【C++】stl_list介绍和实现,list和vector区别,list vector string 迭代器失效
本篇博客详细介绍list的实现&细节讲解,并且在文章末对list和vector,string进行区分和复习

list的基本结构就是双向带头循环链表,链表和顺序表的差别我们在前面数据结构的时候早就学过了,不再赘述
在使用stl库里面list时,要加上头文件
快速高效编辑查找元素 用vector
大批量增删数据 用list
目录
1.基本框架的实现
2.很细节的函数实现
3.vector和list对比
4.迭代器失效
1.基本框架的实现
定义模板T 还是表示每个节点data的类型
首先我们需要思考:
这个链表的每个节点的类型是什么?_list_node<T>
节点里面包含什么?当然 不要忘记构造函数

list的成员类型基本上都是迭代器,当然链表都是在用指针在玩,这里的迭代器和我们之前写顺序表就很不一样,因为之前是连续存储的结构,可以用[ ]的方式,所以迭代器是原生指针,数组的结构正好支持迭代器行为
但是这里原生指针的类型是node* ,不能满足迭代器的行为
但是我们可以用封装+运算符重载搞定
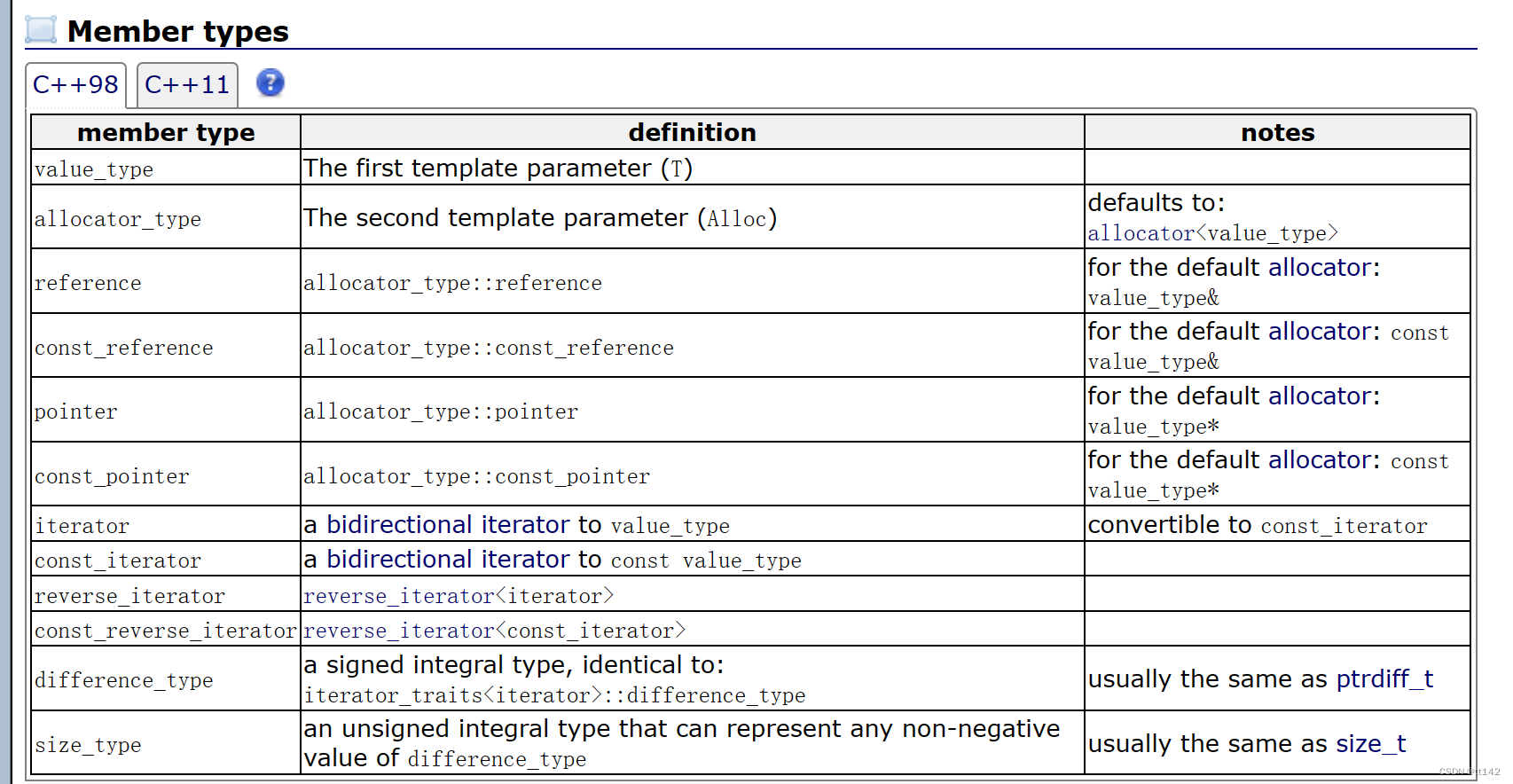
我们实现最基本的push——back()功能之后,基本上的框架就搭好了
void push_back(const T& x){node* newnode = new node(x);node* tail = head->_prev;//head tail newnodetail->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = head;newnode->_prev = tail;head->_prev = newnode;}目前的代码
namespace wrt
{template <typename T>struct _list_node{_list_node<T>* _prev;_list_node<T>* _next;T data;_list_node(const T& x) //用x初始化节点:_prev(nullptr),_next(nullptr),data(x){}};template <class T>struct __list_iterator{typedef _list_node<T> node;node* _pnode;__list_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}T& operator*(){return _pnode->data;}__list_iterator<T>& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};template <typename T>class list{typedef _list_node<T> node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T> iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(head);}list(){head = new node(T());head->_next = head;head->_prev = head;}void push_back(const T& x){node* newnode = new node(x);node* tail = head->_prev;//head tail newnodetail->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = head;newnode->_prev = tail;head->_prev = newnode;}private :node* head;};void test(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);lt.push_back(6);lt.push_back(7);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it <<" ";++it;}cout <<endl;}
}2.值得注意的函数
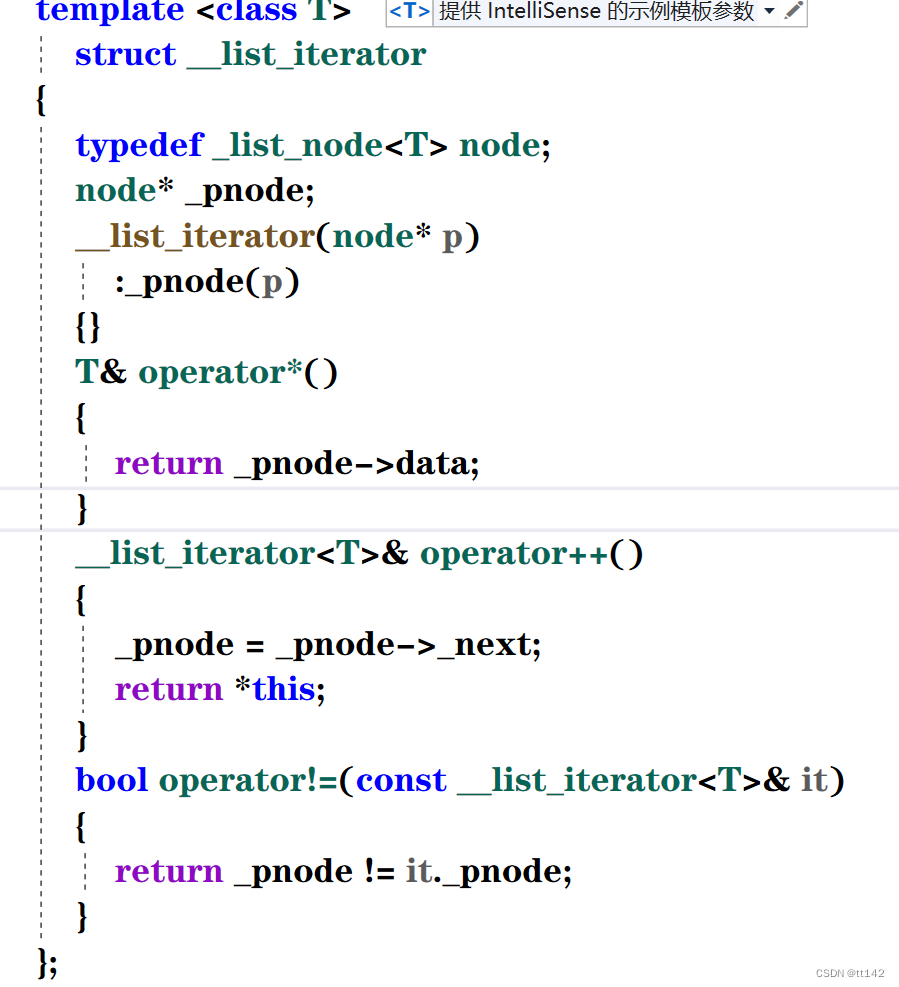
list为什么要支持sort,不可以使用algorithm文件里面的吗
算法库里面使用了first-last 但是很显然list是不支持节点相减的
2.很细节的函数实现
一个合格的list是支持增删查改的
push_back()已经实现过了
下面看insert()
 注意到它是有返回值的 ,返回迭代器,在头部增加数据当然是可以的
注意到它是有返回值的 ,返回迭代器,在头部增加数据当然是可以的
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){node* newnode = new node(x);node* cur = pos._pnode;node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev newnode curprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;newnode->_prev = prev;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}对应的erase()

