Rust vs Go:常用语法对比(七)

题图来自 Go vs Rust: Which will be the top pick in programming?[1]
121. UDP listen and read
Listen UDP traffic on port p and read 1024 bytes into buffer b.
听端口p上的UDP流量,并将1024字节读入缓冲区b。
import (
"fmt"
"net"
"os"
)
ServerAddr,err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp",p)
if err != nil {
return err
}
ServerConn, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", ServerAddr)
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer ServerConn.Close()
n,addr,err := ServerConn.ReadFromUDP(b[:1024])
if err != nil {
return err
}
if n<1024 {
return fmt.Errorf("Only %d bytes could be read.", n)
}
use std::net::UdpSocket;
let mut b = [0 as u8; 1024];
let sock = UdpSocket::bind(("localhost", p)).unwrap();
sock.recv_from(&mut b).unwrap();
122. Declare enumeration
Create an enumerated type Suit with 4 possible values SPADES, HEARTS, DIAMONDS, CLUBS.
声明枚举值
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type Suit int
const (
Spades Suit = iota
Hearts
Diamonds
Clubs
)
func main() {
fmt.Printf("Hearts has type %T and value %d", Hearts, Hearts)
}
Hearts has type main.Suit and value 1
enum Suit {
Spades,
Hearts,
Diamonds,
Clubs,
}
fn main() {
let _x = Suit::Diamonds;
}
123. Assert condition
Verify that predicate isConsistent returns true, otherwise report assertion violation. Explain if the assertion is executed even in production environment or not.
断言条件
package main
import "fmt"
//
// The code may look fine, but
// obviously we have a bug.
//
func main() {
salary = 65000
employees = 120000
totalPayroll = salary * employees
if !isConsistent() {
panic("State consistency violated")
}
fmt.Println("Everything fine")
}
var salary int32
var employees int32
var totalPayroll int32
func isConsistent() bool {
return salary >= 0 &&
employees >= 0 &&
totalPayroll >= 0
}
fn main() {
// i is odd
let i = 23687;
let ii = i * i;
let is_consistent = ii % 2 == 1;
// i*i must be odd
assert!(is_consistent);
println!("Cool.")
}
Cool.
124. Binary search for a value in sorted array
Write function binarySearch which returns the index of an element having value x in sorted array a, or -1 if no such element.
排序数组中值的二分搜索法
二分查找
package main
import "fmt"
func binarySearch(a []T, x T) int {
imin, imax := 0, len(a)-1
for imin <= imax {
imid := (imin + imax) / 2
switch {
case a[imid] == x:
return imid
case a[imid] < x:
imin = imid + 1
default:
imax = imid - 1
}
}
return -1
}
type T int
func main() {
a := []T{-2, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 6, 8, 8, 9, 10}
for x := T(-5); x <= 15; x++ {
i := binarySearch(a, x)
if i == -1 {
fmt.Println("Value", x, "not found")
} else {
fmt.Println("Value", x, "found at index", i)
}
}
}
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
func binarySearch(a []int, x int) int {
i := sort.SearchInts(a, x)
if i < len(a) && a[i] == x {
return i
}
return -1
}
func main() {
a := []int{-2, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 6, 8, 8, 9, 10}
for x := -5; x <= 15; x++ {
i := binarySearch(a, x)
if i == -1 {
fmt.Println("Value", x, "not found")
} else {
fmt.Println("Value", x, "found at index", i)
}
}
}
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
func binarySearch(a []T, x T) int {
f := func(i int) bool { return a[i] >= x }
i := sort.Search(len(a), f)
if i < len(a) && a[i] == x {
return i
}
return -1
}
type T int
func main() {
a := []T{-2, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 6, 8, 8, 9, 10}
for x := T(-5); x <= 15; x++ {
i := binarySearch(a, x)
if i == -1 {
fmt.Println("Value", x, "not found")
} else {
fmt.Println("Value", x, "found at index", i)
}
}
}
125. Measure function call duration
measure the duration t, in nano seconds, of a call to the function foo. Print this duration.
函数调用时间
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
t1 := time.Now()
foo()
t := time.Since(t1)
ns := int64(t / time.Nanosecond)
// Note that the clock is fixed in the Playground, so the resulting duration is always zero
fmt.Printf("%dns\n", ns)
}
func foo() {
fmt.Println("Hello")
}
Hello
0ns
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
t1 := time.Now()
foo()
t := time.Since(t1)
ns := t.Nanoseconds()
fmt.Printf("%dns\n", ns)
}
func foo() {
fmt.Println("Hello")
}
Hello
0ns
use std::time::{Duration, Instant};
let start = Instant::now();
foo();
let duration = start.elapsed();
println!("{}", duration);
126. Multiple return values
Write a function foo that returns a string and a boolean value.
多个返回值
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
s, b := foo()
fmt.Println(s, b)
}
func foo() (string, bool) {
return "Too good to be", true
}
Too good to be true
fn foo() -> (String, bool) {
(String::from("bar"), true)
}
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", foo());
}
("bar", true)
128. Breadth-first traversing of a tree
Call a function f on every node of a tree, in breadth-first prefix order
树的广度优先遍历
package main
import "fmt"
func (root *Tree) Bfs(f func(*Tree)) {
if root == nil {
return
}
queue := []*Tree{root}
for len(queue) > 0 {
t := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
f(t)
queue = append(queue, t.Children...)
