algorithm算法库学习之——不修改序列的操作
algorithm此头文件是算法库的一部分。本篇介绍不修改序列的操作函数。
不修改序列的操作 | |
| all_ofany_ofnone_of (C++11)(C++11)(C++11) | 检查谓词是否对范围中所有、任一或无元素为 true (函数模板) |
| for_each | 应用函数到范围中的元素 (函数模板) |
| for_each_n (C++17) | 应用一个函数对象到序列的前 n 个元素 (函数模板) |
| countcount_if | 返回满足指定判别标准的元素数 (函数模板) |
| mismatch | 寻找两个范围出现不同的首个位置 (函数模板) |
| findfind_iffind_if_not (C++11) | 寻找首个满足特定判别标准的元素 (函数模板) |
| find_end | 在特定范围中寻找最后出现的元素序列 (函数模板) |
| find_first_of | 搜索元素集合中的任意元素 (函数模板) |
| adjacent_find | 查找首对相邻的相同(或满足给定谓词的)元素 (函数模板) |
| search | 搜索一个元素范围 (函数模板) |
| search_n | 在范围中搜索一定量的某个元素的连续副本 (函数模板) |
示例代码:
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <utility> // std::pair
#include <vector>
#include <array>
#include <cctype> // std::tolowervoid myfunction(int i) { // function:std::cout << ' ' << i;
}struct myclass { // function object type:void operator() (int i) { std::cout << ' ' << i; }
} myobject;bool IsOdd(int i) { return ((i % 2) == 1); }bool mypredicate(int i, int j) {return (i == j);
}bool myfunction8(int i, int j) {return (i == j);
}bool comp_case_insensitive9(char c1, char c2) {return (std::tolower(c1) == std::tolower(c2));
}bool myfunction10(int i, int j) {return (i == j);
}bool mypredicate11(int i, int j) {return (i == j);
}bool mypredicate12(int i, int j) {return (i == j);
}int main()
{// all_of example 检查谓词是否对范围中所有、任一或无元素为 truestd::array<int, 8> foo = { 3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23 };if (std::all_of(foo.begin(), foo.end(), [](int i) {return i % 2; }))std::cout << "All the elements are odd numbers.\n";// any_of examplestd::array<int, 7> foo2 = { 0,1,-1,3,-3,5,-5 };if (std::any_of(foo2.begin(), foo2.end(), [](int i) {return i < 0; }))std::cout << "There are negative elements in the range.\n";// none_of examplestd::array<int, 8> foo3 = { 1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128 };if (std::none_of(foo3.begin(), foo3.end(), [](int i) {return i < 0; }))std::cout << "There are no negative elements in the range.\n";// for_each example 应用函数到范围中的元素 std::vector<int> myvector;myvector.push_back(10);myvector.push_back(20);myvector.push_back(30);std::cout << "myvector contains:";for_each(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), myfunction);std::cout << '\n';// or:std::cout << "myvector contains:";for_each(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), myobject);std::cout << '\n';// count algorithm example 返回满足指定判别标准的元素数 // counting elements in array:int myints[] = { 10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20,10,20 }; // 8 elementsint mycount = std::count(myints, myints + 8, 10);std::cout << "10 appears " << mycount << " times.\n";// counting elements in container:std::vector<int> myvector2(myints, myints + 10);mycount = std::count(myvector2.begin(), myvector2.end(), 20);std::cout << "20 appears " << mycount << " times.\n";// count_if examplestd::vector<int> myvector3;for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) myvector3.push_back(i); // myvector: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9int mycount3 = count_if(myvector3.begin(), myvector3.end(), IsOdd);std::cout << "myvector3 contains " << mycount3 << " odd values.\n";// mismatch algorithm example 寻找两个范围出现不同的首个位置 std::vector<int> myvector4;for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) myvector4.push_back(i * 10); // myvector4: 10 20 30 40 50int myints4[] = { 10,20,80,320,1024 }; // myints4: 10 20 80 320 1024std::pair<std::vector<int>::iterator, int*> mypair4;// using default comparison:mypair4 = std::mismatch(myvector4.begin(), myvector4.end(), myints4);std::cout << "First mismatching elements: " << *mypair4.first;std::cout << " and " << *mypair4.second << '\n';++mypair4.first; ++mypair4.second;// using predicate comparison:mypair4 = std::mismatch(mypair4.first, myvector4.end(), mypair4.second, mypredicate);std::cout << "Second mismatching elements: " << *mypair4.first;std::cout << " and " << *mypair4.second << '\n';// find example// using std::find with array and pointer:int myints5[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 };int *p;p = std::find(myints5, myints5 + 4, 30);if (p != myints5 + 4)std::cout << "Element found in myints5: " << *p << '\n';elsestd::cout << "Element not found in myints5\n";// using std::find with vector and iterator:std::vector<int> myvector5(myints5, myints5 + 4);std::vector<int>::iterator it;it = find(myvector5.begin(), myvector5.end(), 30);if (it != myvector5.end())std::cout << "Element found in myvector5: " << *it << '\n';elsestd::cout << "Element not found in myvector5\n";// find_if examplestd::vector<int> myvector6;myvector6.push_back(10);myvector6.push_back(25);myvector6.push_back(40);myvector6.push_back(55);std::vector<int>::iterator it6 = std::find_if(myvector6.begin(), myvector6.end(), IsOdd);std::cout << "The first odd value is " << *it6 << '\n';// find_if_not examplestd::array<int, 5> foo7 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };std::array<int, 5>::iterator it7 = std::find_if_not(foo7.begin(), foo7.end(), [](int i) {return i % 2; });std::cout << "The first even value is " << *it7 << '\n';// find_end exampleint myints8[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,1,2,3,4,5 };std::vector<int> haystack8(myints8, myints8 + 10);int needle1[] = { 1,2,3 };// using default comparison:std::vector<int>::iterator it8;it8 = std::find_end(haystack8.begin(), haystack8.end(), needle1, needle1 + 3);if (it8 != haystack8.end())std::cout << "needle1 last found at position " << (it8 - haystack8.begin()) << '\n';int needle2[] = { 4,5,1 };// using predicate comparison:it8 = std::find_end(haystack8.begin(), haystack8.end(), needle2, needle2 + 3, myfunction8);if (it8 != haystack8.end())std::cout << "needle2 last found at position " << (it8 - haystack8.begin()) << '\n';// find_first_of exampleint mychars9[] = { 'a','b','c','A','B','C' };std::vector<char> haystack9(mychars9, mychars9 + 6);std::vector<char>::iterator it9;int needle9[] = { 'A','B','C' };// using default comparison:it9 = find_first_of(haystack9.begin(), haystack9.end(), needle9, needle9 + 3);if (it9 != haystack9.end())std::cout << "The first match is: " << *it9 << '\n';// using predicate comparison:it9 = find_first_of(haystack9.begin(), haystack9.end(),needle9, needle9 + 3, comp_case_insensitive9);if (it9 != haystack9.end())std::cout << "The first match is: " << *it9 << '\n';// adjacent_find exampleint myints10[] = { 5,20,5,30,30,20,10,10,20 };std::vector<int> myvector10(myints10, myints10 + 8);std::vector<int>::iterator it10;// using default comparison:it10 = std::adjacent_find(myvector10.begin(), myvector10.end());if (it10 != myvector10.end())std::cout << "the first pair of repeated elements are: " << *it10 << '\n';//using predicate comparison:it10 = std::adjacent_find(++it10, myvector10.end(), myfunction10);if (it10 != myvector10.end())std::cout << "the second pair of repeated elements are: " << *it10 << '\n';// search algorithm examplestd::vector<int> haystack11;// set some values: haystack11: 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) haystack11.push_back(i * 10);// using default comparison:int needle11[] = { 40,50,60,70 };std::vector<int>::iterator it11;it11 = std::search(haystack11.begin(), haystack11.end(), needle11, needle11 + 4);if (it11 != haystack11.end())std::cout << "needle11 found at position " << (it11 - haystack11.begin()) << '\n';elsestd::cout << "needle11 not found\n";// using predicate comparison:int needle21[] = { 20,30,50 };it11 = std::search(haystack11.begin(), haystack11.end(), needle21, needle21 + 3, mypredicate11);if (it11 != haystack11.end())std::cout << "needle21 found at position " << (it11 - haystack11.begin()) << '\n';elsestd::cout << "needle21 not found\n";// search_n exampleint myints12[] = { 10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20 };std::vector<int> myvector12(myints12, myints12 + 8);std::vector<int>::iterator it12;// using default comparison:it12 = std::search_n(myvector12.begin(), myvector12.end(), 2, 30);if (it12 != myvector12.end())std::cout << "two 30s found at position " << (it12 - myvector12.begin()) << '\n';elsestd::cout << "match not found\n";// using predicate comparison:it12 = std::search_n(myvector12.begin(), myvector12.end(), 2, 10, mypredicate12);if (it12 != myvector12.end())std::cout << "two 10s found at position " << int(it12 - myvector12.begin()) << '\n';elsestd::cout << "match not found\n";std::cout << "hello world\n";return 0;
}运行结果:
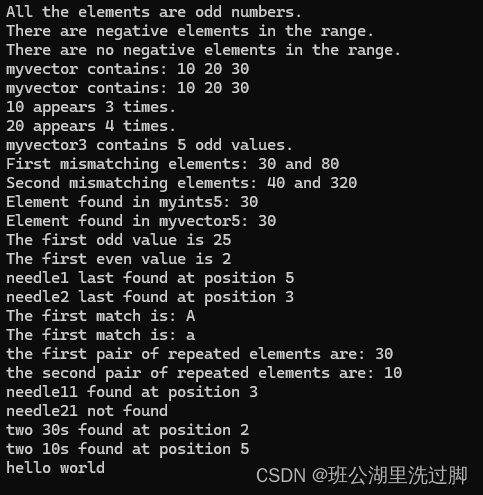
参考:
https://cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/
https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/header/algorithm
相关文章:

algorithm算法库学习之——不修改序列的操作
algorithm此头文件是算法库的一部分。本篇介绍不修改序列的操作函数。 不修改序列的操作 all_ofany_ofnone_of (C11)(C11)(C11) 检查谓词是否对范围中所有、任一或无元素为 true (函数模板) for_each 应用函数到范围中的元素 (函数模板) for_each_n (C17) 应用一个函数对象到序…...

idea创建的maven项目pom文件引入的坐标报红原因
如下所示 我们在引入某些依赖坐标的时候,即使点击了右上角的mavne刷新之后还是报红。 其实这是正常现象,实际上是我们的本地仓库当中没有这些依赖坐标,而idea就会通过报红来标记这些依赖来说明在我们的本地仓库是不存在的。 那有的同学就会…...
是什么?有什么优点?)
Python面试题:Python 中的生成器(generator)是什么?有什么优点?
在Python中,生成器(generator)是一种特殊的迭代器,使用yield关键字生成值,可以逐个生成序列中的值,而不需要一次性将所有值加载到内存中。生成器函数在定义时使用def关键字,并包含一个或多个yie…...
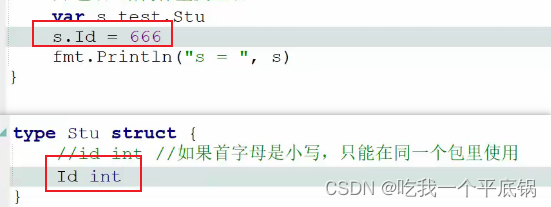
Go语言--复合类型之map、结构体
map Go 语言中的 map(映射、字典)是一种内置的数据结构,它是一个无序的 key-value 对的集合,比如以身份证号作为唯一键来标识一个人的信息。 格式 map [keyType]valueType 在一个 map 里所有的键都是唯一的,而且必须是支持和!操作符的类型…...
Stable Diffusion图像的脸部细节控制——采样器全解析
文章目录 艺术地掌控人物形象好易智算原因分析为什么在使用Stable Diffusion生成全身图像时,脸部细节往往不够精细? 解决策略 局部重绘采样器总结 艺术地掌控人物形象 在运用Stable Diffusion这一功能强大的AI绘图工具时,我们往往会发现自己…...
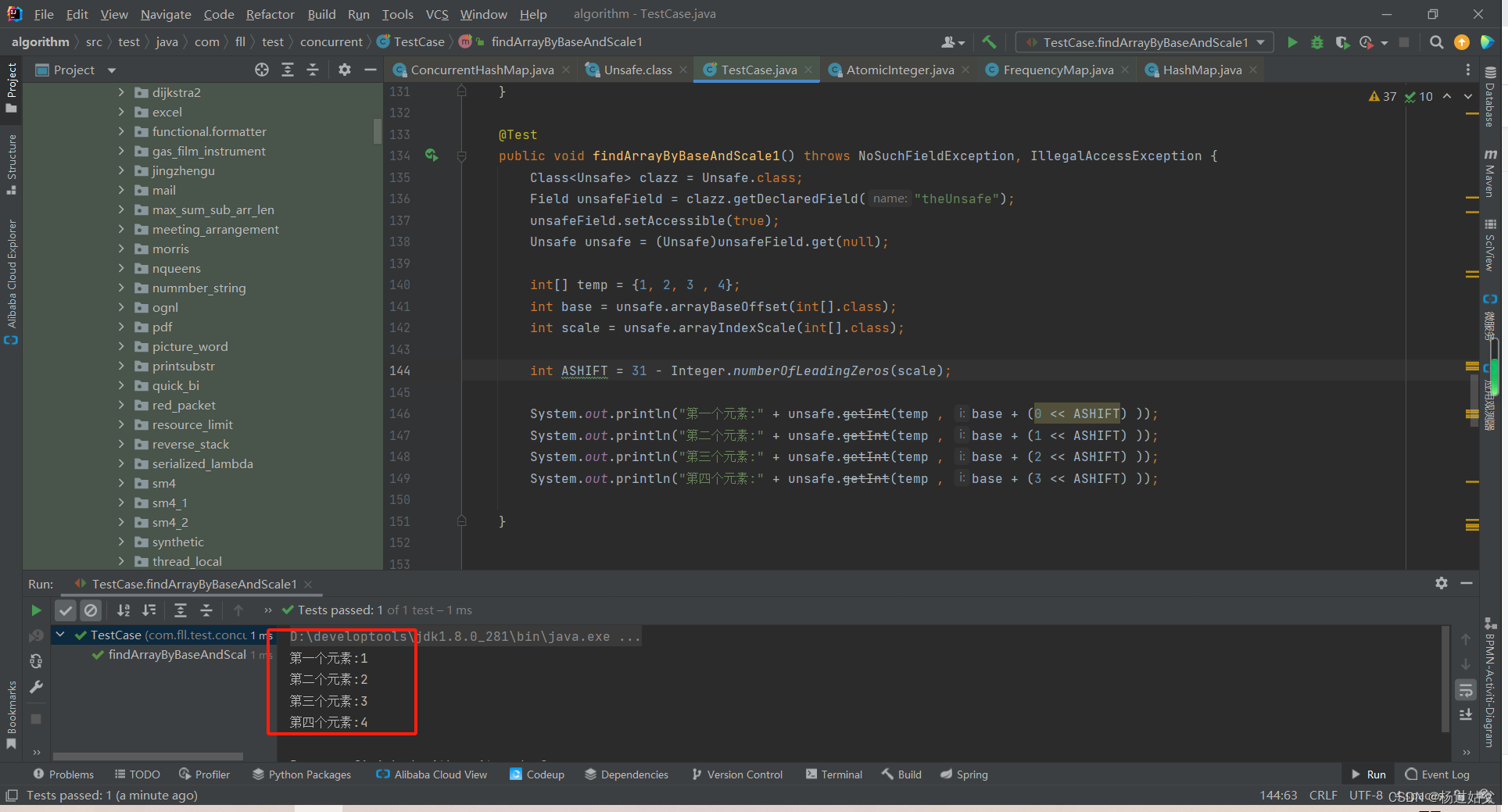
CurrentHashMap巧妙利用位运算获取数组指定下标元素
先来了解一下数组对象在堆中的存储形式【数组长度,数组元素类型信息等】 【存放元素对象的空间】 Ma 基础信息实例数据内存填充Mark Word,ClassPointer,数组长度第一个元素第二个元素固定的填充内容 所以我们想要获取某个下标的元素首先要获取这个元素的起始位置…...

