矩阵:Input-Output Interpretation of Matrices (中英双语)
矩阵的输入-输出解释:深入理解与应用
在线性代数中,矩阵与向量的乘积 ( y = A x y = Ax y=Ax ) 是一个极为重要的关系。通过这一公式,我们可以将矩阵 ( A A A ) 看作一个将输入向量 ( x x x ) 映射到输出向量 ( y y y ) 的线性变换。在这种输入-输出解释中,向量 ( x x x ) 表示输入,而向量 ( y y y ) 表示对应的输出,而矩阵 ( A A A ) 则充当转换关系的核心。这种解释在许多领域都有广泛的应用,包括物理、数据科学、机器学习和工程等。
1. 基本定义与形式
对于一个 ( m × n m \times n m×n ) 矩阵 ( A A A ),如果我们有一个 ( n n n )-维输入向量 ( x x x ),通过矩阵-向量乘法 ( y = A x y = Ax y=Ax ),可以得到一个 ( m m m )-维输出向量 ( y y y )。用公式表示为:
y i = ∑ k = 1 n A i k x k = A i 1 x 1 + A i 2 x 2 + ⋯ + A i n x n , i = 1 , … , m . y_i = \sum_{k=1}^n A_{ik} x_k = A_{i1}x_1 + A_{i2}x_2 + \cdots + A_{in}x_n, \quad i = 1, \dots, m. yi=k=1∑nAikxk=Ai1x1+Ai2x2+⋯+Ainxn,i=1,…,m.
这里,
- ( y i y_i yi ) 是输出向量 ( y y y ) 的第 ( i i i ) 个分量,
- ( A i k A_{ik} Aik ) 是矩阵 ( A A A ) 的第 ( i i i ) 行、第 ( k k k ) 列的元素,
- ( x k x_k xk ) 是输入向量 ( x x x ) 的第 ( k k k ) 个分量。
这种形式表明,输出向量 ( y y y ) 的每个分量 ( y i y_i yi ) 都是输入向量 ( x x x ) 的各个分量 ( x k x_k xk ) 经过 ( A i k A_{ik} Aik ) 加权后的线性组合。
2. 矩阵元素的解释
矩阵 ( A A A ) 的元素 ( A i j A_{ij} Aij ) 可以解释为 输入向量 ( x j x_j xj ) 对输出向量 ( y i y_i yi ) 的贡献因子。换句话说,矩阵元素 ( A i j A_{ij} Aij ) 表示 ( x j x_j xj ) 对 ( y i y_i yi ) 的影响大小和方向。这种解释可以带来以下结论:
-
正负关系
- 如果 ( A i j > 0 A_{ij} > 0 Aij>0 ),则 ( x j x_j xj ) 的增大会导致 ( y i y_i yi ) 增大。
- 如果 ( A i j < 0 A_{ij} < 0 Aij<0 ),则 ( x j x_j xj ) 的增大会导致 ( y i y_i yi ) 减小。
-
强弱关系
- 如果 ( A i j A_{ij} Aij ) 值很大,说明 ( y i y_i yi ) 对 ( x j x_j xj ) 的依赖程度很强。
- 如果 ( A i j A_{ij} Aij ) 值接近零,说明 ( x j x_j xj ) 对 ( y i y_i yi ) 几乎没有影响。
-
行或列的相对大小
- 如果矩阵第 ( i i i ) 行中某个元素 ( A i j A_{ij} Aij ) 比其他元素大很多,那么输出 ( y i y_i yi ) 主要依赖于 ( x j x_j xj )。
- 如果第 ( j j j ) 列的元素都很大,说明 ( x j x_j xj ) 对多个 ( y i y_i yi ) 都有较大的影响。
3. 矩阵特殊结构的解释
矩阵的结构对输入-输出关系有重要影响,以下是几个常见的矩阵结构及其对应的解释:
-
下三角矩阵(Lower Triangular Matrix)
如果矩阵 ( A A A ) 是下三角矩阵,即 ( A i j = 0 A_{ij} = 0 Aij=0 ) 当 ( j > i j > i j>i ) 时,则:- 输出 ( y i y_i yi ) 仅依赖于输入 ( x 1 , x 2 , … , x i x_1, x_2, \dots, x_i x1,x2,…,xi )。
- 这种结构经常出现在递归或因果关系中,例如动态系统的时间序列建模。
-
对角矩阵(Diagonal Matrix)
如果 ( A A A ) 是对角矩阵,即 ( A i j = 0 A_{ij} = 0 Aij=0 ) 当 ( i ≠ j i \neq j i=j ) 时,则:- 每个 ( y i y_i yi ) 只依赖于对应的 ( x i x_i xi ),没有其他分量的影响。
- 这种结构常用于独立变量的缩放(Scaling)或权重调整。
-
稀疏矩阵(Sparse Matrix)
如果 ( A A A ) 是稀疏矩阵(大部分元素为零),则:- 只有非零元素所在列的输入 ( x j x_j xj ) 会对某些 ( y i y_i yi ) 产生影响。
- 稀疏矩阵广泛用于表示稀疏网络、关系图或局部连接结构。
4. 具体例子
示例 1:简单矩阵输入-输出关系
假设我们有如下矩阵 ( A A A ) 和输入向量 ( x x x ):
A = [ 2 − 1 0 0 1 3 4 0 2 ] , x = [ 1 2 3 ] . A = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & -1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 3 \\ 4 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix}, \quad x = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix}. A= 204−110032 ,x= 123 .
