Spring中Bean的相关注解
目录
1.Spring IoC&DI
2.关于Bean存储的相关注解(类注解与方法注解)
Bean的获取方式
类注解和方法注解的重命名
2.1 类注解
2.1.1 @Controller
2.1.2 @Service
2.1.3 @Repository
2.1.4 @Component
2.1.5 @Configuration
2.2 方法注解-@Bean
2.2.1 定义多个对象
2.2.2 扫描路径-@ComponentScan
3.DI注入方式-@Autowired
3.1 属性注入
3.2 Setter方法注入
3.3 构造方法注入
3.4 三种注入方式的优缺点
3.5 @Autowired存在的问题及解决方法
1.Spring IoC&DI
Spring是包含了众多工具方法的一个IoC容器
- IoC(Inversion of Control,控制反转),是Spring的一个核心思想,简单来说就是将对象之间层层的依赖关系反转过来(一开始是使用方创建并控制依赖对象,现在是把依赖对象注入到当前对象中),使得依赖对象无论发生什么改变,当前类都不受影响,大大降低了代码的耦合度
- IoC容器就是创建并管理这些对象的容器,不再需要用户自己去创建对象,而是交给IoC容器去创建并对对象进行统一管理(将对象的控制权交给Spring)
- DI(Dependency Injection,依赖注入),是IoC的一种具体实现,依赖注入是一个过程,在Ioc容器在创建Bean时,去提供运行时所依赖的资源,这个资源就是对象,简单点说,依赖注入就是把对象取出来放到某个类的属性中
2.关于Bean存储的相关注解(类注解与方法注解)
Bean:Spring是一个IoC容器,而IoC容器中装的就是Bean(对象)
Bean的获取方式
Bean的获取方式有很多,常用的是以下三种
| Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException | 根据Bean名称获取Bean |
| <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException | 根据Bean名称和类型获取Bean |
| <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException | 根据类型获取Bean |
Bean名称:当使用的是类注解时,Bean的名称为类名的小驼峰(第一个单词以小写字母开始,后面每个单词首字母大写),如果类名前两个字母都是大写,则Bean名称为类名;当使用的是方法注解时,Bean名称就是方法名
注:对同一个类获取多次Bean,指向的是同一个对象(类似单例模式,有且仅有一个对象)
类注解和方法注解的重命名
类注解重命名:类注解+(新名称)
//启动类代码
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserComponent userComponent=(UserComponent) context.getBean("user1");//获取名称为user1的Bean//如果再去获取原来名称为userComponent的Bean,会报错userComponent.sayHi();}
}//UserComponent类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("user1")//重命名为user1
public class UserComponent {public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi, I'm UserComponent");}
}方法注解重命名:@Bean+(新名称)
//启动类代码
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserInfo userInfo1=(UserInfo) context.getBean("user1");UserInfo userInfo2=(UserInfo) context.getBean("user2");System.out.println(userInfo1);System.out.println(userInfo2);}
}//BeanTest类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class BeanTest {@Bean("user1")//重命名为user1public UserInfo userInfo1(){return new UserInfo("zhangsan",1);}@Bean("user2")//重命名为user2public UserInfo userInfo2(){return new UserInfo("lisi",2);}
}注:类注解和方法注解的重命名的名称可以有多个, 使用{ }来标识,例如@Component({"user1","user2"})
2.1 类注解
类注解总共有五种,这些注解都有各自不同的应用场景
- @Controller:控制层(Controller),接收请求,对请求进行处理并进行响应
- @Service:业务逻辑层(Service),处理具体的业务逻辑
- @Repository:数据访问层(Dao),负责数据访问操作
- @Configuration:配置层,处理项目中的一些配置信息
- @Component:元注解,上述四种注解都含有@Component
2.1.1 @Controller
//启动类代码(从Spring中获取Bean)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserController userController=(UserController) context.getBean("userController");userController.sayHi();}
}//UserController类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller//将对象存储到Spring中
public class UserController {public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserController");}
}2.1.2 @Service
//启动类代码(从Spring中获取Bean)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserService userService=(UserService) context.getBean("userService");userService.sayHi();}
}//UserService类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service//将对象存储到Spring中
public class UserService {public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi, I'm UserService");}
}2.1.3 @Repository
//启动类代码(从Spring中获取Bean)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserRepository userRepository=(UserRepository) context.getBean("userRepository");userRepository.sayHi();}
}//UserRepository类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository//将对象存储到Spring中
public class UserRepository {public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserRepository");}
}2.1.4 @Component
//启动类代码(从Spring中获取Bean)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserComponent userComponent=(UserComponent) context.getBean("userComponent");userComponent.sayHi();}
}//UserComponent类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component//将对象存储到Spring中
public class UserComponent {public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi, I'm UserComponent");}
}2.1.5 @Configuration
//启动类代码(从Spring中获取Bean)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserConfiguration userConfiguration=(UserConfiguration) context.getBean("userConfiguration");userConfiguration.sayHi();}
}//UserConfiguration类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration//将对象存储到Spring中
public class UserConfiguration {public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserConfiguration");}
}
2.2 方法注解-@Bean
当一个类需要多个对象,或者需要使用外部包里的类时,使用类注解无法满足需求,这时就需要用到方法注解@Bean
2.2.1 定义多个对象