实现antd designable平台的组件拖拽功能
平台:designable设计器 github:designable 目录 1 背景2 技术栈3 组件拖拽和放置3.1 类型定义3.2 拖拽3.3 放置 1 背景 由于业务需求,我们需要实现designable平台的一个简易版的组件拖拽功能。 #mermaid-svg-QrxSDGe9YyGG3LbQ {font-family:…...
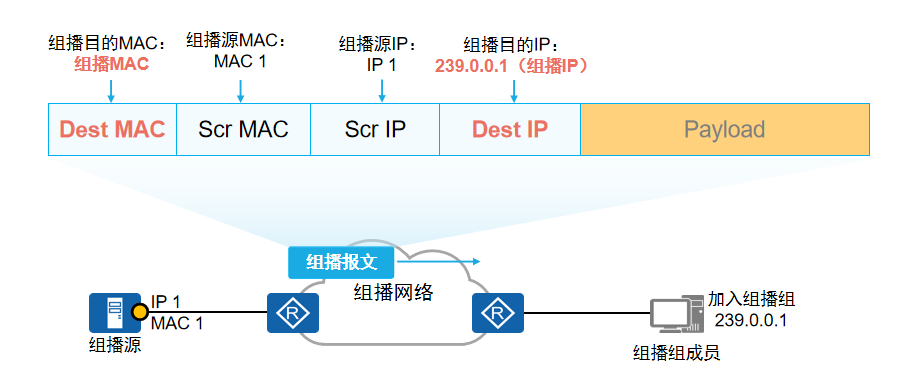
计算机网络-IP组播基础
一、概述 在前面的学习交换机和路由协议,二层通信是数据链路层间通信,在同一个广播域间通过源MAC地址和目的MAC地址进行通信,当两台主机第一次通信由于不清楚目的MAC地址需要进行广播泛洪,目的主机回复自身MAC地址,然后…...

