小白零基础--CPP多线程
进程
- 进程就是运行中的程序
- 线程=进程中的进程
1、C++11 Thread线程库基础
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include<string>void printthread(std::string msg){std::cout<<msg<<std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++){std::cout<<"my "<<i<<std::endl;}return;
}int main(){//std::thread t(入口)//1、创建线程std::thread t(printthread,"hello thread");//2、保证等待线程结束,主线程在结束// t.join();//3、分离线程//t.detach();//4、joinable 判断是否可以调用joinbool isjoin = t.joinable();if(isjoin){t.join();}std::cout<<"over"<<std::endl;system( "pause");return 0;
}
2、线程函数中的数据未定义错误
2.1 临时变量
错误例子
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>void foo(int& x){x+=1;
}int main(){//std::thread t(foo,1);t.join();system( "pause");return 0;
}
正确方案
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>void foo(int& x){x+=1;
}int main(){//int i=1;std::thread t(foo,std::ref(i));t.join();std::cout<<i<<std::endl;system( "pause");return 0;
}
2.2 传递指针/引用指向局部变量
2.1 的 i 在 main中,那要是不在呢?
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>std::thread t;
void foo(int& x){x+=1;
}void externi(){int i=1;t=std::thread (foo,std::ref(i));
}int main(){//externi();t.join();system( "pause");return 0;
}
会报错
那怎么办呢?
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>std::thread t;int i=1;
void foo(int& x){x+=1;
}void externi(){t=std::thread (foo,std::ref(i));
}int main(){//externi();t.join();std::cout<<i<<std::endl;system( "pause");return 0;
}
2.3 参数被提前手动释放
智能指针
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <memory>class myclass
{
private:/* data */
public:void foo(){std::cout<<"mememem"<<std::endl;}
};int main(){std::shared_ptr<myclass> a=std::make_shared<myclass> ();std::thread t(&myclass::foo,a);system( "pause");return 0;
}
2.4 类的private函数
友元
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <memory>class myclass
{
private:friend void foo_thread();void foo(){std::cout<<"mememem"<<std::endl;}
public:};
void foo_thread(){std::shared_ptr<myclass> a=std::make_shared<myclass> ();std::thread t(&myclass::foo,a);t.join();
}
int main(){foo_thread();system( "pause");return 0;
}
3互斥量
3.1数据共享–数据竞争问题
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>int a = 0;
void func(){for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++){a+=1;}}
int main(){std::thread t1(func);std::thread t2(func);t1.join();t2.join();std::cout<<a<<std::endl;system( "pause");return 0;
}
3.2 互斥锁
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
int a = 0;std::mutex mt;
void func(){for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++){ mt.lock();a+=1;mt.unlock();}}
int main(){std::thread t1(func);std::thread t2(func);t1.join();t2.join();std::cout<<a<<std::endl;system( "pause");return 0;
}
3.3 理解线程安全
4互斥量死锁
4.1 死锁的概念
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;mutex m1,m2;
void func1(){for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){ m1.lock();m2.lock();m1.unlock();m2.unlock();}}
void func2(){for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){ m1.lock();m2.lock();m2.unlock();m1.unlock();}
}
int main(){thread t1(func1);thread t2(func2);t1.join();t2.join();cout<<"over<<"<<endl;system( "pause");return 0;
}
4.2 解决方案
5 lock_guard 和 std::unique_lock
5.1 lock_guard
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
int a=0;
mutex m1;
void func1(){for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){lock_guard<mutex> gm(m1);a++;}
}int main(){thread t1(func1);t1.join();cout<<a<<endl;system( "pause");return 0;
}
5.2 std::unique_lock
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
int a=0;
mutex m1;
void func1(){for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){unique_lock<mutex> gm(m1);a++;}
}int main(){thread t1(func1);t1.join();cout<<a<<endl;system( "pause");return 0;
}
6 call_once
6.1 单例模式
6.2 例子:日志类
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
class Log{
public:Log(){};Log(const Log& log)=delete;Log &operator =(const Log& log)=delete;static Log& GetInstance(){static Log log;//懒汉模式return log;//饿汉模式/**static Log *log=nullptr;if(!log) log = new Log;return *log;*/}void PrintLog(string msg){cout << __TIME__ <<" " <<msg<<endl;}
};int main(){Log::GetInstance().PrintLog("error");system( "pause");return 0;
}
6.3 call_once
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <vector>using namespace std;// 需要一次性初始化的共享资源
class DatabaseConfig {
private:string serverAddress;int port;DatabaseConfig() : serverAddress("127.0.0.1"), port(3306) {cout << "数据库配置初始化完成!" << endl;}public:static DatabaseConfig& getInstance() {static once_flag initFlag;static DatabaseConfig* instance = nullptr;call_once(initFlag, []() {instance = new DatabaseConfig();});return *instance;}void showConfig() {cout << "Server: " << serverAddress << ":" << port << endl;}
};// 多线程测试函数
void threadTask(int id) {this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(100 * id));auto& config = DatabaseConfig::getInstance();cout << "线程" << id << "获取配置:";config.showConfig();
}int main() {vector<thread> threads;// 创建10个线程竞争访问for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {threads.emplace_back(threadTask, i);}// 等待所有线程完成for(auto& t : threads) {t.join();}system("pause");return 0;
}
- 合理使用 call_once 可以让多线程代码更简洁、更安全,尤其适合需要一次性初始化的场景
7 condition_variable
7.1 生产者-消费者模式概述
生产者-消费者模式是多线程编程中经典的同步问题,需要满足以下条件:
- 生产者线程生成数据并放入共享缓冲区。
- 消费者线程从缓冲区取出数据并处理。
- 同步要求:
- 缓冲区满时,生产者等待消费者消费数据。
- 缓冲区空时,消费者等待生产者生产数据。
7.2 核心组件
- 共享缓冲区:通常使用队列(
std::queue)实现。 - 互斥锁(
std::mutex):保护对缓冲区的并发访问。 - 条件变量(
std::condition_variable):not_full:生产者等待缓冲区非满。not_empty:消费者等待缓冲区非空。
7.3实现代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <chrono>using namespace std;const int BUFFER_SIZE = 5; // 缓冲区容量
