laserOdometry.cpp源码注释
本博客用于a-loam源码学习,用于和slam初学者一起学习。
#include <cmath>
#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
//这两行代码是C++中包含头文件的指令,它们用于在ROS(Robot Operating System)节点的代码中引入nav_msgs包中的两个消息类型:Odometry和Path。
-
nav_msgs/Odometry.h:这个头文件定义了Odometry消息类型,它用于传送关于机器人的里程计数据。这种消息类型通常包含机器人的位姿(位置和方向)、速度(线性和角速度),以及时间戳和参考坐标帧信息。 -
nav_msgs/Path.h:这个头文件定义了Path消息类型,它用于表示一系列的位姿,通常用于描述机器人的路径。这种消息类型包含了一系列位姿(每个位姿包含位置和方向),以及时间戳和参考坐标帧信息。
#include <geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h>
//geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h定义了PoseStamped消息类型,它是一种在ROS中常用的消息,用于传送具有时间戳的位姿(位置和方向)。这种消息类型通常包含:
header:包含时间戳和坐标帧信息的头部。pose:包含位置(点)和方向(四元数)的位姿。
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/Imu.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h>
//用于在代码中包含ROS(Robot Operating System)的sensor_msgs包中的两个消息类型的头文件。
-
sensor_msgs/Imu.h:这个头文件定义了Imu消息类型,它用于传送惯性测量单元(IMU)的数据。IMU通常包括三轴陀螺仪(测量角速度)和三轴加速度计(测量线性加速度)。Imu消息还可能包含磁场数据和时间戳。这种消息类型在机器人导航、运动跟踪和姿态估计中非常有用。 -
sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h:这个头文件定义了PointCloud2消息类型,它用于传送点云数据。点云是一组在三维空间中的点的集合,每个点通常包含位置(x, y, z)和可能的其他信息,如颜色或强度。PointCloud2是一种高效的点云数据格式,它支持压缩和大数据集。这种消息类型在三维感知、环境建模和激光雷达数据处理中非常常见。
#include <tf/transform_datatypes.h>
#include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h>
-
tf/transform_datatypes.h:这个头文件定义了tf库中用于表示变换的数据结构。它包括Transform、Vector3、Quaternion等类型,这些都是在处理坐标变换时常用的数学实体。 -
tf/transform_broadcaster.h:这个头文件定义了TransformBroadcaster类,它用于在ROS中广播坐标变换。坐标变换是连接不同坐标参考帧(例如,从“世界”坐标系到“机器人”坐标系)的桥梁。
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Dense>
#include <mutex>
//#include <mutex> 是一个预处理器指令,用于包含标准库中的互斥锁(mutex)头文件。互斥锁是一种同步原语,用于保护共享数据不被多个线程同时访问,从而避免竞态条件和数据损坏。
#include <queue>
#include "aloam_velodyne/common.h"
#include "aloam_velodyne/tic_toc.h"
#include "lidarFactor.hpp"
#define DISTORTION 0
//预定义畸变为0。
//constexpr 是 C++11 引入的一个关键字,用于声明一个常量表达式。常量表达式是在编译时就能确定其值的表达式,因此 constexpr 修饰的变量或函数可以在编译时被求值,这有助于提高程序的效率和性能。
int corner_correspondence = 0, plane_correspondence = 0;
//能用于存储角点对应和平面对应点的数量
constexpr double SCAN_PERIOD = 0.1;//扫描周期0.1秒,扫描频率10hz。
constexpr double DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD = 25;
//定义了一个平方距离阈值,用于比较两点之间的距离。
constexpr double NEARBY_SCAN = 2.5;
int skipFrameNum = 5;//用于控制帧跳过的数量。
bool systemInited = false;
double timeCornerPointsSharp = 0;
double timeCornerPointsLessSharp = 0;
double timeSurfPointsFlat = 0;
double timeSurfPointsLessFlat = 0;
double timeLaserCloudFullRes = 0;
//用于存储不同处理步骤的计时信息。
//pcl::KdTreeFLANN<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr:这是一个指向 pcl::KdTreeFLANN 类的智能指针,该类用于创建和使用k-d树,这是一种用于快速近似最近邻搜索的数据结构。
pcl::KdTreeFLANN<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr kdtreeCornerLast(new pcl::KdTreeFLANN<pcl::PointXYZI>());
pcl::KdTreeFLANN<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr kdtreeSurfLast(new pcl::KdTreeFLANN<pcl::PointXYZI>());
//为角点和面点分别初始化了两个kd树。
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr cornerPointsSharp(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr cornerPointsLessSharp(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr surfPointsFlat(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr surfPointsLessFlat(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
//用于存储不同类型的特征点云。
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudCornerLast(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudSurfLast(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudFullRes(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
//用于存储上一帧的点云数据。
int laserCloudCornerLastNum = 0;
int laserCloudSurfLastNum = 0;
// Transformation from current frame to world frame
Eigen::Quaterniond q_w_curr(1, 0, 0, 0); //单位四元数,表示没有旋转
Eigen::Vector3d t_w_curr(0, 0, 0);
// q_curr_last(x, y, z, w), t_curr_last
double para_q[4] = {0, 0, 0, 1};
//定义了一个包含四个元素的数组 para_q,用于存储四元数的参数。这里同样表示没有旋转。
double para_t[3] = {0, 0, 0};
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Quaterniond> q_last_curr(para_q);
//Eigen::Map<Eigen::Quaterniond> q_last_curr(para_q);:使用 Eigen::Map 将数组 para_q 映射到一个四元数对象 q_last_curr。Eigen::Map 允许 Eigen 库直接操作现有的数组,而不需要复制数据。
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector3d> t_last_curr(para_t);
std::queue<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr> cornerSharpBuf;
std::queue<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr> cornerLessSharpBuf;
std::queue<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr> surfFlatBuf;
std::queue<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr> surfLessFlatBuf;
std::queue<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr> fullPointsBuf;
std::mutex mBuf;
// undistort lidar point 从雷达坐标系中变换到世界坐标系
void TransformToStart(PointType const *const pi, PointType *const po)
{
//
PointType const *const pi: 指向输入点的指针,即原始点云中的点。PointType *const po: 指向输出点的指针,即变换后的点云中的点。
//interpolation ratio
double s;//插值比率
if (DISTORTION)
s = (pi->intensity - int(pi->intensity)) / SCAN_PERIOD;
//如果定义了 DISTORTION 且不为0,则根据点的强度值计算插值比率 s。
else
s = 1.0;
//s = 1;如果没有定义 DISTORTION 或其值为0,则插值比率设为1,表示没有时间上的插值,直接应用完整的变换。
Eigen::Quaterniond q_point_last = Eigen::Quaterniond::Identity().slerp(s, q_last_curr);
//计算从当前点到上一个点的旋转。这里使用了球面线性插值(Slerp),它在两个四元数之间进行插值,得到一个新的四元数 q_point_last。
Eigen::Vector3d t_point_last = s * t_last_curr;
Eigen::Vector3d point(pi->x, pi->y, pi->z);
//将输入点的坐标转换为 Eigen 库中的三维向量。
Eigen::Vector3d un_point = q_point_last * point + t_point_last;
po->x = un_point.x();
po->y = un_point.y();
po->z = un_point.z();
po->intensity = pi->intensity;
}
// transform all lidar points to the start of the next frame
//从世界坐标系变换到雷达坐标系
void TransformToEnd(PointType const *const pi, PointType *const po)
{
// undistort point first
pcl::PointXYZI un_point_tmp;
TransformToStart(pi, &un_point_tmp);
Eigen::Vector3d un_point(un_point_tmp.x, un_point_tmp.y, un_point_tmp.z);
Eigen::Vector3d point_end = q_last_curr.inverse() * (un_point - t_last_curr);
// Eigen::Vector3d un_point = q_point_last * point + t_point_last;逆变换,从世界坐标系转回雷达坐标系。
po->x = point_end.x();
po->y = point_end.y();
po->z = point_end.z();
//Remove distortion time info
po->intensity = int(pi->intensity);
}
//根据曲率将特征分为四个等级,sharp,lesssharp,flat,lessflat,分别接收数据。
void laserCloudSharpHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &cornerPointsSharp2)
{
mBuf.lock();
cornerSharpBuf.push(cornerPointsSharp2);
mBuf.unlock();
}
