理解分布式id生成算法SnowFlake
理解分布式id生成算法SnowFlake
分布式id生成算法的有很多种,Twitter的SnowFlake就是其中经典的一种。
概述
SnowFlake算法生成id的结果是一个64bit大小的整数,它的结构如下图:
}
public function __construct(){
$this->r=new Redis();
$this->r->connect('127.0.0.1', 6379);
}
function set_queue_id($ids){
if(is_array($ids) && isset($ids)){
foreach ($ids as $id){
$this->r->LPUSH('next_autoincrement',$id);
}
}
}
function get_next_autoincrement(){
return $this->r->LPOP('next_autoincrement');
}
}
$createid=array();
while(count($createid)<20){
$num=rand(1000,4000);
if(!in_array($num,$createid))
$createid[]=$num;
}
$id=new common();
$id->set_queue_id($createid);
var_dump($id->get_next_autoincrement());1位 ,不用。二进制中最高位为1的都是负数,但是我们生成的id一般都使用整数,所以这个最高
位固定是0
41位 ,用来记录时间戳(毫秒)。
41位可以表示2^{41}-1241−1个数字,
如果只用来表示正整数(计算机中正数包含0),可以表示的数值范围是:0 至
2^{41}-1241−1,减1是因为可表示的数值范围是从0开始算的,而不是1。
也就是说41位可以表示2^{41}-1241−1个毫秒的值,转化成单位年则是(2^{41}-1) / (1000 *
60 * 60 * 24 * 365) = 69(241−1)/(1000∗60∗60∗24∗365)=69年
10位 ,用来记录工作机器id。
可以部署在2^{10} = 1024210=1024个节点,包括 5位datacenterId 和 5位workerId
5位(bit) 可以表示的最大正整数是2^{5}-1 = 3125−1=31,即可以用0、1、2、3、....31这
32个数字,来表示不同的datecenterId或workerId
12位 ,序列号,用来记录同毫秒内产生的不同id。
12位(bit) 可以表示的最大正整数是2^{12}-1 = 4095212−1=4095,即可以用0、1、2、
3、....4094这4095个数字,来表示同一机器同一时间截(毫秒)内产生的4095个ID序号
由于在Java中64bit的整数是long类型,所以在Java中SnowFlake算法生成的id就是long来存储的。
SnowFlake可以保证:
所有生成的id按时间趋势递增
整个分布式系统内不会产生重复id(因为有datacenterId和workerId来做区分)
Talk is cheap, show you the code
以下是Twitter官方原版的,用Scala写的,(当成Java看即可):
/** Copyright 2010-2012 Twitter, Inc.*/
package com.twitter.service.snowflake
import com.twitter.ostrich.stats.Stats
import com.twitter.service.snowflake.gen._
import java.util.Random
import com.twitter.logging.Logger
/**
* An object that generates IDs.
* This is broken into a separate class in case
* we ever want to support multiple worker threads
* per process
*/
class IdWorker(
val workerId: Long,
val datacenterId: Long,
private val reporter: Reporter,
var sequence: Long = 0L) extends Snowflake.Iface {
private[this] def genCounter(agent: String) = {
Stats.incr("ids_generated")
Stats.incr("ids_generated_%s".format(agent))
}
private[this] val exceptionCounter = Stats.getCounter("exceptions")
private[this] val log = Logger.get
private[this] val rand = new Randomval twepoch = 1288834974657L
private[this] val workerIdBits = 5L
private[this] val datacenterIdBits = 5L
private[this] val maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits)
private[this] val maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits)
private[this] val sequenceBits = 12L
private[this] val workerIdShift = sequenceBits
private[this] val datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits
private[this] val timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits +
datacenterIdBits
private[this] val sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits)
private[this] var lastTimestamp = -1L
// sanity check for workerId
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("worker Id can't be greater than %d or
less than 0".format(maxWorkerId))
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or
less than 0".format(maxDatacenterId))
}
log.info("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d,
worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d",
timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId)
def get_id(useragent: String): Long = {
if (!validUseragent(useragent)) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new InvalidUserAgentError
}
val id = nextId()
genCounter(useragent)
reporter.report(new AuditLogEntry(id, useragent, rand.nextLong))
id
}
def get_worker_id(): Long = workerId
def get_datacenter_id(): Long = datacenterId
def get_timestamp() = System.currentTimeMillis
protected[snowflake] def nextId(): Long = synchronized {
var timestamp = timeGen()
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
log.error("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.",
lastTimestamp);throw new InvalidSystemClock("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate
id for %d milliseconds".format(
lastTimestamp - timestamp))
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp)
}
} else {
sequence = 0
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp
((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) |
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |
(workerId << workerIdShift) |
sequence
}
protected def tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp: Long): Long = {
var timestamp = timeGen()
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen()
}
timestamp
}
protected def timeGen(): Long = System.currentTimeMillis()
val AgentParser = """([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z\-0-9]*)""".r
def validUseragent(useragent: String): Boolean = useragent match {
case AgentParser(_) => true
case _ => false
}
}
Scala是一门可以编译成字节码的语言,简单理解是在Java语法基础上加上了很多语法糖,例如不用每条
语句后写分号,可以使用动态类型等等。抱着试一试的心态,我把Scala版的代码“翻译”成Java版本的,
对scala代码改动的地方如下:
/** Copyright 2010-2012 Twitter, Inc.*/
package com.twitter.service.snowflake
import com.twitter.ostrich.stats.Stats
import com.twitter.service.snowflake.gen._
import java.util.Random
import com.twitter.logging.Logger
/**
* An object that generates IDs.
* This is broken into a separate class in case
* we ever want to support multiple worker threads
* per process
*/class IdWorker( // |
val workerId: Long, // |
val datacenterId: Long, // |<--这部分改成Java的构造函
数形式
private val reporter: Reporter,//日志相关,删 // |
var sequence: Long = 0L) // |
extends Snowflake.Iface { //接口找不到,删 // |
