29.利用fminbnd 求解 最大容积问题(matlab程序)
1.简述
用于求某个给定函数的最小值点。
使用方法是:
x=fminbnd(func,x1,x2)
func是函数句柄,然后x1和x2就是函数的区间,得到的结果就是使func取最小值的x值
当然也可以使用[x,fv]=fminbnd(func,x1,x2)的方式,这个时候fv就是函数 的最小值,即有:fv=f(x)
测试程序如下:
>> f=@(x) exp(x)-4*sin(x)+5;
>> [x,fv]=fminbnd(f,0,1)
x =
0.9048
fv =
4.3262
当然,如果在某个区间上是单调的,结果就有点意思了:
>> clear
>> f=@(x) x^-2*x-3;
>> [x,fv]=fminbnd(f,2,3)
x =
2.9999
fv =
-2.6667
看样子MATLAB是使用了定长小区间的方式计算的,而且结果也是错误的,这不免让人对这个函数的可靠性产生怀疑……
2.代码
主程序:
%% 最大容积问题
[xo,fo]=fminbnd('f1216',0,2)
子程序:
function [xf,fval,exitflag,output] = fminbnd(funfcn,ax,bx,options,varargin)
%FMINBND Single-variable bounded nonlinear function minimization.
% X = FMINBND(FUN,x1,x2) attempts to find a local minimizer X of the function
% FUN in the interval x1 < X < x2. FUN is a function handle. FUN accepts
% scalar input X and returns a scalar function value F evaluated at X.
%
% X = FMINBND(FUN,x1,x2,OPTIONS) minimizes with the default optimization
% parameters replaced by values in the structure OPTIONS, created with
% the OPTIMSET function. See OPTIMSET for details. FMINBND uses these
% options: Display, TolX, MaxFunEval, MaxIter, FunValCheck, PlotFcns,
% and OutputFcn.
%
% X = FMINBND(PROBLEM) finds the minimum for PROBLEM. PROBLEM is a
% structure with the function FUN in PROBLEM.objective, the interval
% in PROBLEM.x1 and PROBLEM.x2, the options structure in PROBLEM.options,
% and solver name 'fminbnd' in PROBLEM.solver.
%
% [X,FVAL] = FMINBND(...) also returns the value of the objective function,
% FVAL, computed in FUN, at X.
%
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG] = FMINBND(...) also returns an EXITFLAG that
% describes the exit condition. Possible values of EXITFLAG and the
% corresponding exit conditions are
%
% 1 FMINBND converged with a solution X based on OPTIONS.TolX.
% 0 Maximum number of function evaluations or iterations reached.
% -1 Algorithm terminated by the output function.
% -2 Bounds are inconsistent (that is, ax > bx).
%
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT] = FMINBND(...) also returns a structure
% OUTPUT with the number of iterations taken in OUTPUT.iterations, the
% number of function evaluations in OUTPUT.funcCount, the algorithm name
% in OUTPUT.algorithm, and the exit message in OUTPUT.message.
%
% Examples
% FUN can be specified using @:
% X = fminbnd(@cos,3,4)
% computes pi to a few decimal places and gives a message upon termination.
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG] = fminbnd(@cos,3,4,optimset('TolX',1e-12,'Display','off'))
% computes pi to about 12 decimal places, suppresses output, returns the
% function value at x, and returns an EXITFLAG of 1.
%
% FUN can be an anonymous function:
% X = fminbnd(@(x) sin(x)+3,2,5)
%
% FUN can be a parameterized function. Use an anonymous function to
% capture the problem-dependent parameters:
% f = @(x,c) (x-c).^2; % The parameterized function.
% c = 1.5; % The parameter.
% X = fminbnd(@(x) f(x,c),0,1)
%
% See also OPTIMSET, FMINSEARCH, FZERO, FUNCTION_HANDLE.
% References:
% "Algorithms for Minimization Without Derivatives",
% R. P. Brent, Prentice-Hall, 1973, Dover, 2002.
%
% "Computer Methods for Mathematical Computations",
% Forsythe, Malcolm, and Moler, Prentice-Hall, 1976.
% Original coding by Duane Hanselman, University of Maine.
% Copyright 1984-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
% Set default options
defaultopt = struct( ...
'Display','notify', ...
'FunValCheck','off', ...
'MaxFunEvals',500, ...
'MaxIter',500, ...
'OutputFcn',[], ...
'PlotFcns',[], ...
'TolX',1e-4);
% If just 'defaults' passed in, return the default options in X
if nargin==1 && nargout <= 1 && strcmpi(funfcn,'defaults')
xf = defaultopt;
return
end
% initialization
if nargin<4
options = [];
end
% Detect problem structure input
problemInput = false;
if nargin == 1
if isa(funfcn,'struct')
problemInput = true;
[funfcn,ax,bx,options] = separateOptimStruct(funfcn);
else % Single input and non-structure.
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:InputArg',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:InputArg')));
end
end
if nargin < 3 && ~problemInput
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:NotEnoughInputs',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:NotEnoughInputs')));
end
% Check for non-double inputs
if ~isa(ax,'double') || ~isa(bx,'double')
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:NonDoubleInput',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:NonDoubleInput')));
end
% Check that options is a struct
if ~isempty(options) && ~isa(options,'struct')
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:ArgNotStruct',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:commonMessages:ArgNotStruct', 4)));
end
printtype = optimget(options,'Display',defaultopt,'fast');
tol = optimget(options,'TolX',defaultopt,'fast');
funValCheck = strcmp(optimget(options,'FunValCheck',defaultopt,'fast'),'on');
maxfun = optimget(options,'MaxFunEvals',defaultopt,'fast');
maxiter = optimget(options,'MaxIter',defaultopt,'fast');
% Check that MaxFunEvals and MaxIter are scalar double values;
