Objects and Classes (对象和类)
Objects and Classes [对象和类]
- 1. Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming (过程性编程和面向对象编程)
- 2. Abstraction and Classes (抽象和类)
- 2.1. Classes in C++ (C++ 中的类)
- 2.2. Implementing Class Member Functions (实现类成员函数)
- 2.3. Using Classes (使用类)
- References
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a particular conceptual approach to designing programs, and C++ has enhanced C with features that ease the way to applying that approach.
面向对象编程 (OOP) 是一种特殊的、设计程序的概念性方法,C++ 通过一些特性改进了 C 语言,使得应用这种方法更容易。
ease [iːz]:v. 缓解,减轻,放松,降低 n. 容易,安逸,自在,舒适
The following are the most important OOP features:
- Abstraction (抽象)
- Encapsulation and data hiding (封装和数据隐藏)
- Polymorphism (多态)
- Inheritance (继承)
- Reusability of code (代码的可重用性)
The class is the single most important C++ enhancement for implementing these features and tying them together.
为了实现这些特性并将它们组合在一起,C++ 所做的最重要的改进是提供了类。
1. Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming (过程性编程和面向对象编程)
In short, with a procedural approach, you first concentrate on the procedures you will follow and then think about how to represent the data.
采用过程性编程方法时,首先考虑要遵循的步骤,然后考虑如何表示这些数据。
In short, with an OOP approach, you concentrate on the object as the user perceives it, thinking about the data you need to describe the object and the operations that will describe the user’s interaction with the data. After you develop a description of that interface, you move on to decide how to implement the interface and data storage. Finally, you put together a program to use your new design.
采用 OOP 方法时,首先从用户的角度考虑对象,描述对象所需的数据以及描述用户与数据交互所需的操作。完成对接口的描述后,需要确定如何实现接口和数据存储。最后,使用新的设计方案创建出程序。
perceive [pə(r)ˈsiːv]:v. 认为,意识到,注意到,察觉到
2. Abstraction and Classes (抽象和类)
Life is full of complexities, and one way we cope with complexity is to frame simplifying abstractions. From abstraction, it is a short step to the user-defined type, which in C++ is a class design that implements the abstract interface.
生活中充满复杂性,处理复杂性的方法之一是简化和抽象。抽象是通往用户定义类型的捷径,在 C++ 中,用户定义类型指的是实现抽象接口的类设计。
For built-in types, the information about operations is built in to the compiler. But when you define a user-defined type in C++, you have to provide the same kind of information yourself. In exchange for this extra work, you gain the power and flexibility to custom fit new data types to match real-world requirements.
对于内置类型来说,有关操作的信息被内置到编译器中。但在 C++ 中定义用户自定义的类型时,必须自己提供这些信息。付出这些劳动换来了根据实际需要定制新数据类型的强大功能和灵活性。
2.1. Classes in C++ (C++ 中的类)
A class is a C++ vehicle for translating an abstraction to a user-defined type. It combines data representation and methods for manipulating that data into one neat package.
类是一种将抽象转换为用户定义类型的 C++ 工具,它将数据表示和操纵数据的方法组合成一个整洁的包。
Generally, a class specification has two parts:
-
A class declaration, which describes the data component, in terms of data members, and the public interface, in terms of member functions, termed methods
类声明:以数据成员的方式描述数据部分,以成员函数 (被称为方法) 的方式描述公有接口。 -
The class method definitions, which describe how certain class member functions are implemented
类方法定义:描述如何实现类成员函数。
Roughly speaking, the class declaration provides a class overview, whereas the method definitions supply the details.
类声明提供了类的蓝图,而方法定义则提供了细节。
An interface is a shared framework for interactions between two systems. But in any case, to use a class, you need to know its public interface; to write a class, you need to create its public interface.
接口是一个共享框架,供两个系统交互时使用。要使用某个类,必须了解其公共接口;要编写类,必须创建其公共接口。
Typically, C++ programmers place the interface, in the form of a class definition, in a header file and place the implementation, in the form of code for the class methods, in a source code file.
C++ 程序员将接口 (类定义) 放在头文件中,并将实现 (类方法的代码) 放在源代码文件中。
In this context the keywords class and typename are not synonymous the way they were in template parameters; typename can’t be used here.
C++ 关键字 class 指出这些代码定义了一个类设计,在这里关键字 class 和 typename 不是同义词,不能使用 typename 代替 class (不同于在模板参数中)。Stock 是这个新类的类型名,该声明让我们能够声明 Stock 类型的变量称为对象或实例。
- stock.h
#ifndef STOCK_H_
#define STOCK_H_#include <string>// class declaration
class Stock {
private:std::string company_;int shares_;double share_val_;double total_val_;void SetTot() { total_val_ = shares_ * share_val_; }
public:Stock(); // Default constructorStock(const std::string &company, const long num = 0, const double price = 0.0);~Stock();void Buy(const long num, const double price);void Sell(const long num, const double price);void Update(const double price);void Show()const;const Stock &TopVal(const Stock &stock) const;
}; // Note semicolon at the end#endif1. Access Control (访问控制)
Also new are the keywords private and public. These labels describe access control for class members. Any program that uses an object of a particular class can access the public portions directly. A program can access the private members of an object only by using the public member functions (or via a friend function). For example, the only way to alter the shares_ member of the Stock class is to use one of the Stock member functions. Thus, the public member functions act as go-betweens between a program and an object’s private members; they provide the interface between object and program. This insulation of data from direct access by a program is called data hiding.
关键字 private,public 和 protected 描述了对类成员的访问控制。使用类对象的程序都可以直接访问公有部分,但只能通过公有成员函数 (或友元函数) 来访问对象的私有成员。例如,要修改 Stock 类的 shares_ 成员,只能通过 Stock 的成员函数。因此,公有成员函数是程序和对象的私有成员之间的桥梁,提供了对象和程序之间的接口。防止程序直接访问数据被称为数据隐藏。
insulation [ˌɪnsjʊˈleɪʃ(ə)n]:n. 绝缘,隔热,隔音,隔热材料

