Kotlin - 协程结构化并发Structured Concurrency
前言
Kotlin的Project Lead,Roman Elizarov的一片文章https://elizarov.medium.com/structured-concurrency-722d765aa952介绍了Structured Concurrency发展的背景。相对Kotlin1.1时代,后来新增的Structured Concurrency理念,也就是我们现在所熟悉的协程版本所具备的特性,解决了各种复杂业务场景下,例如协程嵌套、异步等等使用方式时所面临的生命周期管理问题。本文通过梳理源码来试图理解Structured Concurrency的具体含义和实现原理。
概念理解
常见的业务场景如下:
suspend fun loadAndCombine(name1: String, name2: String): Image { val deferred1 = async { loadImage(name1) }val deferred2 = async { loadImage(name2) }return combineImages(deferred1.await(), deferred2.await())
}deferred1和deferred2都是异步执行的,最终需要将二者的执行结果合并后返回。而如果此时其中一个loadImage执行异常,或者主动取消,很难去通知另一个LoadImage及时停止执行,释放资源。
或者如下场景:
val scope = CoroutineScope(Job())
scope.launch {printLog("launch1")
launch {delay(20000)printLog("launch1-1")}printLog("launch1 done")cancel()}在外层的launch执行到最后,希望cancel内部所有的子协程。在没有Structrued Concurrency特性的时候,要实现这种逻辑需要类似使用线程时的处理方式。而Structrued Concurrency特性可以让我们在cancel外层协程时,自动cancel其里面所有的子协程。
这就是所谓的对协程生命周期的管理。为了能够将所有协程的生命周期完全管理起来,Kotlin使用了CoroutineScope。
Coroutines are always related to some local scope in your application, which is an entity with a limited life-time, like a UI element.
CoroutineScope相当于圈定了一个空间,所有的协程都在这个空间里面执行。这样所有协程的声明周期就可以通过CoroutineScope来进行管理了。
实现原理
我们知道每个launch都是一个Job。Job和CoroutineScope的关系如下:
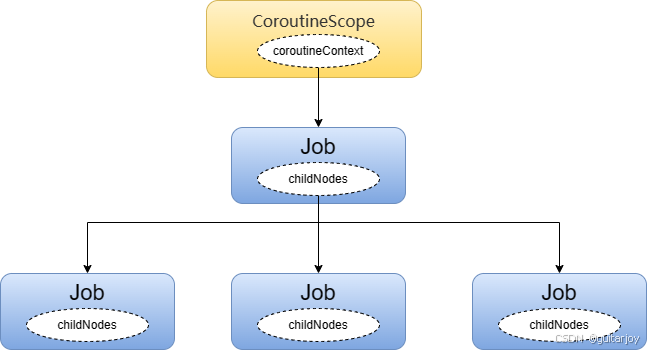
再次根据这个例子,看这种关系如何实现的:
val scope = CoroutineScope(Job())
scope.launch {printLog("launch1")
launch {delay(20000)printLog("launch1-1")}printLog("launch1 done")cancel()}
首先看新建CoroutineScope(Job())
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\CoroutineScope.ktpublic fun CoroutineScope(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineScope =ContextScope(if (context[Job] != null) context else context + Job())internal class ContextScope(context: CoroutineContext) : CoroutineScope {override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext = context// CoroutineScope is used intentionally for user-friendly representationoverride fun toString(): String = "CoroutineScope(coroutineContext=$coroutineContext)"
}
CoroutineScope本身是一个接口,这里的CoroutineScope不是构造函数,而是一个顶层函数。这里有两个关注点:
context[Job]和context + Job()
所有的Job、CoroutineDispatcher都继承于CoroutineContext。因此CoroutineScope函数的参数我们可以新建一个Job(), 也可以传一个CoroutineDispatcher。以Job()为例,看下其实现:
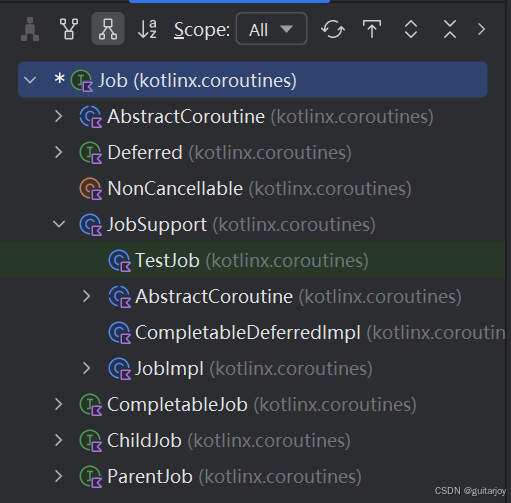
public interface Job : CoroutineContext.Element {/**
* Key for [Job] instance in the coroutine context.
*/public companion object Key : CoroutineContext.Key<Job>Job继承于CoroutineContext.Element,
public interface Element : CoroutineContext {/**
* A key of this coroutine context element.
*/public val key: Key<*>public override operator fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E? =@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")if (this.key == key) this as E else nullpublic override fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R =operation(initial, this)public override fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext =if (this.key == key) EmptyCoroutineContext else this}注意这里的get函数,其返回值取决于key。key在哪里赋值的?
Job也是一个接口,其Job()也是一个顶层函数:
public fun Job(parent: Job? = null): CompletableJob = JobImpl(parent)internal open class JobImpl(parent: Job?) : JobSupport(true), CompletableJob {JobImp继承JobSupport,而JobSupport是Job的具体实现
public open class JobSupport constructor(active: Boolean) : Job, ChildJob, ParentJob {final override val key: CoroutineContext.Key<*> get() = Job可以看到key的实际值为Job。
所以,如果CoroutineScope(...)的参数传入的是Job(), 则context[Job]返回的是Job。
那context + Job()代表什么呢?
在CoroutineContext的接口声明里看到了plus操作符重载:
public operator fun plus(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext =if (context === EmptyCoroutineContext) this else // fast path -- avoid lambda creation
context.fold(this) { acc, element ->val removed = acc.minusKey(element.key)if (removed === EmptyCoroutineContext) element else {// make sure interceptor is always last in the context (and thus is fast to get when present)val interceptor = removed[ContinuationInterceptor]if (interceptor == null) CombinedContext(removed, element) else {val left = removed.minusKey(ContinuationInterceptor)if (left === EmptyCoroutineContext) CombinedContext(element, interceptor) elseCombinedContext(CombinedContext(left, element), interceptor)}}}是将两个CoroutineContext合并成了CombinedContext。CombinedContext本身也是一个CoroutineContext。
