【数值特性库】入口文件
数值特性库入口文件为lib.rs。该文件定义一系列数字特性的trait(特征),这些特性可以被不同的数字类型实现,从而提供一套通用的数值操作方法。下面是对代码中关键部分的解释:
一、基础设置
- #![doc(html_root_url = “https://docs.rs/num-traits/0.2”)]:指定了文档的根URL,用于在线文档生成。
- #![deny(unconditional_recursion)]:禁止无条件递归,这是一种编译时检查,防止无限递归。
- #![no_std]:表明这个crate不依赖Rust标准库,使其可以在没有标准库的环境(如裸机或嵌入式系统)中使用。
二、条件编译
- #[cfg(feature = “std”)]:当启用std特性时,编译这部分代码。这通常用于在有无标准库支持时提供不同的实现。
三、引入依赖
- 引入了Rust核心库中的一些基本功能,如格式化(fmt)、包装类型(Wrapping)、基本的算术操作(Add, Div, Mul, Rem, Sub等)及其赋值操作(AddAssign, DivAssign, MulAssign, RemAssign, SubAssign)。
四、公开的特性
- 通过pub use语句,公开了库中定义的一系列特性(traits)和常量,使得外部可以直接通过这些路径访问它们。例如,Bounded用于表示有边界的数字类型,Float和FloatConst提供了浮点数的操作和常量,NumCast用于类型转换等。
五、核心trait定义:
- Num:定义了数值类型的基础特性,包括比较、基本数值操作、字符串转换等。
- NumOps:为实现了基本算术运算符(+, -, *, /, %)的类型自动实现。
- NumRef和RefNum:提供了对引用类型数值操作的支持。
- NumAssignOps:为实现了赋值运算符(如+=, -=)的类型自动实现。
六、宏和模块:
- 通过#[macro_use]引入了宏定义(在macros模块中),这些宏可能用于简化代码或提供额外的功能。
- 定义了多个模块(如bounds, cast, float, identities, int, ops, pow, real, sign),每个模块都负责特定的数值操作或特性。
七、总结及源码
整体而言,这段代码定义了一个丰富的数字特性库,为Rust中的数值类型提供了一套通用的接口和操作方法。通过实现这些trait,不同的数值类型可以享受到这些通用操作带来的便利,同时也为开发者提供了一种灵活的方式来处理不同类型的数值。源码如下:
//!为泛型准备的数字特征库 #![doc(html_root_url = "https://docs.rs/num-traits/0.2")]
#![deny(unconditional_recursion)]
#![no_std]// 需要显式地将crate引入固有的float方法。Need to explicitly bring the crate in for inherent float methods
#[cfg(feature = "std")]
extern crate std;use core::fmt;
use core::num::Wrapping;
use core::ops::{Add, Div, Mul, Rem, Sub};
use core::ops::{AddAssign, DivAssign, MulAssign, RemAssign, SubAssign};pub use crate::bounds::Bounded; // 1 边界特性
#[cfg(any(feature = "std", feature = "libm"))]
pub use crate::float::Float; // 2
pub use crate::float::FloatConst; // 3pub use crate::cast::{cast, AsPrimitive, FromPrimitive, NumCast, ToPrimitive}; // 4
pub use crate::identities::{one, zero, ConstOne, ConstZero, One, Zero}; // 5
pub use crate::int::PrimInt; // 6
pub use crate::ops::bytes::{FromBytes, ToBytes}; // 7
pub use crate::ops::checked::{CheckedAdd, CheckedDiv, CheckedMul, CheckedNeg, CheckedRem, CheckedShl, CheckedShr, CheckedSub,
}; // 8
pub use crate::ops::euclid::{CheckedEuclid, Euclid}; // 9
pub use crate::ops::inv::Inv; // 10
pub use crate::ops::mul_add::{MulAdd, MulAddAssign}; // 11
pub use crate::ops::saturating::{Saturating, SaturatingAdd, SaturatingMul, SaturatingSub}; // 12
pub use crate::ops::wrapping::{WrappingAdd, WrappingMul, WrappingNeg, WrappingShl, WrappingShr, WrappingSub,
}; // 13
pub use crate::pow::{checked_pow, pow, Pow}; // 14
pub use crate::sign::{abs, abs_sub, signum, Signed, Unsigned}; // 15#[macro_use]
mod macros;pub mod bounds;
pub mod cast;
pub mod float;
pub mod identities;
pub mod int;
pub mod ops;
pub mod pow;
pub mod real;
pub mod sign;/// The base trait for numeric types, covering `0` and `1` values,
/// comparisons, basic numeric operations, and string conversion.
pub trait Num: PartialEq + Zero + One + NumOps {type FromStrRadixErr;/// Convert from a string and radix (typically `2..=36`).////// # Examples////// ```rust/// use num_traits::Num;////// let result = <i32 as Num>::from_str_radix("27", 10);/// assert_eq!(result, Ok(27));////// let result = <i32 as Num>::from_str_radix("foo", 10);/// assert!(result.is_err());/// ```////// # Supported radices////// The exact range of supported radices is at the discretion of each type implementation. For/// primitive integers, this is implemented by the inherent `from_str_radix` methods in the/// standard library, which **panic** if the radix is not in the range from 2 to 36. The/// implementation in this crate for primitive floats is similar.////// For third-party types, it is suggested that implementations should follow suit and at least/// accept `2..=36` without panicking, but an `Err` may be returned for any unsupported radix./// It's possible that a type might not even support the common radix 10, nor any, if string/// parsing doesn't make sense for that type.fn from_str_radix(str: &str, radix: u32) -> Result<Self, Self::FromStrRadixErr>;
}/// Generic trait for types implementing basic numeric operations
///
/// This is automatically implemented for types which implement the operators.
pub trait NumOps<Rhs = Self, Output = Self>:Add<Rhs, Output = Output>+ Sub<Rhs, Output = Output>+ Mul<Rhs, Output = Output>+ Div<Rhs, Output = Output>+ Rem<Rhs, Output = Output>