queue<int> buffer; // 共享缓冲区
mutex mtx; // 互斥锁
condition_variable not_full; // 缓冲区非满条件
condition_variable not_empty; // 缓冲区非空条件// 生产者函数
void producer(int id) {for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {unique_lock<mutex> lock(mtx);// 如果缓冲区满,等待消费者消费not_full.wait(lock, [] { return buffer.size() < BUFFER_SIZE; });// 生产数据int data = id * 100 + i;buffer.push(data);cout << "生产者 " << id << " 生产数据: " << data << endl;lock.unlock();not_empty.notify_one(); // 通知消费者this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(100));}
}// 消费者函数
void consumer(int id) {for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {unique_lock<mutex> lock(mtx);// 如果缓冲区空,等待生产者生产not_empty.wait(lock, [] { return !buffer.empty(); });// 消费数据int data = buffer.front();buffer.pop();cout << "消费者 " << id << " 消费数据: " << data << endl;lock.unlock();not_full.notify_one(); // 通知生产者this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(200));}
}int main() {thread producers[2];thread consumers[3];// 启动2个生产者线程for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {producers[i] = thread(producer, i);}// 启动3个消费者线程for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {consumers[i] = thread(consumer, i);}// 等待所有线程结束for (auto& t : producers) t.join();for (auto& t : consumers) t.join();return 0;
}
7.4 代码解析
-
共享资源保护:
- 所有对缓冲区的操作(
push、pop)均在互斥锁mtx的保护下进行。 - 使用
unique_lock自动管理锁的生命周期。
- 所有对缓冲区的操作(
-
条件变量的使用:
- 生产者等待条件:
not_full.wait(lock, predicate)
当缓冲区满时(buffer.size() >= BUFFER_SIZE),生产者线程阻塞,直到消费者消费数据后通过not_full.notify_one()唤醒。 - 消费者等待条件:
not_empty.wait(lock, predicate)
当缓冲区空时(buffer.empty()),消费者线程阻塞,直到生产者生产数据后通过not_empty.notify_one()唤醒。
- 生产者等待条件:
-
通知机制:
- 生产者生产数据后调用
not_empty.notify_one(),唤醒一个等待的消费者。 - 消费者消费数据后调用
not_full.notify_one(),唤醒一个等待的生产者。
- 生产者生产数据后调用
7.5 运行结果示例
生产者 0 生产数据: 0
消费者 0 消费数据: 0
生产者 1 生产数据: 100
消费者 1 消费数据: 100
生产者 0 生产数据: 1
消费者 2 消费数据: 1
...
(输出将展示生产与消费的交替过程)
7.6 关键点总结
-
防止虚假唤醒:
条件变量的wait必须配合谓词(如buffer.size() < BUFFER_SIZE)使用,确保即使被意外唤醒也能重新检查条件。 -
资源管理:
unique_lock在wait时自动释放锁,唤醒后重新获取锁。- 使用
notify_one而非notify_all,减少不必要的线程竞争。
-
死锁避免:
- 确保在调用
notify_one前释放锁(通过lock.unlock())。 - 避免在持有锁时进行耗时操作(如示例中的
sleep_for在锁外执行)。
- 确保在调用
7.7 扩展场景
-
多生产者和多消费者:
当前代码已支持多个生产者和消费者,通过调整线程数量即可验证。 -
动态缓冲区大小:
可将BUFFER_SIZE设为动态值,根据需求调整。 -
复杂数据类型:
将queue<int>替换为自定义数据类型队列,实现更复杂的生产-消费逻辑。
此实现完整展示了如何利用condition_variable实现线程安全的生产者-消费者模式,可直接用于实际项目中的任务队列、线程池等场景。
8 跨平台线程池
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <memory>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <future>
#include <functional>
#include <stdexcept>class ThreadPool {
public:// 构造函数,启动指定数量的工作线程ThreadPool(size_t threads = std::thread::hardware_concurrency()): stop(false) {for(size_t i = 0; i < threads; ++i)workers.emplace_back([this] {for(;;) {std::function<void()> task;{std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(this->queue_mutex);this->condition.wait(lock,[this]{ return this->stop || !this->tasks.empty(); });if(this->stop && this->tasks.empty())return;task = std::move(this->tasks.front());this->tasks.pop();}task();}});}// 将任务添加到任务队列,返回一个future以便获取结果template<class F, class... Args>auto enqueue(F&& f, Args&&... args) -> std::future<typename std::result_of<F(Args...)>::type> {using return_type = typename std::result_of<F(Args...)>::type;auto task = std::make_shared< std::packaged_task<return_type()> >(std::bind(std::forward<F>(f), std::forward<Args>(args)...));std::future<return_type> res = task->get_future();{std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex);// 不允许在停止线程池后添加新任务if(stop)throw std::runtime_error("enqueue on stopped ThreadPool");tasks.emplace([task](){ (*task)(); });}condition.notify_one();return res;}// 析构函数,等待所有任务完成并停止所有线程~ThreadPool() {{std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex);stop = true;}condition.notify_all();for(std::thread &worker : workers)worker.join();}private:std::vector<std::thread> workers; // 工作线程集合std::queue<std::function<void()>> tasks; // 任务队列std::mutex queue_mutex; // 任务队列互斥锁std::condition_variable condition; // 条件变量bool stop; // 停止标志
};// 使用示例
int main() {ThreadPool pool(4); // 创建4个工作线程// 提交多个任务到线程池std::vector<std::future<int>> results;for(int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {results.emplace_back(pool.enqueue([i] {std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));return i*i;}));}// 获取任务结果for(auto && result : results)std::cout << result.get() << ' ';std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}
9 异步并发 async future packaged task promise
#include <iostream>
#include <future>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <vector>int compute(int x) {std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1)); // 模拟耗时操作return x * x;
}int main() {// 使用 std::async 启动多个异步任务std::vector<std::future<int>> futures;for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {futures.push_back(std::async(std::launch::async, compute, i));}// 获取所有任务的结果for (auto& future : futures) {std::cout << "Result: " << future.get() << std::endl;}// 使用 std::packaged_task 手动控制任务执行std::packaged_task<int(int)> task(compute);std::future<int> future = task.get_future();std::thread t(std::move(task), 10);t.join(); // 等待线程完成std::cout << "Packaged Task Result: " << future.get() << std::endl;return 0;
}
10 原子操作atomic
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <atomic>
using namespace std;atomic<int> a(0); // 使用 atomic<int> 替代普通 intvoid func1() {for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {a++; // 原子操作,无需额外的互斥锁}
}int main() {thread t1(func1);t1.join();cout << a << endl; // 输出最终结果system("pause");return 0;
}
相关文章:

