f);输出结果:
1.1 2.1
1.1 2.1 3.1 3.1 3.1
1.1 11.1 11.2 11.3 2.1 3.1 3.1 3.1
1.1 11.1 11.2 11.3 25.1 25.2 2.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 emplace_after
在指定位置后面构造一个元素。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{MyStruct(float num1, int num2){std::cout << "construct " << num1 << " " << num2 << std::endl;}
};std::forward_list<MyStruct> f;
f.emplace_after(f.before_begin(), 1.4f, 2);
f.emplace_after(f.before_begin(), 3.2f, 5);输出结果:
construct 1.4 2
construct 3.2 5erase_after
移除指定位置后面的元素或者移除某个范围内的元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::forward_list<float> f = {1.5f, 2.5f, 3.5f, 4.5f, 5.5f};
f.erase_after(f.begin());
print_func(f);
f.erase_after(f.begin(), std::next(f.begin(), 3));
print_func(f);输出结果:
1.5 3.5 4.5 5.5
1.5 5.5 push_front
在起始位置插入一个元素。代码示例:
std::forward_list<float> f = {1.1f, 2.1f};
std::cout << "f front is: " << f.front() << std::endl;
f.push_front(3.1f);
std::cout << "f front is: " << f.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
f front is: 1.1
f front is: 3.1emplace_front
在起始位置构造一个元素。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{MyStruct(float num1, int num2){std::cout << "construct " << num1 << " " << num2 << std::endl;}
};std::forward_list<MyStruct> f;
f.emplace_front(2.1f, 5);
f.emplace_front(2.5f, 3);输出结果:
construct 2.1 5
construct 2.5 3pop_front
移除forward_list的首个元素。代码示例:
std::forward_list<float> f = {1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f};
std::cout << "f front is: " << f.front() << std::endl;
f.pop_front();
std::cout << "f front is: " << f.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
f front is: 1.1
f front is: 2.1resize
重新设置元素的个数。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::forward_list<float> f = {1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f, 4.1f};
print_func(f);
f.resize(2);
print_func(f);输出结果:
1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1
1.1 2.1 swap
和另一个forward_list交换元素内容。代码示例:
std::forward_list<float> f1 = {1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f};
std::forward_list<float> f2 = {11.5f, 12.5f, 13.5f, 14.5f};
f1.swap(f2);
std::cout << "f1 front is: " << f1.front() << std::endl;
std::cout << "f2 front is: " << f2.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
f1 front is: 11.5
f2 front is: 1.1操作
sort
对元素进行排序。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::forward_list<int> f = {5, 2, 18, 9};
print_func(f);f.sort();
print_func(f);f.sort([](int a, int b){return a > b;});
print_func(f);输出结果:
5 2 18 9
2 5 9 18
18 9 5 2 merge
合并两个有序的列表。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};{std::forward_list<int> f1 = {1, 5, 7, 19};std::forward_list<int> f2 = {2, 3, 14, 15};f1.merge(f2);print_func(f1);
}{std::forward_list<int> f1 = {1, 5, 7, 19};std::forward_list<int> f2 = {2, 3, 14, 15};f1.merge(f2,[](int a, int b){return a > b;});print_func(f1);
}输出结果:
1 2 3 5 7 14 15 19
2 3 14 15 1 5 7 19 splice_after
将另一个列表中的一些元素移动到this列表指定的位置。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](std::string tag, const std::forward_list<float>& list)