//const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &cornerPointsSharp2: 这是一个指向 sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 类型的常量指针的智能指针。sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 是 ROS 中用于传输点云数据的标准消息类型。
//mBuf.lock();: 调用 mBuf(可能是一个互斥锁)的 lock 方法来锁定缓冲区。这是为了确保在多线程环境中对缓冲区的访问是线程安全的。
cornerSharpBuf.push(cornerPointsSharp2);: 将接收到的尖锐角点的点云数据推送到 cornerSharpBuf 缓冲区。cornerSharpBuf 可能是一个线程安全的队列或缓冲区,用于存储接收到的点云数据。
mBuf.unlock();: 在数据推送完成后,调用 mBuf 的 unlock 方法来解锁缓冲区。这允许其他线程访问缓冲区。
void laserCloudLessSharpHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &cornerPointsLessSharp2)
{
mBuf.lock();
cornerLessSharpBuf.push(cornerPointsLessSharp2);
mBuf.unlock();
}
//函数 laserCloudSharpHandler 是一个回调函数,它会被设计为在订阅的话题 /laser_cloud_sharp 上接收到新的 sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 消息时自动调用。这个过程是在 ROS(Robot Operating System)环境中进行的。
void laserCloudFlatHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &surfPointsFlat2)
{
mBuf.lock();
surfFlatBuf.push(surfPointsFlat2);
mBuf.unlock();
}
void laserCloudLessFlatHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &surfPointsLessFlat2)
{
mBuf.lock();
surfLessFlatBuf.push(surfPointsLessFlat2);
mBuf.unlock();
}
//receive all point cloud 接收全部数据
void laserCloudFullResHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &laserCloudFullRes2)
{
mBuf.lock();
fullPointsBuf.push(laserCloudFullRes2);
mBuf.unlock();
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "laserOdometry");//初始化ROS节点,节点名为 "laserOdometry"。
ros::NodeHandle nh;//创建一个ROS节点句柄,用于处理参数和订阅/发布消息。
nh.param<int>("mapping_skip_frame", skipFrameNum, 2);
printf("Mapping %d Hz \n", 10 / skipFrameNum);
ros::Subscriber subCornerPointsSharp = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_sharp", 100, laserCloudSharpHandler);
ros::Subscriber subCornerPointsLessSharp = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_less_sharp", 100, laserCloudLessSharpHandler);
ros::Subscriber subSurfPointsFlat = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_flat", 100, laserCloudFlatHandler);
ros::Subscriber subSurfPointsLessFlat = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_less_flat", 100, laserCloudLessFlatHandler);
ros::Subscriber subLaserCloudFullRes = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/velodyne_cloud_2", 100, laserCloudFullResHandler);
//代码subscribe了多个激光雷达点云数据topic,每个主题都关联了一个处理函数:
/laser_cloud_sharp: 尖锐角点的点云数据。/laser_cloud_less_sharp: 较不尖锐的角点的点云数据。/laser_cloud_flat: 平面点的点云数据。/laser_cloud_less_flat: 较不平坦的点的点云数据。/velodyne_cloud_2: 高分辨率的原始激光雷达点云数据。
ros::Publisher pubLaserCloudCornerLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_corner_last", 100);
ros::Publisher pubLaserCloudSurfLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_surf_last", 100);
ros::Publisher pubLaserCloudFullRes = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/velodyne_cloud_3", 100);
ros::Publisher pubLaserOdometry = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("/laser_odom_to_init", 100);
ros::Publisher pubLaserPath = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("/laser_odom_path", 100);
//代码发布了处理后的点云数据和里程计信息到以下topic:
/laser_cloud_corner_last: 处理后的尖锐角点的点云数据。/laser_cloud_surf_last: 处理后的平面点的点云数据。/velodyne_cloud_3: 处理后的高分辨率点云数据。/laser_odom_to_init: 激光雷达里程计数据,用于定位。/laser_odom_path: 激光雷达的路径信息。
nav_msgs::Path laserPath;
//声明了一个 nav_msgs::Path 类型的消息,用于存储和发布激光雷达的路径信息。
int frameCount = 0;
ros::Rate rate(100);
//ros::Rate rate(100);: 创建了一个 ros::Rate 对象并设置为100Hz。这意味着 rate 对象将用于以100次每秒的频率控制循环的速率。
while (ros::ok()) //当一次初始化的时候,执行if内的代码,再对参数初始化;0.01秒之后,第二次即执行else中的点云处理语句。
{
ros::spinOnce();
//主循环中调用 ros::spinOnce(),以确保所有订阅的消息都能被及时处理。
if (!cornerSharpBuf.empty() && !cornerLessSharpBuf.empty() &&
!surfFlatBuf.empty() && !surfLessFlatBuf.empty() &&
!fullPointsBuf.empty())
{
timeCornerPointsSharp = cornerSharpBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
timeCornerPointsLessSharp = cornerLessSharpBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
timeSurfPointsFlat = surfFlatBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
timeSurfPointsLessFlat = surfLessFlatBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
timeLaserCloudFullRes = fullPointsBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
//每个缓冲区(cornerSharpBuf, cornerLessSharpBuf, surfFlatBuf, surfLessFlatBuf, fullPointsBuf)的前端数据(即最新数据)的时间戳被提取出来,并转换为秒(toSec() 方法)。
if (timeCornerPointsSharp != timeLaserCloudFullRes ||
timeCornerPointsLessSharp != timeLaserCloudFullRes ||
timeSurfPointsFlat != timeLaserCloudFullRes ||
timeSurfPointsLessFlat != timeLaserCloudFullRes)
{
printf("unsync messeage!");//检测到不同步的数据,输出错误!
ROS_BREAK();
}
mBuf.lock();
cornerPointsSharp->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*cornerSharpBuf.front(), *cornerPointsSharp);
//pcl::fromROSMsg(*cornerSharpBuf.front(), *cornerPointsSharp);: 将ROS消息格式的点云数据转换为PCL格式,并存储在 cornerPointsSharp 点云对象中。cornerSharpBuf.front() 获取缓冲区中的第一个元素。
cornerSharpBuf.pop();
//cornerSharpBuf.pop();: 从缓冲区中移除第一个元素。然后再将cornerSharpBuf中的第二个元素转换为PCL格式存储在cornerPointsSharp 点云对象。
cornerPointsLessSharp->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*cornerLessSharpBuf.front(), *cornerPointsLessSharp);
cornerLessSharpBuf.pop();
surfPointsFlat->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*surfFlatBuf.front(), *surfPointsFlat);
surfFlatBuf.pop();
surfPointsLessFlat->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*surfLessFlatBuf.front(), *surfPointsLessFlat);
surfLessFlatBuf.pop();
laserCloudFullRes->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*fullPointsBuf.front(), *laserCloudFullRes);
fullPointsBuf.pop();
mBuf.unlock();
TicToc t_whole;
//创建一个名为 t_whole 的 TicToc 实例,用于测量整个代码块或程序的执行时间。
// initializing
if (!systemInited)
{
systemInited = true;
std::cout << "Initialization finished \n";
}
//
if (!systemInited): 检查systemInited布尔变量是否为false,即系统是否未初始化。systemInited = true;: 如果未初始化,则将其设置为true,表示系统现在已初始化。std::cout << "Initialization finished \n";: 打印一条消息到控制台,告知用户初始化已完成。
else
{
int cornerPointsSharpNum = cornerPointsSharp->points.size();
int surfPointsFlatNum = surfPointsFlat->points.size();
TicToc t_opt;
for (size_t opti_counter = 0; opti_counter < 2; ++opti_counter)
{
corner_correspondence = 0;
plane_correspondence = 0;
//ceres::LossFunction *loss_function = NULL;
ceres::LossFunction *loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(0.1);
//HuberLoss 是一种常用的损失函数,它在误差较小时表现为二次损失,在误差较大时表现为线性损失,有助于提高鲁棒性。