private[this] def genCounter(agent: String) = { // |
Stats.incr("ids_generated") // |
Stats.incr("ids_generated_%s".format(agent)) // |<--错
误、日志处理相关,删
} // |
private[this] val exceptionCounter = Stats.getCounter("exceptions") // |
private[this] val log = Logger.get // |
private[this] val rand = new Random // |
val twepoch = 1288834974657L
private[this] val workerIdBits = 5L
private[this] val datacenterIdBits = 5L
private[this] val maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits)
private[this] val maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits)
private[this] val sequenceBits = 12L
private[this] val workerIdShift = sequenceBits
private[this] val datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits
private[this] val timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits +
datacenterIdBits
private[this] val sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits)
private[this] var lastTimestamp = -1L
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------//
// sanity check for workerId
//
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
//
exceptionCounter.incr(1) //<--错误处理相关,删
//
throw new IllegalArgumentException("worker Id can't be greater than %d or
less than 0".format(maxWorkerId)) //这
// |-->改成:throw new IllegalArgumentException
//部
// (String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than
0",maxWorkerId)) //分
}
//放
//到
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
//构
exceptionCounter.incr(1) //<--错误处理相关,删
//造
throw new IllegalArgumentException("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or
less than 0".format(maxDatacenterId)) //函// |-->改成:throw new IllegalArgumentException
//数
// (String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less
than 0",maxDatacenterId)) //中
}
//
//
log.info("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d,
worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d", //
timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId)
//
// |-->改成:System.out.printf("worker...%d...",timestampLeftShift,...);
//
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------//
//-------------------------------------------------------------------//
//这个函数删除错误处理相关的代码后,剩下一行代码:val id = nextId() //
//所以我们直接调用nextId()函数可以了,所以在“翻译”时可以删除这个函数 //
def get_id(useragent: String): Long = { //
if (!validUseragent(useragent)) { //
exceptionCounter.incr(1) //
throw new InvalidUserAgentError //删
} //除
//
val id = nextId() //
genCounter(useragent) //
//
reporter.report(new AuditLogEntry(id, useragent, rand.nextLong)) //
id //
} //
//-------------------------------------------------------------------//
def get_worker_id(): Long = workerId // |
def get_datacenter_id(): Long = datacenterId // |<--改成Java函数
def get_timestamp() = System.currentTimeMillis // |
protected[snowflake] def nextId(): Long = synchronized { // 改成Java函数
var timestamp = timeGen()
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1) // 错误处理相关,删
log.error("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.",
lastTimestamp); // 改成System.err.printf(...)
throw new InvalidSystemClock("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate
id for %d milliseconds".format(
lastTimestamp - timestamp)) // 改成RumTimeException
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp)
}
} else {
sequence = 0
}lastTimestamp = timestamp
((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | // |<--加上关键字return
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | // |
(workerId << workerIdShift) | // |
sequence // |
}
protected def tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp: Long): Long = { // 改成Java函数
var timestamp = timeGen()
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen()
}
timestamp // 加上关键字return
}
protected def timeGen(): Long = System.currentTimeMillis() // 改成Java函数
val AgentParser = """([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z\-0-9]*)""".r // |
// |
def validUseragent(useragent: String): Boolean = useragent match { // |<--日志
相关,删
case AgentParser(_) => true // |
case _ => false // |
} // |
}
改出来的Java版:
public class IdWorker{
private long workerId;
private long datacenterId;
private long sequence;
public IdWorker(long workerId, long datacenterId, long sequence){
// sanity check for workerId
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be
greater than %d or less than 0",maxWorkerId));
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can't
be greater than %d or less than 0",maxDatacenterId));
}
System.out.printf("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter
id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d",
timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits,
workerId);
this.workerId = workerId;
this.datacenterId = datacenterId;
this.sequence = sequence;
}
private long twepoch = 1288834974657L;private long workerIdBits = 5L;
private long datacenterIdBits = 5L;
private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
private long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits);
private long sequenceBits = 12L;
private long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
private long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
private long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits +
datacenterIdBits;
private long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
public long getWorkerId(){
return workerId;
}
public long getDatacenterId(){
return datacenterId;
}
public long getTimestamp(){
