pytorch view、expand、transpose、permute、reshape、repeat、repeat_interleave
非contiguous操作
There are a few operations on Tensors in PyTorch that do not change the contents of a tensor, but change the way the data is organized. These operations include:
narrow(), view(), expand() and transpose() permute()
This is where the concept of contiguous comes in. In the example above, x is contiguous but y is not because its memory layout is different to that of a tensor of same shape made from scratch. Note that the word “contiguous” is a bit misleading because it’s not that the content of the tensor is spread out around disconnected blocks of memory. Here bytes are still allocated in one block of memory but the order of the elements is different!
When you call contiguous(), it actually makes a copy of the tensor such that the order of its elements in memory is the same as if it had been created from scratch with the same data.
transpose()
permute() and tranpose() are similar. transpose() can only swap two dimension. But permute() can swap all the dimensions. For example:
x = torch.rand(16, 32, 3)
y = x.tranpose(0, 2)z = x.permute(2, 1, 0)
permute
Returns a view of the original tensor input with its dimensions permuted.
>>> x = torch.randn(2, 3, 5)
>>> x.size()
torch.Size([2, 3, 5])
>>> torch.permute(x, (2, 0, 1)).size()
torch.Size([5, 2, 3])
expand
More than one element of an expanded tensor may refer to a single memory location. As a result, in-place operations (especially ones that are vectorized) may result in incorrect behavior. If you need to write to the tensors, please clone them first.
>>> x = torch.tensor([[1], [2], [3]])
>>> x.size()
torch.Size([3, 1])
>>> x.expand(3, 4)
tensor([[ 1, 1, 1, 1],[ 2, 2, 2, 2],[ 3, 3, 3, 3]])
>>> x.expand(-1, 4) # -1 means not changing the size of that dimension
tensor([[ 1, 1, 1, 1],[ 2, 2, 2, 2],[ 3, 3, 3, 3]])
Difference Between view() and reshape()
1/ view(): Does NOT make a copy of the original tensor. It changes the dimensional interpretation (striding) on the original data. In other words, it uses the same chunk of data with the original tensor, so it ONLY works with contiguous data.
2/ reshape(): Returns a view while possible (i.e., when the data is contiguous). If not (i.e., the data is not contiguous), then it copies the data into a contiguous data chunk, and as a copy, it would take up memory space, and also the change in the new tensor would not affect the value in the original tensor.
With contiguous data, reshape() returns a view.
When data is contiguous
x = torch.arange(1,13)
x
>> tensor([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12])
Reshape returns a view with the new dimension
y = x.reshape(4,3)
y
>>
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],[ 4, 5, 6],[ 7, 8, 9],[10, 11, 12]])
How do we know it’s a view? Because the element change in new tensor y would affect the value in x, and vice versa
y[0,0] = 100
y
>>
tensor([[100, 2, 3],[ 4, 5, 6],[ 7, 8, 9],[ 10, 11, 12]])
print(x)
>>
tensor([100, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12])
Next, let’s see how reshape() works on non-contiguous data.
# After transpose(), the data is non-contiguous
x = torch.arange(1,13).view(6,2).transpose(0,1)
x
>>
tensor([[ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11],[ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12]])
# Reshape() works fine on a non-contiguous data
y = x.reshape(4,3)
y
>>
tensor([[ 1, 3, 5],[ 7, 9, 11],[ 2, 4, 6],[ 8, 10, 12]])
# Change an element in y
y[0,0] = 100
y
>>
tensor([[100, 3, 5],[ 7, 9, 11],[ 2, 4, 6],[ 8, 10, 12]])
# Check the original tensor, and nothing was changed
x
>>
tensor([[ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11],[ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12]])
Finally, let’s see if view() can work on non-contiguous data.
No, it can’t!
# After transpose(), the data is non-contiguous
x = torch.arange(1,13).view(6,2).transpose(0,1)
x
>>
tensor([[ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11],[ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12]])
# Try to use view on the non-contiguous data
y = x.view(4,3)
y
>>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
----> 1 y = x.view(4,3)2 yRuntimeError: view size is not compatible with input tensor's size and stride (at least one dimension spans across two contiguous subspaces). Use .reshape(...) instead.
contiguous操作
reshape是能返回view就view,不能view就拷贝一份
>>> a = torch.arange(4.)
>>> torch.reshape(a, (2, 2))
tensor([[ 0., 1.],[ 2., 3.]])
>>> b = torch.tensor([[0, 1], [2, 3]])
>>> torch.reshape(b, (-1,))
tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3])
repeat是新克隆内存,但是expand是原地更新stride
import torch
a = torch.arange(10).reshape(2,5)
# b = a.expand(4,5) #这就崩了,多维上没法expand,用repeat
b = a.repeat(2,2)
print('b={}'.format(b))
'''
b=tensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]])
'''
c = torch.arange(3).reshape(1,3)
print('c={} c.stride()={}'.format(c, c.stride()))
d = c.expand(2,3)
print('d={} d.stride()={}'.format(d, d.stride()))
'''
c=tensor([[0, 1, 2]]) c.stride()=(3, 1), 在dim=0上迈3步,在dim=1上迈1步
d=tensor([[0, 1, 2],[0, 1, 2]]) d.stride()=(0, 1), 在dim=0上迈0步,在dim=1上迈1步
'''
d[0][0] = 5
print('c={} d={}'.format(c, d))
'''
c=tensor([[5, 1, 2]]) d=tensor([[5, 1, 2],[5, 1, 2]])
'''
repeat_interleave是把相邻着重复放,但是repeat是整体重复。所以repeat_interleave要指定下dim,但是repeat一次多维重复
This is different from torch.Tensor.repeat() but similar to numpy.repeat.
>>> x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> x.repeat_interleave(2)
tensor([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3])
>>> y = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
>>> torch.repeat_interleave(y, 2)
tensor([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4])
>>> torch.repeat_interleave(y, 3, dim=1)
tensor([[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2],[3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4]])
# 第一行重复1遍,第二行重复2遍
>>> torch.repeat_interleave(y, torch.tensor([1, 2]), dim=0)
tensor([[1, 2],[3, 4],[3, 4]])
>>> torch.repeat_interleave(y, torch.tensor([1, 2]), dim=0, output_size=3)
tensor([[1, 2],[3, 4],[3, 4]])- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48915810/what-does-contiguous-do-in-pytorch
- https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/pytorch-contiguous-vs-non-contiguous-tensor-view-understanding-view-reshape-73e10cdfa0dd
相关文章:

pytorch view、expand、transpose、permute、reshape、repeat、repeat_interleave
非contiguous操作 There are a few operations on Tensors in PyTorch that do not change the contents of a tensor, but change the way the data is organized. These operations include: narrow(), view(), expand() and transpose() permute() This is where the con…...
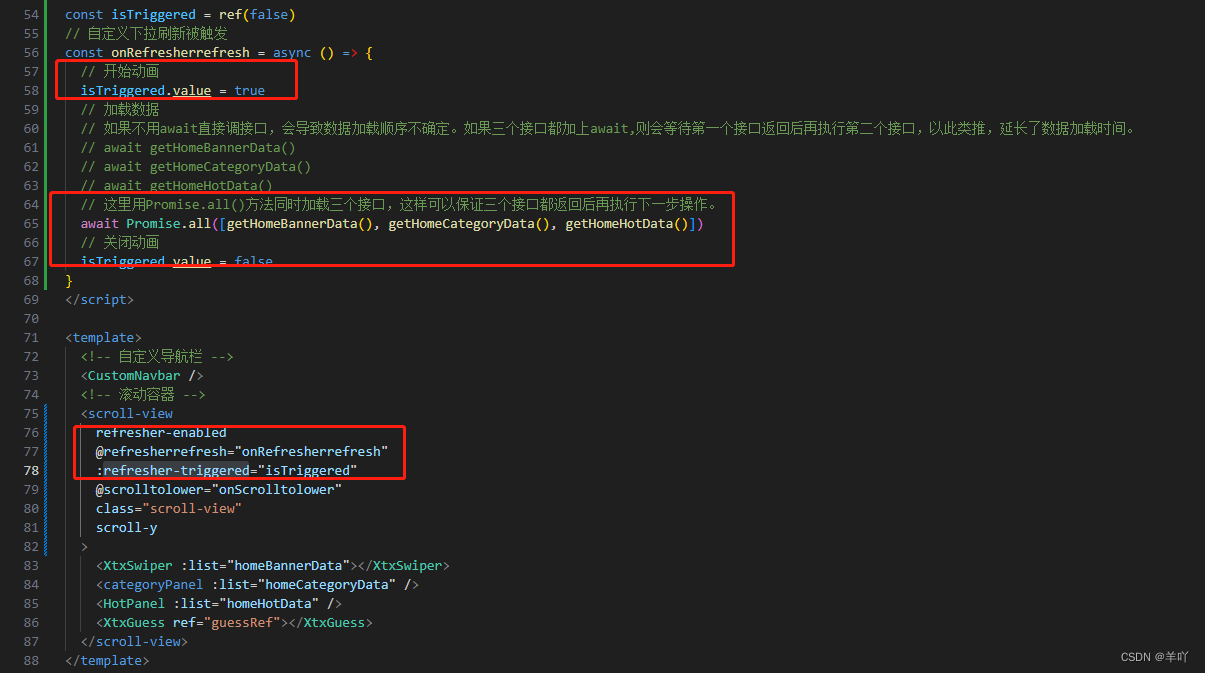
uni-app实现下拉刷新
业务逻辑如下: 1.在滚动容器中加入refresher-enabled属性,表示为开启下拉刷新 2.监听事件,添加refresherrefresh事件 3.在事件监听函数中加载数据 4.关闭动画,添加refresher-triggered属性,在数据请求前开启刷新动画…...