也是有返回值,并且不能在头结点位置删除,哨兵位不能动
iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());node* cur = pos._pnode;node* prev = cur->_prev;node* next = cur->_next;//prev cur nextprev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);}那么头尾的增删就可以复用啦
void pop_back(){erase(--end());}
void pop_front(){erase(begin());}
void push_back(const T& x){//node* newnode = new node(x);//node* tail = head->_prev;head tail newnode//tail->_next = newnode;//newnode->_next = head;//newnode->_prev = tail;//head->_prev = newnode;insert(end(), x);}
void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}然后就是clear(),注意头结点不能删
void clear(){iterator it = begin();while(it!=end()){it=erase(it);}//头节点不能删除}析构函数
~list(){clear();//此时需要把头节点也删除delete head;head = nullptr;}下面是拷贝构造
//拷贝构造
//l2=l1list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& l){if (*this != l){clear();for (const auto&e :l){push_back(e);}}return *this;}为了写着更方便,把头结点的开辟封装成函数
void empty_initialize(){head = new node(T());head->_next = head;head->_prev = head;}//l2(l1)list(const list <T>& l){empty_initialize();for (const auto& e : l){push_back(e);}}迭代器还有const版本怎么实现
最简单想到的就是直接在iterator类里面加上一个const修饰*运算符重载![]()
template <class T>struct __list_iterator{typedef _list_node<T> node;node* _pnode;__list_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}T& operator*(){return _pnode->data;}//在同一个类里面实现就是不行,因为const——iterator只能遍历,不能++/* const T& operator*() const {return _pnode->data;}*/__list_iterator<T>& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};但是这个真的对么?很显然不对,因为iterator可以遍历,++ 但是const_iterator只能遍历无法++
所以很自然想到写在两个类里面
template <class T>struct __list_iterator{typedef _list_node<T> node;node* _pnode;__list_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}T& operator*(){return _pnode->data;}//在同一个类里面实现就是不行,因为const——iterator只能遍历,不能++/* const T& operator*() const {return _pnode->data;}*/__list_iterator<T>& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};template <class T>struct __list_const_iterator{typedef _list_node<T> node;node* _pnode;__list_const_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}const T& operator*() const {return _pnode->data;}__list_const_iterator<T>& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}bool operator!=(const __list_const_iterator<T>& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};这两个类只在*运算符重载 还有名称上有区别
但是这是我们的想法,看一下源码就知道大佬果然是大佬
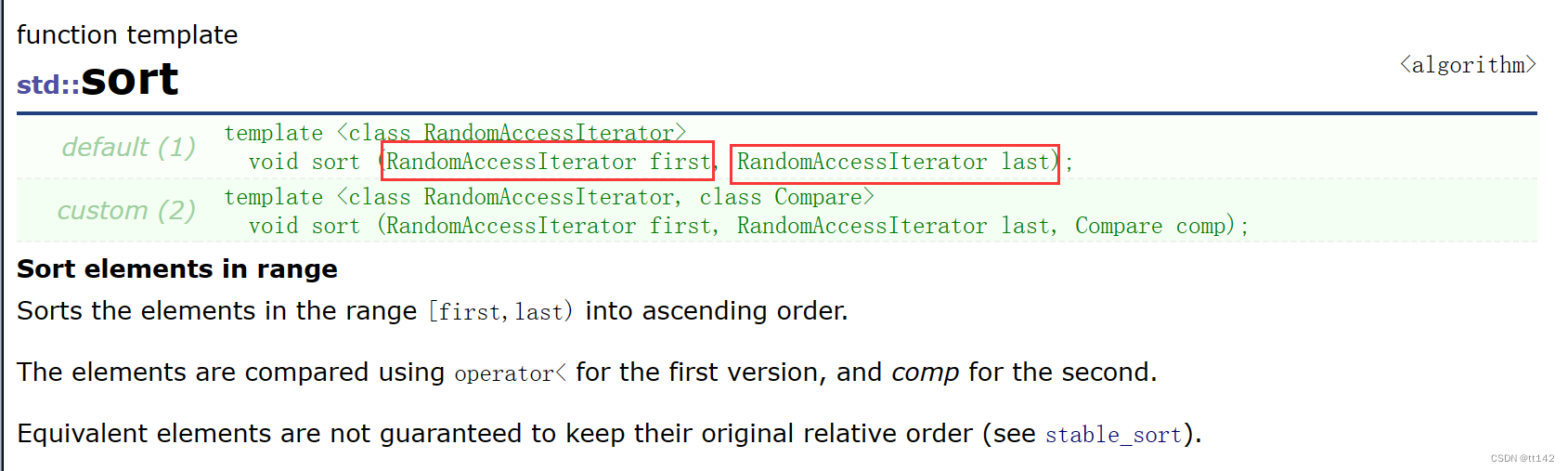
直接用两个模板参数解决问题
template <typename T, typename Ref>struct __list_iterator{typedef _list_node<T> node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref> Self;node* _pnode;__list_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}Ref operator*(){return _pnode->data;}//在同一个类里面实现就是不行,因为const——iterator只能遍历,不能++/* const T& operator*() const {return _pnode->data;}*/Self& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};拷贝构造可有现代写法哦,此时同样需要一个构造函数用迭代器初始化的