A class design attempts to separate the public interface from the specifics of the implementation. The public interface represents the abstraction component of the design. Gathering the implementation details together and separating them from the abstraction is called encapsulation. Data hiding (putting data into the private section of a class) is an instance of encapsulation, and so is hiding functional details of an implementation in the private section, as the Stock class does with SetTot(). Another example of encapsulation is the usual practice of placing class function definitions in a separate file from the class declaration.
类设计尽可能将公有接口与实现细节分开。公有接口表示设计的抽象组件,将实现细节放在一起并将它们与抽象分开被称为封装。数据隐藏 (将数据放在类的私有部分中) 是一种封装,将实现的细节隐藏在私有部分中,就像 Stock 类对 SetTot() 所做的那样,也是一种封装。封装的另一个例子是将类函数定义和类声明放在不同的文件中。
OOP is a programming style that you can use to some degree with any language.
OOP 是一种编程风格,从某种程度说,它用于任何一种语言中。
Note that data hiding not only prevents you from accessing data directly, but it also absolves you (in the roll as a user of the class) from needing to know how the data is represented.
数据隐藏不仅可以防止直接访问数据,还让开发者 (类的用户) 无需了解数据是如何被表示的。
absolve [əbˈzɒlv]:v. 宣告 ... 无罪,判定 ... 无责,赦免 ... 的罪
2. Member Access Control (控制对成员的访问)
You can declare class members, whether they are data items or member functions, either in the public or the private section of a class. But because one of the main precepts of OOP is to hide the data, data items normally go into the private section. The member functions that constitute the class interface go into the public section; otherwise, you can’t call those functions from a program. As the Stock declaration shows, you can also put member functions in the private section. You can’t call such functions directly from a program, but the public methods can use them. Typically, you use private member functions to handle implementation details that don’t form part of the public interface.
无论类成员是数据成员还是成员函数,都可以在类的公有部分或私有部分中声明它。但由于隐藏数据是 OOP 主要的目标之一,因此数据项通常放在私有部分,组成类接口的成员函数放在公有部分;否则,就无法从程序中调用这些函数。正如 Stock 声明所表明的,也可以把成员函数放在私有部分中。不能直接从程序中调用这种函数,但公有方法却可以使用它们。通常,程序员使用私有成员函数来处理不属于公有接口的实现细节。
You don’t have to use the keyword private in class declarations because that is the default access control for class objects:
class World
{float mass_; // private by defaultchar name_[20]; // private by default
public:void TellAll(void);...
};
However, this book explicitly uses the private label in order to emphasize the concept of data hiding.
然而,为强调数据隐藏的概念,本书显式地使用了 private。
Class descriptions look much like structure declarations with the addition of member functions and the public and private visibility labels. In fact, C++ extends to structures the same features classes have. The only difference is that the default access type for a structure is public, whereas the default type for a class is private. C++ programmers commonly use classes to implement class descriptions while restricting structures to representing pure data objects (often called plain-old data structures, or POD structures).
类描述看上去很像是包含成员函数以及 public 和 private 可见性标签的结构声明。实际上,C++ 对 struct 进行了扩展,使之具有与 class 相同的特性。它们之间唯一的区别是,struct 的默认访问类型是 public,而 class 的默认访问类型为 private。C++ 程序员通常使用类来实现类描述,而把结构限制为只表示纯粹的数据对象,常被称为普通老式数据结构 (Plain Old Data,POD)。
2.2. Implementing Class Member Functions (实现类成员函数)
Member function definitions are much like regular function definitions. Each has a function header and a function body. Member function definitions can have return types and arguments. But they also have two special characteristics:
- When you define a member function, you use the scope-resolution operator (
::) to identify the class to which the function belongs.
定义成员函数时,使用作用域解析运算符 (::) 来标识函数所属的类。 - Class methods can access the private components of the class.
类方法可以访问类的private组件。
The function header for a member function uses the scope-resolution operator (::) to indicate to which class the function belongs.
成员函数的函数头使用作用域运算符解析 (::) 来指出函数所属的类。
For example, the header for the Update() member function looks like this:
void Stock::Update(double price)
This notation means you are defining the Update() function that is a member of the Stock class. Not only does this identify Update() as a member function, it means you can use the same name for a member function for a different class.
For example, an Update() function for a Elephant class would have this function header:
void Elephant::Update()
Thus, the scope-resolution operator resolves the identity of the class to which a method definition applies. We say that the identifier Update() has class scope. Other member functions of the Stock class can, if necessary, use the Update() method without using the scope-resolution operator. That’s because they belong to the same class, making Update() in scope.
因此,作用域解析运算符确定了方法定义对应的类的身份。我们说,标识符 Update() 具有类作用域 (class scope)。Stock 类的其他成员函数不必使用作用域解析运算符就可以使用 Update() 方法,这是因为它们属于同一个类,因此 Update() 是可见的。
One way of looking at method names is that the complete name of a class method includes the class name. Stock::Update() is called the qualified name of the function. A simple Update(), on the other hand, is an abbreviation (the unqualified name) for the full name - one that can be used just in class scope.
类方法的完整名称中包括类名。Stock::Update() 是函数的限定名 (qualified name),而简单的 Update() 是全名的缩写 (非限定名,unqualified name) ,它只能在类作用域中使用。
The second special characteristic of methods is that a method can access the private members of a class.
方法可以访问类的私有成员。
If you try to use a nonmember function to access these data members, the compiler stops you cold in your tracks. (However, friend functions provide an exception.)
如果试图使用非成员函数访问这些数据成员,编译器禁止这样做 (友元函数例外)。
- stock.cpp
#include <iostream>#include "stock.h"// Default constructor
Stock::Stock() {std::cout << "Stock::Stock()" << "\n";company_ = "default name";shares_ = 0;share_val_ = 0.0;total_val_ = 0.0;
}Stock::Stock(const std::string &company, const long num, const double price) {std::cout << "Stock::Stock(const std::string &company, const long num = 0, const double price = 0.0): " << company << "\n";company_ = company;if (num < 0) {std::cout << "Number of shares_ can't be negative; " << company_ << " shares_ set to 0.\n";shares_ = 0;}else {shares_ = num;}share_val_ = price;SetTot();
}// Destructor
Stock::~Stock() {std::cout << "Stock::~Stock(): " << company_ << "\n";
}void Stock::Buy(const long num, const double price) {if (num < 0) {std::cout << "Number of shares_ purchased can't be negative. " << "Transaction is aborted.\n";}else {shares_ += num;share_val_ = price;SetTot();}
}void Stock::Sell(const long num, const double price) {if (num < 0) {std::cout << "Number of shares_ sold can't be negative. " << "Transaction is aborted.\n";}else if (num > shares_) {std::cout << "You can't sell more than you have! " << "Transaction is aborted.\n";}else {shares_ -= num;share_val_ = price;SetTot();}
}void Stock::Update(const double price) {share_val_ = price;SetTot();
}void Stock::Show() const {// set format to #.###std::ios_base::fmtflags original = std::cout.setf(std::ios_base::fixed, std::ios_base::floatfield);std::streamsize precision = std::cout.precision(3);std::cout << "Company: " << company_ << "\n Shares = " << shares_;std::cout << " Share Price = $" << share_val_;// set format to #.##std::cout.precision(2);std::cout << " Total Worth = $" << total_val_ << '\n';// restore original formatstd::cout.setf(original, std::ios_base::floatfield);std::cout.precision(precision);
}const Stock & Stock::TopVal(const Stock & stock) const {if (stock.total_val_ > total_val_) {return stock; // argument object}else {return *this; // invoking object}
}1. Member Function Notes (成员函数说明)
Because this function is merely the means of implementing the code and not part of the public interface, the class makes SetTot() a private member function. (That is, SetTot() is a member function used by the person writing the class but not used by someone writing code that uses the class.)
由于 SetTot() 只是实现代码的一种方式,而不是公有接口的组成部分,因此这个类将其声明为私有成员函数 (即编写这个类的人可以使用它,但编写代码来使用这个类的人不能使用) 。
2. Inline Methods (内联方法)
Any function with a definition in the class declaration automatically becomes an inline function. Thus, Stock::SetTot() is an inline function. Class declarations often use inline functions for short member functions, and SetTot() qualifies on that account.
定义位于类声明中的函数都将自动成为内联函数,因此 Stock::SetTot() 是一个内联函数。类声明常将短小的成员函数作为内联函数,SetTot() 符合这样的要求。
You can, if you like, define a member function outside the class declaration and still make it inline. To do so, you just use the inline qualifier when you define the function in the class implementation section:
如果愿意,也可以在类声明之外定义成员函数,并使其成为内联函数。为此,只需在类实现部分中定义函数时使用 inline 限定符即可:
class Stock
{
private:...void SetTot(); // definition kept separate
public:...
};inline void Stock::SetTot() // use inline in definition
{total_val_ = shares_ * share_val_;
}
The special rules for inline functions require that they be defined in each file in which they are used. The easiest way to make sure that inline definitions are available to all files in a multifile program is to include the inline definition in the same header file in which the corresponding class is defined.
内联函数的特殊规则要求在每个使用它们的文件中都对其进行定义。确保内联定义对多文件程序中的所有文件都可用的、最简便的方法是:将内联定义放在定义类的头文件中 。
Incidentally, according to the rewrite rule, defining a method within a class declaration is equivalent to replacing the method definition with a prototype and then rewriting the definition as an inline function immediately after the class declaration. That is, the original inline definition of SetTot() is equivalent to the one just shown, with the definition following the class declaration.
根据改写规则 (rewrite rule),在类声明中定义方法等同于用原型替换方法定义,然后在类声明的后面将定义改写为内联函数。程序清单中 SetTot() 的内联定义与上述代码 (定义紧跟在类声明之后) 是等价的。
When you call a member function, it uses the data members of the particular object used to invoke the member function.
调用成员函数时,它将使用被用来调用它的对象的数据成员。
Each new object you create contains storage for its own internal variables, the class members. But all objects of the same class share the same set of class methods, with just one copy of each method.
所创建的每个新对象都有自己的存储空间,用于存储其内部变量和类成员;但同一个类的所有对象共享同一组类方法,即每种方法只有一个副本。
They just apply the code to different data. Calling a member function is what some OOP languages term sending a message. Thus, sending the same message to two different objects invokes the same method but applies it to two different objects
它们将执行同一个代码块,只是将这些代码用于不同的数据。在 OOP 中,调用成员函数被称为发送消息,因此将同样的消息发送给两个不同的对象将调用同一个方法,但该方法被用于两个不同的对象。