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public synchronized long nextId() {
long timestamp = timeGen();
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
System.err.printf("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests
until %d.", lastTimestamp);
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards.
Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds",
lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
} else {
sequence = 0;
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp;
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) |
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |
(workerId << workerIdShift) |
sequence;
}
private long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen();
}代码理解
上面的代码中,有部分位运算的代码,如:
为了能更好理解,我对相关知识研究了一下。
负数的二进制表示
在计算机中,负数的二进制是用 补码 来表示的。
假设我是用Java中的int类型来存储数字的,
int类型的大小是32个二进制位(bit),即4个字节(byte)。(1 byte = 8 bit)
那么十进制数字 3 在二进制中的表示应该是这样的:
那数字 -3 在二进制中应该如何表示?
我们可以反过来想想,因为-3+3=0,
在二进制运算中 把-3的二进制看成未知数x来求解 ,
求解算式的二进制表示如下:
反推x的值,3的二进制加上什么值才使结果变成 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ?:
return timestamp;
}
private long timeGen(){
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
//---------------测试---------------
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdWorker worker = new IdWorker(1,1,1);
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
System.out.println(worker.nextId());
}
}
}
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) |
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |
(workerId << workerIdShift) |
sequence;
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011
// 3的二进制表示,就是原码
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 //3,原码
+ xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx //-3,补码
-----------------------------------------------
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000反推的思路是3的二进制数从最低位开始逐位加1,使溢出的1不断向高位溢出,直到溢出到第33位。然
后由于int类型最多只能保存32个二进制位,所以最高位的1溢出了,剩下的32位就成了(十进制的)
0。
补码的意义就是可以拿补码和原码(
3的二进制)相加,最终加出一个“溢出的0”
以上是理解的过程,实际中记住公式就很容易算出来:
补码 = 反码 + 1
补码 = (原码 - 1)再取反码
因此 -1 的二进制应该这样算:
用位运算计算n个bit能表示的最大数值
比如这样一行代码:
上面代码换成这样看方便一点:
long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << 5L)
咋一看真的看不准哪个部分先计算,于是查了一下Java运算符的优先级表:
所以上面那行代码中,运行顺序是:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 //3,原码
+ 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111101 //-3,补码
-----------------------------------------------
1 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 //原码:1的二进制
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111110 //取反码:1的二进制的反码
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 //加1:-1的二进制表示(补码)
private long workerIdBits = 5L;
private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);-1 左移 5,得结果a
-1 异或 a
long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << 5L) 的二进制运算过程如下:
-1 左移 5,得结果a :
-1 异或 a :
最终结果是31,二进制 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 转十进制可以这么算:
2^4 + 2^3 + 2^2 + 2^1 + 2^0 = 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1 =3124+23+22+21+20=16+8+4+2+1=31
那既然现在知道算出来 long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << 5L) 中的 maxWorkerId = 31 ,有什么
含义?为什么要用左移5来算?如果你看过 概述 部分,请找到这段内容看看:
5位(bit) 可以表示的最大正整数是2^{5}-1 = 3125−1=31,即可以用0、1、2、3、....31这32个
数字,来表示不同的datecenterId或workerId
用mask防止溢出
有一段有趣的代码:
分别用不同的值测试一下,你就知道它怎么有趣了:
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 //-1的二进制表示(补码)
11111 11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000 //高位溢出的不要,低位补0
11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000 //结果a
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 //-1的二进制表示(补码)
^ 11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000 //两个操作数的位中,相同则为0,不同则为1
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 //最终结果31
-1L ^ (-1L << 5L)`结果是`31`,2^{5}-125−1的结果也是`31`,所以在代码中,`-1L ^ (-1L <<
5L)`的写法是`利用位运算计算出5位能表示的最大正整数是多少
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
long seqMask = -1L ^ (-1L << 12L); //计算12位能耐存储的最大正整数,相当于:
2^12-1 = 4095
System.out.println("seqMask: "+seqMask);
System.out.println(1L & seqMask);
System.out.println(2L & seqMask);
System.out.println(3L & seqMask);
System.out.println(4L & seqMask);
System.out.println(4095L & seqMask);
System.out.println(4096L & seqMask);
System.out.println(4097L & seqMask);
System.out.println(4098L & seqMask);
/**
seqMask: 4095
1
2这段代码通过 位与 运算保证计算的结果范围始终是 0-4095 !
用位运算汇总结果
还有另外一段诡异的代码:
为了弄清楚这段代码,
首先 需要计算一下相关的值:
其次 写个测试,把参数都写死,并运行打印信息,方便后面来核对计算结果:
3
4
4095
0
1
2
*/
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) |
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |
(workerId << workerIdShift) |
sequence;
private long twepoch = 1288834974657L; //起始时间戳,用于用当前时间戳减去这个时间
戳,算出偏移量
private long workerIdBits = 5L; //workerId占用的位数:5
private long datacenterIdBits = 5L; //datacenterId占用的位数:5
private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits); // workerId可以使用的
最大数值:31
private long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits); //
datacenterId可以使用的最大数值:31
private long sequenceBits = 12L;//序列号占用的位数:12
private long workerIdShift = sequenceBits; // 12
private long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits; // 12+5 = 17
private long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits +
datacenterIdBits; // 12+5+5 = 22
private long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);//4095
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
//---------------测试---------------
public static void main(String[] args) {
long timestamp = 1505914988849L;
