缩放算法优化步骤详解
添加链接描述
背景
假设数据存放在在unsigned char* m_pData 里面,宽和高分别是:m_nDataWidth m_nDataHeight
给定缩放比例:fXZoom fYZoom,返回缩放后的unsigned char* dataZoom
这里采用最简单的缩放算法即:
根据比例计算原图和缩放后图坐标的对应关系:缩放后图坐标*缩放比例 = 原图坐标
原始代码 未优化
#pragma once
class zoomBlock
{
public:zoomBlock() {};~zoomBlock();void zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom);void zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom);void test(float fXZoom =0.5, float fYZoom=0.5);void init(int DataWidth, int DataHeight);
private:void computeSrcValues(int* srcValues, size_t size, float zoom, int dataSize);private:unsigned char* m_pData = nullptr;float m_fXZoom = 1 ;//x轴缩放比例 m_nXZoom=1时 不缩放float m_fYZoom = 1 ;//y轴缩放比例int m_nDataWidth = 0;int m_nDataHeight = 0;
};#include "zoomBlock.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#define SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(p) { if( (p) != NULL ) delete[] (p); (p) = NULL; }zoomBlock::~zoomBlock()
{SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(m_pData);
}
void zoomBlock::init(int DataWidth, int DataHeight)
{m_nDataWidth = DataWidth;m_nDataHeight = DataHeight;m_pData = new unsigned char[m_nDataWidth* m_nDataHeight];for (int i = 0; i < m_nDataWidth * m_nDataHeight; ++i){m_pData[i] = static_cast<unsigned char>(i); // Replace this with your data initialization logic}
}void zoomBlock::zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;for (size_t row = 0; row < nZoomDataHeight; row++){for (size_t column = 0; column < nZoomDataWidth; column ++){//1int srcx = std::min(int(row / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcy = std::min(int(column / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);//2int srcPos = srcx * m_nDataHeight + srcy;int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}
}void zoomBlock::test(float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
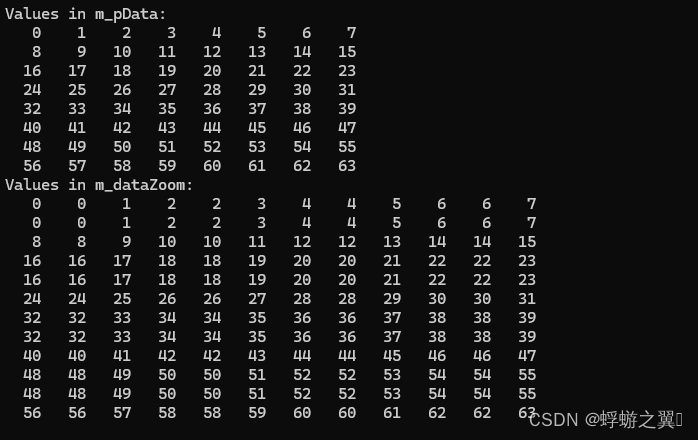
{init(8,8);std::cout << "Values in m_pData:" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < m_nDataWidth * m_nDataHeight; ++i){std::cout << std::setw(4) << static_cast<int>(m_pData[i]) << " ";if ((i + 1) % m_nDataWidth == 0) { // Adjust the value based on your datastd::cout << std::endl;}}unsigned char* dataZoom = new unsigned char[fXZoom * m_nDataWidth * fYZoom * m_nDataHeight];zoomData(dataZoom, fXZoom, fYZoom);// Print or inspect the values in m_dataZoomint nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;std::cout << "Values in m_dataZoom:" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < nZoomDataHeight * nZoomDataWidth; ++i){std::cout << std::setw(4)<< static_cast<int>(dataZoom[i]) << " ";if ((i + 1) % nZoomDataWidth == 0) { // Adjust the value based on your datastd::cout << std::endl;}}SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(dataZoom);}
测试代码
int main()
{zoomBlock zoomBlocktest;zoomBlocktest.test(1.5,1.5);return 0;
}
其中函数
·void zoomBlock::zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)·
没有使用任何加速优化,现在来分析它。
sse128
我们知道sse128可以一次性处理4个int类型,所以我们把最后一层for循环改成,4个坐标的算法,不满4个的单独计算
void zoomBlock::zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;for (size_t row = 0; row < nZoomDataHeight; row++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 4;for (size_t column = 0; column < nZoomDataWidth - remian; column += 4){//第一个坐标int srcx = std::min(int(row / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcy = std::min(int(column / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcx * m_nDataHeight + srcy;int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];//第二个坐标int srcx1 = std::min(int((row+1) / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcy1 = std::min(int((column+1) / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos1 = srcx1 * m_nDataHeight + srcy1;int desPos1 = (row+1) * nZoomDataHeight + column+1;dataZoom[desPos1] = m_pData[srcPos1];//第3个坐标// 。。。//第4个坐标// 。。。}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t column = nZoomDataWidth - remian; column < nZoomDataWidth; column++){int srcx = std::min(int(row / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcy = std::min(int(column / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcx * m_nDataHeight + srcy;int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}
}
上面 一次处理四个坐标的代码要改成sse的代码
在最里层的循环里面,每次都要计算 row / fYZoom 和 column / fXZoom,这个实际上可以挪出for循环,计算一次存到数组里
数据坐标desPos和srcPos ,必须放在最内存的循环里
所以我们用calculateSrcIndex函数单独处理 row / fYZoom 和 column / fXZoom,希望达到如下效果:
void calculateSrcIndex(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom,int max)
{for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){srcValues[i] = std::min(int(i/zoom),max);}
}
改成sse:
void calculateSrcIndex(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom,int max)
{__m128i mmIndex, mmSrcValue, mmMax;mmMax = _mm_set1_epi32(max);float zoomReciprocal = 1.0f / zoom;int remian = size % 4;for (size_t i = 0; i < size - remian; i += 4){mmIndex = _mm_set_epi32(i + 3, i + 2, i + 1, i);mmSrcValue = _mm_cvtps_epi32(_mm_mul_ps(_mm_cvtepi32_ps(mmIndex), _mm_set1_ps(zoomReciprocal)));// Ensure srcValues are within the valid range [0, max]mmSrcValue = _mm_min_epi32(mmSrcValue, mmMax);// Store the result to the srcValues array_mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(&srcValues[i]), mmSrcValue);}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t i = size - remian; i < size; i++){srcValues[i] = std::min(int(i / zoom), max);}
}
解释:
这里主要处理int型数据,为了使用sse加速,要使用__m128i类型来存储4个int
加载int到__m128i:
-
__m128i _mm_set1_epi32(int i);
这个指令是使用1个i,来设置__m128i,将__m128i看做4个32位的部分,则每个部分都被赋为i; -
__m128i _mm_set_epi32(int i3, int i2,int i1, int i0);
说明:使用4个int(32bits)变量来设置__m128i变量;
返回值:如果返回值__m128i,分为r0,r1,r2,r3返回值规则如下:
r0 := i0
r1 := i1
r2 := i2
r3 := i3
- __m128i _mm_cvtps_epi32 (__m128 a)
Converts packed 32-bit integers in a to packed single-precision (32-bit) floating-point elements.
加载float到__m128
- __m128 _mm_set1_ps(float w)
对应于_mm_load1_ps的功能,不需要字节对齐,需要多条指令。(r0 = r1 = r2 = r3 = w) - __m128 _mm_cvtepi32_ps (__m128i a)
Converts packed 32-bit integers in a to packed single-precision (32-bit) floating-point elements.
float乘法
__m128 dst = _mm_mul_ps (__m128 a, __m128 b)
将a, b中的32位浮点数相乘,结果打包给dst
取最小值
__m128i _mm_min_epi32 (__m128i a, __m128i b)
Compare packed signed 32-bit integers in a and b, and store packed minimum values in dst.
Operation
FOR j := 0 to 3
i := j*32
dst[i+31:i] := MIN(a[i+31:i], b[i+31:i])
ENDFOR
所以代码修改为
int* srcX = new int[nZoomDataHeight];int* srcY = new int[nZoomDataWidth];calculateSrcIndex(srcX, nZoomDataHeight, fXZoom , m_nDataHeight - 1);calculateSrcIndex(srcY, nZoomDataWidth, fYZoom, m_nDataWidth - 1);for (size_t row = 0; row < nZoomDataHeight; row++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 4;for (size_t column = 0; column < nZoomDataWidth - remian; column += 4){//第一个坐标int srcPos = srcX[row] * m_nDataHeight + srcY[column];int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];...}}
然后把坐标的计算转为sse
