【C++】用红黑树封装set和map
在C++标准库中,set容器和map容器的底层都是红黑树,它们的各种接口都是基于红黑树来实现的,我们在这篇文章中已经模拟实现了红黑树 ->【C++】红黑树,接下来我们在此红黑树的基础上来看看如何封装set和map。
一、共用一颗红黑树
我们在这篇文章中 ->【C++】set容器和map容器的基本使用,清楚set是key搜索场景的结构,map是key/value搜索场景的结构。所以要用红黑树封装它们两个就需要2棵红黑树,这两颗红黑树整体逻辑差不多一样,只是结点中的元素数据类型不一样,一个是K类型,一个是pair<K,V>类型。两棵极为相似的树,只是一点不同,如果实现两个会显得冗余,那么我们就可以考虑使用模板来将结点中的数据类型泛型化,使set和map底层共用一个红黑树。
我在先前的文章中已经实现了红黑树,它是解决key/value搜索场景的,我将那篇文章的源代码裁剪了一些重要的部分,大家这里只需看懂这部分的功能:
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{pair<K, V> _kv;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent; Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv(kv), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr){}
};template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)parent = cur,cur = cur->_right;else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)parent = cur,cur = cur->_left;elsereturn false;}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED; if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first)parent->_right = cur;elseparent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED;}else {RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED;}break; }}else {Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else {RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};此时,结点中数据类型是pair,这样我们就把这个结点的数据类型写"死"了,set容器底层就不能用这个红黑树,我们要实现set和map共用一棵红黑树,所以就需要把结点的数据类型泛型化(根据传来的类型来确定具体的类型):
template<class T> //如果是set就传K,如果是map就传pair<K,V>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent; Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr){}
};那么,RBTree也要跟着改:
template<class T>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:bool Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_data.first < data.first)parent = cur,cur = cur->_right;else if (cur->_data.first > data.first)parent = cur,cur = cur->_left;elsereturn false;}cur = new Node(data);cur->_col = RED; if (parent->_data.first < data.first)parent->_right = cur;elseparent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED;}else {RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED;}break; }}else {Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else {RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};封装set:
//MySet.h
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace blue
{template<class K>class set{public:bool insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}private:RBTree<K> _t;};
}封装map:
//MyMap.h
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace blue
{template<class K,class V>class map{public:bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}private:RBTree<pair<K, V>> _t;};
}这样我们就可以通过模板参数T来控制set和map共用一棵红黑树了!
二、 红黑树中Insert带来的问题
通过观察上面红黑中Insert中的代码,其实会有问题:

我们的data可能是K类型,也可能是pair<K,V>类型。如果是后者,那么这样比较当然没问题,那如果是前者,就不能这样比较,所以我们要对这个部分进行修改。
怎么修改呢?去掉.first吗?
我们如果去掉.first,那么不管是K还是pair<K,V>都可以进行比较,以pair<K,V>类型为例,两个pair类型进行比较时先比较K,如果K相同则比较V,这与我们的本意相违背,我们的要求是只比较K的值,不能让V的值参与比较!所以我们要解决问题,不能仅仅是去掉.first。
我们可以在set和map类中写一个仿函数,通过仿函数来获取K,具体做法如下:
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace blue
{template<class K>class set{struct KeyOfSet{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:bool insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}private:RBTree<K,KeyOfSet> _t;};
}#include "RBTree.h"
namespace blue
{template<class K,class V>class map{struct KeyOfMap{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}private:RBTree<pair<K, V>,KeyOfMap> _t;};
}这时我们就需要在红黑树中加一个模板参数:

我们明确知道map是需要这个仿函数来获取K值的,但是在set中也写一个仿函数来获取K值,有人开始会觉得这是多余的,因为set中的元素类型本身就是K类型,但是不要忽略一点,set和map是共用同一份模板的,map需要这个仿函数,那么set也必须有这个仿函数,set这里的仿函数就是为了兼容map,这时,红黑树的第二个模板参数KeyOfT就出现了。
三、erase和find带的来问题
我们知道set容器和map容器都有erase和find接口,这两个接口都是根据K值来进行的,如果我们要在红黑树中实现这两个接口那么必须知道K的值,我们根据K的值来进行删除和查找。但是现在,我们自己实现的这个红黑树中并没有办法拿到K的值,也就是说在我们目前这棵红黑树中若要实现erase和find是做不到的!
为了获取K的值,我们可以在RBTree中再添加一个模板参数K,专门用来获取K的值:

在set中:

在map中:

其实,这里的set中传了两个K,第一个K就是兼容map的。因为map需要这个K,那么在TRBTree中就必须增加一个模板参数,所以set就必须传一个K。
那么在RBTree中erase和find接口就可以这样写:
bool find(const K& key)
{//...
}bool erase(const K& key)
{//...
}四、迭代器
红黑树的迭代器和我们在模拟实现list时思路是一样的,因为红黑树的底层空间是不连续的,所以我们不能直接"typedef Node* iterator",我们要单独用一个类型封装结点的指针,再通过重载运算
符实现,让迭代器具有像指针一样访问的行为:
//Ref和Ptr是为了兼容普通迭代器和const迭代器
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node; //当前结点指针RBTreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->_data);}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}
};因为set和map都是双向迭代器,所以它们的迭代器应该要支持++和--操作,由于它们的迭代器是复用红黑树的,所以红黑树中的迭代器也要实现++和--操作,list迭代器的++或--操作实现起来非常简单,只需利用next指针就好;反观红黑树,它的++/--操作要求必须满足中序遍历规则,红黑树的中序遍历是有序的,假设某棵红黑树的中序遍历是"1 3 5 6 7 9" ,如果迭代器在3这个位置,那么++后就必须到5,--后就必须到1。迭代器++的核心逻辑就是不看全局,只看局部,只考虑当前中序局部要访问的下⼀个结点。
那么如何实现++操作呢?(分为以下几种情况)
假设当前迭代器"指向"cur位置,cur的父结点为parent。
1、cur的右子树存在
++后,只需找到右子树的最左结点即可。
2、cur的右子树为空
(1)cur是parent的左孩子
直接返回parent。(此时parent就是我们需要找的结点)
(2)cur是parent的右孩子
说明以parent为根的子树已经遍历完了,接下来让cur=parent,parent=cur->_parent,然后在做判断。最坏情况下,cur = _root,parent=nullptr,这时直接返回parent即可,我们这里让结束位置为nullptr。
代码实现:
Self& operator++(){Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;if (cur->_right) //右子树不为空,找右子树的最左结点{cur = cur->_right;while (cur->_left)cur = cur->_left;_node = cur;}else{while (parent && parent->_right == cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}//直到cur是parent的左,那么parent就是我们的目标 //极端情况下,parent走到nullptr,这说明整棵树已经访问完了,直接返回nullptr(parent)_node = parent;}return *this;}那么如何实现--操作呢?(分为以下几种情况)
迭代器--的实现跟++的思路完全类似,逻辑正好反过来即可,因为它访问顺序是右子树->根结点->
左子树。
假设当前迭代器"指向"cur位置,cur的父结点为parent。
1、cur的左子树存在
--后,只需找到左子树的最右结点即可。
2、cur的左子树为空
(1)cur是parent的右孩子
直接返回parent。(此时parent就是我们需要找的结点)
(2)cur是parent的左孩子
说明以parent为根的子树已经遍历完了,接下来让cur=parent,parent=cur->_parent,然后在做判断。
代码实现:
Self& operator--(){Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;if (cur->_left) //左子树不为空,找左子树的最右结点{cur = cur->_left;while (cur->_right)cur = cur->_right;_node = cur;}else{while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}//直到cur是parent的右,那么parent就是我们的目标 _node = parent;}return *this;}完成这一步,我们迭代器的封装任务差不多已经完成了,接下来我们需要在红黑树中实现Begin和End:
public:typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator; //普通迭代器typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T&,const T*> ConstIterator; //const迭代器Iterator Begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur->_left)cur = cur->_left;return Iterator(cur);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr); //我们这里让nullptr当最终结点}ConstIterator Begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur->_left)cur = cur->_left;return ConstIterator(cur);}ConstIterator End() const{return ConstIterator(nullptr);}在set中:
public:typedef typename RBTree<K, K, KeyOfSet>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, KeyOfSet>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}
在map中:
public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, KeyOfMap>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, KeyOfMap>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}我们大致的任务已经完成了,接下来我们来写一段代码验证一下(看看是否会出现错误):
//Test.cpp
#include "MyMap.h"
#include "MySet.h"void TestSet()
{blue::set<int> s;s.insert(5);s.insert(1);s.insert(3);s.insert(2);s.insert(6);blue::set<int>::iterator sit = s.begin();while (sit != s.end()){cout << *sit << " ";++sit;}cout << endl;
}void TestMap()
{blue::map<string, string> dict;dict.insert({ "sort", "排序" });dict.insert({ "left", "左边" });dict.insert({ "right", "右边" });blue::map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();while (it != dict.end()){cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;
}int main()
{TestSet();cout << "-----------------------" << endl;TestMap();return 0;
}运行结果:

运行结果暂时没有什么问题。
这里有一个bug,看下面测试代码:
void Print(const blue::set<int>& s)
{bit::set<int>::const_iterator it = s.end();while (it != s.begin()){--it;cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;
}我们上面将end()指向nullptr,那么如果逆向遍历,--it就会出现错误,所以我们在--it时先判断一下,如果指向空,那么就修改_node为红黑树的最后一个结点,那么,问题又来了,怎么获得最后一个结点呢?所以我们需要知道红黑树的头结点,所以,我们在RBTreeIterator这个类中还需要一个成员变量来记录根节点:

修改operator--如下:
Self& operator--() {if (_node == nullptr){Node* cur = _root;while (cur->_right)cur = cur->_right;_node = cur;return *this;}Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;if (cur->_left) //左子树不为空,找左子树的最右结点{cur = cur->_left;while (cur->_right)cur = cur->_right;_node = cur;}else{while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}//直到cur是parent的右,那么parent就是我们的目标 _node = parent;}return *this;}解决完上述问题,还有一个问题,set和map中的K的值是不允许修改的,因为若修改就可能会破坏红黑树的结构,但我们写的代码中通过普通迭代器是能够修改的,如果要解决可以这样修改:
在set中:

在map中:

五、[]
好了,好了,到这里我们将上面的坑都踩完了,接下来最后最后一个功能,也是比较重要的,就是处理map中[]的实现逻辑:
map中的[]的逻辑其实就是利用了insert接口。
我们在红黑树中实现Insert的返回值是bool,接下来我们将它改为pair<Iterator,bool>类型:
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;//return true;return { Iterator(_root, _root),true };}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))parent = cur, cur = cur->_right;else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))parent = cur, cur = cur->_left;else//return false;return { Iterator(cur, _root),false };}cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_col = RED; if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))parent->_right = cur;elseparent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED;}else {RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED;}break; }}else {Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else {RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;//return true;return { Iterator(newnode, _root),true };
}完成对Insert的调整后,在set和map的insert也要跟着调:
在set中:

在map中:

接下来,我们就着手实现[],在map中:
V& operator[](const K& key)
{pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({ key,V() });return (ret.first)->second;
}是不是非常简单!
六、其他问题
1、构造函数
RBTree() = default;2、拷贝构造
RBTree(const RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>& t)
{_root = Copy(t._root);
}Node* Copy(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;Node* newnode = new Node(root->_data);newnode->_left = Copy(root->_left);newnode->_right = Copy(root->_right);return newnode;
}3、赋值重载
RBTree& operator=(RBTree tmp)
{swap(tmp._root);return *this;
}4、析构函数
~RBTree()
{Destroy(_root);_root = nullptr;
}void Destroy(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr)return;Destroy(root->_left);Destroy(root->_right);delete root;
}七、源码
(1)RBTree.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;enum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent; Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr){}
};//Ref和Ptr是为了兼容普通迭代器和const迭代器
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node; //当前结点指针Node* _root; //记录红黑树的根结点RBTreeIterator(Node* node,Node* root):_node(node),_root(root){}Self& operator++() {Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;if (cur->_right) //右子树不为空,找右子树的最左结点{cur = cur->_right;while (cur->_left)cur = cur->_left;_node = cur;}else{while (parent && parent->_right == cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}//直到cur是parent的左,那么parent就是我们的目标 //极端情况下,parent走到nullptr,这说明整棵树已经访问完了,直接返回nullptr(parent) _node = parent;}return *this;}Self& operator--() {if (_node == nullptr){Node* cur = _root;while (cur->_right)cur = cur->_right;_node = cur;return *this;}Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;if (cur->_left) //左子树不为空,找左子树的最右结点{cur = cur->_left;while (cur->_right)cur = cur->_right;_node = cur;}else{while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}//直到cur是parent的右,那么parent就是我们的目标 _node = parent;}return *this;}Ref operator*() const{return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->() const{return &(_node->_data);}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return _node == s._node;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return _node != s._node;}
};template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
public:RBTree() = default;RBTree(const RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>& t){_root = Copy(t._root);}RBTree& operator=(RBTree tmp){swap(tmp._root);return *this;}~RBTree(){Destroy(_root);_root = nullptr;}public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T&,const T*> ConstIterator;Iterator Begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur->_left)cur = cur->_left;return Iterator(cur,_root);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr,_root);}ConstIterator Begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur->_left)cur = cur->_left;return ConstIterator(cur,_root);}ConstIterator End() const{return ConstIterator(nullptr,_root);}public:pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;//return true;return { Iterator(_root,_root),true };}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))parent = cur, cur = cur->_right;else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))parent = cur, cur = cur->_left;else//return false;return { Iterator(cur,_root),false };}cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_col = RED; if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))parent->_right = cur;elseparent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED;}else {RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED;}break; }}else {Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else {RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;//return true;return { Iterator(newnode,_root),true };}private:void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* pParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pParent->_left == parent)pParent->_left = subL;elsepParent->_right = subL;subL->_parent = pParent;}}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parentParent == nullptr){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == parentParent->_left)parentParent->_left = subR;elseparentParent->_right = subR;subR->_parent = parentParent;}}Node* Copy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;Node* newnode = new Node(root->_data);newnode->_left = Copy(root->_left);newnode->_right = Copy(root->_right);return newnode;}void Destroy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;Destroy(root->_left);Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};(2)MySet.h
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace blue
{template<class K>class set{struct KeyOfSet{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, KeyOfSet>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, KeyOfSet>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}public:pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}private:RBTree<K, const K, KeyOfSet> _t;};
}(3)MyMap.h
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace blue
{template<class K,class V>class map{struct KeyOfMap{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyOfMap>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyOfMap>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}public:pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({ key,V() });return (ret.first)->second;}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyOfMap> _t;};
}(4)Test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "MyMap.h"
#include "MySet.h"void Print(const blue::set<int>& s)
{blue::set<int>::const_iterator it = s.end();while (it != s.begin()){--it;cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;
}void TestSet()
{blue::set<int> s;s.insert(5);s.insert(1);s.insert(3);s.insert(2);s.insert(6);blue::set<int>::iterator sit = s.begin();//*sit += 10;while (sit != s.end()){cout << *sit << " ";++sit;}cout << endl;Print(s);}void TestMap()
{blue::map<string, string> dict;dict.insert({ "sort", "排序" });dict.insert({ "left", "左边" });dict.insert({ "right", "右边" });dict["left"] = "左边,剩余";dict["insert"] = "插入";dict["string"];blue::map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();while (it != dict.end()){// 不能修改first,可以修改second//it->first += 'x';it->second += 'x';cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;
}int main()
{TestSet();cout << "-----------------------" << endl;TestMap();return 0;
}八、总结
本篇内容到这里就结束啦,主要讲了如何用红黑树来封装set和map容器,希望对大家有帮助,祝生活愉快!
相关文章:

【C++】用红黑树封装set和map
在C标准库中,set容器和map容器的底层都是红黑树,它们的各种接口都是基于红黑树来实现的,我们在这篇文章中已经模拟实现了红黑树 ->【C】红黑树,接下来我们在此红黑树的基础上来看看如何封装set和map。 一、共用一颗红黑树 我…...

【大数据测试HDFS + Flask详细教程与实例】
大数据测试HDFS Flask 1. 环境准备安装工具安装Hadoop(以单机模式为例)安装Flask和HDFS Python客户端 2. HDFS Flask基本架构基本文件结构 3. 创建Flask应用与与HDFS交互步骤1:配置HDFS连接步骤2:构建Flask应用 4. 创建前端界面…...

高级java每日一道面试题-2024年10月31日-RabbitMQ篇-RabbitMQ中vhost的作用是什么?
如果有遗漏,评论区告诉我进行补充 面试官: RabbitMQ中vhost的作用是什么? 我回答: 在Java高级面试中,关于RabbitMQ中vhost(虚拟主机)的作用是一个重要且常见的考点。以下是对vhost的详细解释: 一、vhost的基本概念 vhost&am…...

【日常记录-Java】代码配置Logback
1. 简介 在Logback中,推荐使用配置文件(如logback.xml或logback-spring.xml)来设置日志记录的行为。但在实际应用中,会有动态配置logback的需求。此时可通过编程的方式直接操作LoggerContext以及相关的Logger、Appender、Encoder等…...

HTTP常见的请求头有哪些?都有什么作用?在 Web 应用中使用这些请求头?
HTTP 请求头(Request Headers)用于在 HTTP 请求中携带额外的信息,帮助服务器更好地处理请求。以下是一些常见的 HTTP 请求头及其作用: 常见请求头及其作用 1. Accept 作用:告知服务器客户端可以接受的内容类型。示例…...

电信数据清洗案例:利用MapReduce实现高效数据预处理
电信数据清洗案例:利用MapReduce实现高效数据预处理 在大数据时代,电信行业积累了大量的用户通话、短信、上网等行为数据。在数据分析和机器学习模型训练前,对这些数据进行清洗是至关重要的一步。MapReduce 是一种高效的数据处理模型&#x…...

react 中 FC 模块作用
React.FC 是一个泛型类型,用于定义函数组件的类型 一、类型定义和代码可读性 1. 明确组件类型 使用React.FC定义一个组件时,使得组件的输入(props)和输出(返回的 React 元素)都有明确的类型定义。 impo…...
--CLIP)
多模态大模型(1)--CLIP
CLIP(Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training)模型是一种多模态预训练神经网络,由OpenAI在2021年发布。它通过对比学习的方式,将图像和文本映射到同一个向量空间中,从而实现跨模态的检索和分类。下面介绍其基础功能&…...

opencv入门学习总结
opencv学习总结 不多bb,直接上代码!!! 案例一: import cv2 # 返回当前安装的 OpenCV 库的版本信息 并且是字符串格式 print(cv2.getVersionString()) """ 作用:它可以读取不同格式的图像文…...

C/C++内存管理 | new的机制 | 重载自己的operator new
一、C/C内存分布 1. 内存分区 栈又叫堆栈–非静态局部变量/函数参数/返回值等等,栈是向下增长的。内存映射段是高效的I/O映射方式,用于装载一个共享的动态内存库。用户可使用系统接口创建共享共享内存,做进程间通信 .堆用于程序运行时动态内…...