Git删除了文件拉取时失败
本地删除了一些文件,远端的另一个提交修改了被删除的文件,vs里拉取时提示未处理的提交,无法继续操作,git gui里显示很多unstaged change的项 解决办法: 1、用git bash的git rm --cached filename或 git rm -r --cached…...
【面向就业的Linux基础】从入门到熟练,探索Linux的秘密(十二)-管道、环境变量、常用命令
大致介绍了一下管道、环境变量、一些常用的基本命令,可以当作学习笔记收藏学习一下!!! 文章目录 前言 一、管道 二、环境变量 1.概念 2.查看 3.修改 4.常用环境变量 三、系统状况 总结 前言 大致介绍了一下管道、环境变量、一些常…...

Spring Boot与Apache Kafka Streams的集成
Spring Boot与Apache Kafka Streams的集成 大家好,我是免费搭建查券返利机器人省钱赚佣金就用微赚淘客系统3.0的小编,也是冬天不穿秋裤,天冷也要风度的程序猿! 一、Apache Kafka Streams简介 Apache Kafka Streams是一个用于构…...

Unity中使用VectorGraphics插件时,VectorUtils.RenderSpriteToTexture2D方法返回结果错误的解决方法
Unity中使用VectorGraphics插件时,如果使用VectorUtils.BuildSprite方法创建Sprite,那么得到的Sprite往往是一个三角网格数比较多的Sprite,如果想要得到使用贴图只有两个三角面的方形Sprite,可以使用该插件提供的VectorUtils.Rend…...

用MySQL+node+vue做一个学生信息管理系统(一):配置项目
先用npm init -y生成配置文件 在项目下新建src文件夹,app.js文件。src目录用来放静态资源文件,app.js是服务器文件,index.js是vue的入口文件 使用npm install express下载express框架 在app.js文件夹开启node服务,监听的端口为…...

2024年06月CCF-GESP编程能力等级认证Python编程二级真题解析
本文收录于专栏《Python等级认证CCF-GESP真题解析》,专栏总目录:点这里,订阅后可阅读专栏内所有文章。 一、单选题(每题 2 分,共 30 分) 第 1 题 小杨父母带他到某培训机构给他报名参加CCF组织的GESP认证…...

Unity动画系统(2)
6.1 动画系统基础2-3_哔哩哔哩_bilibili p316 模型添加Animator组件 动画控制器 AnimatorController AnimatorController 可以通过代码控制动画速度 建立动画间的联系 bool值的设定 trigger p318 trigger点击的时候触发,如喊叫,开枪及换子弹等&#x…...

深度网络现代实践 - 深度前馈网络之反向传播和其他的微分算法篇
序言 反向传播(Backpropagation,简称backprop)是神经网络训练过程中最关键的技术之一,尤其在多层神经网络中广泛应用。它是一种与优化方法(如梯度下降法)结合使用的算法,用于计算网络中各参数的…...

自动化设备上位机设计 四
目录 一 设计原型 二 后台代码 一 设计原型 二 后台代码 using SimpleTCP; using SqlSugar; using System.Text;namespace 自动化上位机设计 {public partial class Form1 : Form{SqlHelper sqlHelper new SqlHelper();SqlSugarClient dbContent null;bool IsRun false;i…...

[leetcode hot 150]第二十三题,合并K个升序链表
题目: 给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。 请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。 示例 1: 输入:lists [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:…...