void zoomBlock::zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;int* srcX = new int[nZoomDataWidth];int* srcY = new int[nZoomDataHeight];calculateSrcIndex(srcX, nZoomDataWidth, fXZoom, m_nDataWidth - 1);calculateSrcIndex(srcY, nZoomDataHeight, fYZoom, m_nDataHeight - 1);for (size_t y = 0; y < nZoomDataHeight; y++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 4;for (size_t x = 0; x < nZoomDataWidth - remian; x += 4){__m128i mmsrcX = _mm_set_epi32(srcX[x + 3], srcX[x + 2], srcX[x+1], srcX[x]);__m128i srcPosIndices = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_set1_epi32(srcY[y] * m_nDataWidth),mmsrcX);__m128i desPosIndices = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_set1_epi32(y * nZoomDataWidth),_mm_set_epi32(x + 3, x + 2, x + 1, x));dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[0]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[0]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[1]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[1]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[2]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[2]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[3]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[3]];/*cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[0] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[0] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[1] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[1] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[2] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[2] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[3] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[3] << endl;*/}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t x = nZoomDataWidth - remian; x < nZoomDataWidth; x++){int srcy = std::min(int(y / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcx = std::min(int(x / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcy * m_nDataHeight + srcx;int desPos = y * nZoomDataHeight + x;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}delete[] srcX;delete[] srcY;
}
完整的代码
#pragma once
class zoomBlock
{
public:zoomBlock() {};~zoomBlock();void zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom);void zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom);void test(float fXZoom =0.5, float fYZoom=0.5);void init(int DataWidth, int DataHeight);
private:inline void calculateSrcIndex(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom, int max);private:unsigned char* m_pData = nullptr;float m_fXZoom = 1 ;//x轴缩放比例 m_nXZoom=1时 不缩放float m_fYZoom = 1 ;//y轴缩放比例int m_nDataWidth = 0;int m_nDataHeight = 0;
};#include "zoomBlock.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<immintrin.h>
using namespace std;
#define SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(p) { if( (p) != NULL ) delete[] (p); (p) = NULL; }zoomBlock::~zoomBlock()
{SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(m_pData);
}
void zoomBlock::init(int DataWidth, int DataHeight)
{m_nDataWidth = DataWidth;m_nDataHeight = DataHeight;m_pData = new unsigned char[m_nDataWidth* m_nDataHeight];for (int i = 0; i < m_nDataWidth * m_nDataHeight; ++i){m_pData[i] = static_cast<unsigned char>(i); // Replace this with your data initialization logic}
}void zoomBlock::zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;for (size_t y = 0; y < nZoomDataHeight; y++){for (size_t x = 0; x < nZoomDataWidth; x ++){//1int srcy = std::min(int(y / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcx = std::min(int(x / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);//2int srcPos = srcy * m_nDataWidth + srcx;int desPos = y * nZoomDataWidth + x;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}
}inline void zoomBlock::calculateSrcIndex(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom,int max)
{__m128i mmIndex, mmSrcValue, mmMax;mmMax = _mm_set1_epi32(max);float zoomReciprocal = 1.0f / zoom;int remian = size % 4;for (size_t i = 0; i < size - remian; i += 4){mmIndex = _mm_set_epi32(i + 3, i + 2, i + 1, i);mmSrcValue = _mm_cvttps_epi32(_mm_mul_ps(_mm_cvtepi32_ps(mmIndex), _mm_set1_ps(zoomReciprocal)));// Ensure srcValues are within the valid range [0, max]mmSrcValue = _mm_min_epi32(mmSrcValue, mmMax);// Store the result to the srcValues array_mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(&srcValues[i]), mmSrcValue);}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t i = size - remian; i < size; i++){srcValues[i] = std::min(int(i / zoom), max);}
}void zoomBlock::zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;int* srcX = new int[nZoomDataWidth];int* srcY = new int[nZoomDataHeight];calculateSrcIndex(srcX, nZoomDataWidth, fXZoom, m_nDataWidth - 1);calculateSrcIndex(srcY, nZoomDataHeight, fYZoom, m_nDataHeight - 1);for (size_t y = 0; y < nZoomDataHeight; y++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 4;for (size_t x = 0; x < nZoomDataWidth - remian; x += 4){/*int srcPos = srcx * m_nDataHeight + srcy;int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;*///dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];//__m128i mmsrcY = _mm_loadu_si128((__m128i*)(srcY));__m128i mmsrcX = _mm_set_epi32(srcX[x + 3], srcX[x + 2], srcX[x+1], srcX[x]);__m128i srcPosIndices = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_set1_epi32(srcY[y] * m_nDataWidth),mmsrcX);__m128i desPosIndices = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_set1_epi32(y * nZoomDataWidth),_mm_set_epi32(x + 3, x + 2, x + 1, x));dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[0]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[0]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[1]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[1]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[2]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[2]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[3]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[3]];/*cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[0] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[0] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[1] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[1] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[2] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[2] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[3] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[3] << endl;*/}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t x = nZoomDataWidth - remian; x < nZoomDataWidth; x++){int srcy = std::min(int(y / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcx = std::min(int(x / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcy * m_nDataHeight + srcx;int desPos = y * nZoomDataHeight + x;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}delete[] srcX;delete[] srcY;
}void zoomBlock::test(float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{init(8,4);std::cout << "Values in m_pData:" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < m_nDataWidth * m_nDataHeight; ++i){std::cout << std::setw(4) << static_cast<int>(m_pData[i]) << " ";if ((i + 1) % m_nDataWidth == 0) { // Adjust the value based on your datastd::cout << std::endl;}}int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;unsigned char* dataZoom = new unsigned char[nZoomDataWidth * nZoomDataHeight];zoomDataSSE128(dataZoom, fXZoom, fYZoom);//zoomData(dataZoom, fXZoom, fYZoom);// Print or inspect the values in m_dataZoomstd::cout << "Values in m_dataZoom:" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < nZoomDataHeight * nZoomDataWidth; ++i){std::cout << std::setw(4)<< static_cast<int>(dataZoom[i]) << " ";if ((i + 1) % nZoomDataWidth == 0) { // Adjust the value based on your datastd::cout << std::endl;}}SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(dataZoom);}int main()
{zoomBlock zoomBlocktest;zoomBlocktest.test(2,1);return 0;
}