{
}impl<T, Rhs, Output> NumOps<Rhs, Output> for T whereT: Add<Rhs, Output = Output>+ Sub<Rhs, Output = Output>+ Mul<Rhs, Output = Output>+ Div<Rhs, Output = Output>+ Rem<Rhs, Output = Output>
{
}/// The trait for `Num` types which also implement numeric operations taking
/// the second operand by reference.
///
/// This is automatically implemented for types which implement the operators.
pub trait NumRef: Num + for<'r> NumOps<&'r Self> {}
impl<T> NumRef for T where T: Num + for<'r> NumOps<&'r T> {}/// The trait for `Num` references which implement numeric operations, taking the
/// second operand either by value or by reference.
///
/// This is automatically implemented for all types which implement the operators. It covers
/// every type implementing the operations though, regardless of it being a reference or
/// related to `Num`.
pub trait RefNum<Base>: NumOps<Base, Base> + for<'r> NumOps<&'r Base, Base> {}
impl<T, Base> RefNum<Base> for T where T: NumOps<Base, Base> + for<'r> NumOps<&'r Base, Base> {}/// Generic trait for types implementing numeric assignment operators (like `+=`).
///
/// This is automatically implemented for types which implement the operators.
pub trait NumAssignOps<Rhs = Self>:AddAssign<Rhs> + SubAssign<Rhs> + MulAssign<Rhs> + DivAssign<Rhs> + RemAssign<Rhs>
{
}impl<T, Rhs> NumAssignOps<Rhs> for T whereT: AddAssign<Rhs> + SubAssign<Rhs> + MulAssign<Rhs> + DivAssign<Rhs> + RemAssign<Rhs>
{
}/// The trait for `Num` types which also implement assignment operators.
///
/// This is automatically implemented for types which implement the operators.
pub trait NumAssign: Num + NumAssignOps {}
impl<T> NumAssign for T where T: Num + NumAssignOps {}/// The trait for `NumAssign` types which also implement assignment operations
/// taking the second operand by reference.
///
/// This is automatically implemented for types which implement the operators.
pub trait NumAssignRef: NumAssign + for<'r> NumAssignOps<&'r Self> {}
impl<T> NumAssignRef for T where T: NumAssign + for<'r> NumAssignOps<&'r T> {}macro_rules! int_trait_impl {($name:ident for $($t:ty)*) => ($(impl $name for $t {type FromStrRadixErr = ::core::num::ParseIntError;#[inline]fn from_str_radix(s: &str, radix: u32)-> Result<Self, ::core::num::ParseIntError>{<$t>::from_str_radix(s, radix)}})*)
}
int_trait_impl!(Num for usize u8 u16 u32 u64 u128);
int_trait_impl!(Num for isize i8 i16 i32 i64 i128);impl<T: Num> Num for Wrapping<T>
whereWrapping<T>: NumOps,
{type FromStrRadixErr = T::FromStrRadixErr;fn from_str_radix(str: &str, radix: u32) -> Result<Self, Self::FromStrRadixErr> {T::from_str_radix(str, radix).map(Wrapping)}
}#[derive(Debug)]
pub enum FloatErrorKind {Empty,Invalid,
}
// FIXME: core::num::ParseFloatError is stable in 1.0, but opaque to us,
// so there's not really any way for us to reuse it.
#[derive(Debug)]
pub struct ParseFloatError {pub kind: FloatErrorKind,
}impl fmt::Display for ParseFloatError {fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter<'_>) -> fmt::Result {let description = match self.kind {FloatErrorKind::Empty => "cannot parse float from empty string",FloatErrorKind::Invalid => "invalid float literal",};description.fmt(f)}
}fn str_to_ascii_lower_eq_str(a: &str, b: &str) -> bool {a.len() == b.len()&& a.bytes().zip(b.bytes()).all(|(a, b)| {let a_to_ascii_lower = a | (((b'A' <= a && a <= b'Z') as u8) << 5);a_to_ascii_lower == b})
}// FIXME: The standard library from_str_radix on floats was deprecated, so we're stuck
// with this implementation ourselves until we want to make a breaking change.
// (would have to drop it from `Num` though)
