【源码阅读】 Golang中的database/sql库源码探究
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、整体目录结构
- 二、driver包
- 1、驱动相关driver.Driver
- 2、驱动连接:driver.Conn
- 3、预处理结构:Stmt
- 4、执行结果 driver.Result
- 5、查询结果:driver.Rows
- 6、driver.RowsAffected
- 7、driver.Value
- 8、Value定义转换相关
- 三、sql包
- 1、Open方法
- 2、驱动注册:sql.Register
- 3、dsn驱动连接器:dsnConnector
- 3、OpenDB方法
- 4、数据库实例:sql.DB
- 5、ExecContext
- 6、QueryContext
- 7、连接建立:db.conn
- 8、连接重置:resetSession
- 9、连接池相关可配置参数
- 10、可监控指标
- 二、结语
- 三、参考
前言
在golang中,我们比较熟悉的mysql相关的库就是database/sql,这是golang的内置库,该标准库没有具体实现,只列出第三方库需要实现的具体内容。也就是说,这个库只是定义了接口,并没有具体的实现。Go语言为开发数据库驱动定义了一些标准接口,使用标准接口开发的代码,在迁移数据库时,不需要做任何修改(当然双方数据库都遵守标准接口)。下面我将基于golang1.19的源码探究这个库的实现。
源码地址:https://github.com/golang/go/tree/release-branch.go1.19/src/database/sql
一、整体目录结构
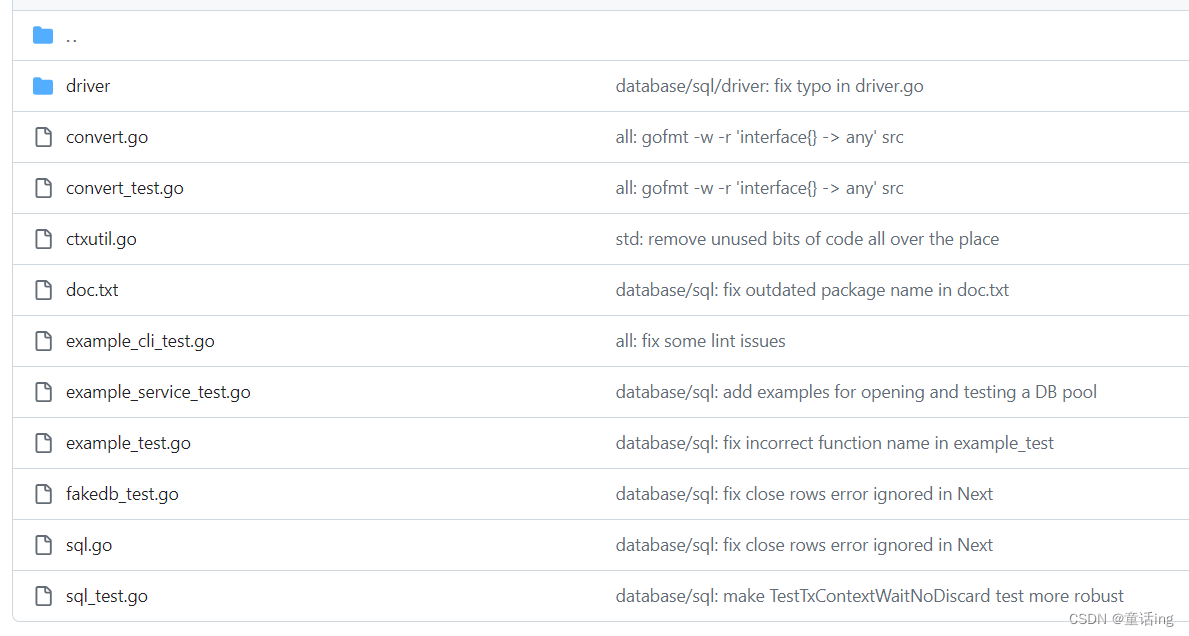
整个目录结构就是这样,包含两个包:sql和driver,这两个包必须一起配合着使用,sql包中主要包含着数据库具体实例、驱动的注册、结果集读取、转换各种定义类型结构等。driver包中主要是与数据库打交道的部分,增删改查的接口定义就在这里面。
sql包:
driver包:
二、driver包
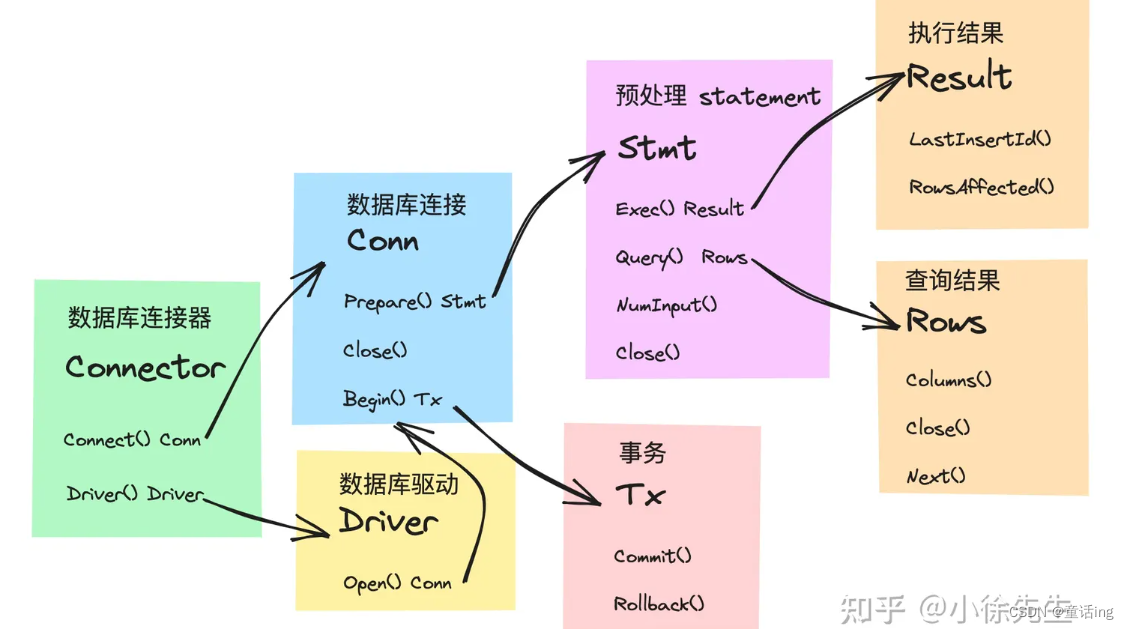
在driver包中,主要有如下的接口定义:
Connector:抽象的数据库连接器,需要具备创建数据库连接以及返回从属的数据库驱动的能力。Driver:抽象的数据库驱动,具备创建数据库连接的能力。Conn:抽象的数据库连接,具备预处理 sql 以及开启事务的能力。Tx:抽象的事务,具备提交和回滚的能力。Statement:抽象的请求预处理状态. 具备实际执行 sql 并返回执行结果的能力。Result/Row:抽象的 sql 执行结果。
1、驱动相关driver.Driver
Driver是一个数据库驱动的接口,定义了 Open(name string) ,该方法返回一个数据库的Conn接口:
// Driver is the interface that must be implemented by a database
// driver.
//
// Database drivers may implement DriverContext for access
// to contexts and to parse the name only once for a pool of connections,
// instead of once per connection.
type Driver interface {// Open returns a new connection to the database.// The name is a string in a driver-specific format.//// Open may return a cached connection (one previously// closed), but doing so is unnecessary; the sql package// maintains a pool of idle connections for efficient re-use.//// The returned connection is only used by one goroutine at a// time.Open(name string) (Conn, error)
}
在上面的源码中,我们可以清晰知道,Driver接口是必须要被所有的数据库驱动程序实现的,提供而一个Open方法用于返回一个连接,这个连接可能是缓存的有效的,也可能是新建的连接。同时也提供了一个DriverContext接口,数据库驱动程序可以实现DriverContext以访问上下文,并仅为连接池解析一次名称,而不是每个连接解析一次。
DriverContext接口提供了一个OpenConnector方法用于返回一个连接器,在连接器中去获取对应的连接。连接器接口Connector提供了两个方法,Connect和Driver,其中Connect用于获取连接,并且可以附带参数ctx,Driver用于获取当前这个连接器的的驱动程序。
// If a Driver implements DriverContext, then sql.DB will call
// OpenConnector to obtain a Connector and then invoke
// that Connector's Connect method to obtain each needed connection,
// instead of invoking the Driver's Open method for each connection.
// The two-step sequence allows drivers to parse the name just once
// and also provides access to per-Conn contexts.
type DriverContext interface {// OpenConnector must parse the name in the same format that Driver.Open// parses the name parameter.OpenConnector(name string) (Connector, error)
}// A Connector represents a driver in a fixed configuration
// and can create any number of equivalent Conns for use
// by multiple goroutines.
//
// A Connector can be passed to sql.OpenDB, to allow drivers
// to implement their own sql.DB constructors, or returned by
// DriverContext's OpenConnector method, to allow drivers
// access to context and to avoid repeated parsing of driver
// configuration.
//
// If a Connector implements io.Closer, the sql package's DB.Close
// method will call Close and return error (if any).
type Connector interface {// Connect returns a connection to the database.// Connect may return a cached connection (one previously// closed), but doing so is unnecessary; the sql package// maintains a pool of idle connections for efficient re-use.//// The provided context.Context is for dialing purposes only// (see net.DialContext) and should not be stored or used for// other purposes. A default timeout should still be used// when dialing as a connection pool may call Connect// asynchronously to any query.//// The returned connection is only used by one goroutine at a// time.Connect(context.Context) (Conn, error)// Driver returns the underlying Driver of the Connector,// mainly to maintain compatibility with the Driver method// on sql.DB.Driver() Driver
}
2、驱动连接:driver.Conn
在驱动连接driver.Conn中,包含着预处理结构statement、网络连接的关闭、以及开启一个事务的方式。
type Conn interface {// Prepare returns a prepared statement, bound to this connection.Prepare(query string) (Stmt, error)// Close invalidates and potentially stops any current// prepared statements and transactions, marking this// connection as no longer in use.//// Because the sql package maintains a free pool of// connections and only calls Close when there's a surplus of// idle connections, it shouldn't be necessary for drivers to// do their own connection caching.//// Drivers must ensure all network calls made by Close// do not block indefinitely (e.g. apply a timeout).Close() error// Begin starts and returns a new transaction.//// Deprecated: Drivers should implement ConnBeginTx instead (or additionally).Begin() (Tx, error)
}Prepare:返回与当前连接相关的执行SQL语句的准备状态(Stmt),可以进行查询、删除等操作。
Close:关闭当前的链接,执行释放连接拥有的资源等清理工作。
Begin: // 返回一个代表事务处理的Tx,通过它可以进行查询、更新等操作,或者对事务进行回滚、递交。
新版本中,Begin方法已经不推荐了,被ConnBeginTx代替了, 新版本中的Begin方法多提供了入参ctx和额外的可选参数opts,便于扩展和控制。
// ConnBeginTx enhances the Conn interface with context and TxOptions.
type ConnBeginTx interface {// BeginTx starts and returns a new transaction.// If the context is canceled by the user the sql package will// call Tx.Rollback before discarding and closing the connection.//// This must check opts.Isolation to determine if there is a set// isolation level. If the driver does not support a non-default// level and one is set or if there is a non-default isolation level// that is not supported, an error must be returned.//// This must also check opts.ReadOnly to determine if the read-only// value is true to either set the read-only transaction property if supported// or return an error if it is not supported.BeginTx(ctx context.Context, opts TxOptions) (Tx, error)
}
3、预处理结构:Stmt
// Stmt is a prepared statement. It is bound to a Conn and not
// used by multiple goroutines concurrently.
type Stmt interface {// Close closes the statement.//// As of Go 1.1, a Stmt will not be closed if it's in use// by any queries.//// Drivers must ensure all network calls made by Close// do not block indefinitely (e.g. apply a timeout).Close() error// NumInput returns the number of placeholder parameters.//// If NumInput returns >= 0, the sql package will sanity check// argument counts from callers and return errors to the caller// before the statement's Exec or Query methods are called.//// NumInput may also return -1, if the driver doesn't know// its number of placeholders. In that case, the sql package// will not sanity check Exec or Query argument counts.NumInput() int// Exec executes a query that doesn't return rows, such// as an INSERT or UPDATE.//// Deprecated: Drivers should implement StmtExecContext instead (or additionally).Exec(args []Value) (Result, error)// Query executes a query that may return rows, such as a// SELECT.//// Deprecated: Drivers should implement StmtQueryContext instead (or additionally).Query(args []Value) (Rows, error)
}// StmtExecContext enhances the Stmt interface by providing Exec with context.
type StmtExecContext interface {// ExecContext executes a query that doesn't return rows, such// as an INSERT or UPDATE.//// ExecContext must honor the context timeout and return when it is canceled.ExecContext(ctx context.Context, args []NamedValue) (Result, error)
}// StmtQueryContext enhances the Stmt interface by providing Query with context.
type StmtQueryContext interface {// QueryContext executes a query that may return rows, such as a// SELECT.//// QueryContext must honor the context timeout and return when it is canceled.QueryContext(ctx context.Context, args []NamedValue) (Rows, error)
}
Close:关闭当前的连接状态,但如果当前正在执行query,query还是会有效返回rows数据。
NumInput:返回当前预留参数的个数,当返回>=0时,数据库驱动会智能检查调用者的参数。 当数据库驱动包不知道预留参数的时候,返回-1。
Exec:执行Prepare准备好的SQL,传入参数执行Update/Insert等操作,返回Result数据,Result中包含最后插入的自增主键序号(LastInsertId)和受影响的行数(RowAffected)。
Query:执行Prepare准备好的SQL,传入需要的参数执行select操作,返回Rows结果集。
4、执行结果 driver.Result
// Result is the result of a query execution.
type Result interface {// LastInsertId returns the database's auto-generated ID// after, for example, an INSERT into a table with primary// key.LastInsertId() (int64, error)// RowsAffected returns the number of rows affected by the// query.RowsAffected() (int64, error)
}
5、查询结果:driver.Rows
// Rows is an iterator over an executed query's results.
type Rows interface {// 该函数返回查询数据库表的字段信息,这个返回的slice和SQL查询的字段一一对应,// 而不是返回整张表的所有字段。Columns() []string// 用来关闭Rows迭代器Close() error// 该函数用来返回下一条数据,把数据赋值给dest .// dest里面元素必须是driver.Value的值(string除外),返回的数据里面所有的 string 都必须转换成// []byte.如果最后没有数据了,Next 函数返回 io.EOF。Next(dest []Value) error
}
可以看到,在新版的源码中,Exec和Query已经被单独拎出去定义了接口,方法中只是为了增加ctx参数,这也是golang为了保持向下兼容而做的,试想,如果直接在原有的接口定义的加入ctx,升级golang版本的时候这块儿肯定得花很大功夫去改造。
6、driver.RowsAffected
RowsAffected 不是别的东西,实际上只是 int64 的别名,但它实现了Result接口,用于底层实现 Result 的表示方式,构建Exec方法返回的结果集。
// RowsAffected implements Result for an INSERT or UPDATE operation
// which mutates a number of rows.
type RowsAffected int64var _ Result = RowsAffected(0)func (RowsAffected) LastInsertId() (int64, error) {return 0, errors.New("LastInsertId is not supported by this driver")
}func (v RowsAffected) RowsAffected() (int64, error) {return int64(v), nil
}
7、driver.Value
Value 其实是一个空接口,可以容纳任何的数据。
// diver 的 Value 是驱动必须能够操作的 Value,Value要么是nil,要么是下面任意一种:
//
// int64
// float64
// bool
// []byte
// string [*] 除了Rows.Next,返回的不能是string
// time.Time
//
type Value interface{}