AVX 256
inline void zoomBlock::calculateSrcIndex256(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom, int max)
{__m256i ymmIndex, ymmSrcValue, ymmMax;ymmMax = _mm256_set1_epi32(max);float zoomReciprocal = 1.0f / zoom;int remian = size % 8;for (size_t i = 0; i < size - remian; i += 8){ymmIndex = _mm256_set_epi32(i + 7, i + 6, i + 5, i + 4, i + 3, i + 2, i + 1, i);ymmSrcValue = _mm256_cvtps_epi32(_mm256_mul_ps(_mm256_cvtepi32_ps(ymmIndex), _mm256_set1_ps(zoomReciprocal)));// Ensure srcValues are within the valid range [0, max]ymmSrcValue = _mm256_min_epi32(ymmSrcValue, ymmMax);// Store the result to the srcValues array_mm256_storeu_si256(reinterpret_cast<__m256i*>(&srcValues[i]), ymmSrcValue);}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without AVX2for (size_t i = size - remian; i < size; i++){srcValues[i] = std::min(int(i / zoom), max);}
}
void zoomBlock::zoomDataAVX2(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;int* srcX = new int[nZoomDataWidth];int* srcY = new int[nZoomDataHeight];calculateSrcIndex(srcX, nZoomDataWidth, fXZoom, m_nDataWidth - 1);calculateSrcIndex(srcY, nZoomDataHeight, fYZoom, m_nDataHeight - 1);for (size_t y = 0; y < nZoomDataHeight; y++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 8;for (size_t x = 0; x < nZoomDataWidth - remian; x += 8){__m256i ymmSrcX = _mm256_set_epi32(srcX[x + 7], srcX[x + 6], srcX[x + 5], srcX[x + 4],srcX[x + 3], srcX[x + 2], srcX[x + 1], srcX[x]);__m256i srcPosIndices = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_set1_epi32(srcY[y] * m_nDataWidth),ymmSrcX);__m256i desPosIndices = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_set1_epi32(y * nZoomDataWidth),_mm256_set_epi32(x + 7, x + 6, x + 5, x + 4, x + 3, x + 2, x + 1, x));dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[0]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[0]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[1]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[1]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[2]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[2]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[3]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[3]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[4]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[4]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[5]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[5]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[6]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[6]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[7]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[7]];}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without AVX2for (size_t x = nZoomDataWidth - remian; x < nZoomDataWidth; x++){int srcy = std::min(int(y / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcx = std::min(int(x / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcy * m_nDataWidth + srcx;int desPos = y * nZoomDataWidth + x;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}delete[] srcX;delete[] srcY;
}
相关文章:

缩放算法优化步骤详解
添加链接描述 背景 假设数据存放在在unsigned char* m_pData 里面,宽和高分别是:m_nDataWidth m_nDataHeight 给定缩放比例:fXZoom fYZoom,返回缩放后的unsigned char* dataZoom 这里采用最简单的缩放算法即: 根据比…...

[axios]使用指南
axios使用指南 Axios 是一个基于 promise 的 HTTP 库,可以用在浏览器和 node.js 中。 axios 安装 npm安装 $ npm install axios 使用cdn <script src"https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> axios API axios(config)…...
HTML5基础2
drag 可以把拖放事件拆分成4个步骤 设置元素为可拖放。为了使元素可拖动,把 draggable 属性设置为 true 。 <img draggable"true"> 拖动什么。ondragstart 和 setData() const dragestart (ev)>{ev.dataTransfer.setData(play,ev.target.id)} …...
数据结构与算法-希尔排序
引言 在计算机科学中,数据结构和算法是构建高效软件系统的基石。而排序算法作为算法领域的重要组成部分,一直在各种应用场景中发挥着关键作用。今天我们将聚焦于一种基于插入排序的改进版本——希尔排序(Shell Sort),深…...

蓝桥杯算法错题记录
这里写目录标题 本文还在跟新,最新更新时间24/3/91. nextInt () next() nextLine() 的注意事项2 . 转换数据类型int ,string,charint -> string , charstring -> int ,charchar -> int , string 进制转换十六进制转化为10 进制 最大公约数 本文还在跟新&am…...

【Python 图像处理 PIL 系列 13 -- PIL 及 Image.convert 函数介绍】
文章目录 Python PIL 介绍PIL 使用介绍PIL convert 介绍PIL convert 使用示例 Python PIL 介绍 PIL 是 Python Image Library 的简称。PIL 库中提供了诸多用来处理图片的模块,可以对图片做类似于 PS(Photoshop) 的编辑。比如:改变…...