macro_rules! float_trait_impl {($name:ident for $($t:ident)*) => ($(impl $name for $t {type FromStrRadixErr = ParseFloatError;fn from_str_radix(src: &str, radix: u32)-> Result<Self, Self::FromStrRadixErr>{use self::FloatErrorKind::*;use self::ParseFloatError as PFE;// Special case radix 10 to use more accurate standard library implementationif radix == 10 {return src.parse().map_err(|_| PFE {kind: if src.is_empty() { Empty } else { Invalid },});}// Special valuesif str_to_ascii_lower_eq_str(src, "inf")|| str_to_ascii_lower_eq_str(src, "infinity"){return Ok(core::$t::INFINITY);} else if str_to_ascii_lower_eq_str(src, "-inf")|| str_to_ascii_lower_eq_str(src, "-infinity"){return Ok(core::$t::NEG_INFINITY);} else if str_to_ascii_lower_eq_str(src, "nan") {return Ok(core::$t::NAN);} else if str_to_ascii_lower_eq_str(src, "-nan") {return Ok(-core::$t::NAN);}fn slice_shift_char(src: &str) -> Option<(char, &str)> {let mut chars = src.chars();Some((chars.next()?, chars.as_str()))}let (is_positive, src) = match slice_shift_char(src) {None => return Err(PFE { kind: Empty }),Some(('-', "")) => return Err(PFE { kind: Empty }),Some(('-', src)) => (false, src),Some((_, _)) => (true, src),};// The significand to accumulatelet mut sig = if is_positive { 0.0 } else { -0.0 };// Necessary to detect overflowlet mut prev_sig = sig;let mut cs = src.chars().enumerate();// Exponent prefix and exponent index offsetlet mut exp_info = None::<(char, usize)>;// Parse the integer part of the significandfor (i, c) in cs.by_ref() {match c.to_digit(radix) {Some(digit) => {// shift significand one digit leftsig *= radix as $t;// add/subtract current digit depending on signif is_positive {sig += (digit as isize) as $t;} else {sig -= (digit as isize) as $t;}// Detect overflow by comparing to last value, except// if we've not seen any non-zero digits.if prev_sig != 0.0 {if is_positive && sig <= prev_sig{ return Ok(core::$t::INFINITY); }if !is_positive && sig >= prev_sig{ return Ok(core::$t::NEG_INFINITY); }// Detect overflow by reversing the shift-and-add processif is_positive && (prev_sig != (sig - digit as $t) / radix as $t){ return Ok(core::$t::INFINITY); }if !is_positive && (prev_sig != (sig + digit as $t) / radix as $t){ return Ok(core::$t::NEG_INFINITY); }}prev_sig = sig;},None => match c {'e' | 'E' | 'p' | 'P' => {exp_info = Some((c, i + 1));break; // start of exponent},'.' => {break; // start of fractional part},_ => {return Err(PFE { kind: Invalid });},},}}// If we are not yet at the exponent parse the fractional// part of the significandif exp_info.is_none() {let mut power = 1.0;for (i, c) in cs.by_ref() {match c.to_digit(radix) {Some(digit) => {// Decrease power one order of magnitudepower /= radix as $t;// add/subtract current digit depending on signsig = if is_positive {sig + (digit as $t) * power} else {sig - (digit as $t) * power};// Detect overflow by comparing to last valueif is_positive && sig < prev_sig{ return Ok(core::$t::INFINITY); }if !is_positive && sig > prev_sig{ return Ok(core::$t::NEG_INFINITY); }prev_sig = sig;},None => match c {'e' | 'E' | 'p' | 'P' => {exp_info = Some((c, i + 1));break; // start of exponent},_ => {return Err(PFE { kind: Invalid });},},}}}// Parse and calculate the exponentlet exp = match exp_info {Some((c, offset)) => {let base = match c {'E' | 'e' if radix == 10 => 10.0,'P' | 'p' if radix == 16 => 2.0,_ => return Err(PFE { kind: Invalid }),};// Parse the exponent as decimal integerlet src = &src[offset..];let (is_positive, exp) = match slice_shift_char(src) {Some(('-', src)) => (false, src.parse::<usize>()),Some(('+', src)) => (true, src.parse::<usize>()),Some((_, _)) => (true, src.parse::<usize>()),None => return Err(PFE { kind: Invalid }),};#[cfg(feature = "std")]fn pow(base: $t, exp: usize) -> $t {Float::powi(base, exp as i32)}// otherwise uses the generic `pow` from the rootmatch (is_positive, exp) {(true, Ok(exp)) => pow(base, exp),(false, Ok(exp)) => 1.0 / pow(base, exp),(_, Err(_)) => return Err(PFE { kind: Invalid }),}},None => 1.0, // no exponent};Ok(sig * exp)}})*)
}
float_trait_impl!(Num for f32 f64);/// A value bounded by a minimum and a maximum
///
/// If input is less than min then this returns min.
/// If input is greater than max then this returns max.
/// Otherwise this returns input.
///
/// **Panics** in debug mode if `!(min <= max)`.
#[inline]
pub fn clamp<T: PartialOrd>(input: T, min: T, max: T) -> T {debug_assert!(min <= max, "min must be less than or equal to max");if input < min {min} else if input > max {max} else {input}
}/// A value bounded by a minimum value
///
/// If input is less than min then this returns min.
/// Otherwise this returns input.
/// `clamp_min(std::f32::NAN, 1.0)` preserves `NAN` different from `f32::min(std::f32::NAN, 1.0)`.
///
/// **Panics** in debug mode if `!(min == min)`. (This occurs if `min` is `NAN`.)
