Istio Pilot源码学习(二):ServiceController服务发现
本文基于Istio 1.18.0版本进行源码学习
4、服务发现:ServiceController
ServiceController是服务发现的核心模块,主要功能是监听底层平台的服务注册中心,将平台服务模型转换成Istio服务模型并缓存;同时根据服务的变化,触发相关服务的事件处理回调函数的执行
1)、ServiceController的核心接口
ServiceController可以同时支持多个服务注册中心,因为它包含不同的注册中心控制器,它们的聚合是通过抽象聚合接口(aggregate.Controller)完成的,该接口相关定义如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/aggregate/controller.go
// 聚合所有底层注册中心的数据,并监控数据的变化
type Controller struct {// meshConfigmeshHolder mesh.Holder// The lock is used to protect the registries and controller's running status.storeLock sync.RWMutex// 注册中心的集合registries []*registryEntry// indicates whether the controller has run.// if true, all the registries added later should be run manually.running bool// 控制器回调函数的集合,当添加了某一注册中心时,控制器会向其注册回调函数handlers model.ControllerHandlers// 按照集群区分的回调函数handlersByCluster map[cluster.ID]*model.ControllerHandlersmodel.NetworkGatewaysHandler
}type registryEntry struct {serviceregistry.Instance// stop if not nil is the per-registry stop chan. If null, the server stop chan should be used to Run the registry.stop <-chan struct{}
}
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/instance.go
// 注册中心接口
type Instance interface {// 控制器接口model.Controller// 服务发现接口model.ServiceDiscovery// Provider backing this service registry (i.e. Kubernetes etc.)Provider() provider.ID// Cluster for which the service registry applies. Only needed for multicluster systems.Cluster() cluster.ID
}
注册中心接口Instance实现了Istio通用的控制器接口Controller及服务发现接口ServiceDiscovery,接口定义如下:
// pilot/pkg/model/controller.go
// 控制器接口,用于注册事件处理回调函数
// 注册中心控制器会接收资源更新事件,并执行相应的事件处理回调函数
type Controller interface {// Note: AppendXXXHandler is used to register high level handlers.// For per cluster handlers, they should be registered by the `AppendXXXHandlerForCluster` interface.// AppendServiceHandler notifies about changes to the service catalog.// 注册服务的事件处理回调函数AppendServiceHandler(f ServiceHandler)// AppendWorkloadHandler notifies about changes to workloads. This differs from InstanceHandler,// which deals with service instances (the result of a merge of Service and Workload)// 注册服务实例的事件处理回调函数,主要是为了支持kubernetes service和istio serviceEntry交叉选择服务实例AppendWorkloadHandler(f func(*WorkloadInstance, Event))// Run until a signal is received// 运行控制器Run(stop <-chan struct{})// HasSynced returns true after initial cache synchronization is complete// 同步检查控制器的缓存HasSynced() bool
}
// pilot/pkg/model/service.go
// 服务发现接口提供对服务模型的查询功能
type ServiceDiscovery interface {NetworkGatewaysWatcher// Services list declarations of all services in the system// 查询网格中的所有服务Services() []*Service// GetService retrieves a service by host name if it exists// 根据hostname查询服务GetService(hostname host.Name) *Service// InstancesByPort retrieves instances for a service on the given ports with labels that match// any of the supplied labels. All instances match an empty tag list.//// For example, consider an example of catalog.mystore.com:// Instances(catalog.myservice.com, 80) ->// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.1:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(foo=bar)// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.2:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(foo=bar)// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.3:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(kitty=cat)// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.4:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(kitty=cat)//// Calling Instances with specific labels returns a trimmed list.// e.g., Instances(catalog.myservice.com, 80, foo=bar) ->// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.1:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(foo=bar)// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.2:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(foo=bar)//// Similar concepts apply for calling this function with a specific// port, hostname and labels.//// Introduced in Istio 0.8. It is only called with 1 port.// CDS (clusters.go) calls it for building 'dnslb' type clusters.// EDS calls it for building the endpoints result.// Consult istio-dev before using this for anything else (except debugging/tools)// 根据服务及端口获取服务实例InstancesByPort(svc *Service, servicePort int) []*ServiceInstance// GetProxyServiceInstances returns the service instances that co-located with a given Proxy//// Co-located generally means running in the same network namespace and security context.//// A Proxy operating as a Sidecar will return a non-empty slice. A stand-alone Proxy// will return an empty slice.//// There are two reasons why this returns multiple ServiceInstances instead of one:// - A ServiceInstance has a single IstioEndpoint which has a single Port. But a Service// may have many ports. So a workload implementing such a Service would need// multiple ServiceInstances, one for each port.// - A single workload may implement multiple logical Services.//// In the second case, multiple services may be implemented by the same physical port number,// though with a different ServicePort and IstioEndpoint for each. If any of these overlapping// services are not HTTP or H2-based, behavior is undefined, since the listener may not be able to// determine the intended destination of a connection without a Host header on the request.// 获取与sidecar代理相关的服务实例GetProxyServiceInstances(*Proxy) []*ServiceInstance// 获取proxy工作负载的标签GetProxyWorkloadLabels(*Proxy) labels.Instance// MCSServices returns information about the services that have been exported/imported via the// Kubernetes Multi-Cluster Services (MCS) ServiceExport API. Only applies to services in// Kubernetes clusters.MCSServices() []MCSServiceInfoAmbientIndexes
}
2)、ServiceController的初始化
Kubernetes ServiceController初始化流程如下:

核心方法是pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go中的NewController()方法,代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go
func NewController(kubeClient kubelib.Client, options Options) *Controller {// 实例化kubernetes注册中心的控制器c := &Controller{opts: options,client: kubeClient,queue: queue.NewQueueWithID(1*time.Second, string(options.ClusterID)),servicesMap: make(map[host.Name]*model.Service),nodeSelectorsForServices: make(map[host.Name]labels.Instance),nodeInfoMap: make(map[string]kubernetesNode),externalNameSvcInstanceMap: make(map[host.Name][]*model.ServiceInstance),workloadInstancesIndex: workloadinstances.NewIndex(),initialSyncTimedout: atomic.NewBool(false),networkManager: initNetworkManager(options),configCluster: options.ConfigCluster,}c.namespaces = kclient.New[*v1.Namespace](kubeClient)if c.opts.SystemNamespace != "" {registerHandlers[*v1.Namespace](c,c.namespaces,"Namespaces",func(old *v1.Namespace, cur *v1.Namespace, event model.Event) error {if cur.Name == c.opts.SystemNamespace {return c.onSystemNamespaceEvent(old, cur, event)}return nil},nil,)}if c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter == nil {c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter = namespace.NewDiscoveryNamespacesFilter(c.namespaces, options.MeshWatcher.Mesh().DiscoverySelectors)}c.initDiscoveryHandlers(options.MeshWatcher, c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter)c.services = kclient.NewFiltered[*v1.Service](kubeClient, kclient.Filter{ObjectFilter: c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter.Filter})// 注册service对应的事件处理回调函数registerHandlers[*v1.Service](c, c.services, "Services", c.onServiceEvent, nil)switch options.EndpointMode {case EndpointSliceOnly:c.endpoints = newEndpointSliceController(c)default: // nolint: gocriticlog.Errorf("unknown endpoints mode: %v", options.EndpointMode)fallthroughcase EndpointsOnly:// 实例化endpointsController,注册endpoints对应的事件处理回调函数c.endpoints = newEndpointsController(c)}// This is for getting the node IPs of a selected set of nodesc.nodes = kclient.NewFiltered[*v1.Node](kubeClient, kclient.Filter{ObjectTransform: kubelib.StripNodeUnusedFields})// 注册node对应的事件处理回调函数registerHandlers[*v1.Node](c, c.nodes, "Nodes", c.onNodeEvent, nil)c.podsClient = kclient.NewFiltered[*v1.Pod](kubeClient, kclient.Filter{ObjectFilter: c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter.Filter,ObjectTransform: kubelib.StripPodUnusedFields,})c.pods = newPodCache(c, c.podsClient, func(key types.NamespacedName) {c.queue.Push(func() error {return c.endpoints.sync(key.Name, key.Namespace, model.EventAdd, true)})})// 注册pod对应的事件处理回调函数registerHandlers[*v1.Pod](c, c.podsClient, "Pods", c.pods.onEvent, c.pods.labelFilter)if features.EnableMCSServiceDiscovery || features.EnableMCSHost {c.crdWatcher = crdwatcher.NewController(kubeClient)}if features.EnableAmbientControllers {c.configController = options.ConfigControllerc.ambientIndex = c.setupIndex()}c.exports = newServiceExportCache(c)c.imports = newServiceImportCache(c)c.meshWatcher = options.MeshWatcherif c.opts.MeshNetworksWatcher != nil {c.opts.MeshNetworksWatcher.AddNetworksHandler(func() {c.reloadMeshNetworks()c.onNetworkChange()})c.reloadMeshNetworks()}return c
}
NewController()方法中实例化了Kubernetes注册中心的控制器,Kubernetes注册中心的控制器定义如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go
type Controller struct {opts Optionsclient kubelib.Client// 控制器的任务队列queue queue.Instancenamespaces kclient.Client[*v1.Namespace]services kclient.Client[*v1.Service]// kubernetes的endpoints控制器抽象接口,支持endpoint和endpointSliceendpoints kubeEndpointsController// Used to watch node accessible from remote cluster.// In multi-cluster(shared control plane multi-networks) scenario, ingress gateway service can be of nodePort type.// With this, we can populate mesh's gateway address with the node ips.nodes kclient.Client[*v1.Node]crdWatcher *crdwatcher.Controller// 多集群服务serviceExport的资源处理接口exports serviceExportCache// 多集群服务serviceImport的资源处理接口imports serviceImportCache// 包含kclient.Client[*v1.Pod]pods *PodCachecrdHandlers []func(name string)// service及pod实例的事件处理函数handlers model.ControllerHandlersnamespaceDiscoveryHandlers []func(ns string, event model.Event)// This is only used for teststop chan struct{}sync.RWMutex// servicesMap stores hostname ==> service, it is used to reduce convertService calls.// istio服务模型的缓存servicesMap map[host.Name]*model.Service// nodeSelectorsForServices stores hostname => label selectors that can be used to// refine the set of node port IPs for a service.nodeSelectorsForServices map[host.Name]labels.Instance// map of node name and its address+labels - this is the only thing we need from nodes// for vm to k8s or cross cluster. When node port services select specific nodes by labels,// we run through the label selectors here to pick only ones that we need.// Only nodes with ExternalIP addresses are included in this map !// node的缓存nodeInfoMap map[string]kubernetesNode// externalNameSvcInstanceMap stores hostname ==> instance, is used to store instances for ExternalName k8s services// externalName类型的服务实例缓存externalNameSvcInstanceMap map[host.Name][]*model.ServiceInstance// index over workload instances from workload entries// 工作负载实例的索引workloadInstancesIndex workloadinstances.IndexnetworkManager// initialSyncTimedout is set to true after performing an initial processing timed out.initialSyncTimedout *atomic.BoolmeshWatcher mesh.WatcherpodsClient kclient.Client[*v1.Pod]ambientIndex *AmbientIndexconfigController model.ConfigStoreControllerconfigCluster bool
}
Controller中services、nodes、podsClient属性都是Client[T controllers.Object]类型的,Client[T controllers.Object]封装了对应的资源操作客户端,定义如下:
// pkg/kube/kclient/interfaces.go
// Client wraps a Kubernetes client providing cached read access and direct write access.
type Client[T controllers.Object] interface {Reader[T]Writer[T]Informer[T]
}
Kubernetes控制器关键属性的初始化方式如下图:
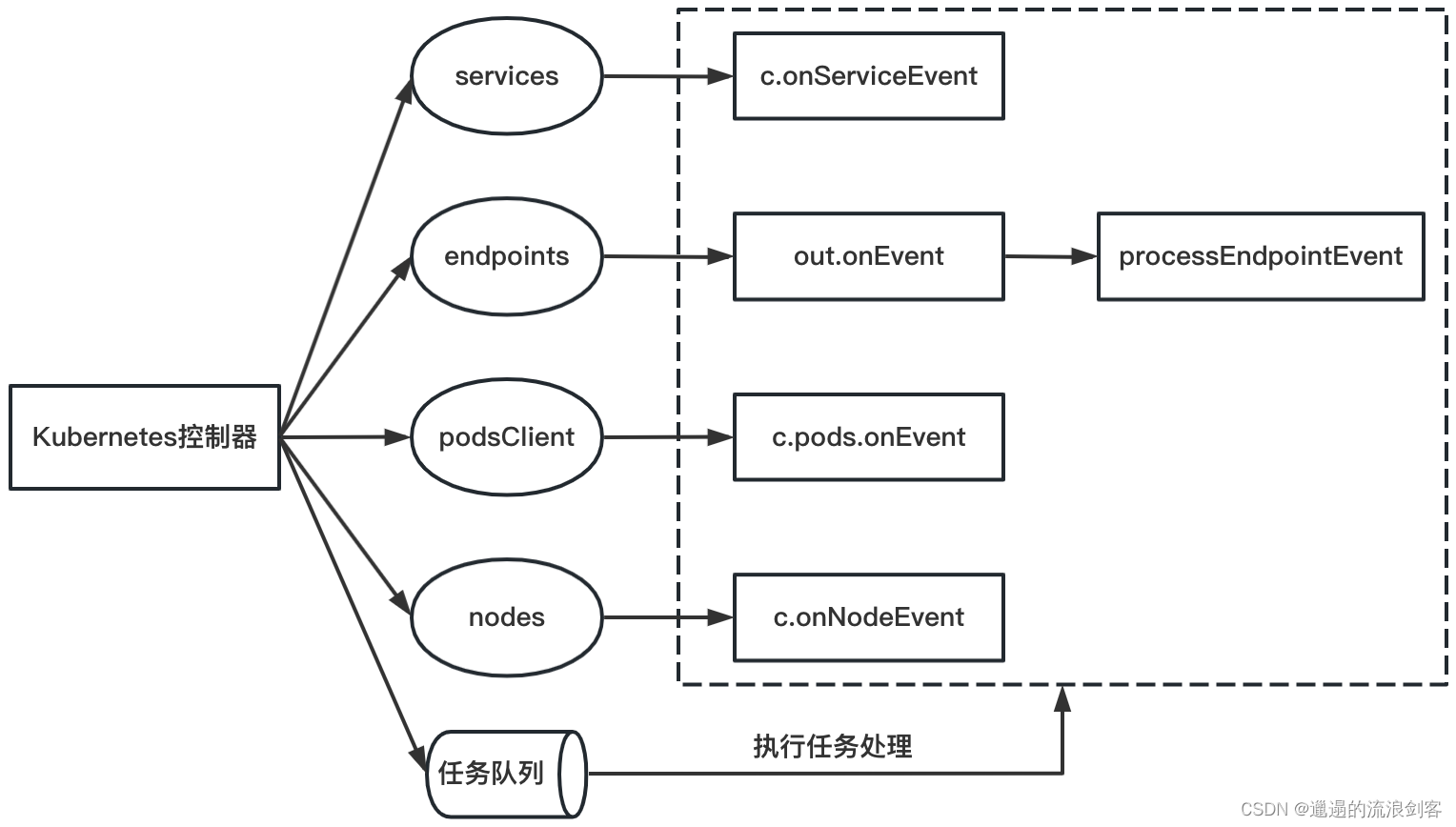
Kubernetes控制器的核心就是监听Kubernetes相关资源(Service、Endpoint、EndpointSlice、Pod、Node)的更新事件,执行相应的事件处理回调函数;并且进行从Kubernetes资源对象到Istio资源对象的转换,提供一定的缓存能力,主要是缓存Istio Service与WorkloadInstance
3)、ServiceController的工作机制
ServiceController为4种资源分别创建了Informer,用于监听Kubernetes资源的更新,并为其注册EventHandler
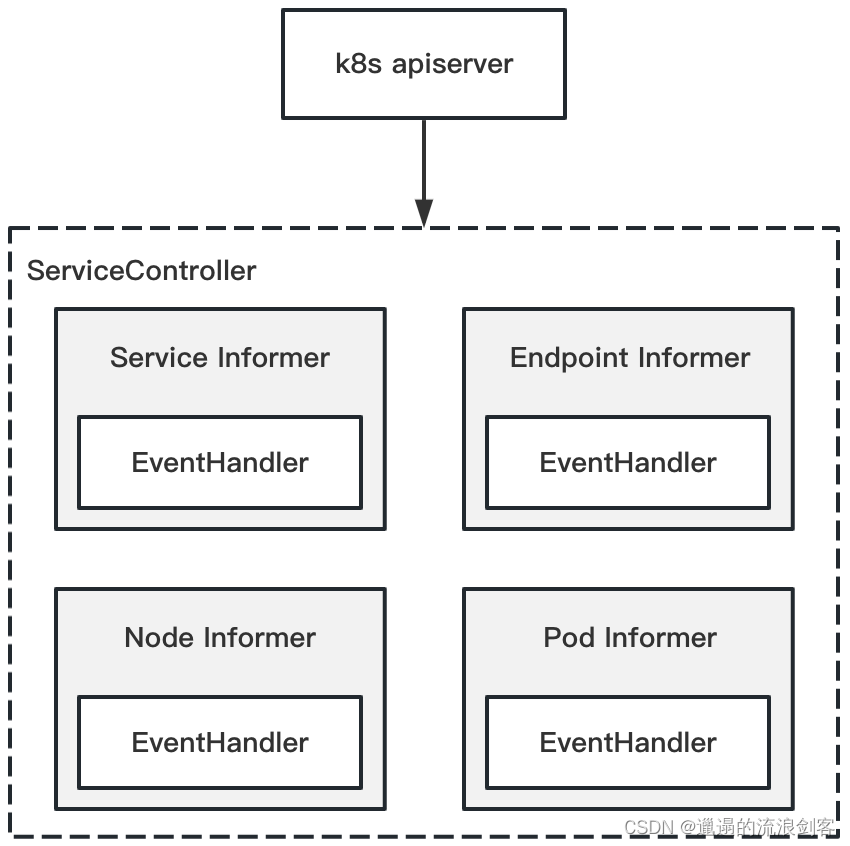
NewController()方法中调用registerHandlers()方法为4种资源注册EventHandler,registerHandlers()方法代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go
func registerHandlers[T controllers.ComparableObject](c *Controller,informer kclient.Informer[T], otype string,handler func(T, T, model.Event) error, filter FilterOutFunc[T],