{std::cout << tag;for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};{std::forward_list<float> f1 = {1.5f, 5.5f, 7.5f, 19.5f};std::forward_list<float> f2 = {2.4f, 3.4f, 14.4f, 15.4f};f1.splice_after(f1.begin(), f2);print_func("f1 = ", f1);print_func("f2 = ", f2);
}{std::forward_list<float> f1 = {1.5f, 5.5f, 7.5f, 19.5f};std::forward_list<float> f2 = {2.4f, 3.4f, 14.4f, 15.4f};f1.splice_after(std::next(f1.begin(), 2), f2, std::next(f2.begin(), 1));print_func("f1 = ", f1);print_func("f2 = ", f2);
}{std::forward_list<float> f1 = {1.5f, 5.5f, 7.5f, 19.5f};std::forward_list<float> f2 = {2.4f, 3.4f, 14.4f, 15.4f};f1.splice_after(f1.begin(), f2, f2.begin(), std::next(f2.begin(), 2));print_func("f1 = ", f1);print_func("f2 = ", f2);
}输出结果:
f1 = 1.5 2.4 3.4 14.4 15.4 5.5 7.5 19.5
f2 =
f1 = 1.5 5.5 7.5 14.4 19.5
f2 = 2.4 3.4 15.4
f1 = 1.5 3.4 5.5 7.5 19.5
f2 = 2.4 14.4 15.4 remove、remove_if
remove移除等于指定值的元素。remove_if移除满足指定要求的元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::forward_list<int> f = {5, 9, 17, 27, 15, 5, 5};
print_func(f);f.remove(5);
print_func(f);f.remove_if([](int n){return n > 15;});
print_func(f);输出结果:
5 9 17 27 15 5 5
9 17 27 15
9 15 reverse
反转元素的顺序。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::forward_list<float> f = {1.1f, 3.1f, 19.1f, 7.1f};
print_func(f);
f.reverse();
print_func(f);输出结果:
1.1 3.1 19.1 7.1
7.1 19.1 3.1 1.1 unique
删除连续的重复元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::forward_list<int> f = {1, 3, 3, 17, 7, 3, 17, 17, 19, 1, 3, 1};
print_func(f);
f.unique();
print_func(f);输出结果:
1 3 3 17 7 3 17 17 19 1 3 1
1 3 17 7 3 17 19 1 3 1 非成员函数
比较运算符
operator==,!=,<,<=,>,>=用于比较两个forward_list。代码示例:
std::forward_list<int> f1 = {1, 2, 3, 4};
std::forward_list<int> f2 = {1, 5};
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "f1 == f2: " << (f1 == f2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "f1 != f2: " << (f1 != f2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "f1 < f2: " << (f1 < f2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "f1 <= f2: " << (f1 <= f2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "f1 > f2: " << (f1 > f2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "f1 >= f2: " << (f1 >= f2) << std::endl;输出结果:
f1 == f2: false
f1 != f2: true
f1 < f2: true
f1 <= f2: true
f1 > f2: false
f1 >= f2: falseswap
交换两个列表的元素内容。示例代码:
std::forward_list<float> f1 = {1.5f, 2.5f};
std::forward_list<float> f2 = {17.1f, 15.1f, 27.1f};
std::swap(f1, f2);
std::cout << "f1 front is: " << f1.front() << std::endl;
std::cout << "f2 front is: " << f2.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
f1 front is: 17.1
f2 front is: 1.5erase、erase_if
erase删除等于指定值的元素,erase_if删除满足条件的元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::forward_list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::forward_list<int> f = {5, 7, 17, 29, 7, 7, 35};
print_func(f);std::erase(f, 7);
print_func(f);std::erase_if(f,[](int a){return a > 17;});
print_func(f);输出结果:
5 7 17 29 7 7 35
5 17 29 35
5 17 相关文章:
-std::forward_list)
容器库(4)-std::forward_list
std::forward_list是可以从任何位置快速插入和移除元素的容器,不支持快速随机访问,只支持正向迭代。 本文章的代码库: https://gitee.com/gamestorm577/CppStd 成员函数 构造、析构和赋值 构造函数 可以用元素、元素列表、迭代器或者另…...