% Their default values for some solvers are strings
if ischar(maxfun) || isstring(maxfun)
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:CharMaxFunEvals',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:CharMaxFunEvals')));
end
if ischar(maxiter) || isstring(maxiter)
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:CharMaxIter',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:CharMaxIter')));
end
funccount = 0;
iter = 0;
xf = []; fx = [];
switch printtype
case {'notify','notify-detailed'}
print = 1;
case {'none','off'}
print = 0;
case {'iter','iter-detailed'}
print = 3;
case {'final','final-detailed'}
print = 2;
otherwise
print = 1;
end
% Handle the output
outputfcn = optimget(options,'OutputFcn',defaultopt,'fast');
if isempty(outputfcn)
haveoutputfcn = false;
else
haveoutputfcn = true;
% Parse OutputFcn which is needed to support cell array syntax for OutputFcn.
outputfcn = createCellArrayOfFunctions(outputfcn,'OutputFcn');
end
% Handle the plot
plotfcns = optimget(options,'PlotFcns',defaultopt,'fast');
if isempty(plotfcns)
haveplotfcn = false;
else
haveplotfcn = true;
% Parse PlotFcns which is needed to support cell array syntax for PlotFcns.
plotfcns = createCellArrayOfFunctions(plotfcns,'PlotFcns');
end
% checkbounds
if ax > bx
exitflag = -2;
xf=[]; fval = [];
msg=getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:ExitingLowerBoundExceedsUpperBound'));
if print > 0
disp(' ')
disp(msg)
end
output.iterations = 0;
output.funcCount = 0;
output.algorithm = 'golden section search, parabolic interpolation';
output.message = msg;
% Have not initialized OutputFcn; do not need to call it before returning
return
end
% Assume we'll converge
exitflag = 1;
header = ' Func-count x f(x) Procedure';
procedure=' initial';
% Convert to function handle as needed.
if isstring(funfcn)
funfcn = char(funfcn);
end
funfcn = fcnchk(funfcn,length(varargin));
if funValCheck
% Add a wrapper function, CHECKFUN, to check for NaN/complex values without
% having to change the calls that look like this:
% f = funfcn(x,varargin{:});
% x is the first argument to CHECKFUN, then the user's function,
% then the elements of varargin. To accomplish this we need to add the
% user's function to the beginning of varargin, and change funfcn to be
% CHECKFUN.
varargin = [{funfcn}, varargin];
funfcn = @checkfun;
end
% Initialize the output and plot functions.
if haveoutputfcn || haveplotfcn
[xOutputfcn, optimValues, stop] = callOutputAndPlotFcns(outputfcn,plotfcns,xf,'init',funccount,iter, ...
fx,procedure,varargin{:});
if stop
[xf,fval,exitflag,output] = cleanUpInterrupt(xOutputfcn,optimValues);
if print > 0
disp(output.message)
end
return;
end
end
% Compute the start point
seps = sqrt(eps);
c = 0.5*(3.0 - sqrt(5.0));
a = ax; b = bx;
v = a + c*(b-a);
w = v; xf = v;
d = 0.0; e = 0.0;
x= xf; fx = funfcn(x,varargin{:});
funccount = funccount + 1;
% Check that the objective value is a scalar
if numel(fx) ~= 1
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:NonScalarObj',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:NonScalarObj')));
end
% Display the start point if required
if print > 2
disp(' ')
disp(header)
fprintf('%5.0f %12.6g %12.6g %s\n',funccount,xf,fx,procedure)
end
% OutputFcn and PlotFcns call
% Last x passed to outputfcn/plotfcns; has the input x's shape
if haveoutputfcn || haveplotfcn
[xOutputfcn, optimValues, stop] = callOutputAndPlotFcns(outputfcn,plotfcns,xf,'iter',funccount,iter, ...
fx,procedure,varargin{:});
if stop % Stop per user request.
[xf,fval,exitflag,output] = cleanUpInterrupt(xOutputfcn,optimValues);
if print > 0
disp(output.message)
end
return;
end
end
fv = fx; fw = fx;
xm = 0.5*(a+b);
tol1 = seps*abs(xf) + tol/3.0;
tol2 = 2.0*tol1;
% Main loop
while ( abs(xf-xm) > (tol2 - 0.5*(b-a)) )
gs = 1;
% Is a parabolic fit possible
if abs(e) > tol1
% Yes, so fit parabola
gs = 0;
r = (xf-w)*(fx-fv);
q = (xf-v)*(fx-fw);
p = (xf-v)*q-(xf-w)*r;
q = 2.0*(q-r);
if q > 0.0, p = -p; end
q = abs(q);
r = e; e = d;
% Is the parabola acceptable
if ( (abs(p)<abs(0.5*q*r)) && (p>q*(a-xf)) && (p<q*(b-xf)) )
% Yes, parabolic interpolation step
d = p/q;
x = xf+d;
procedure = ' parabolic';
% f must not be evaluated too close to ax or bx
if ((x-a) < tol2) || ((b-x) < tol2)
si = sign(xm-xf) + ((xm-xf) == 0);
d = tol1*si;
end
else
% Not acceptable, must do a golden section step
gs=1;
end
end
if gs
% A golden-section step is required
if xf >= xm
e = a-xf;
else
e = b-xf;
end
d = c*e;
procedure = ' golden';
end
% The function must not be evaluated too close to xf
si = sign(d) + (d == 0);
x = xf + si * max( abs(d), tol1 );
fu = funfcn(x,varargin{:});
funccount = funccount + 1;
iter = iter + 1;
if print > 2
fprintf('%5.0f %12.6g %12.6g %s\n',funccount, x, fu, procedure);
end
% OutputFcn and PlotFcns call
if haveoutputfcn || haveplotfcn
[xOutputfcn, optimValues, stop] = callOutputAndPlotFcns(outputfcn,plotfcns,x,'iter',funccount,iter, ...
fu,procedure,varargin{:});
if stop % Stop per user request.
[xf,fval,exitflag,output] = cleanUpInterrupt(xOutputfcn,optimValues);
if print > 0
disp(output.message);
end
return;
end
end