}
}
type key string
type value string
type Tree struct {
Key key
Deco value
Children []*Tree
}
func (this *Tree) AddChild(x key, v value) {
child := &Tree{Key: x, Deco: v}
this.Children = append(this.Children, child)
}
func NodePrint(node *Tree) {
fmt.Printf("%v (%v)\n", node.Key, node.Deco)
}
func main() {
tree := &Tree{Key: "World", Deco: "Our planet"}
tree.AddChild("Europe", "A continent")
tree.Children[0].AddChild("Germany", "A country")
tree.Children[0].AddChild("Ireland", "A country")
tree.Children[0].AddChild("Mediterranean Sea", "A sea")
tree.AddChild("Asia", "A continent")
tree.Children[0].AddChild("Japan", "A country")
tree.Children[0].AddChild("Thailand", "A country")
tree.Bfs(NodePrint)
}
World (Our planet)
Europe (A continent)
Asia (A continent)
Germany (A country)
Ireland (A country)
Mediterranean Sea (A sea)
Japan (A country)
Thailand (A country)
use std::collections::VecDeque;
struct Tree<V> {
children: Vec<Tree<V>>,
value: V
}
impl<V> Tree<V> {
fn bfs(&self, f: impl Fn(&V)) {
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back(self);
while let Some(t) = q.pop_front() {
(f)(&t.value);
for child in &t.children {
q.push_back(child);
}
}
}
}
fn main() {
let t = Tree {
children: vec![
Tree {
children: vec![
Tree { children: vec![], value: 5 },
Tree { children: vec![], value: 6 }
],
value: 2
},
Tree { children: vec![], value: 3 },
Tree { children: vec![], value: 4 },
],
value: 1
};
t.bfs(|v| println!("{}", v));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
129. Breadth-first traversing in a graph
Call a function f on every vertex accessible from vertex start, in breadth-first prefix order
图的广度优先遍历
package main
import "fmt"
func (start *Vertex) Bfs(f func(*Vertex)) {
queue := []*Vertex{start}
seen := map[*Vertex]bool{start: true}
for len(queue) > 0 {
v := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
f(v)
for next, isEdge := range v.Neighbours {
if isEdge && !seen[next] {
queue = append(queue, next)
seen[next] = true
}
}
}
}
type Vertex struct {
Id int
Label string
Neighbours map[*Vertex]bool
}
type Graph []*Vertex
func NewVertex(id int, label string) *Vertex {
return &Vertex{
Id: id,
Label: label,
Neighbours: make(map[*Vertex]bool),
}
}
func (v *Vertex) AddNeighbour(w *Vertex) {
v.Neighbours[w] = true
}
func VertexPrint(v *Vertex) {
fmt.Printf("%v (%v)\n", v.Id, v.Label)
}
func main() {
// Some cities
london := NewVertex(0, "London")
ny := NewVertex(1, "New York City")
berlin := NewVertex(2, "Berlin")
paris := NewVertex(3, "Paris")
tokyo := NewVertex(4, "Tokyo")
g := Graph{
london,
ny,
berlin,
paris,
tokyo,
}
_ = g
london.AddNeighbour(paris)
london.AddNeighbour(ny)
ny.AddNeighbour(london)
ny.AddNeighbour(paris)
ny.AddNeighbour(tokyo)
tokyo.AddNeighbour(paris)
paris.AddNeighbour(tokyo)
paris.AddNeighbour(berlin)
london.Bfs(VertexPrint)
}
0 (London)
3 (Paris)
1 (New York City)
2 (Berlin)
4 (Tokyo)
use std::rc::{Rc, Weak};
use std::cell::RefCell;
struct Vertex<V> {
value: V,
neighbours: Vec<Weak<RefCell<Vertex<V>>>>,
}
type RcVertex<V> = Rc<RefCell<Vertex<V>>>;
struct Graph<V> {
vertices: Vec<RcVertex<V>>,
}
impl<V> Graph<V> {
fn new() -> Self {
Graph { vertices: vec![] }
}
fn new_vertex(&mut self, value: V) -> RcVertex<V> {
self.add_vertex(Vertex { value, neighbours: Vec::new() })
}
fn add_vertex(&mut self, v: Vertex<V>) -> RcVertex<V> {
let v = Rc::new(RefCell::new(v));
self.vertices.push(Rc::clone(&v));
v
}
fn add_edge(&mut self, v1: &RcVertex<V>, v2: &RcVertex<V>) {
v1.borrow_mut().neighbours.push(Rc::downgrade(&v2));
v2.borrow_mut().neighbours.push(Rc::downgrade(&v1));
}
fn bft(start: RcVertex<V>, f: impl Fn(&V)) {
let mut q = vec![start];
let mut i = 0;
while i < q.len() {
let v = Rc::clone(&q[i]);
i += 1;
(f)(&v.borrow().value);
for n in &v.borrow().neighbours {
let n = n.upgrade().expect("Invalid neighbour");
if q.iter().all(|v| v.as_ptr() != n.as_ptr()) {
q.push(n);
}
}
}
}
}
fn main() {
let mut g = Graph::new();
let v1 = g.new_vertex(1);
let v2 = g.new_vertex(2);
let v3 = g.new_vertex(3);
let v4 = g.new_vertex(4);
let v5 = g.new_vertex(5);
g.add_edge(&v1, &v2);
g.add_edge(&v1, &v3);
g.add_edge(&v1, &v4);
g.add_edge(&v2, &v5);
g.add_edge(&v3, &v4);
g.add_edge(&v4, &v5);
Graph::bft(v1, |v| println!("{}", v));
}
1
2
3
4
5
130. Depth-first traversing in a graph
Call a function f on every vertex accessible for vertex v, in depth-first prefix order
图的深度优先遍历
package main
import "fmt"
func (v *Vertex) Dfs(f func(*Vertex), seen map[*Vertex]bool) {
seen[v] = true
f(v)
for next, isEdge := range v.Neighbours {
if isEdge && !seen[next] {
next.Dfs(f, seen)
}
}
}
type Vertex struct {
Id int
Label string
Neighbours map[*Vertex]bool
}
type Graph []*Vertex
func NewVertex(id int, label string) *Vertex {
return &Vertex{
Id: id,
Label: label,
Neighbours: make(map[*Vertex]bool),
}
}
func (v *Vertex) AddNeighbour(w *Vertex) {
v.Neighbours[w] = true
}
func VertexPrint(v *Vertex) {
fmt.Printf("%v (%v)\n", v.Id, v.Label)
}
func main() {
// Some cities
london := NewVertex(0, "London")
ny := NewVertex(1, "New York City")
berlin := NewVertex(2, "Berlin")
paris := NewVertex(3, "Paris")
tokyo := NewVertex(4, "Tokyo")
g := Graph{
london,
ny,
berlin,
paris,
tokyo,
}
_ = g
london.AddNeighbour(paris)
london.AddNeighbour(ny)
ny.AddNeighbour(london)
ny.AddNeighbour(paris)
ny.AddNeighbour(tokyo)
tokyo.AddNeighbour(paris)
paris.AddNeighbour(tokyo)
paris.AddNeighbour(berlin)
alreadySeen := map[*Vertex]bool{}
london.Dfs(VertexPrint, alreadySeen)
}
0 (London)
3 (Paris)
4 (Tokyo)
2 (Berlin)
1 (New York City)
use std::rc::{Rc, Weak};
use std::cell::RefCell;
struct Vertex<V> {
value: V,
neighbours: Vec<Weak<RefCell<Vertex<V>>>>,
}
type RcVertex<V> = Rc<RefCell<Vertex<V>>>;
struct Graph<V> {
vertices: Vec<RcVertex<V>>,
}
impl<V> Graph<V> {
fn new() -> Self {
Graph { vertices: vec![] }
}
fn new_vertex(&mut self, value: V) -> RcVertex<V> {
self.add_vertex(Vertex { value, neighbours: Vec::new() })
}
fn add_vertex(&mut self, v: Vertex<V>) -> RcVertex<V> {
let v = Rc::new(RefCell::new(v));
self.vertices.push(Rc::clone(&v));
v
}
fn add_edge(&mut self, v1: &RcVertex<V>, v2: &RcVertex<V>) {
v1.borrow_mut().neighbours.push(Rc::downgrade(&v2));
v2.borrow_mut().neighbours.push(Rc::downgrade(&v1));
}
fn dft(start: RcVertex<V>, f: impl Fn(&V)) {
let mut s = vec![];
Self::dft_helper(start, &f, &mut s);
}
fn dft_helper(start: RcVertex<V>, f: &impl Fn(&V), s: &mut Vec<*const Vertex<V>>) {
s.push(start.as_ptr());
(f)(&start.borrow().value);
for n in &start.borrow().neighbours {
let n = n.upgrade().expect("Invalid neighbor");
if s.iter().all(|&p| p != n.as_ptr()) {
Self::dft_helper(n, f, s);
}
}
}
}
fn main() {
let mut g = Graph::new();
let v1 = g.new_vertex(1);
let v2 = g.new_vertex(2);
let v3 = g.new_vertex(3);
let v4 = g.new_vertex(4);
let v5 = g.new_vertex(5);
g.add_edge(&v1, &v2);
g.add_edge(&v1, &v4);
g.add_edge(&v1, &v5);
g.add_edge(&v2, &v3);
g.add_edge(&v3, &v4);
g.add_edge(&v4, &v5);
Graph::dft(v1, |v| println!("{}", v));
}
1
2
3
4
5
131. Successive conditions
Execute f1 if condition c1 is true, or else f2 if condition c2 is true, or else f3 if condition c3 is true. Don't evaluate a condition when a previous condition was true.