Netty Review - 服务端channel注册流程源码解析
文章目录 PreNetty主从Reactor线程模型服务端channel注册流程源码解读入口 serverBootstrap.bind(port) 源码流程图 Pre Netty Review - ServerBootstrap源码解析 Netty Review - NioServerSocketChannel源码分析 Netty主从Reactor线程模型 Netty 使用主从 Reactor 线程模型…...

冒泡排序平均需要跑多少趟:拉马努金Q函数初探
摘要: 拉马努金Q函数在算法分析中的应用,初步体验 【对算法,数学,计算机感兴趣的同学,欢迎关注我哈,阅读更多原创文章】 我的网站:潮汐朝夕的生活实验室 我的公众号:算法题刷刷 我的知乎&#x…...
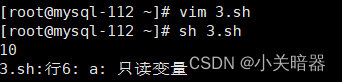
Shell 学习笔记(三)-shell变量
Shell 语言是一种动态类型和弱类型语言, 因此,在Shell中无需显示地声明变量, 且变量的类型会根据不同的操作符而发生变化. 静态类型语言: 在程序编译期间就确定变量类型的语言, 如java, C等 动态类型语言: 在程序运行期间才确定变量类型的语言, 如PHP, Python等. 一 shell变量…...

新冠:2022和2024两次新冠感染的对比
第一次 2022年底第一次放开管控,95%以上的人都感染了一次奥密克戎 症状 第一天:流涕,咽痛。 第二天:高烧40度,全身疼痛,动不了。没有胃口,头晕想吐。 吃了白加黑退烧药,清开灵颗粒…...

笔记:《NCT全国青少年编程能力等级测试教程Python语言编程二级》
NCT全国青少年编程能力等级测试教程Python语言编程二级 ISBN:9787302565857 绪论 专题1 模块化编程 考查方向 考点清单 考点 模块化编程 (一)模块化编程思想:结构清晰、降低复杂度;提高代码复用率;易于扩展、维护,方便阅读、优化。 …...

顶级思维方式——认知篇五(思想的觉醒)
目录 1、 女性的地位觉醒 2、电视剧《天道》之高人思维:丁元英为什么讲“人间黑白颠倒”? 3、 创业公司, 更应该大胆的创新. 4、 做到一定职务的时候, 你一定想到在你这个地位上你要做什么 1、 女性的地位觉醒 过去引以为鉴的例子&…...

面试技术栈 —— 2024网易雷火暑期实习真题
面试技术栈 —— 2024网易雷火暑期实习真题 1. 最长递增子序列。2. 集中限流和单机限流你觉得哪个好?3. redis部署服务器配置,为什么不用哨兵?4. 讲讲分布式session的原理。5. 数据库:表数据量大了,如何分表࿱…...
【小赛1】蓝桥杯双周赛第5场(小白)思路回顾
我的成绩:小白(5/6) 完稿时间:2024-2-13 比赛地址:https://www.lanqiao.cn/oj-contest/newbie-5/ 相关资料: 1、出题人题解:“蓝桥杯双周赛第5次强者挑战赛/小白入门赛”出题人题解 - 知乎 (zhihu.com) 2、矩阵快速幂&…...
-yum二进制部署)
docker (二)-yum二进制部署
yum安装docker(Linux) 安装环境:CentOS 7.9 一 如果之前安装了旧版docker,请先删除 sudo yum remove docker \docker-client \docker-client-latest \docker-common \docker-latest \docker-latest-logrotate \docker-logrotat…...
)
【深度学习】S2 数学基础 P2 线性代数(下)
目录 范数的意义范数的数学意义范数之于深度学习的意义 L1 范数与 L2 范数L1 范数L2 范数 小结 本节博文是线性代数第二部分,主要内容为 L 1 L1 L1 范数与 L 2 L2 L2 范数;有关线性代数基础知识,请访问:【深度学习】S2 数学基础…...

【软考高级信息系统项目管理师--考试内容大纲篇】
🚀 作者 :“码上有前” 🚀 文章简介 :软考高级–信息系统项目管理师 🚀 欢迎小伙伴们 点赞👍、收藏⭐、留言💬 软考高级信息系统项目管理师--考试内容大纲篇 1.信息化发展2.信息技术发展3.信息系…...

C语言——枚举类型
📝前言: 在之前的文章中我们已经讲解了自定义类型中的结构体类型和联合体类型,现在我们再充分学习一下C语言中的枚举类型: 1,什么是枚举类型 2,枚举类型的定义和变量的声明 3,对变量进行赋值 &a…...

linux---内存管理
一 虚拟内存 即使是现代操作系统中,内存依然是计算机中很宝贵的资源,看看你电脑几个T固态硬盘,再看看内存大小就知道了。 为了充分利用和管理系统内存资源,Linux采用虚拟内存管理技术,利用虚拟内存技术让每个进程都有…...