) {// 包装传入的handler方法wrappedHandler := func(prev, curr T, event model.Event) error {curr = informer.Get(curr.GetName(), curr.GetNamespace())if controllers.IsNil(curr) {// this can happen when an immediate delete after update// the delete event can be handled laterreturn nil}return handler(prev, curr, event)}informer.AddEventHandler(controllers.EventHandler[T]{AddFunc: func(obj T) {incrementEvent(otype, "add")// 创建资源处理任务并将其推送到任务队列c.queue.Push(func() error {return wrappedHandler(ptr.Empty[T](), obj, model.EventAdd)})},UpdateFunc: func(old, cur T) {if filter != nil {if filter(old, cur) {incrementEvent(otype, "updatesame")return}}incrementEvent(otype, "update")c.queue.Push(func() error {return wrappedHandler(old, cur, model.EventUpdate)})},DeleteFunc: func(obj T) {incrementEvent(otype, "delete")c.queue.Push(func() error {return handler(ptr.Empty[T](), obj, model.EventDelete)})},})
}
当监听到Service、Endpoint、Pod、Node资源更新时,EventHandler会创建资源处理任务并将其推送到任务队列,然后由任务处理协程阻塞式地接收任务对象,最终调用任务处理函数完成对资源对象的事件处理
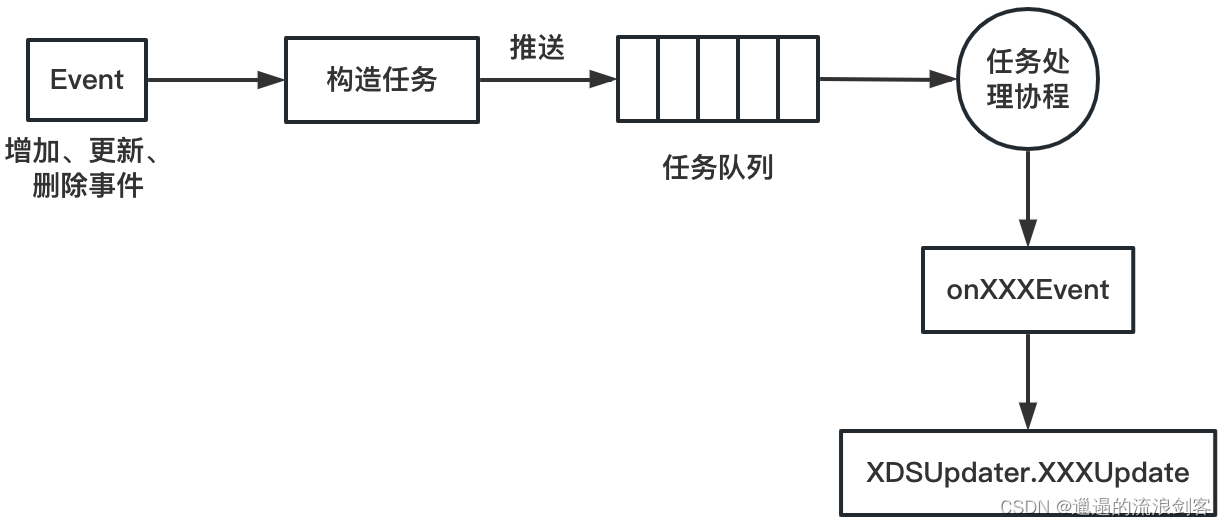
1)Service事件处理
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go
func (c *Controller) onServiceEvent(_, curr *v1.Service, event model.Event) error {log.Debugf("Handle event %s for service %s in namespace %s", event, curr.Name, curr.Namespace)// Create the standard (cluster.local) service.// 将kubernetes service转换成istio servicesvcConv := kube.ConvertService(*curr, c.opts.DomainSuffix, c.Cluster())switch event {case model.EventDelete:// 删除servicec.deleteService(svcConv)default:// 创建或更新servicec.addOrUpdateService(curr, svcConv, event, false)}return nil
}func (c *Controller) addOrUpdateService(curr *v1.Service, currConv *model.Service, event model.Event, updateEDSCache bool) {needsFullPush := false// First, process nodePort gateway service, whose externalIPs specified// and loadbalancer gateway serviceif !currConv.Attributes.ClusterExternalAddresses.IsEmpty() {needsFullPush = c.extractGatewaysFromService(currConv)} else if isNodePortGatewayService(curr) {// We need to know which services are using node selectors because during node events,// we have to update all the node port services accordingly.nodeSelector := getNodeSelectorsForService(curr)c.Lock()// only add when it is nodePort gateway servicec.nodeSelectorsForServices[currConv.Hostname] = nodeSelectorc.Unlock()needsFullPush = c.updateServiceNodePortAddresses(currConv)}var prevConv *model.Service// instance conversion is only required when service is added/updated.instances := kube.ExternalNameServiceInstances(curr, currConv)c.Lock()prevConv = c.servicesMap[currConv.Hostname]c.servicesMap[currConv.Hostname] = currConvif len(instances) > 0 {c.externalNameSvcInstanceMap[currConv.Hostname] = instances}c.Unlock()// This full push needed to update ALL ends endpoints, even though we do a full push on service add/update// as that full push is only triggered for the specific service.if needsFullPush {// networks are different, we need to update all eds endpointsc.opts.XDSUpdater.ConfigUpdate(&model.PushRequest{Full: true, Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.NetworksTrigger}})}shard := model.ShardKeyFromRegistry(c)ns := currConv.Attributes.Namespace// We also need to update when the Service changes. For Kubernetes, a service change will result in Endpoint updates,// but workload entries will also need to be updated.// TODO(nmittler): Build different sets of endpoints for cluster.local and clusterset.local.if updateEDSCache || features.EnableK8SServiceSelectWorkloadEntries {endpoints := c.buildEndpointsForService(currConv, updateEDSCache)if len(endpoints) > 0 {c.opts.XDSUpdater.EDSCacheUpdate(shard, string(currConv.Hostname), ns, endpoints)}}// 更新服务缓存c.opts.XDSUpdater.SvcUpdate(shard, string(currConv.Hostname), ns, event)// 触发service事件处理函数c.handlers.NotifyServiceHandlers(prevConv, currConv, event)
}
Service事件处理器会将根据事件的类型更新服务缓存,然后调用serviceHandlers的事件处理器进行回调。serviceHandlers是通过ServiceController的AppendServiceHandler()注册的,注册代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/bootstrap/server.go
func (s *Server) initRegistryEventHandlers() {log.Info("initializing registry event handlers")// Flush cached discovery responses whenever services configuration change.serviceHandler := func(prev, curr *model.Service, event model.Event) {needsPush := trueif event == model.EventUpdate {needsPush = serviceUpdateNeedsPush(prev, curr)}if needsPush {// 触发xds全量更新pushReq := &model.PushRequest{Full: true,ConfigsUpdated: sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.ServiceEntry, Name: string(curr.Hostname), Namespace: curr.Attributes.Namespace}),Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.ServiceUpdate},}s.XDSServer.ConfigUpdate(pushReq)}}// 注册service的事件处理函数s.ServiceController().AppendServiceHandler(serviceHandler)...
2)Endpoint事件处理
Endpoint事件处理器在NewController()中调用newEndpointsController()创建endpointsController的时候注册:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/endpoints.go
func newEndpointsController(c *Controller) *endpointsController {endpoints := kclient.NewFiltered[*v1.Endpoints](c.client, kclient.Filter{ObjectFilter: c.opts.GetFilter()})out := &endpointsController{endpoints: endpoints,c: c,}// 注册endpoint对应的事件处理回调函数registerHandlers[*v1.Endpoints](c, endpoints, "Endpoints", out.onEvent, endpointsEqual)return out
}func (e *endpointsController) onEvent(_, ep *v1.Endpoints, event model.Event) error {return processEndpointEvent(e.c, e, ep.Name, ep.Namespace, event, ep)
}
Endpoint事件处理函数是processEndpointEvent(),实现如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/endpointcontroller.go
func processEndpointEvent(c *Controller, epc kubeEndpointsController, name string, namespace string, event model.Event, ep any) error {// Update internal endpoint cache no matter what kind of service, even headless service.// As for gateways, the cluster discovery type is `EDS` for headless service.// 更新edsupdateEDS(c, epc, ep, event)if svc := c.services.Get(name, namespace); svc != nil {// if the service is headless service, trigger a full push if EnableHeadlessService is true,// otherwise push endpoint updates - needed for NDS output.// 如果是headlessService,触发xds全量更新if svc.Spec.ClusterIP == v1.ClusterIPNone {for _, modelSvc := range c.servicesForNamespacedName(config.NamespacedName(svc)) {c.opts.XDSUpdater.ConfigUpdate(&model.PushRequest{Full: features.EnableHeadlessService,// TODO: extend and set service instance type, so no need to re-init push contextConfigsUpdated: sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.ServiceEntry, Name: modelSvc.Hostname.String(), Namespace: svc.Namespace}),Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.HeadlessEndpointUpdate},})return nil}}}return nil
