windows内存管理
一 windows系统的内存管理涉及哪些
1.1 虚拟内存管理机制
- windows操作系统使用虚拟内存技术,将磁盘文件,通过映射对象(存储在物理内存)关联,映射到虚拟内存作为文件试图。即用户操作"虚拟内存中File View Object"-> 物理内存中"File Mapping" -> 磁盘文件。
1.2 分页和分段机制
- windows采用分页机制,将内存划分为固定大写的页面,通过页表来映射虚拟地址和物理地址
- 分段机制是将内存划分为不同大小的段,通过段表来管理。
1.3 内存保护
windows通过硬件机制保护系统内存资源,防止程序对内存的非法访问,确保系统的稳定性和安全性
1.4 高级内存管理
windows还提供内存压缩、内存回收、内存优化等功能
内存压缩可以节省生存空间,内存回收能释放不再使用的内存资源,而内存优化则旨在提高系统性能和响应速度。
二 虚拟内存的实现技术 - 文件映射
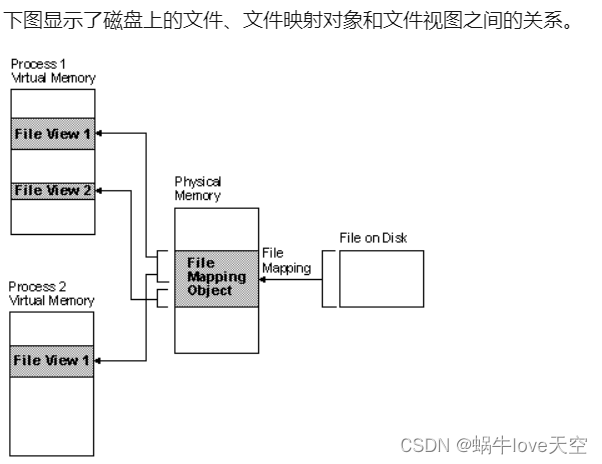
2.1 磁盘文件,文件映射对象,文件视图的关系
MSDN - 文件映射
注:
文件映射: 将文件内存(File on Disk)于进程的一部分虚拟地址空间关联。
文件映射对象:调用CreateFileMapping创建文件映射对象,维护磁盘文件和虚拟地址关联。
文件视图: 进程用来访问磁盘文件的虚拟地址空间部分。如果使用指针从文件视图读取和写入文件视图的过程,就像使用动态分配的内存一样。使用文件映射可提高可提高效率,因为文件驻留在磁盘上,但文件视图驻留在内存中。
2.2 应用场景(为什么要用文件映射?)
1)解决大文件频繁读写效率问题
直接加载文件到内存(传统方式)
C++读取txt文件
1 逐行读取
void readTxt(string file)
{ifstream infile; infile.open(file.data()); //将文件流对象与文件连接起来 assert(infile.is_open()); //若失败,则输出错误消息,并终止程序运行 string s;while(getline(infile,s)){cout<<s<<endl;}infile.close(); //关闭文件输入流
}
传统方式,将磁盘文件,加载到内存中,频繁操作磁盘文件。
文件映射方式,将磁盘文件,通过关联到文件映射对象中,读取IO效率更高。减少磁盘文件访问次数。
2) 解决多个进程访问共享磁盘文件场景
多个进程,都可以访问文件映射对象。解决IPC通信,数据复制的开销。
2.3 原理
通过文件映射机制,进程可以通过访问内存的方式直接读写磁盘文件,修改内容后由操作系统自动同步的文件进行更新。使用FlushViewOfFile可刷新缓存区,将映射在虚拟内存当中的数据立即回写到磁盘文件。
过程如下所示:
1. CreateFileMapping创建文件映射对象(内核对象,多进程可访问),关联磁盘文件(文件句柄hFile)
2. MapViewOfFile将文件映射对象,映射到进程虚拟地址
2.4 代码
/*This program demonstrates file mapping, especially how to align aview with the system file allocation granularity.
*/#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <tchar.h>#define BUFFSIZE 1024 // size of the memory to examine at any one time#define FILE_MAP_START 138240 // starting point within the file of// the data to examine (135K)/* The test file. The code below creates the file and populates it,so there is no need to supply it in advance. */TCHAR * lpcTheFile = TEXT("fmtest.txt"); // the file to be manipulatedint main(void)
{HANDLE hMapFile; // handle for the file's memory-mapped regionHANDLE hFile; // the file handleBOOL bFlag; // a result holderDWORD dBytesWritten; // number of bytes writtenDWORD dwFileSize; // temporary storage for file sizesDWORD dwFileMapSize; // size of the file mappingDWORD dwMapViewSize; // the size of the viewDWORD dwFileMapStart; // where to start the file map viewDWORD dwSysGran; // system allocation granularitySYSTEM_INFO SysInfo; // system information; used to get granularityLPVOID lpMapAddress; // pointer to the base address of the// memory-mapped regionchar * pData; // pointer to the dataint i; // loop counterint iData; // on success contains the first int of dataint iViewDelta; // the offset into the view where the data//shows up// Create the test file. Open it "Create Always" to overwrite any// existing file. The data is re-created belowhFile = CreateFile(lpcTheFile,GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_WRITE,0,NULL,CREATE_ALWAYS,FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL,NULL);if (hFile == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE){_tprintf(TEXT("hFile is NULL\n"));_tprintf(TEXT("Target file is %s\n"),lpcTheFile);return 4;}// Get the system allocation granularity.GetSystemInfo(&SysInfo);dwSysGran = SysInfo.dwAllocationGranularity;// Now calculate a few variables. Calculate the file offsets as// 64-bit values, and then get the low-order 32 bits for the// function calls.