% Update a, b, v, w, x, xm, tol1, tol2
if fu <= fx
if x >= xf
a = xf;
else
b = xf;
end
v = w; fv = fw;
w = xf; fw = fx;
xf = x; fx = fu;
else % fu > fx
if x < xf
a = x;
else
b = x;
end
if ( (fu <= fw) || (w == xf) )
v = w; fv = fw;
w = x; fw = fu;
elseif ( (fu <= fv) || (v == xf) || (v == w) )
v = x; fv = fu;
end
end
xm = 0.5*(a+b);
tol1 = seps*abs(xf) + tol/3.0; tol2 = 2.0*tol1;
if funccount >= maxfun || iter >= maxiter
exitflag = 0;
output.iterations = iter;
output.funcCount = funccount;
output.algorithm = 'golden section search, parabolic interpolation';
fval = fx;
msg = terminate(xf,exitflag,fval,funccount,maxfun,iter,maxiter,tol,print);
output.message = msg;
% OutputFcn and PlotFcns call
if haveoutputfcn || haveplotfcn
callOutputAndPlotFcns(outputfcn,plotfcns,xf,'done',funccount,iter,fval,procedure,varargin{:});
end
return
end
end % while
fval = fx;
output.iterations = iter;
output.funcCount = funccount;
output.algorithm = 'golden section search, parabolic interpolation';
msg = terminate(xf,exitflag,fval,funccount,maxfun,iter,maxiter,tol,print);
output.message = msg;
% OutputFcn and PlotFcns call
if haveoutputfcn || haveplotfcn
callOutputAndPlotFcns(outputfcn,plotfcns,xf,'done',funccount,iter,fval,procedure,varargin{:});
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function msg = terminate(~,exitflag,finalf,funccount,maxfun,~,~,tol,print)
switch exitflag
case 1
msg = ...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:OptimizationTerminatedXSatisfiesCriteria', sprintf('%e',tol)));
if print > 1 % only print msg if not 'off' or 'notify'
disp(' ')
disp(msg)
end
case 0
if funccount >= maxfun
msg = getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:ExitingMaxFunctionEvals', sprintf('%f',finalf)));
if print > 0
disp(' ')
disp(msg)
end
else
msg = getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:ExitingMaxIterations', sprintf('%f',finalf)));
if print > 0
disp(' ')
disp(msg)
end
end
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [xOutputfcn, optimValues, stop] = callOutputAndPlotFcns(outputfcn,plotfcns,x,state,funccount,iter, ...
f,procedure,varargin)
% CALLOUTPUTANDPLOTFCNS assigns values to the struct OptimValues and then calls the
% outputfcn/plotfcns. outputfcn and plotfcns are assumed to not be string
% objects but can be strings or handles.
%
% state - can have the values 'init','iter', or 'done'.
% For the 'done' state we do not check the value of 'stop' because the
% optimization is already done.
optimValues.funccount = funccount;
optimValues.iteration = iter;
optimValues.fval = f;
optimValues.procedure = procedure;
xOutputfcn = x; % Set xOutputfcn to be x
stop = false;
state = char(state); % in case string objects are ever passed in the future
% Call output functions
if ~isempty(outputfcn)
switch state
case {'iter','init'}
stop = callAllOptimOutputFcns(outputfcn,xOutputfcn,optimValues,state,varargin{:}) || stop;
case 'done'
callAllOptimOutputFcns(outputfcn,xOutputfcn,optimValues,state,varargin{:});
end
end
% Call plot functions
if ~isempty(plotfcns)
switch state
case {'iter','init'}
stop = callAllOptimPlotFcns(plotfcns,xOutputfcn,optimValues,state,varargin{:}) || stop;
case 'done'
callAllOptimPlotFcns(plotfcns,xOutputfcn,optimValues,state,varargin{:});
end
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [x,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT] = cleanUpInterrupt(xOutputfcn,optimValues)
% CLEANUPINTERRUPT updates or sets all the output arguments of FMINBND when the optimization
% is interrupted.
% Call plot function driver to finalize the plot function figure window. If
% no plot functions have been specified or the plot function figure no
% longer exists, this call just returns.
callAllOptimPlotFcns('cleanuponstopsignal');
x = xOutputfcn;
FVAL = optimValues.fval;
EXITFLAG = -1;
OUTPUT.iterations = optimValues.iteration;
OUTPUT.funcCount = optimValues.funccount;
OUTPUT.algorithm = 'golden section search, parabolic interpolation';
OUTPUT.message = getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:OptimizationTerminatedPrematurelyByUser'));
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
function f = checkfun(x,userfcn,varargin)
% CHECKFUN checks for complex or NaN results from userfcn.
f = userfcn(x,varargin{:});
% Note: we do not check for Inf as FMINBND handles it naturally.
if isnan(f)
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:checkfun:NaNFval',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:checkfun:NaNFval', localChar( userfcn ), sprintf( '%g', x ))));
elseif ~isreal(f)
error('MATLAB:fminbnd:checkfun:ComplexFval',...
getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:checkfun:ComplexFval', localChar( userfcn ), sprintf( '%g', x ))));
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
function strfcn = localChar(fcn)
% Convert the fcn to a character array for printing
if ischar(fcn)
strfcn = fcn;
elseif isstring(fcn) || isa(fcn,'inline')
strfcn = char(fcn);
elseif isa(fcn,'function_handle')
strfcn = func2str(fcn);
else
try
strfcn = char(fcn);
catch
strfcn = getString(message('MATLAB:optimfun:fminbnd:NameNotPrintable'));
end
end
3.运行结果