8、Value定义转换相关
在driver/types.go中,还定义了ValueConverter将一个普通的值(any)转换成driver.Value的接口、Valuer接口用于获取driver.Value等,就不逐个展开了。
// ValueConverter is the interface providing the ConvertValue method.
//
// Various implementations of ValueConverter are provided by the
// driver package to provide consistent implementations of conversions
// between drivers. The ValueConverters have several uses:
//
// - converting from the Value types as provided by the sql package
// into a database table's specific column type and making sure it
// fits, such as making sure a particular int64 fits in a
// table's uint16 column.
//
// - converting a value as given from the database into one of the
// driver Value types.
//
// - by the sql package, for converting from a driver's Value type
// to a user's type in a scan.
type ValueConverter interface {// ConvertValue converts a value to a driver Value.ConvertValue(v any) (Value, error)
}// Valuer is the interface providing the Value method.
//
// Types implementing Valuer interface are able to convert
// themselves to a driver Value.
type Valuer interface {// Value returns a driver Value.// Value must not panic.Value() (Value, error)
}
三、sql包
在sql包中,包含着我们最熟悉的Open方法,返回一个DB实例,这个DB实例,对应为数据库的具象化实例。内部维护着连接池相关的信息。
1、Open方法
Open方法返回一个db实例,且这个DB实例是可以在多个gorountine中使用的,当调用Open方法的时候,会先从一个全局的驱动注册器(drivers)中获取对应的驱动,如果没注册对应的驱动,则会出错。如果这个驱动实现了DriverContext接口,则会调用OpenConnector方法创建一个对应的连接器,用于连接数据库。否则调用dsnConnector结构,组装返回一个对应的db实例。
// Open opens a database specified by its database driver name and a
// driver-specific data source name, usually consisting of at least a
// database name and connection information.
//
// Most users will open a database via a driver-specific connection
// helper function that returns a *DB. No database drivers are included
// in the Go standard library. See https://golang.org/s/sqldrivers for
// a list of third-party drivers.
//
// Open may just validate its arguments without creating a connection
// to the database. To verify that the data source name is valid, call
// Ping.
//
// The returned DB is safe for concurrent use by multiple goroutines
// and maintains its own pool of idle connections. Thus, the Open
// function should be called just once. It is rarely necessary to
// close a DB.
func Open(driverName, dataSourceName string) (*DB, error) {driversMu.RLock()driveri, ok := drivers[driverName]driversMu.RUnlock()if !ok {return nil, fmt.Errorf("sql: unknown driver %q (forgotten import?)", driverName)}if driverCtx, ok := driveri.(driver.DriverContext); ok {connector, err := driverCtx.OpenConnector(dataSourceName)if err != nil {return nil, err}return OpenDB(connector), nil}return OpenDB(dsnConnector{dsn: dataSourceName, driver: driveri}), nil
}
2、驱动注册:sql.Register
在各种驱动的实现中,一般都会在init方法中调用database/sql提供的注册方法注册对应的驱动。但同时只允许注册一种类型的驱动,否则会panic。
全局驱动注册器
driversMu sync.RWMutex
drivers = make(map[string]driver.Driver)
// 驱动注册
func Register(name string, driver driver.Driver) {driversMu.Lock()defer driversMu.Unlock()if driver == nil {panic("sql: Register driver is nil")}if _, dup := drivers[name]; dup {panic("sql: Register called twice for driver " + name)}drivers[name] = driver
}
3、dsn驱动连接器:dsnConnector
该结构很简单的实现了两个方法,一个是调用驱动的Open方法创建一个连接,另一个则是返回当前的驱动实例。
sql.go dsn驱动连接器
type dsnConnector struct {dsn stringdriver driver.Driver
}func (t dsnConnector) Connect(_ context.Context) (driver.Conn, error) {return t.driver.Open(t.dsn)
}func (t dsnConnector) Driver() driver.Driver {return t.driver
}
3、OpenDB方法
从上面我们知道,最终获得连接器后,都会调用这个方法创建一个db实例返回。
// OpenDB opens a database using a Connector, allowing drivers to
// bypass a string based data source name.
//
// Most users will open a database via a driver-specific connection
// helper function that returns a *DB. No database drivers are included
// in the Go standard library. See https://golang.org/s/sqldrivers for
// a list of third-party drivers.
//
// OpenDB may just validate its arguments without creating a connection
// to the database. To verify that the data source name is valid, call
// Ping.
//
// The returned DB is safe for concurrent use by multiple goroutines
// and maintains its own pool of idle connections. Thus, the OpenDB
// function should be called just once. It is rarely necessary to
// close a DB.
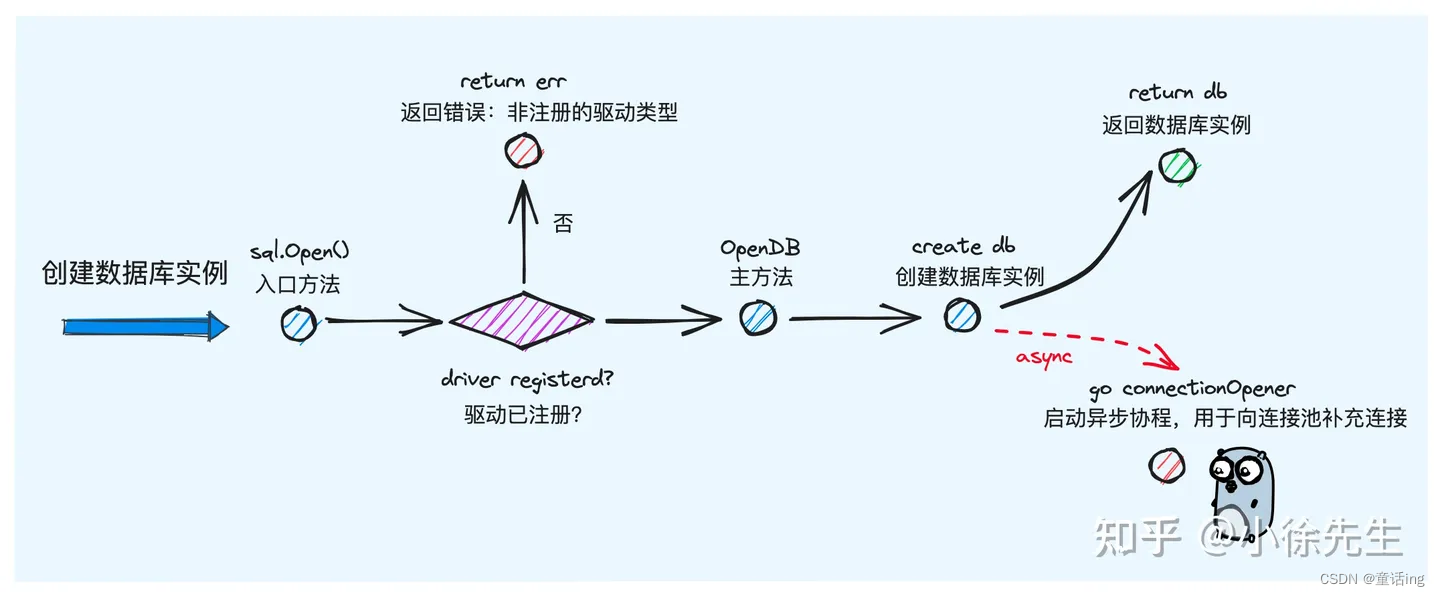
func OpenDB(c driver.Connector) *DB {ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())db := &DB{connector: c,openerCh: make(chan struct{}, connectionRequestQueueSize),lastPut: make(map[*driverConn]string),connRequests: make(map[uint64]chan connRequest),stop: cancel,}go db.connectionOpener(ctx)return db
}
同时,我们还注意到,OpenDB方法中,除了正常的构建一个DB实例外,还起了一个协程,并且传入ctx作为入参,这个协程主要作用就是在接收到通道 openerCh 有数据(在真正执行query、exec时候发现连接不够用或者driver.ErrBadConn错误时候给这个通道发送消息)的时候,调用openNewConnection创建一个新的连接。传入ctx主要是为了便于控制协程的退出。因此从这里我们知道,连接池中的连接并不是一开始就创建好了的,而是在真正执行sql的时候才会创建,因此,不必担心调用多次Open方法创建多个DB实例会导致创建很多连接。
// Runs in a separate goroutine, opens new connections when requested.
func (db *DB) connectionOpener(ctx context.Context) {for {select {case <-ctx.Done():returncase <-db.openerCh:db.openNewConnection(ctx)}}
}
///openNewConnection//
// Open one new connection
func (db *DB) openNewConnection(ctx context.Context) {// maybeOpenNewConnections has already executed db.numOpen++ before it sent// on db.openerCh. This function must execute db.numOpen-- if the// connection fails or is closed before returning.ci, err := db.connector.Connect(ctx)db.mu.Lock()defer db.mu.Unlock()if db.closed {if err == nil {ci.Close()}db.numOpen--return}if err != nil {db.numOpen--db.putConnDBLocked(nil, err)db.maybeOpenNewConnections()return}dc := &driverConn{db: db,createdAt: nowFunc(),returnedAt: nowFunc(),ci: ci,}if db.putConnDBLocked(dc, err) {db.addDepLocked(dc, dc)} else {db.numOpen--ci.Close()}
}
/maybeOpenNewConnections///// Assumes db.mu is locked.
// If there are connRequests and the connection limit hasn't been reached,
// then tell the connectionOpener to open new connections.
func (db *DB) maybeOpenNewConnections() {numRequests := len(db.connRequests)if db.maxOpen > 0 {numCanOpen := db.maxOpen - db.numOpenif numRequests > numCanOpen {numRequests = numCanOpen}}for numRequests > 0 {db.numOpen++ // optimisticallynumRequests--if db.closed {return}db.openerCh <- struct{}{}}
}4、数据库实例:sql.DB
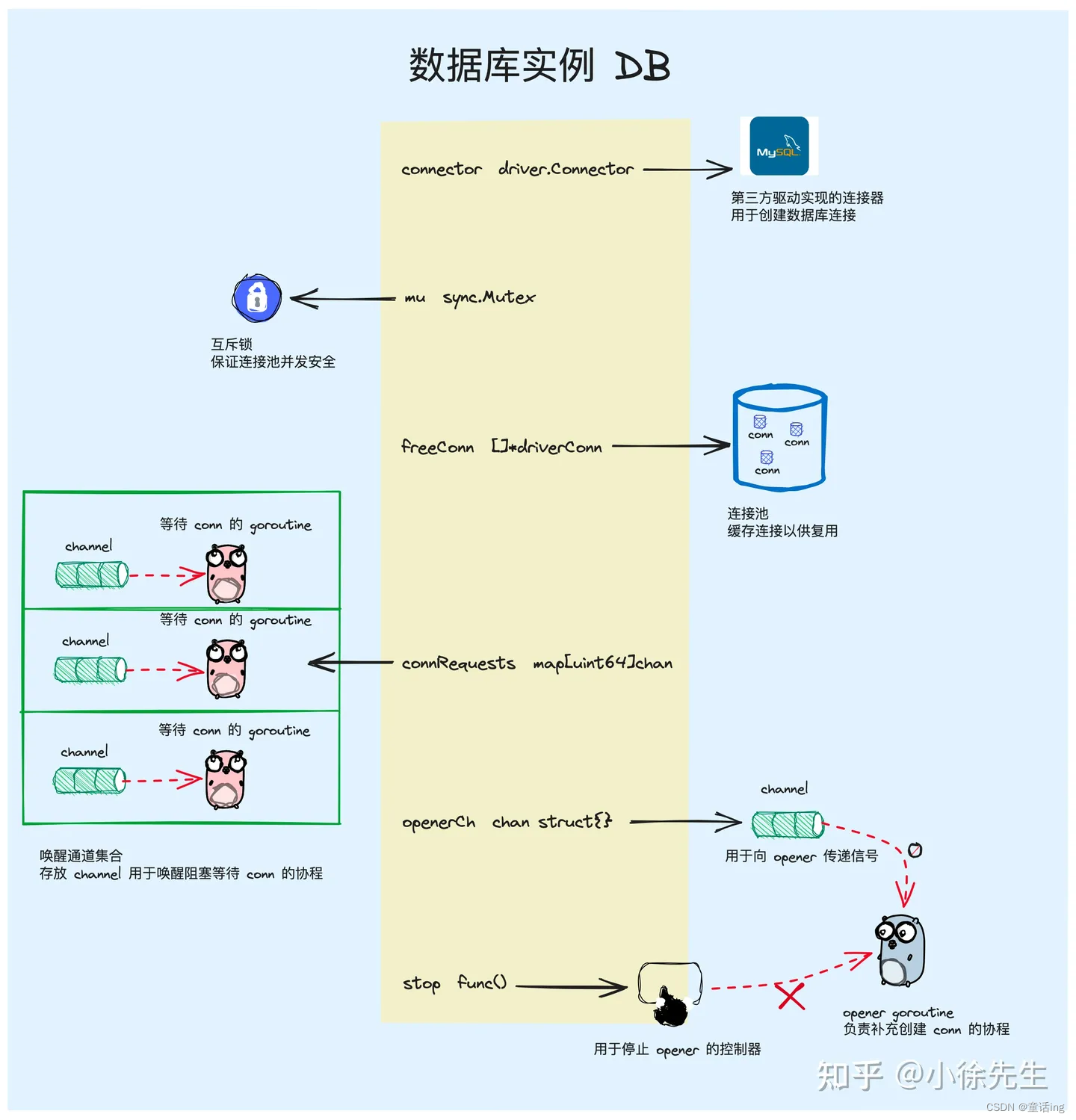
整个DB实例是sql包中非常核心的部分,其中有几个主要的字段,其他字段大部分都是和连接池参数相关的,整体围绕着连接池进行设计,方便复用连接:
connector:用于创建数据库连接的抽象连接器,由第三方数据库提供具体实现。freeConn:数据库连接池,缓存可用的连接以供后续复用。connRequests:唤醒通道集合,和阻塞等待连接的协程是一对一的关系。openerCh:创建连接信号通道. 用于向连接创建协程 opener goroutine 发送信号。stop:连接创建协程 opener goroutine 的终止器,用于停止该协程。
// DB is a database handle representing a pool of zero or more
// underlying connections. It's safe for concurrent use by multiple
// goroutines.
//
// The sql package creates and frees connections automatically; it
// also maintains a free pool of idle connections. If the database has
// a concept of per-connection state, such state can be reliably observed
// within a transaction (Tx) or connection (Conn). Once DB.Begin is called, the
// returned Tx is bound to a single connection. Once Commit or
// Rollback is called on the transaction, that transaction's
// connection is returned to DB's idle connection pool. The pool size
// can be controlled with SetMaxIdleConns.
type DB struct {// Atomic access only. At top of struct to prevent mis-alignment// on 32-bit platforms. Of type time.Duration.waitDuration int64 // Total time waited for new connections.connector driver.Connector// numClosed is an atomic counter which represents a total number of// closed connections. Stmt.openStmt checks it before cleaning closed// connections in Stmt.css.numClosed uint64mu sync.Mutex // protects following fieldsfreeConn []*driverConn // free connections ordered by returnedAt oldest to newestconnRequests map[uint64]chan connRequestnextRequest uint64 // Next key to use in connRequests.numOpen int // number of opened and pending open connections// Used to signal the need for new connections// a goroutine running connectionOpener() reads on this chan and// maybeOpenNewConnections sends on the chan (one send per needed connection)// It is closed during db.Close(). The close tells the connectionOpener// goroutine to exit.openerCh chan struct{}closed booldep map[finalCloser]depSetlastPut map[*driverConn]string // stacktrace of last conn's put; debug onlymaxIdleCount int // zero means defaultMaxIdleConns; negative means 0maxOpen int // <= 0 means unlimitedmaxLifetime time.Duration // maximum amount of time a connection may be reusedmaxIdleTime time.Duration // maximum amount of time a connection may be idle before being closedcleanerCh chan struct{}waitCount int64 // Total number of connections waited for.maxIdleClosed int64 // Total number of connections closed due to idle count.maxIdleTimeClosed int64 // Total number of connections closed due to idle time.maxLifetimeClosed int64 // Total number of connections closed due to max connection lifetime limit.stop func() // stop cancels the connection opener.
}
DB结构主要作用如下:
DB实例中关乎我们sql执行的最重要的两个方法Exec和Query,下面将介绍它们。
5、ExecContext
ExecContext主要用于执行delete、update、insert等语句,可以看到,在该方法中会对连接进行重试,如果连接过期了(exec方法返回了driver.ErrBadConn错误),那么将会重试。重试过程中携带的连接建立策略是cachedOrNewConn,如果重试次数达到上限并且连接被标记为isBadConn (一般是mysql server主动断开连接使得连接失效),那么将直接调用exec方法,将连接的建立策略修改为alwaysNewConn。
// ExecContext executes a query without returning any rows.
// The args are for any placeholder parameters in the query.