long twepoch = 1288834974657L;
long datacenterId = 17L;
long workerId = 25L;
long sequence = 0L;
System.out.printf("\ntimestamp: %d \n",timestamp);
System.out.printf("twepoch: %d \n",twepoch);
System.out.printf("datacenterId: %d \n",datacenterId);
System.out.printf("workerId: %d \n",workerId);System.out.printf("sequence: %d \n",sequence);
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("(timestamp - twepoch): %d \n",(timestamp - twepoch));
System.out.printf("((timestamp - twepoch) << 22L): %d \n",((timestamp -
twepoch) << 22L));
System.out.printf("(datacenterId << 17L): %d \n" ,(datacenterId <<
17L));
System.out.printf("(workerId << 12L): %d \n",(workerId << 12L));
System.out.printf("sequence: %d \n",sequence);
long result = ((timestamp - twepoch) << 22L) |
(datacenterId << 17L) |
(workerId << 12L) |
sequence;
System.out.println(result);
}
/** 打印信息:
timestamp: 1505914988849
twepoch: 1288834974657
datacenterId: 17
workerId: 25
sequence: 0
(timestamp - twepoch): 217080014192
((timestamp - twepoch) << 22L): 910499571845562368
(datacenterId << 17L): 2228224
(workerId << 12L): 102400
sequence: 0
910499571847892992
*/
代入位移的值得之后,就是这样:
return ((timestamp - 1288834974657) << 22) |
(datacenterId << 17) |
(workerId << 12) |
sequence;
对于尚未知道的值,我们可以先看看 概述 中对SnowFlake结构的解释,再代入在合法范围的值
(windows系统可以用计算器方便计算这些值的二进制),来了解计算的过程。
当然,由于我的测试代码已经把这些值写死了,那直接用这些值来手工验证计算结果即可:现在知道了每个部分左移后的值(la,lb,lc),代码可以简化成下面这样去理解:
long timestamp = 1505914988849L;
long twepoch = 1288834974657L;
long datacenterId = 17L;
long workerId = 25L;
long sequence = 0L;
设:timestamp = 1505914988849,twepoch = 1288834974657
1505914988849 - 1288834974657 = 217080014192 (timestamp相对于起始时间的毫秒偏移量),其
(a)二进制左移22位计算过程如下:
|<--这里开始左右22位
00000000 00000000 000000|00 00110010 10001010 11111010 00100101 01110000 // a =
217080014192
00001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|000000 00000000 00000000 // a左移
22位后的值(la)
|<--这里后面的位补0
设:datacenterId = 17,其(b)二进制左移17位计算过程如下:
|<--这里开始左移17位
00000000 00000000 0|0000000
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00010001 // b =
17
0000000
0 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 0010001|0 00000000 00000000 // b左移
17位后的值(lb)
|<--这里后面的位补0
设:workerId = 25,其(c)二进制左移12位计算过程如下:
|<--这里开始左移12位
00000000 0000|0000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011001
// c =
25
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 1001|0000 00000000
// c左移
12位后的值(lc)
|<--这里后面的位补0
设:sequence = 0,其二进制如下:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 0000
0000 00000000
//
sequence = 0上面的管道符号 | 在Java中也是一个位运算符。其含义是:
x的第n位和y的第n位 只要有一个是1,则结果的第n位也为1,否则为0 ,因此,我们对四个数的 位或运算 如
下:
结果计算过程:
1) 从至左列出1出现的下标(从0开始算):
2) 各个下标作为2的幂数来计算,并相加:
$ 2^{59}+2^{58}+2^{55}+2^{53}+2^{49}+2^{47}+2^{45}+2^{44}+2^{43}+
2^{42}+2^{41}+2^{39}+2^{35}+2^{32}+2^{30}+2^{28}+2^{27}+2^{26}+
2^{21}+2^{17}+2^{16}+2^{15}+2^{2} $
return ((timestamp - 1288834974657) << 22) |
(datacenterId << 17) |
(workerId << 12) |
sequence;
-----------------------------
|
|简化
\|/
-----------------------------
return (la) |
(lb) |
(lc) |
sequence;
1 | 41 | 5 | 5 | 12
0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|00000|0 0000|0000 00000000
//la
0|000000
0 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|10001|0 0000|0000 00000000
//lb
0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|00000|1 1001|0000 00000000
//lc
or 0|0000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00|00000|0 0000|
0000 00000000
//sequence
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------
0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|10001|1 1001|
0000 00000000
//
结果:910499571847892992
0000 1 1 00 1 0 1 000 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 000 1 00 1 0
1 0 1 1 1 0000 1 000 1 1 1 00 1
0000 0000 0000
59 58 55 53 49 47 45 44 43 42 41 39 35 32
30 28 27 26 21 17 16 15 12
2^59} : 576460752303423488
2^58} : 288230376151711744
2^55} : 36028797018963968
2^53} : 9007199254740992
2^49} : 562949953421312
2^47} : 140737488355328
2^45} : 35184372088832
2^44} : 17592186044416计算截图:
跟测试程序打印出来的结果一样,手工验证完毕!
观察
2^43} : 8796093022208
2^42} : 4398046511104
2^41} : 2199023255552
2^39} : 549755813888
2^35} : 34359738368
2^32} : 4294967296
2^30} : 1073741824
2^28} : 268435456
2^27} : 134217728
2^26} : 67108864
2^21} : 2097152
2^17} : 131072
2^16} : 65536
2^15} : 32768
+ 2^12} : 4096
----------------------------------------
910499571847892992上面的64位我按1、41、5、5、12的位数截开了,方便观察。
纵向 观察发现:
在41位那一段,除了la一行有值,其它行(lb、lc、sequence)都是0,(我爸其它)
在左起第一个5位那一段,除了lb一行有值,其它行都是0
在左起第二个5位那一段,除了lc一行有值,其它行都是0
按照这规律,如果sequence是0以外的其它值,12位那段也会有值的,其它行都是0
横向 观察发现:
在la行,由于左移了5+5+12位,5、5、12这三段都补0了,所以la行除了41那段外,其它肯
定都是0
同理,lb、lc、sequnece行也以此类推
正因为左移的操作,使四个不同的值移到了SnowFlake理论上相应的位置,然后四行做 位或
运算(只要有1结果就是1),就把4段的二进制数合并成一个二进制数。
结论:
所以,在这段代码中
左移运算是为了将数值移动到对应的段(41、5、5,12那段因为本来就在最右,因此不用左移)。
然后对每个左移后的值(la、lb、lc、sequence)做位或运算,是为了把各个短的数据合并起来,合并成一
个二进制数。
最后转换成10进制,就是最终生成的id
扩展
在理解了这个算法之后,其实还有一些扩展的事情可以做:
1. 根据自己业务修改每个位段存储的信息。算法是通用的,可以根据自己需求适当调整每段的大小以
及存储的信息。
2. 解密id,由于id的每段都保存了特定的信息,所以拿到一个id,应该可以尝试反推出原始的每个段
的信息。反推出的信息可以帮助我们分析。比如作为订单,可以知道该订单的生成日期,负责处理
的数据中心等等。
1 | 41 | 5 | 5 | 12
0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00| | |
//la
0| |10001| |
//lb
0| | |1 1001|
//lc
or 0| | | |
0000 00000000
//sequence
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------
0|0001100 10100010 10111110 10001001 01011100 00|10001|1 1001|
0000 00000000
//
结果:910499571847892992
return ((timestamp - 1288834974657) << 22) |
(datacenterId << 17) |
(workerId << 12) |
相关文章:

理解分布式id生成算法SnowFlake
理解分布式id生成算法SnowFlake 分布式id生成算法的有很多种,Twitter的SnowFlake就是其中经典的一种。 概述 SnowFlake算法生成id的结果是一个64bit大小的整数,它的结构如下图: } public function __construct(){ $this->rnew…...
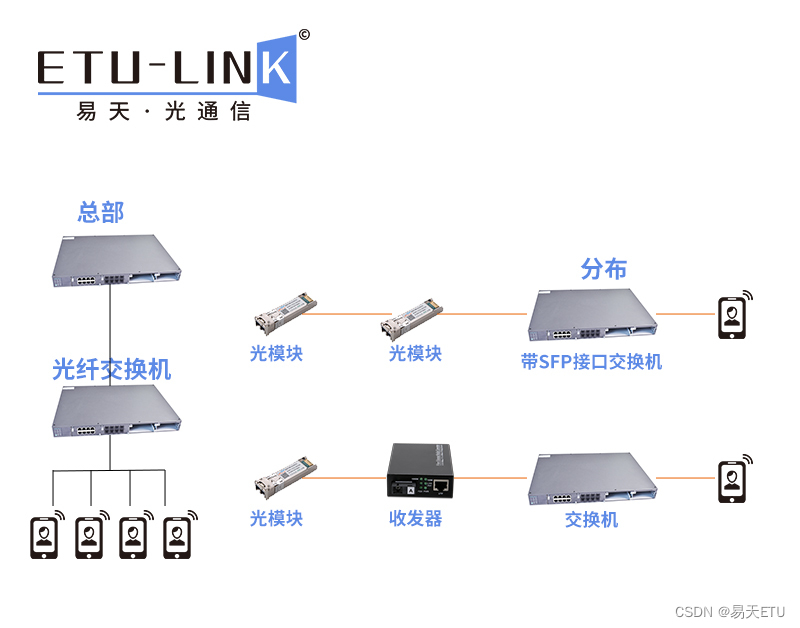
光纤收发器可以连接光模块吗?
随着科技的进步发展,城市信息化速度的加快,光通信产品在数据中心和安防监控等场景中的运用越来越广泛,而这之间的连接则需要光模块和光纤收发器来实现。很多用户对光模块和光纤收发器的使用有些疑虑,两者该如何连接?又…...
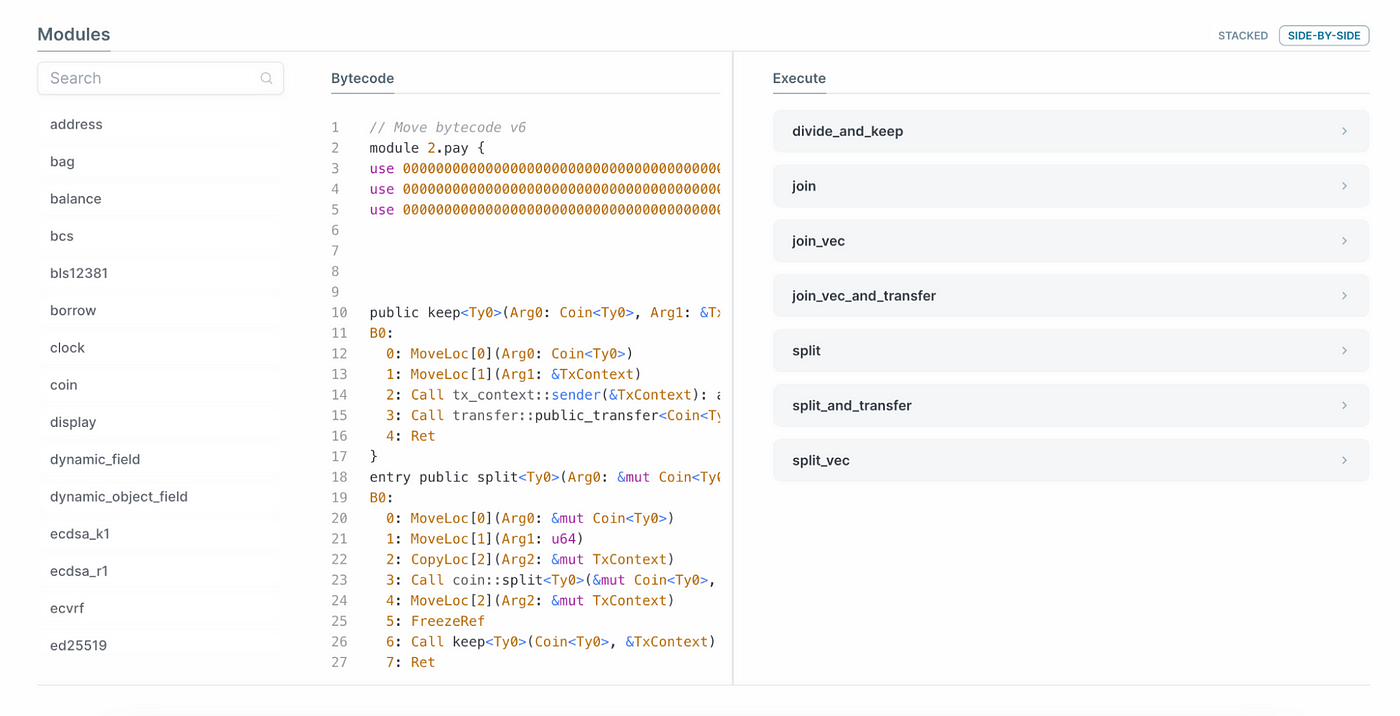
一文快速了解浏览器Sui Explorer
Sui作为一条基于第一原理重新设计和构建而成的L1公链,所有区块和交易信息皆公开透明,每个人都能自行查看。通过Sui链上浏览器,用户可以迅速了解链上的交易情况,比如当前的TPS和Gas价格,也可以使用Digest来查看特定交易…...

