AIGC笔记--Stable Diffusion源码剖析之DDIM
1--前言
以论文《High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models》 开源的项目为例,剖析Stable Diffusion经典组成部分,巩固学习加深印象。
2--DDIM
一个可以debug的小demo:SD_DDIM
以文生图为例,剖析SD中DDIM的核心组成模块。 本质上SD的DDIM遵循论文DENOISING DIFFUSION IMPLICIT MODELS的核心公式。
3--核心模块剖析
见SD_DDIM
4--完整代码
import torch
import pytorch_lightning as plimport numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
from functools import partial# From https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/blob/main/ldm/modules/diffusionmodules/util.py
def make_ddim_sampling_parameters(alphacums, ddim_timesteps, eta, verbose = True):# select alphas for computing the variance schedulealphas = alphacums[ddim_timesteps] # 由于alphacums来自DDPM,所以本质上还是调用了DDPM的alphas_cumprod,即[0.9983, 0.9804, ..., 0.0058]alphas_prev = np.asarray([alphacums[0]] + alphacums[ddim_timesteps[:-1]].tolist()) # 构成alphas_prev的方法是保留前49个alphas,同时在最前面添加DDPM的alphas_cumprod[0], 即[0.9991]# according the the formula provided in https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502 论文中的公式16sigmas = eta * np.sqrt((1 - alphas_prev) / (1 - alphas) * (1 - alphas / alphas_prev))if verbose:print(f'Selected alphas for ddim sampler: a_t: {alphas}; a_(t-1): {alphas_prev}')print(f'For the chosen value of eta, which is {eta}, 'f'this results in the following sigma_t schedule for ddim sampler {sigmas}')return sigmas, alphas, alphas_prev# From https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/blob/main/ldm/modules/diffusionmodules/util.py
# 获取 ddim 的timesteps
def make_ddim_timesteps(ddim_discr_method, num_ddim_timesteps, num_ddpm_timesteps, verbose = True):if ddim_discr_method == 'uniform':c = num_ddpm_timesteps // num_ddim_timesteps # 1000 // 50 = 20ddim_timesteps = np.asarray(list(range(0, num_ddpm_timesteps, c))) # 间隔c取样elif ddim_discr_method == 'quad':ddim_timesteps = ((np.linspace(0, np.sqrt(num_ddpm_timesteps * .8), num_ddim_timesteps)) ** 2).astype(int)else:raise NotImplementedError(f'There is no ddim discretization method called "{ddim_discr_method}"')# assert ddim_timesteps.shape[0] == num_ddim_timesteps# add one to get the final alpha values right (the ones from first scale to data during sampling)steps_out = ddim_timesteps + 1 # 每个数值加1if verbose:print(f'Selected timesteps for ddim sampler: {steps_out}')return steps_out # [1, 21, 41, ..., 981]# From https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/blob/main/ldm/modules/diffusionmodules/util.py
def noise_like(shape, device, repeat = False):repeat_noise = lambda: torch.randn((1, *shape[1:]), device=device).repeat(shape[0], *((1,) * (len(shape) - 1)))noise = lambda: torch.randn(shape, device=device)return repeat_noise() if repeat else noise()# From https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/blob/main/ldm/modules/diffusionmodules/util.py
def make_beta_schedule(schedule, n_timestep, linear_start = 1e-4, linear_end = 2e-2, cosine_s = 8e-3):if schedule == "linear":betas = (torch.linspace(linear_start ** 0.5, linear_end ** 0.5, n_timestep, dtype = torch.float64) ** 2)elif schedule == "cosine":timesteps = (torch.arange(n_timestep + 1, dtype=torch.float64) / n_timestep + cosine_s)alphas = timesteps / (1 + cosine_s) * np.pi / 2alphas = torch.cos(alphas).pow(2)alphas = alphas / alphas[0]betas = 1 - alphas[1:] / alphas[:-1]betas = np.clip(betas, a_min=0, a_max=0.999)elif schedule == "sqrt_linear":betas = torch.linspace(linear_start, linear_end, n_timestep, dtype = torch.float64)elif schedule == "sqrt":betas = torch.linspace(linear_start, linear_end, n_timestep, dtype = torch.float64) ** 0.5else:raise ValueError(f"schedule '{schedule}' unknown.")return betas.numpy()# origin from https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/blob/main/ldm/models/diffusion/ddpm.py, modified by ljf
class DDPM(pl.LightningModule):def __init__(self, given_betas = None, beta_schedule = "linear", timesteps = 1000, linear_start = 0.00085, linear_end = 0.012, cosine_s = 8e-3):super().__init__()self.v_posterior = 0.0self.parameterization = "eps"self.register_schedule(given_betas = given_betas, beta_schedule = beta_schedule, timesteps = timesteps,linear_start = linear_start, linear_end = linear_end, cosine_s = cosine_s)def register_schedule(self, given_betas=None, beta_schedule="linear", timesteps=1000,linear_start=1e-4, linear_end=2e-2, cosine_s=8e-3):betas = make_beta_schedule(beta_schedule, timesteps, linear_start=linear_start, linear_end=linear_end,cosine_s=cosine_s) # 计算 betas [0.00085, 0.0008547, ..., 0.012] # total 1000alphas = 1. - betas # 根据betas计算alphas [0.99915, 0.9991453, ..., 0.988] # total 1000alphas_cumprod = np.cumprod(alphas, axis=0) # 计算alphas_cumprod [0.99915, 0.99915*0.9991453, ..., ..