func (db *DB) ExecContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (Result, error) {var res Resultvar err errorvar isBadConn boolfor i := 0; i < maxBadConnRetries; i++ {res, err = db.exec(ctx, query, args, cachedOrNewConn)isBadConn = errors.Is(err, driver.ErrBadConn)if !isBadConn {break}}if isBadConn {return db.exec(ctx, query, args, alwaysNewConn)}return res, err
}
连接建立策略
- alwaysNewConn:表示强制请求建立一个新的数据库连接。
- cachedOrNewConn:表示从连接池中获取,如果没有,那么将会阻塞等待连接可用;或者也可以请求创建一个新的连接。
// connReuseStrategy determines how (*DB).conn returns database connections.
type connReuseStrategy uint8const (// alwaysNewConn forces a new connection to the database.alwaysNewConn connReuseStrategy = iota// cachedOrNewConn returns a cached connection, if available, else waits// for one to become available (if MaxOpenConns has been reached) or// creates a new database connection.cachedOrNewConn
)/ 核心exec方法
func (db *DB) exec(ctx context.Context, query string, args []any, strategy connReuseStrategy) (Result, error) {dc, err := db.conn(ctx, strategy)if err != nil {return nil, err}return db.execDC(ctx, dc, dc.releaseConn, query, args)
}6、QueryContext
Query方法也是类似,这里不再赘述。
// QueryContext executes a query that returns rows, typically a SELECT.
// The args are for any placeholder parameters in the query.
func (db *DB) QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error) {var rows *Rowsvar err errorvar isBadConn boolfor i := 0; i < maxBadConnRetries; i++ {rows, err = db.query(ctx, query, args, cachedOrNewConn)isBadConn = errors.Is(err, driver.ErrBadConn)if !isBadConn {break}}if isBadConn {return db.query(ctx, query, args, alwaysNewConn)}return rows, err
}
核心query
func (db *DB) query(ctx context.Context, query string, args []any, strategy connReuseStrategy) (*Rows, error) {dc, err := db.conn(ctx, strategy)if err != nil {return nil, err}return db.queryDC(ctx, nil, dc, dc.releaseConn, query, args)
}
在 queryDC 、execDC方法中,主要都是依赖于具体的驱动实现来完成请求的执行,主要完成下面几个动作:
- 首先通过连接将 sql 预处理成 statement。
- 向数据库发包执行请求,并返回对应的结果。
- 最后需要将连接放回连接池,倘若连接池已满或者连接已过期,则需要关闭连接。
// queryDC executes a query on the given connection.
// The connection gets released by the releaseConn function.
// The ctx context is from a query method and the txctx context is from an
// optional transaction context.
func (db *DB) queryDC(ctx, txctx context.Context, dc *driverConn, releaseConn func(error), query string, args []any) (*Rows, error) {queryerCtx, ok := dc.ci.(driver.QueryerContext)var queryer driver.Queryerif !ok {queryer, ok = dc.ci.(driver.Queryer)}if ok {var nvdargs []driver.NamedValuevar rowsi driver.Rowsvar err errorwithLock(dc, func() {nvdargs, err = driverArgsConnLocked(dc.ci, nil, args)if err != nil {return}rowsi, err = ctxDriverQuery(ctx, queryerCtx, queryer, query, nvdargs)})if err != driver.ErrSkip {if err != nil {releaseConn(err)return nil, err}// Note: ownership of dc passes to the *Rows, to be freed// with releaseConn.rows := &Rows{dc: dc,releaseConn: releaseConn,rowsi: rowsi,}rows.initContextClose(ctx, txctx)return rows, nil}}var si driver.Stmtvar err errorwithLock(dc, func() {si, err = ctxDriverPrepare(ctx, dc.ci, query)})if err != nil {releaseConn(err)return nil, err}ds := &driverStmt{Locker: dc, si: si}rowsi, err := rowsiFromStatement(ctx, dc.ci, ds, args...)if err != nil {ds.Close()releaseConn(err)return nil, err}// Note: ownership of ci passes to the *Rows, to be freed// with releaseConn.rows := &Rows{dc: dc,releaseConn: releaseConn,rowsi: rowsi,closeStmt: ds,}rows.initContextClose(ctx, txctx)return rows, nil
}
7、连接建立:db.conn
从上面我们知道,无论是query还是exec,都会进行连接的建立,并且还有策略的区别。下面我们将进行两种策略下连接建立的探索。
从上面我们知道,连接的获取有两种策略,一种是alwaysNewConn,一种是cachedOrNewConn。
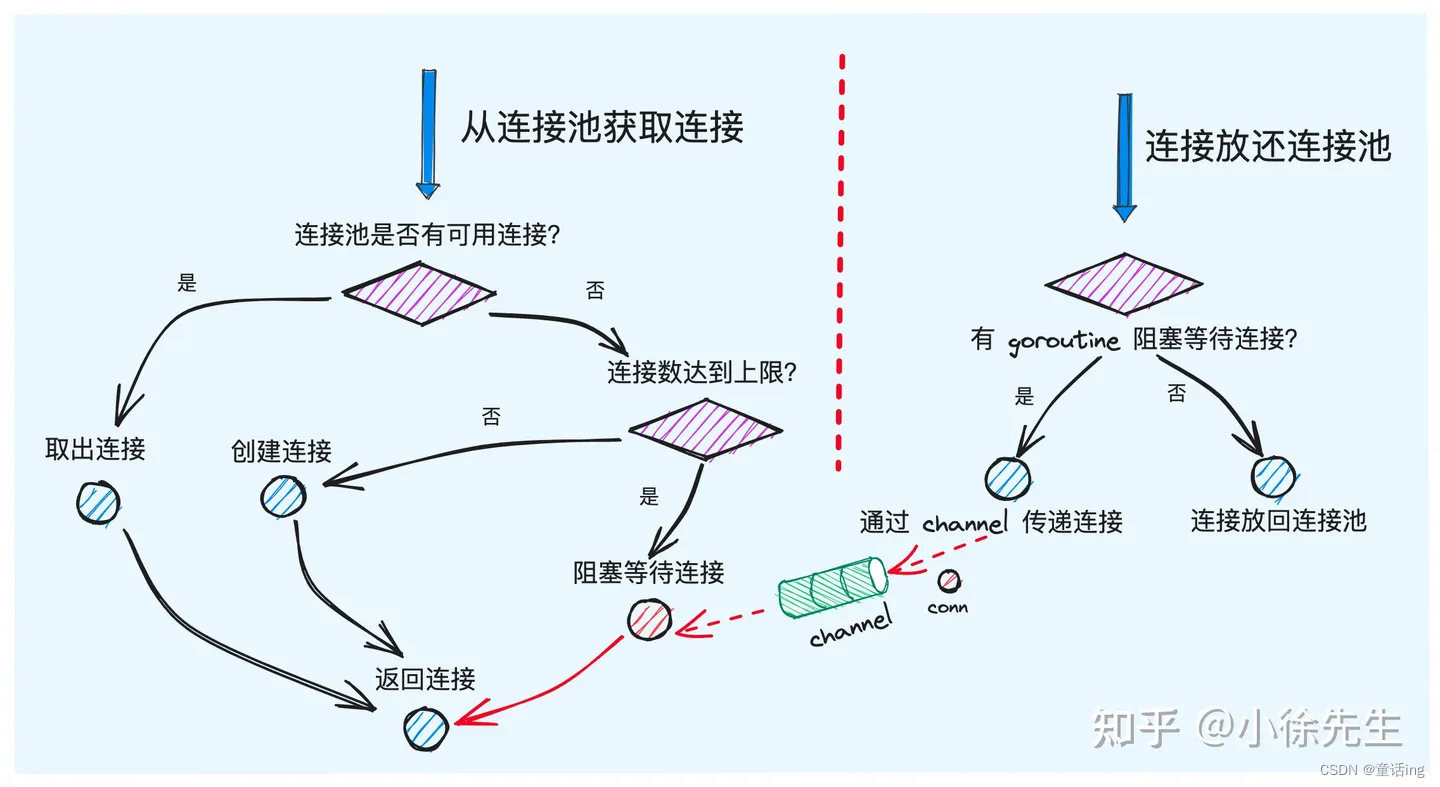
- 在cachedOrNewConn策略下,a:如果有空闲连接可用,那么将从连接池中获取连接并调用expire方法检查连接是否有效,如果失效就返回driver.ErrBadConn,接下来会调用resetSession方法,检查这个连接是否需要重置session信息,如果需要则重置,重制失败并且返回driver.ErrBadConn会关闭当前连接,然后再进行重试。b:如果没有连接可用,且连接达到上限
db.numOpen >= db.maxOpen,则会将当前协程挂起,建立对应的 channel 添加到 connRequests map 中,等待有连接释放时被唤醒。 - 在alwaysNewConn策略下,a:如果没有连接可用,且连接达到上限
db.numOpen >= db.maxOpen,则会将当前协程挂起,建立对应的 channel 添加到 connRequests map 中,等待有连接释放时被唤醒。b:如果连接数未达上限,则会调用第三方驱动的 connector 完成新连接的创建。
// conn returns a newly-opened or cached *driverConn.
func (db *DB) conn(ctx context.Context, strategy connReuseStrategy) (*driverConn, error) {db.mu.Lock()if db.closed {db.mu.Unlock()return nil, errDBClosed}// Check if the context is expired.select {default:case <-ctx.Done():db.mu.Unlock()return nil, ctx.Err()}lifetime := db.maxLifetime// Prefer a free connection, if possible.last := len(db.freeConn) - 1if strategy == cachedOrNewConn && last >= 0 {// Reuse the lowest idle time connection so we can close// connections which remain idle as soon as possible.conn := db.freeConn[last]db.freeConn = db.freeConn[:last]conn.inUse = trueif conn.expired(lifetime) {db.maxLifetimeClosed++db.mu.Unlock()conn.Close()return nil, driver.ErrBadConn}db.mu.Unlock()// Reset the session if required.if err := conn.resetSession(ctx); errors.Is(err, driver.ErrBadConn) {conn.Close()return nil, err}return conn, nil}// Out of free connections or we were asked not to use one. If we're not// allowed to open any more connections, make a request and wait.if db.maxOpen > 0 && db.numOpen >= db.maxOpen {// Make the connRequest channel. It's buffered so that the// connectionOpener doesn't block while waiting for the req to be read.req := make(chan connRequest, 1)reqKey := db.nextRequestKeyLocked()db.connRequests[reqKey] = reqdb.waitCount++db.mu.Unlock()waitStart := nowFunc()// Timeout the connection request with the context.select {case <-ctx.Done():// Remove the connection request and ensure no value has been sent// on it after removing.db.mu.Lock()delete(db.connRequests, reqKey)db.mu.Unlock()atomic.AddInt64(&db.waitDuration, int64(time.Since(waitStart)))select {default:case ret, ok := <-req:if ok && ret.conn != nil {db.putConn(ret.conn, ret.err, false)}}return nil, ctx.Err()case ret, ok := <-req:atomic.AddInt64(&db.waitDuration, int64(time.Since(waitStart)))if !ok {return nil, errDBClosed}// Only check if the connection is expired if the strategy is cachedOrNewConns.// If we require a new connection, just re-use the connection without looking// at the expiry time. If it is expired, it will be checked when it is placed// back into the connection pool.// This prioritizes giving a valid connection to a client over the exact connection// lifetime, which could expire exactly after this point anyway.if strategy == cachedOrNewConn && ret.err == nil && ret.conn.expired(lifetime) {db.mu.Lock()db.maxLifetimeClosed++db.mu.Unlock()ret.conn.Close()return nil, driver.ErrBadConn}if ret.conn == nil {return nil, ret.err}// Reset the session if required.if err := ret.conn.resetSession(ctx); errors.Is(err, driver.ErrBadConn) {ret.conn.Close()return nil, err}return ret.conn, ret.err}}db.numOpen++ // optimisticallydb.mu.Unlock()ci, err := db.connector.Connect(ctx)if err != nil {db.mu.Lock()db.numOpen-- // correct for earlier optimismdb.maybeOpenNewConnections()db.mu.Unlock()return nil, err}db.mu.Lock()dc := &driverConn{db: db,createdAt: nowFunc(),returnedAt: nowFunc(),ci: ci,inUse: true,}db.addDepLocked(dc, dc)db.mu.Unlock()return dc, nil
}
8、连接重置:resetSession
resetSession方法是用于重置数据库会话的方法。当调用resetSession方法时,会话将被重置为初始状态,包括清除任何未提交的事务、关闭任何打开的连接以及清除任何会话级别的设置。这可以帮助确保会话处于干净的状态,以便进行下一个操作或查询。
// resetSession checks if the driver connection needs the
// session to be reset and if required, resets it.
func (dc *driverConn) resetSession(ctx context.Context) error {dc.Lock()defer dc.Unlock()if !dc.needReset {return nil}if cr, ok := dc.ci.(driver.SessionResetter); ok {return cr.ResetSession(ctx)}return nil
}
9、连接池相关可配置参数
func (db *DB) SetConnMaxIdleTime(d time.Duration) // 空闲连接生存的最长时间
func (db *DB) SetConnMaxLifetime(d time.Duration) // 连接存活的最长时间,也就是这个连接能够重复使用的最长时间。设置为0表示永久复用,但可能真正执行的时候会收到BadConn的错误日志,因为mysql server可能设置了wait_timeout、超时后将主动断开这个连接。
func (db *DB) SetMaxOpenConns(n int) // 最大连接数
func (db *DB) SetMaxIdleConns(n int) // 最大空闲连接数,最大不能超过MaxOpenConns
10、可监控指标
在sql包中还有一个结构叫DBStats,其中的字段主要都是描述整体连接的一些使用情况,并且可以通过Stats方法能够获取这些指标,方便我们对这块儿进行一些监控等。
// DBStats contains database statistics.
type DBStats struct {MaxOpenConnections int // Maximum number of open connections to the database.// Pool StatusOpenConnections int // The number of established connections both in use and idle.InUse int // The number of connections currently in use.Idle int // The number of idle connections.// CountersWaitCount int64 // The total number of connections waited for.WaitDuration time.Duration // The total time blocked waiting for a new connection.MaxIdleClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetMaxIdleConns.MaxIdleTimeClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetConnMaxIdleTime.MaxLifetimeClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetConnMaxLifetime.
}// Stats returns database statistics.
func (db *DB) Stats() DBStats {wait := atomic.LoadInt64(&db.waitDuration)db.mu.Lock()defer db.mu.Unlock()stats := DBStats{MaxOpenConnections: db.maxOpen,Idle: len(db.freeConn),OpenConnections: db.numOpen,InUse: db.numOpen - len(db.freeConn),WaitCount: db.waitCount,WaitDuration: time.Duration(wait),MaxIdleClosed: db.maxIdleClosed,MaxIdleTimeClosed: db.maxIdleTimeClosed,MaxLifetimeClosed: db.maxLifetimeClosed,}return stats
}
最后,我们借助参考中的第二篇文献中的两张图总结请求的执行流程、连接获取。
- 创建数据库实例
 * 请求执行流程
* 请求执行流程
- 数据库连接的获取
- 连接的清理
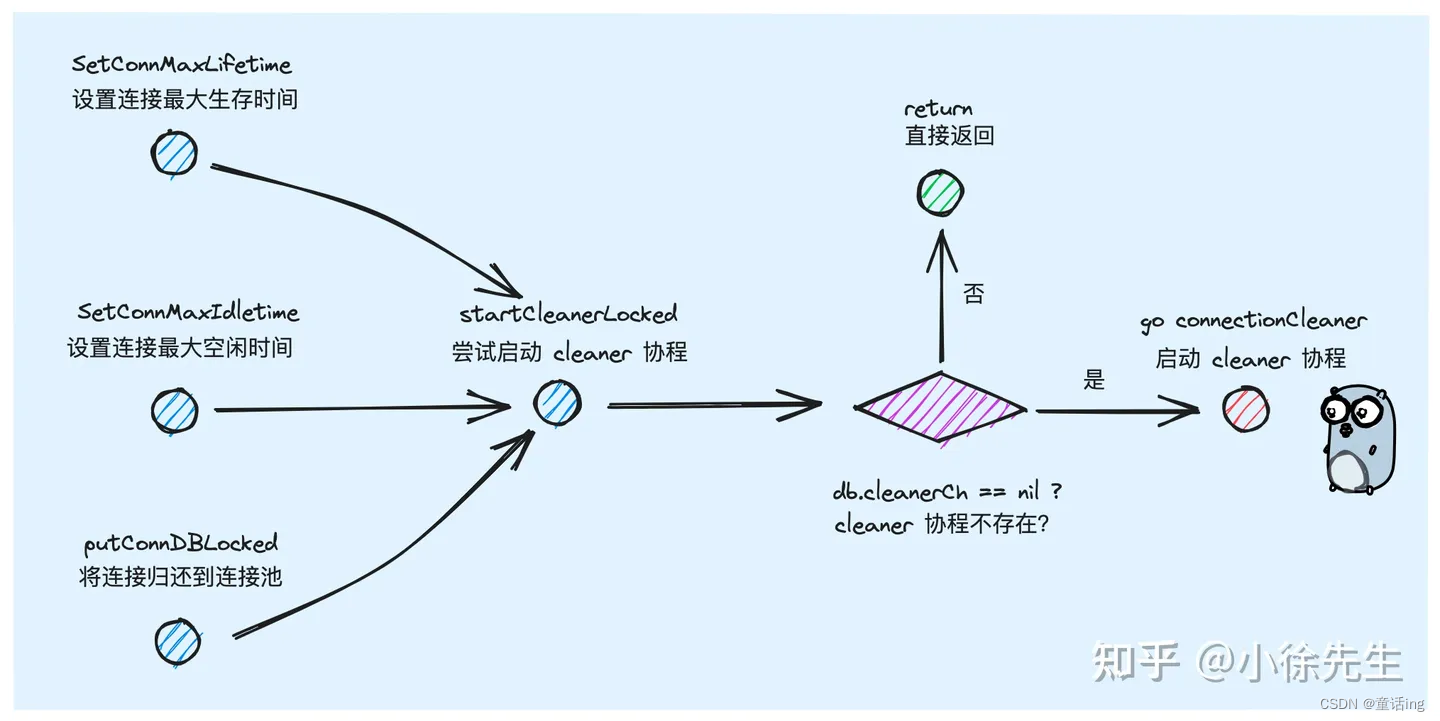
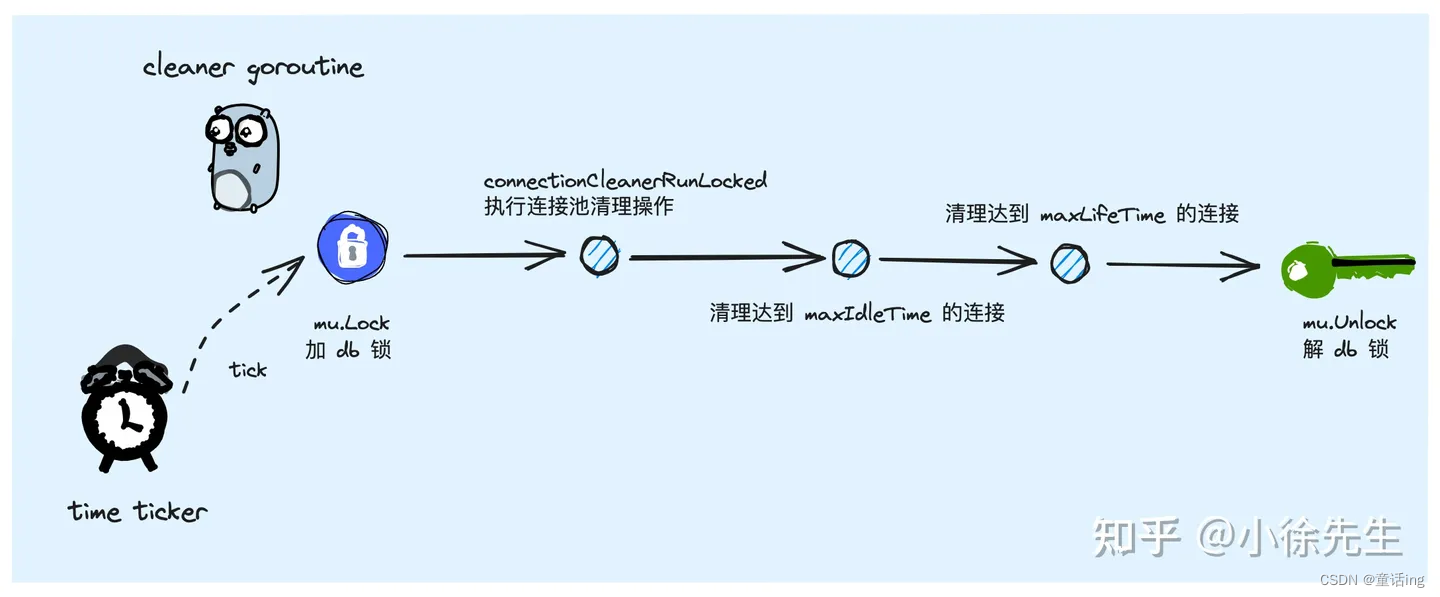
二、结语
本章中我们基于go1.19阅读了golang中database/sql的源码,了解了整个database/sql最大的特点就是定义接口,不做具体实现,从而让使用方去方便使用不同的驱动实现。同时提供了DB实例,内置连接池,方便管理连接的创建和销毁。
最后,非常感谢知乎小徐大佬的图,画的太赞了,传送链接:Golang sql 标准库源码解析
三、参考
1、Go database/sql连接池 - 源码学习
2、强烈推荐看这篇:Golang sql 标准库源码解析
相关文章:

【源码阅读】 Golang中的database/sql库源码探究
文章目录 前言一、整体目录结构二、driver包1、驱动相关driver.Driver2、驱动连接:driver.Conn3、预处理结构:Stmt4、执行结果 driver.Result5、查询结果:driver.Rows6、driver.RowsAffected7、driver.Value8、Value定义转换相关 三、sql包1、…...

什么是容器微隔离 - 容器微隔离技术有哪些
如果您对容器安全有任何问题可以联系安全狗对您的容器进行安全防护。 容器微隔离是一种在容器化环境中实现安全隔离的技术。随着云计算和容器化技术的广泛应用,容器已成为企业IT架构中的重要组成部分。然而,随着容器数量的增加,容器之间的交…...
(成品论文22页)24深圳杯数学建模A题1-4问完整代码+参考论文重磅更新!!!!
论文如下: 基于三球定位的多个火箭残骸的准确定位 针对问题一:为了进行单个残骸的精确定位,确定单个火箭残骸发生音爆 时的精确位置和时间,本文基于三球定位模型,考虑到解的存在性和唯一性, 选取了四个监测…...
ThreeJs模拟工厂生产过程八
这节算是给这个车间场景收个尾,等了几天并没有人发设备模型给我,只能自己找了一个凑合用了。加载模型之前,首先要把货架上的料箱合并,以防加载模型之后因模型数量多出现卡顿,方法和之前介绍的合并传送带方法相同&#…...

