list的模拟实现
前言
list是STL中重要的容器,了解它的原理对于我们掌握它是有很多的帮助的,一般list和vector都是一起来使用的,因为它们的优缺点不同,刚好可以互补。list的优点是任意位置的插入和删除都很快,它的缺点是不支持随机访问,而vector的优点是支持随机访问,进而就可以很好的支持排序算法,二分查找,堆算法等,它的缺点是扩容要付出一定的代价,而且除了尾上的插入和删除外其他位置的插入和删除都不快(因为要挪动数据)。下面让我们一起来实现一下list吧。
list的实现代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace qyy
{
template<class T>
struct __list_node
{__list_node(const T& data = T())//构造函数函数:_prev(nullptr), _next(nullptr), _data(data){ }__list_node<T>* _prev;//前指针__list_node<T>* _next;//后指针T _data;//数据
};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator//对链表的迭代器进行封装
{typedef __list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator< T, Ref, Ptr> iterator;__list_iterator(Node* node)//构造函数:_node(node){ }//对指针行为的模仿Ref operator* (){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->_data);}iterator& operator++()//前置++{_node = _node->_next;return *this;}iterator& operator--()//前置--{_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}iterator operator++(int)//后置++{//Node tmp(_node);iterator tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}iterator operator--(int)//后置--{//Node tmp(_node);iterator tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator==(const iterator& it){return _node == it._node;}bool operator!=(const iterator& it){return _node != it._node;}public:Node* _node;//存放一个节点的指针
};template<class T>
class list//带头双向循环链表
{
public:typedef __list_node<T> Node;//节点的重定义typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;//迭代器重定义typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}list()//构造函数:_head(new Node){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}list(const list<T>& l1)//拷贝构造{_head = new Node;//初始化头结点_head->_next = _head;_head-> _prev = _head;const_iterator it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){push_back(it._node->_data);//将节点插入++it;}}list<T>& operator=(list<T> l1)//现代写法{if (this != &l1){swap(_head, l1._head);}return *this;}list<T> operator=(const list<T> l1)const{clear();const_iterator it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){push_back(it._node->_data);//将节点插入++it;}return *this;}~list(){clear();//删除头结点以外的其他节点delete _head;//删除头结点}void clear()//除了头结点剩下的节点全部删除{if (begin() != end())//判断不能删除头结点{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);//删除当前节点之后迭代器就会 失效,所以要用it来接收下一个节点的迭代器}}}void push_back(const T& data)//尾插{//Node* tail = _head->_prev;//Node* newNode = new Node(data);//申请节点三个节点的相互链接//tail->_next = newNode;//newNode->_prev = tail;//_head->_prev = newNode;//newNode->_next = _head;insert(end(), data);//调用任意节点的插入来实现头删}void pop_back()//尾删{//assert(_head->_next != _head);//除了头结点还有其他节点——因为头结点是不可以被删除的//Node* tail = _head->_prev;//找到尾节点断开链接//Node* newtail = tail->_prev;//找新的尾节点进行头尾链接//newtail->_next = _head;//_head->_prev = newtail;//delete tail;//删除尾节点//调用erase进行尾删erase(--end());}void push_front(const T&data)//头插{//Node* newHead = new Node(data);//申请新的节点//Node* oldHead = _head->_next;进行链接//_head->_next = newHead;//newHead->_prev = _head;//newHead->_next = oldHead;//oldHead->_prev = newHead;//调用任意节点的插入和删除insert(begin(), data);}void pop_front()//头删{//assert(_head->_next != _head);//除了头结点还有其他节点——因为头结点是不可以被删除的//Node* head = _head->_next;//找到头节点断开链接//Node* newHead = head->_next;//找新的尾节点进行链接//newHead->_prev = _head;//_head->_next= newHead;//delete head;//删除尾节点//调用erase进行头删erase(begin());}void insert(iterator pos, const T& data)//{//申请新节点Node* newNode = new Node(data);Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;//迭代器前一个节点Node* next =pos._node;//迭代器当前节点prev->_next = newNode;newNode->_prev = prev;next->_prev = newNode;newNode->_next = next;}iterator erase(iterator pos)//删除pos位置的值{assert(pos._node !