vue ts 应用梳理
文章目录 前言一、页面传值1.1 [props](https://cn.vuejs.org/guide/components/props.html)1.2 [emit](https://cn.vuejs.org/guide/components/events.html)1.3 [store](https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/getting-started.html) 二、实时计算2.1 [watch](https://cn.vuejs.org/gui…...
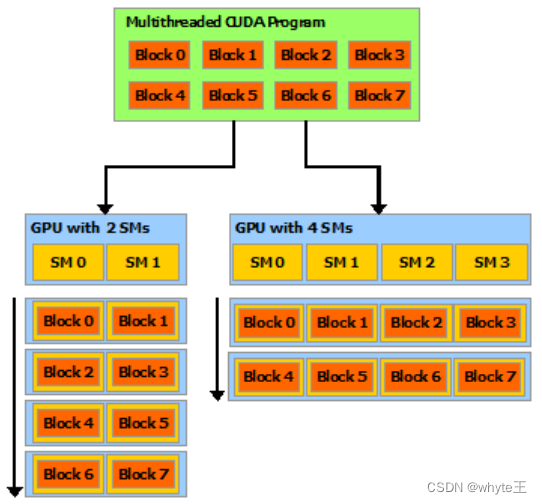
CUDA12.4文档-全文翻译
本博客参考官方文档进行介绍,全网仅此一家进行中文翻译,走过路过不要错过。 官方网址:https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/ 本文档分成多个博客进行介绍,在本人专栏中含有所有内容: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33345365/category_12610860.html CU…...
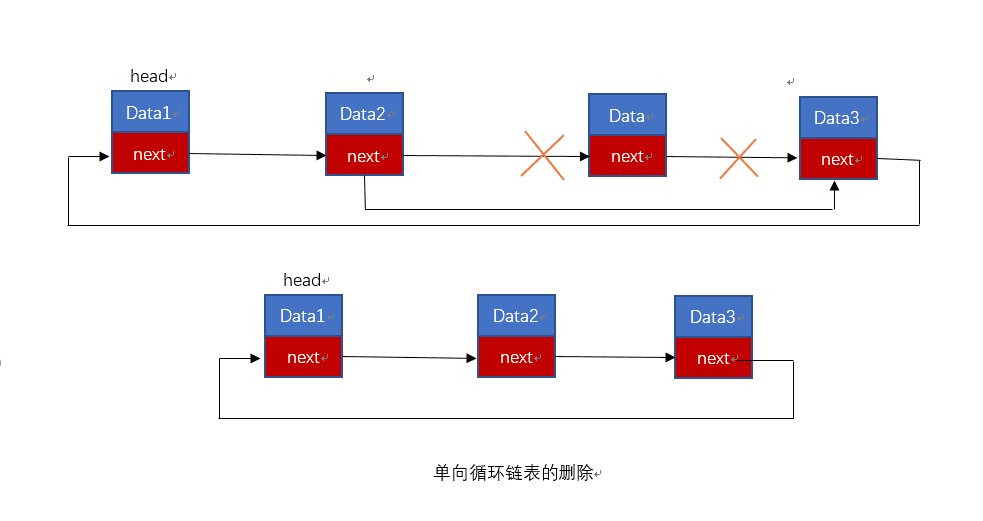
【C 数据结构】循环链表
文章目录 【 1. 基本原理 】【 2. 循环链表的创建 】2.1 循环链表结点设计2.2 循环单链表初始化 【 3. 循环链表的 插入 】【 4. 循环单链表的 删除操作 】【 5. 循环单链表的遍历 】【 6. 实例 - 循环链表的 增删查改 】【 7. 双向循环链表 】 【 1. 基本原理 】 对于单链表以…...