*0.988] # 与本身及前面的数进行相乘alphas_cumprod_prev = np.append(1., alphas_cumprod[:-1]) # 计算alphas_cumprod_prev [1, 0.99915, 0.99915*0.9991453, ...] # 保留前999位timesteps, = betas.shapeself.num_timesteps = int(timesteps)self.linear_start = linear_startself.linear_end = linear_endassert alphas_cumprod.shape[0] == self.num_timesteps, 'alphas have to be defined for each timestep'to_torch = partial(torch.tensor, dtype=torch.float32)self.register_buffer('betas', to_torch(betas))self.register_buffer('alphas_cumprod', to_torch(alphas_cumprod))self.register_buffer('alphas_cumprod_prev', to_torch(alphas_cumprod_prev))# calculations for diffusion q(x_t | x_{t-1}) and othersself.register_buffer('sqrt_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.sqrt(alphas_cumprod)))self.register_buffer('sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.sqrt(1. - alphas_cumprod)))self.register_buffer('log_one_minus_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.log(1. - alphas_cumprod)))self.register_buffer('sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.sqrt(1. / alphas_cumprod)))self.register_buffer('sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.sqrt(1. / alphas_cumprod - 1)))# calculations for posterior q(x_{t-1} | x_t, x_0)posterior_variance = (1 - self.v_posterior) * betas * (1. - alphas_cumprod_prev) / (1. - alphas_cumprod) + self.v_posterior * betas# above: equal to 1. / (1. / (1. - alpha_cumprod_tm1) + alpha_t / beta_t)self.register_buffer('posterior_variance', to_torch(posterior_variance))# below: log calculation clipped because the posterior variance is 0 at the beginning of the diffusion chainself.register_buffer('posterior_log_variance_clipped', to_torch(np.log(np.maximum(posterior_variance, 1e-20))))self.register_buffer('posterior_mean_coef1', to_torch(betas * np.sqrt(alphas_cumprod_prev) / (1. - alphas_cumprod)))self.register_buffer('posterior_mean_coef2', to_torch((1. - alphas_cumprod_prev) * np.sqrt(alphas) / (1. - alphas_cumprod)))if self.parameterization == "eps":lvlb_weights = self.betas ** 2 / (2 * self.posterior_variance * to_torch(alphas) * (1 - self.alphas_cumprod))elif self.parameterization == "x0":lvlb_weights = 0.5 * np.sqrt(torch.Tensor(alphas_cumprod)) / (2. * 1 - torch.Tensor(alphas_cumprod))else:raise NotImplementedError("mu not supported")# TODO how to choose this termlvlb_weights[0] = lvlb_weights[1]self.register_buffer('lvlb_weights', lvlb_weights, persistent=False)assert not torch.isnan(self.lvlb_weights).all()# 模拟 UNet 预测def apply_model(self, x_noisy, t, cond, return_ids=False):return torch.rand(x_noisy.shape) # 随机返回一个latent 预测# Origin from https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/blob/main/ldm/models/diffusion/ddim.py, modified by ljf
class DDIMSampler(object):def __init__(self, model, schedule = "linear", **kwargs):super().__init__()self.model = model # DDPM的modelself.ddpm_num_timesteps = model.num_timestepsself.schedule = scheduledef register_buffer(self, name, attr):if type(attr) == torch.Tensor:if attr.device != torch.device("cuda"):attr = attr.to(torch.device("cuda"))setattr(self, name, attr)def make_schedule(self, ddim_num_steps, ddim_discretize = "uniform", ddim_eta = 0., verbose = True):# 获取ddim的timesteps [1, 21, 41, ..., 981]self.ddim_timesteps = make_ddim_timesteps(ddim_discr_method = ddim_discretize, num_ddim_timesteps = ddim_num_steps,num_ddpm_timesteps = self.ddpm_num_timesteps, verbose = verbose)alphas_cumprod = self.model.alphas_cumprod # 使用ddpm的alphas_cumprodassert alphas_cumprod.shape[0] == self.ddpm_num_timesteps, 'alphas have to be defined for each timestep'to_torch = lambda x: x.clone().detach().to(torch.float32).to(self.model.device) # lambda表达式,对每一个输入实现相同的操作self.register_buffer('betas', to_torch(self.model.betas)) # 使用ddpm的betasself.register_buffer('alphas_cumprod', to_torch(alphas_cumprod)) # 使用ddpm的alphas_cumprodself.register_buffer('alphas_cumprod_prev', to_torch(self.model.alphas_cumprod_prev)) #使用ddpm的alphas_cumprod_prev# calculations for diffusion q(x_t | x_{t-1}) and othersself.register_buffer('sqrt_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.sqrt(alphas_cumprod.cpu())))self.register_buffer('sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.sqrt(1. - alphas_cumprod.cpu())))self.register_buffer('log_one_minus_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.log(1. - alphas_cumprod.cpu())))self.register_buffer('sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.sqrt(1. / alphas_cumprod.cpu())))self.register_buffer('sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod', to_torch(np.sqrt(1. / alphas_cumprod.cpu() - 1)))# ddim sampling parametersddim_sigmas, ddim_alphas, ddim_alphas_prev = make_ddim_sampling_parameters(alphacums = alphas_cumprod.cpu(),ddim_timesteps = self.ddim_timesteps,eta = ddim_eta,verbose = verbose)self.register_buffer('ddim_sigmas', ddim_sigmas)self.register_buffer('ddim_alphas', ddim_alphas)self.register_buffer('ddim_alphas_prev', ddim_alphas_prev)self.register_buffer('ddim_sqrt_one_minus_alphas', np.sqrt(1. - ddim_alphas))sigmas_for_original_sampling_steps = ddim_eta * torch.sqrt((1 - self.alphas_cumprod_prev) / (1 - self.alphas_cumprod) * (1 - self.alphas_cumprod / self.alphas_cumprod_prev))self.register_buffer('ddim_sigmas_for_original_num_steps', sigmas_for_original_sampling_steps)@torch.no_grad()def sample(self, S, batch_size, shape, conditioning = None, callback = None,img_callback = None, quantize_x0 = False, eta = 0., mask = None, x0 = None,temperature = 1., noise_dropout = 0., score_corrector = None, corrector_kwargs = None,verbose = True, x_T = None, log_every_t = 100, unconditional_guidance_scale = 1.,unconditional_conditioning = None):self.make_schedule(ddim_num_steps = S, ddim_eta = eta, verbose = verbose) # 注册各个参数# samplingC, H, W = shape # [4, 64, 64]size = (batch_size, C, H, W) # [3, 4, 64, 64]print(f'Data shape for DDIM sampling is {size}, eta {eta}')samples, intermediates = self.ddim_sampling(conditioning, size,callback = callback,img_callback = img_callback,quantize_denoised = quantize_x0,mask = mask, x0 = x0,ddim_use_original_steps = False,noise_dropout = noise_dropout,temperature = temperature,score_corrector = score_corrector,corrector_kwargs = corrector_kwargs,x_T = x_T,log_every_t = log_every_t,unconditional_guidance_scale = unconditional_guidance_scale,unconditional_conditioning = unconditional_conditioning,)return samples, intermediates@torch.no_grad()def ddim_sampling(self, cond, shape,x_T = None, ddim_use_original_steps = False,callback = None, timesteps = None, quantize_denoised = False,mask = None, x0 = None, img_callback = None, log_every_t = 100,temperature = 1., noise_dropout = 0., score_corrector = None, corrector_kwargs = None,unconditional_guidance_scale = 1., unconditional_conditioning = None):device = self.model.betas.deviceb = shape[0] # batchsizeif x_T is None:img = torch.randn(shape, device=device)else:img = x_Ttimesteps = self.ddim_timestepsintermediates = {'x_inter': [img], 'pred_x0': [img]}time_range = np.flip(timesteps) total_steps = timesteps.shape[0] # 50print(f"Running DDIM Sampling with {total_steps} timesteps")iterator = tqdm(time_range, desc='DDIM Sampler', total=total_steps)for i, step in enumerate(iterator): # 981, 961, ..., 1index = total_steps - i - 1 ts = torch.full((b,), step, device=device, dtype=torch.long) # [981, 981, 981], [961, 961, 961], ...outs = self.p_sample_ddim(img, cond, ts, index=index, use_original_steps=ddim_use_original_steps,quantize_denoised=quantize_denoised, temperature=temperature,noise_dropout=noise_dropout, score_corrector=score_corrector,corrector_kwargs=corrector_kwargs,unconditional_guidance_scale=unconditional_guidance_scale,unconditional_conditioning=unconditional_conditioning)img, pred_x0 = outs # 更新imgif callback: callback(i)if img_callback: img_callback(pred_x0, i)if index % log_every_t == 0 or index == total_steps - 1:intermediates['x_inter'].append(img)intermediates['pred_x0'].append(pred_x0)return img, intermediates@torch.no_grad()def p_sample_ddim(self, x, c, t, index, repeat_noise=False, use_original_steps=False, quantize_denoised=False,temperature=1., noise_dropout=0., score_corrector=None, corrector_kwargs=None,unconditional_guidance_scale=1., unconditional_conditioning=None):b, *_, device = *x.shape, x.deviceif unconditional_conditioning is None or unconditional_guidance_scale == 1.:e_t = self.model.apply_model(x, t, c)else:x_in = torch.cat([x] * 2) # [3, 4, 64, 64] -> [6, 4, 64, 64]t_in = torch.cat([t] * 2) # [3] -> [6]c_in = torch.cat([unconditional_conditioning, c]) # [3, 77, 768] -> [6, 77, 768]e_t_uncond, e_t = self.model.apply_model(x_in, t_in, c_in).chunk(2) # using Unete_t = e_t_uncond + unconditional_guidance_scale * (e_t - e_t_uncond) # free guidance# 使用ddpm的参数或者make_ddim_sampling_parameters()函数生成的参数,这里默认使用了后者alphas = self.model.alphas_cumprod if use_original_steps else self.ddim_alphasalphas_prev = self.model.alphas_cumprod_prev if use_original_steps else self.ddim_alphas_prevsqrt_one_minus_alphas = self.model.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod if use_original_steps else self.ddim_sqrt_one_minus_alphassigmas = self.model.ddim_sigmas_for_original_num_steps if use_original_steps else self.ddim_sigmas# select parameters corresponding to the currently considered timestepa_t = torch.full((b, 1, 1, 1), alphas[index], device = device)a_prev = torch.full((b, 1, 1, 1), alphas_prev[index], device = device)sigma_t = torch.full((b, 1, 1, 1), sigmas[index], device = device)sqrt_one_minus_at = torch.full((b, 1, 1, 1), sqrt_one_minus_alphas[index], device = device)# current prediction for x_0pred_x0 = (x - sqrt_one_minus_at * e_t) / a_t.sqrt() # 论文https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.02502中公式(12)的第一项# direction pointing to x_tdir_xt = (1. - a_prev - sigma_t**2).sqrt() * e_t # 论文https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.02502中公式(12)的第二项 noise = sigma_t * noise_like(x.shape, device, repeat_noise) * temperature # 论文https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.02502中公式(12)的第三项 # 由于输入的eta为0,因此sigma_t为0,因此本式的结果为0if noise_dropout > 0.:noise = torch.nn.functional.dropout(noise, p=noise_dropout)x_prev = a_prev.sqrt() * pred_x0 + dir_xt + noise # 构成论文https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.02502中的公式(12),即根据x_t得到x_(t-1)return x_prev, pred_x0 if __name__ == "__main__":model = DDPM() # 初始化DDPM modelsampler = DDIMSampler(model)# 模拟FrozenCLIPEmbedder的输出batchsize = 3c = torch.rand(batchsize, 77, 768) # 模拟有prompt时的embeddinguc = torch.rand(batchsize, 77, 768) # 模拟无prompt时的embedding# 使用ddim进行去噪shape = [4, 64, 64]scale = 7.5 # unconditional guidance scale: eps = eps(x, empty) + scale * (eps(x, cond) - eps(x, empty))ddim_eta = 0.0 # ddim eta (eta=0.0 corresponds to deterministic samplingsamples_ddim, _ = sampler.sample(S = 50, # 采样50步conditioning = c, # 条件embeddingbatch_size = batchsize,shape = shape,verbose = False,unconditional_guidance_scale = scale,unconditional_conditioning = uc, # 无条件embeddingeta = ddim_eta,x_T = None)assert samples_ddim.shape[0] == batchsizeassert list(samples_ddim[0].shape) == shapeprint("samples_ddim.shape: ", samples_ddim.shape)assert samples_ddim.shape[0] == batchsizeassert list(samples_ddim.shape[1:]) == shapeprint("All Done!")相关文章:

AIGC笔记--Stable Diffusion源码剖析之DDIM
1--前言 以论文《High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models》 开源的项目为例,剖析Stable Diffusion经典组成部分,巩固学习加深印象。 2--DDIM 一个可以debug的小demo:SD_DDIM 以文生图为例,剖析SD中DDIM的…...

【BUUCTF-PWN】13-jarvisoj_level2_x64
参考:BUU pwn jarvisoj_level2_x64 64位函数调用栈 - Nemuzuki - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) 64位,开启了NX保护 执行效果如下: main函数: vulnerable_function函数 read函数存在栈溢出,溢出距离为0x808 查找后门…...

项目实战--Spring Boot 3整合Flink实现大数据文件处理
一、应用背景 公司大数据项目中,需要构建和开发高效、可靠的数据处理子系统,实现大数据文件处理、整库迁移、延迟与乱序处理、数据清洗与过滤、实时数据聚合、增量同步(CDC)、状态管理与恢复、反压问题处理、数据分库分表、跨数据…...

开发者工具攻略:前端测试的极简指南
前言 许多人存在一个常见的误区,认为测试只是测试工程师的工作。实际上,测试是整个开发团队的责任,每个人都应该参与到测试过程中。 在这篇博客我尽量通俗一点地讲讲我们前端开发过程中,该如何去测试 浏览器开发者工具简介 开…...

git保存分支工作状态
git stash...

系统架构设计师——计算机体系结构
分值占比3-4分 计算机硬件组成 计算机硬件组成主要包括主机、存储器和输入/输出设备。 主机:主机是计算机的核心部分,包括运算器、控制器、主存等组件。运算器负责执行算术和逻辑运算;控制器负责协调和控制计算机的各个部件;主存…...
3D鸡哥又上开源项目!单图即可生成,在线可玩
大家好,今天和大家分享几篇最新的工作 1、Unique3D Unique3D从单视图图像高效生成高质量3D网格,具有SOTA水平的保真度和强大的通用性。 如下图所示 Unique3D 在 30 秒内从单视图野生图像生成高保真且多样化的纹理网格。 例如属于一张鸡哥的打球写真照 等…...

设计模式实现思路介绍
设计模式是在软件工程中用于解决特定问题的典型解决方案。它们是在多年的软件开发实践中总结出来的,并且因其重用性、通用性和高效性而被广泛接受。设计模式通常被分为三种主要类型:创建型、结构型和行为型。 创建型设计模式 创建型设计模式专注于如何创…...

Node.js学习教程
Node.js学习教程可以从基础到高级,逐步深入理解和掌握这一强大的JavaScript运行环境。以下是一个详细的Node.js学习教程概述,帮助初学者和进阶者更好地学习Node.js。 一、Node.js基础入门 1. 了解Node.js 定义:Node.js是一个基于Chrome V8…...

