C 标准库 - <stdio.h> 详解
在 C 语言中,stdio.h 是一个非常重要的头文件,定义了一系列用于输入和输出的函数、变量和宏。本文将逐一介绍 stdio.h 中定义的函数,并提供每个函数的完整示例。
变量类型
在 stdio.h 中定义了三个变量类型:
size_t:无符号整数类型,通常用于表示内存大小。FILE:适合存储文件流信息的对象类型。fpos_t:适合存储文件中任何位置的对象类型。
宏定义
stdio.h 中定义了一些常用的宏:
NULL:空指针常量的值。_IOFBF、_IOLBF和_IONBF:用于setvbuf函数的第三个参数。BUFSIZ:setbuf函数使用的缓冲区大小。EOF:表示文件结束的负整数。FOPEN_MAX:系统可以同时打开的文件数量。FILENAME_MAX:字符数组可以存储的文件名的最大长度。L_tmpnam:tmpnam函数创建的临时文件名的最大长度。SEEK_CUR、SEEK_END和SEEK_SET:fseek函数中用于定位不同位置的宏。TMP_MAX:tmpnam函数可生成的独特文件名的最大数量。stderr、stdin和stdout:分别对应标准错误、标准输入和标准输出流。
函数介绍与示例
1. int fclose(FILE *stream)
关闭流 stream。刷新所有的缓冲区。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");fprintf(fp, "This is just a test.\n");fclose(fp);return 0;
}
2. void clearerr(FILE *stream)
清除给定流 stream 的文件结束和错误标识符。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;int c;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");clearerr(fp);while ((c = fgetc(fp)) != EOF) {putchar(c);}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
3. int feof(FILE *stream)
测试给定流 stream 的文件结束标识符。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");while (!feof(fp)) {putchar(fgetc(fp));}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
4. int ferror(FILE *stream)
测试给定流 stream 的错误标识符。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");if (ferror(fp)) {perror("Error reading file");} else {printf("File read successfully.\n");}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
5. int fflush(FILE *stream)
刷新流 stream 的输出缓冲区。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");fprintf(fp, "This is just a test.\n");fflush(fp); // Flush the buffer to ensure data is written immediatelyfclose(fp);return 0;
}
6. int fgetpos(FILE *stream, fpos_t *pos)
获取流 stream 的当前文件位置,并把它写入到 pos。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fpos_t position;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");fgetpos(fp, &position);printf("Current position in file: %lld\n", position);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
7. FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode)
使用给定的模式 mode 打开 filename 所指向的文件。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");if (fp == NULL) {perror("Error opening file");return -1;}fprintf(fp, "This is just a test.\n");fclose(fp);return 0;
}
8. size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)
从给定流 stream 读取数据到 ptr 所指向的数组中。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;char buffer[20];fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");fread(buffer, sizeof(char), 10, fp);printf("Data read: %s\n", buffer);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
9. FILE *freopen(const char *filename, const char *mode, FILE *stream)
把一个新的文件名 filename 与给定的打开的流 stream 关联,同时关闭流中的旧文件。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = freopen("test.txt", "w", stdout);printf("This is redirected to test.txt\n");fclose(fp);return 0;
}
10. int fseek(FILE *stream, long int offset, int whence)
设置流 stream 的文件位置为给定的偏移 offset,参数 whence 意味着从给定的位置查找的字节数。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");fseek(fp, 5, SEEK_SET);printf("Character at position 5: %c\n", fgetc(fp));fclose(fp);return 0;
}
11. int fsetpos(FILE *stream, const fpos_t *pos)
设置给定流 stream 的文件位置为给定的位置。参数 pos 是由函数
fgetpos 给定的位置。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fpos_t position;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");fgetpos(fp, &position);fseek(fp, 10, SEEK_SET);fsetpos(fp, &position);printf("Character at original position after seeking: %c\n", fgetc(fp));fclose(fp);return 0;
}
12. long int ftell(FILE *stream)
返回给定流 stream 的当前文件位置。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;long int position;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);position = ftell(fp);printf("Size of file: %ld bytes\n", position);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
13. size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)
把 ptr 所指向的数组中的数据写入到给定流 stream 中。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;char buffer[20] = "Hello, World!";fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");fwrite(buffer, sizeof(char), 13, fp);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
14. int remove(const char *filename)