Python列表
使用场景:列表是用来存储多组数据的 列表是可变类型 列表支持切片 1.基本规则 1.列表使用[]来表示 2.初始化列表:list [] 3.列表可以一次性存储多个数据:[数据1,数据2,数据3,…] 4.列表中的每一项&#…...

谈谈系列之金融直播展业畅想
近些年直播异常火热,对于各大中小型基金证券公司,也纷纷引入直播作为新型展业渠道。在这其中有一部分直接采用第三方云平台,也有少部分选择自建直播平台。当然自建直播平台也不是纯自研,大抵都是外购第三方厂商整体解决方案&#…...
【C 数据结构】双向链表
文章目录 【 1. 基本原理 】【 2. 双向链表的 创建 】实例 - 输出双向链表 【 3. 双向链表 添加节点 】【 4. 双向链表 删除节点 】【 5. 双向链表查找节点 】【 7. 双向链表更改节点 】【 8. 实例 - 双向链表的 增删查改 】 【 1. 基本原理 】 表中各节点中都只包含一个指针&…...
Leetcode刷题之消失的数字(C语言版)
Leetcode刷题之消失的数字(C语言版) 一、题目描述二、题目解析 一、题目描述 数组nums包含从0到n的所有整数,但其中缺了一个。请编写代码找出那个缺失的整数。你有办法在O(n)时间内完成吗? 注意:本题相对书上原题稍作…...
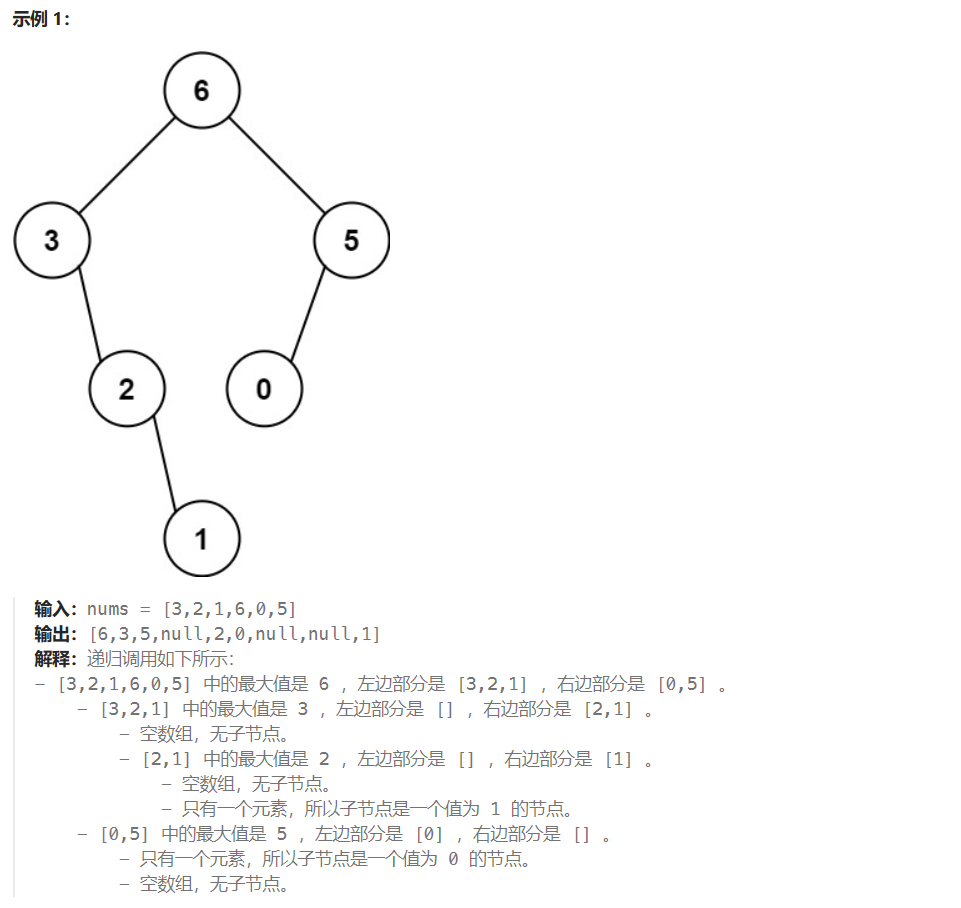
LeetCode654:最大二叉树