2.3. Using Classes (使用类)
The C++ goal is to make using classes as similar as possible to using the basic, built-in types, such as int and char. You can create a class object by declaring a class variable or using new to allocate an object of a class type.
C++ 的目标是使得使用类与使用基本的内置类型 (例如 int 和 char) 尽可能相同。要创建类对象,可以声明类变量,也可以使用 new 为类对象分配存储空间。
- sample.cpp
#include <iostream>#include "stock.h"int main() {Stock yongqiang("strong", 20, 12.50);yongqiang.Show();yongqiang.Buy(15, 18.125);yongqiang.Show();yongqiang.Sell(400, 20.00);yongqiang.Show();yongqiang.Buy(300000, 40.125);yongqiang.Show();yongqiang.Sell(300000, 0.125);yongqiang.Show();return 0;
}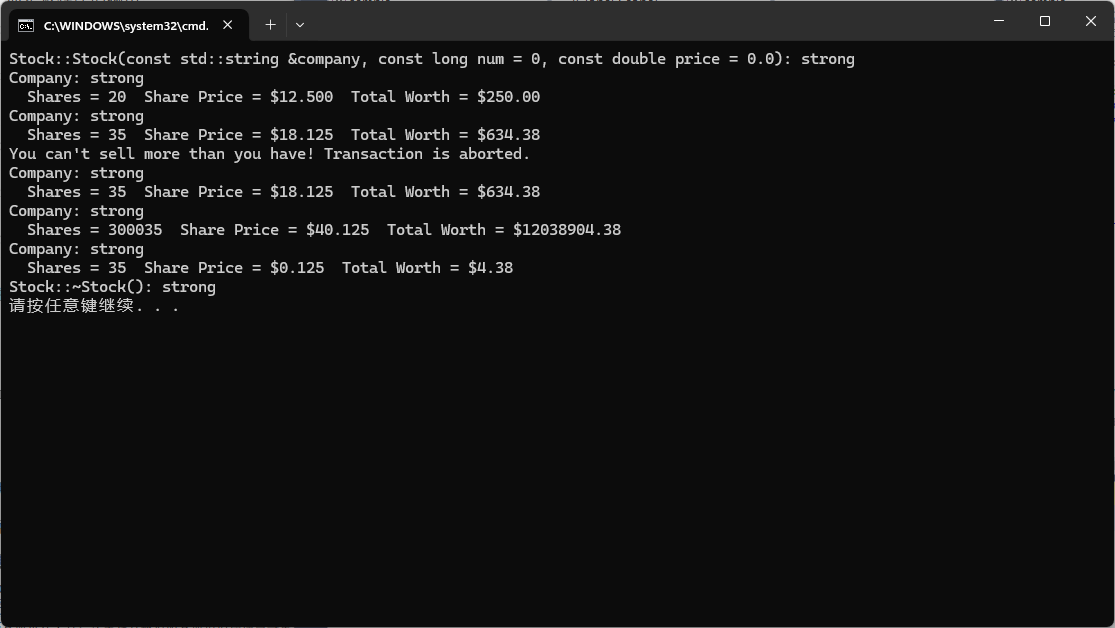
Stock::Stock(const std::string &company, const long num = 0, const double price = 0.0): strong
Company: strongShares = 20 Share Price = $12.500 Total Worth = $250.00
Company: strongShares = 35 Share Price = $18.125 Total Worth = $634.38
You can't sell more than you have! Transaction is aborted.
Company: strongShares = 35 Share Price = $18.125 Total Worth = $634.38
Company: strongShares = 300035 Share Price = $40.125 Total Worth = $12038904.38
Company: strongShares = 35 Share Price = $0.125 Total Worth = $4.38
Stock::~Stock(): strong
请按任意键继续. . .
1. The Client / Server Model
OOP programmers often discuss program design in terms of a client / server model. In this conceptualization, the client is a program that uses the class. The class declaration, including the class methods, constitute the server, which is a resource that is available to the programs that need it. The client uses the server through the publicly defined interface only. This means that the client’s only responsibility, and, by extension, the client’s programmer’s only responsibility, is to know that interface. The server’s responsibility, and, by extension, the server’s designer’s responsibility, is to
see that the server reliably and accurately performs according to that interface. Any changes the server designer makes to the class design should be to details of implementation, not to the interface. This allows programmers to improve the client and the server independently of each other, without changes in the server having unforeseen repercussions on the client’s behavior.
OOP 程序员常依照客户/服务器模型来讨论程序设计。在这个概念中,客户是使用类的程序。类声明 (包括类方法) 构成了服务器,它是程序可以使用的资源。客户只能通过以公有方式定义的接口使用服务器,这意味着客户 (客户程序员) 唯一的责任是了解该接口。服务器 (服务器设计人员) 的责任是确保服务器根据该接口可靠并准确地执行。服务器设计人员只能修改类设计的实现细节,而不能修改接口。这样程序员独立地对客户和服务器进行改进,对服务器的修改不会客户的行为造成意外的影响。
You can avoid e-notation by using the setf() method
std::cout.setf(std::ios_base::fixed, std::ios_base::floatfield);
This sets a flag in the std::cout object instructing cout to use fixed-point notation.
设置 std::cout 对象的一个标记,命令 std::cout 使用定点表示法。使用方法 std::cout.setf(),便可避免科学计数法
Similarly, the following statement causes std::cout to show three places to the right of the decimal when using fixed-point notation.
下面的语句设置 std::cout 在使用定点表示法时,显示 3 位小数
std::cout.precision(3);
The class declaration is modeled after a structure declaration and can include data members and function members. The declaration has a private section, and members declared in that section can be accessed only through the member functions. The declaration also has a public section, and members declared there can be accessed directly by a program using class objects.
类声明类似结构声明,可以包括数据成员和函数成员。声明私有部分,在其中声明的成员只能通过成员函数进行访问;声明公有部分,在其中声明的成员可被使用类对象的程序直接访问。通常,数据成员被放在私有部分中,成员函数被放在公有部分中。
Typically, data members go into the private section and member functions go into the public section, so a typical class declaration has this form:
class ClassName
{
private:data member declarations
public:member function prototypes
};
The contents of the public section constitute the abstract part of the design, the public interface. Encapsulating data in the private section protects the integrity of the data and is called data hiding.
公有部分的内容构成了设计的抽象部分 - 公有接口。将数据封装到私有部分中可以保护数据的完整性,这被称为数据隐藏。
You can use a complete function definition instead of a function prototype in the class declaration, but the usual practice, except with very brief functions, is to provide the function definitions separately. In that case, you need to use the scope-resolution operator to indicate to which class a member function belongs.
可以在类声明中提供完整的函数定义,而不是函数原型,但是通常的做法是单独提供函数定义 (除非函数很小)。在这种情况下,需要使用作用域解析运算符来指出成员函数属于哪个类。
For example, suppose the Giraffe class has a member function called Retort() that returns a pointer to a char. The function header would look like this:
char * Giraffe::Retort()
In other words, Retort() is not just a type char * function; it is a type char * function that belongs to the Giraffe class. The full, or qualified, name of the function is Giraffe::Retort().The name Retort(), on the other hand, is an abbreviation of the qualified name, and it can be used only in certain circumstances, such as in the code for the class methods.
Retort() 不仅是一个 char * 类型的函数,而是一个属于 Giraffe 类的 char * 函数。该函数的全名 (或限定名) 为 Giraffe::Retort()。而名称 Retort() 是限定名的缩写,只能在某些特定的环境中使用。
The name Retort() has class scope, so the scope-resolution operator is needed to qualify the name when it is used outside the class declaration and a class method.
名称 Retort() 的作用域为整个类,因此在类声明和类方法之外使用该名称时,需要使用作用域解析运算符进行限定。
要创建对象 (类的实例),只需将类名视为类型名即可:
Giraffe june;
This works because a class is a user-defined type. You invoke a class member function, or method, by using a class object. You do so by using the dot membership operator: std::cout << june.Retort();
这样做是可行的,因为类是用户定义的类型。类成员函数 (方法) 可通过类对象来调用。为此,需要使用成员运算符句点。
This invokes the Retort() member function, and whenever the code for that function refers to a particular data member, the function uses the value that member has in the june object.
这将调用 Retort() 成员函数,每当其中的代码引用某个数据成员时,该函数都将使用 june 对象中相应成员的值。
References
[1] Yongqiang Cheng, https://yongqiang.blog.csdn.net/
[2] C++ Primer Plus, 6th Edition, https://www.informit.com/store/c-plus-plus-primer-plus-9780321776402
- Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming
- Abstraction and Classes
相关文章:

Objects and Classes (对象和类)
Objects and Classes [对象和类] 1. Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming (过程性编程和面向对象编程)2. Abstraction and Classes (抽象和类)2.1. Classes in C (C 中的类)2.2. Implementing Class Member Functions (实现类成员函数)2.3. Using Classes (使用类) Ref…...
从单点到全景:视频汇聚/安防监控EasyCVR全景视频监控技术的演进之路
在当今日新月异的科技浪潮中,安防监控领域的技术发展日新月异,全景摄像机便是这一领域的杰出代表。它以其独特的360度无死角监控能力,为各行各业提供了前所未有的安全保障,成为现代安防体系中的重要组成部分。 一、全景摄像机的技…...

Java学习 -Golang开发环境+目录结构+编译+部署
开发环境 环境变量设置 GOROOT 指定 golang sdk 的安装目录GOPATH golang 工作目录,项目的源码放在这个目录下PATH 将 GOROOT/bin 放在 Path 路径下,方便命令行能直接运行 golang的命令行工具项目目录结构 |--project // 位于G…...
)
Redis 典型应用——缓存(缓存预热,穿透,雪崩,击穿)
一、缓存 缓存是计算机中一个很经典的概念,核心思路是把一些常用的数据放到访问速度更快的地方,方便随时读取; 但对于计算机硬件来说,往往访问速度越快的设备,成本越高,存储空间越小,缓存是更…...

Sharding-JDBC分库分表的基本使用
前言 传统的小型应用通常一个项目一个数据库,单表的数据量在百万以内,对于数据库的操作不会成为系统性能的瓶颈。但是对于互联网应用,单表的数据量动辄上千万、上亿,此时通过数据库优化、索引优化等手段,对数据库操作…...

7月信用卡新规下:信用卡欠的钱不用还了?
说到信用卡,现在基本上人手一张,大家都有使用过。但你知道吗,使用信用卡不是这么简单容易的事,比如会对你的贷款有影响,透支不还逾期对生活的影响,信用卡新规对持卡人和银行那边的影响。 一、只要不逾期&am…...