// To calculate where to start the file mapping, round down the// offset of the data into the file to the nearest multiple of the// system allocation granularity.dwFileMapStart = (FILE_MAP_START / dwSysGran) * dwSysGran;_tprintf (TEXT("The file map view starts at %ld bytes into the file.\n"),dwFileMapStart);// Calculate the size of the file mapping view.dwMapViewSize = (FILE_MAP_START % dwSysGran) + BUFFSIZE;_tprintf (TEXT("The file map view is %ld bytes large.\n"),dwMapViewSize);// How large will the file mapping object be?dwFileMapSize = FILE_MAP_START + BUFFSIZE;_tprintf (TEXT("The file mapping object is %ld bytes large.\n"),dwFileMapSize);// The data of interest isn't at the beginning of the// view, so determine how far into the view to set the pointer.iViewDelta = FILE_MAP_START - dwFileMapStart;_tprintf (TEXT("The data is %d bytes into the view.\n"),iViewDelta);// Now write a file with data suitable for experimentation. This// provides unique int (4-byte) offsets in the file for easy visual// inspection. Note that this code does not check for storage// medium overflow or other errors, which production code should// do. Because an int is 4 bytes, the value at the pointer to the// data should be one quarter of the desired offset into the filefor (i=0; i<(int)dwSysGran; i++){WriteFile (hFile, &i, sizeof (i), &dBytesWritten, NULL);}// Verify that the correct file size was written.dwFileSize = GetFileSize(hFile, NULL);_tprintf(TEXT("hFile size: %10d\n"), dwFileSize);// Create a file mapping object for the file// Note that it is a good idea to ensure the file size is not zerohMapFile = CreateFileMapping( hFile, // current file handleNULL, // default securityPAGE_READWRITE, // read/write permission0, // size of mapping object, highdwFileMapSize, // size of mapping object, lowNULL); // name of mapping objectif (hMapFile == NULL){_tprintf(TEXT("hMapFile is NULL: last error: %d\n"), GetLastError() );return (2);}// Map the view and test the results.lpMapAddress = MapViewOfFile(hMapFile, // handle to// mapping objectFILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS, // read/write0, // high-order 32// bits of file// offsetdwFileMapStart, // low-order 32// bits of file// offsetdwMapViewSize); // number of bytes// to mapif (lpMapAddress == NULL){_tprintf(TEXT("lpMapAddress is NULL: last error: %d\n"), GetLastError());return 3;}// Calculate the pointer to the data.pData = (char *) lpMapAddress + iViewDelta;// Extract the data, an int. Cast the pointer pData from a "pointer// to char" to a "pointer to int" to get the whole thingiData = *(int *)pData;_tprintf (TEXT("The value at the pointer is %d,\nwhich %s one quarter of the desired file offset.\n"),iData,iData*4 == FILE_MAP_START ? TEXT("is") : TEXT("is not"));// Close the file mapping object and the open filebFlag = UnmapViewOfFile(lpMapAddress);bFlag = CloseHandle(hMapFile); // close the file mapping objectif(!bFlag){_tprintf(TEXT("\nError %ld occurred closing the mapping object!"),GetLastError());}bFlag = CloseHandle(hFile); // close the file itselfif(!bFlag){_tprintf(TEXT("\nError %ld occurred closing the file!"),GetLastError());}return 0;
}
相关文章:

windows内存管理
一 windows系统的内存管理涉及哪些 1.1 虚拟内存管理机制 windows操作系统使用虚拟内存技术,将磁盘文件,通过映射对象(存储在物理内存)关联,映射到虚拟内存作为文件试图。即用户操作"虚拟内存中File View Objec…...
c++ 将指针转换为 void* 后,转换为怎么判断原指针类型?
当将指针转换为void后,擦除了指针所指向对象的类型信息,因此无法通过void指针来判断原始指针的类型。我这里有一套编程入门教程,不仅包含了详细的视频讲解,项目实战。如果你渴望学习编程,不妨点个关注,给个…...

Swift 属性
属性 一、存储属性1、常量结构体实例的存储属性2、延时加载存储属性3、存储属性和实例变量 二、计算属性1、简化 Setter 声明2、简化 Getter 声明3、只读计算属性 三、属性观察器四、属性包装器1、设置被包装属性的初始值2、从属性包装器中呈现一个值 五、全局变量和局部变量六…...

基于maxkey接入jeecgboot并实现账户同步
1. 注册应用 1.1 在统一认证中心注册第三方应用 1.1.1 填写应用名和登录地址 1.1.2 填写认证地址授权方式和作用域 1.1.3 选择权限范围并提交 1.2 配置访问权限 1.2.1 指定用户组 1.1.2 选择注册的应用 1.1.3 在单点登录认证页面查看添加的应用 1.3 同步一个第三方应用的账号…...

kafka Kerberos集群环境部署验证
背景 公司需要对kafka环境进行安全验证,目前考虑到的方案有Kerberos和SSL和SASL_SSL,最终考虑到安全和功能的丰富度,我们最终选择了SASL_SSL方案。处于知识积累的角度,记录一下kafka keberos安装部署的步骤。 机器规划 目前测试环境公搭建了三台kafka主机服务,现在将详细…...
[C++]debug介绍+debug时如何查看指针指向内存处的值
一、简介 预备工具和知识:使用使用VSCode使用Debug。 本文简介:本文将简要介绍debug中Continue,Step Over,Step Into和Restart的功能。并介绍如何在debug时查看动态内存地址(指针)的值; 二、D…...

AI学习指南数学工具篇-凸优化在支持逻辑回归中的应用
AI学习指南数学工具篇-凸优化在支持逻辑回归中的应用 一、引言 在人工智能领域,逻辑回归是一种常见的分类算法,它通过学习样本数据的特征和标签之间的关系,来进行分类预测。而在逻辑回归算法中,凸优化是一种重要的数学工具&…...

