SWIFT Payment
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication
SWIFT——环球银行金融电信协会
SWIFT Payment Useful Link
| ISO 20022 | https://www.iso20022.org/https://www.swift.com/standards/iso-20022 |
| MT and MX Equivalence Tables | https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/rest/v1/publications/stdsmt_mt_mx_eq_tbl/_latest/stdsmt_mt_mx_eq_tbl.pdf |
| Funds MT to MX Mapping | https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/publications/stdsmt_funds_mt_mx_map |
| Standards MT | https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/products/Standards%20MT |
| Standards MX | https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/products/Standards%20MX |
| Specific Message Example | Format Spec: https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/publications/us1m_20220722/?topic=mt101-format-spec.htm Field Spec: https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/publications/us1m_20220722/?topic=mt101-field-spec.htm Message Example: |
| ISO15022 and ISO 20022 (MT & MX Basic Knowledge , The Structure Of A SWIFT Message) | https://www.sepaforcorporates.com/swift-for-corporates/read-swift-message-structure/ |
| BIC | https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/publications/usgi_20220722/2.0?topic=con_31411.htm |
Notes: 内部可以使用 SWIFT Translator & SWIFT Validator。
MT Overview
https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/products/Standards%20MT/publications
- Category 1 - Customer Payments and Cheques
- Category 2 - Financial Institution Transfers
- Category 3 - Treasury Markets - Foreign Exchange, Money Markets and Derivatives
- Category 4 - Collections and Cash Letters
- Category 5 - Securities Markets
- Category 6 - Reference Data
- Category 6 - Treasury Markets - Commodities
- Category 7 - Documentary Credits and Guarantees/Standby Letters of Credit
- Category 8 - Travellers Cheques
- Category 9 - Cash Management and Customer Status
- Category n - Common Group Messages
MX Overview
https://www2.swift.com/knowledgecentre/products/Standards%20MX/publications
- Collateral Management
- Corporate Actions
- Cross-Border Payments and Reporting Plus (CBPR+)
- Funds
- General Meeting
- Securities Clearing
- Settlement and Reconciliation
- Shareholders Identification Disclosure
- Technical
- Total Portfolio Valuation Report
- Triparty Collateral Management
XSD (XML Schema Definition)
XML Schema Definition or XSD is a recommendation by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) to describe and validate the structure and content of an XML document.
ISO 20022 Message Definition: https://www.iso20022.org/iso-20022-message-definitions

Securities: https://www.iso20022.org/iso-20022-message-definitions?business-domain=6