}func updateEDS(c *Controller, epc kubeEndpointsController, ep any, event model.Event) {namespacedName := epc.getServiceNamespacedName(ep)log.Debugf("Handle EDS endpoint %s %s in namespace %s", namespacedName.Name, event, namespacedName.Namespace)var forgottenEndpointsByHost map[host.Name][]*model.IstioEndpointif event == model.EventDelete {forgottenEndpointsByHost = epc.forgetEndpoint(ep)}shard := model.ShardKeyFromRegistry(c)for _, hostName := range c.hostNamesForNamespacedName(namespacedName) {var endpoints []*model.IstioEndpointif forgottenEndpointsByHost != nil {endpoints = forgottenEndpointsByHost[hostName]} else {// 将endpoint转换成istio endpointendpoints = epc.buildIstioEndpoints(ep, hostName)}if features.EnableK8SServiceSelectWorkloadEntries {svc := c.GetService(hostName)if svc != nil {fep := c.collectWorkloadInstanceEndpoints(svc)endpoints = append(endpoints, fep...)} else {log.Debugf("Handle EDS endpoint: skip collecting workload entry endpoints, service %s/%s has not been populated",namespacedName.Namespace, namespacedName.Name)}}// 调用EDSUpdatec.opts.XDSUpdater.EDSUpdate(shard, string(hostName), namespacedName.Namespace, endpoints)}
}
最后调用XDSUpdater.EDSUpdate()进行EDS的缓存更新及触发xDS更新,代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/xds/eds.go
func (s *DiscoveryServer) EDSUpdate(shard model.ShardKey, serviceName string, namespace string,istioEndpoints []*model.IstioEndpoint,
) {inboundEDSUpdates.Increment()// Update the endpoint shards// 更新eds缓存pushType := s.edsCacheUpdate(shard, serviceName, namespace, istioEndpoints)// 触发xds更新if pushType == IncrementalPush || pushType == FullPush {// Trigger a pushs.ConfigUpdate(&model.PushRequest{Full: pushType == FullPush,ConfigsUpdated: sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.ServiceEntry, Name: serviceName, Namespace: namespace}),Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.EndpointUpdate},})}
}func (s *DiscoveryServer) edsCacheUpdate(shard model.ShardKey, hostname string, namespace string,istioEndpoints []*model.IstioEndpoint,
) PushType {if len(istioEndpoints) == 0 {// Should delete the service EndpointShards when endpoints become zero to prevent memory leak,// but we should not delete the keys from EndpointIndex map - that will trigger// unnecessary full push which can become a real problem if a pod is in crashloop and thus endpoints// flip flopping between 1 and 0.// 在endpoint变为0时,应该删除服务的endpointIndex,但是不能删除endpointIndex map中的键值,// 因为假如这时pod状态在crash loop和ready之间跳变,就会引起不必要、频繁的xds全量更新s.Env.EndpointIndex.DeleteServiceShard(shard, hostname, namespace, true)log.Infof("Incremental push, service %s at shard %v has no endpoints", hostname, shard)return IncrementalPush}pushType := IncrementalPush// Find endpoint shard for this service, if it is available - otherwise create a new one.// 找到服务的endpointShard,如果不存在,则创建一个新的ep, created := s.Env.EndpointIndex.GetOrCreateEndpointShard(hostname, namespace)// If we create a new endpoint shard, that means we have not seen the service earlier. We should do a full push.// 如果创建了endpointShard,则需要触发xds全量更新if created {log.Infof("Full push, new service %s/%s", namespace, hostname)pushType = FullPush}ep.Lock()defer ep.Unlock()newIstioEndpoints := istioEndpoints// 支持发送unhealthy endpointsif features.SendUnhealthyEndpoints.Load() {oldIstioEndpoints := ep.Shards[shard]newIstioEndpoints = make([]*model.IstioEndpoint, 0, len(istioEndpoints))// Check if new Endpoints are ready to be pushed. This check// will ensure that if a new pod comes with a non ready endpoint,// we do not unnecessarily push that config to Envoy.// Please note that address is not a unique key. So this may not accurately// identify based on health status and push too many times - which is ok since its an optimization.emap := make(map[string]*model.IstioEndpoint, len(oldIstioEndpoints))nmap := make(map[string]*model.IstioEndpoint, len(newIstioEndpoints))// Add new endpoints only if they are ever ready once to shards// so that full push does not send them from shards.for _, oie := range oldIstioEndpoints {emap[oie.Address] = oie}for _, nie := range istioEndpoints {nmap[nie.Address] = nie}needPush := falsefor _, nie := range istioEndpoints {if oie, exists := emap[nie.Address]; exists {// If endpoint exists already, we should push if it's health status changes.// 如果endpoint存在,判断其健康状态是否发生了变化,仅在发生变化时才需要进行xds推送if oie.HealthStatus != nie.HealthStatus {needPush = true}newIstioEndpoints = append(newIstioEndpoints, nie)} else if nie.HealthStatus == model.Healthy {// If the endpoint does not exist in shards that means it is a// new endpoint. Only send if it is healthy to avoid pushing endpoints// that are not ready to start with.// 如果endpoint原来不存在,仅当其健康时进行xds推送needPush = truenewIstioEndpoints = append(newIstioEndpoints, nie)}}// Next, check for endpoints that were in old but no longer exist. If there are any, there is a// removal so we need to push an update.// 如果检查到endpoint原来存在,但是现在被删除了,则这时也需要进行xds推送for _, oie := range oldIstioEndpoints {if _, f := nmap[oie.Address]; !f {needPush = true}}if pushType != FullPush && !needPush {log.Debugf("No push, either old endpoint health status did not change or new endpoint came with unhealthy status, %v", hostname)pushType = NoPush}}ep.Shards[shard] = newIstioEndpoints// Check if ServiceAccounts have changed. We should do a full push if they have changed.// 检查serviceAccount的变化saUpdated := s.UpdateServiceAccount(ep, hostname)// For existing endpoints, we need to do full push if service accounts change.if saUpdated && pushType != FullPush {// Avoid extra logging if already a full pushlog.Infof("Full push, service accounts changed, %v", hostname)pushType = FullPush}// Clear the cache here. While it would likely be cleared later when we trigger a push, a race// condition is introduced where an XDS response may be generated before the update, but not// completed until after a response after the update. Essentially, we transition from v0 -> v1 ->// v0 -> invalidate -> v1. Reverting a change we pushed violates our contract of monotonically// moving forward in version. In practice, this is pretty rare and self corrects nearly// immediately. However, clearing the cache here has almost no impact on cache performance as we// would clear it shortly after anyways.// 清空xdsCaches.Cache.Clear(sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.ServiceEntry, Name: hostname, Namespace: namespace}))return pushType
}
Endpoint事件处理器根据Endpoint的变化更新与服务相关的缓存,判断本次Endpoint资源的更新是否需要触发全量的xDS更新。在服务网各种变化最多、最快的往往是Endpoint,因为增量EDS的更新能够大大降低系统的资源(CPU、内存、带宽)开销,提升服务网格的稳定性
参考:
《Istio权威指南 下》
2.深入Istio源码:Pilot服务发现
相关文章:

Istio Pilot源码学习(二):ServiceController服务发现
本文基于Istio 1.18.0版本进行源码学习 4、服务发现:ServiceController ServiceController是服务发现的核心模块,主要功能是监听底层平台的服务注册中心,将平台服务模型转换成Istio服务模型并缓存;同时根据服务的变化,…...

Spring框架中的ResourcePatternResolver只能指定jar包内文件,指定容器中文件路径报错:FileNotFoundException
原始代码: public static <T> T getFromFile(String specifiedFile, String defaultClasspathFile, Class<T> expectedClass) {try {ResourcePatternResolver resolver new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();Resource[] resources resolver.ge…...

pytorch工具——认识pytorch
目录 pytorch的基本元素操作创建一个没有初始化的矩阵创建一个有初始化的矩阵创建一个全0矩阵并可指定数据元素类型为long直接通过数据创建张量通过已有的一个张量创建相同尺寸的新张量利用randn_like方法得到相同尺寸张量,并且采用随机初始化的方法为其赋值采用.si…...
解决Jmeter响应内容显示乱码
一、问题描述 jmeter在执行接口请求后,返回的响应体里面出现乱码现象,尽管在调了对应请求的响应编码也无用,现找到解决办法。 二、解决办法 进入到jmeter的bin目录下,找到jmeter.properties,通过按ctrlF快速定位查找到…...

ChatGPT和搜索引擎哪个更好用
目录 ChatGPT和搜索引擎的概念 ChatGPT和搜索引擎的作用 ChatGPT的作用 搜索引擎的作用 ChatGPT和搜索引擎哪个更好用 总结 ChatGPT和搜索引擎的概念 ChatGPT是一种基于对话的人工智能技术,而搜索引擎则是一种用于在互联网上查找和检索信息的工具。它们各自具…...
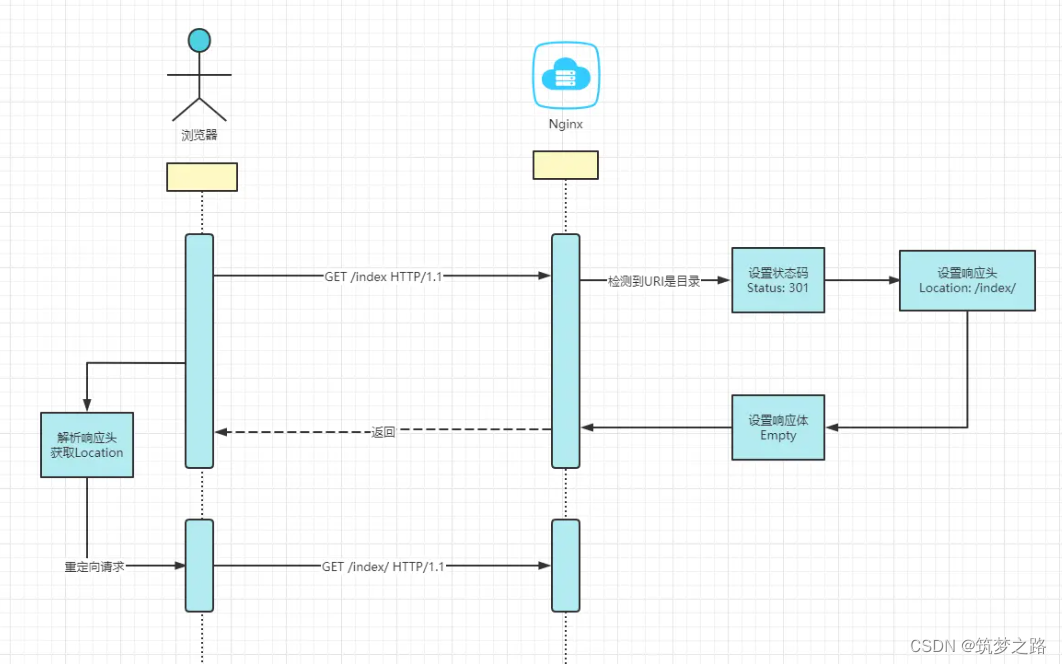
Nginx 301 https跳转后出现跨域和混合内容问题 —— 筑梦之路
问题 在浏览器地址栏敲入url访问静态资源目录时,发现默认跳转到了http协议的地址 如上图所示,客户端https请求先到达API网关,然后网关将请求通过http协议转发到静态资源服务器。 调出浏览器发现客户端发送的https请求收到了一个301状态码的响…...