小白零基础--CPP多线程
进程 进程就是运行中的程序线程进程中的进程 1、C11 Thread线程库基础 #include <iostream> #include <thread> #include<string>void printthread(std::string msg){std::cout<<msg<<std::endl;for (int i 0; i < 1000; i){std::cout<…...

利用deepseek参与软件测试 基本架构如何 又该在什么环节接入deepseek
利用DeepSeek参与软件测试,可以考虑以下基本架构和接入环节: ### 基本架构 - **数据层** - **测试数据存储**:用于存放各种测试数据,包括正常输入数据、边界值数据、异常数据等,这些数据可以作为DeepSeek的输入&…...
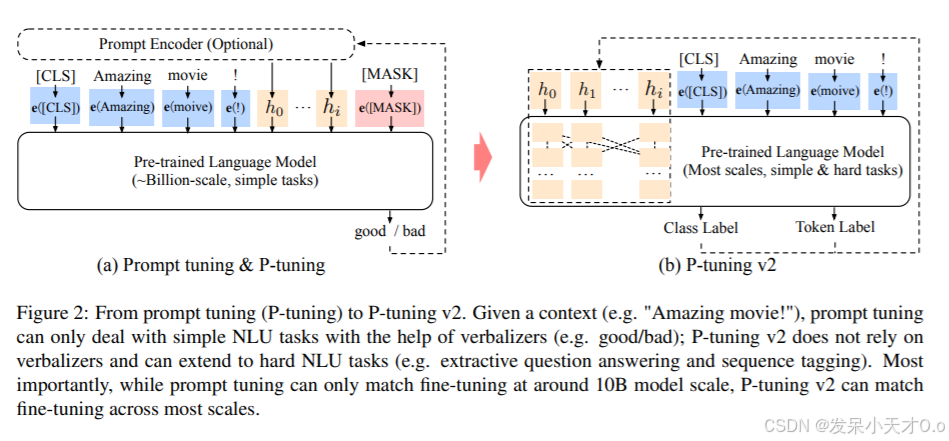
大模型微调技术总结及使用GPU对VisualGLM-6B进行高效微调
1. 概述 在深度学习中,微调(Fine-tuning)是一种重要的技术,用于改进预训练模型的性能。在预训练模型的基础上,针对特定任务(如文本分类、机器翻译、情感分析等),使用相对较小的有监…...
WPF进阶 | WPF 样式与模板:打造个性化用户界面的利器
WPF进阶 | WPF 样式与模板:打造个性化用户界面的利器 一、前言二、WPF 样式基础2.1 什么是样式2.2 样式的定义2.3 样式的应用 三、WPF 模板基础3.1 什么是模板3.2 控件模板3.3 数据模板 四、样式与模板的高级应用4.1 样式继承4.2 模板绑定4.3 资源字典 五、实际应用…...

Java 大视界 -- Java 大数据在自动驾驶中的数据处理与决策支持(68)
💖亲爱的朋友们,热烈欢迎来到 青云交的博客!能与诸位在此相逢,我倍感荣幸。在这飞速更迭的时代,我们都渴望一方心灵净土,而 我的博客 正是这样温暖的所在。这里为你呈上趣味与实用兼具的知识,也…...
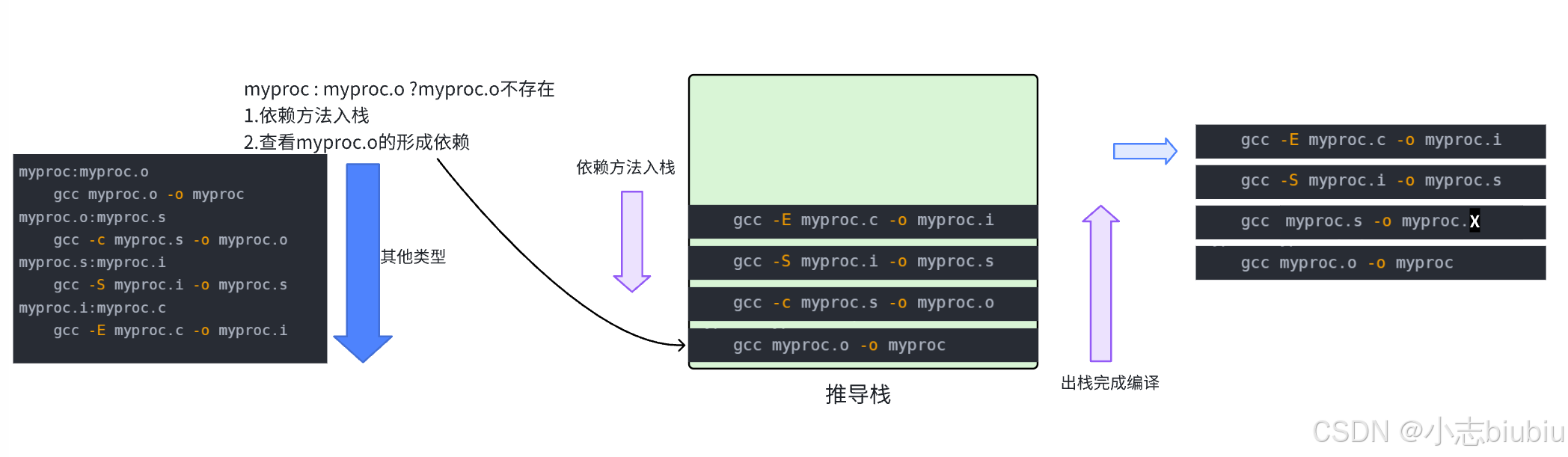
自动化构建-make/Makefile 【Linux基础开发工具】
文章目录 一、背景二、Makefile编译过程三、变量四、变量赋值1、""是最普通的等号2、“:” 表示直接赋值3、“?” 表示如果该变量没有被赋值,4、""和写代码是一样的, 五、预定义变量六、函数**通配符** 七、伪目标 .PHONY八、其他常…...