坑——python的redis库的decode_responses设置
python的redis库查询返回的值默认是返回字节串,可以在redis.Redis()方法中通过设置decode_responses参数,让返回值直接是字符串; 查询返回字节串是因为Redis()方法中decode_responses默认值是False: 设置decode_responses为True就…...
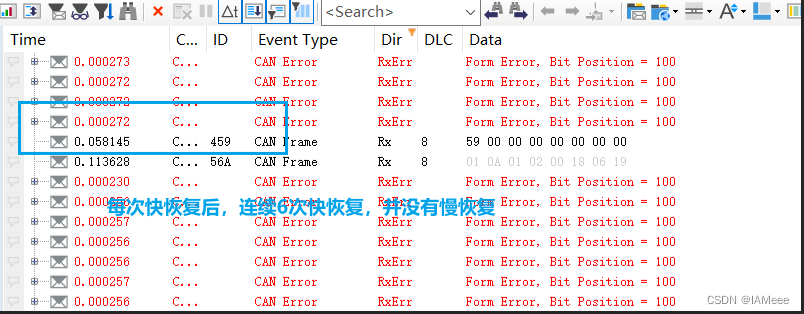
从项目中学习Bus-Off的快慢恢复
0 前言 说到Bus-Off,大家应该都不陌生,使用VH6501干扰仪进行测试的文章在网上数不胜数,但是一般大家都是教怎么去干扰,但是说如何去看快慢恢复以及对快慢恢复做出解释比较少,因此本文以实践的视角来讲解Bus-Off的快慢恢…...
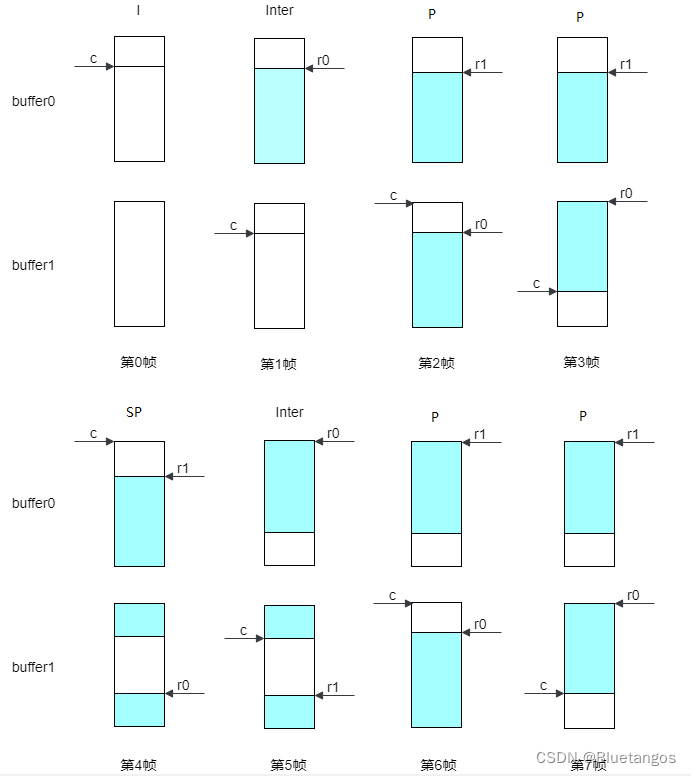
视频参考帧和重构帧复用
1、 视频编码中的参考帧和重构帧 从下图的编码框架可以看出,每编码一帧需要先使用当前帧CU(n)减去当前帧的参考帧CU(n)得到残差。同时,需要将当前帧的重构帧CU*(n)输出,然后再读取重构帧进行预测…...
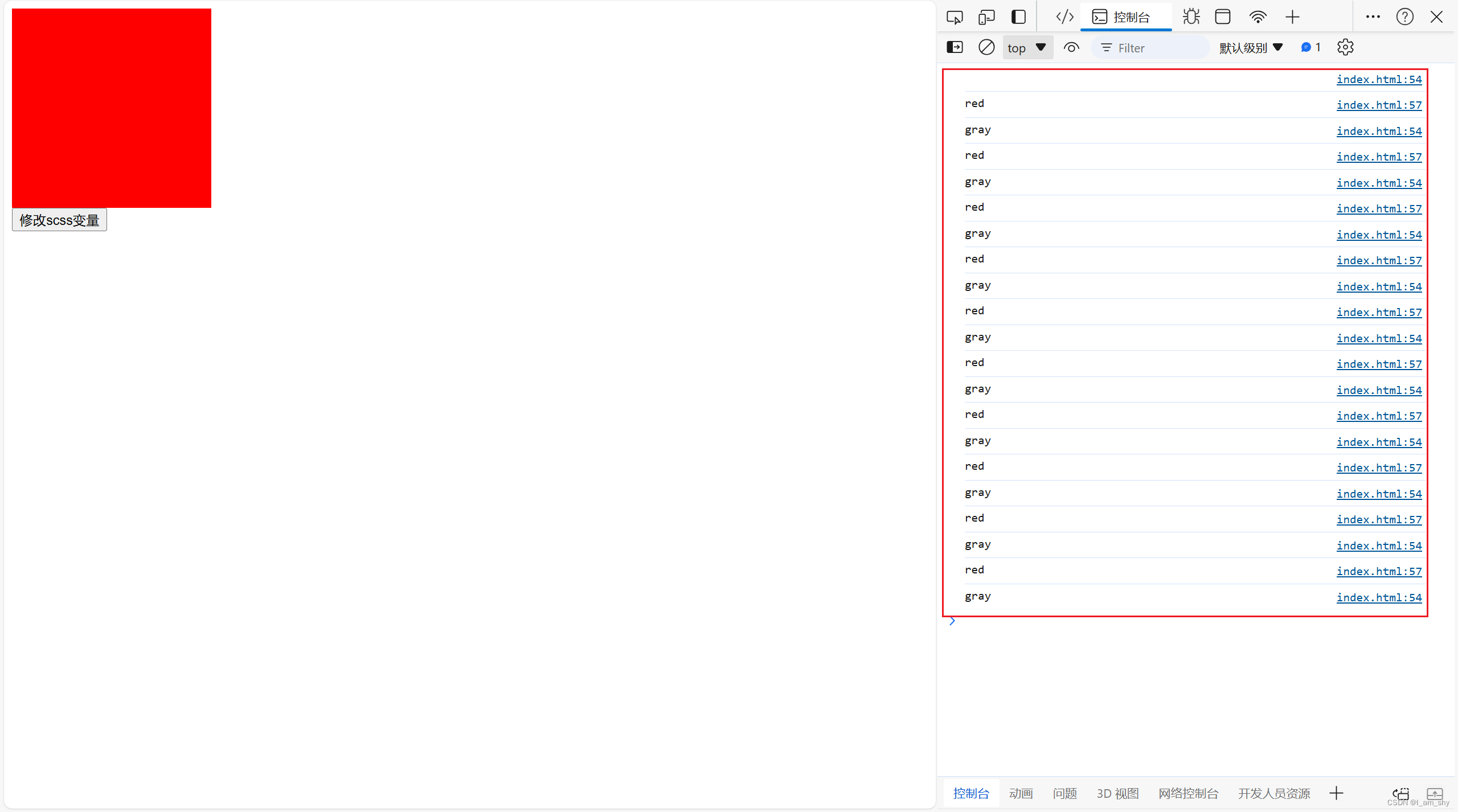
js修改scss变量
style.scss $color : var(--color,#ccc); // 默认值 #ccc .color{background: $color; } 定义了一个scss变量($color),用普通的css变量(--color)给他赋值,这里需要一个默认值,此时css变量(--co…...

【中霖教育怎么样】报考注册会计师有年龄限制吗?
【中霖教育怎么样】报考注册会计师有年龄限制吗? 申请参加注册会计师考试有没有年龄约束? 对于注册会计师的考试,不存在具体的年龄上限。而且该考试的入学门栏相对低,主要对考生的年龄下限规定。 在专业阶段,注册会计师考试要求考生具备…...
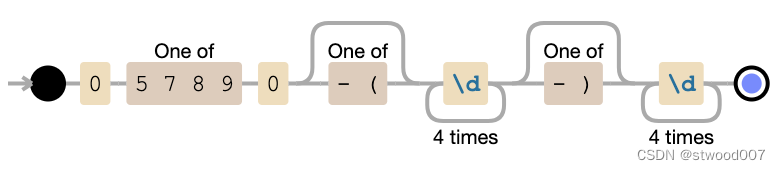
PHP验证日本手机电话号码
首先,您需要了解手机号码的规格。 根据 ,手机和PHS(个人手持电话系统)可以理解为以“070”、“080”和“090”开头的11位数字。 此外,以“050”开头的11位特定IP电话号码也将包含在该目标中。 关于以“060”开头的F…...

Qt 配置ASan
Qt 配置ASan 文章目录 Qt 配置ASan摘要关于ASan(AddressSanitizer)在Qt中配置 ASan1. 安装必要的工具2. 修改项目的 .pro 文件3. 重新构建项目4. 运行应用程序5. 分析错误报告示例注意事项 关键字: Qt、 ASan、 AddressSanitizer 、 GCC …...