=_head);//不能删除头结点Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;Node* next = pos._node->_next;//断开当前迭代器所在节点的位置,将迭代器前后节点进行链接prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;//保存下一个位置的迭代器iterator it1= ++pos;//记录下一个位置的迭代器//删除当前迭代器的节点delete cur;cur = nullptr;return it1;//返回下一个位置的迭代器}
private:Node* _head;//头结点
};
}
1.构造函数和析构函数
1.1构造函数
构造函数主要完成的是对头结点的初始化,如下:
template<class T>//先定义结点类
struct __list_node
{__list_node(const T& data = T())//构造函数函数:_prev(nullptr), _next(nullptr), _data(data){ }__list_node<T>* _prev;//前指针__list_node<T>* _next;//后指针T _data;//数据
};
template<class T>//构造函数多头结点进行初始化
list()//构造函数:_head(new Node)
{_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;
}2.2析构函数
析构函数主要完成对资源的清理,这里通过调用clear对链表的节点进行删除。最后在删除头结点。
~list()
{clear();//删除头结点以外的其他节点delete _head;//删除头结点
}2.operator=的重载和拷贝构造函数
2.2拷贝构造
这里是通过对头结点进行初始化,之后调用push_back函数尾插数据,完成的拷贝构造。
list(const list<T>& l1)//拷贝构造
{_head = new Node;//初始化头结点_head->_next = _head;_head-> _prev = _head;const_iterator it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){push_back(it._node->_data);//将节点插入++it;}
}2.2operator=的重载
operator=赋值有两种写法,一种是传统写法另一种是现代写法,如下:
//传统写法--
list<T>& operator=(const list<T> l1)
{if (this != &l1)//防止对象自己给自己赋值{clear();//先清理之前链表中的内容,然后通过调用push_back将l1中的内容插入const_iterator it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){push_back(it._node->_data);//将节点插入++it;}return *this;}
}
//现代写法
list<T>& operator=(list<T> l1)//现代写法
{if (this != &l1)//先拷贝构造一个对象,然后调用STL中的swap函数交换this指向的头结点的指针和 { //l1中头结点指针,出了作用域临时对象l1就会被析构,不要担心内存泄漏的问题swap(_head, l1._head);}
return *this;
}3.迭代器的实现
list的迭代器比较特殊,他不是原生的指针,而是将节点的指针进行封装,然后重载operator*,operator++,operator--等与指针相关的操作符来模拟指针的行为。
3.1普通迭代器
template<class T>struct __list_node{__list_node(const T & data = T())//构造函数函数:_prev(nullptr),_next(nullptr),_data(data){ }__list_node<T>* _prev;//前指针__list_node<T>* _next;//后指针T _data;//数据};template<class T>struct __list_iterator//对链表的节点进行封装{typedef __list_node<T> Node;__list_iterator(Node*node)//构造函数:_node(node){ }//对指针行为的模仿T& operator* (){return _node->_data;}__list_iterator<T>& operator++()//前置++{_node = _node->_next;return *this;}__list_iterator<T>& operator--()//前置--{_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}__list_iterator<T> operator++(int)//后置++{Node tmp(_node);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}__list_iterator<T> operator--(int)//后置--{Node tmp(_node);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator==(const __list_iterator<T>&it){return _node == it._node;}bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it){return _node != it._node;}T* operator->(){return &(_node->_data);}public:Node *_node;//存放一个节点的指针};注意:实现operator->的意义,如果有下面的这种情况,list存的不是一个内置类型而是一个自定义类型,这时想要通过迭代器去访问里面的成员,就会用来operator->,如下:
class Date{public:Date():_year(0), _month(1), _day(1){ }public:int _year;int _month;int _day;};void TestList2(){list <Date> l1;Date d1, d2;l1.push_back(d1);l1.push_back(d2);list<Date>::iterator it = l1.begin();cout << it->_year << it->_month << it->_day;//访问list中存放的Date}其实 it->_year是it->_node->_year,只是编译器对其进行了简化。
3.2const类型的迭代器