python学opencv|读取图像(五十二)使用cv.matchTemplate()函数实现最佳图像匹配
【1】引言 前序学习了图像的常规读取和基本按位操作技巧,相关文章包括且不限于: python学opencv|读取图像-CSDN博客 python学opencv|读取图像(四十九)原理探究:使用cv2.bitwise()系列函数实现图像按位运算-CSDN博客…...
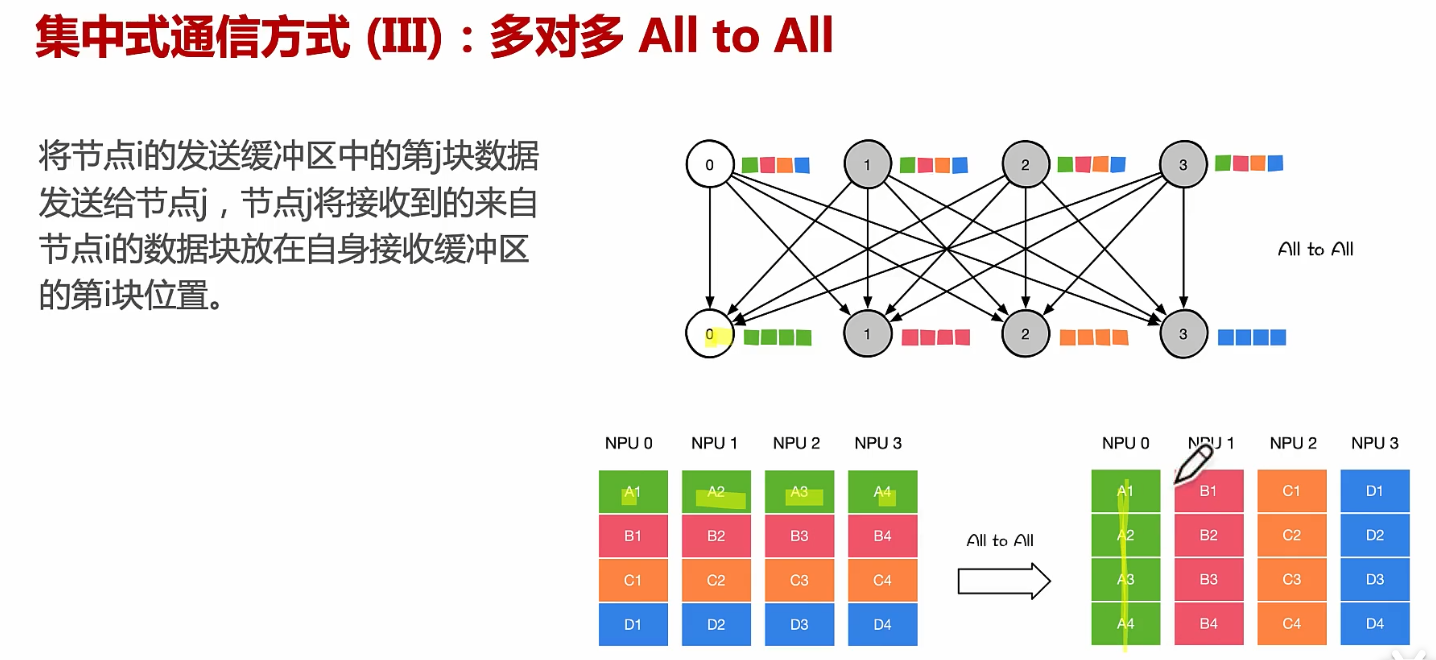
通信方式、点对点通信、集合通信
文章目录 从硬件PCIE、NVLINK、RDMA原理到通信NCCL、MPI原理!通信实现方式:机器内通信、机器间通信通信实现方式:通讯协调通信实现方式:机器内通信:PCIe通信实现方式:机器内通信:NVLink通信实现…...

TCP编程
1.socket函数 int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol); 头文件:include<sys/types.h>,include<sys/socket.h> 参数 int domain AF_INET: IPv4 Internet protocols AF_INET6: IPv6 Internet protocols AF_UNIX, AF_LOCAL : Local…...

OpenAI 实战进阶教程 - 第七节: 与数据库集成 - 生成 SQL 查询与优化
内容目标 学习如何使用 OpenAI 辅助生成和优化多表 SQL 查询了解如何获取数据库结构信息并与 OpenAI 结合使用 实操步骤 1. 创建 SQLite 数据库示例 创建数据库及表结构: import sqlite3# 连接 SQLite 数据库(如果不存在则创建) conn sq…...