v-model原理
v-model原理 v-model原理表单类组件封装v-model简化代码 v-model原理 1.原理: v-model本质上是一个语法糖。例如应用在输入框上,就是value属性 和 input 事件的合写 <template><div id"app" ><input v-model"msg"…...
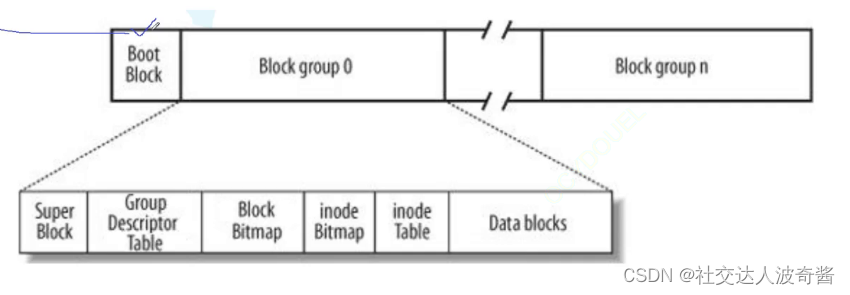
波奇学Linux:文件系统
磁盘认识 磁盘被访问的基本单元是扇区-512字节。 磁盘可以看成多个同心圆,每个同心圆叫做磁道,多个扇区组成同心圆。 我们可以把磁盘看做由无数个扇区构成的存储介质。 要把数据存到磁盘,先定位扇区,用哪一个磁头,…...

项目访问量激增该如何应对
✨✨ 欢迎大家来到喔的嘛呀的博客✨✨ 🎈🎈希望这篇博客对大家能有帮助🎈🎈 目录 引言 一. 优化数据库 1.1 索引优化 1.2 查询优化 1.3 数据库设计优化 1.4 事务优化 1.5 硬件优化 1.6 数据库配置优化 二. 增加服务器资源…...

【Linux环境基础开发工具的使用(yum、vim、gcc、g++、gdb、make/Makefile)】
Linux环境基础开发工具的使用yum、vim、gcc、g、gdb、make/Makefile Linux软件包管理器- yumLinux下安装软件的方式认识yum查找软件包安装软件如何实现本地机器和云服务器之间的文件互传卸载软件 Linux编辑器 - vimvim的基本概念vim下各模式的切换vim命令模式各命令汇总vim底行…...
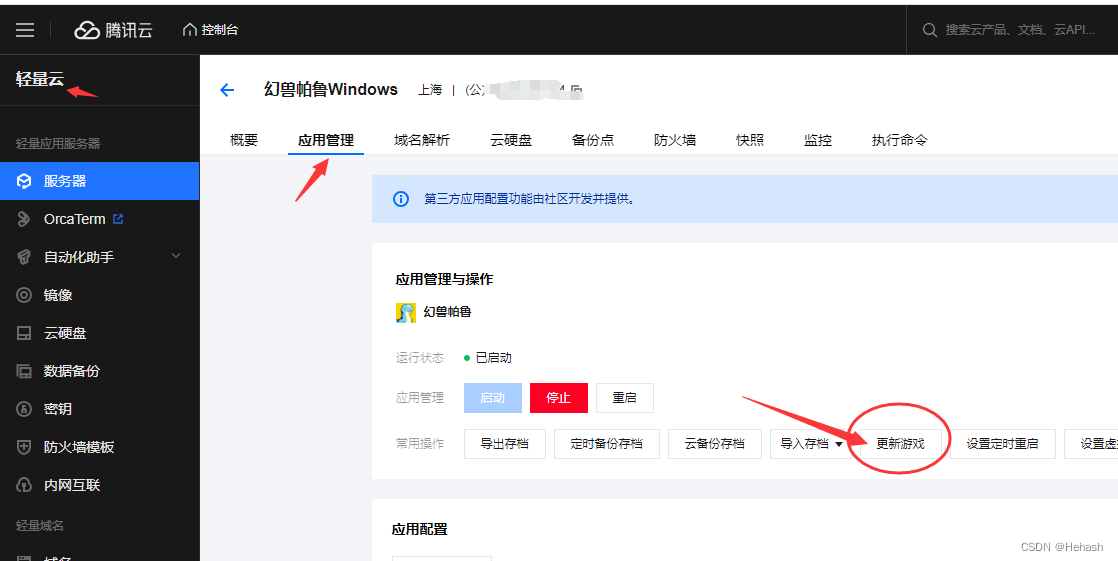
幻兽帕鲁官方更新了,服务器端怎么更新?
幻兽帕鲁官方客户端更新了,那么它的服务器端版本也是需要更新的,不然版本不一致的话,就不能进入游戏了。 具体的更新方法有两种,一是手动输入命令进行更新。第二种是在面板一键更新。 无论你是在阿里云或者腾讯云购买的一键部署…...