连续条件判等
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func conditional(x string) {
switch {
case c1(x):
f1()
case c2(x):
f2()
case c3(x):
f3()
}
}
func main() {
conditional("dog Snoopy")
conditional("fruit Raspberry")
}
func f1() {
fmt.Println("I'm a Human")
}
func f2() {
fmt.Println("I'm a Dog")
}
func f3() {
fmt.Println("I'm a Fruit")
}
var c1, c2, c3 = prefixCheck("human"), prefixCheck("dog"), prefixCheck("fruit")
func prefixCheck(prefix string) func(string) bool {
return func(x string) bool {
return strings.HasPrefix(x, prefix)
}
}
I'm a Dog
I'm a Fruit
if c1 { f1() } else if c2 { f2() } else if c3 { f3() }
or
match true {
_ if c1 => f1(),
_ if c2 => f2(),
_ if c3 => f3(),
_ => (),
}
132. Measure duration of procedure execution
Run procedure f, and return the duration of the execution of f.
度量程序执行时间
package main
import (
"fmt"
"regexp"
"strings"
"time"
)
func clock(f func()) time.Duration {
t := time.Now()
f()
return time.Since(t)
}
func f() {
re := regexp.MustCompilePOSIX("|A+{300}")
re.FindAllString(strings.Repeat("A", 299), -1)
}
func main() {
d := clock(f)
// The result is always zero in the playground, which has a fixed clock!
// Try it on your workstation instead.
fmt.Println(d)
}
0s
use std::time::Instant;
let start = Instant::now();
f();
let duration = start.elapsed();
133. Case-insensitive string contains
Set boolean ok to true if string word is contained in string s as a substring, even if the case doesn't match, or to false otherwise.
不区分大小写的字符串包含
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
// Package _strings has no case-insensitive version of _Contains, so
// we have to make our own.
func containsCaseInsensitive(s, word string) bool {
lowerS, lowerWord := strings.ToLower(s), strings.ToLower(word)
ok := strings.Contains(lowerS, lowerWord)
return ok
}
func main() {
s := "Let's dance the macarena"
word := "Dance"
ok := containsCaseInsensitive(s, word)
fmt.Println(ok)
word = "dance"
ok = containsCaseInsensitive(s, word)
fmt.Println(ok)
word = "Duck"
ok = containsCaseInsensitive(s, word)
fmt.Println(ok)
}
true
true
false
extern crate regex;
use regex::Regex;
fn main() {
let s = "Let's dance the macarena";
{
let word = "Dance";
let re = Regex::new(&format!("(?i){}", regex::escape(word))).unwrap();
let ok = re.is_match(&s);
println!("{}", ok);
}
{
let word = "dance";
let re = Regex::new(&format!("(?i){}", regex::escape(word))).unwrap();
let ok = re.is_match(&s);
println!("{}", ok);
}
{
let word = "Duck";
let re = Regex::new(&format!("(?i){}", regex::escape(word))).unwrap();
let ok = re.is_match(&s);
println!("{}", ok);
}
}
true
true
false
or
use regex::RegexBuilder;
fn main() {
let s = "FooBar";
let word = "foo";
let re = RegexBuilder::new(®ex::escape(word))
.case_insensitive(true)
.build()
.unwrap();
let ok = re.is_match(s);
println!("{:?}", ok);
}
true
or
fn main() {
let s = "Let's dance the macarena";
{
let word = "Dance";
let ok = s.to_ascii_lowercase().contains(&word.to_ascii_lowercase());
println!("{}", ok);
}
{
let word = "dance";
let ok = s.to_ascii_lowercase().contains(&word.to_ascii_lowercase());
println!("{}", ok);
}
{
let word = "Duck";
let ok = s.to_ascii_lowercase().contains(&word.to_ascii_lowercase());
println!("{}", ok);
}
}
true
true
false
134. Create a new list
创建一个新list
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
var a, b, c T = "This", "is", "wonderful"
items := []T{a, b, c}
fmt.Println(items)
}
type T string
[This is wonderful]
fn main() {
let (a, b, c) = (11, 22, 33);
let items = vec![a, b, c];
println!("{:?}", items);
}
[11, 22, 33]
135. Remove item from list, by its value
Remove at most 1 item from list items, having value x. This will alter the original list or return a new list, depending on which is more idiomatic. If there are several occurrences of x in items, remove only one of them. If x is absent, keep items unchanged.
移除列表中的值
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
items := []string{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"}
fmt.Println(items)
x := "c"
for i, y := range items {
if y == x {
items = append(items[:i], items[i+1:]...)
break
}
}
fmt.Println(items)
}
[a b c d e f]
[a b d e f]
or
for i, y := range items {
if y == x {
copy(items[i:], items[i+1:])
items[len(items)-1] = nil
items = items[:len(items)-1]
break
}
}
if let Some(i) = items.first(&x) {
items.remove(i);
}
136. Remove all occurrences of a value from a list
Remove all occurrences of value x from list items. This will alter the original list or return a new list, depending on which is more idiomatic.
从列表中删除所有出现的值
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
items := []T{"b", "a", "b", "a", "r"}
fmt.Println(items)
var x T = "b"
items2 := make([]T, 0, len(items))
for _, v := range items {
if v != x {
items2 = append(items2, v)
}
}
fmt.Println(items2)
}
type T string
[b a b a r]
[a a r]
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
items := []T{"b", "a", "b", "a", "r"}
fmt.Println(items)
x := T("b")
j := 0
for i, v := range items {
if v != x {
items[j] = items[i]
j++
}
}
items = items[:j]
fmt.Println(items)
}
type T string
[b a b a r]
[a a r]
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"runtime"
)
func main() {
var items []*image
{
red := newUniform(rgb{0xFF, 0, 0})
white := newUniform(rgb{0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF})
items = []*image{red, white, red} // Like the flag of Austria
fmt.Println("items =", items)
x := red
j := 0
for i, v := range items {
if v != x {
items[j] = items[i]
j++
}
}
for k := j; k < len(items); k++ {
items[k] = nil
}
items = items[:j]
}
// At this point, red can be garbage collected
printAllocInfo()
fmt.Println("items =", items) // Not the original flag anymore...
fmt.Println("items undelying =", items[:3])
}
type image [1024][1024]rgb
type rgb [3]byte
func newUniform(color rgb) *image {
im := new(image)
for x := range im {
for y := range im[x] {
im[x][y] = color
}
}
return im
}
func printAllocInfo() {
var stats runtime.MemStats
runtime.GC()
runtime.ReadMemStats(&stats)
fmt.Println("Bytes allocated (total):", stats.TotalAlloc)
fmt.Println("Bytes still allocated: ", stats.Alloc)
}
items = [0xc000180000 0xc000480000 0xc000180000]
Bytes allocated (total): 6416688
Bytes still allocated: 3259024
items = [0xc000480000]
items undelying = [0xc000480000 <nil> <nil>]
fn main() {
let x = 1;
let mut items = vec![1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3];
items = items.into_iter().filter(|&item| item != x).collect();
println!("{:?}", items);
}
[2, 3, 2, 3]
137. Check if string contains only digits
Set boolean b to true if string s contains only characters in range '0'..'9', false otherwise.