删除给定的文件名 filename,以便它不再被访问。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {if (remove("test.txt") == 0) {printf("File deleted successfully.\n");} else {perror("Error deleting file");}return 0;
}
15. int rename(const char *old_filename, const char *new_filename)
把 old_filename 所指向的文件名改为 new_filename。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {if (rename("test.txt", "new_test.txt") == 0) {printf("File renamed successfully.\n");} else {perror("Error renaming file");}return 0;
}
16. void rewind(FILE *stream)
设置文件位置为给定流 stream 的文件的开头。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;char c;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");rewind(fp);c = fgetc(fp);printf("First character of file after rewinding: %c\n", c);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
17. void setbuf(FILE *stream, char *buffer)
定义流 stream 应如何缓冲。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;char buffer[BUFSIZ];fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");setbuf(fp, buffer);fprintf(fp, "This is just a test.\n");fclose(fp);return 0;
}
18. int setvbuf(FILE *stream, char *buffer, int mode, size_t size)
另一个定义流 stream 应如何缓冲的函数。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;char buffer[BUFSIZ];fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");setvbuf(fp, buffer, _IOFBF, BUFSIZ);fprintf(fp, "This is just a test.\n");fclose(fp);return 0;
}
19. FILE *tmpfile(void)
以二进制更新模式(wb+)创建临时文件。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *tmpfp;tmpfp = tmpfile();fprintf(tmpfp, "This is a temporary file.\n");fclose(tmpfp);return 0;
}
20. char *tmpnam(char *str)
生成并返回一个有效的临时文件名,该文件名之前是不存在的。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {char buffer[L_tmpnam];tmpnam(buffer);printf("Temporary file name: %s\n", buffer);return 0;
}
21. int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...)
发送格式化输出到流 stream 中。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;int num = 10;fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");fprintf(fp, "The number is: %d\n", num);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
22. int printf(const char *format, ...)
发送格式化输出到标准输出 stdout。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {int num = 10;printf("The number is: %d\n", num);return 0;
}
23. int sprintf(char *str, const char *format, ...)
发送格式化输出到字符串。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {char buffer[20];int num = 10;sprintf(buffer, "The number is: %d\n", num);printf("%s", buffer);return 0;
}
24. int vfprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, va_list arg)
使用参数列表发送格式化输出到流 stream 中。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>int my_printf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...) {va_list arg;int done;va_start(arg, format);done = vfprintf(stream, format, arg);va_end(arg);return done;
}int main() {FILE *fp;int num = 10;fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");my_printf(fp, "The number is: %d\n", num);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
25. int vprintf(const char *format, va_list arg)
使用参数列表发送格式化输出到标准输出 stdout 中。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>int my_printf(const char *format, ...) {va_list arg;int done;va_start(arg, format);done = vprintf(format, arg);va_end(arg);return done;
}int main() {int num = 10;my_printf("The number is: %d\n", num);return 0;
}
26. int vsprintf(char *str, const char *format, va_list arg)
使用参数列表发送格式化输出到字符串。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>int my_sprintf(char *str, const char *format, ...) {va_list arg;int done;va_start(arg, format);done = vsprintf(str, format, arg);va_end(arg);return done;
}int main() {char buffer[20];int num = 10;my_sprintf(buffer, "The number is: %d\n", num);printf("%s", buffer);return 0;
}
27. int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...)
从流 stream 读取格式化输入。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;int num;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");fscanf(fp, "%d", &num);printf("The number read from file is: %d\n", num);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
28. int scanf(const char *format, ...)
从标准输入 stdin 读取格式化输入。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {int num;printf("Enter a number: ");scanf("%d", &num);printf("You entered: %d\n", num);return 0;
}
29. int sscanf(const char *str, const char *format, ...)