计算输出向量 ( y = A x y = Ax y=Ax ):
y 1 = 2 ⋅ 1 + ( − 1 ) ⋅ 2 + 0 ⋅ 3 = 0 , y 2 = 0 ⋅ 1 + 1 ⋅ 2 + 3 ⋅ 3 = 11 , y 3 = 4 ⋅ 1 + 0 ⋅ 2 + 2 ⋅ 3 = 10. y_1 = 2 \cdot 1 + (-1) \cdot 2 + 0 \cdot 3 = 0, y_2 = 0 \cdot 1 + 1 \cdot 2 + 3 \cdot 3 = 11, y_3 = 4 \cdot 1 + 0 \cdot 2 + 2 \cdot 3 = 10. y1=2⋅1+(−1)⋅2+0⋅3=0,y2=0⋅1+1⋅2+3⋅3=11,y3=4⋅1+0⋅2+2⋅3=10.
因此,输出向量为:
y = [ 0 11 10 ] . y = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 11 \\ 10 \end{bmatrix}. y= 01110 .
示例 2:Python 实现
以下是用 Python 实现矩阵-向量乘法的代码:
import numpy as np# 定义矩阵 A 和输入向量 x
A = np.array([[2, -1, 0], [0, 1, 3], [4, 0, 2]])
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])# 计算输出向量 y
y = np.dot(A, x)print("Output vector y:", y)
运行结果为:
Output vector y: [ 0 11 10 ]
5. 应用场景
-
物理建模
在物理系统中,矩阵 ( A A A ) 可以表示某种系统特性(如力的传递系数、热传导系数等),输入向量 ( x x x ) 表示输入条件(如力、热源),输出向量 ( y y y ) 表示系统的响应。 -
机器学习
在神经网络的全连接层中,矩阵-向量乘法被用来将上一层的输出(输入向量 ( x x x ))映射到当前层的输出(向量 ( y y y ))。矩阵 ( A A A ) 表示该层的权重。 -
数据分析
在主成分分析(PCA)中,矩阵 ( A A A ) 是主成分矩阵,输入 ( x x x ) 是原始数据,输出 ( y y y ) 是数据在主成分方向上的投影。 -
信号处理
在数字滤波中,矩阵 ( A A A ) 表示滤波器,输入向量 ( x x x ) 表示信号,输出向量 ( y y y ) 是滤波后的信号。
6. 总结
矩阵 ( A A A ) 的输入-输出解释为我们提供了一种理解线性变换的直观方式,通过分析矩阵元素的大小和符号,我们可以深入理解输入与输出之间的依赖关系。这种分析方法在各种实际场景中具有广泛的应用价值,从物理建模到机器学习,再到信号处理和数据分析,矩阵的输入-输出解释无处不在,是学习和应用线性代数的重要工具。
英文版
Input-Output Interpretation of Matrices: A Detailed Overview
In linear algebra, the equation ( y = A x y = Ax y=Ax ) plays a fundamental role, where ( A A A ) is a matrix, ( x x x ) is an input vector, and ( y y y ) is the corresponding output vector. This relationship can be interpreted as a linear mapping where ( A A A ) transforms the input ( x x x ) into the output ( y y y ). This input-output interpretation provides a conceptual framework that is widely used in physics, machine learning, data science, and engineering.
1. Basic Definition
For an ( m × n m \times n m×n ) matrix ( A A A ), multiplying it by an ( n n n )-dimensional input vector ( x x x ) results in an ( m m m )-dimensional output vector ( y y y ). This process is described as:
y i = ∑ k = 1 n A i k x k = A i 1 x 1 + A i 2 x 2 + ⋯ + A i n x n , i = 1 , … , m . y_i = \sum_{k=1}^n A_{ik} x_k = A_{i1}x_1 + A_{i2}x_2 + \cdots + A_{in}x_n, \quad i = 1, \dots, m. yi=k=1∑nAikxk=Ai1x1+Ai2x2+⋯+Ainxn,i=1,…,m.
Here:
- ( y i y_i yi ) is the ( i i i )-th element of the output vector ( y y y ),
- ( A i k A_{ik} Aik ) is the element in the ( i i i )-th row and ( k k k )-th column of ( A A A ),
- ( x k x_k xk ) is the ( k k k )-th element of the input vector ( x x x ).
This equation tells us that each component ( y i y_i yi ) of the output is a weighted sum of the input components ( x k x_k xk ), where the weights are the elements of the matrix ( A A A ).
2. Meaning of Matrix Elements
The element ( A i j A_{ij} Aij ) in the matrix ( A A A ) has a clear interpretation: it represents the influence of the ( j j j )-th input variable ( x j x_j xj ) on the ( i i i )-th output variable ( y i y_i yi ). Some specific conclusions can be drawn from this:
-
Positive or Negative Relationship
- If ( A i j > 0 A_{ij} > 0 Aij>0 ), then an increase in ( x j x_j xj ) will cause ( y i y_i yi ) to increase.
- If ( A i j < 0 A_{ij} < 0 Aij<0 ), then an increase in ( x j x_j xj ) will cause ( y i y_i yi ) to decrease.
-
Strength of Dependence
- A large magnitude of ( A i j A_{ij} Aij ) indicates that ( y i y_i yi ) strongly depends on ( x j x_j xj ).
- A small ( ∣ A i j ∣ |A_{ij}| ∣Aij∣ ) means that ( x j x_j xj ) has little effect on ( y i y_i yi ).
-
Row and Column Effects
- If ( A i j A_{ij} Aij ) in the ( i i i )-th row is significantly larger than the other elements, ( y i y_i yi ) depends heavily on ( x j x_j xj ).
- If a specific column ( j j j ) contains large values, then ( x j x_j xj ) has a strong influence on multiple output components ( y i y_i yi ).
3. Special Matrix Structures
The structure of the matrix ( A A A ) has a significant impact on how the input and output are related:
-
Lower Triangular Matrix
In a lower triangular matrix (where ( A i j = 0 A_{ij} = 0 Aij=0 ) for ($ j > i$ )):- Each output ( y i y_i yi ) only depends on ( x 1 , … , x i x_1, \dots, x_i x1,…,xi ).
- This is useful for systems with causality or stepwise dependencies, such as dynamic systems or recursive models.