//启动类代码(从Spring中获取Bean)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);//如果这里使用类名获取Bean,会由于得到多个Bean而报错,所以需要使用上述Bean获取方式中的第1或第2种UserInfo userInfo1=(UserInfo) context.getBean("userInfo1");//获取方法名为userInfo1对应的BeanUserInfo userInfo2=(UserInfo) context.getBean("userInfo2");//获取方法名为userInfo2对应的BeanSystem.out.println(userInfo1);System.out.println(userInfo2);}
}//BeanTest类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component//方法注解需要搭配类注解一起使用,否则会报错
public class BeanTest {@Beanpublic UserInfo userInfo1(){return new UserInfo("zhangsan",1);}@Beanpublic UserInfo userInfo2(){return new UserInfo("lisi",2);}
}2.2.2 扫描路径-@ComponentScan
Spring的扫描路径默认为启动类(@SpringBootApplication注释的类)所在的路径,如果路径下有被类注解注释的类,就会将该类的对象存储到Spring中。如果想要修改默认路径,可以通过@ComponentScan来指定扫描路径
//添加到启动类中,路径要和默认路径不同
@ComponentScan("com.example.demo.test")
//指定单个扫描路径
@ComponentScan({"com.example.demo.test","com.example.demo.test1"})
//指定多个扫描路径3.DI注入方式-@Autowired
@Autowired注释的作用主要是从Spring中获取对象,注入到对象的使用方(根据类型注入)。对于DI注入,Spring提供了三种方式,分别是属性注入,Setter方法注入以及构造方法注入
3.1 属性注入
属性注入使用@Autowire实现,以下是使用属性注入实现Service类注入到Controller类的一个简单例子
//启动类代码(获取UserController对象中,调用sayHi方法)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserController userController=(UserController) context.getBean("userController");userController.sayHi();}
}//UserController类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {//使用属性注入将Service类注入到Controller类中@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserController");userService.sayHi();}
}//UserService类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi, I'm UserService");}
}
3.2 Setter方法注入
Setter方法注入即在设置set方法时加上@Autowired注解
//UserController类
//启动类代码和UserService类与属性注入中一致
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {private UserService userService;//使用Setter方法注入将Service类注入到Controller类中@Autowiredpublic void setUserService(UserService userService) {this.userService = userService;}public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserController");userService.sayHi();}
}3.3 构造方法注入
构造方法注入即在类的构造方法中实现注入
注:使用构造方法注入时,如果注入的类只有一个构造方法,那么@Autowired可以省略,如果注入的类有多个构造方法,那么需要添加@Autowired来明确指定使用哪个构造方法,否则会报错
//UserController类
//启动类代码和UserService类与属性注入中一致
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {private UserService userService;//使用构造方法注入将Service类注入到Controller类中@Autowiredpublic UserController(UserService userService) {this.userService = userService;}public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserController");userService.sayHi();}
}3.4 三种注入方式的优缺点
属性注入
- 优点:简介,方便使用
- 缺点:只能用于Ioc容器;不能注入一个Final修饰的属性
Setter方法注入
- 优点:方便在类实例之后,重新对该对象进行配置或者注入
- 缺点:不能注入一个Final修饰的属性;注入对象可能会被改变
构造方法注入
- 优点:可以注入Final修饰的属性;注入的对象不会被修改;依赖对象被使用前一定会被完全初始化;通用性好,更换任何框架都可适用
- 缺点:注入多个对象时,代码比较繁琐
3.5 @Autowired存在的问题及解决方法
当同一个类型存在多个Bean时,使用@Autowired会存在问题
//启动类代码
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo3Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(Demo3Application.class, args);UserController userController=context.getBean(UserController.class);userController.sayHi();}
}//UserController类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {@Autowired//注入UserInfoprivate UserInfo userInfo;public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserController");System.out.println(userInfo);}
}//BeanTest类
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class BeanTest {@Beanpublic UserInfo userInfo1(){return new UserInfo("zhangsan",1);}@Beanpublic UserInfo userInfo2(){return new UserInfo("lisi",2);}
}@Autowired注解会根据类型UserInfo去查找Bean,找到userInfo1和userInfo2两个方法,由于查找到的Bean只能是唯一的,所以程序会报错(非唯一的Bean)。那么如何解决这个问题呢?Spring提供了几个解决方法:@Primary,@Qualifier,@Resource
@Primary:当同个类型存在多个Bean注入时,添加@Primary注解用来确定默认的实现
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class BeanTest {@Primary//指定该Bean为Bean的默认实现@Beanpublic UserInfo userInfo1(){return new UserInfo("zhangsan",1);}@Beanpublic UserInfo userInfo2(){return new UserInfo("lisi",2);}
}@Qualifier:添加@Qualifier(Bean的名称),指定当前要注入的Bean(@Qualifier需要搭配@Autowired使用,不能单独使用)
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {@Qualifier("userInfo1")//指定Bean名称为userInfo1@Autowiredprivate UserInfo userInfo;public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserController");System.out.println(userInfo);}
}@Resource:与@Qualifier用法相同,也是指定Bean的名称进行注入,但不需要搭配@Autowired
package com.example.demo;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {@Resource(name="userInfo1")//指定Bean名称为userInfo1并注入private UserInfo userInfo;public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserController");System.out.println(userInfo);}
}除了上述三种使用注解的解决方法,还可以通过改变对象名称,使其与要注入的Bean的名称相同
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {@Autowiredprivate UserInfo userInfo1;//注入Bean名称为userInfo1,则对象名称也为userInfo1public void sayHi(){System.out.println("Hi,I'm UserController");System.out.println(userInfo1);}
}相关文章:

Spring中Bean的相关注解
目录 1.Spring IoC&DI 2.关于Bean存储的相关注解(类注解与方法注解) Bean的获取方式 类注解和方法注解的重命名 2.1 类注解 2.1.1 Controller 2.1.2 Service 2.1.3 Repository 2.1.4 Component 2.1.5 Configuration 2.2 方法注解-Bean 2.2.1 定义多个对象 2.2…...

Golang | Leetcode Golang题解之第385题迷你语法分析器
题目: 题解: func deserialize(s string) *NestedInteger {if s[0] ! [ {num, _ : strconv.Atoi(s)ni : &NestedInteger{}ni.SetInteger(num)return ni}stack, num, negative : []*NestedInteger{}, 0, falsefor i, ch : range s {if ch - {negati…...

【Java 优选算法】双指针(上)
欢迎关注个人主页:逸狼 创造不易,可以点点赞吗~ 如有错误,欢迎指出~ 目录 移动零 分析 代码 复写零 分析 代码 快乐数 分析 代码 盛最多水的容器 分析 代码 移动零 题目链接 分析 双指针算法,利用两个指针cur和dest将数组划分为三个区间…...

【自动驾驶】控制算法(八)横向控制Ⅰ | 算法与流程
写在前面: 🌟 欢迎光临 清流君 的博客小天地,这里是我分享技术与心得的温馨角落。📝 个人主页:清流君_CSDN博客,期待与您一同探索 移动机器人 领域的无限可能。 🔍 本文系 清流君 原创之作&…...