l2(l1)相比较来说,现代写法就是多一个工具人帮助复刻l1,然后把数据交换给l2,最后他自己牺牲....
首先是构造函数(用迭代器实现的)
template <class InputIterator>list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last){empty_initialize();while(first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}}然后是swap
void swap(const list<T>& l){std::swap(head, l.head); //两个链表交换只需交换头结点}现代写法
//l2(l1)list(const list<T>& l){empty_initialize();list<T> tmp(l.begin(), l.end());swap(tmp); //tmp出作用域销毁}l2=l1 这是对于一个已经存在的对象l1,无需构造头结点
//l2=l1 这是对于一个已经存在的对象l1,无需构造头结点list <T>& operator=(const list<T>& l){swap(l);return *this;}想象一个场景:你需要统计size(),当然这种操作不能频繁进行,因为每一次都要从头开始遍历有很多消耗,那么最简单的办法是什么?!成员变量加上size

现在凸显出复用的好处了,我虽然实现到一半开始想加上size,也只需要改动几个函数就可以完成功能





其他全是复用,爽歪歪
可以用size实现两个函数
size_t _size(){return size;}bool rmpty(){//return head->next==head;return size==0;}C++兼容c是有前置和后置的(区分于有些语言,觉得前置后置很麻烦就删去后置)
完善一下前面对于迭代器的运算符操作
//前置Self& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}//后置Self& operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_next;return tmp;}//前置Self& operator--(){_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return *this;}//后置Self& operator--(int ){Self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return tmp;}看起来写成这样是不是很完美,但是看一个问题
struct Pos{size_t _row;size_t _col;Pos(size_t row=0,size_t col=0) //一定要时刻记着写一个默认构造!!!!!!:_row(row),_col(col){}};void test(){list<Pos> lt;Pos p1(1, 1);lt.push_back(p1);lt.push_back(p1);lt.push_back(p1);lt.push_back(Pos(2, 2)); //匿名函数lt.push_back(Pos(3, 3));list<Pos>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){//it->_row++;cout << *it << " ";}}思考一下有什么问题???
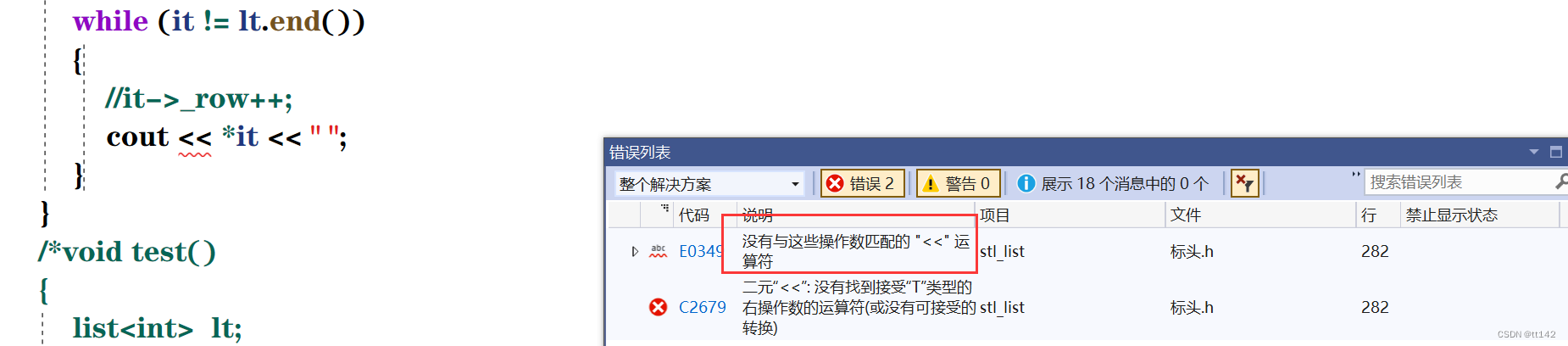
这很尴尬,首先我们思考一下,为什么C++支持cout,因为可以对内置类型可以直接识别然后输出,但是这里的it是个迭代器
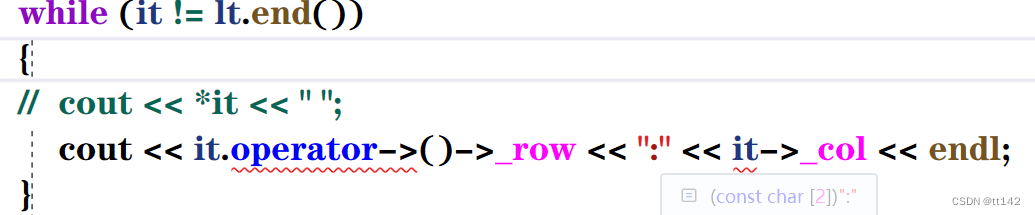
其实这样就可以啦,只需要重载一个->这个运算符
但是我们只有T这个模板类型,没有T*


然后运算符->重载这样写
Ptr operator->(){return &_pnode->data;}注意:脑子一定要清醒,我们提供类T是为了list每个节点的数据类型,Ref是T&(当然还有一个const T&),Ptr是T*(还有const T*)
这里面也体现出我们typedef的智慧

这个模板我们改了很多次,但是我typedef之后,直接修改类型,不需要改名字,都是Self!!!