#[inline]
#[allow(clippy::eq_op)]
pub fn clamp_min<T: PartialOrd>(input: T, min: T) -> T {debug_assert!(min == min, "min must not be NAN");if input < min {min} else {input}
}/// A value bounded by a maximum value
///
/// If input is greater than max then this returns max.
/// Otherwise this returns input.
/// `clamp_max(std::f32::NAN, 1.0)` preserves `NAN` different from `f32::max(std::f32::NAN, 1.0)`.
///
/// **Panics** in debug mode if `!(max == max)`. (This occurs if `max` is `NAN`.)
#[inline]
#[allow(clippy::eq_op)]
pub fn clamp_max<T: PartialOrd>(input: T, max: T) -> T {debug_assert!(max == max, "max must not be NAN");if input > max {max} else {input}
}#[test]
fn clamp_test() {// Int testassert_eq!(1, clamp(1, -1, 2));assert_eq!(-1, clamp(-2, -1, 2));assert_eq!(2, clamp(3, -1, 2));assert_eq!(1, clamp_min(1, -1));assert_eq!(-1, clamp_min(-2, -1));assert_eq!(-1, clamp_max(1, -1));assert_eq!(-2, clamp_max(-2, -1));// Float testassert_eq!(1.0, clamp(1.0, -1.0, 2.0));assert_eq!(-1.0, clamp(-2.0, -1.0, 2.0));assert_eq!(2.0, clamp(3.0, -1.0, 2.0));assert_eq!(1.0, clamp_min(1.0, -1.0));assert_eq!(-1.0, clamp_min(-2.0, -1.0));assert_eq!(-1.0, clamp_max(1.0, -1.0));assert_eq!(-2.0, clamp_max(-2.0, -1.0));assert!(clamp(::core::f32::NAN, -1.0, 1.0).is_nan());assert!(clamp_min(::core::f32::NAN, 1.0).is_nan());assert!(clamp_max(::core::f32::NAN, 1.0).is_nan());
}#[test]
#[should_panic]
#[cfg(debug_assertions)]
fn clamp_nan_min() {clamp(0., ::core::f32::NAN, 1.);
}#[test]
#[should_panic]
#[cfg(debug_assertions)]
fn clamp_nan_max() {clamp(0., -1., ::core::f32::NAN);
}#[test]
#[should_panic]
#[cfg(debug_assertions)]
fn clamp_nan_min_max() {clamp(0., ::core::f32::NAN, ::core::f32::NAN);
}#[test]
#[should_panic]
#[cfg(debug_assertions)]
fn clamp_min_nan_min() {clamp_min(0., ::core::f32::NAN);
}#[test]
#[should_panic]
#[cfg(debug_assertions)]
fn clamp_max_nan_max() {clamp_max(0., ::core::f32::NAN);
}#[test]
fn from_str_radix_unwrap() {// The Result error must impl Debug to allow unwrap()let i: i32 = Num::from_str_radix("0", 10).unwrap();assert_eq!(i, 0);let f: f32 = Num::from_str_radix("0.0", 10).unwrap();assert_eq!(f, 0.0);
}#[test]
fn from_str_radix_multi_byte_fail() {// Ensure parsing doesn't panic, even on invalid sign charactersassert!(f32::from_str_radix("™0.2", 10).is_err());// Even when parsing the exponent signassert!(f32::from_str_radix("0.2E™1", 10).is_err());
}#[test]
fn from_str_radix_ignore_case() {assert_eq!(f32::from_str_radix("InF", 16).unwrap(),::core::f32::INFINITY);assert_eq!(f32::from_str_radix("InfinitY", 16).unwrap(),::core::f32::INFINITY);assert_eq!(f32::from_str_radix("-InF", 8).unwrap(),::core::f32::NEG_INFINITY);assert_eq!(f32::from_str_radix("-InfinitY", 8).unwrap(),::core::f32::NEG_INFINITY);assert!(f32::from_str_radix("nAn", 4).unwrap().is_nan());assert!(f32::from_str_radix("-nAn", 4).unwrap().is_nan());
}#[test]
fn wrapping_is_num() {fn require_num<T: Num>(_: &T) {}require_num(&Wrapping(42_u32));require_num(&Wrapping(-42));
}#[test]
fn wrapping_from_str_radix() {macro_rules! test_wrapping_from_str_radix {($($t:ty)+) => {$(for &(s, r) in &[("42", 10), ("42", 2), ("-13.0", 10), ("foo", 10)] {let w = Wrapping::<$t>::from_str_radix(s, r).map(|w| w.0);assert_eq!(w, <$t as Num>::from_str_radix(s, r));})+};}test_wrapping_from_str_radix!(usize u8 u16 u32 u64 isize i8 i16 i32 i64);
}#[test]
fn check_num_ops() {fn compute<T: Num + Copy>(x: T, y: T) -> T {x * y / y % y + y - y}assert_eq!(compute(1, 2), 1)
}#[test]
fn check_numref_ops() {fn compute<T: NumRef>(x: T, y: &T) -> T {x * y / y % y + y - y}assert_eq!(compute(1, &2), 1)
}#[test]
fn check_refnum_ops() {fn compute<T: Copy>(x: &T, y: T) -> Twherefor<'a> &'a T: RefNum<T>,{&(&(&(&(x * y) / y) % y) + y) - y}assert_eq!(compute(&1, 2), 1)
}#[test]
fn check_refref_ops() {fn compute<T>(x: &T, y: &T) -> Twherefor<'a> &'a T: RefNum<T>,{&(&(&(&(x * y) / y) % y) + y) - y}assert_eq!(compute(&1, &2), 1)
}#[test]
fn check_numassign_ops() {fn compute<T: NumAssign + Copy>(mut x: T, y: T) -> T {x *= y;x /= y;x %= y;x += y;x -= y;x}assert_eq!(compute(1, 2), 1)
}#[test]
fn check_numassignref_ops() {fn compute<T: NumAssignRef + Copy>(mut x: T, y: &T) -> T {x *= y;x /= y;x %= y;x += y;x -= y;x}assert_eq!(compute(1, &2), 1)
}
相关文章:

【数值特性库】入口文件
数值特性库入口文件为lib.rs。该文件定义一系列数字特性的trait(特征),这些特性可以被不同的数字类型实现,从而提供一套通用的数值操作方法。下面是对代码中关键部分的解释: 一、基础设置 #
RestTemplate实时接收Chunked编码传输的HTTP Response
学习调用AI接口的时候,流式响应都是使用的 Transfer-Encoding: chunked,图方便想用RestTemplate,但是平时用到的都是直接返回响应对象的类型。使用bing搜索到一种方式,使用下面的代码来读取,于是掉这个坑里了ÿ…...

GIT区域介绍及码云+GIt配置仓库
GIT区域介绍 创建文件夹git init 1、git有3个区域 工作区(working directory):项目的根目录,不包 括.git在内的其他文件暂存区(stage area):是一个看不见的区域,git add 命令就是将文…...
网络安全怎么学习
当我们谈论网络安全时,我们正在讨论的是保护我们的在线空间,这是我们所有人的共享责任。网络安全涉及保护我们的信息,防止被未经授权的人访问、披露、破坏或修改。 一、网络安全的基本概念 网络安全是一种保护:它涉及保护我们的设…...

PugiXML,一个高效且简单的 C++ XML 解析库!
嗨,大家好!我是一行。今天要给大家介绍 PugiXML,这可是 C 里处理 XML 数据的得力助手。它能轻松地读取、修改和写入 XML 文件,就像一个专业的 XML 小管家,不管是解析配置文件,还是处理网页数据,…...