MySQL常用操作命令大全
文章目录 一、连接与断开数据库1.1 连接数据库1.2 选择数据库1.3 断开数据库 二、数据库操作2.1 创建数据库2.2 查看数据库列表2.3 删除数据库 三、表操作3.1 创建表3.2 查看表结构3.3 修改表结构3.3.1 添加列3.3.2 删除列3.3.3 修改列数据类型 3.4 删除表 四、数据操作4.1 插入…...
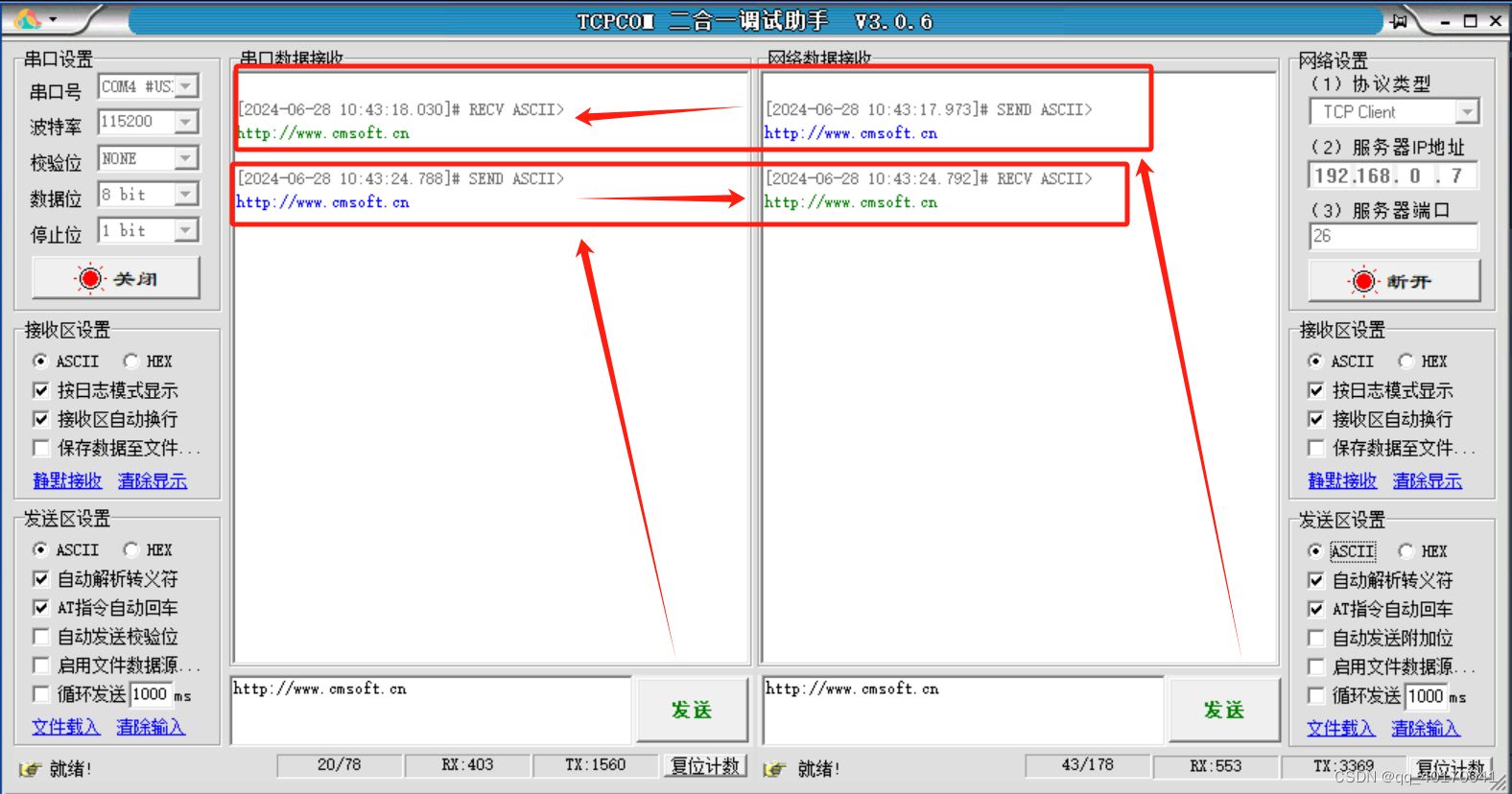
有人物联的串口服务器USR-TCP232-410S基本测试通信和使用方案(485串口和232串口)
1.将 410S(USR-TCP232-410S,简称 410S 下同)的串口通过串口线(或USB 转串口线)与计算机相连接,通过网线将 410S 的网口 PC 的网口相连接,检测硬件连接无错误后,接入我们配送的电源适配器,给 410S 供电。观察指示灯状态…...