Swift Message Structure ISO 15022 and ISO 20022
SWIFT Message types are the format or schema used to send messages to financialinstitutions on the SWIFT network.
The original message types were developed by SWIFT and retrospectively made into an ISOstandard, ISO 15022.
This was later supplemented by a XML based version under ISO 20022
SWIFT MT Message
A SWIFT MT message consists of the following blocks or segments:
- {1:} Basic Header Block
- {2:} Application Header Block
- {3:} User Header Block
- {4:} Text Block
- {5:} Trailer Block
No data is included any data at this point, just the Swift message shell;
{1:}{2:}{3:}{4:
-}
{5:}
SWIFT Message Structure: Basic Header Block
The Basic Header Block provides information about the logical originator of the message
It can be identified by the starting tag {1:
It will typically consist of something like: {1:F01MYXXCODEZABC1234567890} where:
- {1: – Identifies the Block (always 1) – i.e. the Basic Header Block
- F – Indicates the Application Id – in this case, FIN
- F = FIN (financial application)
- A = GPA (general purpose application)
- L = GPA (for logins, and so on)
- 01 – Indicates the Service Id
- 01 = FIN/GPA
- 21 = ACK/NAK
- MYXXCODE– The Logical Terminal Address – which is typically your BIC 8 (MYXXCODE) + Logical Terminal Code (Z) + Branch Code(ABC)
- Logical terminal (LT) address. It is fixed at 12 characters; it must not have X in position 9.
- MYXXCODE is an invalid BIC – the real BIC must be used
- 1234 – Session Number – It is generated by the user's computer and is padded with zeros
- 567890 – Sequence Number – Sequence number that is generated by the user's computer. It is padded with zeros.
- } – Indicated the end of the Basic Header Block
SWIFT Message Structure: Application Header Block
The Application Header Block is identified by starting tag {2:
There are two types of application headers: Input and Output. Both are fixed-length and continuous with no field delimiter
And will look something like: {2:I101MYXXBANKXJKLU3003} where:
- {2: – Indicates the start of the Application Header block
- I – Informs you that you’re in Input mode (i.e. the Sender), O would indicate Output mode – so you would be the recipient of the message
- 101 – Message type – in this case, an MT101
- MYXXBANKXJKL – The recipients BIC address, consisting of their BIC (MYXXBANK) + Recipients Logical Terminal Code (X) + Recipients Branch Code (JKL)
- U = the message priority as follows
- S = System
- N=Normal
- U=Urgent
- U = the message priority as follows
- 3 – Delivery Monitoring – Ask your SWIFT contacts or Service Bureau how you should populate this, if at all – Optional
-
3 = Delivery monitoring field is as follows:
- 1 = Non delivery warning (MT010)
- 2 = Delivery notification (MT011)
- 3 = Both valid = U1 or U3, N2 or N
-
- 003 – Non-delivery notification period – again, ask your SWIFT contacts how to populate this, if at all – Optional
-
003 = Obsolescence period. It specifies when a non-delivery notification is generated as follows:
- Valid for U = 003 (15 minutes)
- Valid for N = 020 (100 minutes)
-
- } – Indicated the end of the Application Header Block
SWIFT Message Structure: User Header Block
The User Header Block will always starts {3:
And will look something like: {3:{113:SEPA}{108:ILOVESEPA}} where:
- {3: – Block ID (always 3)Indicates the start of the User Header Block
- {113:SEPA} This is an optional 4 alphanumeric bank priority code
- {108:ILOVESEPA} – Indicates the Message User Reference (MUR) value, which can be up to 16 characters, and will be returned in the ACK
- } – Indicated the end of the User Header Block
SWIFT Message Structure: Text Block
The Text Block will always starts {4:
And will look something like: {4:
Followed by the details of the message you’re sending. In this case, it is a MT101 – as indicated in Application Header Block message type. For this piece, I strongly recommend that you find and read the appropriate SWIFT message specification – in this instance SWIFT MT101 Format Specifications – and then work with your bank(s) to understand their specific message requirements.
The format, which is variable length and requires use of CRLF as a field delimiter, is as follows:
{4:CRLF
:20:PAYREFTB54302 CRLF
:32A:970103BEF1000000,CRLF
:50:CUSTOMER NAME CRLF
AND ADDRESS CRLF
:59:/123-456-789 CRLF
BENEFICIARY NAME CRLF
AND ADDRESS CRLF
-}
Finally ending with -}
The example above is of type MT100 (Customer Transfer) with only the mandatory fields completed. It is an example of the format of an ISO 7775 message structure. Block 4 fields must be in the order specified for the message type in the appropriate volume of the SWIFT User Handbook.