相关文章:

29.利用fminbnd 求解 最大容积问题(matlab程序)
1.简述 用于求某个给定函数的最小值点。 使用方法是: xfminbnd(func,x1,x2) func是函数句柄,然后x1和x2就是函数的区间,得到的结果就是使func取最小值的x值 当然也可以使用[x,fv]fminbnd(func,x1,x2)的方式,这个时候fv就是函数…...

express学习笔记7 - docker跟mysql篇
安装Docker和Navicat Docker 进官⽹https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/ 选择机型安装即可。 Navicat(也可以在网上找个破解版本) 进官⽹https://www.navicat.com/en/products/navicat-premium 安装完之后连接新建⼀个数据库连接 然后再⾥⾯新建⼀个数…...
:数组、链表部分经典题目详解(JavaScript版))
Leetcode(一):数组、链表部分经典题目详解(JavaScript版)
数组、链表部分算法题 一、数组1. 二分查找2. 移除数组元素3. 有序数组的平方4. 长度最小的子数组5. 螺旋矩阵 二、链表1. 删除链表元素2. 设计链表3.反转链表4.两两交换链表中的节点5.删除链表倒数第n个节点6.环形链表 提前声明:本博客内容均为笔者为了方便个人理解…...
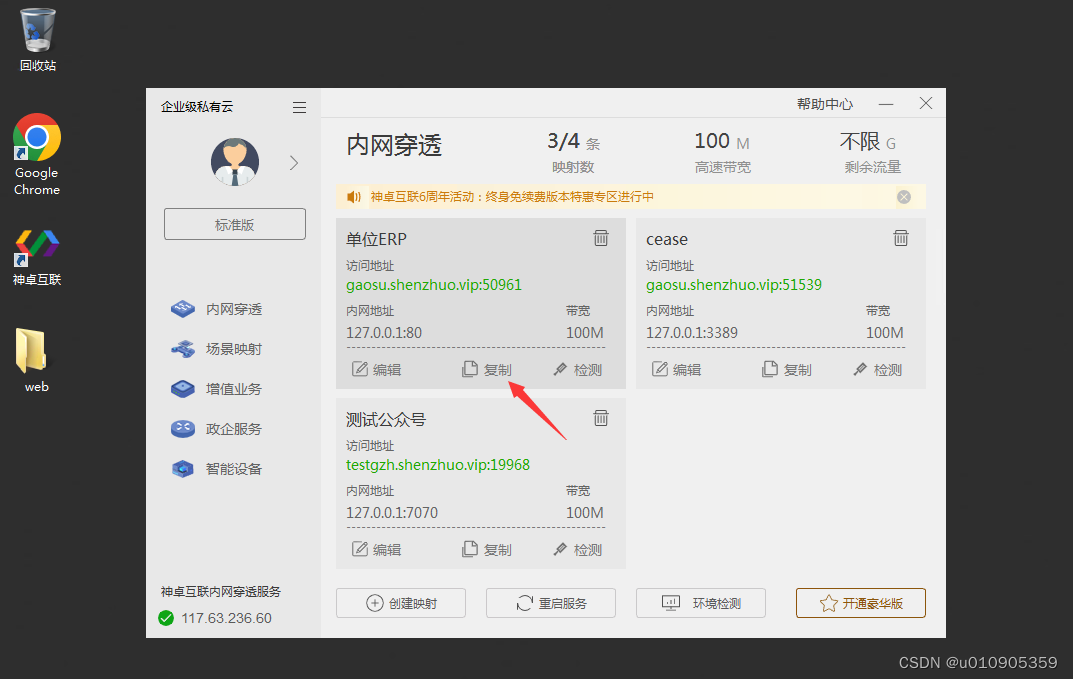
内网穿透的底层原理是什么
目录 内网穿透的功能 内网穿透的底层原理 内网穿透的功能 前段时间研究了一下内网穿透,果真是一个神奇的技术,就拿企业级内网穿透-神卓互联来说,在需要在本地安装一个神卓互联客户端,简单设置一下服务应用的端口号,就…...