从字符串读取格式化输入。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {char str[] = "The number is: 10";int num;sscanf(str, "The number is: %d", &num);printf("Extracted number from string: %d\n", num);return 0;
}
30. int fgetc(FILE *stream)
从指定的流 stream 获取下一个字符(一个无符号字符),并把位置标识符往前移动。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;int c;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");while ((c = fgetc(fp)) != EOF) {putchar(c);}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
31. char *fgets(char *str, int n, FILE *stream)
从指定的流 stream 读取一行,并把它存储在 str 所指向的字符串内。当读取 (n-1) 个字符时,或者读取到换行符时,或者到达文件末尾时,它会停止,具体视情况而定。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;char buffer[255];fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");while (fgets(buffer, 255, fp) != NULL) {printf("%s", buffer);}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
32. int fputc(int char, FILE *stream)
把参数 char 指定的字符(一个无符号字符)写入到指定的流 stream 中,并把位置标识符往前移动。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;int c;fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");for (c = 'A'; c <= 'Z'; ++c) {fputc(c, fp);}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
33. int fputs(const char *str, FILE *stream)
把字符串写入到指定的流 stream 中,但不包括空字符。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");fputs("This is just a test.\n", fp);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
34. int getc(FILE *stream)
从指定的流 stream 获取下一个字符(一个无符号字符),并把位置标识符往前移动。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;int c;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");while ((c = getc(fp)) != EOF) {putchar(c);}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
35. int getchar(void)
从标准输入 stdin 获取一个字符(一个无符号字符)。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {int c;printf("Enter a character: ");c = getchar();printf("You entered: ");putchar(c);return 0;
}
36. char *gets(char *str)
从标准输入 stdin 读取一行,并把它存储在 str 所指向的字符串中。当读取到换行符时,或者到达文件末尾时,它会停止,具体视情况
而定。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {char str[255];printf("Enter a string: ");gets(str);printf("You entered: %s\n", str);return 0;
}
37. int putc(int char, FILE *stream)
把参数 char 指定的字符(一个无符号字符)写入到指定的流 stream 中,并把位置标识符往前移动。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;int c;fp = fopen("test.txt", "w");putc('A', fp);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
38. int putchar(int char)
把参数 char 指定的字符(一个无符号字符)写入到标准输出 stdout 中。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {putchar('A');return 0;
}
39. int puts(const char *str)
把一个字符串写入到标准输出 stdout,直到空字符,但不包括空字符。换行符会被追加到输出中。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {puts("This is just a test.");return 0;
}
40. int ungetc(int char, FILE *stream)
把字符 char(一个无符号字符)推入到指定的流 stream 中,以便它是下一个被读取到的字符。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;int c;fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");c = fgetc(fp);ungetc(c, fp); // Push the character back to the streamprintf("Character pushed back: %c\n", fgetc(fp)); // Now read it againfclose(fp);return 0;
}
41. void perror(const char *str)
把一个描述性错误消息输出到标准错误 stderr。首先输出字符串 str,后跟一个冒号,然后是一个空格。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;fp = fopen("nonexistentfile.txt", "r");if (fp == NULL) {perror("Error opening file");return -1;}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
42. int snprintf(char *str, size_t size, const char *format, ...)
格式字符串到 str 中。
#include <stdio.h>int main() {char buffer[20];int num = 10;snprintf(buffer, 20, "The number is: %d\n", num);printf("%s", buffer);return 0;
}
以上是 stdio.h 中定义的所有函数的详细介绍和示例。该头文件是 C 语言中输入输出操作的核心,熟练掌握其中的函数将对编程工作大有裨益。
相关文章:

C 标准库 - <stdio.h> 详解
在 C 语言中,stdio.h 是一个非常重要的头文件,定义了一系列用于输入和输出的函数、变量和宏。本文将逐一介绍 stdio.h 中定义的函数,并提供每个函数的完整示例。 变量类型 在 stdio.h 中定义了三个变量类型: size_t:…...
)
支付宝小程序中唤起支付(前后端)
Java后台获取支付宝支付唯一订单号 /*** 支付宝小程序支付*/PostMapping(value "/xcxPayZFBTHREE")ResponseBodypublic Map<String,Object> xcxPayZFBTHREE(RequestBody byte[] req) {HashMap<String, Object> objectObjectMap new HashMap<>();…...
AI:139-基于深度学习的语音指令识别与执行
🚀点击这里跳转到本专栏,可查阅专栏顶置最新的指南宝典~ 🎉🎊🎉 你的技术旅程将在这里启航! 从基础到实践,深入学习。无论你是初学者还是经验丰富的老手,对于本专栏案例和项目实践都有参考学习意义。 ✨✨✨ 每一个案例都附带关键代码,详细讲解供大家学习,希望…...
选择 Python IDE(VSCode、Spyder、Visual Studio 2022和 PyCharm)
前言 当选择 Python 开发工具时,你需要考虑自己的需求、偏好和项目类型。下面是对VSCode、Spyder、Visual Studio 2022和 PyCharm的对比推荐总结: 结论 1、如果你专注于“数据科学”,选择SpyDer没错。 内容 Visual Studio Code (VS Code)…...