-
Diagonal Matrix
In a diagonal matrix (where ( A i j = 0 A_{ij} = 0 Aij=0 ) for ( i ≠ j i \neq j i=j )):- Each ( y i y_i yi ) depends only on the corresponding ( x i x_i xi ).
- This represents independent scaling of each input component.
-
Sparse Matrix
In a sparse matrix (with many zero elements):- Only inputs ( x j x_j xj ) corresponding to non-zero entries in ( A A A ) influence the outputs ( y i y_i yi ).
- Sparse matrices are widely used in graph representations and localized systems.
4. Examples
Example 1: Simple Input-Output Relationship
Let the matrix ( A A A ) and input vector ( x x x ) be:
A = [ 2 − 1 0 0 1 3 4 0 2 ] , x = [ 1 2 3 ] . A = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & -1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 3 \\ 4 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix}, \quad x = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix}. A= 204−110032 ,x= 123 .
The output vector ( y = A x y = Ax y=Ax ) is calculated as:
y 1 = 2 ⋅ 1 + ( − 1 ) ⋅ 2 + 0 ⋅ 3 = 0 , y 2 = 0 ⋅ 1 + 1 ⋅ 2 + 3 ⋅ 3 = 11 , y 3 = 4 ⋅ 1 + 0 ⋅ 2 + 2 ⋅ 3 = 10. y_1 = 2 \cdot 1 + (-1) \cdot 2 + 0 \cdot 3 = 0, y_2 = 0 \cdot 1 + 1 \cdot 2 + 3 \cdot 3 = 11, y_3 = 4 \cdot 1 + 0 \cdot 2 + 2 \cdot 3 = 10. y1=2⋅1+(−1)⋅2+0⋅3=0,y2=0⋅1+1⋅2+3⋅3=11,y3=4⋅1+0⋅2+2⋅3=10.
Thus, the output is:
y = [ 0 11 10 ] . y = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 11 \\ 10 \end{bmatrix}. y= 01110 .
Example 2: Python Implementation
Below is the Python implementation of the above example:
import numpy as np# Define matrix A and input vector x
A = np.array([[2, -1, 0], [0, 1, 3], [4, 0, 2]])
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])# Compute output vector y
y = np.dot(A, x)print("Output vector y:", y)
Output:
Output vector y: [ 0 11 10 ]
5. Applications
-
Physics and Engineering
- In physics, the matrix ( A A A ) might represent a system’s characteristics (e.g., thermal conductivity, forces). The input ( x x x ) represents external stimuli (e.g., heat sources, forces), and ( y y y ) is the system’s response.
-
Machine Learning
- In neural networks, matrix-vector multiplication ( y = A x y = Ax y=Ax ) is used in fully connected layers, where ( A A A ) represents the layer’s weights.
-
Data Analysis
- In Principal Component Analysis (PCA), the matrix ( A A A ) transforms high-dimensional data ( x x x ) into lower-dimensional components ( y y y ).
-
Signal Processing
- In digital signal processing, ( A A A ) can represent a filter, with ( x x x ) as the input signal and ( y y y ) as the filtered output.
-
Economics
- Input-output models in economics use ( y = A x y = Ax y=Ax ) to represent how outputs of one sector depend on inputs from others.
6. Conclusion
The input-output interpretation of ( y = A x y = Ax y=Ax ) provides a powerful framework for understanding linear transformations. By analyzing the structure and elements of ( A A A ), we can understand how input components ( x x x ) influence output components ( y y y ). This perspective has broad applications, from physics and engineering to machine learning and data analysis, making it an indispensable tool for both theoretical and practical purposes.
补充