综上, 在新建CoroutineScope的时候,如果传入了一个Job,则使用这个Job,如果没有传入Job(可能传入一个CoroutineDispatcher),则新建一个Job。然后将Job赋值给ContextScope的coroutineContext成员变量。
如此一来,一个新建的CoroutineScope就关联了一个顶层的Job。
使用launch创建一个协程:
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\Builders.common.ktpublic fun CoroutineScope.launch(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
): Job {val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) elseStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)return coroutine
}
首先,launch是CoroutineScope的扩展函数,也就是说只能在CoroutineScope内创建协程。newCoroutineContext(context):
public actual fun CoroutineScope.newCoroutineContext(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext {val combined = foldCopies(coroutineContext, context, true)val debug = if (DEBUG) combined + CoroutineId(COROUTINE_ID.incrementAndGet()) else combinedreturn if (combined !== Dispatchers.Default && combined[ContinuationInterceptor] == null)
debug + Dispatchers.Default else debug
}这里context是EmptyCoroutineContext,coroutineContext是刚才CoroutineScope(Job())传入的顶层Job。经过foldCopies后,返回的combined可以看做是顶层Job的封装。在return语句中可以看到debug(即顶层Job)加上了debug + Dispatchers.Default,这就是为什么默认会运行在Dispatchers.Default线程的原因。
创建了newContext后,如果start.isLazy会构建LazyStandaloneCoroutine,否则构建StandaloneCoroutine。start是协程的执行方式,默认为立即执行,也可以懒加载执行。具体见kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\CoroutineStart.kt
这里构建的是默认的StandaloneCoroutine
private open class StandaloneCoroutine(
parentContext: CoroutineContext,
active: Boolean
) : AbstractCoroutine<Unit>(parentContext, initParentJob = true, active = active) {override fun handleJobException(exception: Throwable): Boolean {handleCoroutineException(context, exception)return true}
}parentContext参数传入的是刚才构建的newContext,也就是顶层Job。initParentJob默认值为true。接着看下他的继承类AbstractCoroutine:
public abstract class AbstractCoroutine<in T>(
parentContext: CoroutineContext,
initParentJob: Boolean,
active: Boolean
) : JobSupport(active), Job, Continuation<T>, CoroutineScope {init {/*
* Setup parent-child relationship between the parent in the context and the current coroutine.
* It may cause this coroutine to become _cancelling_ if the parent is already cancelled.
* It is dangerous to install parent-child relationship here if the coroutine class
* operates its state from within onCancelled or onCancelling
* (with exceptions for rx integrations that can't have any parent)
*/if (initParentJob) initParentJob(parentContext[Job])}AbstractCoroutine继承了JobSupport、Job,也就是说,StandaloneCoroutine实际上是构造了一个Job。看下这里的initParentJob(parentContext[Job]),parentContext是刚才传进来的顶层Job的封装newContext,这里取出其Job传进initParentJob
protected fun initParentJob(parent: Job?) {
assert { parentHandle == null }if (parent == null) {
parentHandle = NonDisposableHandlereturn}
parent.start() // make sure the parent is startedval handle = parent.attachChild(this)
parentHandle = handle// now check our state _after_ registering (see tryFinalizeSimpleState order of actions)if (isCompleted) {
handle.dispose()
parentHandle = NonDisposableHandle // release it just in case, to aid GC}}这里会执行parent.attachChild(this)。字面上理解即将launch创建出来的新Job作为Child加入到顶层的Job中去。
关联父子Job
看下具体实现:
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\JobSupport.kt
public final override fun attachChild(child: ChildJob): ChildHandle {val node = ChildHandleNode(child).also { it.job = this }val added = tryPutNodeIntoList(node) { _, list ->// First, try to add a child along the cancellation handlersval addedBeforeCancellation = list.addLast(
node,
LIST_ON_COMPLETION_PERMISSION or LIST_CHILD_PERMISSION or LIST_CANCELLATION_PERMISSION)...
node.invoke(rootCause)if (addedBeforeCompletion) {/** The root cause can't be null: since the earlier addition to the list failed, this means that
* the job was already cancelled or completed. */
assert { rootCause != null }true} else {/** No sense in retrying: we know it won't succeed, and we already invoked the handler. */return NonDisposableHandle}}}if (added) return node/** We can only end up here if [tryPutNodeIntoList] detected a final state. */
node.invoke((state as? CompletedExceptionally)?.cause)return NonDisposableHandle}首先构造一个ChildHandleNode
private class ChildHandleNode(@JvmField val childJob: ChildJob