使用docker datascience-notebook进行数据分析
Jupyter/datascience-notebook 简介 jupyter/datascience-notebook 是 Docker Hub 上可用的 Docker 镜像:https://hub.docker.com/。该镜像提供了一个开箱即用的环境,用于数据科学任务,包括: Jupyter Notebook: 一个基于 Web 的…...
VR全景技术在VR看房中有哪些应用,能带来哪些好处
引言: 随着科技的不断发展,虚拟现实(VR)技术在房地产行业中的应用也越来越广泛。其中,VR全景技术在VR看房中的运用尤为突出。今天,让我们一起深入探讨VR全景技术在VR看房中的应用及其带来的种种好处。 一、…...
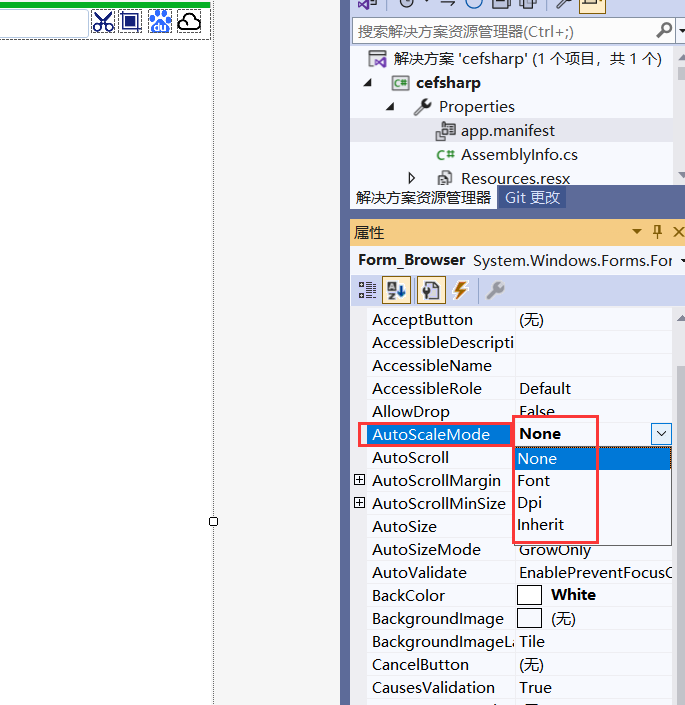
Winform窗体随着屏幕的DPI缩放,会引起窗体变形及字体变形,superTabControl标签字体大小不匹配
一、前言 superTabControl做的浏览器标签(cefsharp)在缩放比例(125%,150%时字体不协调) 物联网浏览器,定制浏览器,多媒体浏览器(支持H264)参考栏目文章即可 二、配置参数 app.manifest参数 dpiAware =true <application xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-c…...
java网络编程 01 IP,端口,域名,TCP/UDP, InetAddress
01.IP 要想让网络中的计算机能够互相通信,必须为计算机指定一个标识号,通过这个标识号来指定要接受数据的计算机和识别发送的计算机,而IP地址就是这个标识号,也就是设备的标识。 ip地址组成: ip地址分类:…...
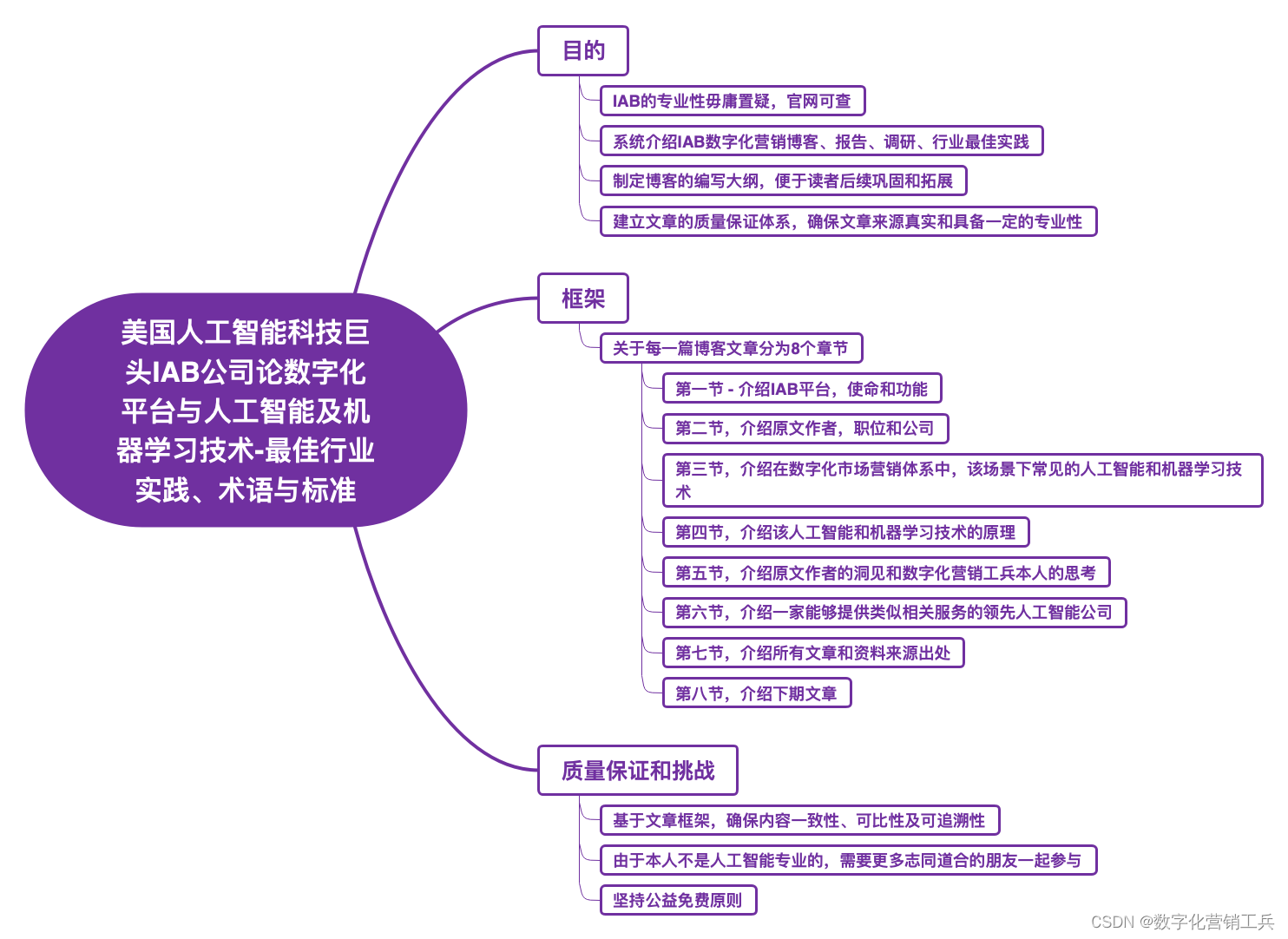
第十篇 - 如何利用人工智能技术做好营销流量整形管理?(Traffic Shaping)- 我为什么要翻译介绍美国人工智能科技巨头IAB公司
IAB平台,使命和功能 IAB成立于1996年,总部位于纽约市。 作为美国的人工智能科技巨头社会媒体和营销专业平台公司,互动广告局(IAB- the Interactive Advertising Bureau)自1996年成立以来,先…...