Rabbitmq 超时异常解决:PRECONDITION_FAILED - Timeout value used: 1800000 ms.
Rabbitmq 超时异常解决:PRECONDITION_FAILED - Timeout value used: 1800000 ms. 在使用 docker 启动 rabbitmq 的时候,执行一个超长时间的任务,出现了报错。 查询了一下发现,这个问题在于 rabbitmq 默认客户端超时时间是30分钟,…...

Java架构师之路二、数据库:SQL语言、关系型数据库、非关系型数据库、数据一致性、事务管理等。
目录 SQL语言: 关系型数据库: 非关系型数据库: 数据一致性: 事务管理: 上篇:Java架构师之路一、Java基础知识:Java语言特性、集合框架、IO流、多线程、反射、注解等基础知识。-CSDN博客 下…...

【Spring Cloud】高并发带来的问题及常见容错方案
文章目录 高并发带来的问题编写代码修改配置压力测试修改配置,并启动软件添加线程组配置线程并发数添加Http取样配置取样,并启动测试访问message方法观察效果 服务雪崩效应常见容错方案常见的容错思路常见的容错组件 总结 欢迎来到阿Q社区 https://bbs.c…...

springAOP落地实现
文章目录 前言一、熟悉相关概念:1、Aspect:2、Pointcut:3、Before:4、AfterReturning:5、AfterThrowing:6、After:7、Around: 二、具体使用case:1.pom文件2.代码 总结 前…...

Linux学习之vi/vim详细介绍
目录 编辑 1. 什么是 vim? 2. vi/vim 的使用 2.1 命令模式 2.2 输入模式 2.3 底线命令模式 3. vi/vim 使用实例 3.1 使用 vi/vim 进入一般模式 3.2 按下 i 进入输入模式(也称为编辑模式),开始编辑文字 3.3 按下 ESC 按钮回到一般模式…...
【AIGC大模型】跑通wonder3D (windows)
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.15008.pdf windows10系统 显卡:NVIDIA rtx 2060 一、安装anaconda 二、安装CUDA 11.7 (CUDA Toolkit 11.7 Downloads | NVIDIA Developer) 和 cudnn 8.9.7(cuDNN Archive | NVIDIA Developer)库 CUDA选择自定…...
Opencv(2)深浅拷贝与基本绘图(c++python
Opencv(2)深浅拷贝与基本绘图 文章目录 Opencv(2)深浅拷贝与基本绘图三、深浅拷贝四、HSV色域(1).意义(2).cvtColor()(3).inRange()(4).适应光线 三、深浅拷贝 浅拷贝是指当图像之间进行赋值时,图像数据并未发生复制,而是两个对象都指向同一块内存块。 …...
二叉树与堆
目录 1.树概念及结构 1.1树的概念 1.2 树的相关概念 1.3 树的表示 1.4 树在实际中的运用(表示文件系统的目录树结构) 2.二叉树概念及结构 2.1概念 2.2现实中的二叉树: 2.3 特殊的二叉树: 2.4 二叉树的性质 2.5 二叉树的…...

神经网络系列---损失函数
文章目录 损失函数均方误差(Mean Squared Error,MSE):平均绝对误差(Mean Absolute Error,MAE):交叉熵损失函数(Cross-Entropy Loss):Hinge Loss&a…...
)
LeetCode每日一题 有效的字母异位词(哈希表)
题目描述 给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。注意:若 s 和 t 中每个字符出现的次数都相同,则称 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。 示例 1: 输入: s "anagram", t "nagaram" 输…...
设计模式学习笔记 - 面向对象 - 8.实践:贫血模型和充血模型的原理及实践
1.Web开发常用的贫血MVC架构违背OOP吗? 前面我们依据讲过了面向对象四大特性、接口和抽象类、面向对象和面向过程编程风格,基于接口而非实现编程和多用组合少用继承设计思想。接下来,通过实战来学习如何将这些理论应用到实际的开发中。 大部…...

AI新纪元:可能的盈利之道
本文来源于Twitter大神宝玉(dotey)在聊 Sora 的时候,总结了 Sora 的价值和可能的盈利方向,我把这部分内容单独摘出来再整理一下。现在的生成式 AI 大家应该不陌生,用它总结文章、翻译、写作、画图,当然真正…...