所以直接->访问就可以啦
他的原理就是

3.vector和list对比

4.迭代器失效
vector:insert和erase都有失效问题
lsit:erase会失效
那么string会有失效问题吗?当然,insert和erase都有,和vecor类似,但是一般不关注string失效,因为string的insert和erase常用接口都是下标支持的,迭代器用的少
最后我们的list实现总代码![]()
.h文件
#pragma once
namespace wrt
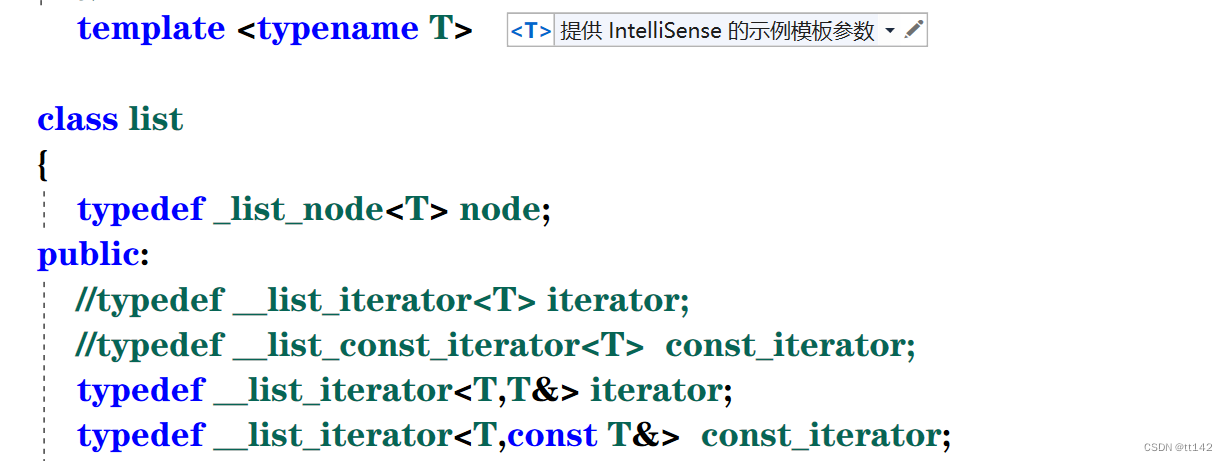
{template <typename T>struct _list_node{_list_node<T>* _prev;_list_node<T>* _next;T data;_list_node(const T& x) //用x初始化节点:_prev(nullptr),_next(nullptr),data(x){}};template <typename T, typename Ref,class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef _list_node<T> node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref,Ptr> Self;node* _pnode;__list_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}Ref operator*(){return _pnode->data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_pnode->data;}//在同一个类里面实现就是不行,因为const——iterator只能遍历,不能++/* const T& operator*() const {return _pnode->data;}*///前置Self& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}//后置Self& operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_next;return tmp;}//前置Self& operator--(){_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return *this;}//后置Self& operator--(int ){Self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};/* template <class T>struct __list_const_iterator{typedef _list_node<T> node;node* _pnode;__list_const_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}const T& operator*() const {return _pnode->data;}__list_const_iterator<T>& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}bool operator!=(const __list_const_iterator<T>& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};*/template <typename T>class list{typedef _list_node<T> node;public://typedef __list_iterator<T> iterator;//typedef __list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,T*> const_iterator;size_t _size(){return size;}bool rmpty(){//return head->next==head?return size == 0 ;}iterator begin(){return iterator(head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(head);}const_iterator begin() const {return iterator(head->_next);}const_iterator end() const {return iterator(head);}void push_back(const T& x){//node* newnode = new node(x);//node* tail = head->_prev;head tail newnode//tail->_next = newnode;//newnode->_next = head;//newnode->_prev = tail;//head->_prev = newnode;insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}~list(){clear();//此时需要把头节点也删除delete head;head = nullptr;size = 0;}//拷贝构造//l2=l1/*list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& l){if (*this != l){clear();for (const auto&e :l){push_back(e);}}return *this;}*/void empty_initialize(){head = new node(T());head->_next = head;head->_prev = head;size = 0;}list(){empty_initialize();}//l2(l1)/* list(const list <T>& l){empty_initialize();for (const auto& e : l){push_back(e);}}*///拷贝构造的现代写法template <class InputIterator>list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last){empty_initialize();while (first != last){push_back(*first);++first;}}void swap(const list<T>& l){std::swap(head, l.head); //两个链表交换只需交换头结点}//l2(l1)list( list<T>& l){empty_initialize();list<T> tmp(l.begin(), l.end());swap(tmp); //tmp出作用域销毁}//l2=l1 这是对于一个已经存在的对象l1,无需构造头结点list <T>& operator=(const list<T>& l){swap(l);return *this;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while(it!=end()){it=erase(it);}//头节点不能删除size = 0;}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){node* newnode = new node(x);node* cur = pos._pnode;node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev newnode curprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;newnode->_prev = prev;cur->_prev = newnode;++size;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());node* cur = pos._pnode;node* prev = cur->_prev;node* next = cur->_next;//prev cur nextprev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;--size;return iterator(next);}private :node* head;size_t size;};struct Pos{size_t _row;size_t _col;Pos(size_t row=0,size_t col=0) //一定要时刻记着写一个默认构造!!!!!!:_row(row),_col(col){}};void test(){list<Pos> lt;Pos p1(1, 1);lt.push_back(p1);lt.push_back(p1);lt.push_back(p1);lt.push_back(Pos(2, 2)); //匿名函数lt.push_back(Pos(3, 3));list<Pos>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){// cout << *it << " ";//cout << it.operator->()->_row << ":" << it->_col << endl;cout << it->_row << ":" << it->_col << ":" << endl;}}/*void test(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);lt.push_back(6);lt.push_back(7);lt.insert(lt.begin(), 5);lt.erase(lt.begin());lt.push_back(40);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it <<" ";++it;}cout <<endl;cout << lt._size() << endl;}*/
}.cpp文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
#include "标头.h"
int main()
{wrt::test();return 0;
}
相关文章:
【C++】stl_list介绍和实现,list和vector区别,list vector string 迭代器失效
本篇博客详细介绍list的实现&细节讲解,并且在文章末对list和vector,string进行区分和复习 list的基本结构就是双向带头循环链表,链表和顺序表的差别我们在前面数据结构的时候早就学过了,不再赘述 在使用stl库里面list时&…...