npm ERR! errno -13具体问题处理
npm ERR! errno -13具体问题处理 出现问题的报错 npm ERR! code EACCES npm ERR! syscall open npm ERR! path /Users/xxxx/.npm/_cache/index-v5/c6/06/xxxxx npm ERR! errno -13 npm ERR! npm ERR! Your cache folder contains root-owned files, due to a bug in npm ERR! …...
【Python】3. 基础语法(2) -- 语句篇
顺序语句 默认情况下, Python 的代码执行顺序是按照从上到下的顺序, 依次执行的. print("1") print("2") print("3")执行结果一定为 “123”, 而不会出现 “321” 或者 “132” 等. 这种按照顺序执行的代码, 我们称为 顺序语句. 这个顺序是很关…...
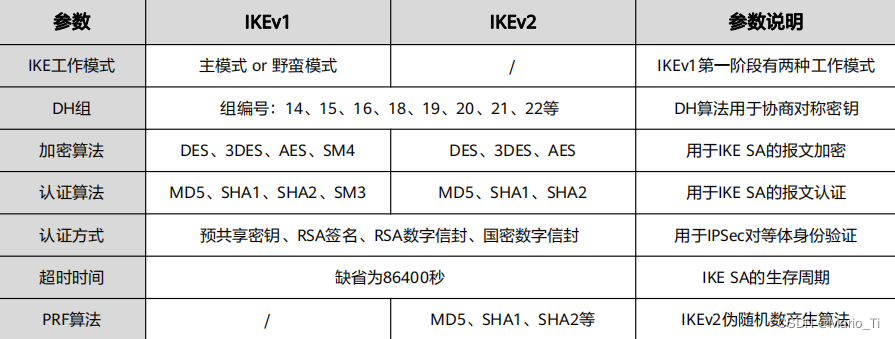
IPsec VPN之安全联盟
一、何为安全联盟 IPsec在两个端点建立安全通信,此时这两个端点被称为IPsec对等体。安全联盟,即SA,是指通信对等体之间对某些要素的约定,定义了两个对等体之间要用何种安全协议、IP报文的封装方式、加密和验证算法。SA是IPsec的基…...