假设我们有一个矩阵 ( A A A ),它的维度是 ( 3 × 3 3 \times 3 3×3 ),并且有一个输入向量 ( x x x ) 和输出向量 ( y y y )。矩阵 ( A A A ) 和向量 ( x x x ) 如下所示:
A = [ 3 1 0 2 4 1 0 0 5 ] , x = [ 1 2 3 ] A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 & 0 \\ 2 & 4 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 5 \end{bmatrix}, \quad x = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix} A= 320140015 ,x= 123
通过矩阵与向量的乘法,输出向量 ( y y y ) 是:
y = A × x = [ 3 1 0 2 4 1 0 0 5 ] × [ 1 2 3 ] = [ 3 × 1 + 1 × 2 + 0 × 3 2 × 1 + 4 × 2 + 1 × 3 0 × 1 + 0 × 2 + 5 × 3 ] = [ 5 13 15 ] y = A \times x = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 & 0 \\ 2 & 4 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 5 \end{bmatrix} \times \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 3 \times 1 + 1 \times 2 + 0 \times 3 \\ 2 \times 1 + 4 \times 2 + 1 \times 3 \\ 0 \times 1 + 0 \times 2 + 5 \times 3 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 5 \\ 13 \\ 15 \end{bmatrix} y=A×x= 320140015 × 123 = 3×1+1×2+0×32×1+4×2+1×30×1+0×2+5×3 = 51315
矩阵 ( A A A ) 的第 ( j j j ) 列的元素表示输入向量 ( x x x ) 的第 ( j j j ) 个分量对多个输出分量的贡献。具体来说,第 ( j j j ) 列的元素如何影响各个输出 ( y i y_i yi ),反映了输入的不同分量如何通过该列的系数影响多个输出。
理解 “如果第 ( j j j ) 列的元素都很大,说明 ( x j x_j xj ) 对多个 ( y i y_i yi ) 都有较大的影响”:
我们来看矩阵 ( A A A ) 的第 ( 2 2 2 ) 列:
A 列2 = [ 1 4 0 ] A_{\text{列2}} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 4 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} A列2= 140
- 该列的元素分别是 ( A 12 = 1 A_{12} = 1 A12=1 ),( A 22 = 4 A_{22} = 4 A22=4 ),和 ( A 32 = 0 A_{32} = 0 A32=0 )。
从矩阵与向量的乘法中,我们看到 ( x 2 = 2 x_2 = 2 x2=2 ),而第 ( 2 2 2 ) 列的元素分别对输出 ( y 1 y_1 y1 ), ( y 2 y_2 y2 ), 和 ( y 3 y_3 y3 ) 有不同的贡献:
- ( y 1 = 3 × 1 + 1 × 2 + 0 × 3 = 5 y_1 = 3 \times 1 + 1 \times 2 + 0 \times 3 = 5 y1=3×1+1×2+0×3=5 ),其中 ( 1 × 2 1 \times 2 1×2 ) 表示 ( x 2 x_2 x2 ) 对 ( y 1 y_1 y1 ) 的贡献是 ( 2 2 2 ),影响较小。
- ( y 2 = 2 × 1 + 4 × 2 + 1 × 3 = 13 y_2 = 2 \times 1 + 4 \times 2 + 1 \times 3 = 13 y2=2×1+4×2+1×3=13 ),其中 ( 4 × 2 4 \times 2 4×2 ) 表示 ( x 2 x_2 x2 ) 对 ( y 2 y_2 y2 ) 的贡献是 ( 8 8 8 ),影响较大。
- ( y 3 = 0 × 1 + 0 × 2 + 5 × 3 = 15 y_3 = 0 \times 1 + 0 \times 2 + 5 \times 3 = 15 y3=0×1+0×2+5×3=15 ),( x 2 x_2 x2 ) 对 ( y 3 y_3 y3 ) 的贡献是 ( 0 0 0 ),没有影响。
所以,如果矩阵的某一列的元素较大,这意味着该输入分量(例如 ( x 2 x_2 x2 ))对多个输出分量(例如 ( y 1 y_1 y1 ) 和 ( y 2 y_2 y2 ))都有较大的影响,并且影响的程度会随系数的大小变化。例如,在第 ( 2 2 2 ) 列中,系数 ( A 22 = 4 A_{22} = 4 A22=4 ) 对输出 ( y 2 y_2 y2 ) 贡献了较大的影响。
总结来说,矩阵的某一列的元素大,意味着该输入项对多个输出项有较强的影响,特别是在相关系数较大的情况下。
后记
2024年12月20日15点13分于上海,在GPT4o大模型辅助下完成。
相关文章:
)
矩阵:Input-Output Interpretation of Matrices (中英双语)
矩阵的输入-输出解释:深入理解与应用 在线性代数中,矩阵与向量的乘积 ( y A x y Ax yAx ) 是一个极为重要的关系。通过这一公式,我们可以将矩阵 ( A A A ) 看作一个将输入向量 ( x x x ) 映射到输出向量 ( y y y ) 的线性变换。在这种…...

excel 使用vlook up找出两列中不同的内容
当使用 VLOOKUP 函数时,您可以将其用于比较两列的内容。假设您要比较 A 列和 B 列的内容,并将结果显示在 C 列,您可以在 C1 单元格中输入以下公式: 这个公式将在 B 列中的每个单元格中查找是否存在于 A 列中。如果在 A 列中找不到…...

YoloV8改进策略:Head改进|DynamicHead,利用注意力机制统一目标检测头部|即插即用
摘要 论文介绍 本文介绍了一种名为DynamicHead的模块,该模块旨在通过注意力机制统一目标检测头部,以提升目标检测的性能。论文详细阐述了DynamicHead的工作原理,并通过实验证明了其在COCO基准测试上的有效性和效率。 创新点 DynamicHead模块的创新之处在于它首次尝试在一…...
两地的日出日落时间差为啥不相等
悟空去延吉玩耍,在下午4点多的时候发来一张照片,说,天已经黑了!我赶紧地图上看了看,延吉居然和北京差了大约15度的经度差,那就是大约一小时的时差哦。次日我随便查了一下两地的日出日落时间,结果…...

Android Https和WebView
系统会提示说不安全,因为网站通过js就能调用你的android代码,如果你确认你的网站没用到JS的话就不要打开这个开关,如果用到了,就添加一个注解忽略它就行了。 后来就使用我们公司的网站了,发现也出不来,后来…...