Apache Iceberg数据湖技术在海量实时数据处理、实时特征工程和模型训练的应用技术方案和具体实施步骤及代码
Apache Iceberg在处理海量实时数据、支持实时特征工程和模型训练方面的强大能力。Iceberg支持实时特征工程和模型训练,特别适用于需要处理海量实时数据的机器学习工作流。 Iceberg作为数据湖,以支持其机器学习平台中的特征存储。Iceberg的分层结构、快照…...
QT交叉编译环境搭建(Cmake和qmake)
介绍一共有两种方法(基于qmake和cmake): 1.直接调用虚拟机中的交叉编译工具编译 2.在QT中新建编译套件kits camke和qmake的区别:CMake 和 qmake 都是自动化构建工具,用于简化构建过程,管理编译设置&…...
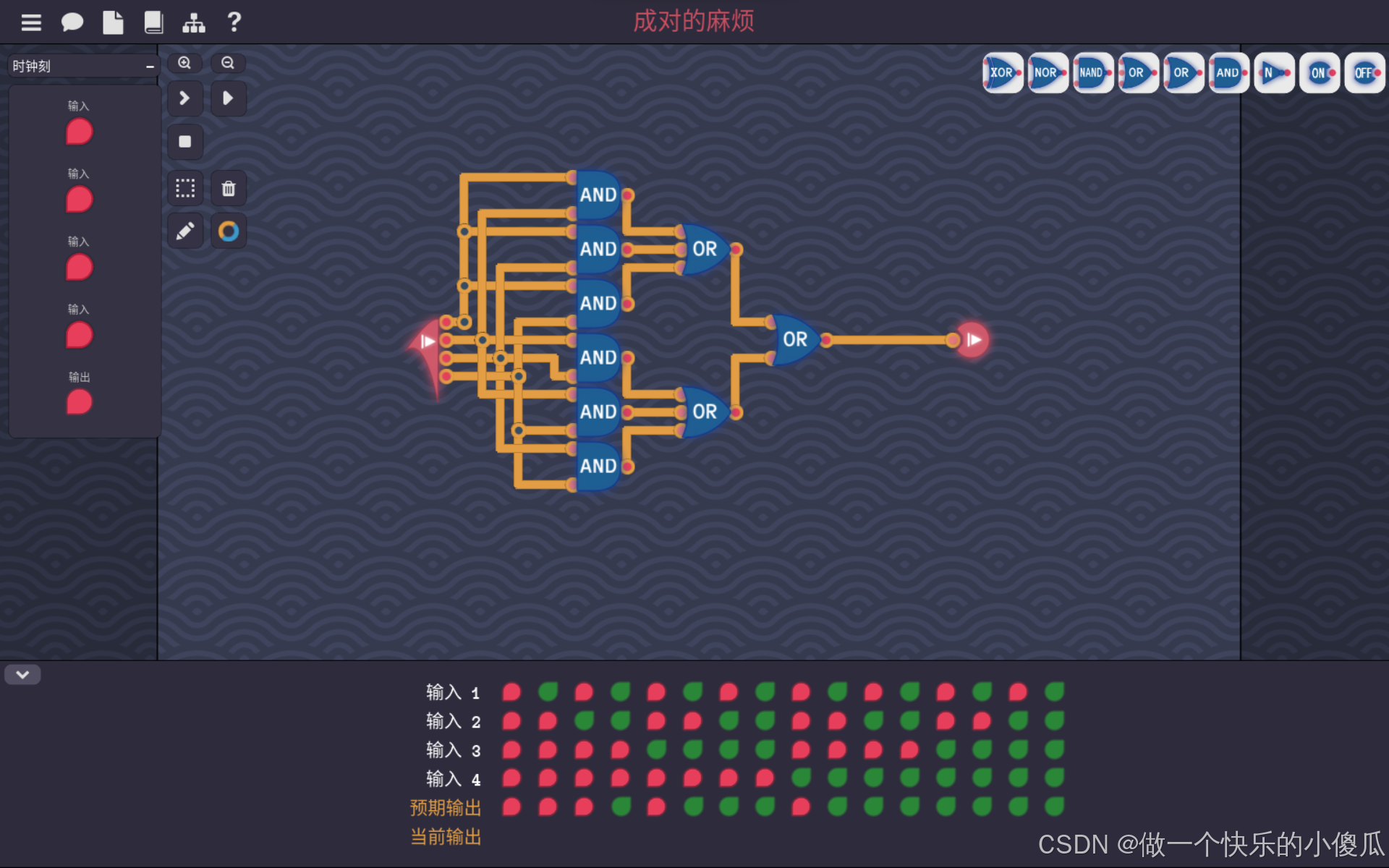
Turing Complete-成对的麻烦
这一关是4个输入,当输入中1的个数大于等于2时,输出1。 那么首先用个与门来检测4个输入中,1的个数是否大于等于2,当大于等于2时,至少会有一个与门输出1,所以再用两级或门讲6个与门的输出取或,得…...