const类型的对象只能使用const类型的迭代器,那么const类型的迭代器如何实现呢、需要再重新封装吗,像上面那样,可以,但是没有必要,因为那样代码的冗余度就会很高,我们只需要给模板增加两个参数就可以了。template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>。实现如下:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator//对链表的迭代器进行封装
{typedef __list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator< T, Ref, Ptr> iterator;__list_iterator(Node* node)//构造函数:_node(node){ }//对指针行为的模仿Ref operator* (){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->_data);}iterator& operator++()//前置++{_node = _node->_next;return *this;}iterator& operator--()//前置--{_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}iterator operator++(int)//后置++{//Node tmp(_node);iterator tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}iterator operator--(int)//后置--{//Node tmp(_node);iterator tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator==(const iterator& it){return _node == it._node;}bool operator!=(const iterator& it){return _node != it._node;}public:Node* _node;//存放一个节点的指针
}; 这样看,貌似看不出来这两个参数有什么用,这两个参数一个代表T*,一个代表T&,这样就可以解决代码冗余的问题,在实例化的时候给模板不同的参数就可以实例化不同的内容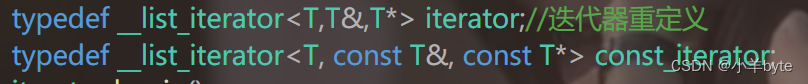
4.增删查改
4.1尾删尾插
void push_back(const T& data)//尾插{Node* tail = _head->_prev;Node* newNode = new Node(data);//申请节点//三个节点的相互链接tail->_next = newNode;newNode->_prev = tail;_head->_prev = newNode;newNode->_next = _head;}void pop_back()//尾删{assert(_head->_next != _head);//除了头结点还有其他节点——因为头结点是不可以被删除的Node* tail = _head->_prev;//找到尾节点//断开链接Node* newtail = tail->_prev;//找新的尾节点//进行头尾链接newtail->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newtail;delete tail;//删除尾节点}4.2任意位置的插入和删除
void insert(iterator pos, const T& data)//{//申请新节点Node* newNode = new Node(data);Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;//迭代器前一个节点Node* next =pos._node;//迭代器当前节点prev->_next = newNode;newNode->_prev = prev;next->_prev = newNode;newNode->_next = next;}iterator erase(iterator pos)//删除pos位置的值{assert(pos._node !=_head);//不能删除头结点Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;Node* next = pos._node->_next;//断开当前迭代器所在节点的位置,将迭代器前后节点进行链接prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;//保存下一个位置的迭代器iterator it1= ++pos;//记录下一个位置的迭代器//删除当前迭代器的节点delete cur;cur = nullptr;return it1;//返回下一个位置的迭代器}4.3头插头删
头插头删可以复用上面的insert和erase,如下:
void push_front(const T&data)//头插{insert(begin(), data);}void pop_front()//头删{erase(begin());}5.测试代码
#include<assert.h>
#include"list.hpp"void Print(const qyy::list<int>& l1);//测试
void TestList()
{qyy::list<int>l1;//头删l1.push_back(1);l1.push_back(2);l1.push_back(3);l1.push_back(4);l1.push_back(5);for (auto& e : l1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;Print(l1);//尾删l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();}
void Print(const qyy::list<int> &l3)
{qyy::list<int>::const_iterator it = l3.begin();while (it != l3.end()){//*it = 1;cout << *it << " ";it++;}cout << endl;
}
void TestList2()
{qyy::list<int> l2;//头插l2.push_front(1);l2.push_front(2);l2.push_front(3);l2.push_front(4);l2.push_front(5);l2.push_front(6);for (auto& e : l2){cout << e << " ";}//头删l2.pop_front();l2.pop_front();l2.pop_front();l2.pop_front();l2.pop_front();l2.pop_front();//l2.pop_front();//l2.clear();
}
void TestList3()
{qyy::list<int> l3;//头插l3.push_back(1);l3.push_back(2);l3.push_back(3);l3.push_back(4);l3.push_back(5);for (auto& e : l3)cout << e << " ";qyy::list<int> l4(l3);l3 = l4;//测试operator=
}
相关文章:

list的模拟实现
前言 list是STL中重要的容器,了解它的原理对于我们掌握它是有很多的帮助的,一般list和vector都是一起来使用的,因为它们的优缺点不同,刚好可以互补。list的优点是任意位置的插入和删除都很快,它的缺点是不支持随机访问…...

ChatGLM简介和SSE聊天接口测试效果
开发公司 智谱AI是由清华大学计算机系技术成果转化而来的公司,致力于打造新一代认知智能通用模型。公司合作研发了双语千亿级超大规模预训练模型GLM-130B,并构建了高精度通用知识图谱,形成数据与知识双轮驱动的认知引擎,基于此模型…...
darknet yolo标注、训练详细说明
文章目录 1、标注数据1.1、标注1.2、生成训练列表文件train.txt1.3、转换数据标注格式 2、训练数据整理2.1、修改train.txt路径2.2、修改yolov3.cfg2.3、obj.name和obj.data2.4、训练脚本文件trian.sh2.5、测试脚本文件test.sh 3、训练 本文对应的脚本文件和程序下载链接 darke…...

chatgpt赋能python:Python如何产生随机整数?
Python如何产生随机整数? Python是一种高级编程语言。它允许程序员轻松地创建各种类型的应用程序,包括生成随机整数。本文将介绍如何在Python中使用内置的随机数函数来生成随机整数。 random模块 Python中的random模块提供了生成随机数的函数。这些函…...

大话Stable-Diffusion-Webui-客制化主题(四)
文章目录 目标效果开始重要说明单选框以及复选框图标样式更改gradio主题构建器上传主题方式代码上传主题方式目标 在DIY的主题中更改gradio单选框组件以及复选框组件的勾选后图标样式 效果 开始 笔者在使用gradio的主题构建器的过程中发现,gradio的复选框以及单选框组件勾选…...

Excel函数VLOOKUP常用方法
一、基础用法 1、精确匹配 公式:VLOOKUP(待匹配值,查找范围,范围列数,查找方式) 定义好要输出表的表头和第一列,第一列即为要查找和匹配的父内容,在第二列输入公式,被查找表中一定也要将待查…...
systemV的工作原理+原理代码
概念 我们知道进程间的通信有管道的方式进程通信管道制作_云的小站的博客-CSDN博客 但是我们的管道通信其实属于一种取巧的方式,利用了打开的文件可读写的特性上,两个进程对此分别进行读写操作就会产生所谓的通信现象,但是外面的管道依旧得…...

Kubeflow--TFJob实现机制学习
2023暑期学习 TF Job实际场景应用Vertex AI TF Job 链接 https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/components/training/tftraining/ https://developer.aliyun.com/article/601779 TFJob实际上遵循Kubernetes标准的API定义. TFJob 对象 apiVersion --> string --> api版本&…...

百度出品,Nature重磅 -- 优化的mRNA设计算法可改善mRNA的稳定性和免疫原性
摘要 尽管mRNA疫苗已用于COVID-19的预防,但仍然面临不稳定和易降解的风险,这是mRNA疫苗存储、配送、效价等面临的重要障碍。先前的研究已表明,增加二级结构可延长mRNA的半衰期,再加上选择优化的密码子,可改善蛋白表达。…...

CKA 01_docker部署Kubernetes 部署docker 使用kubeadm引导集群 安装Pod网络
文章目录 1. 虚拟机步骤2. Docker 部署 Kubernetes2.1 部署 docker2.1.1 环境要求2.1.2 安装 docker 引擎2.1.3 worker 节点对 master 节点免密2.1.4 设定 docker 开机自启2.1.5 打开桥接,查看桥接流量2.1.6 设定 systemd 方式管理 cgroup2.1.7 docker部署完成2.1.8…...