检查字符串是否只包含数字
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
for _, s := range []string{
"123",
"",
"abc123def",
"abc",
"123.456",
"123 456",
} {
b := true
for _, c := range s {
if c < '0' || c > '9' {
b = false
break
}
}
fmt.Println(s, "=>", b)
}
}
123 => true
=> true
abc123def => false
abc => false
123.456 => false
123 456 => false
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
for _, s := range []string{
"123",
"",
"abc123def",
"abc",
"123.456",
"123 456",
} {
isNotDigit := func(c rune) bool { return c < '0' || c > '9' }
b := strings.IndexFunc(s, isNotDigit) == -1
fmt.Println(s, "=>", b)
}
}
123 => true
=> true
abc123def => false
abc => false
123.456 => false
123 456 => false
fn main() {
let s = "1023";
let chars_are_numeric: Vec<bool> = s.chars().map(|c|c.is_numeric()).collect();
let b = !chars_are_numeric.contains(&false);
println!("{}", b);
}
true
or
fn main() {
let b = "0129".chars().all(char::is_numeric);
println!("{}", b);
}
true
138. Create temp file
Create a new temporary file on filesystem.
创建一个新的临时文件
package main
import (
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
content := []byte("Big bag of misc data")
log.Println("Opening new temp file")
tmpfile, err := ioutil.TempFile("", "example")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
tmpfilename := tmpfile.Name()
defer os.Remove(tmpfilename) // clean up
log.Println("Opened new file", tmpfilename)
log.Println("Writing [[", string(content), "]]")
if _, err := tmpfile.Write(content); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err := tmpfile.Close(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
log.Println("Closed", tmpfilename)
log.Println("Opening", tmpfilename)
buffer, err := ioutil.ReadFile(tmpfilename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
log.Println("Read[[", string(buffer), "]]")
}
2009/11/10 23:00:00 Opening new temp file
2009/11/10 23:00:00 Opened new file /tmp/example067319278
2009/11/10 23:00:00 Writing [[ Big bag of misc data ]]
2009/11/10 23:00:00 Closed /tmp/example067319278
2009/11/10 23:00:00 Opening /tmp/example067319278
2009/11/10 23:00:00 Read[[ Big bag of misc data ]]
use tempdir::TempDir;
use std::fs::File;
let temp_dir = TempDir::new("prefix")?;
let temp_file = File::open(temp_dir.path().join("file_name"))?;
139. Create temp directory
Create a new temporary folder on filesystem, for writing.
创建一个临时目录
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"os"
"path/filepath"
)
func main() {
content := []byte("temporary file's content")
dir, err := ioutil.TempDir("", "")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer os.RemoveAll(dir) // clean up
inspect(dir)
tmpfn := filepath.Join(dir, "tmpfile")
err = ioutil.WriteFile(tmpfn, content, 0666)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
inspect(dir)
}
func inspect(dirpath string) {
files, err := ioutil.ReadDir(dirpath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(dirpath, "contains", len(files), "files")
}
/tmp/067319278 contains 0 files
/tmp/067319278 contains 1 files
extern crate tempdir;
use tempdir::TempDir;
let tmp = TempDir::new("prefix")?;
140. Delete map entry
从map中删除某个key
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
m := map[string]int{
"uno": 1,
"dos": 2,
"tres": 3,
}
delete(m, "dos")
delete(m, "cinco")
fmt.Println(m)
}
map[tres:3 uno:1]
fn main() {
use std::collections::HashMap;
let mut m = HashMap::new();
m.insert(5, "a");
m.insert(17, "b");
println!("{:?}", m);
m.remove(&5);
println!("{:?}", m);
}
{17: "b", 5: "a"}
{17: "b"}
参考资料
Go vs Rust: Which will be the top pick in programming?: https://www.appventurez.com/blog/go-vs-rust
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布
相关文章:

Rust vs Go:常用语法对比(七)
题图来自 Go vs Rust: Which will be the top pick in programming?[1] 121. UDP listen and read Listen UDP traffic on port p and read 1024 bytes into buffer b. 听端口p上的UDP流量,并将1024字节读入缓冲区b。 import ( "fmt" "net&qu…...
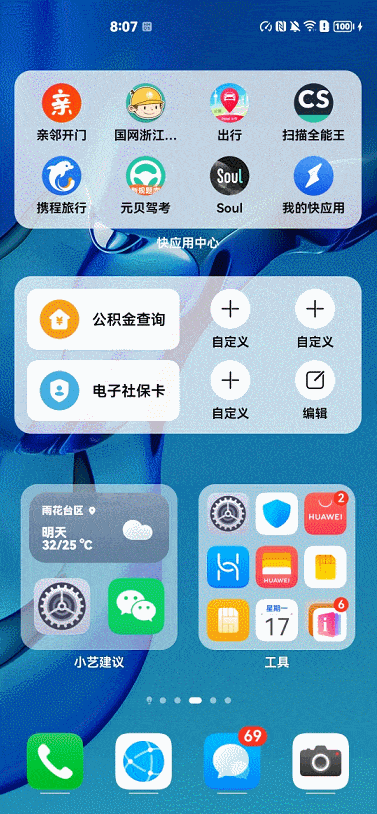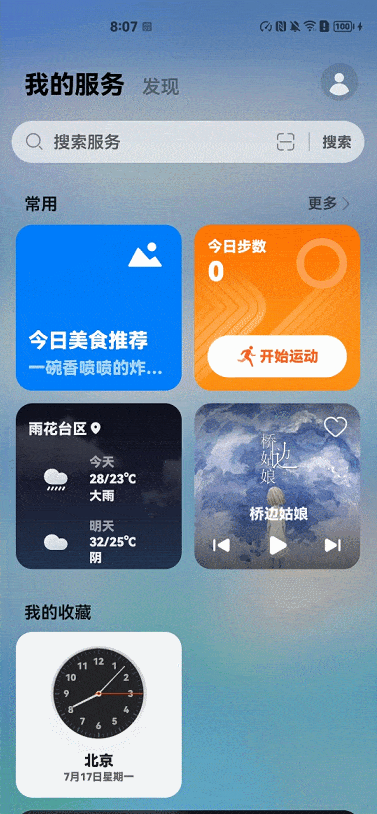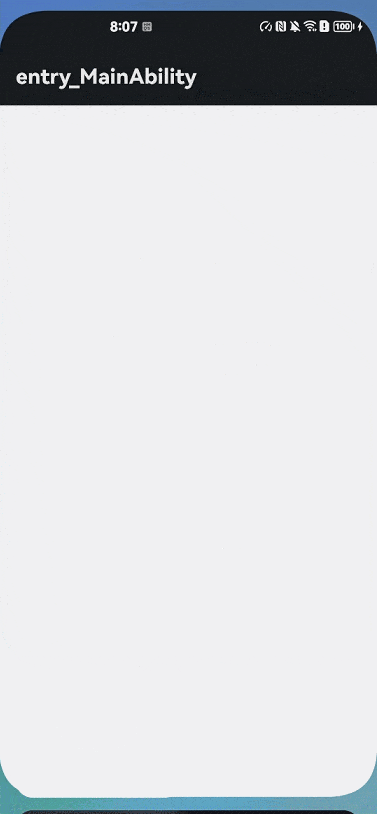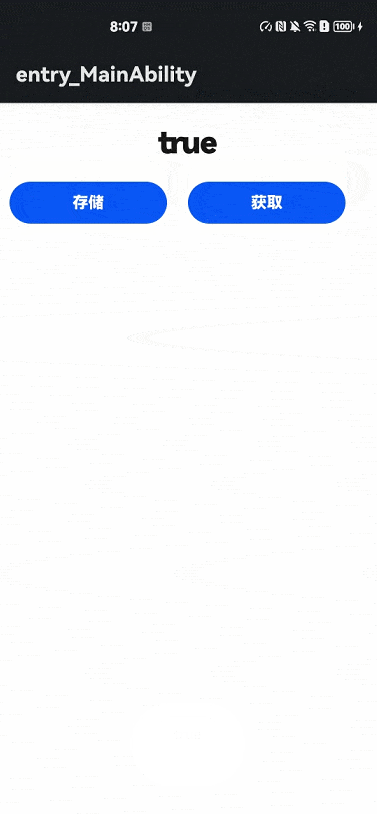
【HarmonyOS】API6使用storage实现轻量级数据存储
写在前面 本篇内容基于API6 JS语言进行开发,通过结合轻量级数据存储开发指导的文档,帮助大家完成一个实际的代码案例,通过这个小案例,可以实现简单数据的存储。 参考文档:文档中心 1、页面布局 首先我们编写一个简单…...