寒假刷题Day20
一、80. 删除有序数组中的重复项 II class Solution { public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {int n nums.size();int stackSize 2;for(int i 2; i < n; i){if(nums[i] ! nums[stackSize - 2]){nums[stackSize] nums[i];}}return min(stackSize, …...
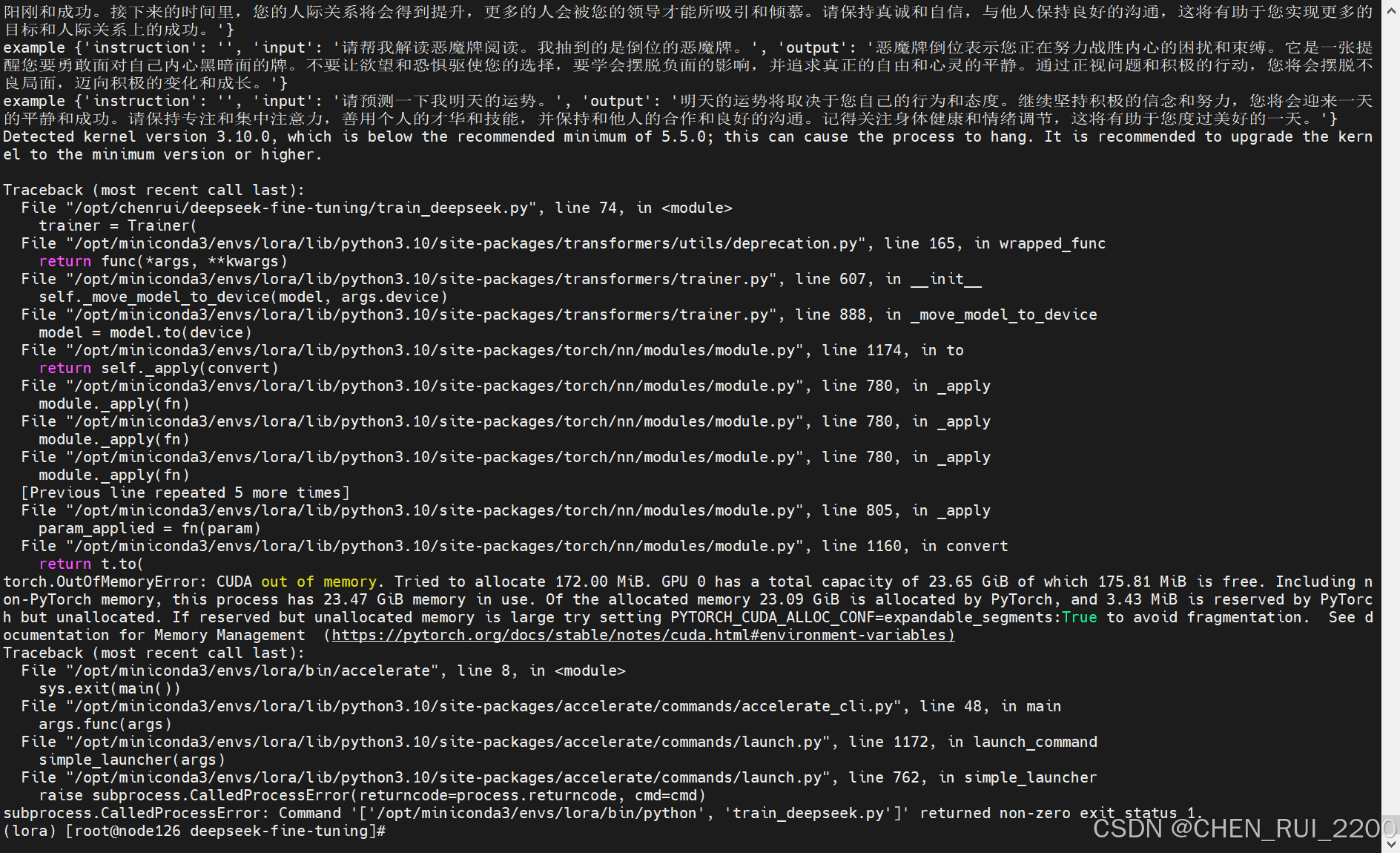
deepseek 本地化部署和小模型微调
安装ollama 因为本人gpu卡的机器系统是centos 7, 直接使用ollama会报 所以ollama使用镜像方式进行部署, 拉取镜像ollama/ollama 启动命令 docker run -d --privileged -v ollama:/root/.ollama -p 11434:11434 --name ollama ollama/ollama 查看ollama 是否启动…...

【Java异步编程】基于任务类型创建不同的线程池
文章目录 一. 按照任务类型对线程池进行分类1. IO密集型任务的线程数2. CPU密集型任务的线程数3. 混合型任务的线程数 二. 线程数越多越好吗三. Redis 单线程的高效性 使用线程池的好处主要有以下三点: 降低资源消耗:线程是稀缺资源,如果无限…...

makailio-alias_db模块详解
ALIAS_DB 模块 作者 Daniel-Constantin Mierla micondagmail.com Elena-Ramona Modroiu ramonaasipto.com 编辑 Daniel-Constantin Mierla micondagmail.com 版权 © 2005 Voice Sistem SRL © 2008 asipto.com 目录 管理员指南 概述依赖 2.1 Kamailio 模块 2.2 外…...
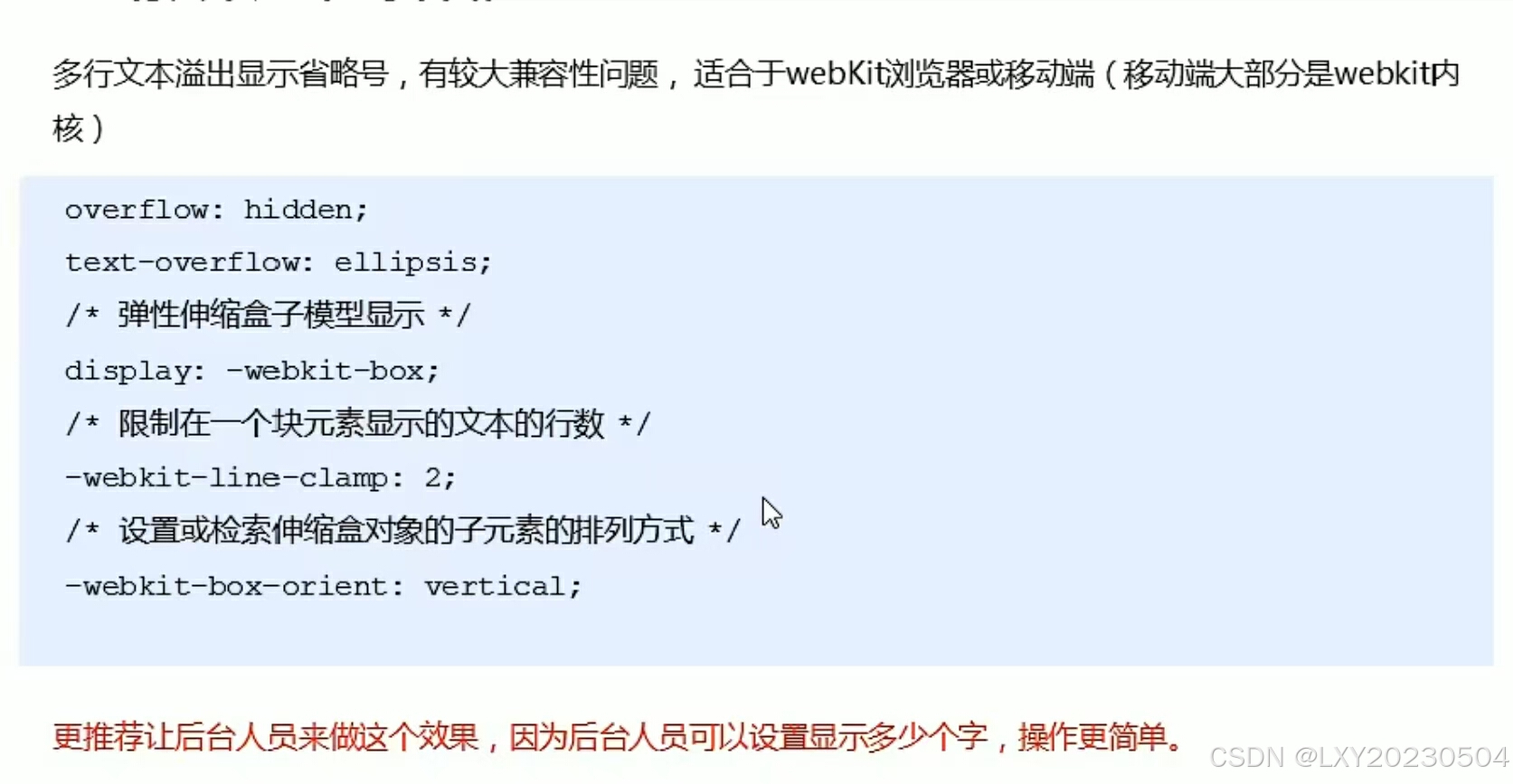
文字显示省略号
多行文本溢出显示省略号...