linux-kernel-ecmp-ipv4
当使用ip route add/del添加或者删除路由时,通过触发netlink发送信息到各协议路由系统注册的netlink处理函数,如add时调用函数为inet_rtm_newroute。Equal Cost Multi Path,在ip交换网络中存在到达同一目的地址的多条不同的路径,而且每条路径…...
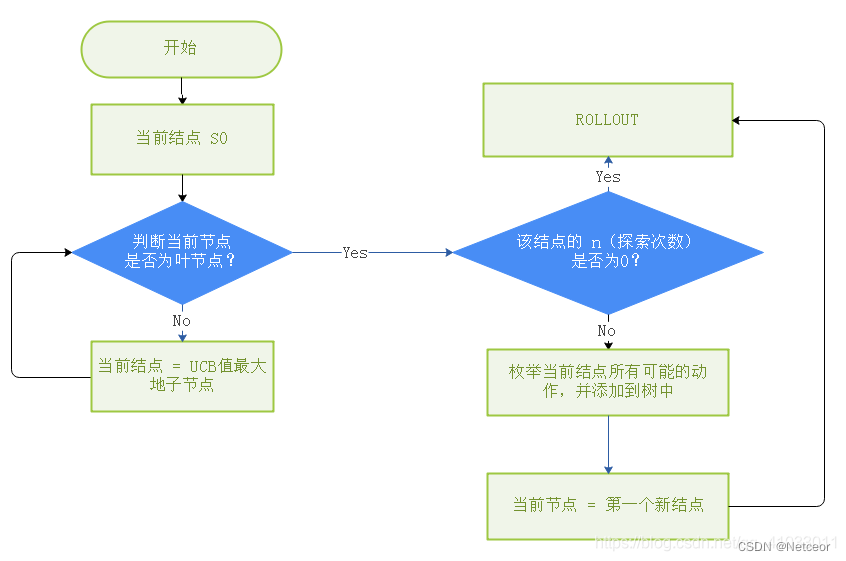
蒙特卡洛树搜索(MTCS)
一、目标 一种启发式的搜索算法,在搜索空间巨大的场景下比较有效 算法完成后得到一棵树,这棵树可以实现:给定一个游戏状态,直接选择最佳的下一步 二、算法四阶段 1、选择(Selection) 父节点选择UCB值最…...
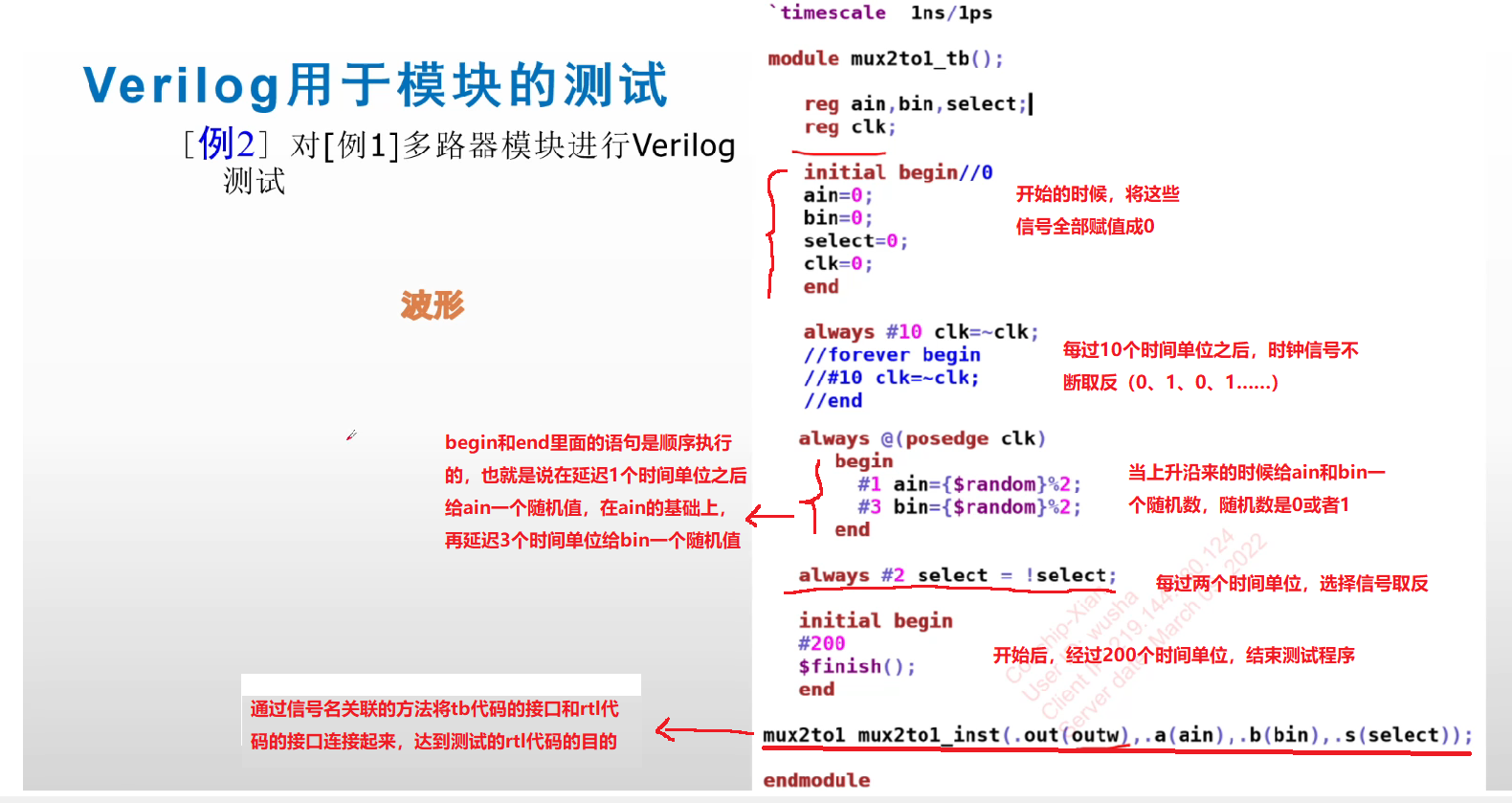
【Verilog】——Verilog简介
目录 1.简介 2.什么是HDL以及HDL的功能 3.Verilog和C语言的比较 4.Verilog的用途 5.数字系统的抽象层次 1.系统级 2.算法级 3.RTL级(寄存器变换级) 6.数字系统抽象层级 7.自顶向下的结构化设计方法 8.Verilog建模 9.Verilog概述 10.Verilog模块的基本…...