ceres::LocalParameterization *q_parameterization =
new ceres::EigenQuaternionParameterization();
//创建一个四元数参数化对象,用于优化过程中四元数的更新。
ceres::Problem::Options problem_options;
//创建了一个用于配置问题的选项对象。
ceres::Problem problem(problem_options);
//创建了一个优化问题。
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_q, 4, q_parameterization);
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_t, 3);
//向问题中添加了参数块。para_q 是一个四元数数组,用于表示旋转,para_t 是一个三维向量,用于表示平移。每个参数块的大小分别是4和3。
pcl::PointXYZI pointSel;
std::vector<int> pointSearchInd;
std::vector<float> pointSearchSqDis;
TicToc t_data;
// find correspondence for corner features
for (int i = 0; i < cornerPointsSharpNum; ++i)
{
TransformToStart(&(cornerPointsSharp->points[i]), &pointSel);
//通过TransformToStart,完成坐标系的转换,并给pointSel赋值。
kdtreeCornerLast->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 1, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
//补充一下nearestKSearch 的定义
pcl::KdTreeFLANN<PointT, Dist>::nearestKSearch (const PointT &point, int k,
std::vector<int> &k_indices,
std::vector<float> &k_distances) const
int closestPointInd = -1, minPointInd2 = -1;
if (pointSearchSqDis[0] < DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD)
{//DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD==25
closestPointInd = pointSearchInd[0];
int closestPointScanID = int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].intensity);
//获取最近点的扫描标识符,它存储在点的intensity字段中。这通常用于区分不同扫描或时间点获取的数据。
double minPointSqDis2 = DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD;
// search in the direction of increasing scan line
for (int j = closestPointInd + 1; j < (int)laserCloudCornerLast->points.size(); ++j)
{
// if in the same scan line, continue
if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) <= closestPointScanID)
continue;//这行代码检查当前遍历的点是否在同一扫描线上。如果是,那么跳过这个点,继续下一个循环迭代。
//关于laserCloudCornerLast什么时候指向的cornerPointsLessSharp,在后面的代码中有体现。
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudTemp = cornerPointsLessSharp;
cornerPointsLessSharp = laserCloudCornerLast;
laserCloudCornerLast = laserCloudTemp; // if not in nearby scans, end the loop
if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) > (closestPointScanID + NEARBY_SCAN))
//这行代码检查当前遍历的点是否在相邻的扫描范围内。如果不是,那么结束循环。
break;
double pointSqDis = (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2)
{
// find nearer point
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
//在同一条扫描线上,或者相邻的扫描范围内再找到最近邻点的最近点。
}
}
//在另一个方向上,重复和上面一样的操作。
// search in the direction of decreasing scan line
for (int j = closestPointInd - 1; j >= 0; --j)
{
// if in the same scan line, continue
if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) >= closestPointScanID)
continue;
// if not in nearby scans, end the loop
if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) < (closestPointScanID - NEARBY_SCAN))
break;
double pointSqDis = (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2)
{
// find nearer point
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
}
}
if (minPointInd2 >= 0) // both closestPointInd and minPointInd2 is valid
{
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point(cornerPointsSharp->points[i].x,
cornerPointsSharp->points[i].y,
cornerPointsSharp->points[i].z);
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_a(laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].x,
laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].y,
laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].z);
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_b(laserCloudCornerLast->points[minPointInd2].x,
laserCloudCornerLast->points[minPointInd2].y,
laserCloudCornerLast->points[minPointInd2].z);
double s;
if (DISTORTION)
s = (cornerPointsSharp->points[i].intensity - int(cornerPointsSharp->points[i].intensity)) / SCAN_PERIOD;
else
s = 1.0;
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function = LidarEdgeFactor::Create(curr_point, last_point_a, last_point_b, s);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, para_q, para_t);
corner_correspondence++;
//AddResidualBlock 是 ceres::Problem 类的一个成员函数,它将一个残差块添加到问题中。 corner_correspondence++;这行代码更新了一个计数器 corner_correspondence,它可能用于跟踪添加到优化问题中的角点对应关系的数量。
}
}
// find correspondence for plane features 面上特征点的匹配和角点特征点的匹配方法是一样的,都是先做坐标系转换,然后使用kd树找到最近邻点,再由最近邻点在同一条扫描线或相邻扫描线上找到最近邻点的最近邻点,然后构建点到面的距离最小作为损失函数。
for (int i = 0; i < surfPointsFlatNum; ++i)
{
TransformToStart(&(surfPointsFlat->points[i]), &pointSel);
kdtreeSurfLast->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 1, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
int closestPointInd = -1, minPointInd2 = -1, minPointInd3 = -1;
if (pointSearchSqDis[0] < DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD)
{
closestPointInd = pointSearchInd[0];
// get closest point's scan ID
int closestPointScanID = int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].intensity);
double minPointSqDis2 = DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD, minPointSqDis3 = DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD; //两个相邻点
// search in the direction of increasing scan line
for (int j = closestPointInd + 1; j < (int)laserCloudSurfLast->points.size(); ++j)
{
// if not in nearby scans, end the loop
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) > (closestPointScanID + NEARBY_SCAN))
break;
double pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
// if in the same or lower scan line
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) <= closestPointScanID && pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2)
{
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
// if in the higher scan line
else if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) > closestPointScanID && pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3)
{
minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd3 = j;
}
}
// search in the direction of decreasing scan line
for (int j = closestPointInd - 1; j >= 0; --j)
{
// if not in nearby scans, end the loop
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) < (closestPointScanID - NEARBY_SCAN))
break;
double pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
// if in the same or higher scan line
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) >= closestPointScanID && pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2)
{
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