012集——显示高考天数倒计时——vba实现
以下代码实现高考倒计时: Sub 高考倒计时() 高考日期 CDate("06,07," & Year(Date)) If Date > 高考日期 Then高考日期 CDate("06-07-" & Year(Date) 1) End If 年月日 Year(Date) & "年" & Month(Date) &am…...
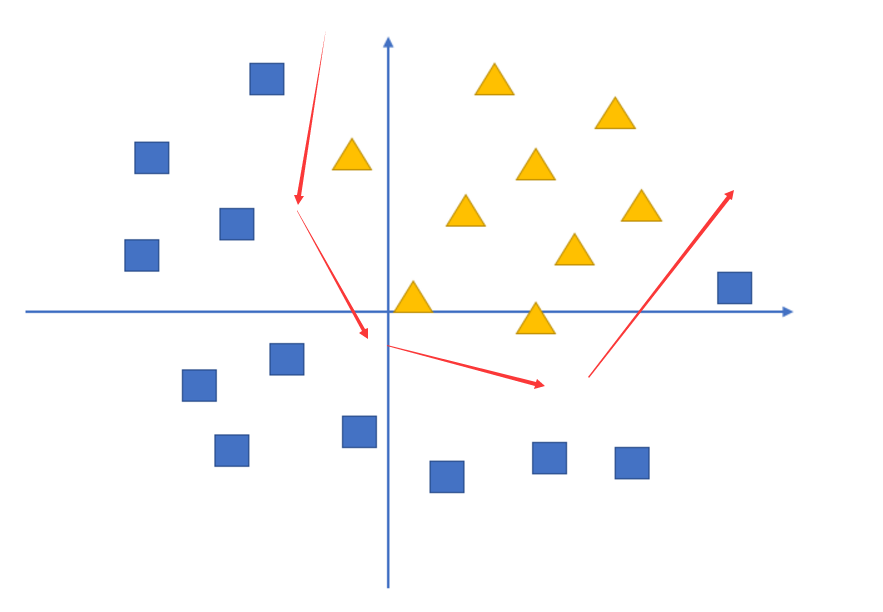
1.1 深度学习和神经网络
首先要说的是:深度学习的内容,真的不难。你要坚持下去。 神经网络 这就是一个神经网络。里面的白色圆圈就是神经元。神经元是其中最小的单位。 神经网络 单层神经网络: 感知机 (双层神经网络) 全连接层: …...

sentinel docker 基础配置学习
1:去官网下载 Releases alibaba/Sentinel GitHub 2:保存到linux 3:编写dockerfile FROM openjdk:8-jreLABEL authors"xxx" #第二步创建一个文件夹Z RUN mkdir /app #第三步复制jar 到app 下 COPY xxxxxx-1.8.7.jar /app/#第四…...

与缓存相关的状态码
与缓存相关的 HTTP 状态码主要涉及客户端和服务器之间对资源缓存的处理和验证,以下是一些常见的与缓存相关的状态码: 1. **200 OK**: - 当服务器成功处理了客户端的请求时,会返回状态码 200 OK。这意味着请求成功,…...

影刀_如何点击桌面图片上的指定区域
问题:如图,桌面上有一张打开的图片,如何点击“J&T极兔快递”的左上角和右下角? 总体流程: 1、用“影刀离线OCR”指令获取目标区域坐标值。 分别是:x1,y1,x2,y2 2、用快捷键ctrlalt键获取图片左上角的…...
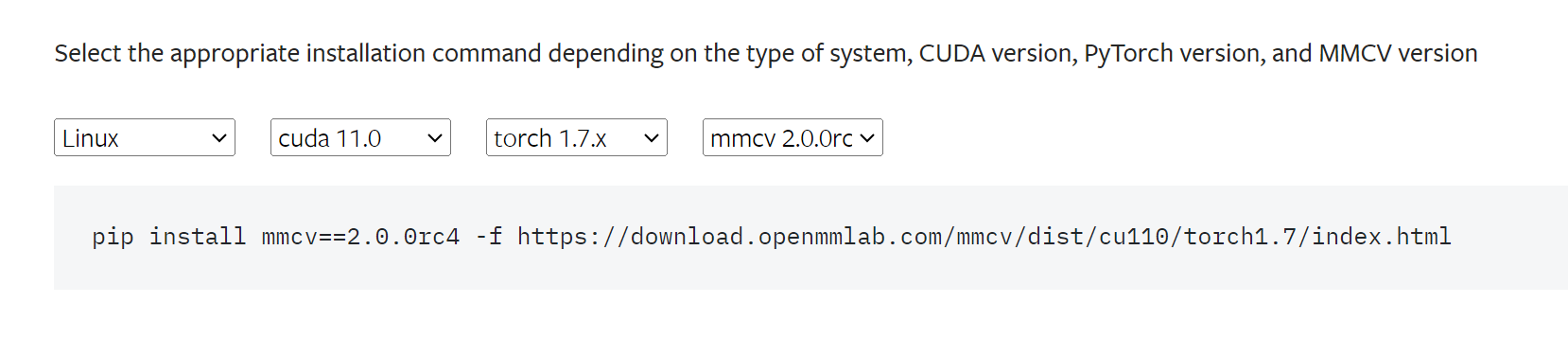
linux安装部署mmdetection,亲测可行
安装了两天,最后终于成功,这里有一些注意事项,版本对应啥的: 这里是mmdetection与MMCV的版本对应关系: mmdet与mmcv的版本对应有一些包因为版本问题直接pip下载不了,这里直接跑到官网去复制下载命令&#…...
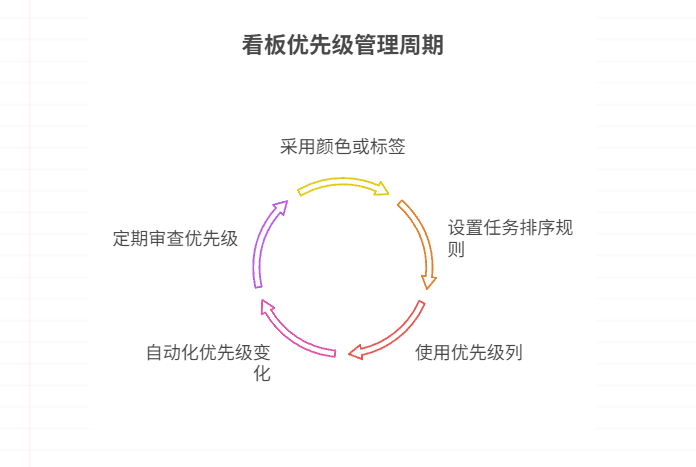
如何在看板中体现优先级变化
在看板中有效体现优先级变化的关键措施包括:采用颜色或标签标识优先级、设置任务排序规则、使用独立的优先级列或泳道、结合自动化规则同步优先级变化、建立定期的优先级审查流程。其中,设置任务排序规则尤其重要,因为它让看板视觉上直观地体…...