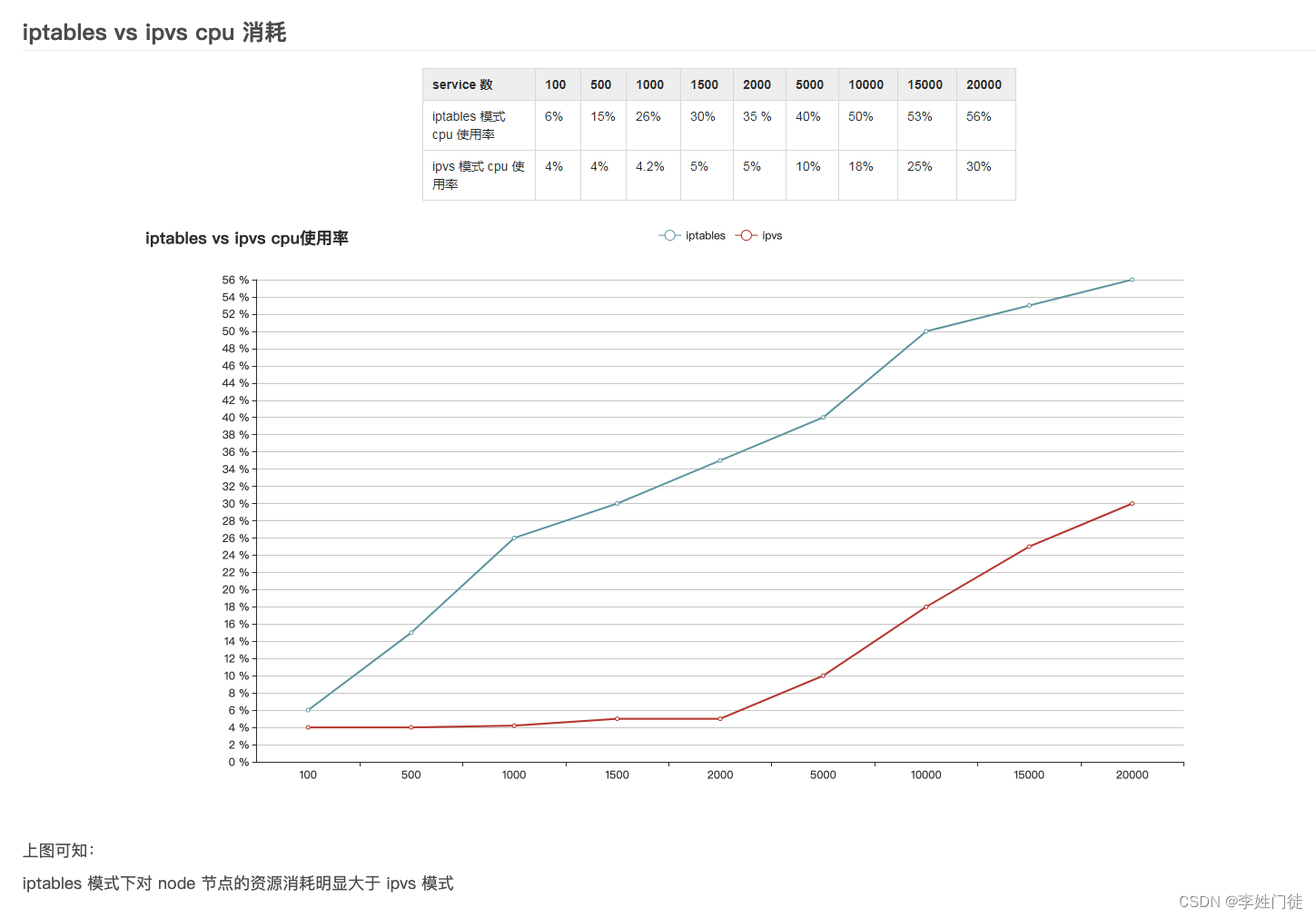
k8s的svc流量通过iptables和ipvs转发到pod的流程解析
文章目录 1. k8s的svc流量转发1.1 service 说明1.2 endpoints说明1.3 pod 说明1.4 svc流量转发的主要工作 2. iptables规则解析2.1 svc涉及的iptables链流程说明2.2 svc涉及的iptables规则实例2.2.1 KUBE-SERVICES规则链2.2.2 KUBE-SVC-EFPSQH5654KMWHJ5规则链2.2.3 KUBE-SEP-L…...