题目描述 给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建: 创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。 递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。 递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。 返回 nums 构建的 …...
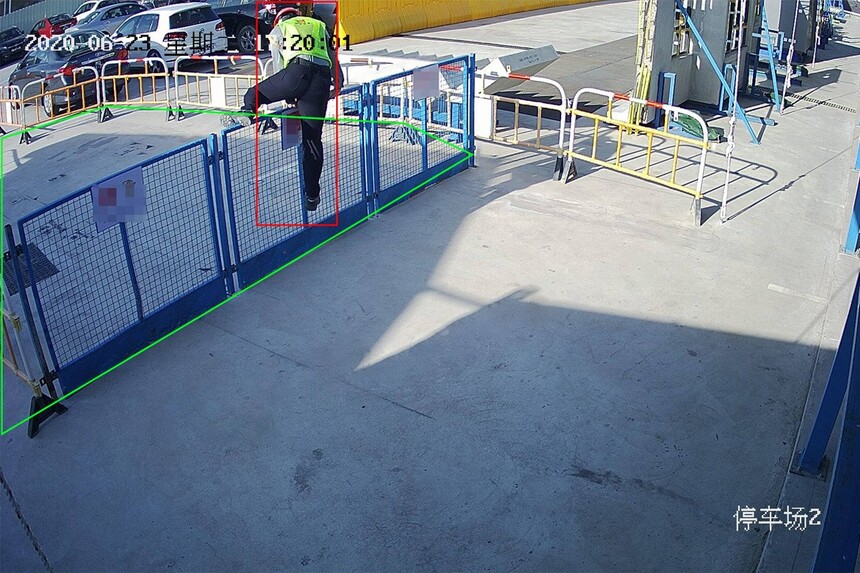

AI禁区徘徊监测识别摄像机
AI禁区徘徊监测识别摄像机是一种基于人工智能技术的智能监控设备,用于监测禁止进入或逗留的区域。这种摄像机通过高清摄像头实时捕捉场景图像,利用AI算法对人员徘徊行为进行识别和监测,有助于提高安全防范水平,减少潜在的安全风险…...
【学习】什么是信创适配性测试?信创适配性测试的重要性有哪些?
随着信息技术的快速发展和广泛应用,信息技术应用创新(信创)已成为推动我国产业升级和经济发展的重要力量。在信创领域,适配性测试至关重要,它不仅关系到信创产品的质量和性能,还直接影响到用户的使用体验和…...

linux 配置服务开机启动
一、Centos 中配置进程开启启动 1、使用 systemd 服务: (1)创建一个名为 myapp.service 的服务文件: [Unit] DescriptionMyApp #描述 After #描述服务类别 [Service] Typefork…...