记录--关于前端的音频可视化-Web Audio
这里给大家分享我在网上总结出来的一些知识,希望对大家有所帮助 背景 最近听音乐的时候,看到各种动效,突然好奇这些音频数据是如何获取并展示出来的,于是花了几天功夫去研究相关的内容,这里只是给大家一些代码实例&…...
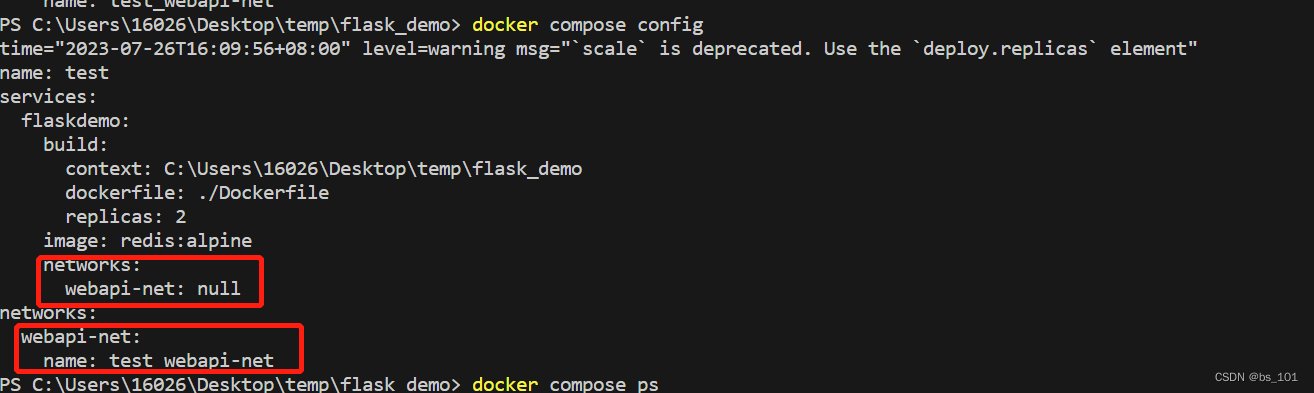
docker-compose yml配置、常用命令
下载完docker-compose后,如果想使用docker-compose命令开头,需要创建软连接 sudo ln -s /usr/local/lib/docker/cli-plugins/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-compose 1.docker-compose.yml文件编排 一个 docker-compose.yml 文件的顶层元素有ÿ…...
 —— React17+React Hook+TS4 最佳实践,仿 Jira 企业级项目(十三))
【实战】 七、Hook,路由,与 URL 状态管理(下) —— React17+React Hook+TS4 最佳实践,仿 Jira 企业级项目(十三)
文章目录 一、项目起航:项目初始化与配置二、React 与 Hook 应用:实现项目列表三、TS 应用:JS神助攻 - 强类型四、JWT、用户认证与异步请求五、CSS 其实很简单 - 用 CSS-in-JS 添加样式六、用户体验优化 - 加载中和错误状态处理七、Hook&…...

【MySQL】_5.MySQL的联合查询
目录 1. 笛卡尔积 2. 内连接 2.1 示例1:查询许仙同学的成绩 2.2 示例2: 查询所有同学的总成绩,及同学的个人信息 2.3 示例3:查询所有同学的科目及各科成绩,及同学的个人信息 3. 外连接 3.1 情况一:两…...

【后端面经】微服务构架 (1-3) | 熔断:熔断-恢复-熔断-恢复,抖来抖去怎么办?
文章目录 一、前置知识1、什么是熔断?2、什么是限流?3、什么是降级?4、怎么判断微服务出现了问题?A、指标有哪些?B、阈值如何选择?C、超过阈值之后,要不要持续一段时间才触发熔断?5、服务恢复正常二、面试环节1、面试准备2、面试基本思路三、总结 在微服务构架中…...

对UITextField输入内容的各种限制-总结
使用代理方法来限制输入框中的字数,输入的符号,输入的数字大小等各种限制 限制输入字数 已经有小数点了,就不能继续输入小数点 不能输入以0为开头的内容 不能输入以.为开头的内容 小数点后只允许输入一位数 只能输入100以下的数值 **不能包括…...