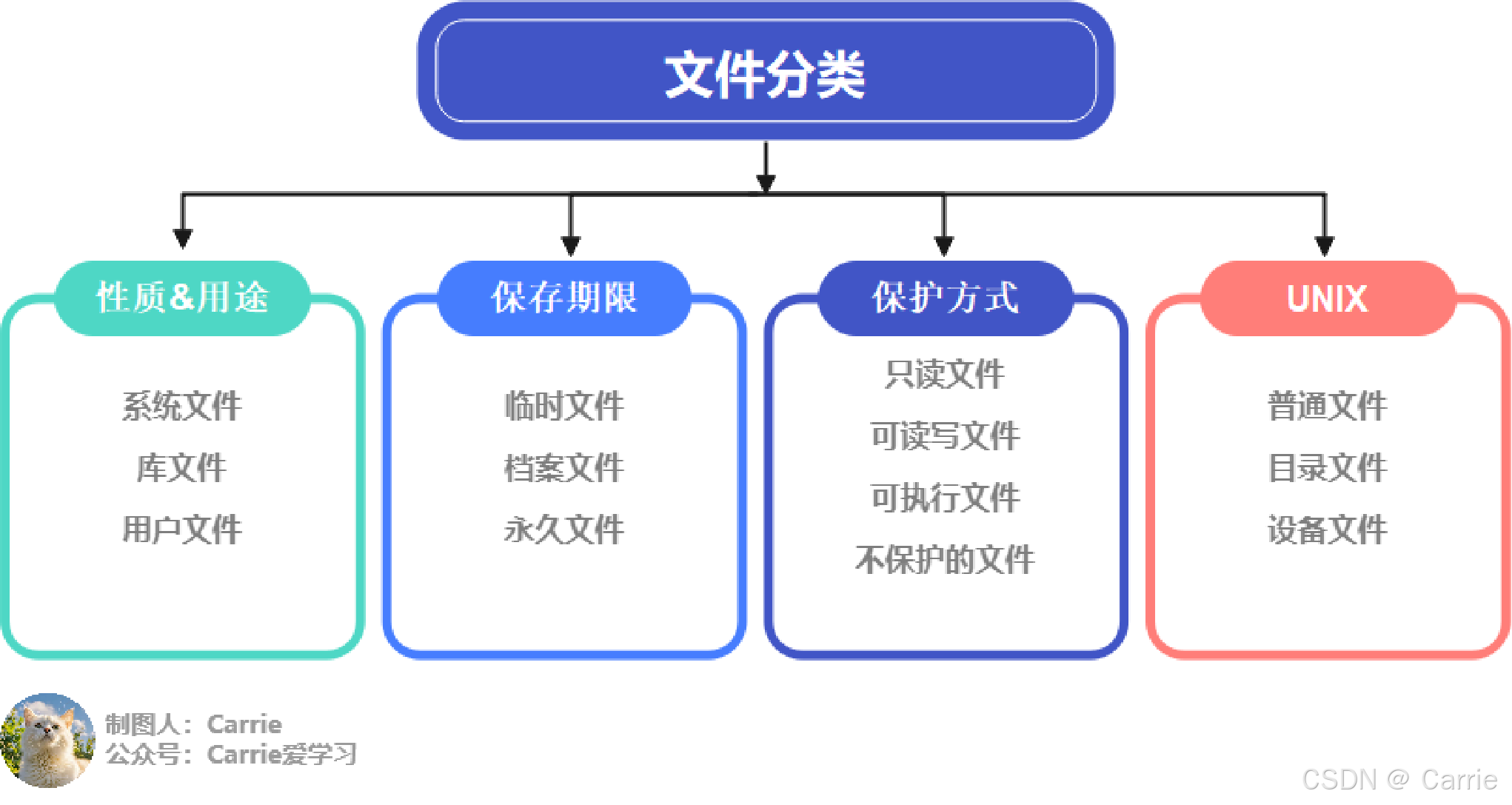
2.5.1 文件管理基本概念
文章目录 文件文件系统文件分类 文件 文件:具有符号名,逻辑上有完整意义的一组相关信息的集合。 文件包含文件体、文件说明两部分。文件体存储文件的真实内容,文件说明存放操作系统管理文件所用的信息。 文件说明包含文件名、内部标识、类型、…...
在 PowerShell 中优雅地显示 Python 虚拟环境
在使用 Python 进行开发时,虚拟环境管理是一个非常重要的部分。无论是使用 venv 还是 conda,我们都希望能够清晰地看到当前所处的虚拟环境。本文将介绍如何在 PowerShell 中配置提示符,使其能够优雅地显示不同类型的 Python 虚拟环境。 问题…...
K8S Ingress 服务配置步骤说明
部署Pod服务 分别使用kubectl run和kubectl apply 部署nginx和tomcat服务 # 快速启动一个nginx服务 kubectl run my-nginx --imagenginx --port80# 使用yaml创建tomcat服务 kubectl apply -f my-tomcat.yamlmy-tomcat.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata:n…...
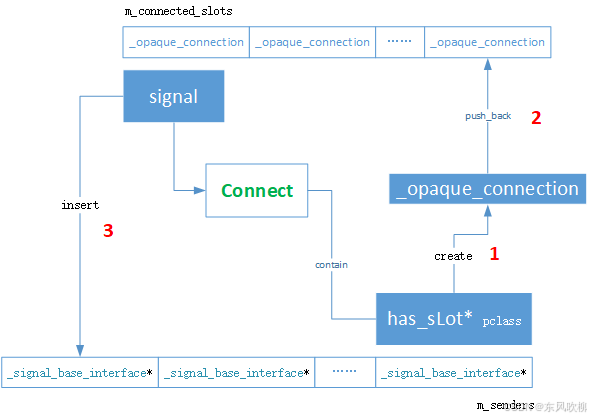
观察者模式(sigslot in C++)
大家,我是东风,今天抽点时间整理一下我很久前关注的一个不错的库,可以支持我们在使用标准C的时候使用信号槽机制进行观察者模式设计,sigslot 官网: http://sigslot.sourceforge.net/ 本文较为详尽探讨了一种观察者模…...

python使用pip进行库的下载
前言 现如今有太多的python编译软件,其库的下载也是五花八门,但在作者看来,无论是哪种方法都是万变不离其宗,即pip下载。 pip是python的包管理工具,无论你是用的什么python软件,都可以用pip进行库的下载。 …...
)
C#(委托)
一、基本定义 在C#中,委托(Delegate)是一种引用类型,它用于封装一个方法(具有特定的参数列表和返回类型)。可以把委托想象成一个能存储方法的变量,这个变量能够像调用普通方法一样来调用它所存…...

《点点之歌》“意外”诞生记
世界是“点点”的,“点点”是世界的。 (笔记模板由python脚本于2024年12月23日 19:28:25创建,本篇笔记适合喜欢诗文的coder翻阅) 【学习的细节是欢悦的历程】 Python 官网:https://www.python.org/ Free:大咖免费“圣经”教程《 …...