Flutter 中的 AspectRatio 小部件:全面指南
Flutter 中的 AspectRatio 小部件:全面指南 Flutter 是一个流行的跨平台 UI 框架,它提供了丰富的小部件来帮助开发者构建高质量的应用程序。在 Flutter 的小部件库中,AspectRatio 是一个非常有用的小部件,它允许开发者以一种简单…...

应用程序中的会话管理和Cookie安全指南
应用程序中的会话管理和Cookie安全指南 在现代应用程序中,会话管理和Cookie安全是确保用户信息和数据安全的重要组成部分。本文将详细介绍会话管理的最佳实践以及如何通过安全的Cookie设置来保护会话ID的交换。 单点登录(SSO)及会话管理机制…...

备战秋招c++ 【持续更新】
T1 牛牛的快递 原题链接:牛牛的快递_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com) 题目类型:模拟 审题&确定思路: 1、超过1kg和不足1kg有两种不同收费方案 ---- 起步价问题 2、超出部分不足1kg的按1kg计算 ----- 向上取整 3、向上取整的实现思路…...

整数拆分~
way:process //上一个拆出来的数是pre //还剩下rest需要去拆 //返回拆解的方法数 #include<iostream> using namespace std;//上一个拆出来的数是pre //还剩下rest需要去拆 //返回拆解的方法数 int process(int pre, int rest) {if(rest0) return 1;//因为后…...
【Qt Creator】跨平台的C++图形用户界面应用程序开发框架---QT
🍁你好,我是 RO-BERRY 📗 致力于C、C、数据结构、TCP/IP、数据库等等一系列知识 🎄感谢你的陪伴与支持 ,故事既有了开头,就要画上一个完美的句号,让我们一起加油 目录 1.互联网的核心岗位以及职…...
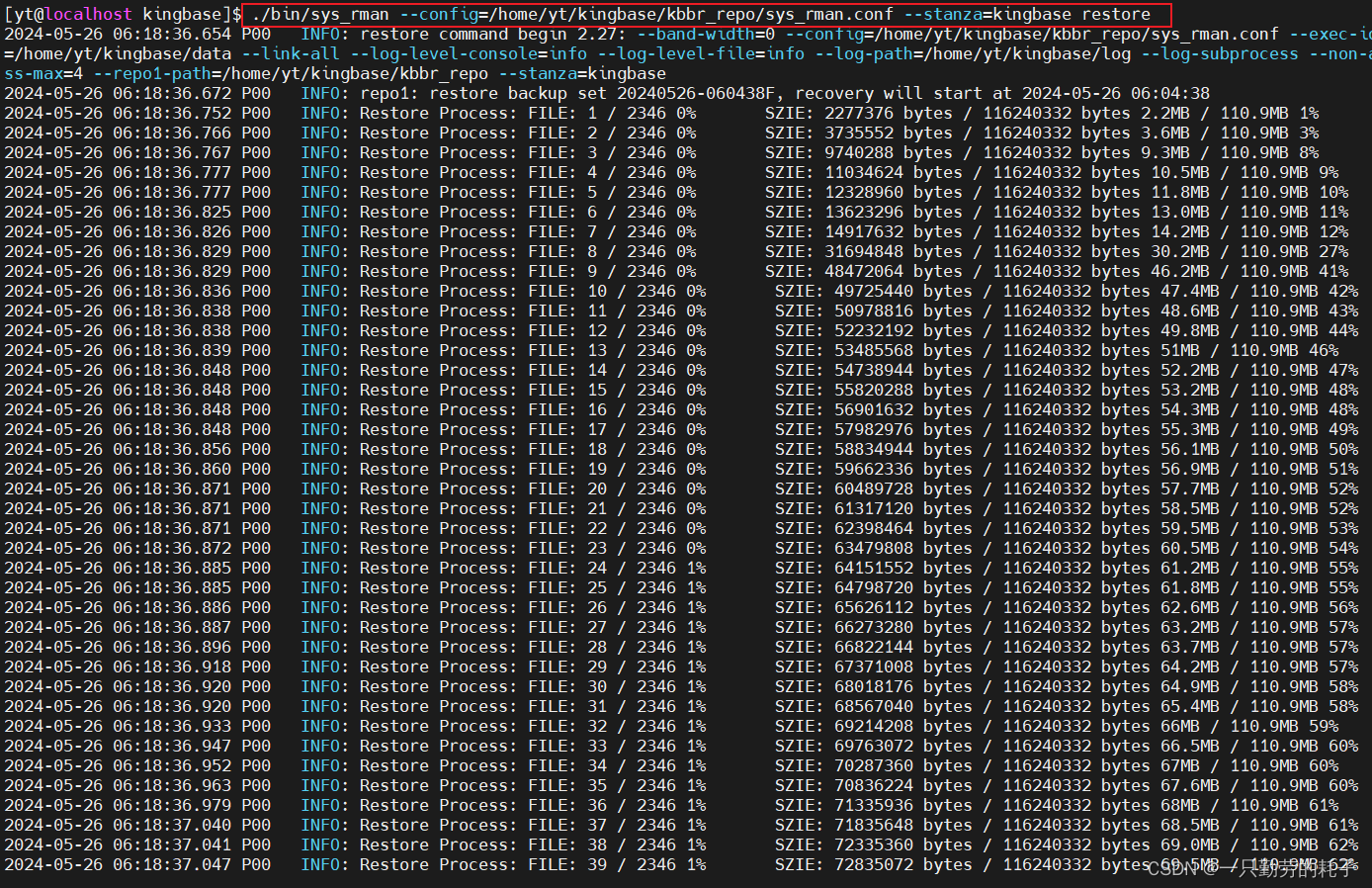
KingbaseES数据库物理备份还原sys_rman
数据库版本:KingbaseES V008R006C008B0014 简介 sys_rman 是 KingbaseES 数据库中重要的物理备份还原工具,支持不同类型的全量备份、差异备份、增量备份,保证数据库在遇到故障时及时使用 sys_rman 来恢复到数据库先前状态。 文章目录如下 1.…...