) : JobNode(), ChildHandle {override val parent: Job get() = joboverride val onCancelling: Boolean get() = trueoverride fun invoke(cause: Throwable?) = childJob.parentCancelled(job)override fun childCancelled(cause: Throwable): Boolean = job.childCancelled(cause)
}这里parent传入的是顶层Job,childJob是launch新建的Job
tryPutNodeIntoList
private inline fun tryPutNodeIntoList(
node: JobNode,
tryAdd: (Incomplete, NodeList) -> Boolean): Boolean {
loopOnState { state ->when (state) {is Empty -> { // EMPTY_X state -- no completion handlersif (state.isActive) {// try to move to the SINGLE stateif (_state.compareAndSet(state, node)) return true} elsepromoteEmptyToNodeList(state) // that way we can add listener for non-active coroutine}is Incomplete -> when (val list = state.list) {null -> promoteSingleToNodeList(state as JobNode)else -> if (tryAdd(state, list)) return true}else -> return false}}}private val _state = atomic<Any?>(if (active) EMPTY_ACTIVE else EMPTY_NEW)private inline fun loopOnState(block: (Any?) -> Unit): Nothing {while (true) {block(state)}}state是什么?
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\JobSupport.ktprivate val EMPTY_NEW = Empty(false)
private val EMPTY_ACTIVE = Empty(true)在JobSupport中,维护了一个状态机,管理Job的不同状态阶段。这里EMPTY_NEW和 EMPTY_ACTIVE是其具体状态。
private class Empty(override val isActive: Boolean) : Incomplete {override val list: NodeList? get() = nulloverride fun toString(): String = "Empty{${if (isActive) "Active" else "New" }}"
}其内维护了一个list
简言之,就是tryAdd(state, list)会将自己的state内的list传递给调用它的tryPutNodeIntoList,在回头看tryPutNodeIntoList,
val addedBeforeCompletion = list.addLast(
node,
LIST_CHILD_PERMISSION or LIST_ON_COMPLETION_PERMISSION)会将子Job加到list中。
由此一来,CoroutineScope边构建了它的Job树。
Job的执行
回到CoroutineScope.launch
public fun CoroutineScope.launch(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
): Job {val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) elseStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)return coroutine
}在构建完coroutine后,执行coroutine.start
public fun <R> start(start: CoroutineStart, receiver: R, block: suspend R.() -> T) {start(block, receiver, this)}public enum class CoroutineStart {
...
public operator fun <R, T> invoke(block: suspend R.() -> T, receiver: R, completion: Continuation<T>): Unit =when (this) {
DEFAULT -> block.startCoroutineCancellable(receiver, completion)
ATOMIC -> block.startCoroutine(receiver, completion)
UNDISPATCHED -> block.startCoroutineUndispatched(receiver, completion)
LAZY -> Unit // will start lazily}在这里开始执行协程。
Structured Concurrency的典型作用:协程的cancel
当执行scope的cancel时:
public fun CoroutineScope.cancel(cause: CancellationException? = null) {val job = coroutineContext[Job] ?: error("Scope cannot be cancelled because it does not have a job: $this")
job.cancel(cause)
}是通过coroutineContext[Job]获取了顶层Job,然后执行其cancel
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\JobSupport.kt
public override fun cancel(cause: CancellationException?) {cancelInternal(cause ?: defaultCancellationException())}public open fun cancelInternal(cause: Throwable) {cancelImpl(cause)}internal fun cancelImpl(cause: Any?): Boolean {var finalState: Any? = COMPLETING_ALREADYif (onCancelComplete) {// make sure it is completing, if cancelMakeCompleting returns state it means it had make it// completing and had recorded exception
finalState = cancelMakeCompleting(cause)if (finalState === COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN) return true}if (finalState === COMPLETING_ALREADY) {
finalState = makeCancelling(cause)}return when {
finalState === COMPLETING_ALREADY -> true
finalState === COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN -> true
finalState === TOO_LATE_TO_CANCEL -> falseelse -> {afterCompletion(finalState)true}}}以makeCancelling为例
private fun makeCancelling(cause: Any?): Any? {var causeExceptionCache: Throwable? = null // lazily init result of createCauseException(cause)
loopOnState { state ->when (state) {is Finishing -> { // already finishing -- collect exceptionsval notifyRootCause = synchronized(state) {if (state.isSealed) return TOO_LATE_TO_CANCEL // already sealed -- cannot add exception nor mark cancelled// add exception, do nothing is parent is cancelling child that is already being cancelledval wasCancelling = state.isCancelling // will notify if was not cancelling// Materialize missing exception if it is the first exception (otherwise -- don't)if (cause != null || !wasCancelling) {val causeException = causeExceptionCache ?: createCauseException(cause).also { causeExceptionCache = it }