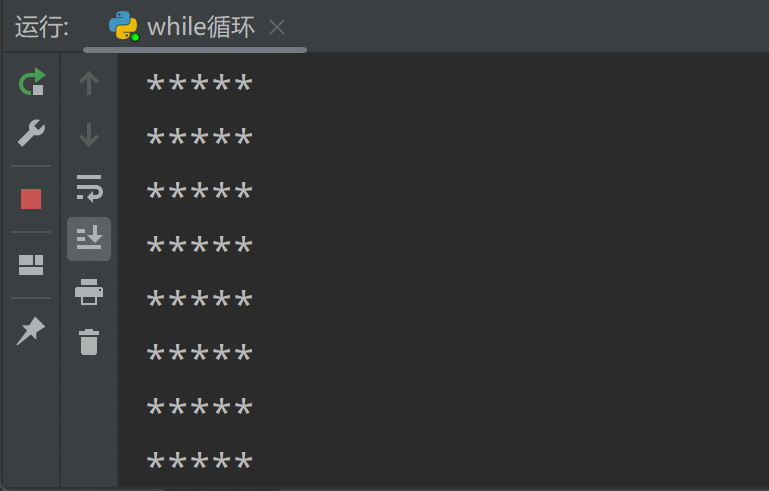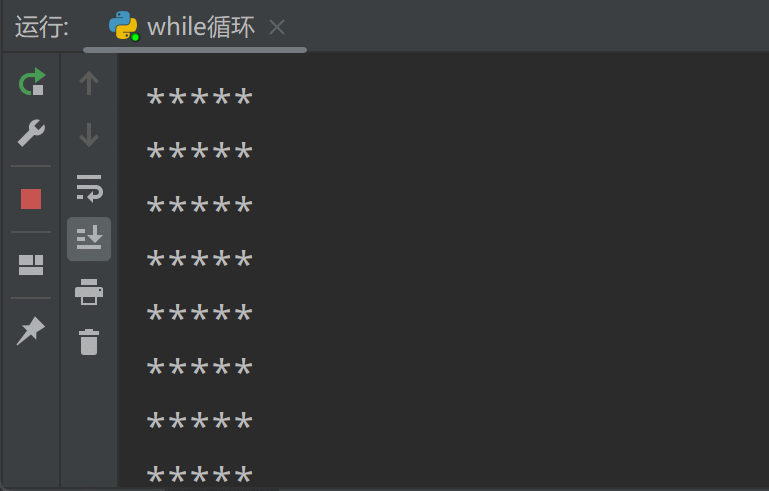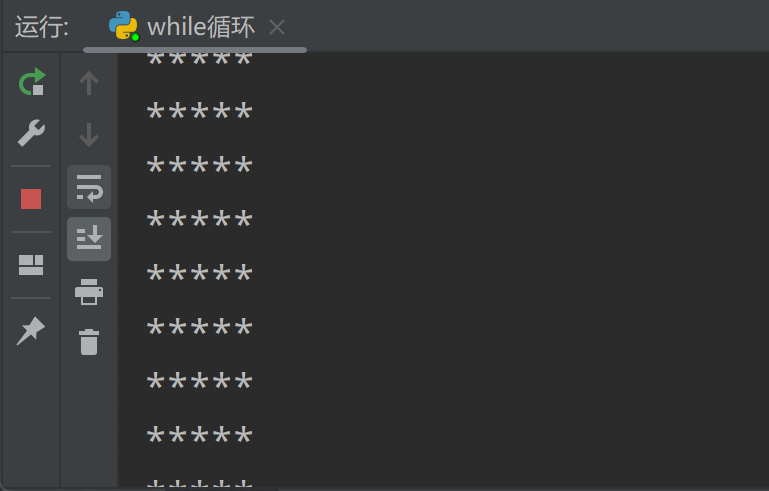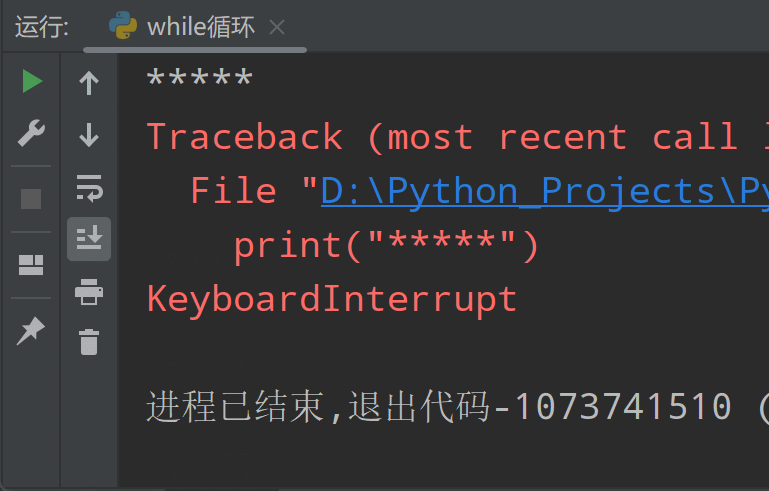
【Python从入门到进阶】10、流程控制语句-循环语句(for-while)
接上篇《9、流程控制语句-条件语句(if-else)》 上一篇我们学习了Python的控制流语句的概念,以及其中的条件语句(if/else),本篇我们来学习控制流语句中的循环语句(for/while)。 一、Python中的循环 Python的循环结构就是让程序“杀个回马枪”࿰…...
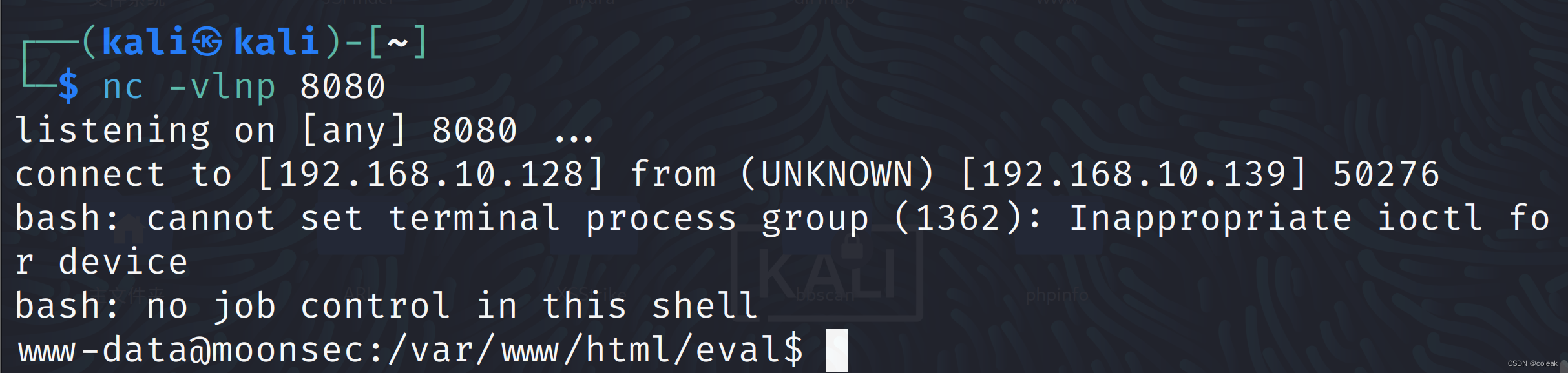
超全的命令(代码)执行漏洞无回显的姿势总结(附带详细代码和测试分析过程)
目录 漏洞代码 突破方式 重定向 dnslog外部通信 burpsuite burpcollaborator外部通信 日志监听 netcat监听 反弹shell的各种姿势 漏洞代码 <?php shell_exec($_GET[a]); ?>这里使用了无回显的shell执行函数shell_exec,给html目录的权限是777 突破方…...