项目页面优化,我们该怎么做呢?
避免页面卡顿 怎么衡量页面卡顿的情况呢? 失帧和帧率FPS 60Hz就是帧率fps,即一秒钟60帧,换句话说,一秒钟的动画是由60幅静态图片连在一起形成的。 卡了,失帧了,或者掉帧了,一秒钟没有60个画面&…...
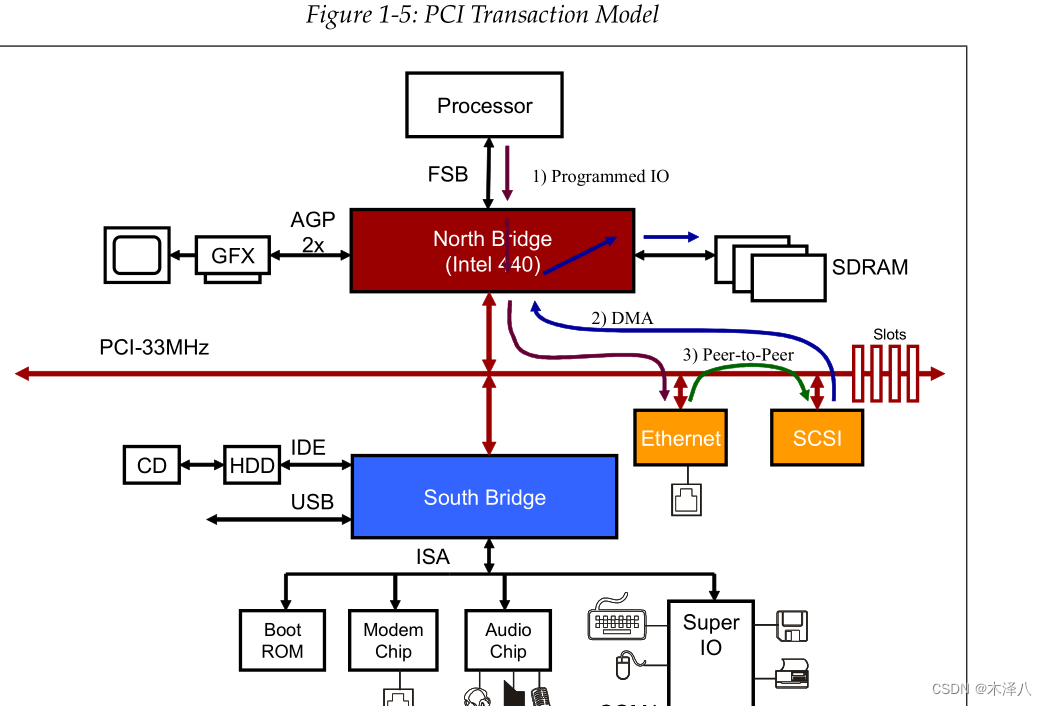
【PCIe】P2P DMA
PCIe P2P (peer-to-peer communication)是PCIe的一种特性,它使两个PCIe设备之间可以直接传输数据,而不需要使用主机RAM作为临时存储。如下图3的走向 比如EP1要发送和数据给EP2,操作流程如下: 1. 打开EP1的dma控制器;--client侧 …...

Linux shell编程学习笔记62: top命令 linux下的任务管理器
0 前言 top命令是Unix 和 Linux下常用的性能分析工具,提供了一个动态的、交互式的实时视图,显示系统的整体性能信息,以及正在运行的进程的相关信息,包括各个进程的资源占用状况,类似于Windows的任务管理器。 1 top命令…...