state.addExceptionLocked(causeException)}// take cause for notification if was not in cancelling state before
state.rootCause.takeIf { !wasCancelling }}
notifyRootCause?.let { notifyCancelling(state.list, it) }return COMPLETING_ALREADY}is Incomplete -> {// Not yet finishing -- try to make it cancellingval causeException = causeExceptionCache ?: createCauseException(cause).also { causeExceptionCache = it }if (state.isActive) {// active state becomes cancellingif (tryMakeCancelling(state, causeException)) return COMPLETING_ALREADY} else {// non active state starts completingval finalState = tryMakeCompleting(state, CompletedExceptionally(causeException))when {
finalState === COMPLETING_ALREADY -> error("Cannot happen in $state")
finalState === COMPLETING_RETRY -> return@loopOnStateelse -> return finalState}}}else -> return TOO_LATE_TO_CANCEL // already complete}}}假如协程在运行中,则执行tryMakeCancelling
private fun tryMakeCancelling(state: Incomplete, rootCause: Throwable): Boolean {
assert { state !is Finishing } // only for non-finishing states
assert { state.isActive } // only for active states// get state's list or else promote to list to correctly operate on child listsval list = getOrPromoteCancellingList(state) ?: return false// Create cancelling state (with rootCause!)val cancelling = Finishing(list, false, rootCause)if (!_state.compareAndSet(state, cancelling)) return false// Notify listenersnotifyCancelling(list, rootCause)return true}state.compareAndSet进行状态机切换,随后执行notifyCancelling
private fun notifyCancelling(list: NodeList, cause: Throwable) {// first cancel our own childrenonCancelling(cause)
list.close(LIST_CANCELLATION_PERMISSION)notifyHandlers(list, cause) { it.onCancelling }// then cancel parentcancelParent(cause) // tentative cancellation -- does not matter if there is no parent}private fun notifyCancelling(list: NodeList, cause: Throwable) {// first cancel our own childrenonCancelling(cause)
list.close(LIST_CANCELLATION_PERMISSION)notifyHandlers(list, cause) { it.onCancelling }// then cancel parentcancelParent(cause) // tentative cancellation -- does not matter if there is no parent}private inline fun notifyHandlers(list: NodeList, cause: Throwable?, predicate: (JobNode) -> Boolean) {var exception: Throwable? = null
list.forEach { node ->if (node is JobNode && predicate(node)) {try {
node.invoke(cause)} catch (ex: Throwable) {
exception?.apply { addSuppressed(ex) } ?: run {
exception = CompletionHandlerException("Exception in completion handler $node for $this", ex)}}}}
exception?.let { handleOnCompletionException(it) }node.invoke(cause)的实现
private class InvokeOnCancelling(private val handler: CompletionHandler
) : JobNode() {// delegate handler shall be invoked at most once, so here is an additional flagprivate val _invoked = atomic(false)override val onCancelling get() = trueoverride fun invoke(cause: Throwable?) {if (_invoked.compareAndSet(expect = false, update = true)) handler.invoke(cause)}
}private fun cancelParent(cause: Throwable): Boolean {// Is scoped coroutine -- don't propagate, will be rethrownif (isScopedCoroutine) return true/* CancellationException is considered "normal" and parent usually is not cancelled when child produces it.
* This allow parent to cancel its children (normally) without being cancelled itself, unless
* child crashes and produce some other exception during its completion.
*/val isCancellation = cause is CancellationExceptionval parent = parentHandle// No parent -- ignore CE, report other exceptions.if (parent === null || parent === NonDisposableHandle) {return isCancellation}// Notify parent but don't forget to check cancellationreturn parent.childCancelled(cause) || isCancellation}即先将自己的状态切换到取消中,随后notifyHandlers通过遍历list通知自己的children执行cancel。最后再通过cancelParent告知父Job自己的分支cancel完毕。
总结:
- 所有协程都运行在CoroutineScope中,这种限定是通过launch、async、runBlock等构建协程的函数都是作为CoroutineScope扩展函数来实现的。
- CoroutineScope创建过程中,必定会构建一个顶层Job(后者外部传入),通过coroutineContext与其关联。
- 每个launch都响应构建了一个Job,并将此Job加入到父Job的list中,由此维护了一个Job树。
- Structure Concurrency 的 具体实现 是 通过 维护 Job 树 的生命周期 完成 的 。
相关文章:

Kotlin - 协程结构化并发Structured Concurrency
前言 Kotlin的Project Lead,Roman Elizarov的一片文章https://elizarov.medium.com/structured-concurrency-722d765aa952介绍了Structured Concurrency发展的背景。相对Kotlin1.1时代,后来新增的Structured Concurrency理念,也就是我们现在所…...

新版国标GB28181设备端Android版EasyGBD支持国标GB28181-2022,支持语音对讲,支持位置上报,开源在Github
经过近3个月的迭代开发,新版本的国标GB28181设备端EasyGBD安卓Android版终于在昨天发布到Github了,最新的EasyGBD支持了国标GB28181-2022版,还支持了语音对讲、位置上报、本地录像等功能,比原有GB28181-2016版的EasyGBD更加高效、…...

豆包MarsCode测评:编程效率再提升
豆包MarsCode测评:编程效率再提升 本文正在参与豆包MarsCode AI 编程体验家活动 随着人工智能技术的发展,编程的方式也在悄然发生变化。最近,豆包推出的 AI 编程工具 MarsCode 在开发者社区引发了不小的关注。这是一款支持多种主流编程语言…...

二叉树 -- 堆(详解)
目录 1、堆的概念及结构 2、堆的实现(附代码) 2.1、向下调整算法建堆 3、堆的应用(附代码) 3.1、堆排序 3.2、TOP-K问题 1、堆的概念及结构 如果有一个关键码的集合K { k0,k1 ,k2 ,…,k(n-1) },把它的所有元素…...