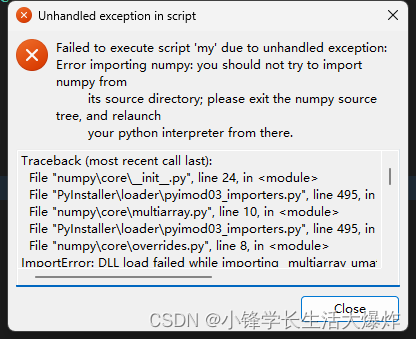
【踩坑】修复报错 you should not try to import numpy from its source directory
转载请注明出处:小锋学长生活大爆炸[xfxuezhang.cn] 报错如下: 修复方法一: pip install pyinstaller5.9 修复方法二: pip install numpy1.24.1...

预测脱碳企业的信用评级-论文代码复现
文献来源 【Forecasting credit ratings of decarbonized firms: Comparative assessmentof machine learning models】 文章有代码复现有两个基本工作,1.是提取每个算法的重要性;2.计算每个算法的评价指标 算法有 CRT 分类决策树 ANN 人工神经网络 R…...

目标检测——KITTI目标跟踪数据集
KITTI目标跟踪数据集是由德国卡尔斯鲁厄理工学院和丰田美国技术研究院联合创建的一个大规模自动驾驶场景下的计算机视觉算法评测数据集。这个数据集主要用于评估立体图像、光流、视觉测距、3D物体检测和3D跟踪等计算机视觉技术在车载环境下的性能这个数据集包含了在市区、乡村和…...
)
uniapp 对接腾讯云IM群组成员管理(增删改查)
UniApp 实战:腾讯云IM群组成员管理(增删改查) 一、前言 在社交类App开发中,群组成员管理是核心功能之一。本文将基于UniApp框架,结合腾讯云IM SDK,详细讲解如何实现群组成员的增删改查全流程。 权限校验…...
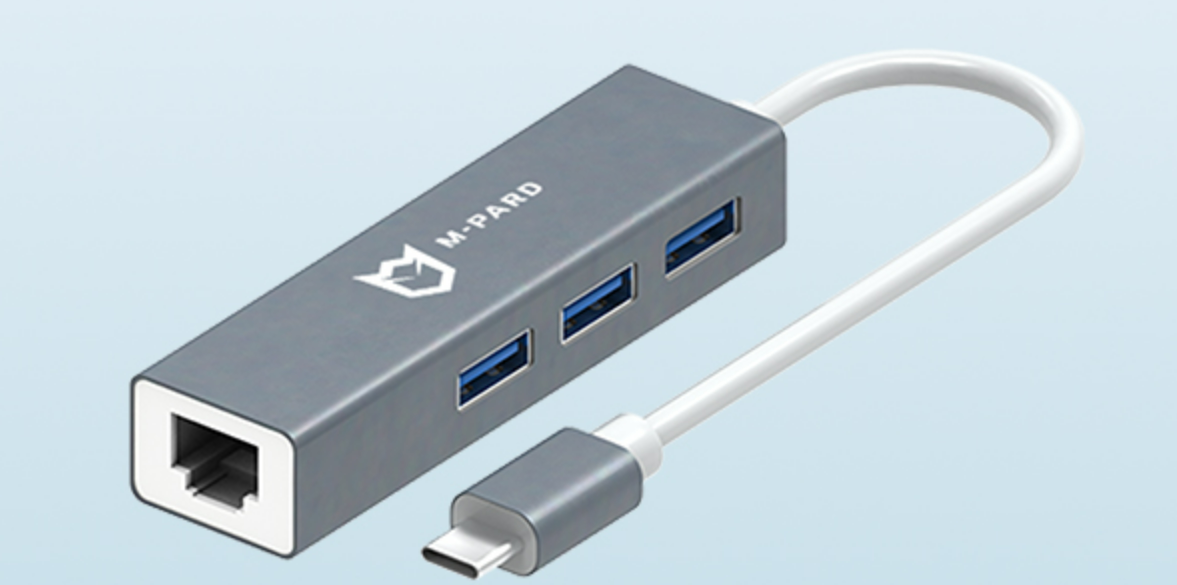

铭豹扩展坞 USB转网口 突然无法识别解决方法
当 USB 转网口扩展坞在一台笔记本上无法识别,但在其他电脑上正常工作时,问题通常出在笔记本自身或其与扩展坞的兼容性上。以下是系统化的定位思路和排查步骤,帮助你快速找到故障原因: 背景: 一个M-pard(铭豹)扩展坞的网卡突然无法识别了,扩展出来的三个USB接口正常。…...