else if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) < closestPointScanID && pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3)
{
// find nearer point
minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd3 = j;
}
}
if (minPointInd2 >= 0 && minPointInd3 >= 0)
{
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point(surfPointsFlat->points[i].x,
surfPointsFlat->points[i].y,
surfPointsFlat->points[i].z);
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_a(laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].x,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].y,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].z);
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_b(laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd2].x,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd2].y,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd2].z);
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_c(laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd3].x,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd3].y,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd3].z);
double s;
if (DISTORTION)
s = (surfPointsFlat->points[i].intensity - int(surfPointsFlat->points[i].intensity)) / SCAN_PERIOD;
else
s = 1.0;
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function = LidarPlaneFactor::Create(curr_point, last_point_a, last_point_b, last_point_c, s);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, para_q, para_t);
plane_correspondence++;
}
}
}
//printf("coner_correspondance %d, plane_correspondence %d \n", corner_correspondence, plane_correspondence);
printf("data association time %f ms \n", t_data.toc());
if ((corner_correspondence + plane_correspondence) < 10)
{
printf("less correspondence! *************************************************\n");
}
TicToc t_solver;
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR;
//设置线性求解器类型为 DENSE_QR,即密集矩阵的 QR 分解。这是 Ceres Solver 用于解决线性系统的算法之一。
options.max_num_iterations = 4;
//设置最大迭代次数为 4。
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = false;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
//调用 ceres::Solve 函数来解决优化问题。options 是配置选项,problem 是定义好的优化问题,summary 是优化过程的总结。
printf("solver time %f ms \n", t_solver.toc());
}
printf("optimization twice time %f \n", t_opt.toc());
t_w_curr = t_w_curr + q_w_curr * t_last_curr;
q_w_curr = q_w_curr * q_last_curr;
}
TicToc t_pub;
// publish odometry
nav_msgs::Odometry laserOdometry;
laserOdometry.header.frame_id = "camera_init";
laserOdometry.child_frame_id = "/laser_odom";
laserOdometry.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeSurfPointsLessFlat);
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation.x = q_w_curr.x();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation.y = q_w_curr.y();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation.z = q_w_curr.z();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation.w = q_w_curr.w();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.x = t_w_curr.x();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.y = t_w_curr.y();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.z = t_w_curr.z();
pubLaserOdometry.publish(laserOdometry);
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped laserPose;
laserPose.header = laserOdometry.header;
laserPose.pose = laserOdometry.pose.pose;
laserPath.header.stamp = laserOdometry.header.stamp;
laserPath.poses.push_back(laserPose);
laserPath.header.frame_id = "camera_init";
pubLaserPath.publish(laserPath);
// transform corner features and plane features to the scan end point
if (0) //条件 if (0) 永远是假的,因此大括号内的代码在编译时会被忽略,不会执行。
{
int cornerPointsLessSharpNum = cornerPointsLessSharp->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cornerPointsLessSharpNum; i++)
{
TransformToEnd(&cornerPointsLessSharp->points[i], &cornerPointsLessSharp->points[i]);
}
int surfPointsLessFlatNum = surfPointsLessFlat->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < surfPointsLessFlatNum; i++)
{
TransformToEnd(&surfPointsLessFlat->points[i], &surfPointsLessFlat->points[i]);
}
int laserCloudFullResNum = laserCloudFullRes->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudFullResNum; i++)
{
TransformToEnd(&laserCloudFullRes->points[i], &laserCloudFullRes->points[i]);
}
}
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudTemp = cornerPointsLessSharp;
cornerPointsLessSharp = laserCloudCornerLast;
laserCloudCornerLast = laserCloudTemp;
laserCloudTemp = surfPointsLessFlat;
surfPointsLessFlat = laserCloudSurfLast;
laserCloudSurfLast = laserCloudTemp;
laserCloudCornerLastNum = laserCloudCornerLast->points.size();
laserCloudSurfLastNum = laserCloudSurfLast->points.size();
// std::cout << "the size of corner last is " << laserCloudCornerLastNum << ", and the size of surf last is " << laserCloudSurfLastNum << '\n';
kdtreeCornerLast->setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerLast);
kdtreeSurfLast->setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfLast);
if (frameCount % skipFrameNum == 0)
{
frameCount = 0;
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudCornerLast2;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudCornerLast, laserCloudCornerLast2);
laserCloudCornerLast2.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeSurfPointsLessFlat);
laserCloudCornerLast2.header.frame_id = "camera";
pubLaserCloudCornerLast.publish(laserCloudCornerLast2);
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudSurfLast2;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudSurfLast, laserCloudSurfLast2);
laserCloudSurfLast2.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeSurfPointsLessFlat);
laserCloudSurfLast2.header.frame_id = "camera";
pubLaserCloudSurfLast.publish(laserCloudSurfLast2);
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudFullRes3;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudFullRes, laserCloudFullRes3);
laserCloudFullRes3.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeSurfPointsLessFlat);
laserCloudFullRes3.header.frame_id = "camera";
pubLaserCloudFullRes.publish(laserCloudFullRes3);
}
printf("publication time %f ms \n", t_pub.toc());
printf("whole laserOdometry time %f ms \n \n", t_whole.toc());
if(t_whole.toc() > 100)
ROS_WARN("odometry process over 100ms");
frameCount++;
}
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
相关文章:

laserOdometry.cpp源码注释
本博客用于a-loam源码学习,用于和slam初学者一起学习。 #include <cmath>#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>#include <nav_msgs/Path.h> //这两行代码是C中包含头文件的指令,它们用于在ROS(Robot Operating System…...

STM32时钟配置图详解
一图概述: 左侧输入时钟源 Input Frequency (LSE/LSI/HSI/HSE) LSE (Low-Speed External):外部32.768 kHz晶体振荡器,通常用于RTC(实时时钟)。LSI (Low-Speed Internal):内部低速时钟,频率为…...

Vscode——调试时,修改变量值
第一步:点击变量,鼠标右键 第二步:点击 设置值...
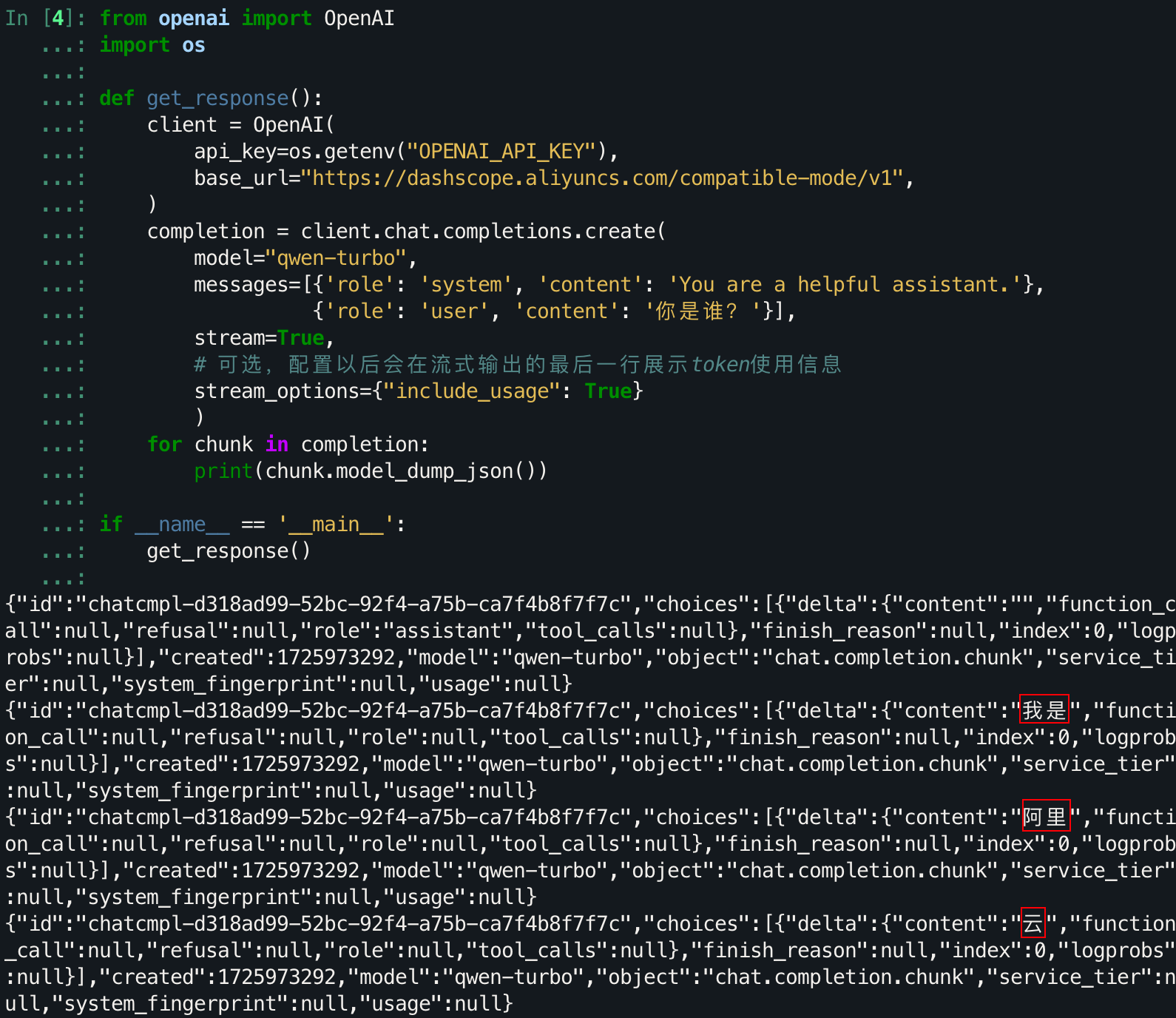
1. 初识LLM API:环境配置与多轮对话演示
其实AI应用并不是一个什么很高大上的东西,你可以将它当作一个文字的“调库”行为,“调库”只需要知道库名就行了,这里实际也是如此。甚至你只需要知道你想问什么,将你的消息作为输入,就能从大模型得到输出。而这个“库…...