知识库管理系统:企业数字化转型的加速器
在数字化转型的大潮中,知识库管理系统(KBMS)已成为企业提升效率和创新能力的关键工具。本文将探讨知识库管理系统的定义、企业建立知识库的必要性,以及如何快速搭建企业知识库。 知识库管理系统是什么? 知识库管理系统…...
)
uniapp 如何使用vuex store (亲测)
首先是安装: npm install vuexnext --save 安装之后,Vue2 这样写 不管在哪里,建立一个JS文件,假设命名:store.js 代码这样写: import Vue from vue; import Vuex from vuex;Vue.use(Vuex);const store…...

[编译报错]ImportError: No module named _sqlite3解决办法
1. 问题描述: 在使用python进行代码编译时,提示下面报错: "/home/bspuser/BaseTools/Source/Python/Workspace/WorkspaceDatabase.py", line 18, in <module>import sqlite3File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/sqlite3/_…...

【旷视科技-注册/登录安全分析报告】
前言 由于网站注册入口容易被黑客攻击,存在如下安全问题: 暴力破解密码,造成用户信息泄露短信盗刷的安全问题,影响业务及导致用户投诉带来经济损失,尤其是后付费客户,风险巨大,造成亏损无底洞…...

python学习记录16
字符串总结 python程序使用unicode编码,中文字符与英文字符都占一个字符,但英文字符只占一个字节,中文字符若按照utf-8格式编码占3个字节。 (1)字符串常用方法 1)大小写转化 string.upper()#将所有字母…...

AI 大模型在软件开发中的角色

React中类组件和函数组件的理解和区别
react代码模块分为类组件和函数组件。 从语法和定义、内部状态管理、生命周期、性能、可读性和维护性、上下文、集成状态管理库等角度对比React中类组件和函数组件。 1、语法和定义 类组件: 使用 ES6 的类(class)语法定义的 React 组件。…...
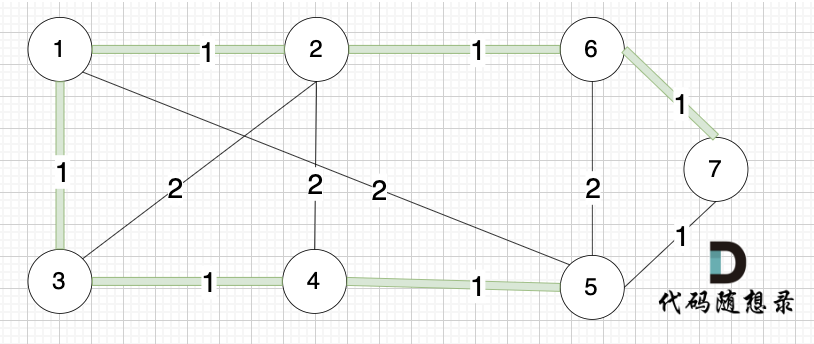
Day62||prim算法精讲 |kruskal算法精讲
prim算法精讲 53. 寻宝(第七期模拟笔试) 题目描述 在世界的某个区域,有一些分散的神秘岛屿,每个岛屿上都有一种珍稀的资源或者宝藏。国王打算在这些岛屿上建公路,方便运输。 不同岛屿之间,路途距离不同&…...

upload-labs通关练习
目录 环境搭建 第一关 第二关 第三关 第四关 第五关 第六关 第七关 第八关 第九关 第十关 第十一关 第十二关 第十三关 第十四关 第十五关 第十六关 第十七关 第十八关 第十九关 第二十关 总结 环境搭建 upload-labs是一个使用php语言编写的,…...

wordpress搭建主题可配置json
网站首页展示 在线访问链接 http://dahua.bloggo.chat/ 配置json文件 我使用的是argon主题,你需要先安装好主题,然后可以导入我的json文件一键配置。 需要json界面配置文件的,可以在评论区回复,看见评论我会私发给你。~...