STM32MP157-Linux音频应用编程-简易语音助手
文章目录前言STM32MP157简易语音助手alsa-lib简介:移植alsa-lib库:libcurl库简介:移植libcurl库:API调用修改asrmain.c文件修改token.c文件录音文件IO打开音频文件硬件控制sysfs文件系统数据解析和控制多线程主循环实现效果及注意…...

Python-OpenCV图像处理:学习图像算术运算,如加减法、图像混合、按位运算,以及如何实现它们
目录 目标 图像添加 图像混合算法 按位运算 目标 学习对图像的几种算术运算,如加法、减法、位运算等。了解这些功能:cv.add()、...
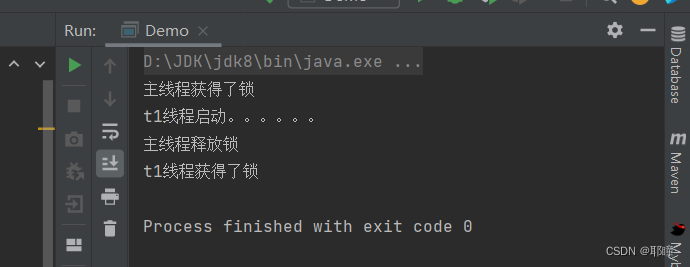
并发编程——ReentrantLock
如果有兴趣了解更多相关内容,欢迎来我的个人网站看看:耶瞳空间 一:基本介绍 从Java 5开始,引入了一个高级的处理并发的java.util.concurrent包,它提供了大量更高级的并发功能,能大大简化多线程程序的编写…...
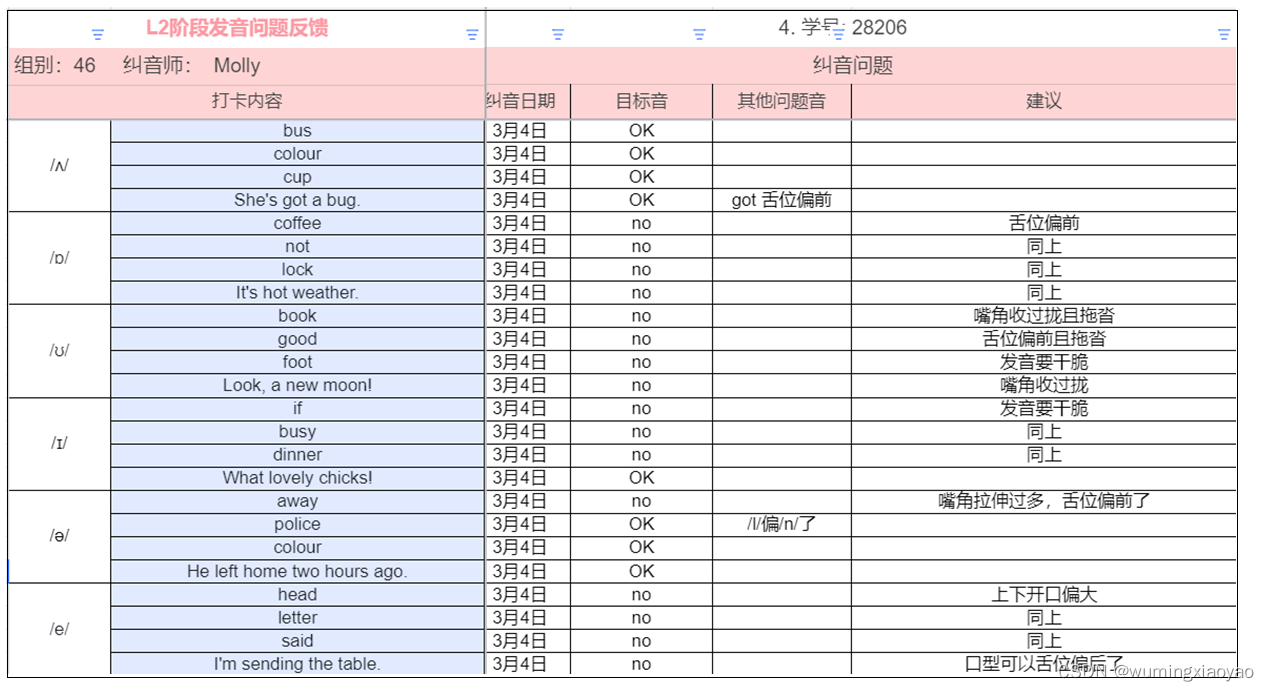
English Learning - L2 第 3 次小组纠音 [ʌ] [ɒ] [ʊ] [ɪ] [ə] [e] 2023.3.4 周六
English Learning - L2 第 3 次小组纠音 [ʌ] [ɒ] [ʊ] [ɪ] [ə] [e] 2023.3.4 周六共性问题小元音 [ʌ]小元音 [ɒ]小元音 [ʊ]小元音 [ɪ]小元音 [ə]小元音 [e]我的发音问题纠音过程共性问题 小元音 [ʌ] 口型容易偏大 解决办法:因为嘴角没有放松,…...
STM32之关门狗
看门狗介绍在由单片机构成的微型计算机系统中,由于单片机的工作常常会受到来自外界电磁场的干扰,造成程序的跑飞,而陷入死循环,程序的正常运行被打断,由单片机控制的系统无法继续工作,会造成整个系统的陷入…...

Apollo控制部分1-- ControlComponent组件介绍
Apollo控制部分1-- ControlComponent组件介绍摘要一、ControlComponent1、启动文件解析2、ControlComponent()组件函数解析1)ControlComponent::ControlComponent() 构造函数2)ControlComponent::Init() 初始化函数(执行一次)3&am…...

0626-0631韩顺平Java Buffered字节处理流 学习笔记
如何去构建字节流package com.hspedu.outputstream_;import java.io.*;/*** author abner* version 1.0*/ public class BufferedCopy02 {public static void main(String[] args) {String srcFilePath "D:\\Users\\Pictures\\Camera Roll\\Pierre-Auguste_Renoir,_Le_Mo…...
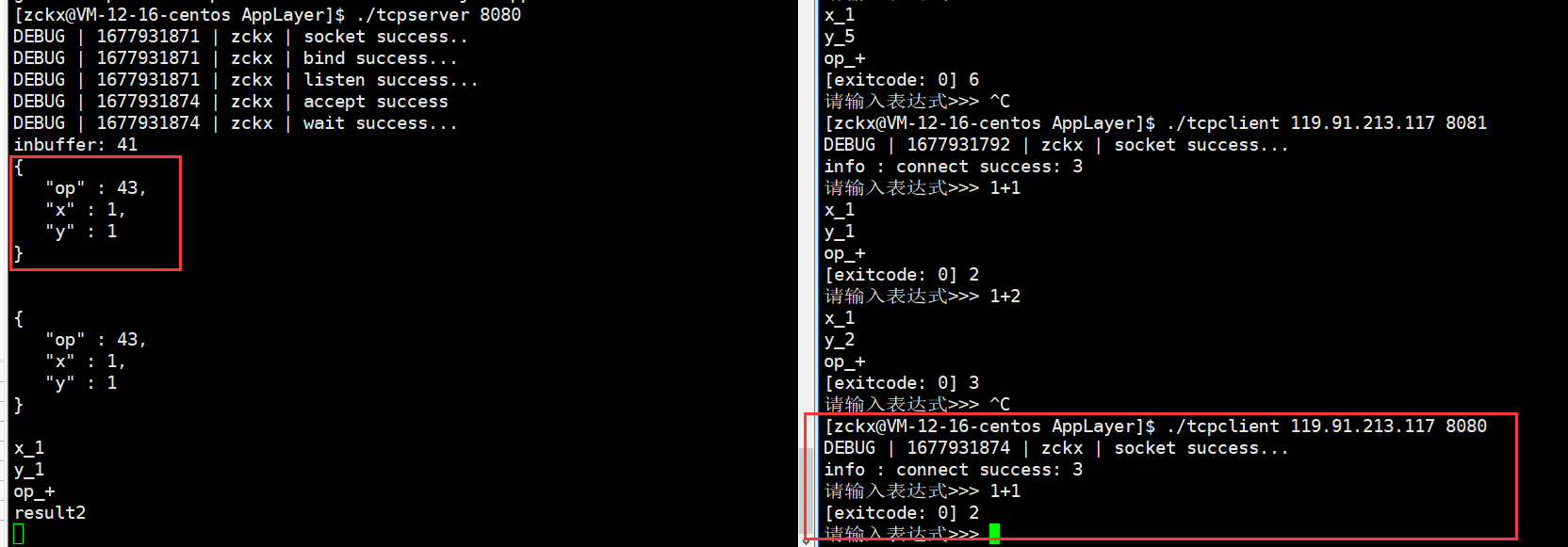
【网络】序列化和反序列化
🥁作者: 华丞臧. 📕专栏:【网络】 各位读者老爷如果觉得博主写的不错,请诸位多多支持(点赞收藏关注)。如果有错误的地方,欢迎在评论区指出。 推荐一款刷题网站 👉 LeetCode刷题网站 文章…...