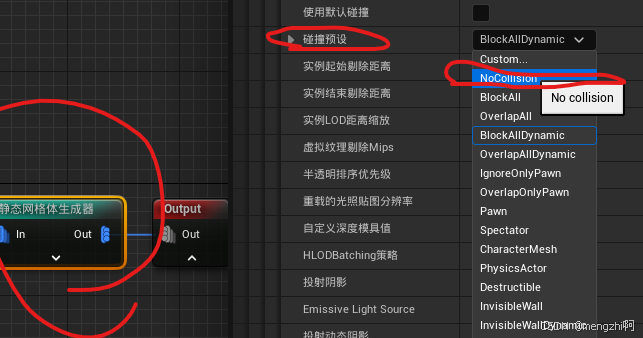
ue5 pcg(程序内容生成)真的简单方便,就5个节点
总结: 前情提示 鼠标单击右键平移节点 1.编辑-》插件-》procedural->勾选两个插件 2.右键-》pcg图表-》拖拽进入场景 3.先看点point 右键-》调试(快捷键d)->右侧设置粒子数 3.1调整粒子数 可以在右侧输入框,使用加减乘除 4.1 表面采样器 …...

32岁前端干了8年,是继续做前端开发,还是转其它工作
前端发展有瓶颈,变来变去都是那一套,只是换了框架换了环境。换了框架后又得去学习,虽然很快上手,但是那些刚毕业的也很快上手了,入门门槛越来越低,想转行或继续卷,该如何破圈 这是一位网友的自述…...
【演化博弈】期望收益函数公式、复制动态方程——化简功能技巧
期望化简 在演化博弈论的研究中,期望收益函数和复制动态方程是核心工具。化简这些公式的功能技巧具有以下几个重要作用: 提高公式的可读性和理解度 复杂的数学表达式可能让人感到困惑。通过化简,公式变得更加简单和易读,使研究者…...

opencv中的各种滤波器简介
在 OpenCV 中,滤波器是图像处理中的重要工具,用于对图像进行平滑、去噪、边缘检测等操作。以下是几种常见滤波器的简单介绍。 1. 均值滤波 (Mean Filter) 功能: 对图像进行平滑处理,减少噪声。 应用场景: 去除图像…...

[Effective C++]条款36-37 两个绝不
本文初发于 “天目中云的小站”,同步转载于此。 条款36 : 绝不重新定义继承而来的non-virtual函数 本条款很容易理解, 援引以前的条款就可以说明为什么 : 条款34中就提到过 : non-virtual函数意味着接口 强制性实现继承, 它不应当被改变. 重新定义继承而来的non-…...
)
各种网站(学习资源及其他)
欢迎围观笔者的个人博客~ 也欢迎通过RSS网址https://kangaroogao.github.io/atom.xml进行订阅~ 大学指南 上海交通大学生存手册中国科学技术大学人工智能与数据科学学院本科进阶指南USTC不完全入学指南大学生活质量指北科研论 信息搜集 AI信息搜集USTC飞跃网站计算机保研 技…...

docker怎么部署高斯数据库
部署高斯数据库(openGauss)到Docker的步骤如下: 安装Docker: 如果您的系统尚未安装Docker,需要先进行安装。以CentOS为例,可以使用以下命令安装Docker: yum install -y docker拉取镜像ÿ…...
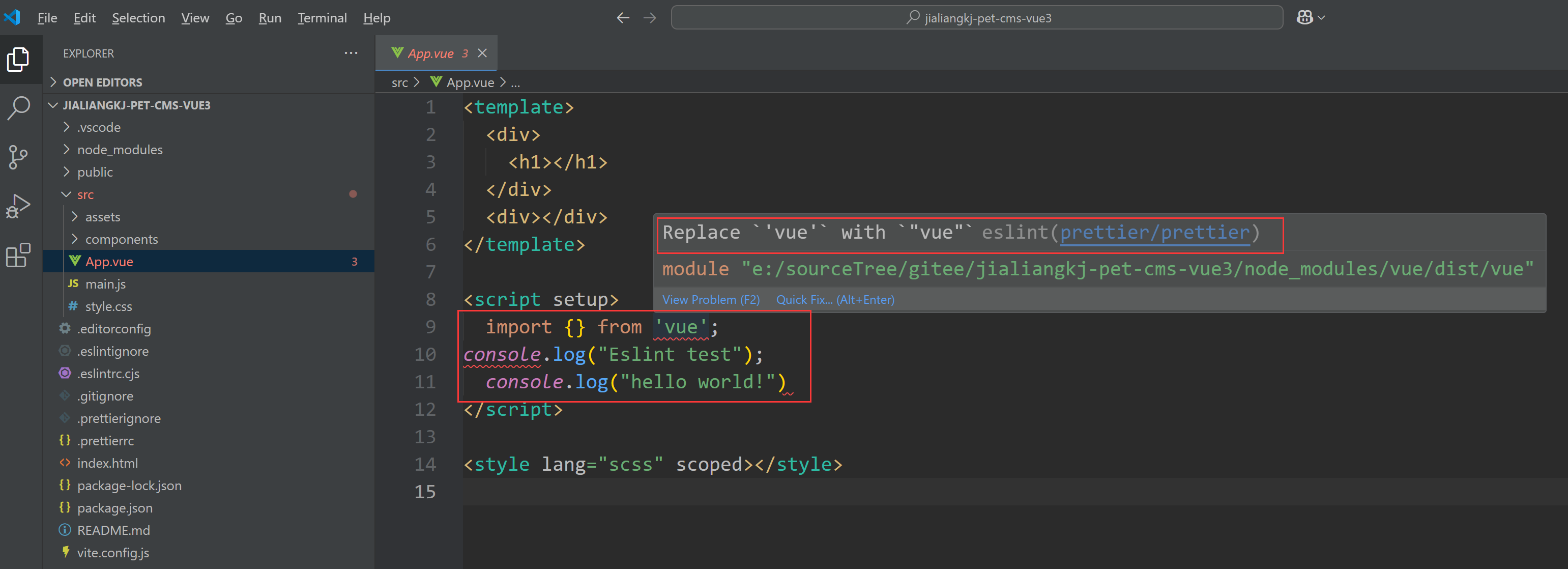
VScode中配置ESlint+Prettier详细步骤(图文详情)
VScode中配置ESlintPrettier详细步骤(图文详情) 前置环境: node 18.19.0 vite 3.2.11 vue 3.2.47 本文将不在演示vue3基础工程创建,如果还没有vue3项目工程请参考文章: Vite创建Vue3工程并引入ElementPlus&#x…...