Android SSE 单向接收数据
Server-Sent Events(SSE)是一种在客户端和服务器之间实现单向实时通信的技术。它允许服务器向客户端推送数据,但客户端无法使用 SSE 向服务器发送数据。这使得其适用于需要持续接收服务器数据的应用场景(如实时通知、股票行情、社…...

排序《数据结构》
排序 《数据结构》 1.排序的概念及其运用1.1 排序的概念1.2 排序运用1.3常见的排序算法1.4 排序动图演示 2.常见排序算法的实现2.1 插入排序2.2希尔排序2.3 快排左边做keyi,右边先走,可以保证相遇位置比keyi小 2.4 快速排序优化快排(非递归&a…...

flutter 提示框2 Dialog
flutter 提示框 写在点击的方法体中 child里放自己喜欢的 showDialog( context: context, builder: (BuildContext context) { final Dialog alertDialog Dialog( backgroundColor: Colors.transparent,shadowColor:Colors.transparent,child: Container(height: mediawi…...

如何选择SDR无线图传方案
在开源软件定义无线电(SDR)领域,有几个项目提供了无线图传的解决方案。以下是一些开源SDR无线图传方案: 1. **OpenHD**:这是一个远程高清数字图像传输的开源解决方案,它使用SDR技术来实现高清视频的无线传…...
解析)
关于Python类中方法__init__()解析
# import numpy as npclass Car():def __init__(self, maker, name, year):self.maker makerself.name nameself.year yearprint(self.searchMakrt() "123")def searchMakrt(self):print("汽车制作厂家为: " self.maker)# passreturn &quo…...

微信小程序 自定义组件
1. 微信小程序 自定义组件 微信小程序支持组件化开发,这有助于我们复用代码,提高开发效率。下面我将给出一个简单的微信小程序组件化示例,包括一个自定义组件的创建和使用。 1.1. 创建自定义组件 首先,在项目的 components 目录…...

Mac+Pycharm配置PyQt6教程
安装包 pip install PyQt6 PyQt6-tools #查看Qt版本 pip show PyQt6 pip show pyqt6-tools 配置扩展工具 QTD(界面设计) Program:/Users/wan/PycharmProjects/NewDemo/venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/qt6_applications/Qt/bin/Designer.app Working directo…...

如何保证Redis与Mysql双写一致性?
https://www.cnblogs.com/coderacademy/p/18137480 延迟双删 对于上面链接的文章,里面的延迟双删没有给出具体的例子,也没有直接指出具体解决的问题是针对那种缓存策略,这里补充一下,延时双删缓存针对的是Cache aside pattern(缓…...

9.8笔试记录
1.在c中哪些运算符不能重载? 在 C 中,有以下几个运算符不能被重载: . :成员访问运算符。例如obj.member中的.不能被重载。 :: :作用域解析运算符。用于指定命名空间、类等的作用域,不能被重载。 ?: ࿱…...

SRE-系统管理篇
SRE-系统管理篇 进程管理 进程的概念: 运行起来的程序,命令,服务等等都可以称作进行,进程都是运行在内存当中的。 程序的概念: 一般指安装包,程序代码,应用它们存放在磁盘上面的。 守护进程的概念: 守护进程,一直运行的进程,也可以叫做服务。 进程的分类 僵…...
傅里叶级数,傅里叶变换
先读文章:傅里叶分析之掐死教程(完整版)更新于2014.06.06 - 知乎 (zhihu.com) 傅里叶级数 一、内容:每个周期性函数都可以表示为无穷多个不同频率的正弦函数的叠加。 二、公式: 三、从时域到频域所保留的三点信息&…...