MODBUS TCP转CANopen 技术赋能高效协同作业
在现代工业自动化领域,MODBUS TCP和CANopen两种通讯协议因其稳定性和高效性被广泛应用于各种设备和系统中。而随着科技的不断进步,这两种通讯协议也正在被逐步融合,形成了一种新型的通讯方式——开疆智能MODBUS TCP转CANopen网关KJ-TCPC-CANP…...

高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景
高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景 高危文件识别旨在检测可能导致安全威胁的文件,如包含恶意代码、敏感数据或欺诈内容的文档,在企业协同办公环境中(如Teams、Google Workspace)尤为重要。结合大模型技术&…...

Axios请求超时重发机制
Axios 超时重新请求实现方案 在 Axios 中实现超时重新请求可以通过以下几种方式: 1. 使用拦截器实现自动重试 import axios from axios;// 创建axios实例 const instance axios.create();// 设置超时时间 instance.defaults.timeout 5000;// 最大重试次数 cons…...
k8s业务程序联调工具-KtConnect
概述 原理 工具作用是建立了一个从本地到集群的单向VPN,根据VPN原理,打通两个内网必然需要借助一个公共中继节点,ktconnect工具巧妙的利用k8s原生的portforward能力,简化了建立连接的过程,apiserver间接起到了中继节…...

Device Mapper 机制
Device Mapper 机制详解 Device Mapper(简称 DM)是 Linux 内核中的一套通用块设备映射框架,为 LVM、加密磁盘、RAID 等提供底层支持。本文将详细介绍 Device Mapper 的原理、实现、内核配置、常用工具、操作测试流程,并配以详细的…...

在web-view 加载的本地及远程HTML中调用uniapp的API及网页和vue页面是如何通讯的?
uni-app 中 Web-view 与 Vue 页面的通讯机制详解 一、Web-view 简介 Web-view 是 uni-app 提供的一个重要组件,用于在原生应用中加载 HTML 页面: 支持加载本地 HTML 文件支持加载远程 HTML 页面实现 Web 与原生的双向通讯可用于嵌入第三方网页或 H5 应…...

服务器--宝塔命令
一、宝塔面板安装命令 ⚠️ 必须使用 root 用户 或 sudo 权限执行! sudo su - 1. CentOS 系统: yum install -y wget && wget -O install.sh http://download.bt.cn/install/install_6.0.sh && sh install.sh2. Ubuntu / Debian 系统…...

智能AI电话机器人系统的识别能力现状与发展水平
一、引言 随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI电话机器人系统已经从简单的自动应答工具演变为具备复杂交互能力的智能助手。这类系统结合了语音识别、自然语言处理、情感计算和机器学习等多项前沿技术,在客户服务、营销推广、信息查询等领域发挥着越来越重要…...
基于TurtleBot3在Gazebo地图实现机器人远程控制
1. TurtleBot3环境配置 # 下载TurtleBot3核心包 mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src cd ~/catkin_ws/src git clone -b noetic-devel https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3.git git clone -b noetic https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_msgs.git git clone -b noetic-dev…...