在软件开发中正确使用MySQL日期时间类型的深度解析
在日常软件开发场景中,时间信息的存储是底层且核心的需求。从金融交易的精确记账时间、用户操作的行为日志,到供应链系统的物流节点时间戳,时间数据的准确性直接决定业务逻辑的可靠性。MySQL作为主流关系型数据库,其日期时间类型的…...
label-studio的使用教程(导入本地路径)
文章目录 1. 准备环境2. 脚本启动2.1 Windows2.2 Linux 3. 安装label-studio机器学习后端3.1 pip安装(推荐)3.2 GitHub仓库安装 4. 后端配置4.1 yolo环境4.2 引入后端模型4.3 修改脚本4.4 启动后端 5. 标注工程5.1 创建工程5.2 配置图片路径5.3 配置工程类型标签5.4 配置模型5.…...
Map相关知识
数据结构 二叉树 二叉树,顾名思义,每个节点最多有两个“叉”,也就是两个子节点,分别是左子 节点和右子节点。不过,二叉树并不要求每个节点都有两个子节点,有的节点只 有左子节点,有的节点只有…...
企业如何增强终端安全?
在数字化转型加速的今天,企业的业务运行越来越依赖于终端设备。从员工的笔记本电脑、智能手机,到工厂里的物联网设备、智能传感器,这些终端构成了企业与外部世界连接的 “神经末梢”。然而,随着远程办公的常态化和设备接入的爆炸式…...

【Java学习笔记】BigInteger 和 BigDecimal 类
BigInteger 和 BigDecimal 类 二者共有的常见方法 方法功能add加subtract减multiply乘divide除 注意点:传参类型必须是类对象 一、BigInteger 1. 作用:适合保存比较大的整型数 2. 使用说明 创建BigInteger对象 传入字符串 3. 代码示例 import j…...

IP如何挑?2025年海外专线IP如何购买?
你花了时间和预算买了IP,结果IP质量不佳,项目效率低下不说,还可能带来莫名的网络问题,是不是太闹心了?尤其是在面对海外专线IP时,到底怎么才能买到适合自己的呢?所以,挑IP绝对是个技…...

Scrapy-Redis分布式爬虫架构的可扩展性与容错性增强:基于微服务与容器化的解决方案
在大数据时代,海量数据的采集与处理成为企业和研究机构获取信息的关键环节。Scrapy-Redis作为一种经典的分布式爬虫架构,在处理大规模数据抓取任务时展现出强大的能力。然而,随着业务规模的不断扩大和数据抓取需求的日益复杂,传统…...
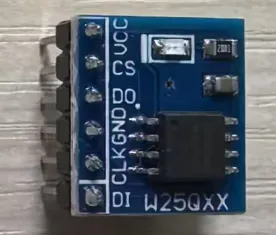
基于stm32F10x 系列微控制器的智能电子琴(附完整项目源码、详细接线及讲解视频)
注:文章末尾网盘链接中自取成品使用演示视频、项目源码、项目文档 所用硬件:STM32F103C8T6、无源蜂鸣器、44矩阵键盘、flash存储模块、OLED显示屏、RGB三色灯、面包板、杜邦线、usb转ttl串口 stm32f103c8t6 面包板 …...

大数据驱动企业决策智能化的路径与实践
📝个人主页🌹:慌ZHANG-CSDN博客 🌹🌹期待您的关注 🌹🌹 一、引言:数据驱动的企业竞争力重构 在这个瞬息万变的商业时代,“快者胜”的竞争逻辑愈发明显。企业如何在复杂环…...

shell脚本质数判断
shell脚本质数判断 shell输入一个正整数,判断是否为质数(素数)shell求1-100内的质数shell求给定数组输出其中的质数 shell输入一个正整数,判断是否为质数(素数) 思路: 1:1 2:1 2 3:1 2 3 4:1 2 3 4 5:1 2 3 4 5-------> 3:2 4:2 3 5:2 3…...