Bash配置文件
当Bash以登录Shell启动的时候,会首先读取并执行文件“/etc/profile”中的命令。 接着,Bash会依次查找文件“~/.bash_profile”,“~/.bash_login”,“~/.profile”,读取并执行找到的第一个文件中的命令。也就是说&…...

写Acknowledgement的时候,latex日志出现警告
用latex写论文的时候,\section{Conclusion}下面添加 \backmatter \bmhead{Acknowledgments}时报错:错误log: \bmhead Package hyperref Warning: Difference (4) between bookmark levels is greater than one, level....错误原因ÿ…...

GCC生成map文件
要生成GCC的map文件,可以使用以下指令: gcc <source_files> -Wl,-Map<output_file>.map 其中, <source_files>是要编译的源文件列表,<output_file>是生成的map文件的名称-Wl选项告诉GCC将后面的参数传…...
IOS看书最终选择|源阅读转换|开源阅读|IOS自签
环境:IOS想使用 换源阅读 问题:换新手机,源阅读下架后,没有好的APP阅读小说 解决办法:自签APP 转换源仓库书源 最终预览 :https://rc.real9.cn/ 背景:自从我换了新iPhone手机,就无法…...
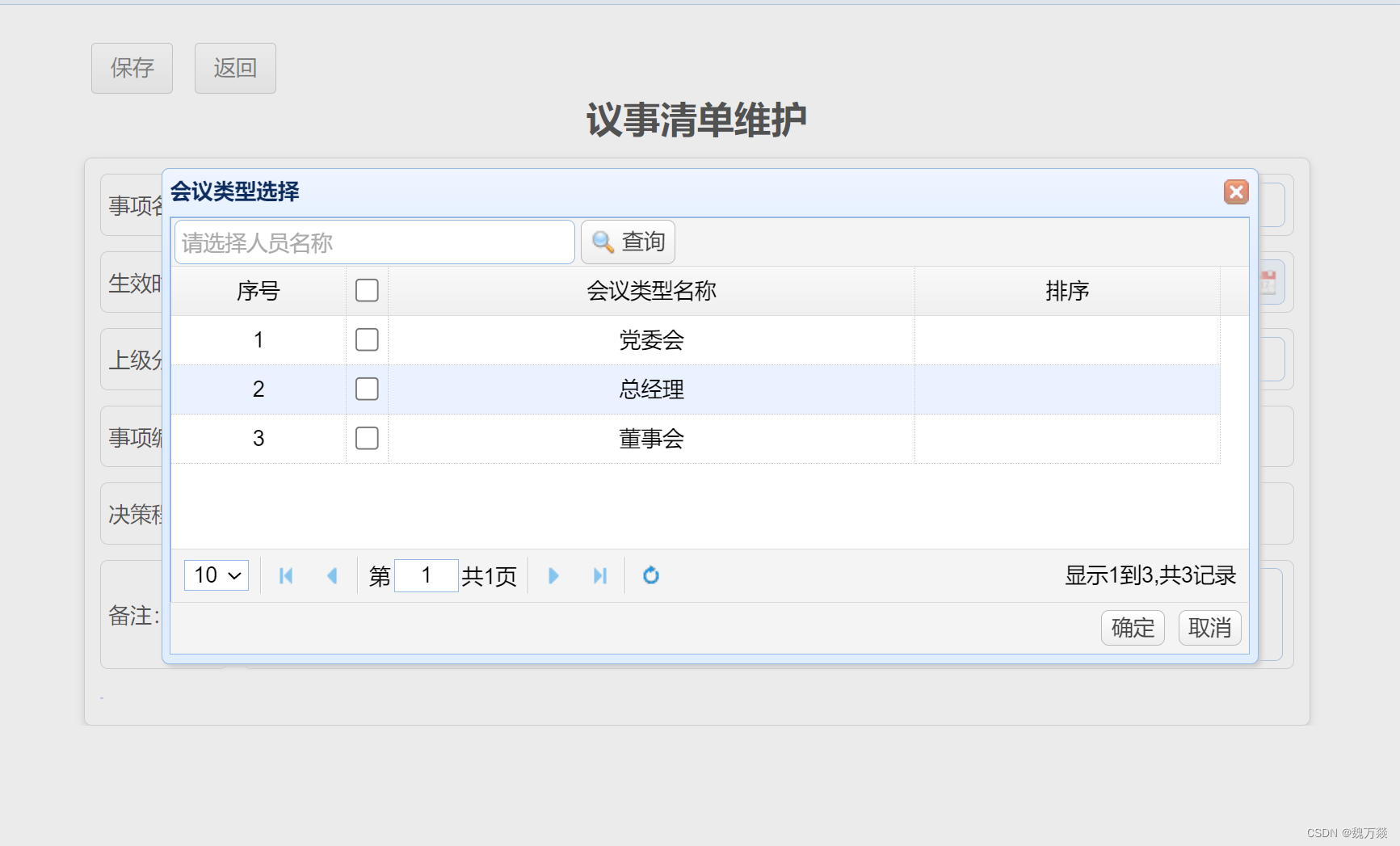
easyui实用点
easyui实用点 1.下拉框(input框只能选不能手动输入编辑) data-options"editable:false"//不可编辑2.日期框,下拉框,文本框等class class"easyui-datebox"//不带时分秒 class"easyui-datetimebox"…...