二维码登录的原理
二维码登录的原理: 二维码登录是一种基于移动设备和网络技术的便捷登录方式。其原理主要依赖于以下几个关键要素: 随机生成:服务器端随机生成一个具有唯一性和时效性的二维码。编码信息:这个二维码包含了特定的登录信息,例如用户标识、会话标识、时间戳等。扫描识别:用户…...
归并排序详解(递归与非递归)
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效算法。该算法是采用分治法的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列间断有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,成为二路归并。 一…...
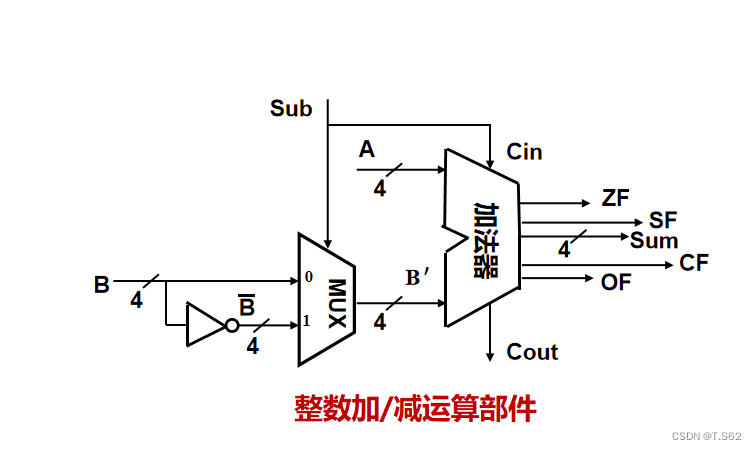
计算机系统基础(二)
1.数值数据的表示 为什么采用二进制? 二进制只有两种基本状态,两个物理器件就可以表示0和1二进制的编码、技术、运算规则都很简单0和1与逻辑命题的真假对应,方便通过逻辑门电路实现算术运算 数值数据表示的三要素 进位记数制(十…...
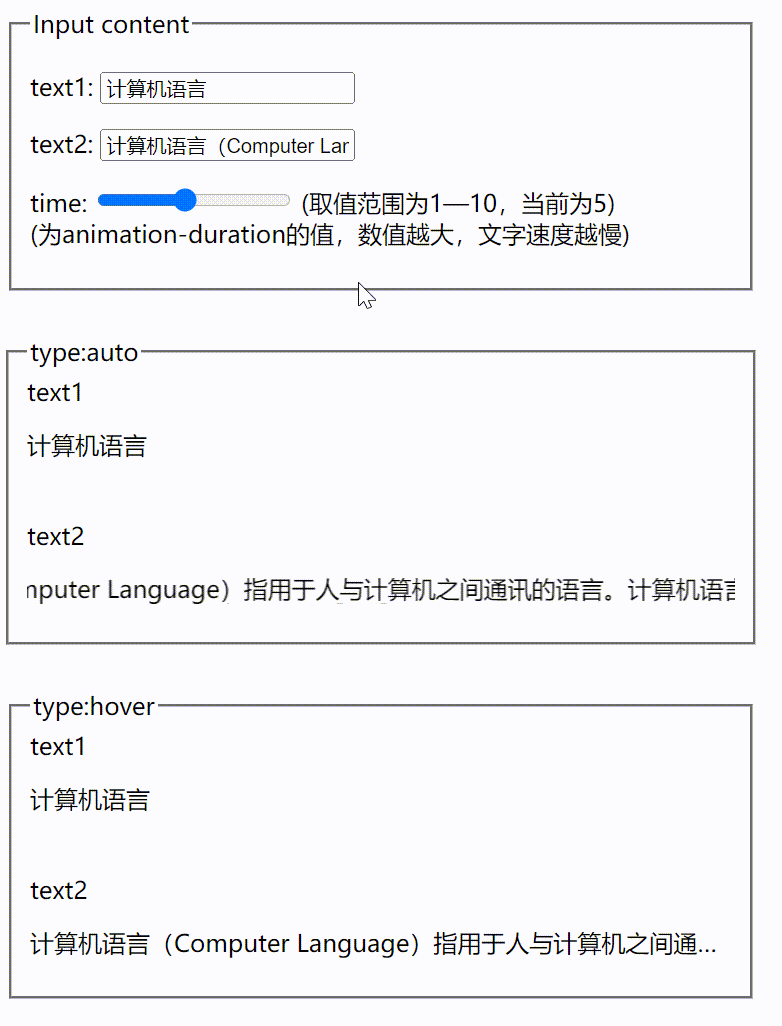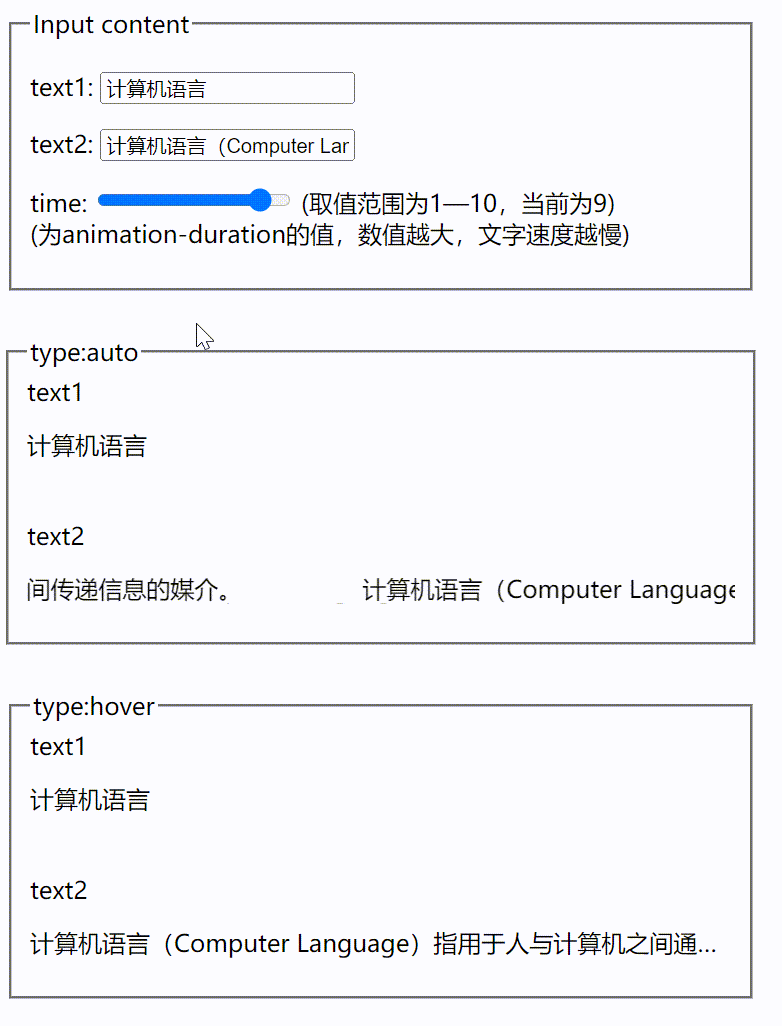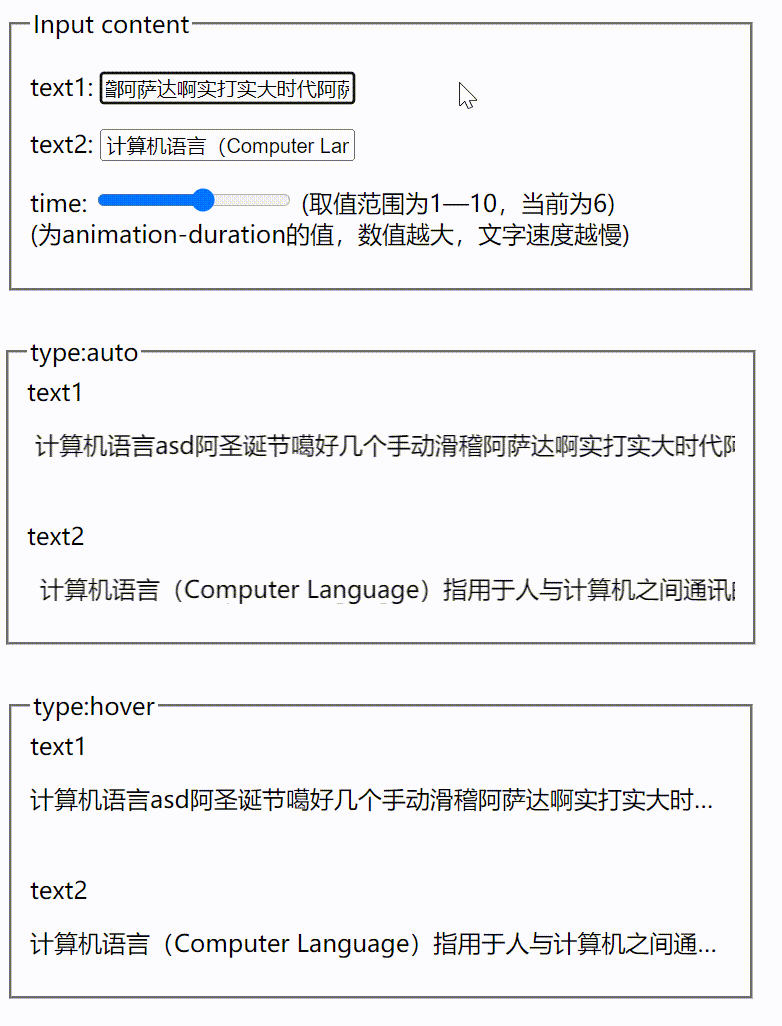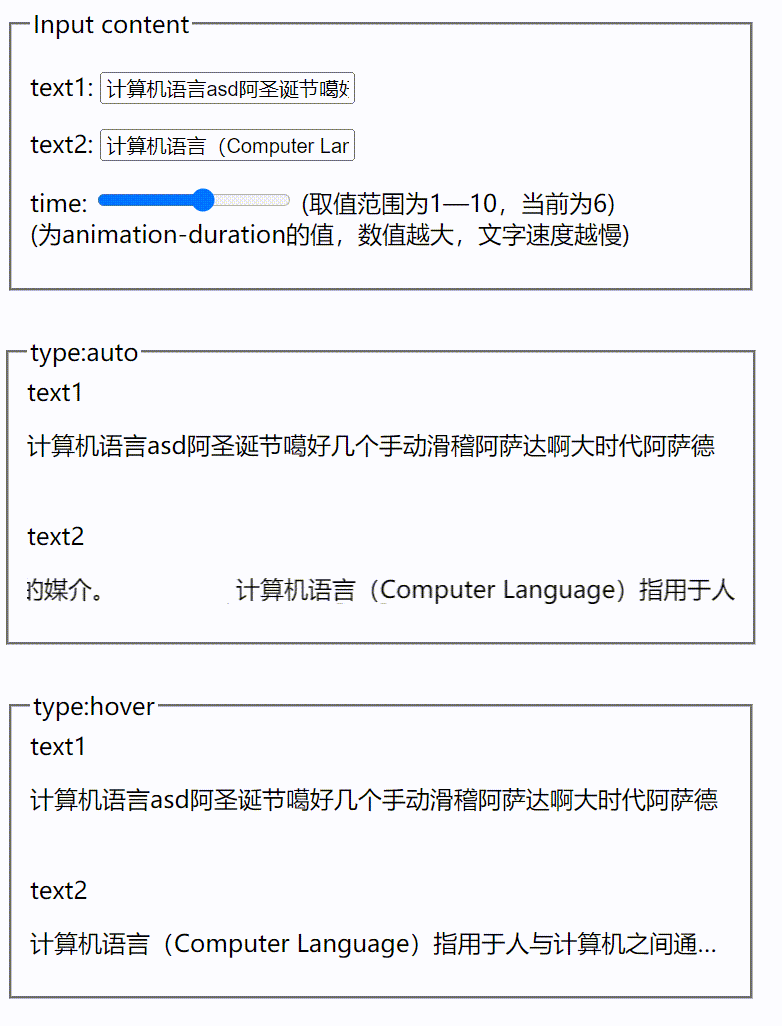
vue根据文字长短展示跑马灯效果
介绍 为大家介绍一个我编写的vue组件 auto-marquee ,他可以根据要展示文本是否超出展示区域,来判断是否使用跑马灯效果,效果图如下所示 假设要展示区域的宽度为500px,当要展示文本的长度小于500px时,只会展示文本&…...
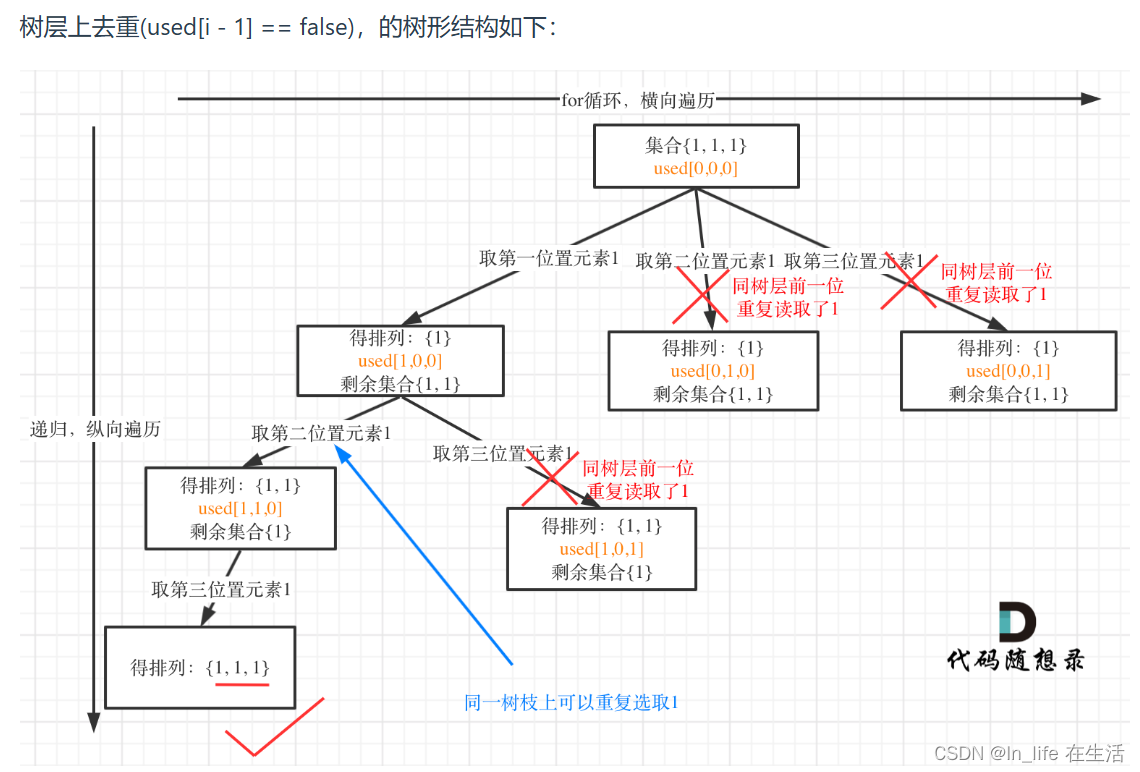
leetcode-21-回溯-全排列及其去重
一、[46]全排列 给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。 示例: 输入: [1,2,3]输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [3,2,1] ] 其中,不需要使用startIndex used数组,其实就是记录此时path里都有哪些元素…...