axios-retry 响应异常
最近项目中遇到 axios 异步请求异常中断, 错误码为 “ECONNABORTED” 奇怪的是排查前端代码并没有发现有主动调用 abort 取消请求的 由于为何网络请求失败的原因找不到, 但是重试请求就是成功的, 所以计划使用 axios-retry 在网络错误时重新请求 import axiosRetry from axios…...

SkyWalking 10.2.0 SWCK 配置过程
SkyWalking 10.2.0 & SWCK 配置过程 skywalking oap-server & ui 使用Docker安装在K8S集群以外,K8S集群中的微服务使用initContainer按命名空间将skywalking-java-agent注入到业务容器中。 SWCK有整套的解决方案,全安装在K8S群集中。 具体可参…...
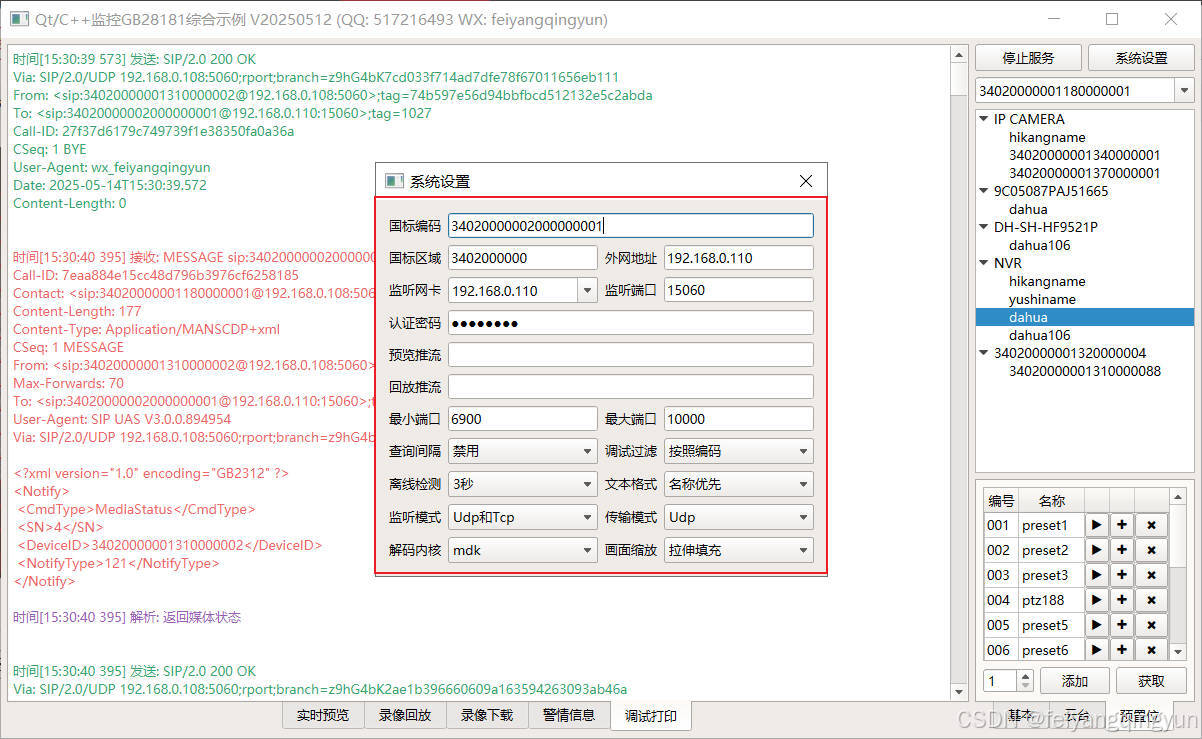
Qt/C++开发监控GB28181系统/取流协议/同时支持udp/tcp被动/tcp主动
一、前言说明 在2011版本的gb28181协议中,拉取视频流只要求udp方式,从2016开始要求新增支持tcp被动和tcp主动两种方式,udp理论上会丢包的,所以实际使用过程可能会出现画面花屏的情况,而tcp肯定不丢包,起码…...
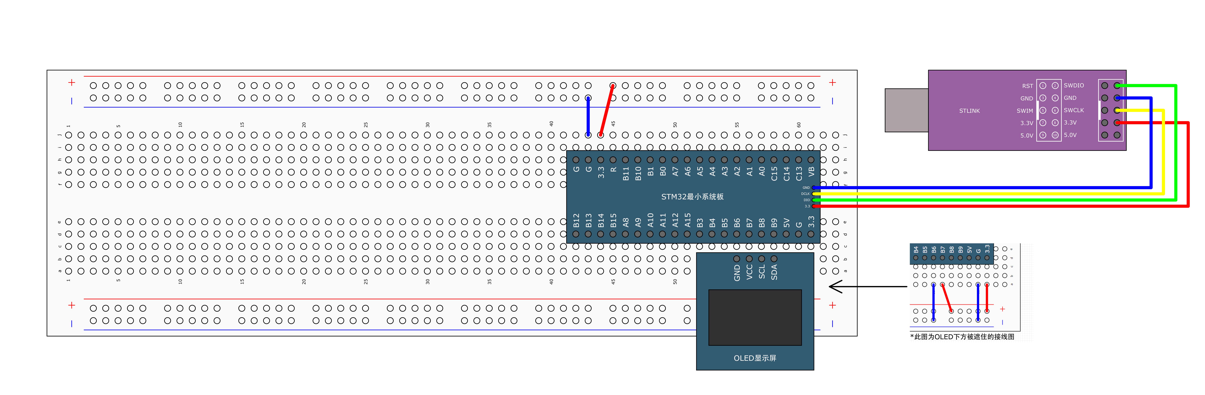
STM32标准库-DMA直接存储器存取
文章目录 一、DMA1.1简介1.2存储器映像1.3DMA框图1.4DMA基本结构1.5DMA请求1.6数据宽度与对齐1.7数据转运DMA1.8ADC扫描模式DMA 二、数据转运DMA2.1接线图2.2代码2.3相关API 一、DMA 1.1简介 DMA(Direct Memory Access)直接存储器存取 DMA可以提供外设…...