The format of block 4 field tags is:
:nna:
nn = Numbers
a = Optional letter, which may be present on selected tags
For example:
:20: = Transaction reference number
:58A: = Beneficiary bank
SWIFT Message Structure: Trailer Block
The Trailer Block will always starts {5:
This is usually automatically added by the systemand specified in the proprietary SWIFT implementation
And ends with }
A message always ends in a trailer with the following format:
{5: {MAC:12345678}{CHK:123456789ABC}
This block is for SWIFT system use and contains a number of fields that are denoted by keywords such as the following:
MAC
Message Authentication Code calculated based on the entire contents of the message using a key that has been exchanged with the destination and a secret algorithm. Found on message categories 1,2,4,5,7,8, most 6s and 304.
CHK
Checksum calculated for all message types.
PDE
Possible Duplicate Emission added if user thinks the same message was sent previously
DLM
Added by SWIFT if an urgent message (U) has not been delivered within 15 minutes, or a normal message (N) within 100 minutes.
Overview of SWIFT MT Categories:
| Message Type | Description |
| MT0xx | System Messages |
| MT1xx | Customer Payments and Cheques |
| MT2xx | Financial Institution Transfers |
| MT3xx | Treasury Markets |
| MT4xx | Collection and Cash Letters |
| MT5xx | Securities Markets |
| MT6xx | Treasury Markets - Metals and Syndications |
| MT7xx | Documentary Credits and Guarantees |
| MT8xx | Travellers Cheques |
| MT9xx | Cash Management and Customer Status |
All SWIFT messages include the literal "MT" (Message Type). This is followed by a three-digit number that denotes the message category, group and type. Consider the following example, which is an order to buy or sell via a third party:
- Example 1 : MT304
The first digit (3) represents the category. A category denotes messages that relate to particular financial instruments or services such as Precious Metals (6), Treasury (3), or Travellers Cheques (8). The category denoted by 3 is Treasury Markets.
The second digit (0) represents a group of related parts in a transaction life cycle. The group indicated by 0 is a Financial Institution Transfer.
The third digit (4) is the type that denotes the specific message. There are several hundred message types across the categories. The type represented by 4 is a notification.
- Example 2 : MT103
The first digit (1) represents the category. A category denotes messages that relate to particular financial instruments or services such as Cash Transfer(1), Treasury (3), or Cash Management (9). The category denoted by 1 is Cash Transfer.
The second digit (0) represents a group of related parts in a transaction life cycle. The group indicated by 0 is a Financial Institution Transfer.
The third digit (3) is the type that denotes the specific message. There are several hundred message types across the categories. The type represented by 3 is a notification.
ISO 20022 MX
A new message type expressed in XML syntax, which is more flexible and easier to implement than the previous generation of message types (MT). These message types are developed in accordance with ISO 20022 standard.
Current syntax is as following: xxxx.nnn.aaa.bb, where
- xxxx is an alphabetic code in four positions (fixed length) identifying the Business Process,
- nnn is an alphanumeric code in three positions (fixed length) identifying the Message Functionality,
- aaa is a numeric code in three positions (fixed length) identifying a particular flavour (variant) of Message Functionality,
- bb is a numeric code in two positions (fixed length) identifying the version.
Consider the following example: TREA.001.001.02
- TREA refers to ‘Treasury’
- 001 refers to ‘NDF opening (notification)’
- 001 refers to the variant
- 02 refers to the version message format, in this case version 2 of ‘NDF opening’ type.
SWIFT Standards for MX Messages:
| MX Identifier | Description |
| acmt.xxx.xxx.xx | Account Management |
| admi.xxx.xxx.xx | Administration |
| camt.xxx.xxx.xx | Cash Management |
| defp.xxx.xxx.xx | Derivatives |
| pacs.xxx.xxx.xx | Payments Clearing and Settlement |
| pain.xxx.xxx.xx | Payments Initiation |
| reda.xxx.xxx.xx | Reference Data |
| seev.xxx.xxx.xx | Securities Events |
| semt.xxx.xxx.xx | Securities Management |
| sese.xxx.xxx.xx | Securities Settlement |
| setr.xxx.xxx.xx | Securities Trade |
| trea.xxx.xxx.xx | Treasury |
| tsmt.xxx.xxx.xx | Trade Services Management |
相关文章:

SWIFT Payment
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication SWIFT——环球银行金融电信协会 SWIFT Payment Useful Link ISO 20022https://www.iso20022.org/https://www.swift.com/standards/iso-20022MT and MX Equivalence Tableshttps://www2.swift…...

数据结构之红黑树实现(全)
一、红黑树 红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉搜索树,它通过约束节点的颜色和结构来保持平衡。红黑树是由 Rudolf Bayer 在1972年发明的,被认为是一种优秀的平衡树结构,广泛应用于各种数据结构和算法中。 1.红黑树的性质 1. 每个结点是红的或者黑的…...

冷热数据分离
优质博文:IT-BLOG-CN 一、背景 随着机票业务的快速发展,订单量持续增长对业务性能带来影响,需要进行冷热数据分离。目前机票订单模块主要使用Mysql(InnoDB)作为数据库存储,历史订单信息状态修改频率低并占用大量数据库存储空间&…...

朝花夕拾:多模态图文预训练的前世今生
Diffusion Models专栏文章汇总:入门与实战 前言:时间来到2024年,多模态大模型炙手可热。在上一个时代的【多模态图文预训练】宛若时代的遗珠,本文的时间线从2019年到2022年,从BERT横空出世讲到ViT大杀四方,…...

亳州自闭症寄宿制学校,关注孩子的学习和生活
在特殊教育领域,自闭症儿童的教育与成长一直是社会各界关注的焦点。近年来,随着对自闭症认识的加深,越来越多的寄宿制学校应运而生,致力于为这些特殊的孩子提供全面、个性化的教育服务。在安徽亳州,这样的学校正努力为…...

Root me CTF all the day靶场ssrf+redis漏洞
Rootme CTF all the day靶场ssrfredis漏洞 一、环境介绍1、漏洞地址2、漏洞介绍 二、 搭建环境三、测试过程3.1 读取系统文件3.2 探测开放的服务器端口(dict协议)3.3 redis未授权访问3.3.1 利用redis来写ssh密钥(gopher协议写入)3.3.2 利用redis写定时任…...

C#中Json序列化的进阶用法
本文所有json序列化,都使用的Newtonsoft.Json包 1 JsonIgnore 在 Newtonsoft.Json 中,如果你不想将某些属性转换为 JSON 字符串,可以使用多种方法来实现。以下是几种常见的方法: 1.1 使用 [JsonIgnore] 特性 [JsonIgnore] 特性…...

IO相关的常用工具包
常用工具包Commons-io Commons-io是apache开源基金组织提供的一组有关IO操作的开源工具包。 作用:提高IO流的开发效率。 使用步骤: 1、在项目中创建一个文件夹:lib 2、将jar包复制粘贴到lib文件夹 3、右键点击jar包,选择Add as Library--->点击OK …...

Spring Boot集成RBloomFilter快速入门Demo
在大数据处理和缓存优化的场景中,布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)因其高效的空间利用和快速的查询性能而被广泛应用。RBloomFilter是布隆过滤器的一种实现,通常用于判断一个元素是否存在于一个集合中,尽管它存在一定的误判率…...

布局性能优化
布局使用不当回导致卡顿、掉帧、响应慢等问题 一、布局流程 1、应用侧会根据前端UI描述创建后端的页面节点树,其中包含了处理UI组件属性更新、布局测算、事件处理等逻辑 2、页面节点树创建完成后,UI线程会对每个元素进行测算(Measure&#…...

智云人才推荐与管理系统
1.产品介绍 产品名称:智云人才推荐与管理系统 主要功能: 智能人才匹配引擎 功能描述:利用先进的人工智能算法,根据企业岗位需求(如技能要求、工作经验、教育背景等)自动从海量人才库中筛选并推荐最合适的…...

git在远程分支上新建分支
需求: 在远程分支release/test的基础上创建一个新的分支test_20241009 确保本地仓库的信息是最新的 git fetch origin执行了 git fetch,本地仓库已经包含了 origin/release/test 的最新信息。当基于这个远程跟踪分支创建新分支时,会得到一个包…...

用Python实现的高校教师资格考试题库程序
最近朋友参加了高校教师资格考试,在考试前需要刷题来保证通过。但是教资网站上的题库只有接近考试才更新,并且官方题库的刷题效率还是有点低。 👆官方题库的样子 于是想到了是否能够将官方题库内容记录下来,然后自己创建一个高效…...

OpenVINO基本操作流程
环境配置: conda env list:可以查看有哪些环境 conda activate intel:启动某个环境 pip list:可以查看此环境下都下载了哪些软件包 from openvino.inference_engine import IEcore#从OpenVINO推理引擎中导入IECore类 import numpy as np import cv2 1&…...

Spring MVC 注解详解:@RequestBody,@RequestParam 和 @PathVariable
Spring MVC 提供了一系列注解,用于简化请求数据的获取和处理。了解并掌握这些注解的使用,对于开发RESTful API和处理HTTP请求至关重要。本文将详细介绍 RequestBody,RequestParam 和 PathVariable 注解,并附带具体的代码示例&…...