React中State管理的4 个关键解决方案
在 React 应用开发中,状态(state)管理是非常重要的一部分。合理地管理状态可以确保组件的行为正确,提高应用的可维护性和性能。然而,在实际使用 React 的 state 时,开发者常常会遇到一些常见的问题和陷阱。 本文将从解决问题的角度,总结 React 中 state 管理的4个关键技巧: 使…...
Testng测试框架(6)--@Factory动态地创建测试类的实例
工厂允许您动态地创建测试。例如,假设您想创建一个测试方法,该方法将多次访问网站上的某个页面,并且您希望使用不同的值来调用它。 public class TestWebServer {Test(parameters { "number-of-times" })public void accessPage(…...
运维实战:案例解析与代码实践)
Kubernetes(K8s)运维实战:案例解析与代码实践
一、引言 随着容器技术的普及,Kubernetes(K8s)作为容器编排领域的领军者,已成为企业运维不可或缺的工具。K8s以其强大的自动化管理、可扩展性和高可用性等特点,为运维人员提供了便捷、高效的管理手段。本文将结合具体案…...

nginx反向代理配置详解
首先配置端口 server {listen 3080; server_name 172.20.109.27 localhost;}为了解决刷新后显示404的问题,增加配置如下: location / {root html;index index.html index.htm;try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/ mongrel;}location mongrel {# ip…...
【LeetCode】单调栈类题目详解
所有题目均来自于LeetCode,刷题代码使用的Python3版本 单调栈 通常针对一维数组的问题,如果需要寻找一个元素右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置,就可以使用单调栈,时间复杂度为O(n) 单调栈的本质是空间换时间&#…...

Python上解决TypeError: not all arguments converted during string formatting错误
目录 背景尝试1: pymysql模块的escape_string方法尝试2: 修改pandas.read_excel引擎尝试3: 回退xlrd版本总结 背景 在Linux上部署的时候, 使用pandas模块读取Excel, 然后pymysql模块入库, 结果发生了错误 Traceback (most recent call last):File "/usr/local/lib64/pyth…...
ASUS华硕ROG幻16Air笔记本电脑GU605M原装出厂Win11系统工厂包下载,带有ASUSRecovery一键重置还原
适用型号:GU605MI、GU605MY、GU605MZ、GU605MV、GU605MU 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1YBmZZbTKpIu883jYCS9KfA?pwd9jd4 提取码:9jd4 华硕原厂Windows11系统带有ASUS RECOVERY恢复功能、自带所有驱动、出厂主题壁纸、系统属性联机支持…...
LBE-LEX系列工业语音播放器|预警播报器|喇叭蜂鸣器的上位机配置操作说明
LBE-LEX系列工业语音播放器|预警播报器|喇叭蜂鸣器专为工业环境精心打造,完美适配AGV和无人叉车。同时,集成以太网与语音合成技术,为各类高级系统(如MES、调度系统、库位管理、立库等)提供高效便捷的语音交互体验。 L…...

生成xcframework
打包 XCFramework 的方法 XCFramework 是苹果推出的一种多平台二进制分发格式,可以包含多个架构和平台的代码。打包 XCFramework 通常用于分发库或框架。 使用 Xcode 命令行工具打包 通过 xcodebuild 命令可以打包 XCFramework。确保项目已经配置好需要支持的平台…...
微信小程序之bind和catch
这两个呢,都是绑定事件用的,具体使用有些小区别。 官方文档: 事件冒泡处理不同 bind:绑定的事件会向上冒泡,即触发当前组件的事件后,还会继续触发父组件的相同事件。例如,有一个子视图绑定了b…...