Redis的使用规范小建议
Redis 核心技术与实战 笔记 作者: 蒋德钧 毕竟,高性能和节省内存,是我们的两个目标,只有规范地使用Redis,才能真正实现这两个目标。如果说之前的内容教会了你怎么用,那么今天的内容,就是帮助你用…...
操作受限的线性表——栈
本文主要内容:本文主要讲解栈的基本概念、基本操作和栈的顺序、链式实现。 目录 栈一、栈的基本概念1、基本概念2、基本操作 二、栈的顺序存储结构1、顺序栈的实现2、顺序栈的基本运算1)初始化2)判栈空3)进栈4)出栈5&a…...
父类指针访问子类成员变量(需要dynamic_cast))
C++基类指针或引用指向或引用派生类对象(实现动态多态四种手段)父类指针访问子类成员变量(需要dynamic_cast)
文章目录 背景多态示例:父类指针指向子类对象父类指针指向子类对象,如何通过父类指针访问到子类特定的成员变量实现动态多态的四种手段:基类的指针或引用指向或引用一个派生类对象(new或不new) 背景 比如有父类Animal…...
WTM框架运行报错0308010C:digital envelope routines::unsupported
WTM框架运行报错0308010C:digital envelope routines::unsupported 错误描述报错原因解决方式 错误描述 我所使用WTM搭建的程序是选择的.net5.0Vue前后端分离的方式,项目结构选择的是“各层分离的多个项目”;本人并非初次使用WTM平台框架搭建项目&#…...
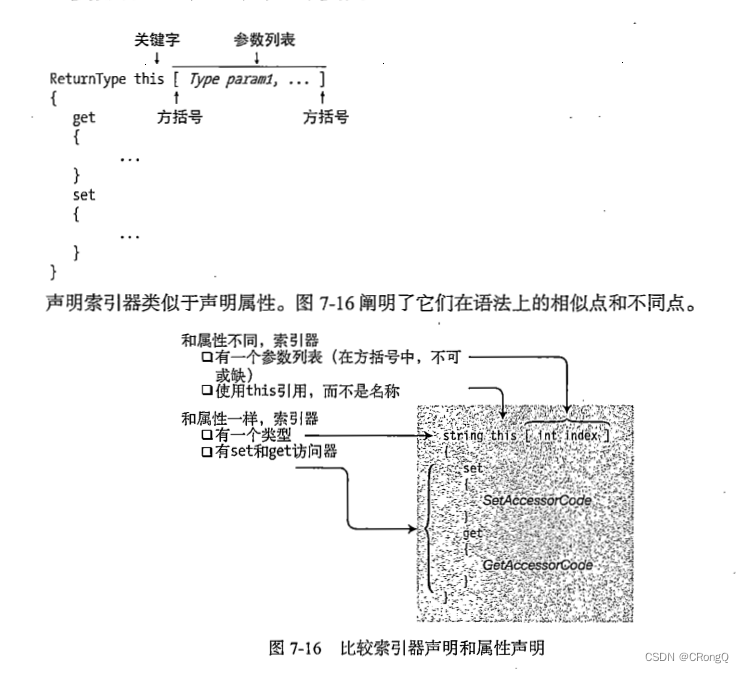
(二)CSharp-索引器
1、索引器定义 什么是索引器 索引器(indexer)是这样一种成员:它使对象能够用与数组相同的方式(即使用下标)进行索引 索引器的声明参见 C# 语言定义文档注意:没有静态索引器 索引器是一组 get 和 set 访问…...

配合AI刷leetcode 实现1170
题目如下: 1170. 比较字符串最小字母出现频次 难度中等 75 定义一个函数 f(s),统计 s 中(按字典序比较)最小字母的出现频次 ,其中 s 是一个非空字符串。 例如,若 s "dcce",那么…...

English Learning - L3 作业打卡 Lesson5 Day36 2023.6.9 周五
English Learning - L3 作业打卡 Lesson5 Day36 2023.6.9 周五 引言🍉句1: So next time you are on a train, look around and see what other people are reading, but dont jump to any conclusions.成分划分弱读连读爆破语调 🍉句2: You will probab…...
前端框架笔记
Vue.js的安装 安装Vue.js有两种方法: (1)类似于Bootstrap或jQuery,直接通过HTML文件中的标签引用。为了方便开发者使用,Vue.js提供了相关的CDN,通过如下代码可以引用最新版本的Vue.js: <sc…...

详细设计文档
1. 引言 1.1 目的 1.2 范围 1.3 定义、缩略语和缩写 1.4 参考文献 1.5 概述 2. 系统架构设计 2.1 总体架构 2.2 模块划分 2.3 数据流程设计 2.4 接口设计 3. 模块详细设计 3.1 登录模块详细设计 3.1.1 类设计 3.1.2 方法设计 3.1.3 数据库表设计 3.1.4 界面设计 3.2 文章管理模…...
)
Java011——Java数据类型转换(基本数据类型)
回顾:Java八大基本数据类型 大类 类型名称 关键字 占用内存 取值范围 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|字节型 byte 1 字节 -128~127 整型 |短整型 short 2 字节 -32768~32…...