Python Flask构建微信小程序订餐系统 (十二)
🔥 创建切换商品分类状态的JS文件 🔥 ; var food_act_ops={init:function(){this.eventBind();},eventBind:function(){//表示作用域var that = this;$(".wrap_search select[name=status]").change(function(){$(".wrap_search").submit();});$(&qu…...

C++——模板的作用2:特例化
目录 模板的形式: 一.模板的多参数应用: 例: 错误使用1:使用不标准的模板形参表 编辑 错误使用2:使用变量作为实参传递给函数模板 二.模板的特例化: 类模板: 针对模板的特化步骤&am…...
Python Web开发技巧VII
目录 装饰器inject_serializer 装饰器atomic rebase git 清理add的数据 查看git的当前工作目录 makemigrations文件名称 action(detailTrue, methods["GET"]) 如何只取序列化器的一个字段进行返回 Response和JsonResponse有什么区别 序列化器填表和单字段如…...

LaTex4【下载模板、引入文献】
下载latex模板:(模板官网一般都有,去找) 我这随便找了一个: 下载得到一个压缩包,然后用overleaf打开👇: (然后改里面的内容就好啦) 另外,有很多在线的数学公式编辑器&am…...
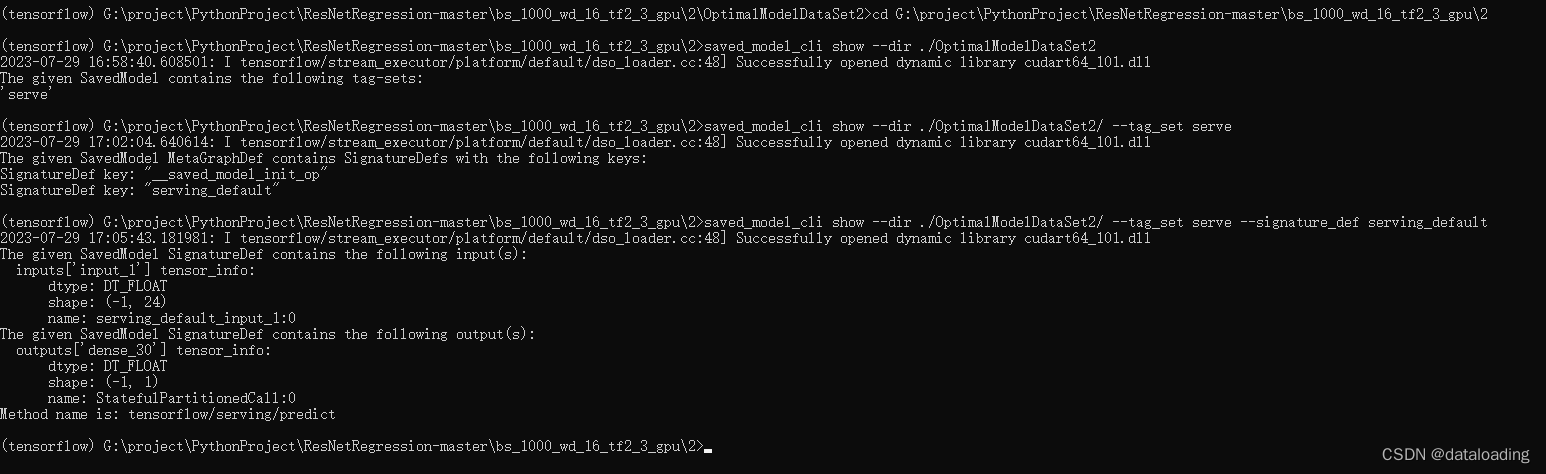
【VSCode部署模型】导出TensorFlow2.X训练好的模型信息
参考tensorflow2.0 C加载python训练保存的pb模型 经过模型训练及保存,我们得到“OptimalModelDataSet2”文件夹,模型的保存方法(.h5或.pb文件),参考【Visual Studio Code】c/c部署tensorflow训练的模型 其中“OptimalModelDataSet2”文件夹保…...
windows环境下,安装elasticsearch
目录 前言准备安装 jdk 安装nodejsElasticSearch下载ElasticSearch-head 下载 安装ElasticSearch安装ElasticSearch-head插件设置用户名密码访问ElasticSearch 默认用户名和密码参考 前言 win10elasticsearch 8.9.0 准备 安装 jdk ElasticSearch 是基于lucence开发的&#…...
)
Elasticsearch入门笔记(一)
环境搭建 Elasticsearch是搜索引擎,是常见的搜索工具之一。 Kibana 是一个开源的分析和可视化平台,旨在与 Elasticsearch 合作。Kibana 提供搜索、查看和与存储在 Elasticsearch 索引中的数据进行交互的功能。开发者或运维人员可以轻松地执行高级数据分析…...
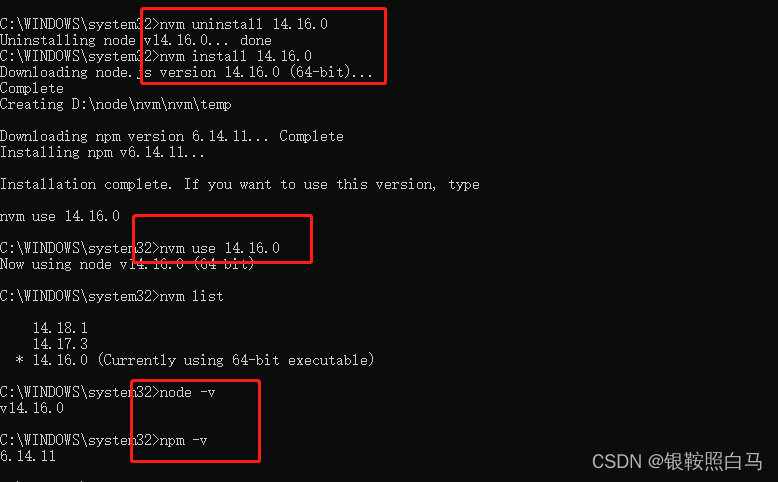
记一次安装nvm切换node.js版本实例详解
最后效果如下: 背景:由于我以前安装过node.js,后续想安装nvm将node.js管理起来。 问题:nvm-use命令行运行成功,但是nvm-list显示并没有成功。 原因:因为安装过node.js,所以原先的node.js不收n…...