【图论】二分图
二分图,即可以将图中的所有顶点分层两个点集,每个点集内部没有边 判定图为二分图的充要条件:有向连通图不含奇数环 1、染色法 可以解决二分图判断的问题 步骤与基本思路 遍历图中每一个点,若该点未被染色,则遍历该…...
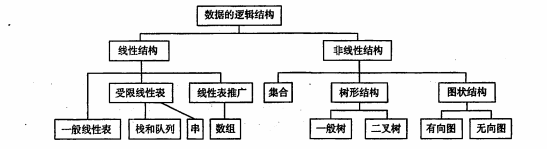
数据结构——(一)绪论
👉数据元素整体思维导图 欢迎补充 一、基本概念❤️ 1.1基本术语⭐️ (1)数据 客观事务属性的数字、字符。 (2)数据元素 数据元素是数据的基本单位,一个数据元素可由若干数据项组成,数据项是…...
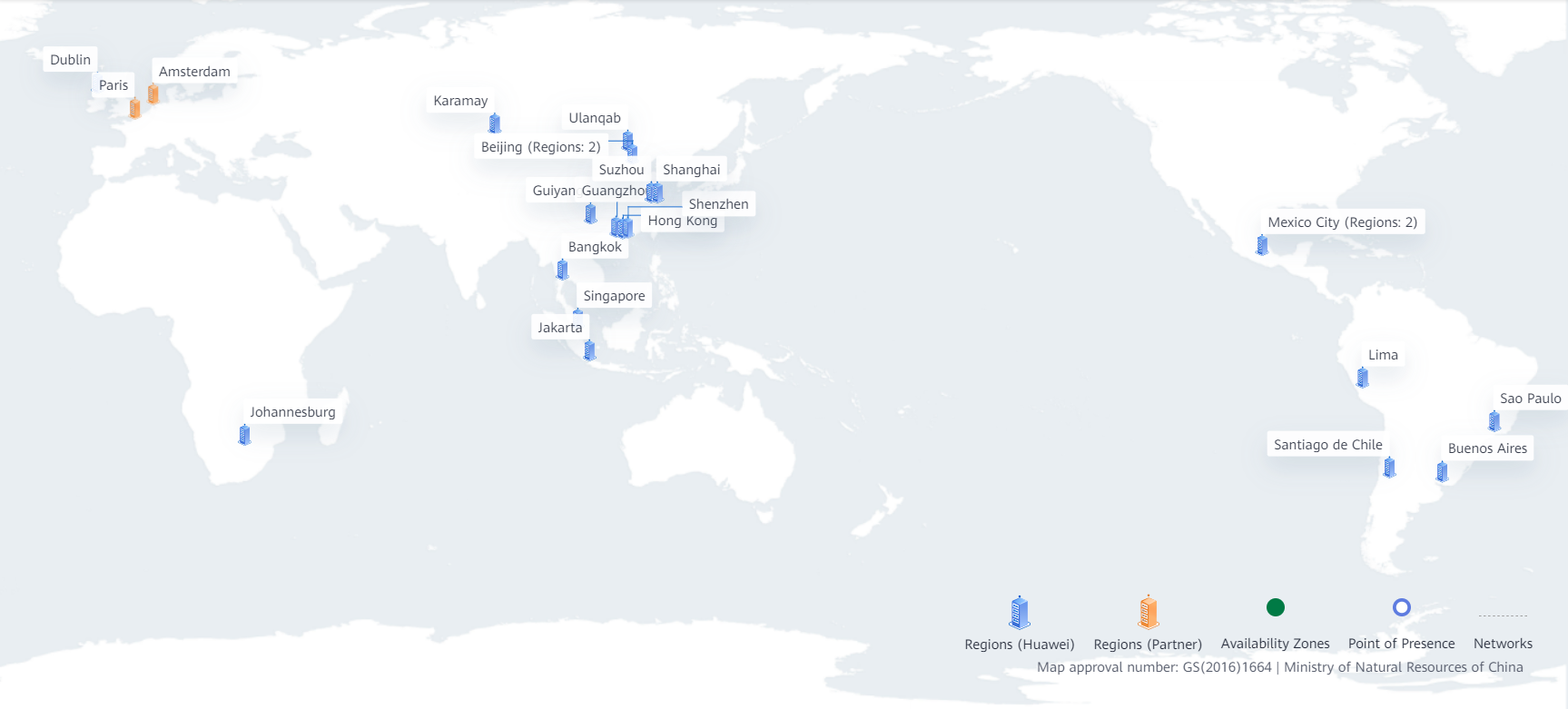
[ 华为云 ] 云计算中Region、VPC、AZ 是什么,他们又是什么关系,应该如何抉择
前几天看到一个问答帖,我回答完了才发现这个帖子居然是去年的也没人回复,其中他问了一些华为云的问题,对于其中的一些概念,这里来总结讲解一下,希望对学习华为云的小伙伴有所帮助。 文章目录 区域(Region&a…...

表单验证:输入的字符串以回车分隔并验证是否有
公司项目开发时,有一个需求,需要对输入的字符串按回车分隔并验证是否有重复项,效果如下: 表单代码: <el-form-item label"IP地址条目:" prop"ipAddressEntry"><el-inputtype&…...

智能财务分析-亿发财务报表管理系统,赋能中小企业财务数字化转型
对于许多中小企业来说,企业重要部门往往是财务和业务部门。业务负责创收,财务负责控制成本,降低税收风险。但因管理机制和公司运行制度的原因,中小企业往往面临着业务与财务割裂的问题,财务数据不清晰,无法…...

图为科技T501赋能工业机器人 革新传统工业流程
工业机器人已成为一个国家制造技术与科技水平的重要衡量标准,在2019年,中国工业机器人的组装量与产量均位居了全球首位。 当前,工业机器人被广泛用于电子、物流、化工等多个领域之中,是一种通过电子科技和机械关节制作出来的智能机…...
安全狗深度参与编写的《云原生安全配置基线规范》正式发布!
7月25日,由中国信息通信研究院、中国通信标准化协会主办的2023可信云大会在北京顺利开幕。 作为国内云原生安全领导厂商,安全狗受邀出席此次活动。 厦门服云信息科技有限公司(品牌名:安全狗)成立于2013年,…...
如何在3ds max中创建可用于真人场景的巨型机器人:第 2 部分
推荐: NSDT场景编辑器助你快速搭建可二次开发的3D应用场景 1. 创建主体 步骤 1 打开 3ds Max。选择机器人头部后,二次单击鼠标并选择隐藏未选中。机器人的其他部分 除了头部之外,将被隐藏。 打开 3ds Max 步骤 2 在人脸选择模式下&#x…...

日语AI面试高效通关秘籍:专业解读与青柚面试智能助攻
在如今就业市场竞争日益激烈的背景下,越来越多的求职者将目光投向了日本及中日双语岗位。但是,一场日语面试往往让许多人感到步履维艰。你是否也曾因为面试官抛出的“刁钻问题”而心生畏惧?面对生疏的日语交流环境,即便提前恶补了…...
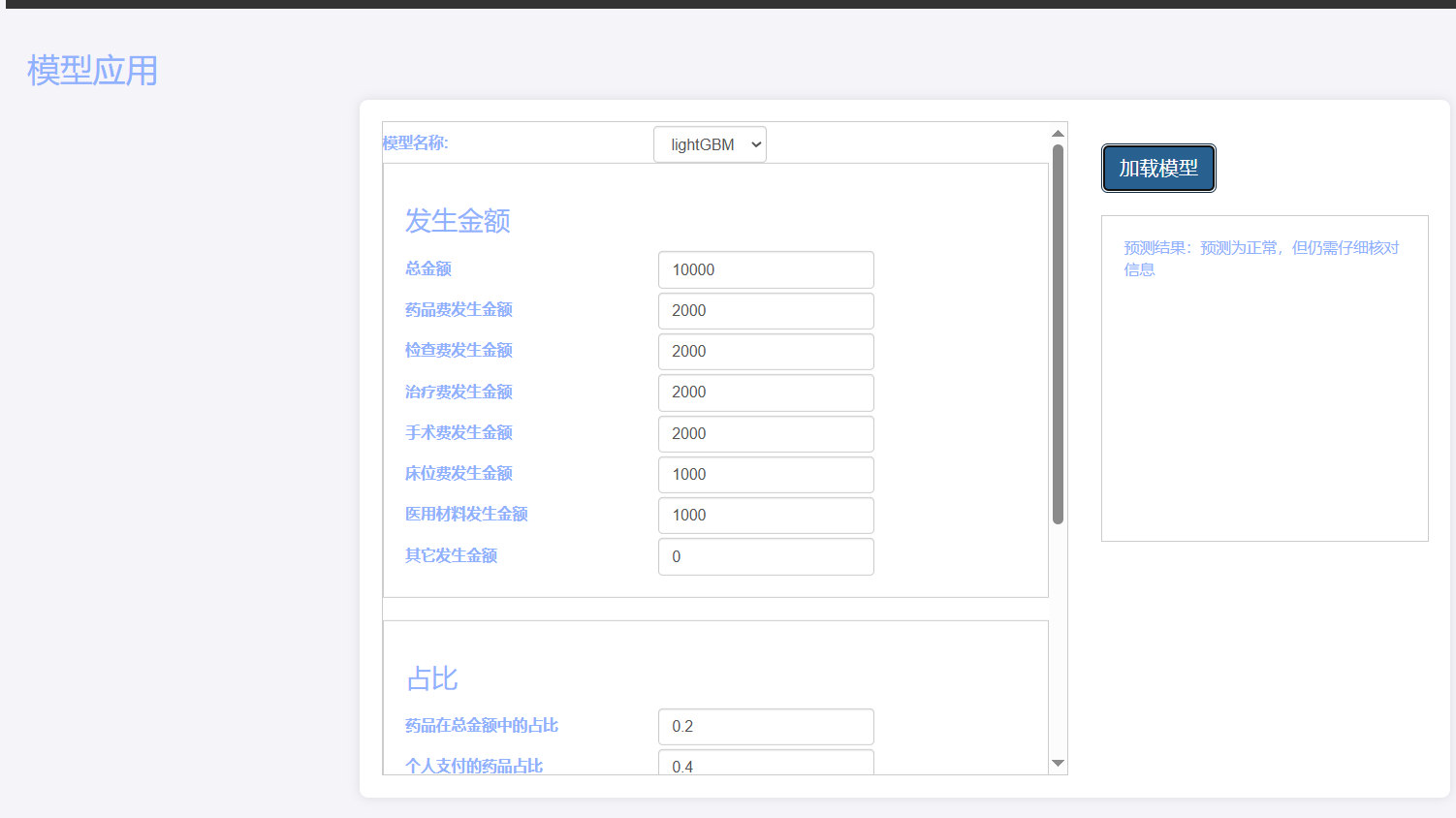
基于Flask实现的医疗保险欺诈识别监测模型
基于Flask实现的医疗保险欺诈识别监测模型 项目截图 项目简介 社会医疗保险是国家通过立法形式强制实施,由雇主和个人按一定比例缴纳保险费,建立社会医疗保险基金,支付雇员医疗费用的一种医疗保险制度, 它是促进社会文明和进步的…...