Linux设备树的驱动开发
概述 本文介绍了platform框架下的设备驱动开发流程和方法,主要包括设备树、驱动程序和应用程序的开发。以随机数驱动为例,实现了应用程序调用库函数,通过系统调用陷入内核,最后执行硬件驱动,获取真随机数的过程。 添…...

连锁?下沉?AI?2025年餐饮新活力!
如果要用几个词来形容 2024 年的餐饮业,这些词大概率会是「卷、难、惨」,用著名商业顾问刘润的话来说就是「卷到极致」。虽然餐饮人在社交平台上叫苦连天,但当我们查看餐饮大盘数据时发现,大盘在涨,与个体餐饮人的实感…...

Javascript中如何实现函数缓存?函数缓存有哪些应用场景?
今天要聊的一个很经典的问题——如何在JavaScript中实现函数缓存,以及它有哪些应用场景。 我们先来明确一下,函数缓存是什么。简单来说,函数缓存是将函数的运算结果存储起来,以便下次用到相同的输入时,可以直接返回结…...

子页面访问父页面
子页面访问父页面的方式主要依赖于页面之间的关系,特别是它们是否处于同一域、是否是嵌套在 <iframe> 中、或者通过弹出窗口打开。下面是几种常见的子页面访问父页面的方法: 1. 通过 window.parent 访问父页面(适用于嵌套的 iframe&am…...

芯片级IO (Pad) Ring IP Checklist
SoC top顶层数字后端实现都会涉及到IO Ring (PAD Ring)的设计。这里面包括VDD IO,VDDIO IO, Signal IO, Corner IO,Filler IO,IO power cut cell等等。 数字后端零基础入门系列 | Innovus零基础LAB学习Day2 数字IC后端实现TOP F…...

计算机毕业设计论文指导
计算机毕业设计论文指导 计算机毕业设计辅导一站式!太香了💪 [赞R][赞R][赞R]嗨喽!计算机专业的宝子们! 计算机毕设辅导专业靠谱的他来了!! 是不是还在为选题程序不会做而感到苦难? 论文没思路赶…...

Electron-Vue 开发下 dev/prod/webpack server各种路径设置汇总
背景 在实际开发中,我发现团队对于这几个路径的设置上是纯靠猜的,通过一点点地尝试来找到可行的路径,这是不应该的,我们应该很清晰地了解这几个概念,以下通过截图和代码进行细节讲解。 npm run dev 下的路径如何处理&…...

Vue.js前端框架教程9:Vue插槽slot用法
文章目录 插槽(Slots)无名插槽(默认插槽)具名插槽reference 插槽使用 v-slot 的缩写语法 插槽(Slots) 在 Vue 中,插槽(Slots)是一种组件内容分发的机制,允许…...

初学stm32 --- NVIC中断
目录 STM32 NVIC 中断优先级管理 NVIC_Type: ISER[8]: ICER[8]: ISPR[8]: ICPR[8]: IABR[8]: IP[240]: STM32 的中断分组: 中断优先级分组函数 NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig 中断初始化函…...

Jest 入门指南:从零开始编写 JavaScript 单元测试
前言 在前端开发中,单元测试已经成为确保代码质量和稳定性的关键步骤。Jest 作为由 Facebook 开发和维护的功能强大的 JavaScript 测试框架,以其易于配置、丰富的功能和开箱即用的特性,成为众多开发者的首选工具。本文旨在引导你从零开始&am…...

【Java Web】Axios实现前后端数据异步交互
目录 一、Promise概述 二、Promise基本用法 三、async和await关键字 四、Axios介绍 4.1 Axios基本用法 4.2 Axios简化用法之get和post方法 五、Axios拦截器 六、跨域问题处理 一、Promise概述 axios是代替原生的ajax实现前后端数据交互的一套新解决方案,而…...

React 第十七节 useMemo用法详解
概述 useMemo 是React 中的一个HOOK,用于根据依赖在每次渲染时候缓存计算结果; 大白话就是,只有依赖项发生变化时候,才会重新渲染为新计算的值,否则就还是取原来的值,有点类似 vue 中的 computed 计算属性…...

鸿蒙项目云捐助第十五讲云数据库的初步使用
鸿蒙项目云捐助第十五讲云数据库的初步使用 在华为云技术使用中,前面使用了云函数,接下来看一下华为云技术中的另外一个技术云数据库的使用。 一、云数据库的创建 这里使用华为云数据库也需要登录到AppGallery Connect平台中,点击进入到之…...