零知识证明在BSV网络上的应用
发表时间:2023年6月15日 2024年7月19日,BSV区块链主网上成功通过使用零知识证明验证了一笔交易。 零知识证明是一种技术,它允许一方(证明者)在不透露任何秘密的情况下,向另一方(验证者&…...
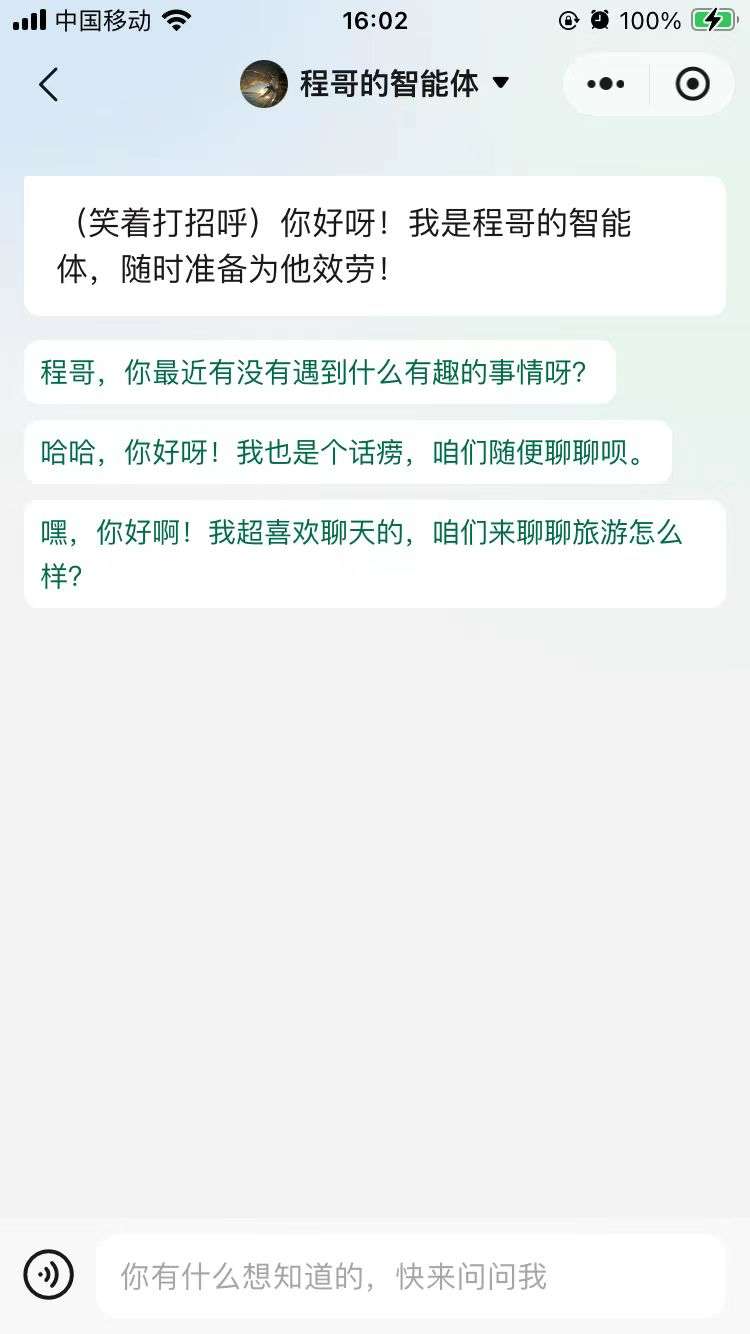
无任何门槛!3分钟5步,发布属于你的第一个智能体小程序,99%的人还不知道怎么用
相信大家都用微信小程序,但是大部分人应该还没有过属于自己的小程序吧。 