生态共建丨YashanDB与构力科技完成兼容互认证
近日,深圳计算科学研究院崖山数据库系统YashanDB V22.2与北京构力科技有限公司BIMBase云平台完成兼容性互认证。经严格测试,双方产品完全兼容、运行稳定。 崖山数据库系统YashanDB是深算院自主研发设计的新型数据库系统,融入原创理论…...

React从入门到实战-react脚手架,消息订阅与发布
创建项目并启动 全局安装 npm install -g create-react-app切换到想创建项目的目录,使用命令:create-react-app 项目名称 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存中…(iQ6hEUgAABpQAAAD1CAYAAABeIRZoAAAAAXNSR0IArs4c6QAAIABJREFUe…...
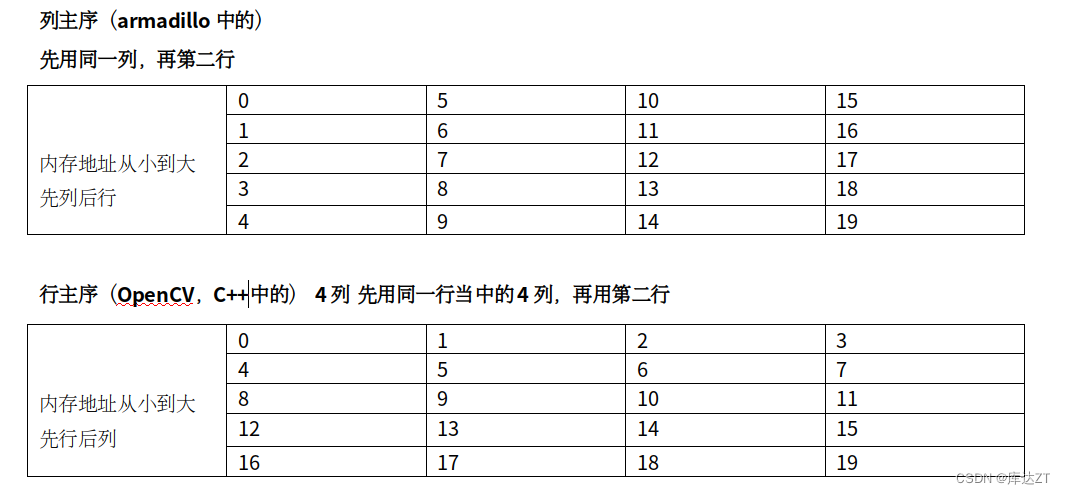
从零构建深度学习推理框架-1 简介和Tensor
源代码作者:https://github.com/zjhellofss 本文仅作为个人学习心得领悟 ,将原作品提炼,更加适合新手 什么是推理框架? 深度学习推理框架用于对已训练完成的神经网络进行预测,也就是说,能够将深度训练框…...

使用WGCLOUD监测安卓(Android)设备的运行状态
WGCLOUD是一款开源运维监控软件,除了能监控各种服务器、主机、进程应用、端口、接口、docker容器、日志、数据等资源 WGCLOUD还可以监测安卓设备,比如安卓手机、安卓设备等 我们只要下载对应的安卓客户端,部署运行即可,如下是下…...
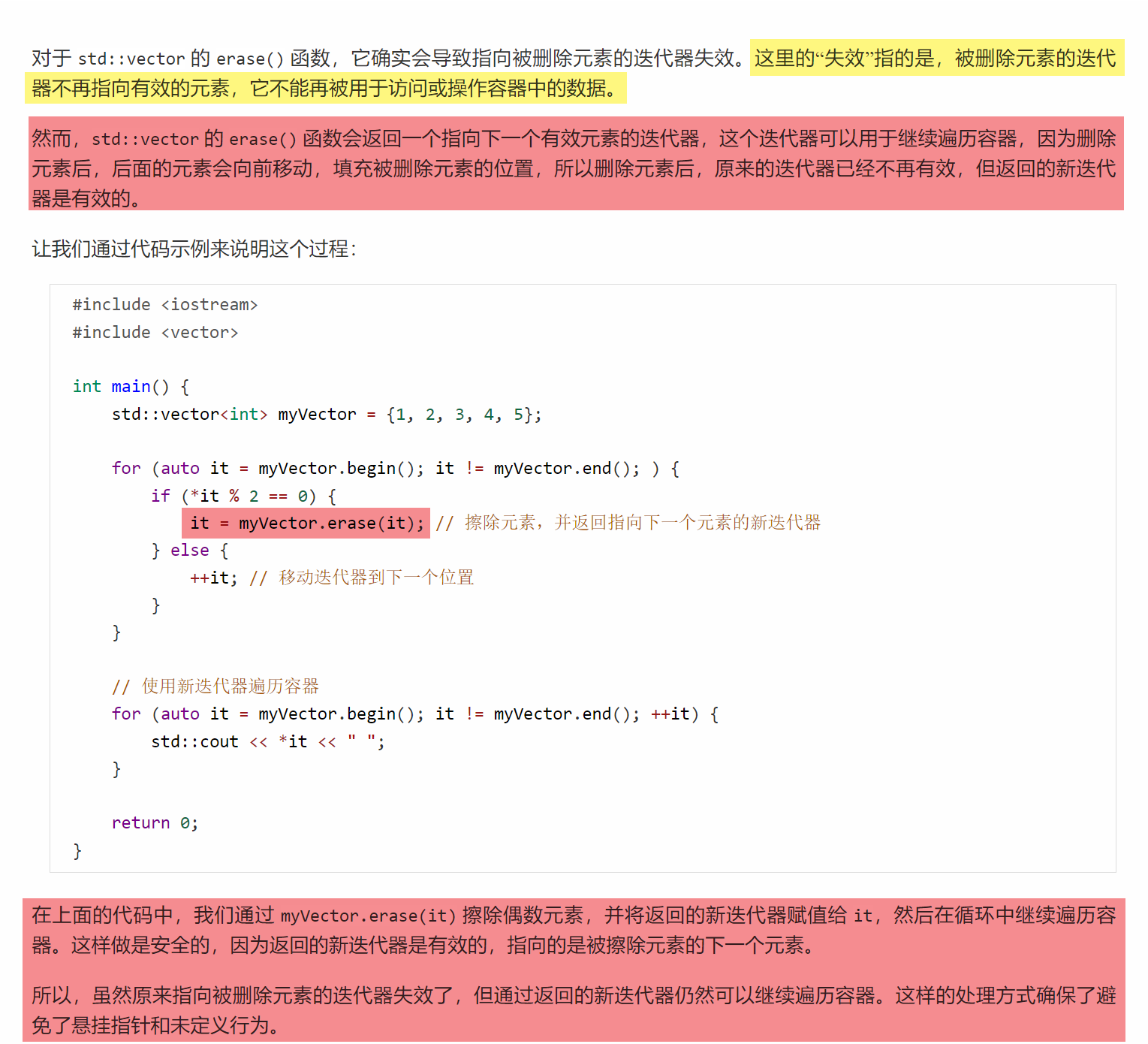
C++笔记之迭代器失效问题处理
C笔记之迭代器失效问题处理 code review! 参考博文:CSTL迭代器失效的几种情况总结 文章目录 C笔记之迭代器失效问题处理一.使用返回新迭代器的插入和删除操作二.对std::vector 来说,擦除(erase)元素会导致迭代器失效 一.使用返回…...