【AI编程助手】VsCode插件--通义灵码
目录 摘要 一、插件安装 二、“通义灵码” 使用 三、官网教程 四、总结 五、参考信息 摘要 通义灵码是一款强大的 AI 编程助手。它能够理解编程相关的复杂逻辑,为开发者提供高效、准确的代码生成与优化建议。在编程过程中,它可以辅助处理各种任务&…...

9月10号的学习
//界面1 头文件 signals://界面1的自定义信号void my_signal(); private slots:void on_pushButton_2_clicked();void on_pushButton_clicked(); //界面1 .cpp文件 void Widget::on_pushButton_2_clicked() {QMessageBox msg(QMessageBox::Warning,"警告","是否…...

QtC++截图支持窗口获取
介绍 在截图工具中你会发现,接触到窗口后会自动圈出目标窗口,个别强大一点的还能进行元素识别可以自动圈出元素,那么今天简单分析一下QTc如何获取窗口并圈出当前鼠标下的窗口。 介绍1.如何获取所有窗口2.比较函数3.实现窗口判断 结尾 1.如何获取所有窗口…...

料品档案没有配置主供应商信息
这个问题经常会出现在普通用户的面前。没有合适的工程人员去打理料品档案。信息是缺漏的。用友给出来的提示,也让人摸不着头脑。只能是记下来备用吧。...

springboot属性加载优先级和常见命令行属性
属性加载优先级: 1.SpringApplication:启动的main方法里注入的属性 2.PropertySource:通过注解 加载的数据配置文件 3.Config data file:application.yml/.properties 4.OS environment variable:环境变量 5.Command l…...