Chapter03-Authentication vulnerabilities
文章目录 1. 身份验证简介1.1 What is authentication1.2 difference between authentication and authorization1.3 身份验证机制失效的原因1.4 身份验证机制失效的影响 2. 基于登录功能的漏洞2.1 密码爆破2.2 用户名枚举2.3 有缺陷的暴力破解防护2.3.1 如果用户登录尝试失败次…...
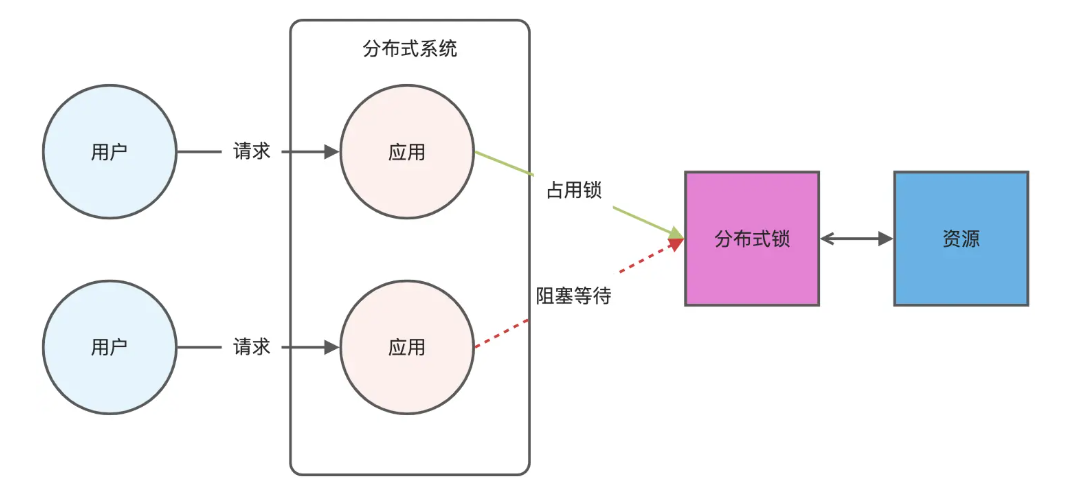
Redis相关知识总结(缓存雪崩,缓存穿透,缓存击穿,Redis实现分布式锁,如何保持数据库和缓存一致)
文章目录 1.什么是Redis?2.为什么要使用redis作为mysql的缓存?3.什么是缓存雪崩、缓存穿透、缓存击穿?3.1缓存雪崩3.1.1 大量缓存同时过期3.1.2 Redis宕机 3.2 缓存击穿3.3 缓存穿透3.4 总结 4. 数据库和缓存如何保持一致性5. Redis实现分布式…...

2024年赣州旅游投资集团社会招聘笔试真
2024年赣州旅游投资集团社会招聘笔试真 题 ( 满 分 1 0 0 分 时 间 1 2 0 分 钟 ) 一、单选题(每题只有一个正确答案,答错、不答或多答均不得分) 1.纪要的特点不包括()。 A.概括重点 B.指导传达 C. 客观纪实 D.有言必录 【答案】: D 2.1864年,()预言了电磁波的存在,并指出…...