如何构建一个可信的联邦RAG系统。
今天给大家分享一篇论文。 题目是:C-RAG:如何构建一个可信的联邦检索RAG系统。 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.13163 论文概述 尽管大型语言模型 (LLM) 在各种应用中展现出令人印象深刻的能力,但它们仍然存在可信度问题ÿ…...

【深度学习之三】FPN与PAN网络详解
FPN与PAN:深度学习中的特征金字塔网络与路径聚合网络 在深度学习的领域里,特征金字塔网络(Feature Pyramid Networks,简称FPN) 和 路径聚合网络(Path Aggregation Network,简称PAN)…...
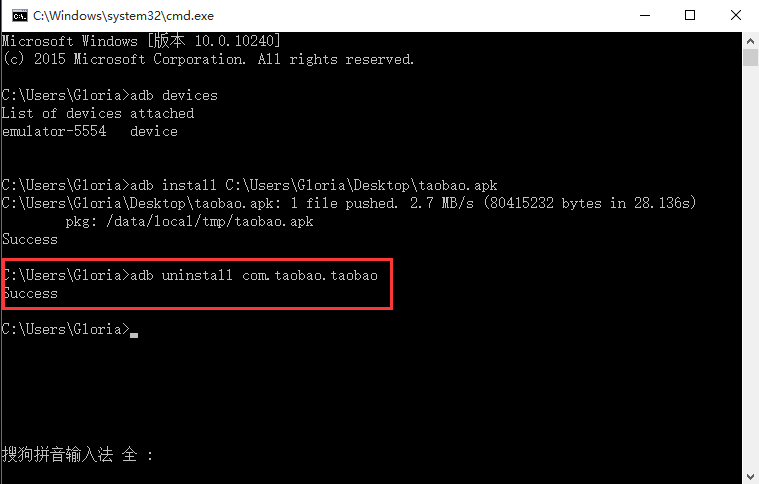
Appium+python自动化(十六)- ADB命令
简介 Android 调试桥(adb)是多种用途的工具,该工具可以帮助你你管理设备或模拟器 的状态。 adb ( Android Debug Bridge)是一个通用命令行工具,其允许您与模拟器实例或连接的 Android 设备进行通信。它可为各种设备操作提供便利,如安装和调试…...
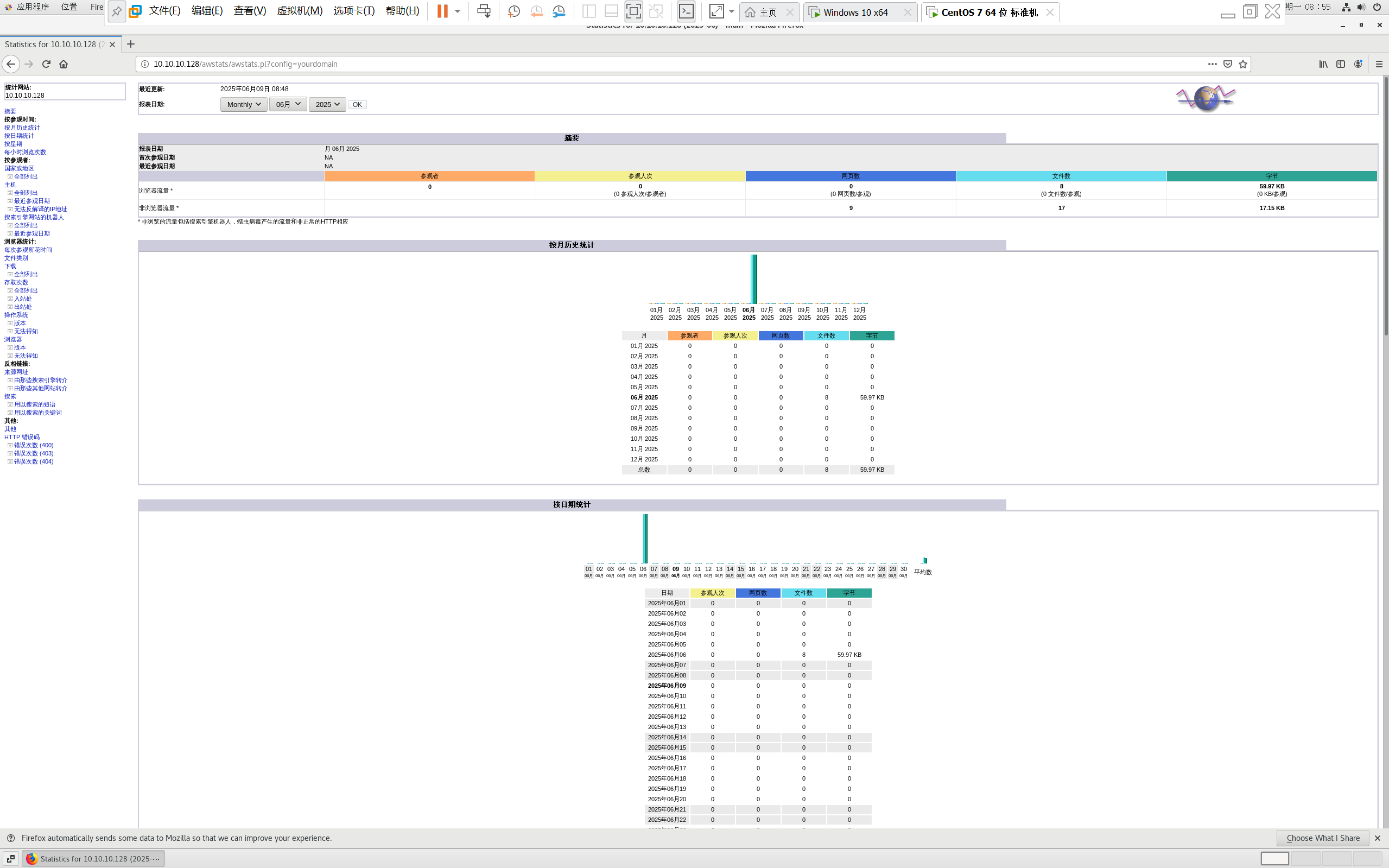
centos 7 部署awstats 网站访问检测
一、基础环境准备(两种安装方式都要做) bash # 安装必要依赖 yum install -y httpd perl mod_perl perl-Time-HiRes perl-DateTime systemctl enable httpd # 设置 Apache 开机自启 systemctl start httpd # 启动 Apache二、安装 AWStats࿰…...