Math Reference Notes: 因式定理
文章目录 1. 因式定理的定义2. 因式定理的数学表达:3. 因式定理的推导4. 因式定理的含义5. 因式定理的应用6. 因式定理与余式定理的关系7. 因式定理的应用领域8.因式定理的局限性 因式定理是多项式代数中的一个重要工具,帮助我们通过多项式的根来因式分解…...

Kubernetes------Service
目录 一、属性说明 二、定义和基本配置 1、定义 2、创建Service 2.1、typeClusterIP 2.2、typeNodePort 2.3、固定IP访问 三、Service、EndPoint、Pod之间的关系 四、服务发现 1、基于Service中IP访问外部服务 2、基于Service中域名访问外部服务 五、Ingress的安装和使…...

C#的LINQ语句
在 C# 中,LINQ(Language Integrated Query)是一种强大的查询技术,它允许你使用熟悉的 C# 语法来查询数据集合。LINQ 可以用于查询各种数据源,包括数组、列表、数据集、SQL数据库等。 以下是一些基本的 LINQ 语句示例&…...

项目实战系列三: 家居购项目 第三部分
文章目录 🍃后台分页🍅后台分页导航 🍃首页分页🍅首页分页导航🍅首页搜索🍅两个奇怪的问题🍅会员显示登录名🍅注销登录🍅验证码 🍃后台分页 程序框架图 1.…...

【WPF】Border的使用
在 WPF 中,Border 控件是一个非常实用的容器控件,它可以用来为其他控件添加边框、背景颜色、边距等样式。Border 本身没有内置的行为,但是它可以包含一个子元素,并且可以通过各种属性来自定义外观。 Border基本属性 Child: 表示…...

机器学习(西瓜书)第 4 章 决策树
4.1 决策树基本流程 决策树模型 基本流程 在第⑵种情形下,我们把当前结点标记为叶结点,并将其类别设定为该结点所含样本最多的类别;在第⑶种情形下,同样把当前结点标记为叶结点,但将其类别设定为其父结点所含样本最多…...

8、值、指针、引用作为参数或返回值
一、作为参数 1、值传递 #include <iostream> using namespace std;void swap(int a, int b) {cout << __FUNCTION__ << "交换前a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl;int tmp a;a b;b tmp;cout << __FUN…...

向量——通俗地解释
1. 向量 向量是一个既有大小(模)又有方向的对象,它可以用来描述空间中的位置、力或速度等量。我们可以从物理、数学和计算机的角度来看待向量,这三种观点看似不同却有关联。 (1)在物理专业视角下,向量是空间中的箭头&a…...

新书宣传:《量子安全:信息保护新纪元》
《量子安全:信息保护新纪元》 前言本书的看点本书的目录结语 前言 你好! 这是我第一次发布类广告的博文,目的也很单纯,希望以作者的身份介绍一下自己出版的图书——《量子安全:信息保护新纪元》。此书于2024年7月出版…...

Android Framework(五)WMS-窗口显示流程——窗口布局与绘制显示
文章目录 relayoutWindow流程概览应用端处理——ViewRootImpl::setView -> relayoutWindowViewRootImpl::setViewViewRootImpl::performTraversalsViewRootImpl::relayoutWindow Surface的创建WindowManagerService::relayoutWindow了解容器类型和Buff类型的SurfaceBuff类型…...

【计网】计算机网络基础
当自律变成一种本能的习惯, 你就会享受到它的快乐。 --- 村上春树 --- 初识计算机网络 1 初识协议1.1 协议分层1.2 OSI七层模型1.3 TCP / IP协议 2 初识局域网2.1 什么是局域网2.2 MAC地址2.3 局域网通信 3 简单认识IP地址 1 初识协议 1.1 协议分层 首先&#…...

基于ASP.NET+ SQL Server实现(Web)医院信息管理系统
医院信息管理系统 1. 课程设计内容 在 visual studio 2017 平台上,开发一个“医院信息管理系统”Web 程序。 2. 课程设计目的 综合运用 c#.net 知识,在 vs 2017 平台上,进行 ASP.NET 应用程序和简易网站的开发;初步熟悉开发一…...

PL0语法,分析器实现!
简介 PL/0 是一种简单的编程语言,通常用于教学编译原理。它的语法结构清晰,功能包括常量定义、变量声明、过程(子程序)定义以及基本的控制结构(如条件语句和循环语句)。 PL/0 语法规范 PL/0 是一种教学用的小型编程语言,由 Niklaus Wirth 设计,用于展示编译原理的核…...