【CV】视频图像背景分割MOG2,KNN,GMG
当涉及背景分割器(Background Subtractor)时,Mixture of Gaussians(MOG2)、K-Nearest Neighbors(KNN)和Geometric Multigid(GMG)是常用的算法。它们都用于从视频流中提取…...

使用 Python 简单几步去除 PDF 水印
推荐一个AI网站,免费使用豆包AI模型,快去白嫖👉海鲸AI 在处理 PDF 文件时,水印有时会影响文件的可读性或美观性。幸运的是,Python 提供了多种库来操作 PDF 文件,其中 PyMuPDF(又名 fitz…...
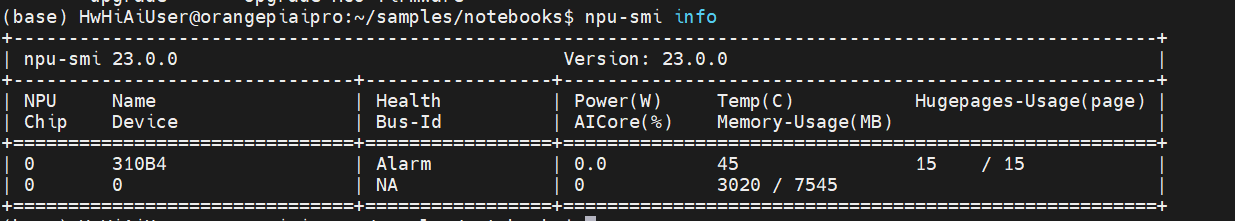
【香橙派 AIpro】OrangePi AIpro :教育、机器人、无人机领域的超级AI大脑,华为昇腾处理器驱动的AI开发板新标杆
【OrangePi AIpro:教育、机器人、无人机领域的超级AI大脑,华为昇腾处理器驱动的AI开发板新标杆】 文章目录 一、开箱与初印象1. 初印象2. 上手开机3. 安装和运行 TightVNC 远程桌面3.1. 安装 TightVNC 服务器3.2. 启动 VNC 服务器3.3. 在 Windows 上使用…...