Tomcat的startup.bat文件出现闪退问题
对于双击Tomcat的startup.bat文件出现闪退问题,您提供的分析是正确的。主要原因是Tomcat需要Java Development Kit (JDK)的支持,而如果没有正确配置JAVA_HOME环境变量,Tomcat将无法找到JDK并启动,从而导致闪退。 以下是解决该问题…...

JAVA8-lambda表达式8:在设计模式-模板方法中的应用
传送门 JAVA8-lambda表达式1:什么是lambda表达式 JAVA8-lambda表达式2:常用的集合类api JAVA8-lambda表达式3:并行流,提升效率的利器? JAVA8-lambda表达式4:Optional用法 java8-lambda表达式5…...

React之组件间通信
React之组件间通信 组件通信: 简单讲就是组件之间的传值,包括state、函数等 1、父子组件通信 父组件给子组件传值 核心:1、自定义属性;2、props 父组件中: 自定义属性传值 import Header from /components/Headerconst Home ()…...
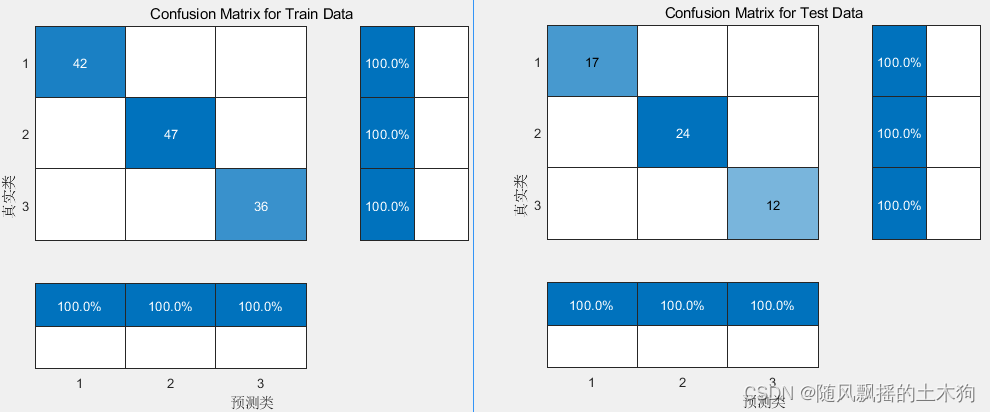
【MATLAB第58期】基于MATLAB的PCA-Kmeans、PCA-LVQ与BP神经网络分类预测模型对比
【MATLAB第58期】基于MATLAB的PCA-Kmeans、PCA-LVQ与BP神经网络分类预测模型对比 一、数据介绍 基于UCI葡萄酒数据集进行葡萄酒分类及产地预测 共包含178组样本数据,来源于三个葡萄酒产地,每组数据包含产地标签及13种化学元素含量,即已知类…...
CF1833 A-E
A题 题目链接:https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1833/A 基本思路:for循环遍历字符串s,依次截取字符串s的子串str,并保存到集合中,最后输出集合内元素的数目即可 AC代码: #include <iostrea…...
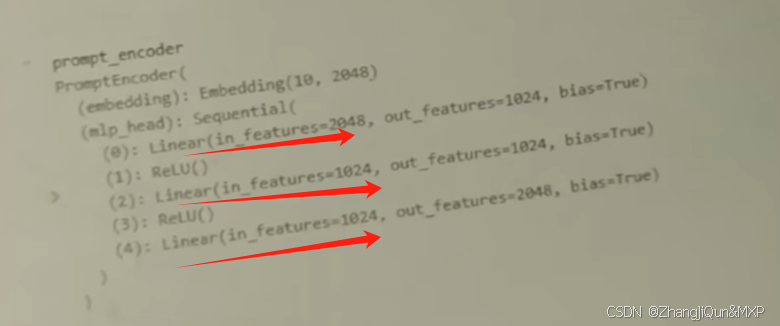
Prompt Tuning、P-Tuning、Prefix Tuning的区别
一、Prompt Tuning、P-Tuning、Prefix Tuning的区别 1. Prompt Tuning(提示调优) 核心思想:固定预训练模型参数,仅学习额外的连续提示向量(通常是嵌入层的一部分)。实现方式:在输入文本前添加可训练的连续向量(软提示),模型只更新这些提示参数。优势:参数量少(仅提…...
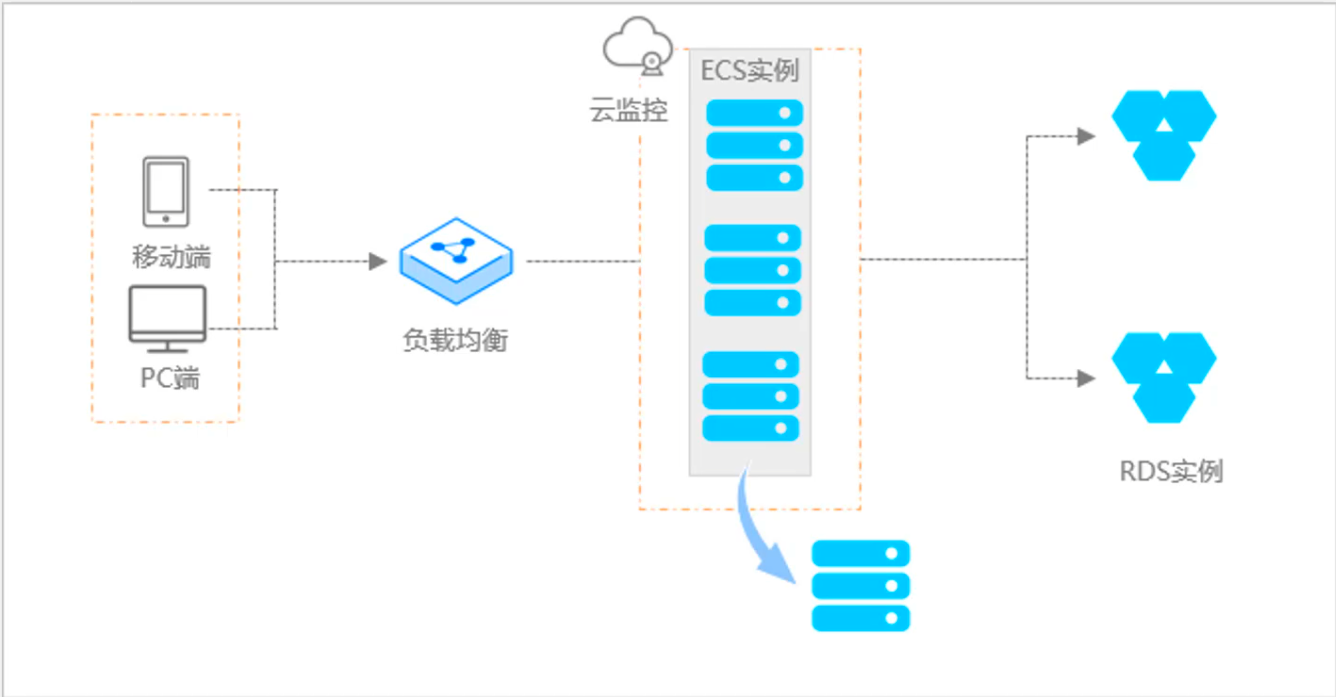
阿里云ACP云计算备考笔记 (5)——弹性伸缩
目录 第一章 概述 第二章 弹性伸缩简介 1、弹性伸缩 2、垂直伸缩 3、优势 4、应用场景 ① 无规律的业务量波动 ② 有规律的业务量波动 ③ 无明显业务量波动 ④ 混合型业务 ⑤ 消息通知 ⑥ 生命周期挂钩 ⑦ 自定义方式 ⑧ 滚的升级 5、使用限制 第三章 主要定义 …...