如何在Java中实现高性能的网络通信
如何在Java中实现高性能的网络通信 大家好,我是免费搭建查券返利机器人省钱赚佣金就用微赚淘客系统3.0的小编,也是冬天不穿秋裤,天冷也要风度的程序猿! 1. 引言 在当今互联网时代,高性能的网络通信是构建大规模分布…...
政务单位网站SSL证书选择策略
在数字化快速发展的今天,政务单位网站作为政府与公众沟通的重要桥梁,其安全性和可信度显得尤为重要。SSL证书作为保障网站安全的重要手段,其选择对于政务单位网站来说至关重要。本文将探讨政务单位网站在选择SSL证书时应该考虑的因素…...
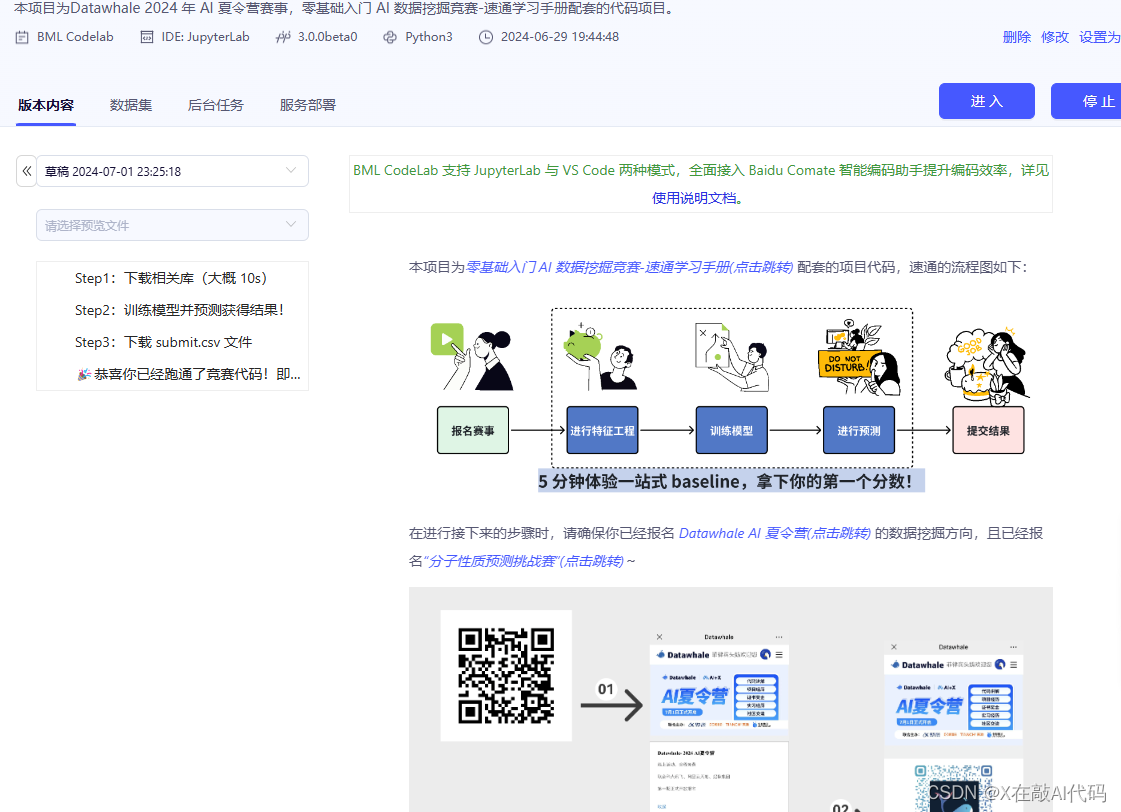
零基础入门 Ai 数据挖掘竞赛-速通 Baseline-1
#AI夏令营 #Datawhale #夏令营 本项目为Datawhale 2024 年 AI 夏令营赛事,零基础入门 AI 数据挖掘竞赛-速通学习手册配套的代码项目。 项目链接:https://aistudio.baidu.com/bd-cpu-02/user/2961857/8113198/home#codelab 任务目标 根据给的test&…...
(Python))
第二十六章 生成器(generator)(Python)
文章目录 前言一、生成器函数 前言 在 Python 中,使用了 yield 的函数被称为生成器(generator) yield 是一个关键字,用于定义生成器函数,生成器函数是一种特殊的函数,可以在迭代过程中逐步产生值ÿ…...

Vue通过Key管理状态
Vue通过Key管理状态 Vue 默认按照“就地更新”的策略来更新,通过 v-for 渲染的元素列表。当数据项的顺序改变时,Vue 不会随之移动 DOM 元素的顺序,而是就地更新每个元素,确保它们在原本指定的索引位置上渲染。为了给 Vue 一个提示…...
鸿蒙 HarmonyOs 网络请求 快速入门
官方文档: ArkUI简介-ArkUI(方舟UI框架)-应用框架 | 华为开发者联盟 (huawei.com) 一、通过原有的http组件进行网络请求(方式一) 1.1 HttpRequestOptions的操作 名称类型描述methodRequestMethod请求方式ÿ…...

Kubernetes云原生存储解决方案openebs部署实践-4.0.1版本(helm部署)
Kubernetes云原生存储解决方案openebs部署实践-4.0.1版本(helm部署) 简介 OpenEBS 是一种开源云原生存储解决方案。OpenEBS 可以将 Kubernetes 工作节点可用的任何存储转化为本地或复制的 Kubernetes 持久卷。OpenEBS 帮助应用和平台团队轻松地部署需要…...

如何使用Pip生成requirements.txt文件:全面指南与实践示例
如何使用Pip生成requirements.txt文件:全面指南与实践示例 Python的包管理工具Pip是Python开发中不可或缺的一部分。它不仅可以帮助我们安装和管理Python包,还可以通过生成requirements.txt文件来记录项目所需的所有依赖。本文将详细介绍如何使用Pip生成…...

日语AI面试高效通关秘籍:专业解读与青柚面试智能助攻
在如今就业市场竞争日益激烈的背景下,越来越多的求职者将目光投向了日本及中日双语岗位。但是,一场日语面试往往让许多人感到步履维艰。你是否也曾因为面试官抛出的“刁钻问题”而心生畏惧?面对生疏的日语交流环境,即便提前恶补了…...

STM32+rt-thread判断是否联网
一、根据NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP位判断 static bool is_conncected(void) {struct netdev *dev RT_NULL;dev netdev_get_first_by_flags(NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP);if (dev RT_NULL){printf("wait netdev internet up...");return false;}else{printf("loc…...

Linux简单的操作
ls ls 查看当前目录 ll 查看详细内容 ls -a 查看所有的内容 ls --help 查看方法文档 pwd pwd 查看当前路径 cd cd 转路径 cd .. 转上一级路径 cd 名 转换路径 …...