算法训练营第五十六天||● 583. 两个字符串的删除操作 ● 72. 编辑距离 ● 编辑距离总结篇
● 583. 两个字符串的删除操作 这道题涉及到两个字符串删除操作,注意递推公式,理解不到位,需要再次做 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义 dp[i][j]:以i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和以j-1位结尾…...
C语言每日一题:10.不使用+-*/实现加法+找到所有数组中消失的数。
题目一: 题目链接: 思路一: 1.两个数二进制之间进行异或如果不产生进位操作那么两个数的和就是就是两个数进行异或的结果。 举例:5(0101)2(0010)进行异或等于:7…...
LibreSSL SSL_connect: SSL_ERROR_SYSCALL in connection to github.com:443
1、问题: https://github.com/CocoaPods/Specs.git/:LibreSSL SSL_connect: SSL_ERROR_SYSCALL in connection to github.com:443的解决办法 出现这个问题的原因基本都是代理的问题: 只需要加上代理就可以了: #http代理 git conf…...

JS数组的详解与使用
什么是数组? 数组是一种有序的集合,有长度和索引,以及身上有许多的API方法 面试题:数组和伪数组的区别:数组和伪数组都有长度和索引,区别是数组身上有许多的API方法 而伪数组身上不存在这些API方法创建数组…...

c++ / python / java / PHP / SQL / Ruby / Objective-C / JavaScript 发展史
c发展史 C是由丹尼斯里奇和肯汤普森在1970年代早期开发的C语言的扩展。C最初被称为“C with Classes”,是在1980年代初期由比雅尼斯特劳斯特鲁普开发的。 1983年,斯特劳斯特鲁普将C with Classes重新命名为C。在1985年,C编译器的第一个版本被…...

Linux第一个小程序-进度条(缓冲区概念)
1.\r和\n C语言中有很多字符 a.可显字符 b.控制字符 对于回车其实有两个动作,首先换行,在将光标指向最左侧 \r :回车 \n:换行 下面举个例子: 把\n去掉会怎样 什么都没输出。为什么? 2.缓冲区概念 观察下两个…...
CentOS7环境安装tomcat
环境准备 由于是在练习,为了方便,我们可以 1.关闭防火墙 systemctl disable firewalld.service systemctl stop firewalld.service 2.关闭selinux 在/etc/selinux/config中,设置: SELINUXdisabled 3.准备jdk---》jdk-8u333-li…...

C# 中使用ValueTask优化异步方法
概要 我们在开发过程中,经常使用async的异步方法,但是有些时候,异步的方法中,可能包含一些同步的处理。本文主要介绍通过ValueTask这个struct,优化异步处理的方法性能。 代码及实现 有些时候我们会缓存一些数据在内…...

KVM创建新的虚拟机(图形化)
1.启动kvm管理器 [rootlocalhost ~]# virt-manager2.点击创建虚拟机 3.选择所需os安装镜像 4.选择合适的内存大小和CPU 5.创建所需磁盘 6.命名创建的虚拟机...