iPhone密码忘记了办?iPhoneUnlocker,iPhone解锁工具Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 高级注册版分享
平时用 iPhone 的时候,难免会碰到解锁的麻烦事。比如密码忘了、人脸识别 / 指纹识别突然不灵,或者买了二手 iPhone 却被原来的 iCloud 账号锁住,这时候就需要靠谱的解锁工具来帮忙了。Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 就是专门解决这些问题的软件&…...

spring:实例工厂方法获取bean
spring处理使用静态工厂方法获取bean实例,也可以通过实例工厂方法获取bean实例。 实例工厂方法步骤如下: 定义实例工厂类(Java代码),定义实例工厂(xml),定义调用实例工厂ÿ…...

Robots.txt 文件
什么是robots.txt? robots.txt 是一个位于网站根目录下的文本文件(如:https://example.com/robots.txt),它用于指导网络爬虫(如搜索引擎的蜘蛛程序)如何抓取该网站的内容。这个文件遵循 Robots…...

QT: `long long` 类型转换为 `QString` 2025.6.5
在 Qt 中,将 long long 类型转换为 QString 可以通过以下两种常用方法实现: 方法 1:使用 QString::number() 直接调用 QString 的静态方法 number(),将数值转换为字符串: long long value 1234567890123456789LL; …...
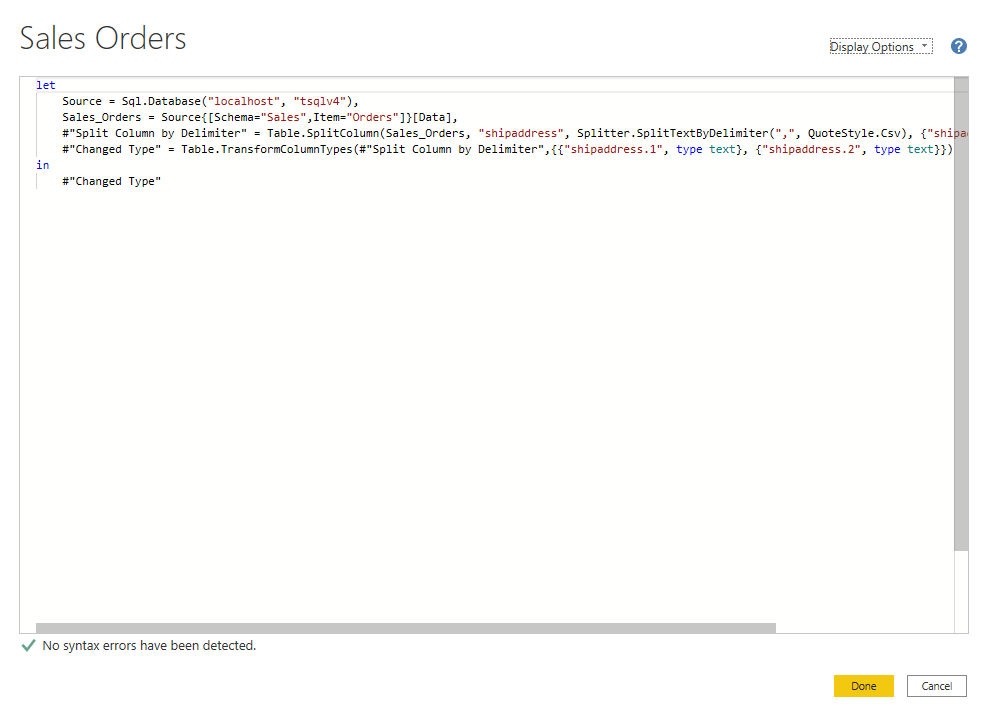
微软PowerBI考试 PL300-在 Power BI 中清理、转换和加载数据
微软PowerBI考试 PL300-在 Power BI 中清理、转换和加载数据 Power Query 具有大量专门帮助您清理和准备数据以供分析的功能。 您将了解如何简化复杂模型、更改数据类型、重命名对象和透视数据。 您还将了解如何分析列,以便知晓哪些列包含有价值的数据,…...
安装docker)
Linux离线(zip方式)安装docker
目录 基础信息操作系统信息docker信息 安装实例安装步骤示例 遇到的问题问题1:修改默认工作路径启动失败问题2 找不到对应组 基础信息 操作系统信息 OS版本:CentOS 7 64位 内核版本:3.10.0 相关命令: uname -rcat /etc/os-rele…...

【Linux】Linux 系统默认的目录及作用说明
博主介绍:✌全网粉丝23W,CSDN博客专家、Java领域优质创作者,掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java技术领域✌ 技术范围:SpringBoot、SpringCloud、Vue、SSM、HTML、Nodejs、Python、MySQL、PostgreSQL、大数据、物…...
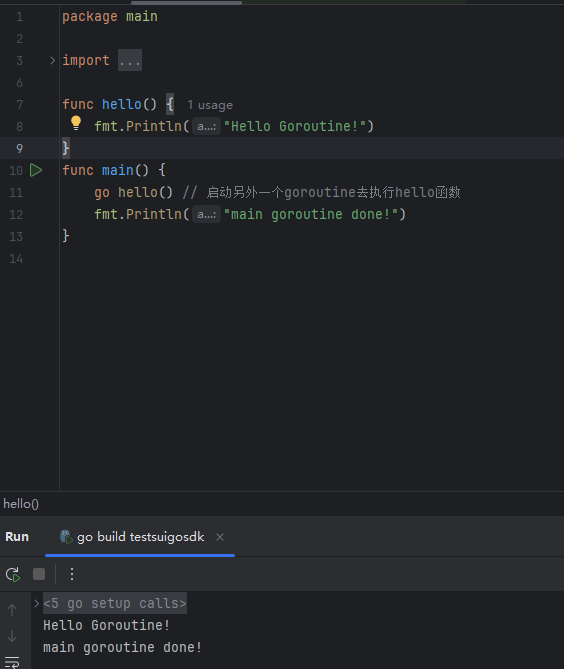
GO协程(Goroutine)问题总结
在使用Go语言来编写代码时,遇到的一些问题总结一下 [参考文档]:https://www.topgoer.com/%E5%B9%B6%E5%8F%91%E7%BC%96%E7%A8%8B/goroutine.html 1. main()函数默认的Goroutine 场景再现: 今天在看到这个教程的时候,在自己的电…...