CTF show Web 红包题第六弹
提示 1.不是SQL注入 2.需要找关键源码 思路 进入页面发现是一个登录框,很难让人不联想到SQL注入,但提示都说了不是SQL注入,所以就不往这方面想了 先查看一下网页源码,发现一段JavaScript代码,有一个关键类ctfs…...

Golang 面试经典题:map 的 key 可以是什么类型?哪些不可以?
Golang 面试经典题:map 的 key 可以是什么类型?哪些不可以? 在 Golang 的面试中,map 类型的使用是一个常见的考点,其中对 key 类型的合法性 是一道常被提及的基础却很容易被忽视的问题。本文将带你深入理解 Golang 中…...
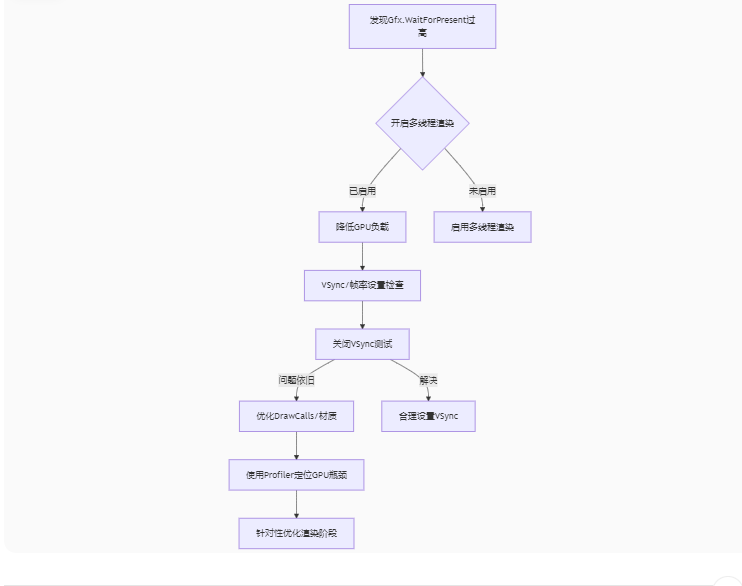
Unity3D中Gfx.WaitForPresent优化方案
前言 在Unity中,Gfx.WaitForPresent占用CPU过高通常表示主线程在等待GPU完成渲染(即CPU被阻塞),这表明存在GPU瓶颈或垂直同步/帧率设置问题。以下是系统的优化方案: 对惹,这里有一个游戏开发交流小组&…...
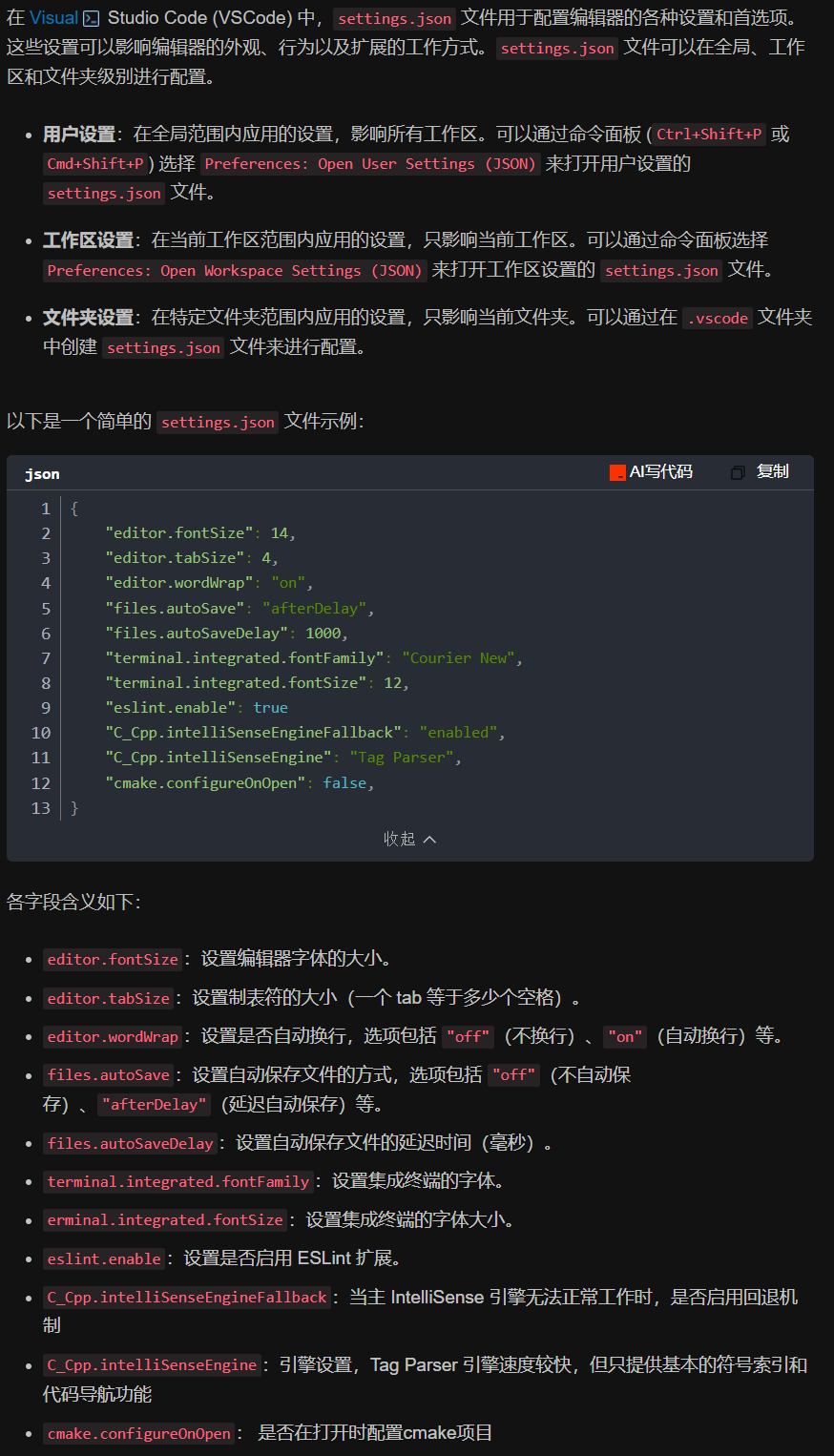
vscode(仍待补充)
写于2025 6.9 主包将加入vscode这个更权威的圈子 vscode的基本使用 侧边栏 vscode还能连接ssh? debug时使用的launch文件 1.task.json {"tasks": [{"type": "cppbuild","label": "C/C: gcc.exe 生成活动文件"…...