python中lambda、yield、map、filter、reduce的使用
1、 匿名函数lambda python中允许使用lambda关键字定义一个匿名函数。所谓的匿名函数就是说使用一次或者几次之后就不再需要的函数,属于“一次性”函数。 #例1:求两数之和 f lambda x, y: x y print(f(5, 1))#例2:求平方和 print((lambda…...

第十八章 使用LNMP架构部署动态网站环境
文章目录 第十八章 使用LNMP架构部署动态网站环境一、源码包程序1、源码包的优势2、基本步骤(1)、下载及解压源码包文件(2)、编译源码包代码(3)、生成二进制安装程序(4)、运行二进制…...
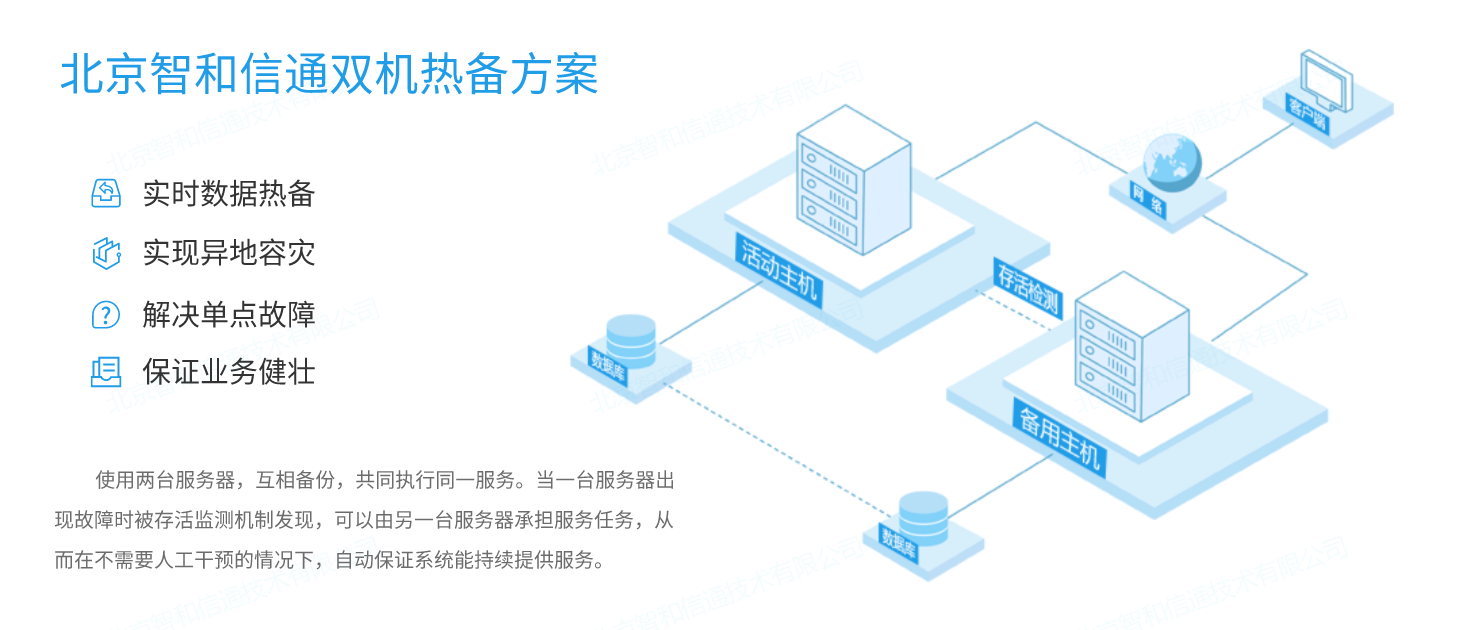
无人值守的IDC机房动环综合运维方案
企业数字化转型以及5G、物联网、云计算、人工智能等新业态带动了数据中心的发展,在国家一体化大数据中心及“东数西算”节点布局的推动下,数据中心机房已成为各大企事业单位维持业务正常运营的重要组成部分,网络设备、系统、业务应用数量与日…...
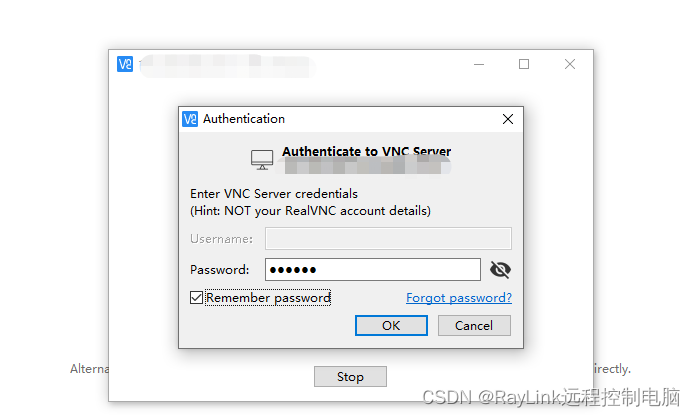
桌面远程工具推荐
目前市面上的远程工具多如牛毛,很多人不知道怎么选择,下面小编介绍两种桌面远程工具,它们都是跨平台的,均支持Windows,Mac OS,IOS和安卓,分别是RayLink,VNC,好用…...
MySQL高级——第15章_锁
第15章_锁 1. 概述 锁是计算机协调多个进程或线程并发访问某一资源的机制。在程序开发中会存在多线程同步的问题,当多个线程并发访问某个数据的时候,尤其是针对一-些敏感的数据(比如订单、金额等),我们就需要保证这个数据在任何 时刻最多只…...
【ROS】Ubuntu22.04安装ROS2(Humble Hawksbill)
0、版本说明 Ubuntu22.04对应的ROS2的版本为Humble Hawksbill(ros-humble) 如果不是在Ubuntu22.04中安装ROS,请参考下面Ubuntu和ROS的版本对应关系 1、更新apt包列表 $ sudo apt update2、设置编码 将ubuntu环境语言编码设置为en_US en_…...
【ChatGPT】体验一下ChatGPT
体验一下ChatGPT 可以帮你写代码、写邮件、编故事的神器 最近OpenAI 发布了备受期待的原型通用 ChatGPT,这是一种基于对话的 AI 聊天界面,算是GPT-3(Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3)的继承者,今天记录一下体验的过程,以前…...