【SpringBoot】100、SpringBoot中使用自定义注解+AOP实现参数自动解密
在实际项目中,用户注册、登录、修改密码等操作,都涉及到参数传输安全问题。所以我们需要在前端对账户、密码等敏感信息加密传输,在后端接收到数据后能自动解密。 1、引入依赖 <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...
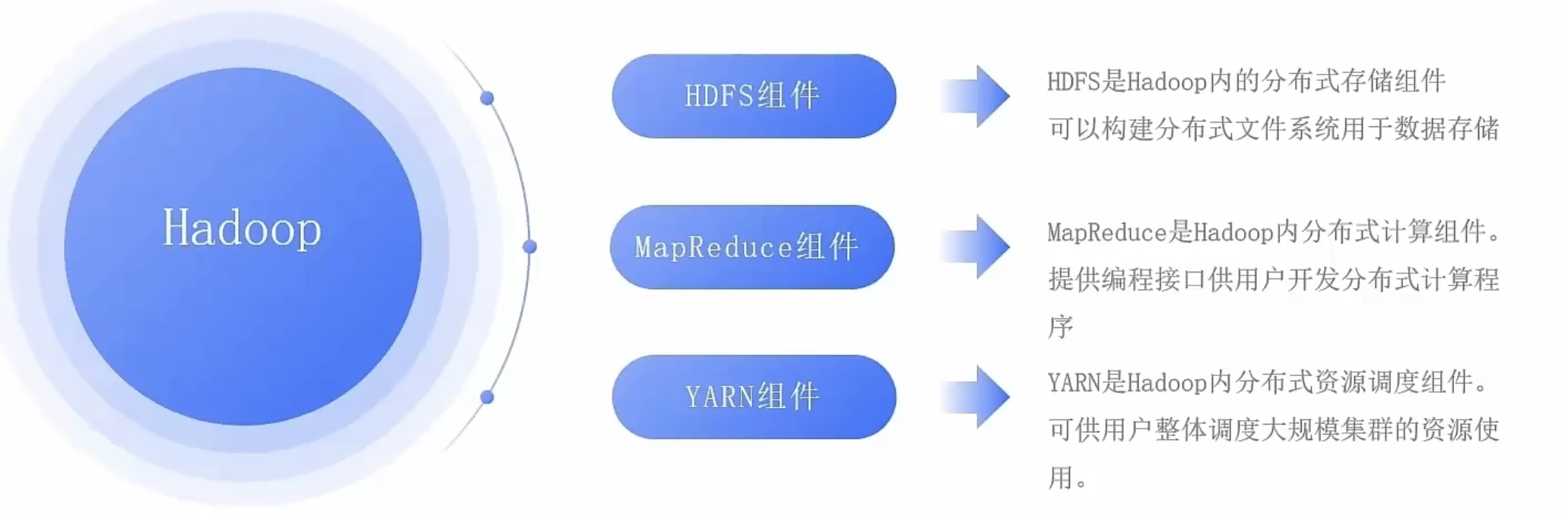
大数据零基础学习day1之环境准备和大数据初步理解
学习大数据会使用到多台Linux服务器。 一、环境准备 1、VMware 基于VMware构建Linux虚拟机 是大数据从业者或者IT从业者的必备技能之一也是成本低廉的方案 所以VMware虚拟机方案是必须要学习的。 (1)设置网关 打开VMware虚拟机,点击编辑…...

镜像里切换为普通用户
如果你登录远程虚拟机默认就是 root 用户,但你不希望用 root 权限运行 ns-3(这是对的,ns3 工具会拒绝 root),你可以按以下方法创建一个 非 root 用户账号 并切换到它运行 ns-3。 一次性解决方案:创建非 roo…...

智能分布式爬虫的数据处理流水线优化:基于深度强化学习的数据质量控制
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,数据已成为企业和研究机构的核心资产。智能分布式爬虫作为高效的数据采集工具,在大规模数据获取中发挥着关键作用。然而,传统的数据处理流水线在面对复杂多变的网络环境和海量异构数据时,常出现数据质…...