JDK 17 新特性
#JDK 17 新特性 /**************** 文本块 *****************/ python/scala中早就支持,不稀奇 String json “”" { “name”: “Java”, “version”: 17 } “”"; /**************** Switch 语句 -> 表达式 *****************/ 挺好的ÿ…...
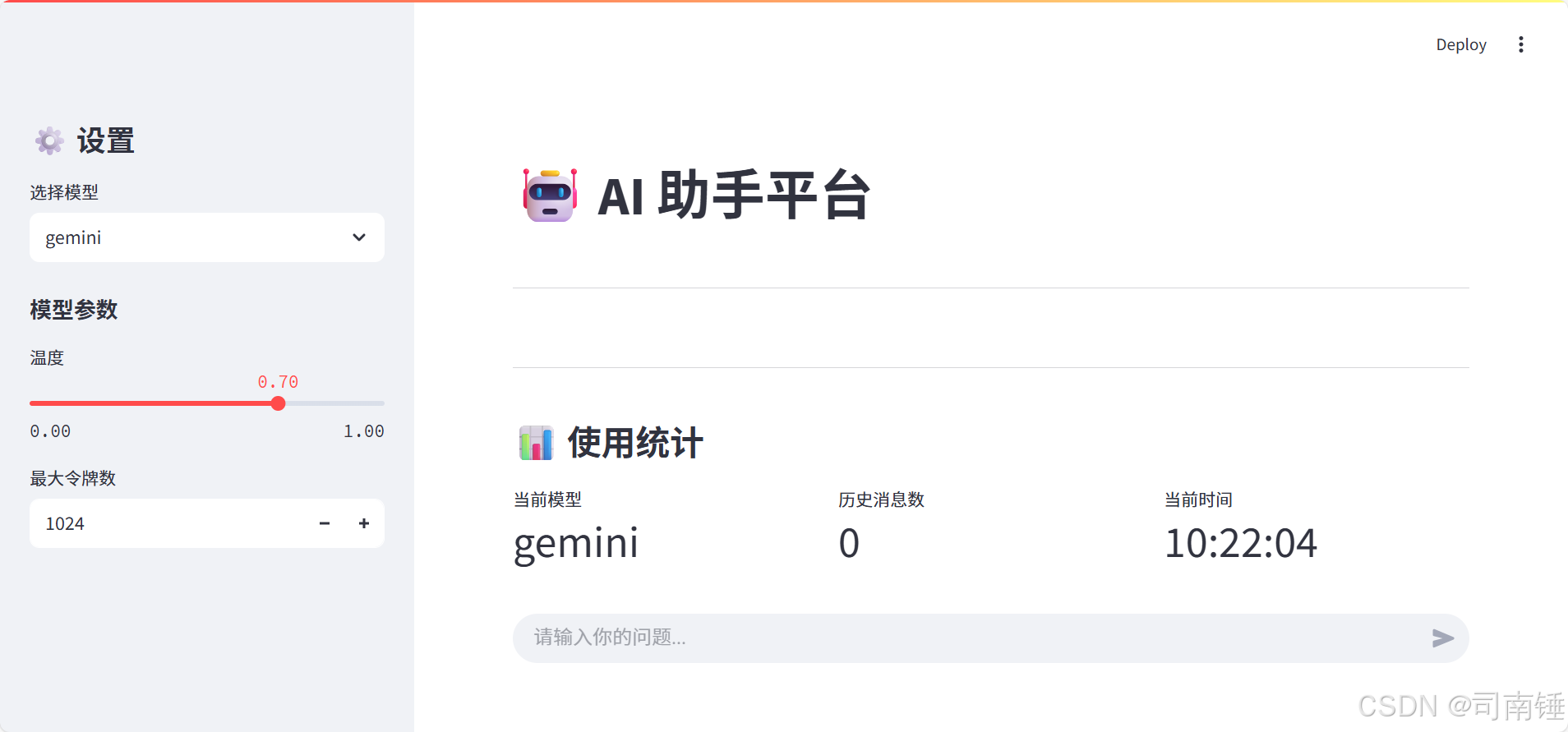
使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台
🎯 使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台 📌 项目背景 随着大语言模型(LLM)的广泛应用,开发者常面临多个挑战: 各大模型(OpenAI、Claude、Gemini、Ollama)接口风格不统一;缺乏一个统一平台进行模型调用与测试;本地模型 Ollama 的集成与前…...
并发编程 - go版
1.并发编程基础概念 进程和线程 A. 进程是程序在操作系统中的一次执行过程,系统进行资源分配和调度的一个独立单位。B. 线程是进程的一个执行实体,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,它是比进程更小的能独立运行的基本单位。C.一个进程可以创建和撤销多个线程;同一个进程中…...