Android 串口通信
可以使用开源usb-serial-for-android 库进行串口通信 添加 usb-serial-for-android 依赖项到项目中。在项目的 build.gradle 文件中添加以下内容: dependencies {// 其他依赖项...implementation com.github.mik3y:usb-serial-for-android:3.5.1// 其他依赖项... …...

Python3 日期和时间
Python 3 提供了强大的日期和时间处理模块,名为 datetime。它可以用于执行日期和时间的各种操作,包括创建、格式化、比较和计算等。 下面是一些常用的日期和时间操作的示例: ### 获取当前日期和时间 要获取当前日期和时间,可以使…...

Go 爬虫三种框架的基本使用介绍
目录 Go 爬虫三种框架的基本使用介绍1. Colly2. Golang.org/x/net/html3. GoQuery Go 爬虫示例使用Go中的http包进行爬虫Step 1:导入包Step 2:发送请求Step 3:读取响应Step 4:解析HTMLStep 5:总结 使用Colley爬虫 结语…...
)
python实现斐波那契数列详解(黄金分割)
今天给各位分享一个常见的题目:求斐波那契数列前n项分别是什么(也称为黄金分割数列),整个数列需满足一个条件即第三项的值等于前两项相加的和,如第一项是1、第二项是1、第三项是2、第四项是 3、第五项是5... 满足公式…...

整合营销和内容营销哪个好,有什么区别
如果想做自媒体运营,不管是品牌还是个体从业者,其实都要学会如何去营销。这个也分为很多种方式,比如整合营销和内容营销。今天,来和大家谈谈整合营销和内容营销哪个好,如何才能将他们应用好? 要想回答这个问题&#x…...
C# | [二进制字符串] 与 [字节数组] 互相转换,一行代码就搞定! - CodePlus系列
C#二进制字符串与字节数组互相转换 文章目录 C#二进制字符串与字节数组互相转换前言示例代码实现思路扩展方法说明引用CodePlus库结束语 前言 开发中有时需要将二进制数据转换为字符串或相反。虽然.NET提供了一些用于二进制数据操作的类库,但是它们的使用有时候会比…...
-Comparator#compare() 升降序确定)
Java 细节汇总(5)-Comparator#compare() 升降序确定
文章目录 1. Comparator#compare() 升降序确定升序分析 1. Comparator#compare() 升降序确定 Java 语言中 Comparator#compare(T o1, T o2) 方法的实现可以决定排序元素的升序降序,但是许多人对升降序如何确定完全没有概念。要理解升降序是如何确定的,首…...