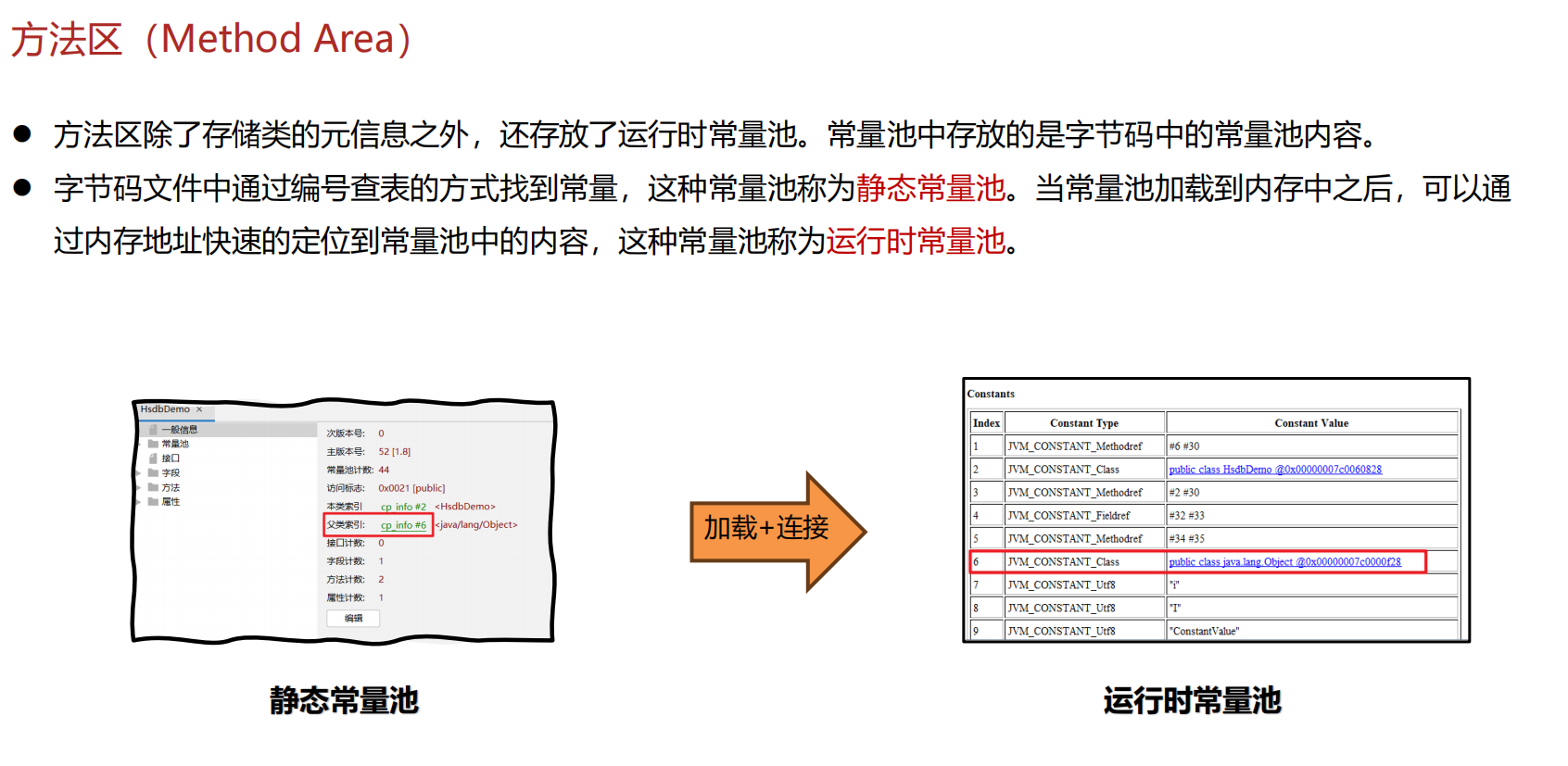
JVM 内存结构 详解
内存结构 运行时数据区: Java虚拟机在运行Java程序过程中管理的内存区域。 程序计数器: 线程私有,程序控制流的指示器,分支、循环、跳转、异常处理、线程恢复等基础功能都依赖这个计数器完成。 每个线程都有一个程序计数…...

面向无人机海岸带生态系统监测的语义分割基准数据集
描述:海岸带生态系统的监测是维护生态平衡和可持续发展的重要任务。语义分割技术在遥感影像中的应用为海岸带生态系统的精准监测提供了有效手段。然而,目前该领域仍面临一个挑战,即缺乏公开的专门面向海岸带生态系统的语义分割基准数据集。受…...
的使用)
Go 并发编程基础:通道(Channel)的使用
在 Go 中,Channel 是 Goroutine 之间通信的核心机制。它提供了一个线程安全的通信方式,用于在多个 Goroutine 之间传递数据,从而实现高效的并发编程。 本章将介绍 Channel 的基本概念、用法、缓冲、关闭机制以及 select 的使用。 一、Channel…...
 error)
【前端异常】JavaScript错误处理:分析 Uncaught (in promise) error
在前端开发中,JavaScript 异常是不可避免的。随着现代前端应用越来越多地使用异步操作(如 Promise、async/await 等),开发者常常会遇到 Uncaught (in promise) error 错误。这个错误是由于未正确处理 Promise 的拒绝(r…...
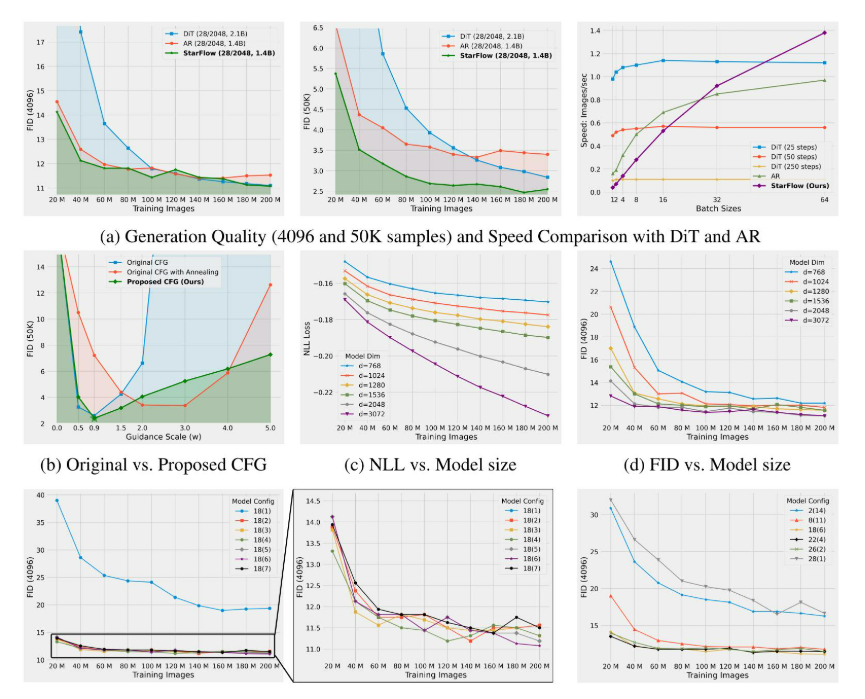
高分辨率图像合成归一化流扩展
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 1 摘要 我们提出了STARFlow,一种基于归一化流的可扩展生成模型,它在高分辨率图像合成方面取得了强大的性能。STARFlow的主要构建块是Transformer自回归流(TARFlow&am…...