【Apache Paimon】-- 11 -- Flink 消费 kakfa 写 S3 File
目录 1、项目构建 2、项目新增和修改 2.1 pom.xml 新增依赖 2.2 本地测试或者 flink on k8s 时,新增 S3FileSystemFactory.java 第一步:创建包=org.apache.flink.fs.s3hadoop 第二步:新增 java 类 S3FileSystemFactory 特别注意 (1)本地测试时需要新增以下内容 (…...
)
SQL MID()
SQL中的MID()函数是一个用于从指定位置开始截取字符串中指定长度的子串的函数。这个函数在数据库查询和数据处理中经常被使用,特别是在需要从较长的文本字段中提取特定信息时。 MID()函数的基本语法是:SELECT MID(column_name, start, length) FROM tab…...

jsp | servlet | spring forEach读取不了对象List
导致这个问题的原因有很多的,这里讲到的只是原因之一 原因 taglib不认识forEach 解决办法 添加<% taglib uri"http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix"c" %> (我忘写这个东西了哈哈哈)...

【ArcGIS Pro微课1000例】0063:处理无人机数据(空三、生成DOM、DSM、DTM)
使用ArcGIS Pro 正射拼接处理无人机数据流程化工具,不需要额外产品许可的支持,只需要桌面是高级版许可即可支持。ArcGIS Pro处理无人机摄影测量数据主要内容有:空三、生成DOM、DSM、DTM。 文章目录 一、创建映射项目二、提交自由空三三、添加控制点优化四、提交产品生产一、…...