今天程哥就带大家花三分钟用五步,来创建一个属于自己的微信小程序。 之前Coze在发布渠道里也有发布小程序的渠道,但是试过的人都知道,这个是有一定门槛的…...
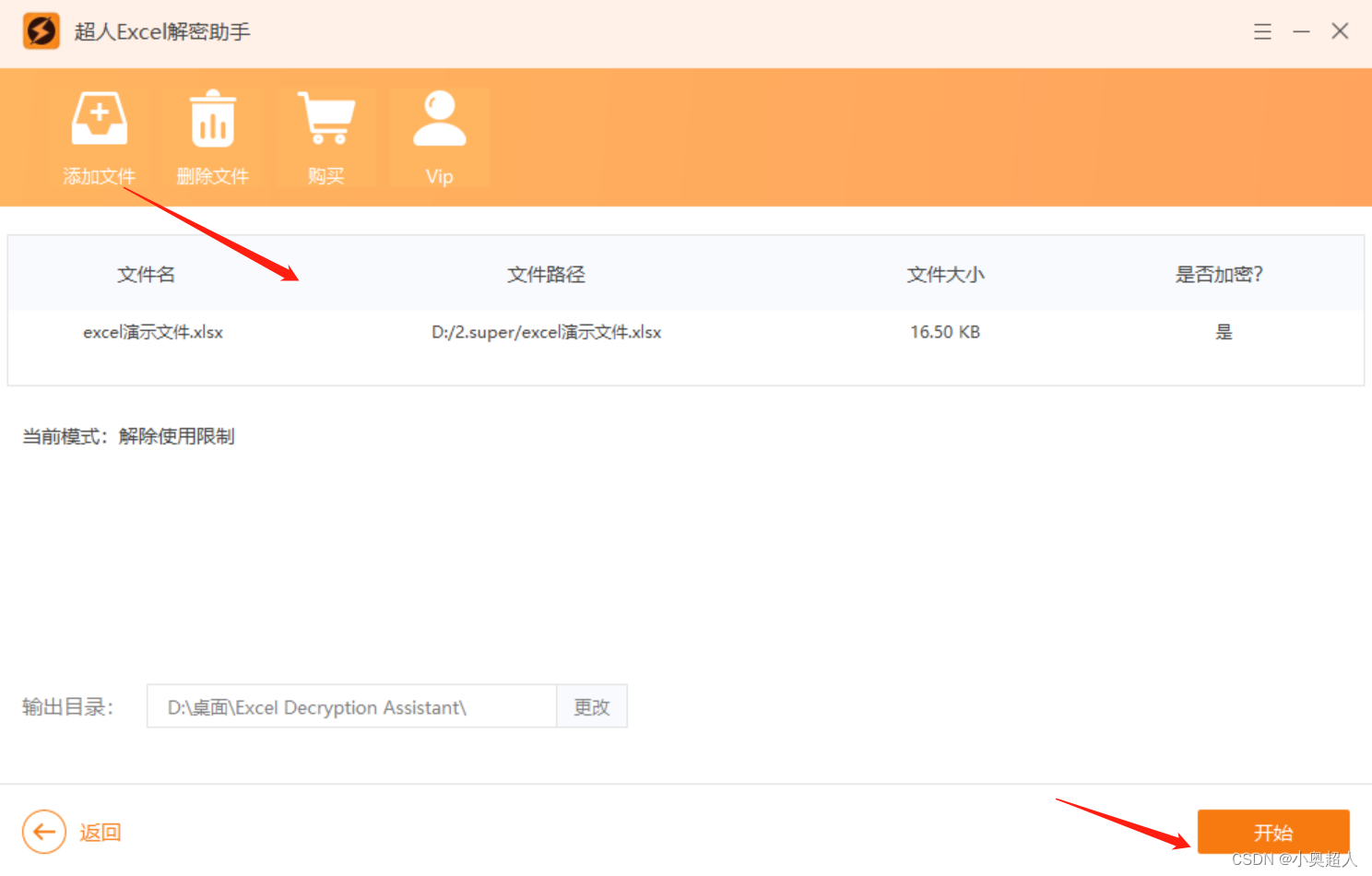
怎么强制撤销excel工作表保护?
经常不是用的Excel文件设置了工作表保护,偶尔打开文件的时候想要编辑文件,但是发现忘记了密码,那么这种情况,我们怎么强制撤销excel工作表保护?今天分享两种解决方法。 方法一、 将excel文件转换为其他文件格式&…...