)
【位运算】消失的两个数字(hard)
消失的两个数字(hard) 题⽬描述:解法(位运算):Java 算法代码:更简便代码 题⽬链接:⾯试题 17.19. 消失的两个数字 题⽬描述: 给定⼀个数组,包含从 1 到 N 所有…...

Linux简单的操作
ls ls 查看当前目录 ll 查看详细内容 ls -a 查看所有的内容 ls --help 查看方法文档 pwd pwd 查看当前路径 cd cd 转路径 cd .. 转上一级路径 cd 名 转换路径 …...

基于Docker Compose部署Java微服务项目
一. 创建根项目 根项目(父项目)主要用于依赖管理 一些需要注意的点: 打包方式需要为 pom<modules>里需要注册子模块不要引入maven的打包插件,否则打包时会出问题 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8…...
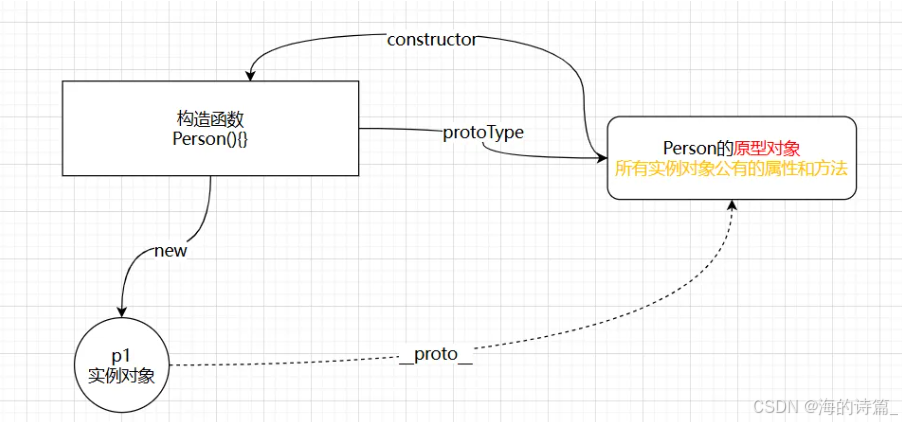
前端开发面试题总结-JavaScript篇(一)
文章目录 JavaScript高频问答一、作用域与闭包1.什么是闭包(Closure)?闭包有什么应用场景和潜在问题?2.解释 JavaScript 的作用域链(Scope Chain) 二、原型与继承3.原型链是什么?如何实现继承&a…...
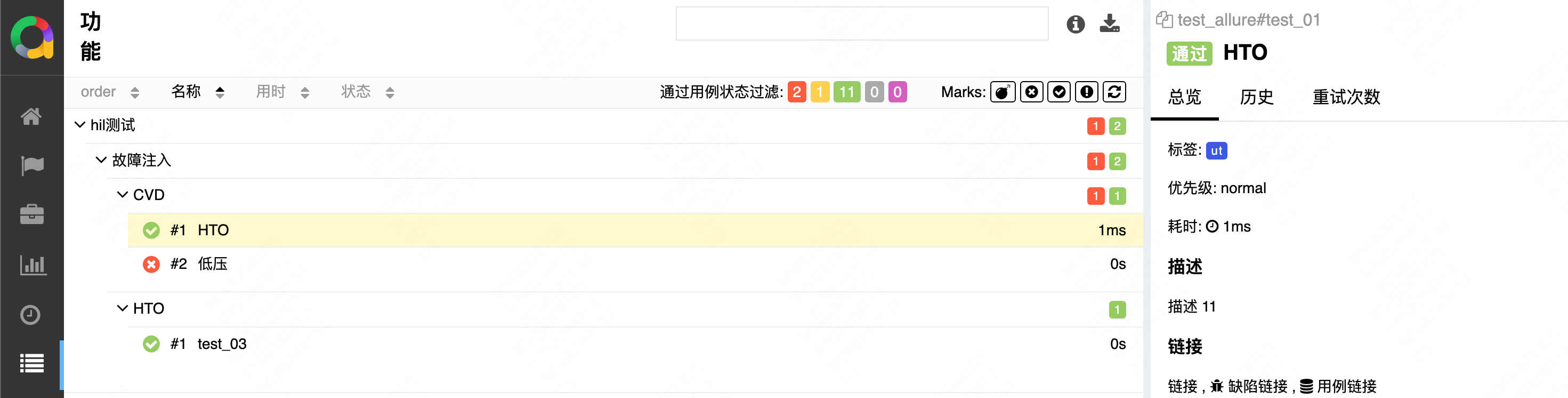
初学 pytest 记录
安装 pip install pytest用例可以是函数也可以是类中的方法 def test_func():print()class TestAdd: # def __init__(self): 在 pytest 中不可以使用__init__方法 # self.cc 12345 pytest.mark.api def test_str(self):res add(1, 2)assert res 12def test_int(self):r…...
并发编程 - go版
1.并发编程基础概念 进程和线程 A. 进程是程序在操作系统中的一次执行过程,系统进行资源分配和调度的一个独立单位。B. 线程是进程的一个执行实体,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,它是比进程更小的能独立运行的基本单位。C.一个进程可以创建和撤销多个线程;同一个进程中…...
[ACTF2020 新生赛]Include 1(php://filter伪协议)
题目 做法 启动靶机,点进去 点进去 查看URL,有 ?fileflag.php说明存在文件包含,原理是php://filter 协议 当它与包含函数结合时,php://filter流会被当作php文件执行。 用php://filter加编码,能让PHP把文件内容…...
Chromium 136 编译指南 Windows篇:depot_tools 配置与源码获取(二)
引言 工欲善其事,必先利其器。在完成了 Visual Studio 2022 和 Windows SDK 的安装后,我们即将接触到 Chromium 开发生态中最核心的工具——depot_tools。这个由 Google 精心打造的工具集,就像是连接开发者与 Chromium 庞大代码库的智能桥梁…...