MybatisPlus实现插入/修改数据自动设置时间
引言 插入数据时自动设置当前时间,更新数据时自动修改日期为修改时的日期。 使用MybatisPlus的扩展接口MetaObjectHandler 步骤 实现接口 实体类加注解 实现接口 package com.example.vueelementson.common;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.M…...

Java语言程序设计篇一
Java语言概述 Java语言起源编程语言最新排名名字起源Java语言发展历程Java语言的特点Java虚拟机垃圾回收Java语言规范Java技术简介Java程序的结构Java程序注意事项:注释编程风格练习 Java语言起源 1990年Sun公司提出一项绿色计划。1992年语言开发成功最初取名为Oak…...

解决AndroidX依赖冲突:appcompat-resources版本与compileSdkVersion不兼容问题
1. 从一次真实的构建失败说起 那天下午,我正在给一个老项目添加一个新功能,像往常一样点击了Android Studio那个绿色的“运行”按钮,满心期待地等着应用在模拟器上启动。结果,等来的不是熟悉的启动画面,而是一大段刺眼…...

ChatGPT提示词开源实战:从零构建高效对话系统的关键技巧
ChatGPT提示词开源实战:从零构建高效对话系统的关键技巧 最近在做一个智能客服项目,用到了ChatGPT的API。一开始觉得提示词(Prompt)不就是写几句话吗?结果踩坑无数。要么AI答非所问,要么回复冗长低效&…...

MiniCPM-V-2_6令牌密度优势:640 token处理1344x1344图像深度解读
MiniCPM-V-2_6令牌密度优势:640 token处理1344x1344图像深度解读 1. 引言:当视觉大模型遇上“像素压缩”黑科技 想象一下,你有一张分辨率高达1344x1344的图片,总像素接近180万。如果让一个普通的视觉大模型去理解它,…...

Phi-3 Forest Laboratory API接口调用全指南:从鉴权到流式响应
Phi-3 Forest Laboratory API接口调用全指南:从鉴权到流式响应 你是不是也对那些能对话、能写代码的AI模型感到好奇,想自己动手调用一下试试?今天咱们就来聊聊怎么通过代码,跟一个叫Phi-3 Forest Laboratory的模型“说上话”。别…...

AudioSeal部署案例:CUDA加速下16kHz单声道音频实时水印检测实录
AudioSeal部署案例:CUDA加速下16kHz单声道音频实时水印检测实录 1. 引言 你有没有想过,一段AI生成的语音,怎么才能被识别出来?就像给图片打上肉眼看不见的水印一样,音频也需要一种“隐形身份证”。今天要聊的AudioSe…...

高速多串激光泵浦二极管驱动电路:可扩展、高电流、高电压、多重安全保护电路架构参考
高速多串激光泵浦二极管驱动电路,可扩展, 连续电流可达25A,支持最高电压90V; 调制频率可达10kHz 多重安全保护电路; 可单独屏蔽故障电流串; 闭环控制,带电流输出; 电路架构是基于多年…...

微电网二次控制:下垂控制与基于数据采样二次控制的奇妙融合
微电网二次控制,下垂控制,基于数据采样的二次控制,补偿了下垂控制的偏差,实现了有功均分,效果好在微电网的运行控制领域,下垂控制和基于数据采样的二次控制是两个关键的技术点,它们相互配合&…...

中兴B860AV2.1全系列线刷指南:S905L2芯片安卓9.0免拆机ROOT实战
1. 为什么选择给中兴B860AV2.1刷机?聊聊我的折腾经历 如果你手头正好有一台闲置的中兴B860AV2.1机顶盒,是不是觉得它除了看运营商的IPTV,其他啥也干不了?开机慢、自带应用商店软件少、存储空间动不动就告急,想装个第三…...

生产环境 SQL 卡死?金仓连接条件下推教你一招解决
告别SQL性能焦虑:金仓数据库“连接条件下推”的性能魔法你是否遇到过这样的场景:一个看似复杂的SQL,在测试环境运行飞快,一到生产环境就“卡死”,一查执行计划,发现子查询生成了一个巨大的中间结果集&#…...

英伟达斥资20亿美元投资Nebius “循环投资”泡沫争议再起
雷递网 乐天 3月11日英伟达(股票代码:NVDA)日前表示,将向人工智能云公司Nebius投资20亿美元,Nebius表示,该合作伙伴关系将帮助Nebius到2030年底部署超过5吉瓦(GW)的英伟达系统,这笔电力大约足以供380万户家庭使用。Neb…...