【pytorch】深度学习计算
1 层和块 块由类(class)表示。它的任何子类都必须定义一个将其输入转换为输出的前向传播函数,并且必须存储任何必需的参数。注意,有些块不需要任何参数。最后,为了计算梯度,块必须具有反向传播函数。 1.1…...

详解磁盘IO、网络IO、零拷贝IO、BIO、NIO、AIO、IO多路复用(select、poll、epoll)
1、什么是I/O 在计算机操作系统中,所谓的I/O就是输入(Input)和输出(Output),也可以理解为读(Read)和写(Write),针对不同的对象,I/O模式可以划分为…...

VPN技术-GRE隧道的配置
GRE隧道的配置 1, 在AR1上配置DHCP接口地址池,AR3上配置DHCP全局地址池 2, PC1获取的IP地址为10.10.10.253,PC2获取的IP地址为10.10.30.253 3,通过ip route-static将目的地址为10.10.30.253的流量引入到Tunnel #配…...

【spring-cloud-gateway总结】
文章目录 什么是gateway如何导入gateway依赖路由配置gateway配置断路器导包配置 什么是gateway 在微服务架构中,gateway网关是一个服务,它作为系统的唯一入口点,处理所有的客户端请求,然后将这些请求路由到适当的服务。提供了几个…...
数组相关简单算法
目录 1. 数据结构与算法 2. 数组中涉及的算法 2.1 2.2 数值型数组相关运算 2.3 数组赋值 2.4 数组复制/反转 2.5 数组查找 2.6 排序 1. 数据结构与算法 《数据结构与算法》是大学些许专业的必修或选修课,主要包含两方面知识: (1&#…...

在VBA中结合正则表达式和查找功能给文档添加交叉连接
在VBA中搜索文本有两种方式可用,一种是利用Range.Find对象(更常见的形式可能是Selection.Find,Selection是Range的子类,Selection.Find其实就是特殊的Range.Find),另一种方法是利用正则表达式,但…...

动手学深度学习-多层感知机-7前向传播、反向传播和计算图
目录 前向传播 前向传播计算图 反向传播 训练神经网络 小结 我们已经学习了如何用小批量随机梯度下降训练模型。 然而当实现该算法时,我们只考虑了通过前向传播(forward propagation)所涉及的计算。 在计算梯度时,我们只调用…...

【Python】基于Python的CI/CD工具链:实现自动化构建与发布
《Python OpenCV从菜鸟到高手》带你进入图像处理与计算机视觉的大门! 解锁Python编程的无限可能:《奇妙的Python》带你漫游代码世界 在现代软件开发中,持续集成(CI)和持续交付(CD)已经成为提高开发效率和软件质量的重要实践。CI/CD流程帮助开发团队自动化构建、测试、…...

FPGA-PS端编程1:
目标 在小梅哥的zynq 7015上,完成以下目标: 读取 S1 按键的电平, 当 S1 按键为按下状态时,驱动 PS LED 以 1S 的频率闪烁(注意理解 1S 的频率闪烁和 1S的时间翻转两种描述之间的差别), 当 S1 释放后,停止…...

自制数据库迁移工具-C版-06-HappySunshineV1.5-(支持南大Gbase8a、PostgreSQL、达梦DM)
目录 一、环境信息 二、简述 三、架构图 四、升级点 五、支持功能 六、后续计划支持功能 七、安装包下载地址 八、配置参数介绍 九、安装步骤 1、用户创建 2、安装包解压 3、环境变量配置 4、环境变量生效 5、动态库链接检验 (1)HsManage…...