在 Nginx Stream 层“改写”MQTT ngx_stream_mqtt_filter_module
1、为什么要修改 CONNECT 报文? 多租户隔离:自动为接入设备追加租户前缀,后端按 ClientID 拆分队列。零代码鉴权:将入站用户名替换为 OAuth Access-Token,后端 Broker 统一校验。灰度发布:根据 IP/地理位写…...
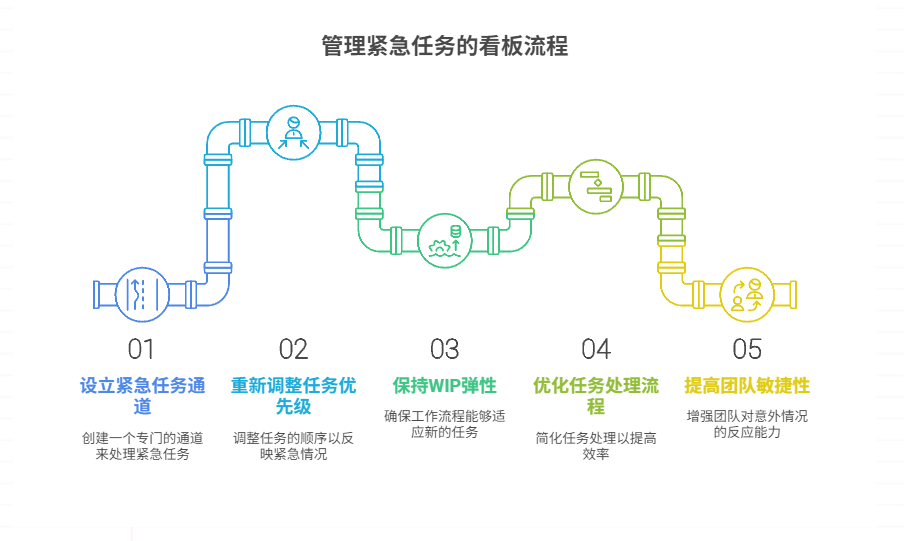
如何在看板中有效管理突发紧急任务
在看板中有效管理突发紧急任务需要:设立专门的紧急任务通道、重新调整任务优先级、保持适度的WIP(Work-in-Progress)弹性、优化任务处理流程、提高团队应对突发情况的敏捷性。其中,设立专门的紧急任务通道尤为重要,这能…...

江苏艾立泰跨国资源接力:废料变黄金的绿色供应链革命
在华东塑料包装行业面临限塑令深度调整的背景下,江苏艾立泰以一场跨国资源接力的创新实践,重新定义了绿色供应链的边界。 跨国回收网络:废料变黄金的全球棋局 艾立泰在欧洲、东南亚建立再生塑料回收点,将海外废弃包装箱通过标准…...