在HarmonyOS ArkTS ArkUI-X 5.0及以上版本中,手势开发全攻略:
在 HarmonyOS 应用开发中,手势交互是连接用户与设备的核心纽带。ArkTS 框架提供了丰富的手势处理能力,既支持点击、长按、拖拽等基础单一手势的精细控制,也能通过多种绑定策略解决父子组件的手势竞争问题。本文将结合官方开发文档,…...
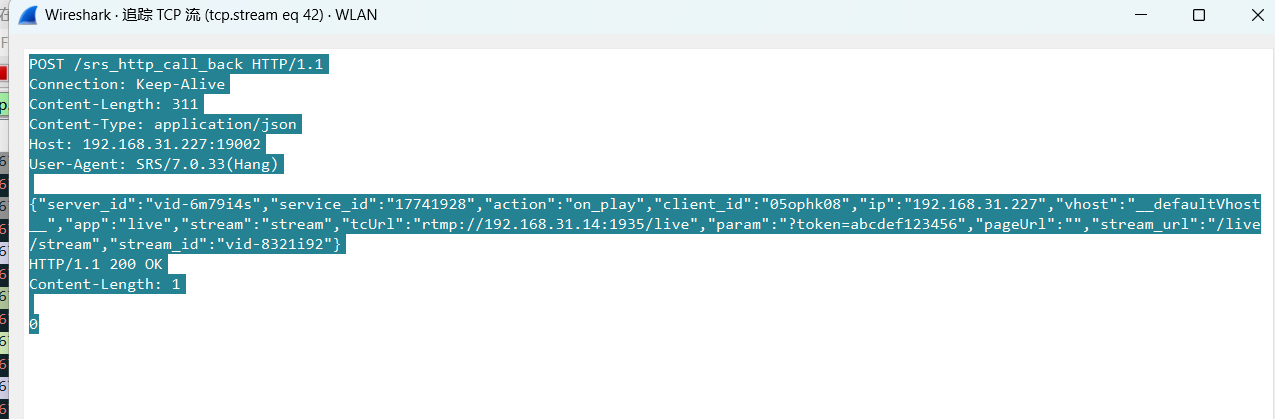
srs linux
下载编译运行 git clone https:///ossrs/srs.git ./configure --h265on make 编译完成后即可启动SRS # 启动 ./objs/srs -c conf/srs.conf # 查看日志 tail -n 30 -f ./objs/srs.log 开放端口 默认RTMP接收推流端口是1935,SRS管理页面端口是8080,可…...

Unit 1 深度强化学习简介
Deep RL Course ——Unit 1 Introduction 从理论和实践层面深入学习深度强化学习。学会使用知名的深度强化学习库,例如 Stable Baselines3、RL Baselines3 Zoo、Sample Factory 和 CleanRL。在独特的环境中训练智能体,比如 SnowballFight、Huggy the Do…...

MySQL 部分重点知识篇
一、数据库对象 1. 主键 定义 :主键是用于唯一标识表中每一行记录的字段或字段组合。它具有唯一性和非空性特点。 作用 :确保数据的完整性,便于数据的查询和管理。 示例 :在学生信息表中,学号可以作为主键ÿ…...

MinIO Docker 部署:仅开放一个端口
MinIO Docker 部署:仅开放一个端口 在实际的服务器部署中,出于安全和管理的考虑,我们可能只能开放一个端口。MinIO 是一个高性能的对象存储服务,支持 Docker 部署,但默认情况下它需要两个端口:一个是 API 端口(用于存储和访问数据),另一个是控制台端口(用于管理界面…...

掌握 HTTP 请求:理解 cURL GET 语法
cURL 是一个强大的命令行工具,用于发送 HTTP 请求和与 Web 服务器交互。在 Web 开发和测试中,cURL 经常用于发送 GET 请求来获取服务器资源。本文将详细介绍 cURL GET 请求的语法和使用方法。 一、cURL 基本概念 cURL 是 "Client URL" 的缩写…...

libfmt: 现代C++的格式化工具库介绍与酷炫功能
libfmt: 现代C的格式化工具库介绍与酷炫功能 libfmt 是一个开源的C格式化库,提供了高效、安全的文本格式化功能,是C20中引入的std::format的基础实现。它比传统的printf和iostream更安全、更灵活、性能更好。 基本介绍 主要特点 类型安全:…...