Chrome 浏览器前端与客户端双向通信实战
Chrome 前端(即页面 JS / Web UI)与客户端(C 后端)的交互机制,是 Chromium 架构中非常核心的一环。下面我将按常见场景,从通道、流程、技术栈几个角度做一套完整的分析,特别适合你这种在分析和改…...

前端中slice和splic的区别
1. slice slice 用于从数组中提取一部分元素,返回一个新的数组。 特点: 不修改原数组:slice 不会改变原数组,而是返回一个新的数组。提取数组的部分:slice 会根据指定的开始索引和结束索引提取数组的一部分。不包含…...

Neko虚拟浏览器远程协作方案:Docker+内网穿透技术部署实践
前言:本文将向开发者介绍一款创新性协作工具——Neko虚拟浏览器。在数字化协作场景中,跨地域的团队常需面对实时共享屏幕、协同编辑文档等需求。通过本指南,你将掌握在Ubuntu系统中使用容器化技术部署该工具的具体方案,并结合内网…...

【深尚想】TPS54618CQRTERQ1汽车级同步降压转换器电源芯片全面解析
1. 元器件定义与技术特点 TPS54618CQRTERQ1 是德州仪器(TI)推出的一款 汽车级同步降压转换器(DC-DC开关稳压器),属于高性能电源管理芯片。核心特性包括: 输入电压范围:2.95V–6V,输…...