Python如何给视频添加音频和字幕
在Python中,给视频添加音频和字幕可以使用电影文件处理库MoviePy和字幕处理库Subtitles。下面将详细介绍如何使用这些库来实现视频的音频和字幕添加,包括必要的代码示例和详细解释。 环境准备 在开始之前,需要安装以下Python库:…...
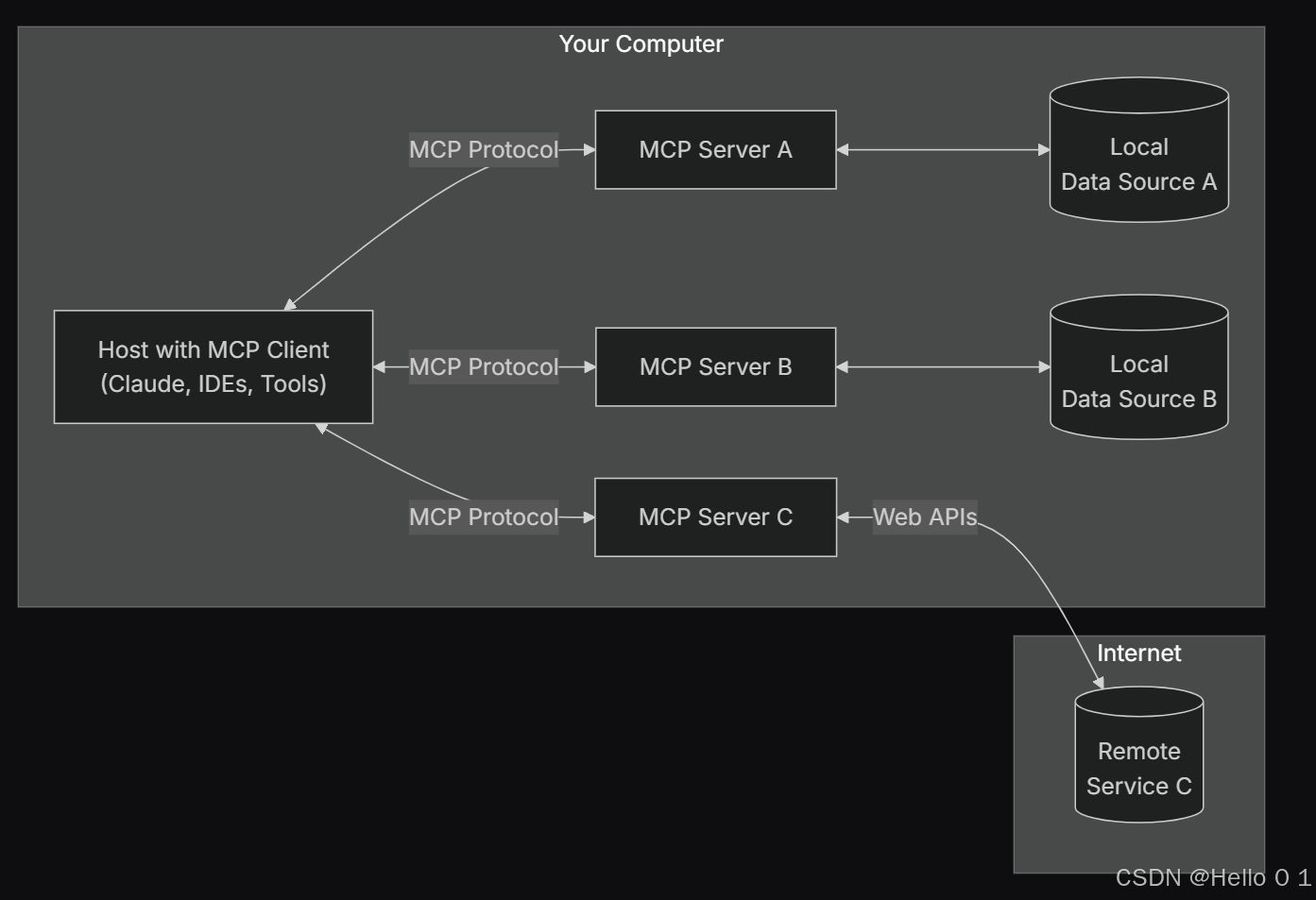
让AI看见世界:MCP协议与服务器的工作原理
让AI看见世界:MCP协议与服务器的工作原理 MCP(Model Context Protocol)是一种创新的通信协议,旨在让大型语言模型能够安全、高效地与外部资源进行交互。在AI技术快速发展的今天,MCP正成为连接AI与现实世界的重要桥梁。…...
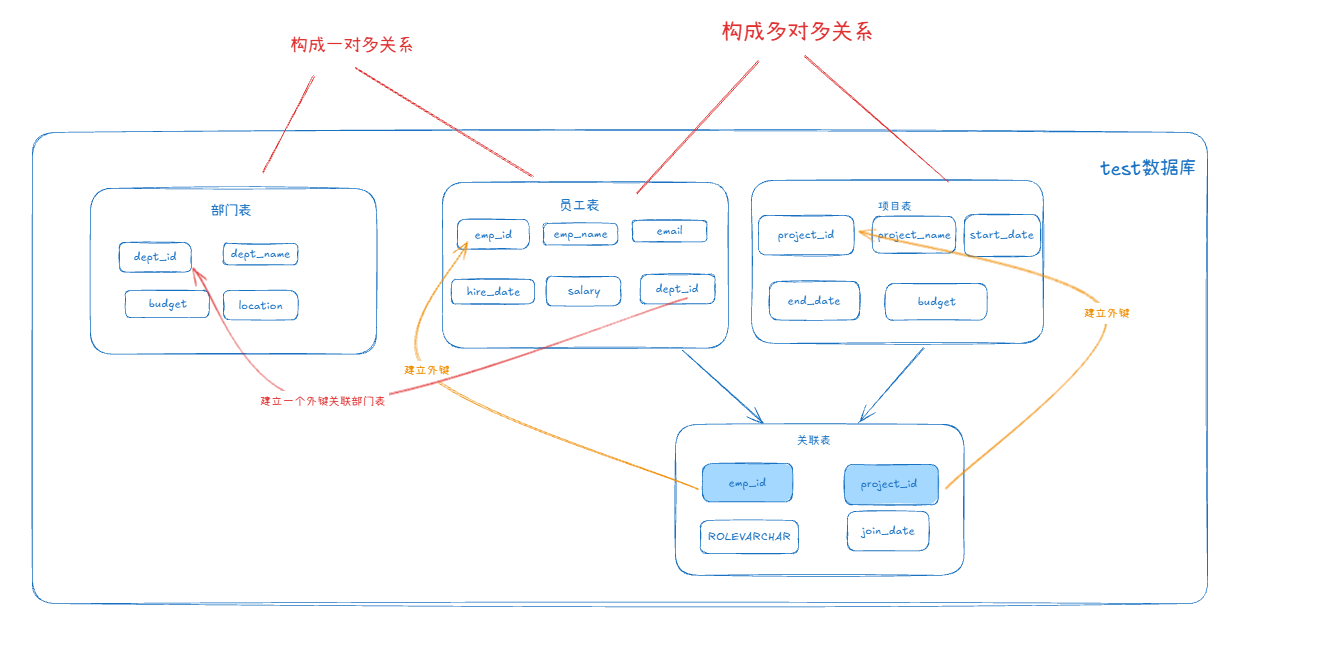
MySQL 知识小结(一)
一、my.cnf配置详解 我们知道安装MySQL有两种方式来安装咱们的MySQL数据库,分别是二进制安装编译数据库或者使用三方yum来进行安装,第三方yum的安装相对于二进制压缩包的安装更快捷,但是文件存放起来数据比较冗余,用二进制能够更好管理咱们M…...

[免费]微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端+Vue管理端)【论文+源码+SQL脚本】
大家好,我是java1234_小锋老师,看到一个不错的微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端)【论文源码SQL脚本】,分享下哈。 项目视频演示 【免费】微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端) Java毕业设计_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 项…...