MySQL 8 中的 sql_mode
MySQL 8 中的 sql_mode 设置:提升数据库安全性与性能 在现代数据库管理中,MySQL 是一个广泛使用的开源关系型数据库。随着数据的增长和复杂性增加,良好的数据库配置显得尤为重要。sql_mode 是 MySQL 提供的一个强大功能,它可以帮…...

13种pod的状态
13种pod的状态 生命周期 Pending:Pod被创建后进入调度阶段,k8s调度器依据pod声明的资源请求量和调度规则,为pod挑选一个适合运行的节点。当集群节点不满足pod调度需求时,pod将会处于pending状态。Running:Pod被调度到节点上,k8s将pod调度到节点上后,进入running状态。S…...

2025考研今天开始预报名!攻略请查收
2025年全国硕士研究生招生考试 今天起开始预报名 有什么流程?需要准备哪些信息? 这份考研报名攻略速查收 ↓↓↓ 全国硕士研究生招生考试报名包括网上报名和网上确认两个阶段: 网上预报名时间为10月9日至10月12日(每日9࿱…...

JS中的Promise经典题目解析
这段代码很有代表性,涵盖了多个 JavaScript 知识点,特别是不同异步操作的执行优先级。 async function async1() {console.log(async1 start);await async2();console.log(async1 end); }async function async2() {console.log(async2); }console.log(s…...

【机器学习】金融预测 —— 风险管理与股市预测
我的主页:2的n次方_ 在金融领域,机器学习(ML)已经成为了不可或缺的工具。金融预测,尤其是风险管理和股市预测,涉及海量数据和复杂模式的分析,而这些正是机器学习擅长处理的领域。通过分析历…...

【Linux】shell脚本忽略错误继续执行
在 shell 脚本中,可以使用 set -e 命令来设置脚本在遇到错误时退出执行。如果你希望脚本忽略错误并继续执行,可以在脚本开头添加 set e 命令来取消该设置。 举例1 #!/bin/bash# 取消 set -e 的设置 set e# 执行命令,并忽略错误 rm somefile…...
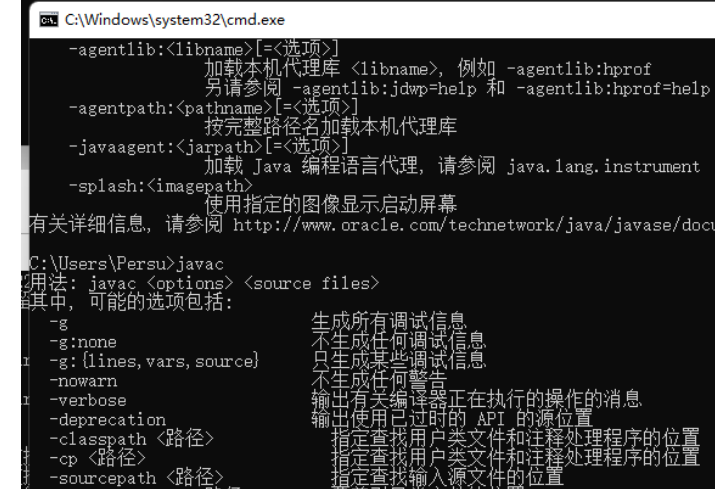
python/java环境配置
环境变量放一起 python: 1.首先下载Python Python下载地址:Download Python | Python.org downloads ---windows -- 64 2.安装Python 下面两个,然后自定义,全选 可以把前4个选上 3.环境配置 1)搜高级系统设置 2…...
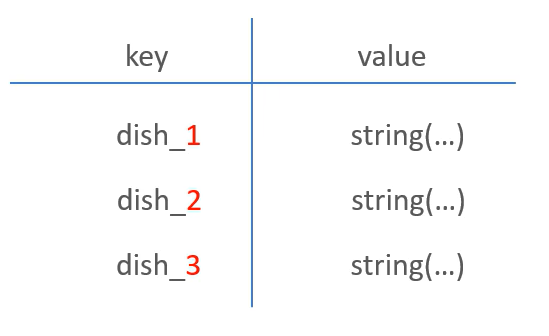
苍穹外卖--缓存菜品
1.问题说明 用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大 2.实现思路 通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。 缓存逻辑分析: ①每个分类下的菜品保持一份缓存数据…...