【HTTP三个基础问题】
面试官您好!HTTP是超文本传输协议,是互联网上客户端和服务器之间传输超文本数据(比如文字、图片、音频、视频等)的核心协议,当前互联网应用最广泛的版本是HTTP1.1,它基于经典的C/S模型,也就是客…...
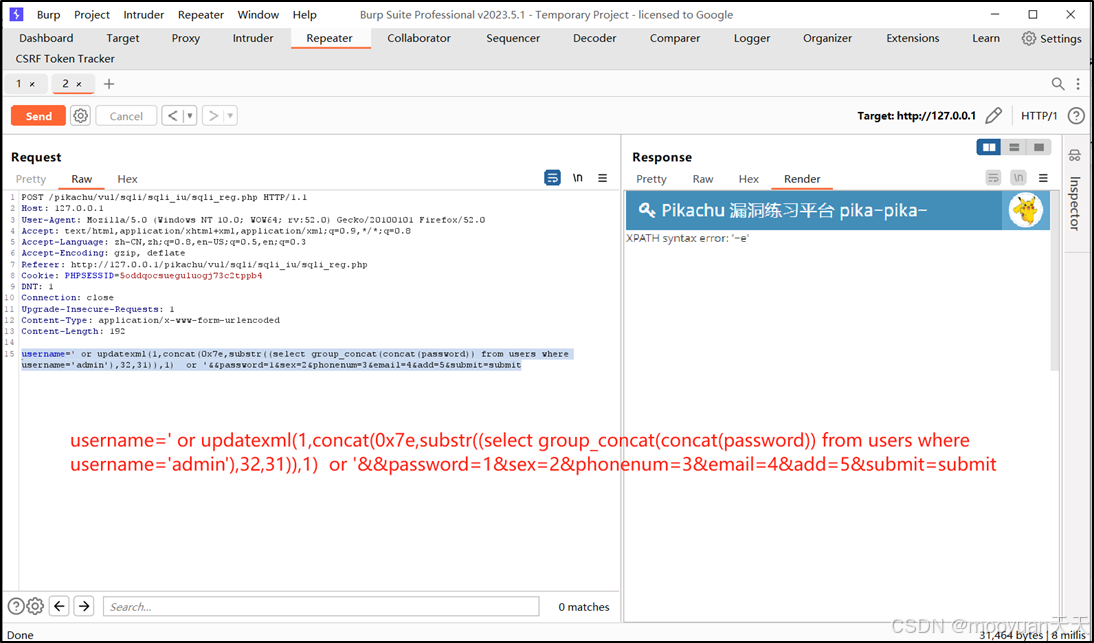
pikachu靶场通关笔记22-1 SQL注入05-1-insert注入(报错法)
目录 一、SQL注入 二、insert注入 三、报错型注入 四、updatexml函数 五、源码审计 六、insert渗透实战 1、渗透准备 2、获取数据库名database 3、获取表名table 4、获取列名column 5、获取字段 本系列为通过《pikachu靶场通关笔记》的SQL注入关卡(共10关࿰…...

全面解析各类VPN技术:GRE、IPsec、L2TP、SSL与MPLS VPN对比
目录 引言 VPN技术概述 GRE VPN 3.1 GRE封装结构 3.2 GRE的应用场景 GRE over IPsec 4.1 GRE over IPsec封装结构 4.2 为什么使用GRE over IPsec? IPsec VPN 5.1 IPsec传输模式(Transport Mode) 5.2 IPsec隧道模式(Tunne…...
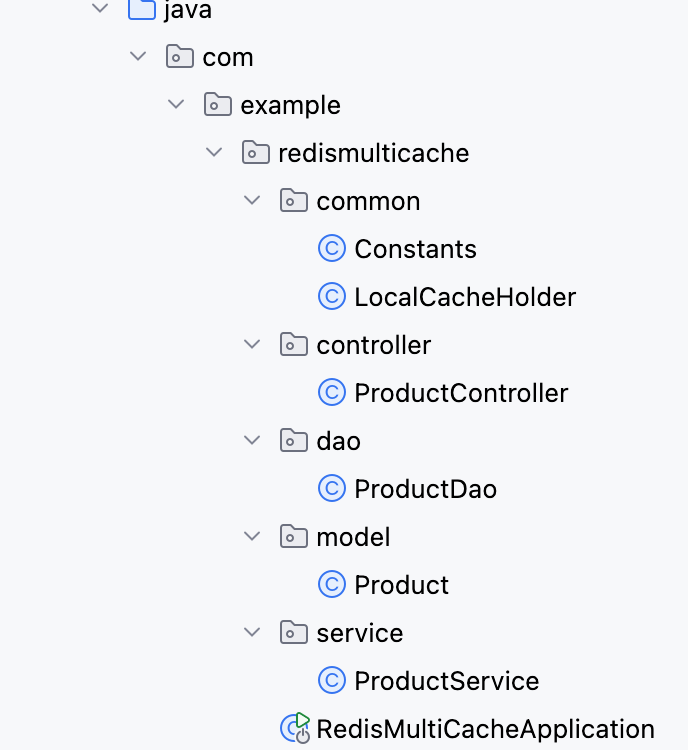
【Redis】笔记|第8节|大厂高并发缓存架构实战与优化
缓存架构 代码结构 代码详情 功能点: 多级缓存,先查本地缓存,再查Redis,最后才查数据库热点数据重建逻辑使用分布式锁,二次查询更新缓存采用读写锁提升性能采用Redis的发布订阅机制通知所有实例更新本地缓存适用读多…...

计算机基础知识解析:从应用到架构的全面拆解
目录 前言 1、 计算机的应用领域:无处不在的数字助手 2、 计算机的进化史:从算盘到量子计算 3、计算机的分类:不止 “台式机和笔记本” 4、计算机的组件:硬件与软件的协同 4.1 硬件:五大核心部件 4.2 软件&#…...

libfmt: 现代C++的格式化工具库介绍与酷炫功能
libfmt: 现代C的格式化工具库介绍与酷炫功能 libfmt 是一个开源的C格式化库,提供了高效、安全的文本格式化功能,是C20中引入的std::format的基础实现。它比传统的printf和iostream更安全、更灵活、性能更好。 基本介绍 主要特点 类型安全:…...

提升移动端网页调试效率:WebDebugX 与常见工具组合实践
在日常移动端开发中,网页调试始终是一个高频但又极具挑战的环节。尤其在面对 iOS 与 Android 的混合技术栈、各种设备差异化行为时,开发者迫切需要一套高效、可靠且跨平台的调试方案。过去,我们或多或少使用过 Chrome DevTools、Remote Debug…...

SpringAI实战:ChatModel智能对话全解
一、引言:Spring AI 与 Chat Model 的核心价值 🚀 在 Java 生态中集成大模型能力,Spring AI 提供了高效的解决方案 🤖。其中 Chat Model 作为核心交互组件,通过标准化接口简化了与大语言模型(LLM࿰…...