[Unity实战]热更新如何预防过度裁剪
情景再现 假设你现在有一个游戏客户端,客户端只打包了入口场景,游戏场景都存放在了AB包。 你打的热更包里使用了协程中的waituntil修复游戏场景中空投补给资源加载时机问题,但是打出来的热更在真机跑报如下错误: TypeLoadExcep…...
)
任务修复实例(8)
Quest Name Counterattack! | 人马无双! Quest ID 4021 -- Adjust Conditions UPDATE world.conditions SET ConditionValue2 8, Comment Regthar Deathgate - On Quest State - Gossip Menu Option Available WHERE SourceTypeOrReferenceId 15 AND Source…...
”和“x.view(x.size(0), -1)”有什么区别?)
torch.flatten(x, 1)”和“x.view(x.size(0), -1)”有什么区别?
这两个操作在 PyTorch 中都用于将张量展平为一维。它们的主要区别在于实现方式和适用情况: torch.flatten(x, 1): 这是一个函数调用,其中 x 是输入张量,1 是指定要展平的起始维度。此函数会将张量 x 从指定的起始维度开始展平&…...
达梦主从数据库实例恢复
测试环境:实时主备数据库 1、在节点1向测试表aaa插入数据 如图可见,会话139695153554808向aaa表插入了10000行数据。事务id460520。 2、提交前在另一个窗口kill掉dmserver进程。 3、查看节点2的数据库日志 上图可见,系统执行alter database…...