Golang dig框架与GraphQL的完美结合
将 Go 的 Dig 依赖注入框架与 GraphQL 结合使用,可以显著提升应用程序的可维护性、可测试性以及灵活性。 Dig 是一个强大的依赖注入容器,能够帮助开发者更好地管理复杂的依赖关系,而 GraphQL 则是一种用于 API 的查询语言,能够提…...
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...
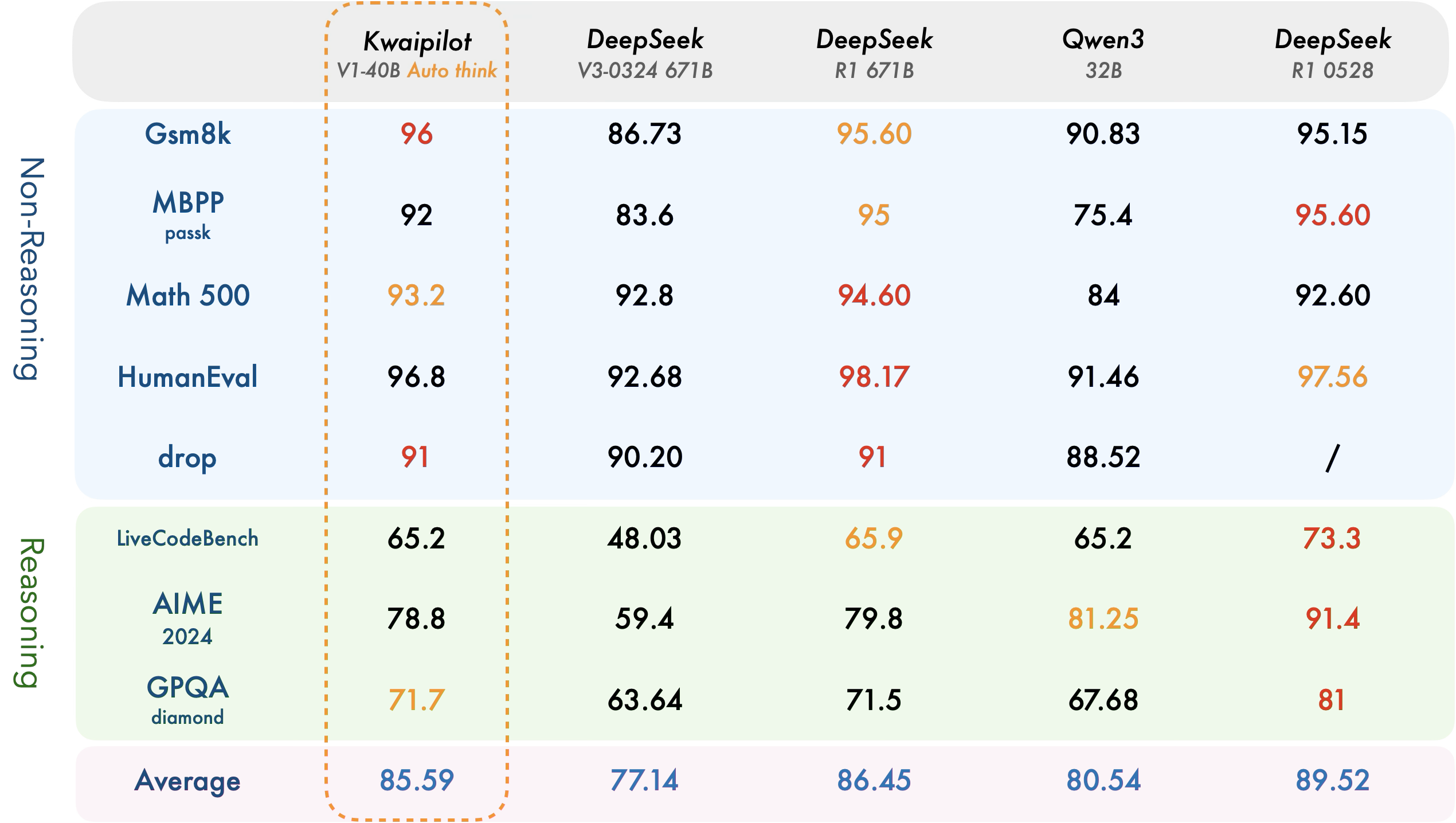
【快手拥抱开源】通过快手团队开源的 KwaiCoder-AutoThink-preview 解锁大语言模型的潜力
引言: 在人工智能快速发展的浪潮中,快手Kwaipilot团队推出的 KwaiCoder-AutoThink-preview 具有里程碑意义——这是首个公开的AutoThink大语言模型(LLM)。该模型代表着该领域的重大突破,通过独特方式融合思考与非思考…...

Nuxt.js 中的路由配置详解
Nuxt.js 通过其内置的路由系统简化了应用的路由配置,使得开发者可以轻松地管理页面导航和 URL 结构。路由配置主要涉及页面组件的组织、动态路由的设置以及路由元信息的配置。 自动路由生成 Nuxt.js 会根据 pages 目录下的文件结构自动生成路由配置。每个文件都会对…...
)
python爬虫:Newspaper3k 的详细使用(好用的新闻网站文章抓取和解析的Python库)
更多内容请见: 爬虫和逆向教程-专栏介绍和目录 文章目录 一、Newspaper3k 概述1.1 Newspaper3k 介绍1.2 主要功能1.3 典型应用场景1.4 安装二、基本用法2.2 提取单篇文章的内容2.2 处理多篇文档三、高级选项3.1 自定义配置3.2 分析文章情感四、实战案例4.1 构建新闻摘要聚合器…...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...

OPENCV形态学基础之二腐蚀
一.腐蚀的原理 (图1) 数学表达式:dst(x,y) erode(src(x,y)) min(x,y)src(xx,yy) 腐蚀也是图像形态学的基本功能之一,腐蚀跟膨胀属于反向操作,膨胀是把图像图像变大,而腐蚀就是把图像变小。腐蚀后的图像变小变暗淡。 腐蚀…...