了解RPC
本文来自智谱清言 --------- RPC(Remote Procedure Call,远程过程调用)是一种允许程序调用位于远程计算机上的子程序或服务的技术。这种技术使得构建分布式计算变得更加容易,因为它提供了强大的远程调用能力,同时保持…...

centos7 安装docker
文章目录 介绍docker特点安装1.前提准备2.下载1.移除旧版docker命令2.切换centos7的镜像源3.配置docker yum源4.安装最新docker5.输入命令验证docker 安装是否成功6.配置docker 镜像加速7.设置为开机自启 总结 介绍 Docker是一种开源的容器化平台,旨在简化应用…...

java_网络服务相关_gateway_nacos_feign区别联系
1. spring-cloud-starter-gateway 作用:作为微服务架构的网关,统一入口,处理所有外部请求。 核心能力: 路由转发(基于路径、服务名等)过滤器(鉴权、限流、日志、Header 处理)支持负…...

R语言AI模型部署方案:精准离线运行详解
R语言AI模型部署方案:精准离线运行详解 一、项目概述 本文将构建一个完整的R语言AI部署解决方案,实现鸢尾花分类模型的训练、保存、离线部署和预测功能。核心特点: 100%离线运行能力自包含环境依赖生产级错误处理跨平台兼容性模型版本管理# 文件结构说明 Iris_AI_Deployme…...

基于服务器使用 apt 安装、配置 Nginx
🧾 一、查看可安装的 Nginx 版本 首先,你可以运行以下命令查看可用版本: apt-cache madison nginx-core输出示例: nginx-core | 1.18.0-6ubuntu14.6 | http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 Packages ng…...
【大模型RAG】Docker 一键部署 Milvus 完整攻略
本文概要 Milvus 2.5 Stand-alone 版可通过 Docker 在几分钟内完成安装;只需暴露 19530(gRPC)与 9091(HTTP/WebUI)两个端口,即可让本地电脑通过 PyMilvus 或浏览器访问远程 Linux 服务器上的 Milvus。下面…...

【Go】3、Go语言进阶与依赖管理
前言 本系列文章参考自稀土掘金上的 【字节内部课】公开课,做自我学习总结整理。 Go语言并发编程 Go语言原生支持并发编程,它的核心机制是 Goroutine 协程、Channel 通道,并基于CSP(Communicating Sequential Processes࿰…...

Spring Boot+Neo4j知识图谱实战:3步搭建智能关系网络!
一、引言 在数据驱动的背景下,知识图谱凭借其高效的信息组织能力,正逐步成为各行业应用的关键技术。本文聚焦 Spring Boot与Neo4j图数据库的技术结合,探讨知识图谱开发的实现细节,帮助读者掌握该技术栈在实际项目中的落地方法。 …...

Python如何给视频添加音频和字幕
在Python中,给视频添加音频和字幕可以使用电影文件处理库MoviePy和字幕处理库Subtitles。下面将详细介绍如何使用这些库来实现视频的音频和字幕添加,包括必要的代码示例和详细解释。 环境准备 在开始之前,需要安装以下Python库:…...
用docker来安装部署freeswitch记录
今天刚才测试一个callcenter的项目,所以尝试安装freeswitch 1、使用轩辕镜像 - 中国开发者首选的专业 Docker 镜像加速服务平台 编辑下面/etc/docker/daemon.json文件为 {"registry-mirrors": ["https://docker.xuanyuan.me"] }同时可以进入轩…...

【学习笔记】深入理解Java虚拟机学习笔记——第4章 虚拟机性能监控,故障处理工具
第2章 虚拟机性能监控,故障处理工具 4.1 概述 略 4.2 基础故障处理工具 4.2.1 jps:虚拟机进程状况工具 命令:jps [options] [hostid] 功能:本地虚拟机进程显示进程ID(与ps相同),可同时显示主类&#x…...
相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?)
Redis的发布订阅模式与专业的 MQ(如 Kafka, RabbitMQ)相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?
Redis 的发布订阅(Pub/Sub)模式与专业的 MQ(Message Queue)如 Kafka、RabbitMQ 进行比较,核心的权衡点在于:简单与速度 vs. 可靠与功能。 下面我们详细展开对比。 Redis Pub/Sub 的核心特点 它是一个发后…...
