机器学习---梯度下降代码
1. 归一化
# Read data from csv
pga = pd.read_csv("pga.csv")
print(type(pga))print(pga.head())

# Normalize the data 归一化值 (x - mean) / (std)
pga.distance = (pga.distance - pga.distance.mean()) / pga.distance.std()
pga.accuracy = (pga.accuracy - pga.accuracy.mean()) / pga.accuracy.std()
print(pga.head())
plt.scatter(pga.distance, pga.accuracy)
plt.xlabel('normalized distance')
plt.ylabel('normalized accuracy')
plt.show()
2. 线性回归
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import numpy as np# We can add a dimension to an array by using np.newaxis
print("Shape of the series:", pga.distance.shape)
print("Shape with newaxis:", pga.distance[:, np.newaxis].shape)# The X variable in LinearRegression.fit() must have 2 dimensions
lm = LinearRegression()
lm.fit(pga.distance[:, np.newaxis], pga.accuracy)
theta1 = lm.coef_[0]
print (theta1)
这段代码是一个示例,展示了如何使用np.newaxis和LinearRegression来进行线性回归。
首先,通过np.newaxis将一维数组pga.distance添加一个新的维度,从而将其转换为二维数
组。通过打印数组的形状,可以看到在添加np.newaxis之前,pga.distance是一个一维数组,形状
为(n,),而添加了np.newaxis之后,形状变为(n, 1)。
然后,创建了一个LinearRegression的实例lm。使用lm.fit()方法,将转换后的特征数据
pga.distance[:, np.newaxis]和目标数据pga.accuracy作为参数,对线性回归模型进行训练拟
合。
最后,通过lm.coef_获取训练后的模型系数(权重),并将第一个特征的系数赋值给变量
theta1。pga.distance和pga.accuracy是示例数据,你需要根据实际情况替换为你自己的数据。
3. 代价函数
# The cost function of a single variable linear model# The c
# 单变量 代价函数
def cost(theta0, theta1, x, y):# Initialize costJ = 0# The number of observationsm = len(x)# Loop through each observation# 通过每次观察进行循环for i in range(m):# Compute the hypothesis # 计算假设h = theta1 * x[i] + theta0# Add to costJ += (h - y[i])**2# Average and normalize costJ /= (2*m)return J# The cost for theta0=0 and theta1=1
print(cost(0, 1, pga.distance, pga.accuracy))theta0 = 100
theta1s = np.linspace(-3,2,100)
costs = []
for theta1 in theta1s:costs.append(cost(theta0, theta1, pga.distance, pga.accuracy))plt.plot(theta1s, costs)
plt.show()
一个简单的单变量线性回归模型的代价函数实现,并且计算了在给定一组参数theta0和theta1
的情况下的代价。在这段代码中,cost()函数接受四个参数:theta0和theta1是线性模型的参数,
x是输入特征,y是目标变量。函数的目标是计算模型的代价。
首先,初始化代价J为0。然后,通过循环遍历每个观察值,计算模型的预测值h。代价J通过累
加每个观察值的误差平方来计算。最后,将代价J除以观察值的数量的两倍,以平均和归一化代
价。在这段代码的后半部分,使用一个给定的theta0值和一组theta1值,计算每个theta1对应的代
价,并将结果存储在costs列表中。然后,使用plt.plot()将theta1s和costs进行绘制,显示出代
价函数随着theta1的变化而变化的趋势。
4. 绘制三维图
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D# Example of a Surface Plot using Matplotlib
# Create x an y variables
x = np.linspace(-10,10,100)
y = np.linspace(-10,10,100)# We must create variables to represent each possible pair of points in x and y
# ie. (-10, 10), (-10, -9.8), ... (0, 0), ... ,(10, 9.8), (10,9.8)
# x and y need to be transformed to 100x100 matrices to represent these coordinates
# np.meshgrid will build a coordinate matrices of x and y
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x,y)
#print(X[:5,:5],"\n",Y[:5,:5])# Compute a 3D parabola