JAVA:jsp+springboot 配置maven兼容版本
Java17 maven依赖:如果中央库和其他镜像找不到包, 可以访问下面的网址找替代包 <!-- Maven Repository: Search/Browse/Explore (mvnrepository.com) -->spring-boot版本号3.2.51.无需配置驱动,有内置数据库驱动 2.能自动扫描配置类。b…...
【Docker】docker部署lnmp和搭建wordpress网站
环境准备 docker:192.168.67.30 虚拟机:4核4G systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld setenforce 0 安装docker #安装依赖包 yum -y install yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 #设置阿里云镜像 yum-config-manager --add…...

C#装箱拆箱是怎么回事
代码如下: int i 123; object o i; // Boxing int j (int)o; // Unboxing 缺点: 当装箱和拆箱发生时,该技术允许将值类型视为对象。虽然非常有益,但它们会带来性能开销。值类型和引用类型之间的转换过多可能会导致垃圾回收…...
JavaEE 初阶篇-深入了解 Junit 单元测试框架和 Java 中的反射机制(使用反射做一个简易版框架)
🔥博客主页: 【小扳_-CSDN博客】 ❤感谢大家点赞👍收藏⭐评论✍ 文章目录 1.0 Junit 单元测试框架概述 1.1 使用 Junit 框架进行测试业务代码 1.2 Junit 单元测试框架的常用注解(Junit 4.xxx 版本) 2.0 反射概述 2.1 获…...