每天学习一个字符串类函数之memmove函数
目录 前言: 一、头文件 二、memmove函数的作用 三、理解memmove函数的定义 1、返回类型 2、参数 四、使用memmove函数 案例1: 案例2: 五、解决数据拷贝之前被覆盖的方法 六、模拟实现memmove函数 前言: 上一篇博客,我…...
】三自由度机器人圆弧轨迹规划仿真实例)
【机器人工具箱Robotics Toolbox开发笔记(十三)】三自由度机器人圆弧轨迹规划仿真实例
在实际应用场景中,我们通常预先明确了目标末端的运动轨迹,随后引导机器人进行相应的动作。本实例具体展示了如何基于给定的两个点,计算出末端的精确位姿,并以此为基础,进一步规划出一条平滑的圆弧轨迹供机器人执行。这样的流程确保了机器人能够沿着预定的路径,精准且高效…...

Java - Mysql数据类型对应
Mysql数据类型java数据类型备注整型INT/INTEGERint / java.lang.Integer–BIGINTlong/java.lang.Long–––浮点型FLOATfloat/java.lang.FloatDOUBLEdouble/java.lang.Double–DECIMAL/NUMERICjava.math.BigDecimal字符串型CHARjava.lang.String固定长度字符串VARCHARjava.lang…...

【git】把本地更改提交远程新分支feature_g
创建并切换新分支 git checkout -b feature_g 添加并提交更改 git add . git commit -m “实现图片上传功能” 推送到远程 git push -u origin feature_g...
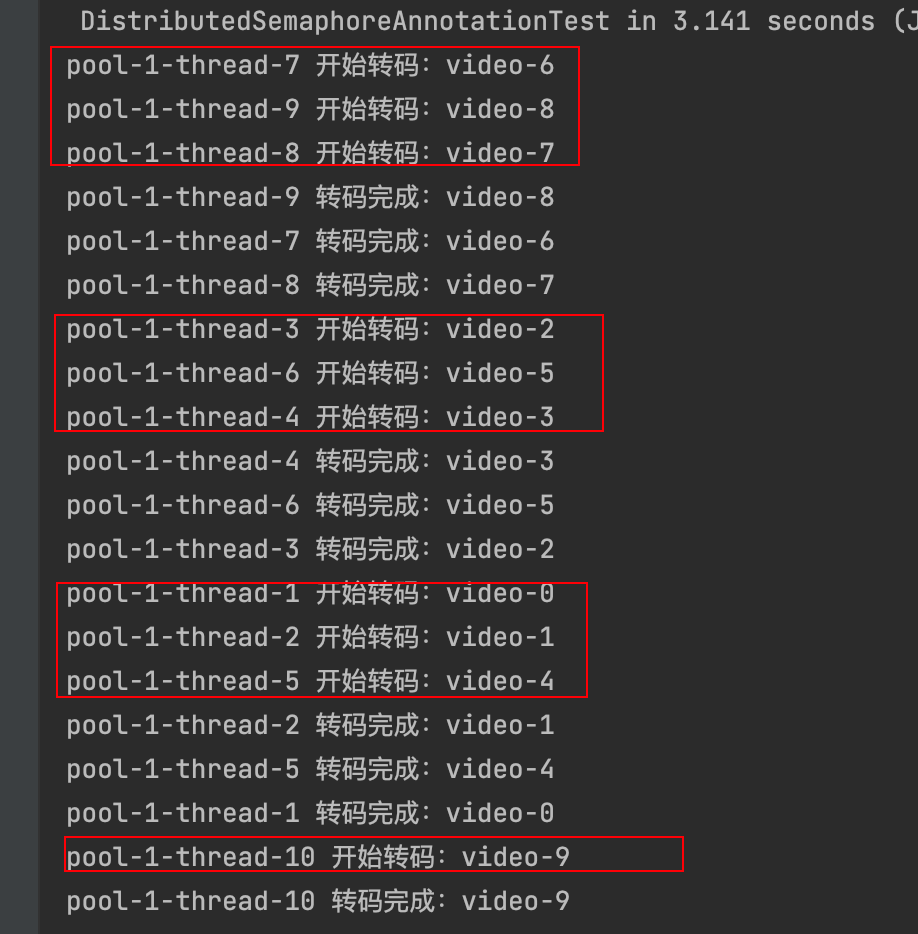
令牌桶 滑动窗口->限流 分布式信号量->限并发的原理 lua脚本分析介绍
文章目录 前言限流限制并发的实际理解限流令牌桶代码实现结果分析令牌桶lua的模拟实现原理总结: 滑动窗口代码实现结果分析lua脚本原理解析 限并发分布式信号量代码实现结果分析lua脚本实现原理 双注解去实现限流 并发结果分析: 实际业务去理解体会统一注…...
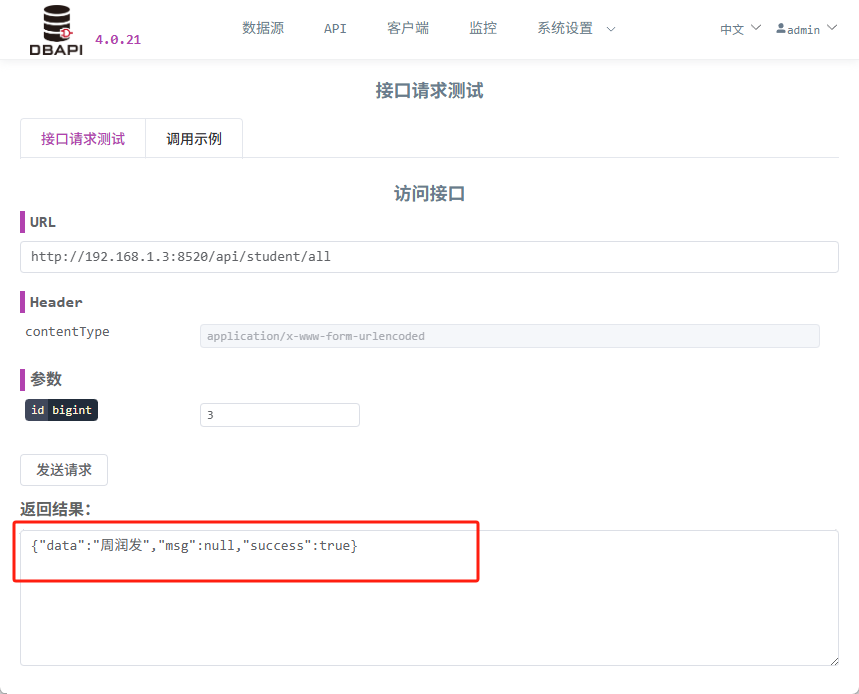
DBAPI如何优雅的获取单条数据
API如何优雅的获取单条数据 案例一 对于查询类API,查询的是单条数据,比如根据主键ID查询用户信息,sql如下: select id, name, age from user where id #{id}API默认返回的数据格式是多条的,如下: {&qu…...
安装docker)
Linux离线(zip方式)安装docker
目录 基础信息操作系统信息docker信息 安装实例安装步骤示例 遇到的问题问题1:修改默认工作路径启动失败问题2 找不到对应组 基础信息 操作系统信息 OS版本:CentOS 7 64位 内核版本:3.10.0 相关命令: uname -rcat /etc/os-rele…...