【Mac】 CleanMyMac X for mac V4.15.2中文修复版安装教程
软件介绍 CleanMyMac X是一款为Mac设计的优秀软件,旨在帮助用户优化其设备的性能并提供清理和维护功能。以下是 CleanMyMac X的一些主要功能和特点: 1.系统性能优化:软件可以扫描和修复潜在的性能问题,包括无效的登录项、大文件…...

单片机通信协议(1):SPI简介
关于SPI SPI(串行外设接口)是板载设备间通信接口之一。它是由摩托罗拉公司(飞思卡尔半导体)推出的。由于其简单性和通用性,它被纳入各种外围设备中,并与飞利浦I2C总线并列。 SPI的三线或四线信号数量比IIC…...
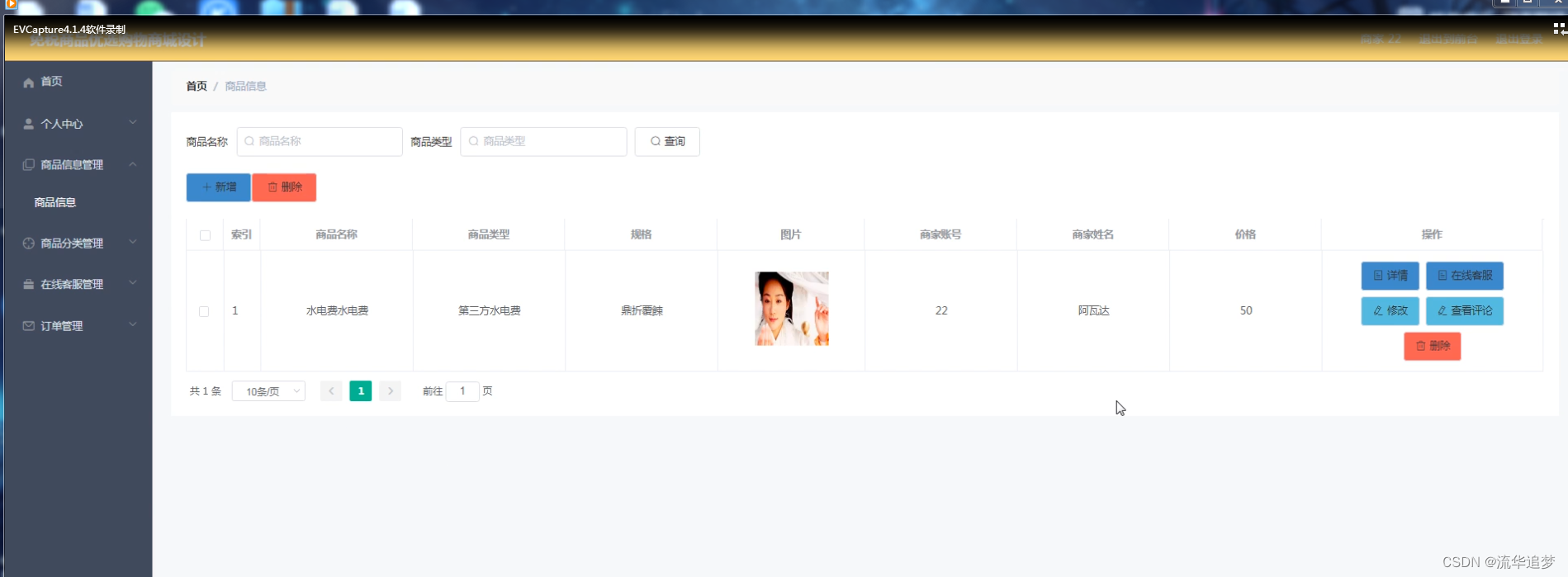
免税商品优选购物商城,基于 SpringBoot+Vue+MySQL 开发的前后端分离的免税商品优选购物商城设计实现
目录 一. 前言 二. 功能模块 2.1. 登录界面 2.2. 管理员功能模块 2.3. 商家功能模块 2.4. 用户前台功能模块 2.5. 用户后台功能模块 三. 部分代码实现 四. 源码下载 一. 前言 随着科学技术的飞速发展,各行各业都在努力与现代先进技术接轨,通过…...
概述)
京准电子、NTP电子时钟系统(网络时钟系统)概述
京准电子、NTP电子时钟系统(网络时钟系统)概述 京准电子、NTP电子时钟系统(网络时钟系统)概述 时钟系统工作原理是由母钟接收GPS/北斗卫星的时间信息,母钟通过串口和NTP以太网接口为其他各系统提供统一的标准时间信号&…...
LBE-LEX系列工业语音播放器|预警播报器|喇叭蜂鸣器的上位机配置操作说明
LBE-LEX系列工业语音播放器|预警播报器|喇叭蜂鸣器专为工业环境精心打造,完美适配AGV和无人叉车。同时,集成以太网与语音合成技术,为各类高级系统(如MES、调度系统、库位管理、立库等)提供高效便捷的语音交互体验。 L…...

Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility
Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility 1. 实验室环境1.1 实验室环境1.2 小测试 2. The Endor System2.1 部署应用2.2 检查现有策略 3. Cilium 策略实体3.1 创建 allow-all 网络策略3.2 在 Hubble CLI 中验证网络策略源3.3 …...

HTML 列表、表格、表单
1 列表标签 作用:布局内容排列整齐的区域 列表分类:无序列表、有序列表、定义列表。 例如: 1.1 无序列表 标签:ul 嵌套 li,ul是无序列表,li是列表条目。 注意事项: ul 标签里面只能包裹 li…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...

论文浅尝 | 基于判别指令微调生成式大语言模型的知识图谱补全方法(ISWC2024)
笔记整理:刘治强,浙江大学硕士生,研究方向为知识图谱表示学习,大语言模型 论文链接:http://arxiv.org/abs/2407.16127 发表会议:ISWC 2024 1. 动机 传统的知识图谱补全(KGC)模型通过…...
)
Typeerror: cannot read properties of undefined (reading ‘XXX‘)
最近需要在离线机器上运行软件,所以得把软件用docker打包起来,大部分功能都没问题,出了一个奇怪的事情。同样的代码,在本机上用vscode可以运行起来,但是打包之后在docker里出现了问题。使用的是dialog组件,…...

AGain DB和倍数增益的关系
我在设置一款索尼CMOS芯片时,Again增益0db变化为6DB,画面的变化只有2倍DN的增益,比如10变为20。 这与dB和线性增益的关系以及传感器处理流程有关。以下是具体原因分析: 1. dB与线性增益的换算关系 6dB对应的理论线性增益应为&…...

Qt 事件处理中 return 的深入解析
Qt 事件处理中 return 的深入解析 在 Qt 事件处理中,return 语句的使用是另一个关键概念,它与 event->accept()/event->ignore() 密切相关但作用不同。让我们详细分析一下它们之间的关系和工作原理。 核心区别:不同层级的事件处理 方…...

Kafka主题运维全指南:从基础配置到故障处理
#作者:张桐瑞 文章目录 主题日常管理1. 修改主题分区。2. 修改主题级别参数。3. 变更副本数。4. 修改主题限速。5.主题分区迁移。6. 常见主题错误处理常见错误1:主题删除失败。常见错误2:__consumer_offsets占用太多的磁盘。 主题日常管理 …...

深入浅出Diffusion模型:从原理到实践的全方位教程
I. 引言:生成式AI的黎明 – Diffusion模型是什么? 近年来,生成式人工智能(Generative AI)领域取得了爆炸性的进展,模型能够根据简单的文本提示创作出逼真的图像、连贯的文本,乃至更多令人惊叹的…...