人力资源管理新视野:挖掘员工潜力,共筑卓越未来
在21世纪的商业环境中,企业的成功不再仅仅依赖于资本、技术和市场策略,而更多地依赖于其人力资源的有效管理。人力资源管理的新视野正致力于挖掘员工的潜力,为企业创造持续的价值,共筑卓越的未来。 一、员工潜力的挖掘 员工是企业…...

rust语言tokio库spawn, blocking_spawn等的使用
目录 tokio的spawn以及spawn_blocking的使用tokio::task::spawn方法解析tokio::task::spawn_blocking()方法解析 时间会遗忘一切 最后更新时间2024.04.29 tokio版本: tokio的spawn以及spawn_blocking的使用 tokio::task::spawn方法解析 tokio的实现原理以及源码…...
Day_1
1. 环境搭建 技术选型 后端项目结构 sky-take-out maven父工程,统一管理依赖版本,聚合其他子模块 sky-common 子模块,存放公共类,例如:工具类、常量类、异常类等 sky-pojo 子模块,存放实体类、VO、DTO…...
2024.05.06作业
自由发挥应用场景,实现登录界面。 要求:尽量每行代码都有注释。 #include "yuanshen.h"yuanshen::yuanshen(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent) {//窗口相关设置this->resize(1600,910);this->setFixedSize(1600,910);//窗口标题this-…...