[LeetCode] 字符串完整版 — 双指针法 | KMP
字符串 基础知识双指针法344# 反转字符串541# 反转字符串II54K 替换数字151# 反转字符串中的单词55K 右旋字符串 KMP 字符串匹配算法28# 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标#459 重复的子字符串 基础知识 字符串的结尾:空终止字符00 char* name "hello"; …...

从零开始部署Dify:后端与前端服务完整指南
从零开始部署Dify:后端与前端服务完整指南 一、环境准备1. 系统要求2. 项目结构 二、后端服务部署1. 中间件启动(Docker Compose)2. 后端环境配置3. 依赖安装与数据库迁移4. 服务启动 三、前端界面搭建1. 环境配置2. 服务启动 四、常见问题排…...
【Axure高保真原型】引导弹窗
今天和大家中分享引导弹窗的原型模板,载入页面后,会显示引导弹窗,适用于引导用户使用页面,点击完成后,会显示下一个引导弹窗,直至最后一个引导弹窗完成后进入首页。具体效果可以点击下方视频观看或打开下方…...

AI Agent与Agentic AI:原理、应用、挑战与未来展望
文章目录 一、引言二、AI Agent与Agentic AI的兴起2.1 技术契机与生态成熟2.2 Agent的定义与特征2.3 Agent的发展历程 三、AI Agent的核心技术栈解密3.1 感知模块代码示例:使用Python和OpenCV进行图像识别 3.2 认知与决策模块代码示例:使用OpenAI GPT-3进…...
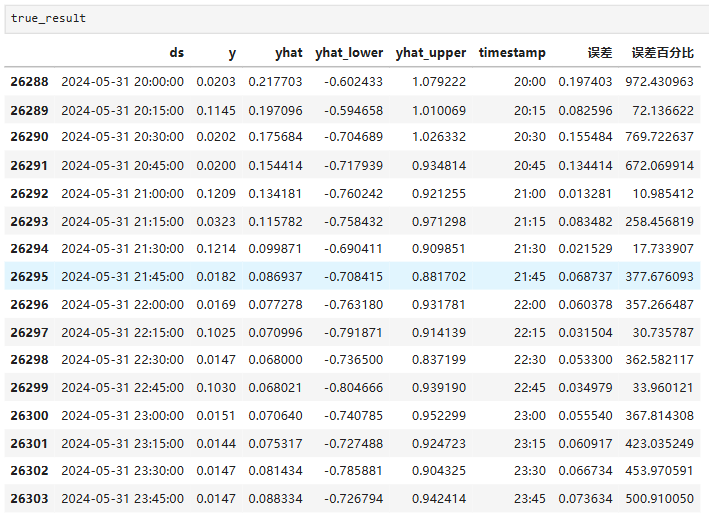
Python实现prophet 理论及参数优化
文章目录 Prophet理论及模型参数介绍Python代码完整实现prophet 添加外部数据进行模型优化 之前初步学习prophet的时候,写过一篇简单实现,后期随着对该模型的深入研究,本次记录涉及到prophet 的公式以及参数调优,从公式可以更直观…...
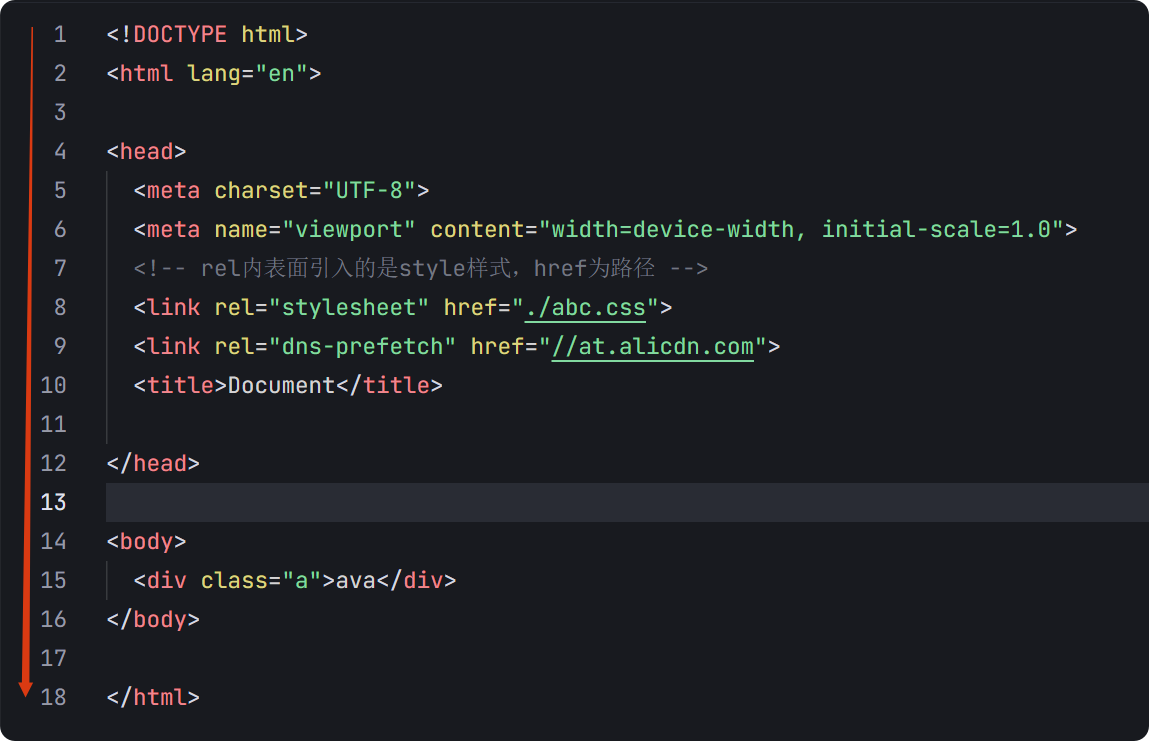
04-初识css
一、css样式引入 1.1.内部样式 <div style"width: 100px;"></div>1.2.外部样式 1.2.1.外部样式1 <style>.aa {width: 100px;} </style> <div class"aa"></div>1.2.2.外部样式2 <!-- rel内表面引入的是style样…...
第 86 场周赛:矩阵中的幻方、钥匙和房间、将数组拆分成斐波那契序列、猜猜这个单词
Q1、[中等] 矩阵中的幻方 1、题目描述 3 x 3 的幻方是一个填充有 从 1 到 9 的不同数字的 3 x 3 矩阵,其中每行,每列以及两条对角线上的各数之和都相等。 给定一个由整数组成的row x col 的 grid,其中有多少个 3 3 的 “幻方” 子矩阵&am…...