C++ 基础特性深度解析
目录 引言 一、命名空间(namespace) C 中的命名空间 与 C 语言的对比 二、缺省参数 C 中的缺省参数 与 C 语言的对比 三、引用(reference) C 中的引用 与 C 语言的对比 四、inline(内联函数…...

UR 协作机器人「三剑客」:精密轻量担当(UR7e)、全能协作主力(UR12e)、重型任务专家(UR15)
UR协作机器人正以其卓越性能在现代制造业自动化中扮演重要角色。UR7e、UR12e和UR15通过创新技术和精准设计满足了不同行业的多样化需求。其中,UR15以其速度、精度及人工智能准备能力成为自动化领域的重要突破。UR7e和UR12e则在负载规格和市场定位上不断优化…...

ip子接口配置及删除
配置永久生效的子接口,2个IP 都可以登录你这一台服务器。重启不失效。 永久的 [应用] vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0修改文件内内容 TYPE"Ethernet" BOOTPROTO"none" NAME"eth0" DEVICE"eth0" ONBOOT&q…...
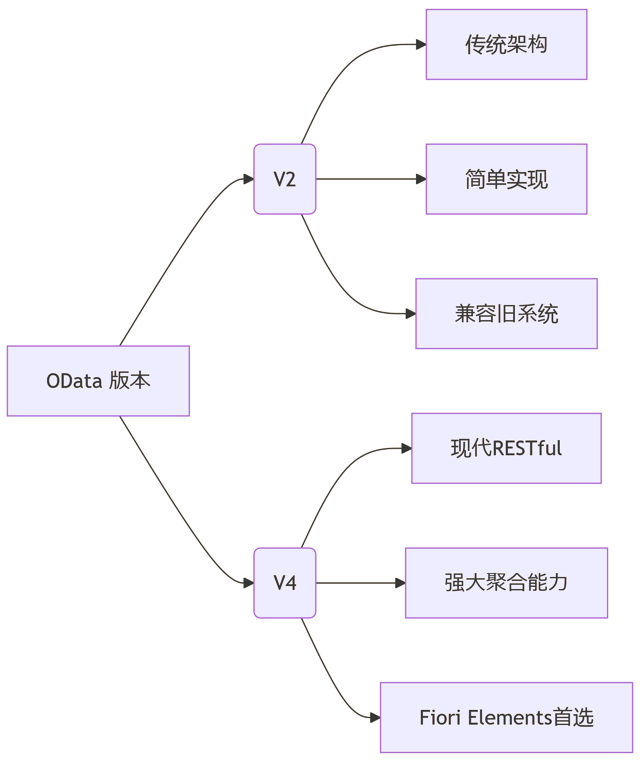
SAP学习笔记 - 开发26 - 前端Fiori开发 OData V2 和 V4 的差异 (Deepseek整理)
上一章用到了V2 的概念,其实 Fiori当中还有 V4,咱们这一章来总结一下 V2 和 V4。 SAP学习笔记 - 开发25 - 前端Fiori开发 Remote OData Service(使用远端Odata服务),代理中间件(ui5-middleware-simpleproxy)-CSDN博客…...

掌握 HTTP 请求:理解 cURL GET 语法
cURL 是一个强大的命令行工具,用于发送 HTTP 请求和与 Web 服务器交互。在 Web 开发和测试中,cURL 经常用于发送 GET 请求来获取服务器资源。本文将详细介绍 cURL GET 请求的语法和使用方法。 一、cURL 基本概念 cURL 是 "Client URL" 的缩写…...

对象回调初步研究
_OBJECT_TYPE结构分析 在介绍什么是对象回调前,首先要熟悉下结构 以我们上篇线程回调介绍过的导出的PsProcessType 结构为例,用_OBJECT_TYPE这个结构来解析它,0x80处就是今天要介绍的回调链表,但是先不着急,先把目光…...

【java】【服务器】线程上下文丢失 是指什么
目录 ■前言 ■正文开始 线程上下文的核心组成部分 为什么会出现上下文丢失? 直观示例说明 为什么上下文如此重要? 解决上下文丢失的关键 总结 ■如果我想在servlet中使用线程,代码应该如何实现 推荐方案:使用 ManagedE…...