什么是抖音橱窗?它和抖音小店有什么区别?普通人更适合做哪个?
大家好,我是电商糖果 相信有很多想在抖音卖货的朋友,都会搞不清抖音橱窗是什么? 甚至会把它和抖音小店当成一个项目,也不知道哪个更适合自己。 自己越了解发现越迷糊,有的说不需要直播,粉丝,…...
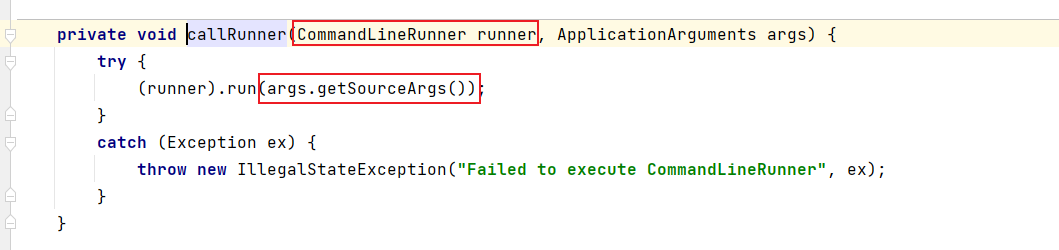
spring高级篇(九)
boot的执行流程分为构造SpringApplication对象、调用run方法两部分 1、Spring Boot 执行流程-构造 通常我们会在SpringBoot的主启动类中写以下的代码: 参数一是当前类的字节码,参数二是main的args参数。 public class StartApplication {public static…...

用wordpress建跨境电商独立站的5大优势
免费和开源 WordPress是一个免费的开源内容管理系统,用户可以自由下载、安装和使用,无需支付版权费用或订阅费用。开源特性也意味着用户可以根据自己的需求修改和定制代码,或者使用其他开发者提供的插件和主题来扩展和美化网站。 易用和灵活…...

Windows中安装的PostgreSQL 数据库如何重启
1. 使用Windows服务管理器 打开“运行”对话框(按WinR键)。输入services.msc并按回车,这将打开服务列表。在服务列表中找到PostgreSQL服务。它通常命名为“PostgreSQL”后面跟着版本号和实例名称,例如“PostgreSQL 13 - mydb”。…...
Linux 文件类型,目录与路径,文件与目录管理
文件类型 后面的字符表示文件类型标志 普通文件:-(纯文本文件,二进制文件,数据格式文件) 如文本文件、图片、程序文件等。 目录文件:d(directory) 用来存放其他文件或子目录。 设备…...

C++:std::is_convertible
C++标志库中提供is_convertible,可以测试一种类型是否可以转换为另一只类型: template <class From, class To> struct is_convertible; 使用举例: #include <iostream> #include <string>using namespace std;struct A { }; struct B : A { };int main…...

汽车生产虚拟实训中的技能提升与生产优化
在制造业蓬勃发展的大背景下,虚拟教学实训宛如一颗璀璨的新星,正发挥着不可或缺且日益凸显的关键作用,源源不断地为企业的稳健前行与创新发展注入磅礴强大的动力。就以汽车制造企业这一极具代表性的行业主体为例,汽车生产线上各类…...

React Native在HarmonyOS 5.0阅读类应用开发中的实践
一、技术选型背景 随着HarmonyOS 5.0对Web兼容层的增强,React Native作为跨平台框架可通过重新编译ArkTS组件实现85%以上的代码复用率。阅读类应用具有UI复杂度低、数据流清晰的特点。 二、核心实现方案 1. 环境配置 (1)使用React Native…...
初学 pytest 记录
安装 pip install pytest用例可以是函数也可以是类中的方法 def test_func():print()class TestAdd: # def __init__(self): 在 pytest 中不可以使用__init__方法 # self.cc 12345 pytest.mark.api def test_str(self):res add(1, 2)assert res 12def test_int(self):r…...

【从零学习JVM|第三篇】类的生命周期(高频面试题)
前言: 在Java编程中,类的生命周期是指类从被加载到内存中开始,到被卸载出内存为止的整个过程。了解类的生命周期对于理解Java程序的运行机制以及性能优化非常重要。本文会深入探寻类的生命周期,让读者对此有深刻印象。 目录 …...

LangFlow技术架构分析
🔧 LangFlow 的可视化技术栈 前端节点编辑器 底层框架:基于 (一个现代化的 React 节点绘图库) 功能: 拖拽式构建 LangGraph 状态机 实时连线定义节点依赖关系 可视化调试循环和分支逻辑 与 LangGraph 的深…...
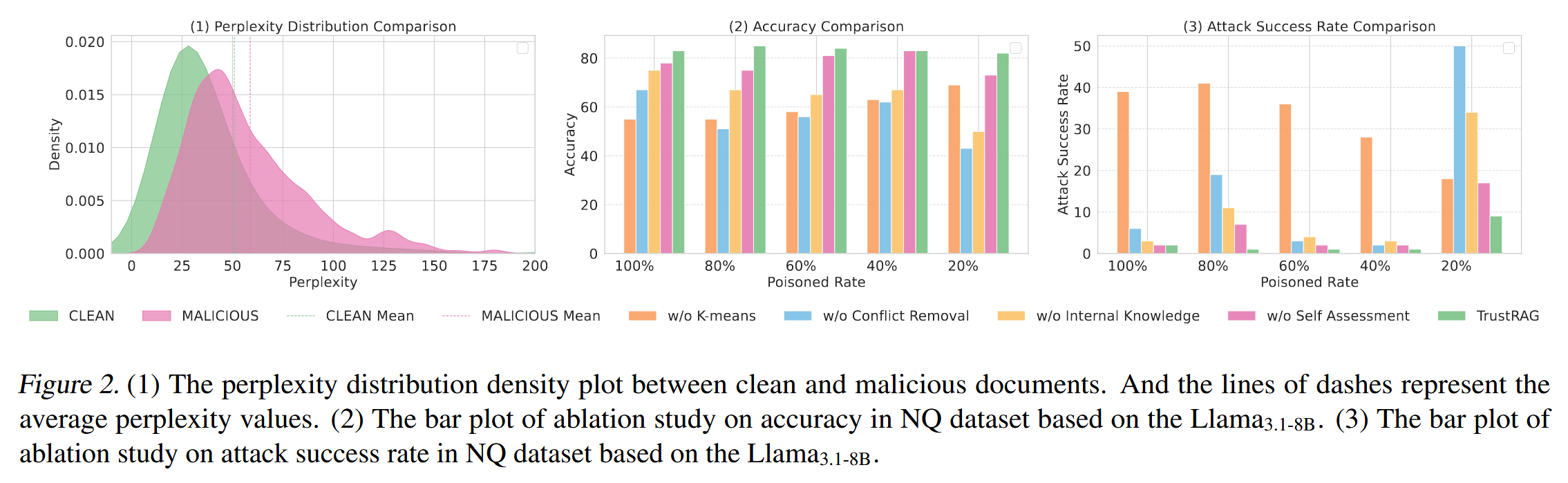
[论文阅读]TrustRAG: Enhancing Robustness and Trustworthiness in RAG
TrustRAG: Enhancing Robustness and Trustworthiness in RAG [2501.00879] TrustRAG: Enhancing Robustness and Trustworthiness in Retrieval-Augmented Generation 代码:HuichiZhou/TrustRAG: Code for "TrustRAG: Enhancing Robustness and Trustworthin…...

Canal环境搭建并实现和ES数据同步
作者:田超凡 日期:2025年6月7日 Canal安装,启动端口11111、8082: 安装canal-deployer服务端: https://github.com/alibaba/canal/releases/1.1.7/canal.deployer-1.1.7.tar.gz cd /opt/homebrew/etc mkdir canal…...

Java多线程实现之Runnable接口深度解析
Java多线程实现之Runnable接口深度解析 一、Runnable接口概述1.1 接口定义1.2 与Thread类的关系1.3 使用Runnable接口的优势 二、Runnable接口的基本实现方式2.1 传统方式实现Runnable接口2.2 使用匿名内部类实现Runnable接口2.3 使用Lambda表达式实现Runnable接口 三、Runnabl…...