Android Bitmap治理全解析:从加载优化到泄漏防控的全生命周期管理
引言 Bitmap(位图)是Android应用内存占用的“头号杀手”。一张1080P(1920x1080)的图片以ARGB_8888格式加载时,内存占用高达8MB(192010804字节)。据统计,超过60%的应用OOM崩溃与Bitm…...
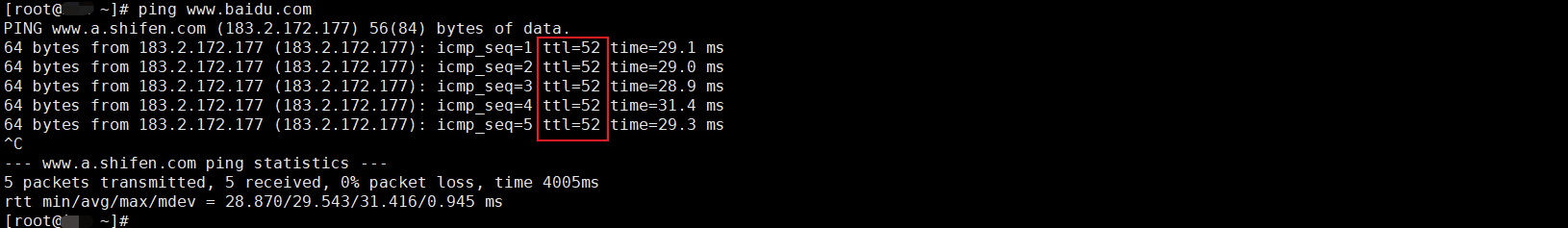
如何理解 IP 数据报中的 TTL?
目录 前言理解 前言 面试灵魂一问:说说对 IP 数据报中 TTL 的理解?我们都知道,IP 数据报由首部和数据两部分组成,首部又分为两部分:固定部分和可变部分,共占 20 字节,而即将讨论的 TTL 就位于首…...
Mobile ALOHA全身模仿学习
一、题目 Mobile ALOHA:通过低成本全身远程操作学习双手移动操作 传统模仿学习(Imitation Learning)缺点:聚焦与桌面操作,缺乏通用任务所需的移动性和灵活性 本论文优点:(1)在ALOHA…...
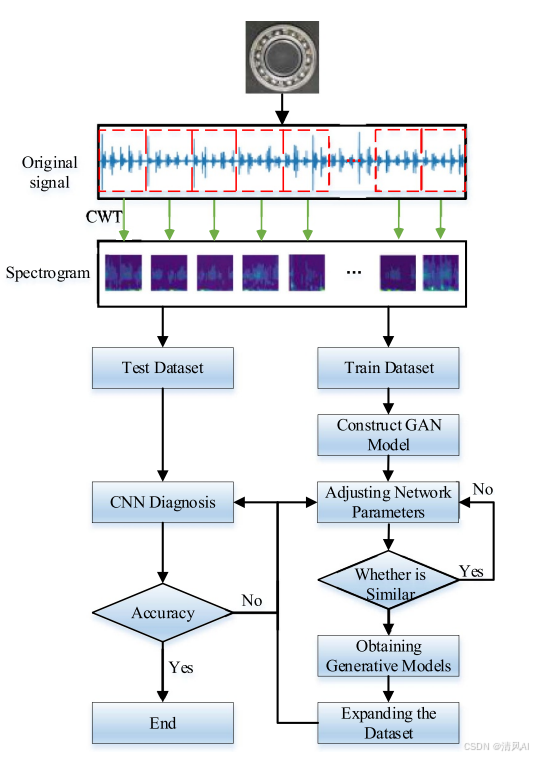
基于IDIG-GAN的小样本电机轴承故障诊断
目录 🔍 核心问题 一、IDIG-GAN模型原理 1. 整体架构 2. 核心创新点 (1) 梯度归一化(Gradient Normalization) (2) 判别器梯度间隙正则化(Discriminator Gradient Gap Regularization) (3) 自注意力机制(Self-Attention) 3. 完整损失函数 二…...

【Android】Android 开发 ADB 常用指令
查看当前连接的设备 adb devices 连接设备 adb connect 设备IP 断开已连接的设备 adb disconnect 设备IP 安装应用 adb install 安装包的路径 卸载应用 adb uninstall 应用包名 查看已安装的应用包名 adb shell pm list packages 查看已安装的第三方应用包名 adb shell pm list…...