Z = X**2 + Y**2 # Open a figure to place the plot on
fig = plt.figure()
# Initialize 3D plot
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# Plot the surface
ax.plot_surface(X=X,Y=Y,Z=Z)plt.show()# Use these for your excerise
theta0s = np.linspace(-2,2,100)
theta1s = np.linspace(-2,2, 100)
COST = np.empty(shape=(100,100))
# Meshgrid for paramaters
T0S, T1S = np.meshgrid(theta0s, theta1s)
# for each parameter combination compute the cost
for i in range(100):for j in range(100):COST[i,j] = cost(T0S[0,i], T1S[j,0], pga.distance, pga.accuracy)# make 3d plot
fig2 = plt.figure()
ax = fig2.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X=T0S,Y=T1S,Z=COST)
plt.show() 

使用Matplotlib绘制三维图形,包括一个二次曲面图和一个代价函数的图。
首先,通过使用np.linspace()函数,创建了从-10到10的等间距的100个点,分别赋值给变量
x和y。
接下来,使用np.meshgrid()函数将x和y转换为100x100的网格矩阵,分别赋值给X和Y。这
样,X和Y矩阵中的每个元素表示一个(x, y)坐标对。
然后,根据二次曲面方程Z = X**2 + Y**2计算出Z矩阵,其中Z矩阵中的每个元素表示对应坐
标点的高度。
通过plt.figure()创建一个新的图形,并通过fig.gca(projection='3d')初始化一个三维图形
的坐标系。使用ax.plot_surface()函数绘制曲面图,其中X、Y和Z分别表示X、Y和Z矩阵。
最后,使用plt.show()显示图形。
在后半部分的代码中,首先创建了两个包含100个均匀分布数值的数组theta0s和theta1s,分
别表示theta0和theta1的取值范围。
接下来,使用np.empty()创建一个空的100x100的数组COST,用于存储代价函数的计算结果。
通过使用np.meshgrid()函数,将theta0s和theta1s转换为网格矩阵T0S和T1S。
然后,通过两个嵌套的循环遍历所有可能的参数组合,并使用cost()函数计算每个参数组合对
应的代价,并将结果存储在COST数组中。
最后,使用plt.figure()创建一个新的图形,并通过fig.gca(projection='3d')初始化一个三
维图形的坐标系。使用ax.plot_surface()函数绘制代价函数的曲面图,其中X、Y和Z分别表示
T0S、T1S和COST矩阵。使用plt.show()显示图形。
5. 求导函数
线性回归模型的偏导数公式可以通过最小化代价函数推导得到。以下是推导过程:
线性回归模型假设函数为:h(x) = theta0 + theta1 * x
代价函数为均方差函数(Mean Squared Error):J(theta0, theta1) = (1/2m) * Σ(h(x) - y)^2
其中,m 是样本数量,h(x) 是模型的预测值,y 是观测值。
为了求解最优的模型参数 theta0 和 theta1,我们需要计算代价函数对这两个参数的偏导数。
首先,计算代价函数对 theta0 的偏导数:
∂J/∂theta0 = (1/m) * Σ(h(x) - y)
然后,计算代价函数对 theta1 的偏导数:
∂J/∂theta1 = (1/m) * Σ(h(x) - y) * x
# 对 theta1 进行求导# 对 thet
def partial_cost_theta1(theta0, theta1, x, y):# Hypothesish = theta0 + theta1*x# Hypothesis minus observed times xdiff = (h - y) * x# Average to compute partial derivativepartial = diff.sum() / (x.shape[0])return partialpartial1 = partial_cost_theta1(0, 5, pga.distance, pga.accuracy)
print("partial1 =", partial1)# 对theta0 进行求导
# Partial derivative of cost in terms of theta0
def partial_cost_theta0(theta0, theta1, x, y):# Hypothesish = theta0 + theta1*x# Difference between hypothesis and observationdiff = (h - y)# Compute partial derivativepartial = diff.sum() / (x.shape[0])return partialpartial0 = partial_cost_theta0(1, 1, pga.distance, pga.accuracy)
print("partial0 =", partial0)
计算代价函数对参数theta1和theta0的偏导数。
首先,定义了一个名为partial_cost_theta1()的函数,接受四个参数:theta0和theta1是线
性模型的参数,x是输入特征,y是目标变量。这个函数用于计算代价函数对theta1的偏导数。在函
数内部,首先计算假设值h,然后计算(h-y)*x,得到假设值与观察值之间的差异乘以输入特征x。
最后,将这些差异的和除以输入特征的数量,得到对theta1的偏导数。然后,通过调用
partial_cost_theta1()函数并传入参数0和5,计算出对应的偏导数partial1。
接下来,定义了一个名为partial_cost_theta0()的函数,接受四个参数:theta0和
theta1是线性模型的参数,x是输入特征,y是目标变量。这个函数用于计算代价函数对theta0的偏