SCAU期末笔记 - 数据分析与数据挖掘题库解析
这门怎么题库答案不全啊日 来简单学一下子来 一、选择题(可多选) 将原始数据进行集成、变换、维度规约、数值规约是在以下哪个步骤的任务?(C) A. 频繁模式挖掘 B.分类和预测 C.数据预处理 D.数据流挖掘 A. 频繁模式挖掘:专注于发现数据中…...

前端导出带有合并单元格的列表
// 导出async function exportExcel(fileName "共识调整.xlsx") {// 所有数据const exportData await getAllMainData();// 表头内容let fitstTitleList [];const secondTitleList [];allColumns.value.forEach(column > {if (!column.children) {fitstTitleL…...

什么?连接服务器也能可视化显示界面?:基于X11 Forwarding + CentOS + MobaXterm实战指南
文章目录 什么是X11?环境准备实战步骤1️⃣ 服务器端配置(CentOS)2️⃣ 客户端配置(MobaXterm)3️⃣ 验证X11 Forwarding4️⃣ 运行自定义GUI程序(Python示例)5️⃣ 成功效果
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】 文章目录 selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】一、声明二、学习目标三、安装依赖3.1 安装selenium库3.2 安装浏览器驱动3.2.1 查看Edge版本3.2.2 驱动安装 四、代码讲解4.1 配置浏览器4.2 加载更多4.3 寻找内容4.4 完整代码 五、报告文件爬取5.1 提…...
什么是Ansible Jinja2
理解 Ansible Jinja2 模板 Ansible 是一款功能强大的开源自动化工具,可让您无缝地管理和配置系统。Ansible 的一大亮点是它使用 Jinja2 模板,允许您根据变量数据动态生成文件、配置设置和脚本。本文将向您介绍 Ansible 中的 Jinja2 模板,并通…...

用机器学习破解新能源领域的“弃风”难题
音乐发烧友深有体会,玩音乐的本质就是玩电网。火电声音偏暖,水电偏冷,风电偏空旷。至于太阳能发的电,则略显朦胧和单薄。 不知你是否有感觉,近两年家里的音响声音越来越冷,听起来越来越单薄? —…...
【笔记】WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录
#工作记录 WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录 1. 运行环境 系统:Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (WSL2)架构:x86_64 (GNU/Linux)Rust 版本:rustc 1.87.0 (2025-05-09)Cargo 版本:cargo 1.87.0 (2025-05-06) 2. 安装 Rust 2.1 使用 Rust 官方安…...

Web中间件--tomcat学习
Web中间件–tomcat Java虚拟机详解 什么是JAVA虚拟机 Java虚拟机是一个抽象的计算机,它可以执行Java字节码。Java虚拟机是Java平台的一部分,Java平台由Java语言、Java API和Java虚拟机组成。Java虚拟机的主要作用是将Java字节码转换为机器代码&#x…...