正则表达式在格式校验中的应用以及包装类的重要性
文章目录 正则表达式:做格式校验包装类:在基本数据类型与引用数据类型间的桥梁总结 在现代IT技术岗位的面试中,掌握正则表达式的应用以及理解包装类的重要性是非常有益的。这篇博客将围绕这两个主题展开,帮助读者更好地面对面试挑…...

Docker使用之java项目工程的部署
同样本文的基础建立在已在目标服务器(以linux为示例)上安装了docker,安装教程请移步度娘 若容器存在请先停止,在删除,然后删除镜像重新编译 //停止容器 sudo docker stop datatransfer//删除容器 sudo docker rm dat…...
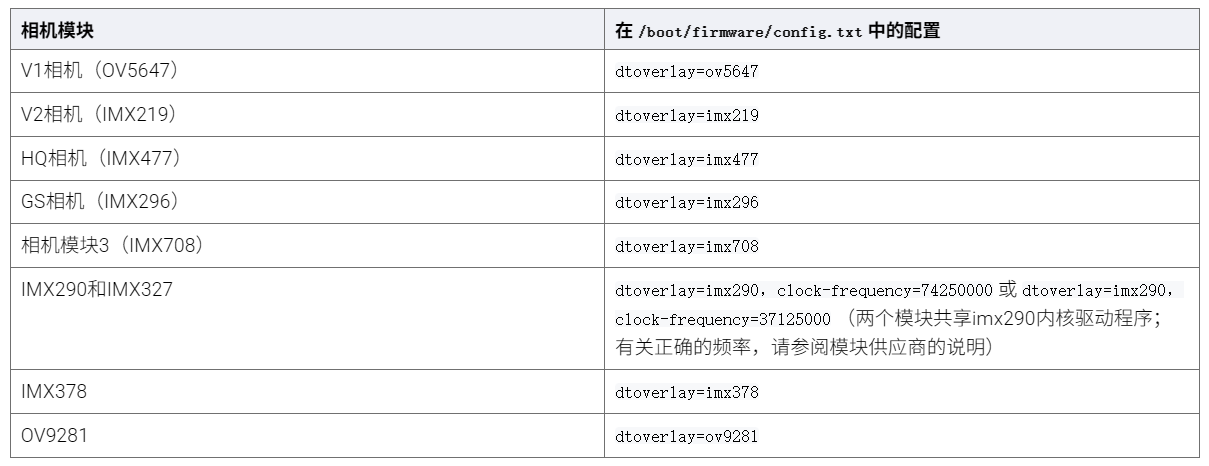
树莓派超全系列教程文档--(61)树莓派摄像头高级使用方法
树莓派摄像头高级使用方法 配置通过调谐文件来调整相机行为 使用多个摄像头安装 libcam 和 rpicam-apps依赖关系开发包 文章来源: http://raspberry.dns8844.cn/documentation 原文网址 配置 大多数用例自动工作,无需更改相机配置。但是,一…...

pam_env.so模块配置解析
在PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules)配置中, /etc/pam.d/su 文件相关配置含义如下: 配置解析 auth required pam_env.so1. 字段分解 字段值说明模块类型auth认证类模块,负责验证用户身份&am…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院挂号小程序
一、开发准备 环境搭建: 安装DevEco Studio 3.0或更高版本配置HarmonyOS SDK申请开发者账号 项目创建: File > New > Create Project > Application (选择"Empty Ability") 二、核心功能实现 1. 医院科室展示 /…...