Chapter03-Authentication vulnerabilities
文章目录 1. 身份验证简介1.1 What is authentication1.2 difference between authentication and authorization1.3 身份验证机制失效的原因1.4 身份验证机制失效的影响 2. 基于登录功能的漏洞2.1 密码爆破2.2 用户名枚举2.3 有缺陷的暴力破解防护2.3.1 如果用户登录尝试失败次…...
23-Oracle 23 ai 区块链表(Blockchain Table)
小伙伴有没有在金融强合规的领域中遇见,必须要保持数据不可变,管理员都无法修改和留痕的要求。比如医疗的电子病历中,影像检查检验结果不可篡改行的,药品追溯过程中数据只可插入无法删除的特性需求;登录日志、修改日志…...

《Playwright:微软的自动化测试工具详解》
Playwright 简介:声明内容来自网络,将内容拼接整理出来的文档 Playwright 是微软开发的自动化测试工具,支持 Chrome、Firefox、Safari 等主流浏览器,提供多语言 API(Python、JavaScript、Java、.NET)。它的特点包括&a…...

Go 语言接口详解
Go 语言接口详解 核心概念 接口定义 在 Go 语言中,接口是一种抽象类型,它定义了一组方法的集合: // 定义接口 type Shape interface {Area() float64Perimeter() float64 } 接口实现 Go 接口的实现是隐式的: // 矩形结构体…...

【论文笔记】若干矿井粉尘检测算法概述
总的来说,传统机器学习、传统机器学习与深度学习的结合、LSTM等算法所需要的数据集来源于矿井传感器测量的粉尘浓度,通过建立回归模型来预测未来矿井的粉尘浓度。传统机器学习算法性能易受数据中极端值的影响。YOLO等计算机视觉算法所需要的数据集来源于…...

生成 Git SSH 证书
🔑 1. 生成 SSH 密钥对 在终端(Windows 使用 Git Bash,Mac/Linux 使用 Terminal)执行命令: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_emailexample.com" 参数说明: -t rsa&#x…...

QT: `long long` 类型转换为 `QString` 2025.6.5
在 Qt 中,将 long long 类型转换为 QString 可以通过以下两种常用方法实现: 方法 1:使用 QString::number() 直接调用 QString 的静态方法 number(),将数值转换为字符串: long long value 1234567890123456789LL; …...

在web-view 加载的本地及远程HTML中调用uniapp的API及网页和vue页面是如何通讯的?
uni-app 中 Web-view 与 Vue 页面的通讯机制详解 一、Web-view 简介 Web-view 是 uni-app 提供的一个重要组件,用于在原生应用中加载 HTML 页面: 支持加载本地 HTML 文件支持加载远程 HTML 页面实现 Web 与原生的双向通讯可用于嵌入第三方网页或 H5 应…...
【笔记】WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录
#工作记录 WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录 1. 运行环境 系统:Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (WSL2)架构:x86_64 (GNU/Linux)Rust 版本:rustc 1.87.0 (2025-05-09)Cargo 版本:cargo 1.87.0 (2025-05-06) 2. 安装 Rust 2.1 使用 Rust 官方安…...

Web中间件--tomcat学习
Web中间件–tomcat Java虚拟机详解 什么是JAVA虚拟机 Java虚拟机是一个抽象的计算机,它可以执行Java字节码。Java虚拟机是Java平台的一部分,Java平台由Java语言、Java API和Java虚拟机组成。Java虚拟机的主要作用是将Java字节码转换为机器代码&#x…...