【解密LSTM、GRU如何解决传统RNN梯度消失问题】
解密LSTM与GRU:如何让RNN变得更聪明? 在深度学习的世界里,循环神经网络(RNN)以其卓越的序列数据处理能力广泛应用于自然语言处理、时间序列预测等领域。然而,传统RNN存在的一个严重问题——梯度消失&#…...
k8s业务程序联调工具-KtConnect
概述 原理 工具作用是建立了一个从本地到集群的单向VPN,根据VPN原理,打通两个内网必然需要借助一个公共中继节点,ktconnect工具巧妙的利用k8s原生的portforward能力,简化了建立连接的过程,apiserver间接起到了中继节…...
第 86 场周赛:矩阵中的幻方、钥匙和房间、将数组拆分成斐波那契序列、猜猜这个单词
Q1、[中等] 矩阵中的幻方 1、题目描述 3 x 3 的幻方是一个填充有 从 1 到 9 的不同数字的 3 x 3 矩阵,其中每行,每列以及两条对角线上的各数之和都相等。 给定一个由整数组成的row x col 的 grid,其中有多少个 3 3 的 “幻方” 子矩阵&am…...
)
.Net Framework 4/C# 关键字(非常用,持续更新...)
一、is 关键字 is 关键字用于检查对象是否于给定类型兼容,如果兼容将返回 true,如果不兼容则返回 false,在进行类型转换前,可以先使用 is 关键字判断对象是否与指定类型兼容,如果兼容才进行转换,这样的转换是安全的。 例如有:首先创建一个字符串对象,然后将字符串对象隐…...