React Native在HarmonyOS 5.0阅读类应用开发中的实践
一、技术选型背景 随着HarmonyOS 5.0对Web兼容层的增强,React Native作为跨平台框架可通过重新编译ArkTS组件实现85%以上的代码复用率。阅读类应用具有UI复杂度低、数据流清晰的特点。 二、核心实现方案 1. 环境配置 (1)使用React Native…...
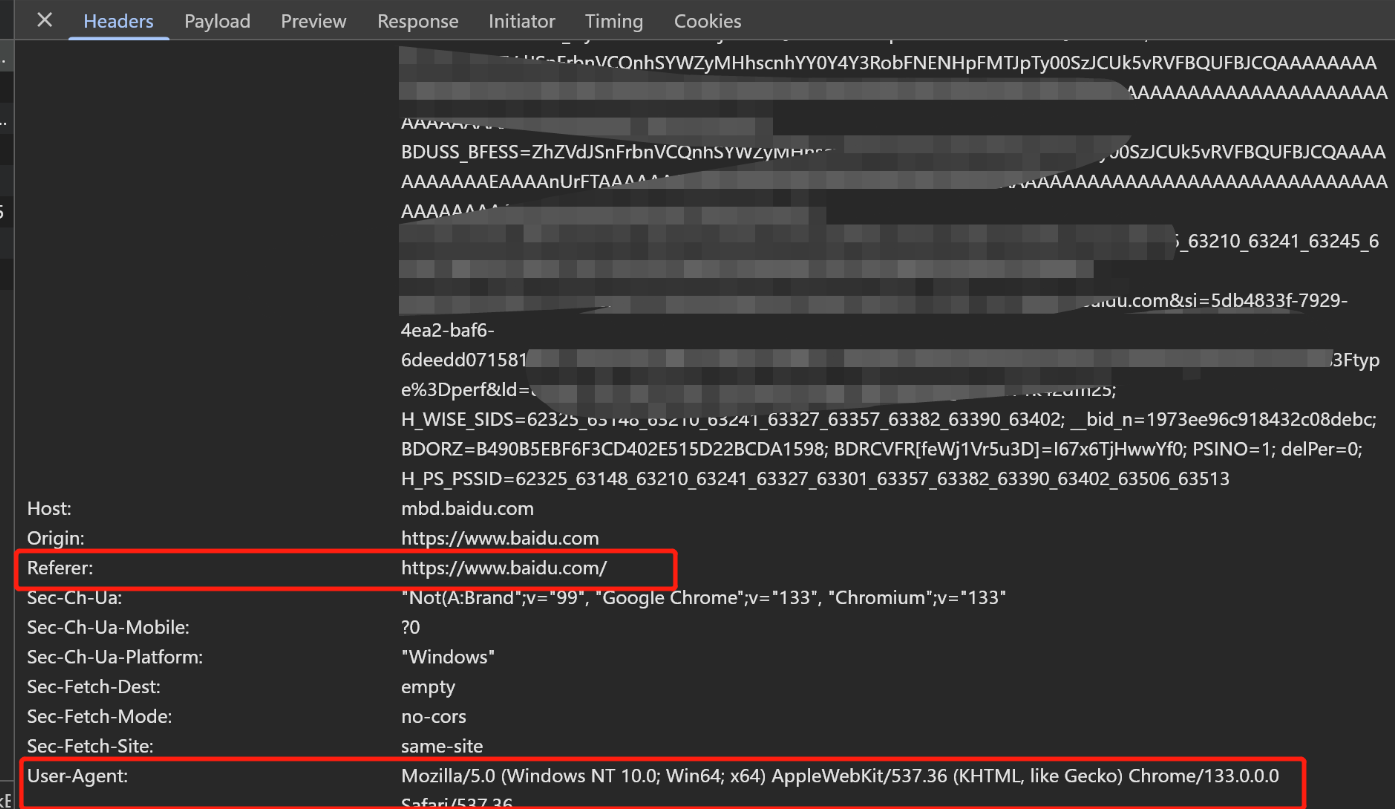
Python爬虫(一):爬虫伪装
一、网站防爬机制概述 在当今互联网环境中,具有一定规模或盈利性质的网站几乎都实施了各种防爬措施。这些措施主要分为两大类: 身份验证机制:直接将未经授权的爬虫阻挡在外反爬技术体系:通过各种技术手段增加爬虫获取数据的难度…...

爬虫基础学习day2
# 爬虫设计领域 工商:企查查、天眼查短视频:抖音、快手、西瓜 ---> 飞瓜电商:京东、淘宝、聚美优品、亚马逊 ---> 分析店铺经营决策标题、排名航空:抓取所有航空公司价格 ---> 去哪儿自媒体:采集自媒体数据进…...
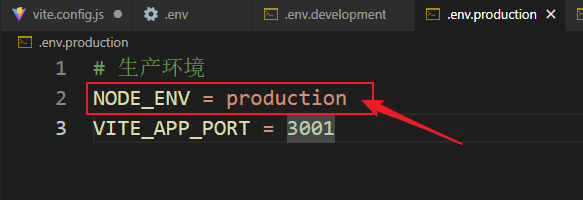
vue3+vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法
vue3vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法 .env文件作用命名规则常用的配置项示例使用方法注意事项在vite.config.js文件中读取环境变量方法 .env文件作用 .env 文件用于定义环境变量,这些变量可以在项目中通过 import.meta.env 进行访问。Vite 会自动加载这些环境变…...
-HIve数据分析)
大数据学习(132)-HIve数据分析
🍋🍋大数据学习🍋🍋 🔥系列专栏: 👑哲学语录: 用力所能及,改变世界。 💖如果觉得博主的文章还不错的话,请点赞👍收藏⭐️留言Ǵ…...

AI,如何重构理解、匹配与决策?
AI 时代,我们如何理解消费? 作者|王彬 封面|Unplash 人们通过信息理解世界。 曾几何时,PC 与移动互联网重塑了人们的购物路径:信息变得唾手可得,商品决策变得高度依赖内容。 但 AI 时代的来…...

无人机侦测与反制技术的进展与应用
国家电网无人机侦测与反制技术的进展与应用 引言 随着无人机(无人驾驶飞行器,UAV)技术的快速发展,其在商业、娱乐和军事领域的广泛应用带来了新的安全挑战。特别是对于关键基础设施如电力系统,无人机的“黑飞”&…...