uniapp 字符包含的相关方法
在uniapp中,如果你想检查一个字符串是否包含另一个子字符串,你可以使用JavaScript中的includes()方法或者indexOf()方法。这两种方法都可以达到目的,但它们在处理方式和返回值上有所不同。 使用includes()方法 includes()方法用于判断一个字…...

4. TypeScript 类型推断与类型组合
一、类型推断 (一) 什么是类型推断 TypeScript 的类型推断会根据变量、函数返回值、对象和数组的赋值和使用方式,自动确定它们的类型。 这一特性减少了显式类型注解的需要,在保持类型安全的同时简化了代码。通过分析上下文和初始值,TypeSc…...

华为OD机试-最短木板长度-二分法(A卷,100分)
此题是一个最大化最小值的典型例题, 因为搜索范围是有界的,上界最大木板长度补充的全部木料长度,下界最小木板长度; 即left0,right10^6; 我们可以设置一个候选值x(mid),将木板的长度全部都补充到x,如果成功…...

Monorepo架构: Nx Cloud 扩展能力与缓存加速
借助 Nx Cloud 实现项目协同与加速构建 1 ) 缓存工作原理分析 在了解了本地缓存和远程缓存之后,我们来探究缓存是如何工作的。以计算文件的哈希串为例,若后续运行任务时文件哈希串未变,系统会直接使用对应的输出和制品文件。 2 …...

CppCon 2015 学习:Time Programming Fundamentals
Civil Time 公历时间 特点: 共 6 个字段: Year(年)Month(月)Day(日)Hour(小时)Minute(分钟)Second(秒) 表示…...