湖北棒球发展报告·棒球5号位
湖北棒球的发展报告与办法应该考虑以下几个因素: 1. 借助政策支持。湖北棒球要想发展,政策支持是必不可少的。政府需要提供足够的资金和政策支持,以帮助俱乐部提高运营能力和加强比赛的组织。获得政府的政策支持,可以促进湖北棒球…...
使用Eclipse 进行远程 Debug 调试
Eclipse远程调试 Java自身支持调试功能,并提供了一个简单的调试工具--JDB,类似于功能强大的GDB,JDB也是一个字符界面的调试环境,并支持设置断点,支持线程线级的调试。 由于部署环境的差异性&am…...

记第一次出差得出的经验
文章目录 1:背景2:过程3:心得 1:背景 由于上家公司的某种原因,离职来到了新公司,内中原因不足道也。新公司业务方向暂且不说,入职后,个人看着以前的产品视频学习了不到两周…...
使用VSCode开发Django指南
使用VSCode开发Django指南 一、概述 Django 是一个高级 Python 框架,专为快速、安全和可扩展的 Web 开发而设计。Django 包含对 URL 路由、页面模板和数据处理的丰富支持。 本文将创建一个简单的 Django 应用,其中包含三个使用通用基本模板的页面。在此…...

<6>-MySQL表的增删查改
目录 一,create(创建表) 二,retrieve(查询表) 1,select列 2,where条件 三,update(更新表) 四,delete(删除表…...

VTK如何让部分单位不可见
最近遇到一个需求,需要让一个vtkDataSet中的部分单元不可见,查阅了一些资料大概有以下几种方式 1.通过颜色映射表来进行,是最正规的做法 vtkNew<vtkLookupTable> lut; //值为0不显示,主要是最后一个参数,透明度…...

CMake控制VS2022项目文件分组
我们可以通过 CMake 控制源文件的组织结构,使它们在 VS 解决方案资源管理器中以“组”(Filter)的形式进行分类展示。 🎯 目标 通过 CMake 脚本将 .cpp、.h 等源文件分组显示在 Visual Studio 2022 的解决方案资源管理器中。 ✅ 支持的方法汇总(共4种) 方法描述是否推荐…...
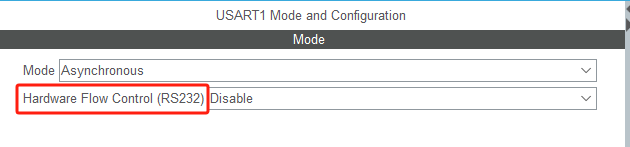
STM32HAL库USART源代码解析及应用
STM32HAL库USART源代码解析 前言STM32CubeIDE配置串口USART和UART的选择使用模式参数设置GPIO配置DMA配置中断配置硬件流控制使能生成代码解析和使用方法串口初始化__UART_HandleTypeDef结构体浅析HAL库代码实际使用方法使用轮询方式发送使用轮询方式接收使用中断方式发送使用中…...

c# 局部函数 定义、功能与示例
C# 局部函数:定义、功能与示例 1. 定义与功能 局部函数(Local Function)是嵌套在另一个方法内部的私有方法,仅在包含它的方法内可见。 • 作用:封装仅用于当前方法的逻辑,避免污染类作用域,提升…...
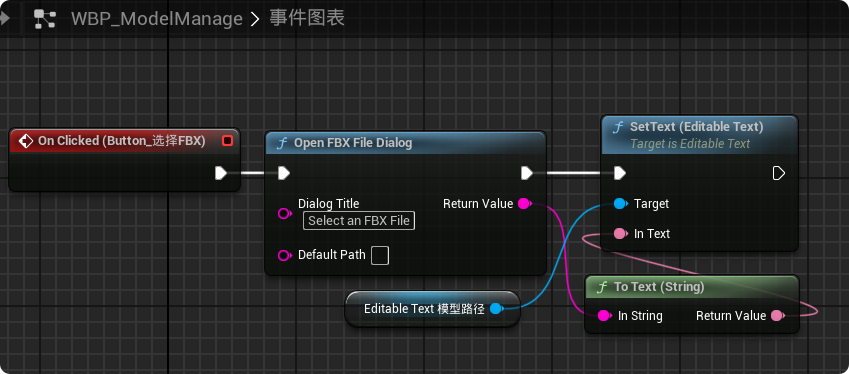
【UE5 C++】通过文件对话框获取选择文件的路径
目录 效果 步骤 源码 效果 步骤 1. 在“xxx.Build.cs”中添加需要使用的模块 ,这里主要使用“DesktopPlatform”模块 2. 添加后闭UE编辑器,右键点击 .uproject 文件,选择 "Generate Visual Studio project files",重…...
阿里云Ubuntu 22.04 64位搭建Flask流程(亲测)
cd /home 进入home盘 安装虚拟环境: 1、安装virtualenv pip install virtualenv 2.创建新的虚拟环境: virtualenv myenv 3、激活虚拟环境(激活环境可以在当前环境下安装包) source myenv/bin/activate 此时,终端…...

用 Rust 重写 Linux 内核模块实战:迈向安全内核的新篇章
用 Rust 重写 Linux 内核模块实战:迈向安全内核的新篇章 摘要: 操作系统内核的安全性、稳定性至关重要。传统 Linux 内核模块开发长期依赖于 C 语言,受限于 C 语言本身的内存安全和并发安全问题,开发复杂模块极易引入难以…...

如何把工业通信协议转换成http websocket
1.现状 工业通信协议多数工作在边缘设备上,比如:PLC、IOT盒子等。上层业务系统需要根据不同的工业协议做对应开发,当设备上用的是modbus从站时,采集设备数据需要开发modbus主站;当设备上用的是西门子PN协议时…...