【代码随想录训练营】【Day32】第八章|贪心算法|122.买卖股票的最佳时机II |55. 跳跃游戏|45.跳跃游戏II
买卖股票的最佳时机II 题目详细:LeetCode.122 买卖股票的最佳时机,怎么都能够想出来个思路,假如我们每天都能预知明天的股票是涨是降,那么贪心策略就是在涨之前买股票,在降的前一天卖掉,这就是买卖股票的…...

constexpr 和 常量表达式
👀👀常量表达式 常量表达式是指值不会改变并且在编译过程就能得到计算结果的表达式。 字面值属于常量表达式,用常量表达式初始化的const对象也是常量表达式。 那么是什么来就决定是不是常量表达式呢?一个对象是不是常量表达式主要…...
Vue响应式原理————Object.defineProperty()和proxy的用法分享
Vue框架一个比较核心的功能就是我们的数据是响应式的,这样我们在修改数据的时候,页面会自动帮我们更新,那么想要实现这个功能就要实现对一个数据的劫持,即在取值和设置值的同时我们能够检测到即数据劫持。vue2响应式的实现原理所依…...

CSDN 编程竞赛三十四期题解
竞赛总览 CSDN 编程竞赛三十四期:比赛详情 (csdn.net) 本期的题目和第三十一期竞赛的题目竟然高度重合,真不知道该写点什么了。 不过,上次那道测试数据有bug的题已经修复了,答题过程挺顺利的,没有遇到新的问题。 竞…...

C#教程06 运算符
文章目录 一、算术运算符加法运算符(+)减法运算符(-)乘法运算符(*)除法运算符(/)二、逻辑运算符与运算符(&&)或运算符(||)非运算符(!)三、比较运算符等于运算符(==)大于运算符(>)小于运算符(<)大于等于运算符(>=)小于等于运算符(<=…...
pytest单元测试)
软测入门(六)pytest单元测试
pytest pytest是python的一种单元测试框架,同自带的unit test测试框架类似,但pytest更简洁高效。 单元测试: 测试 函数、类、方法能不能正常运行测试的结果是否符合我们的预期结果 安装 pip install -U pytest基本使用 通过pytest包使用…...
——CAD)
小带轮(同步带)——CAD
小带轮作为同步带传动系统的核心组件,其设计精度直接影响动力传递的效率与稳定性。在机械传动领域,同步带传动凭借无滑移、传动比精准的特性,广泛应用于数控机床、自动化设备及精密仪器中。小带轮通过与同步带齿槽的精确啮合,将旋…...

Java Web Spring Boot律师事务所案件管理系统系统源码-SpringBoot2+Vue3+MyBatis-Plus+MySQL8.0【含文档】
💡实话实说: 有自己的项目库存,不需要找别人拿货再加价,所以能给到超低价格。 摘要 随着信息技术的快速发展,传统律师事务所的案件管理方式逐渐暴露出效率低下、数据冗余和安全性不足等问题。律师事务所案件管理系统的…...

KOOK真实幻想艺术馆电商应用:服装图案AI生成+风格迁移快速打样
KOOK真实幻想艺术馆电商应用:服装图案AI生成风格迁移快速打样 想象一下,你是一位服装设计师,面对即将到来的新一季发布会,需要设计几十款不同风格的服装图案。传统的流程是什么?手绘草图、扫描、电脑上色、反复修改、…...

ESP32嵌入式GUI终端:天气时钟+MP3播放器全栈实现
1. 项目概述 ESP32天气时钟与SD卡MP3播放器是一个面向嵌入式人机交互场景的综合性硬件项目,融合了网络通信、实时信息获取、图形用户界面渲染、音频解码与播放控制等关键技术模块。该项目并非简单的功能堆砌,而是围绕“桌面智能终端”这一明确应用场景展…...

SpringCloud动态路由利器--router4j
前言 本文介绍Java的动态路由中间件:router4j。router4j用于SpringCloud项目,它可以将某个url请求路由到指定的机器上,也可以将所有请求强制转到指定机器。 问题描述 Java后端在开发SpringCloud项目时如果同一个应用起了多个实例ÿ…...

MySQL数据恢复终极指南:my2sql与binlog2sql对比测试
MySQL数据恢复终极指南:my2sql与binlog2sql对比测试 【免费下载链接】Archery hhyo/Archery: 这是一个用于辅助MySQL数据库管理和开发的Web工具。适合用于需要管理和开发MySQL数据库的场景。特点:易于使用,具有多种数据库管理功能,…...

3个实战案例带你掌握ast-hook-for-js-RE:猿人学、犀牛数据与极验破解
3个实战案例带你掌握ast-hook-for-js-RE:猿人学、犀牛数据与极验破解 【免费下载链接】ast-hook-for-js-RE 浏览器内存漫游解决方案(探索中...) 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/as/ast-hook-for-js-RE ast-hook-for-js-RE是…...

Phi-3-Mini-128K开源镜像部署:中小企业低成本AI助手落地实践
Phi-3-Mini-128K开源镜像部署:中小企业低成本AI助手落地实践 想为你的团队或业务引入一个智能助手,但被动辄数十GB的模型和昂贵的算力成本劝退?今天,我们来聊聊一个真正为中小企业量身定制的解决方案——基于Phi-3-Mini-128K模型…...

3步实现空间信息解析:开源号码定位工具全流程指南
3步实现空间信息解析:开源号码定位工具全流程指南 【免费下载链接】location-to-phone-number This a project to search a location of a specified phone number, and locate the map to the phone number location. 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/…...

全球智能驾驶SoC市场规模与算力分层演进深度分析
随着汽车产业“新四化”的深入,智能驾驶功能正从高端配置向大众市场普及。作为智能汽车的“大脑”,智能驾驶SoC(系统级芯片)的市场规模迅速扩张,并呈现出清晰的高、中、低算力分层演进趋势。本文结合最新市场数据与厂商布局,对此进行专业解读。 一、 市场空间:千亿蓝海…...