导数。在函数内部,首先计算假设值h,然后计算假设值与观察值之间的差异。最后,将这些差异
的和除以输入特征的数量,得到对theta0的偏导数。然后,通过调用partial_cost_theta0()函数
并传入参数1和1,计算出对应的偏导数partial0。
6. 梯度下降
# x is our feature vector -- distance
# y is our target variable -- accuracy
# alpha is the learning rate
# theta0 is the intial theta0
# theta1 is the intial theta1
def gradient_descent(x, y, alpha=0.1, theta0=0, theta1=0):max_epochs = 1000 # Maximum number of iterations 最大迭代次数counter = 0 # Intialize a counter 当前第几次c = cost(theta1, theta0, pga.distance, pga.accuracy) ## Initial cost 当前代价函数costs = [c] # Lets store each update 每次损失值都记录下来# Set a convergence threshold to find where the cost function in minimized# When the difference between the previous cost and current cost # is less than this value we will say the parameters converged# 设置一个收敛的阈值 (两次迭代目标函数值相差没有相差多少,就可以停止了)convergence_thres = 0.000001 cprev = c + 10 theta0s = [theta0]theta1s = [theta1]# When the costs converge or we hit a large number of iterations will we stop updating# 两次间隔迭代目标函数值相差没有相差多少(说明可以停止了)while (np.abs(cprev - c) > convergence_thres) and (counter < max_epochs):cprev = c# Alpha times the partial deriviative is our updated# 先求导, 导数相当于步长update0 = alpha * partial_cost_theta0(theta0, theta1, x, y)update1 = alpha * partial_cost_theta1(theta0, theta1, x, y)# Update theta0 and theta1 at the same time# We want to compute the slopes at the same set of hypothesised parameters# so we update after finding the partial derivatives# -= 梯度下降,+=梯度上升theta0 -= update0theta1 -= update1# Store thetastheta0s.append(theta0)theta1s.append(theta1)# Compute the new cost# 当前迭代之后,参数发生更新 c = cost(theta0, theta1, pga.distance, pga.accuracy)# Store updates,可以进行保存当前代价值costs.append(c)counter += 1 # Count# 将当前的theta0, theta1, costs值都返回去return {'theta0': theta0, 'theta1': theta1, "costs": costs}print("Theta0 =", gradient_descent(pga.distance, pga.accuracy)['theta0'])
print("Theta1 =", gradient_descent(pga.distance, pga.accuracy)['theta1'])
print("costs =", gradient_descent(pga.distance, pga.accuracy)['costs'])descend = gradient_descent(pga.distance, pga.accuracy, alpha=.01)
plt.scatter(range(len(descend["costs"])), descend["costs"])
plt.show()

使用梯度下降法求解线性回归模型中的偏导数以及更新参数的过程。其中,gradient_descent
函数接受输入特征 x 和观测值 y,以及学习率 alpha、初始参数 theta0 和 theta1。在函数中,设
置了最大迭代次数 max_epochs 和收敛阈值 convergence_thres,用于控制算法的停止条件。初始
时,计算了初始的代价函数值 c,并将其存储在 costs 列表中。
在迭代过程中,使用偏导数的公式进行参数更新,即 theta0 -= update0 和 theta1 -=
update1。同时,计算新的代价函数值 c,并将其存储在 costs 列表中。最后,返回更新后的参数
值 theta0 和 theta1,以及代价函数值的变化过程 costs。
最后,调用了 gradient_descent 函数,并打印了最终的参数值和代价函数值。然后,绘制了
代价函数值的变化过程图。
相关文章:

机器学习---梯度下降代码
1. 归一化 # Read data from csv pga pd.read_csv("pga.csv") print(type(pga))print(pga.head())# Normalize the data 归一化值 (x - mean) / (std) pga.distance (pga.distance - pga.distance.mean()) / pga.distance.std() pga.accuracy (pga.accuracy - pg…...
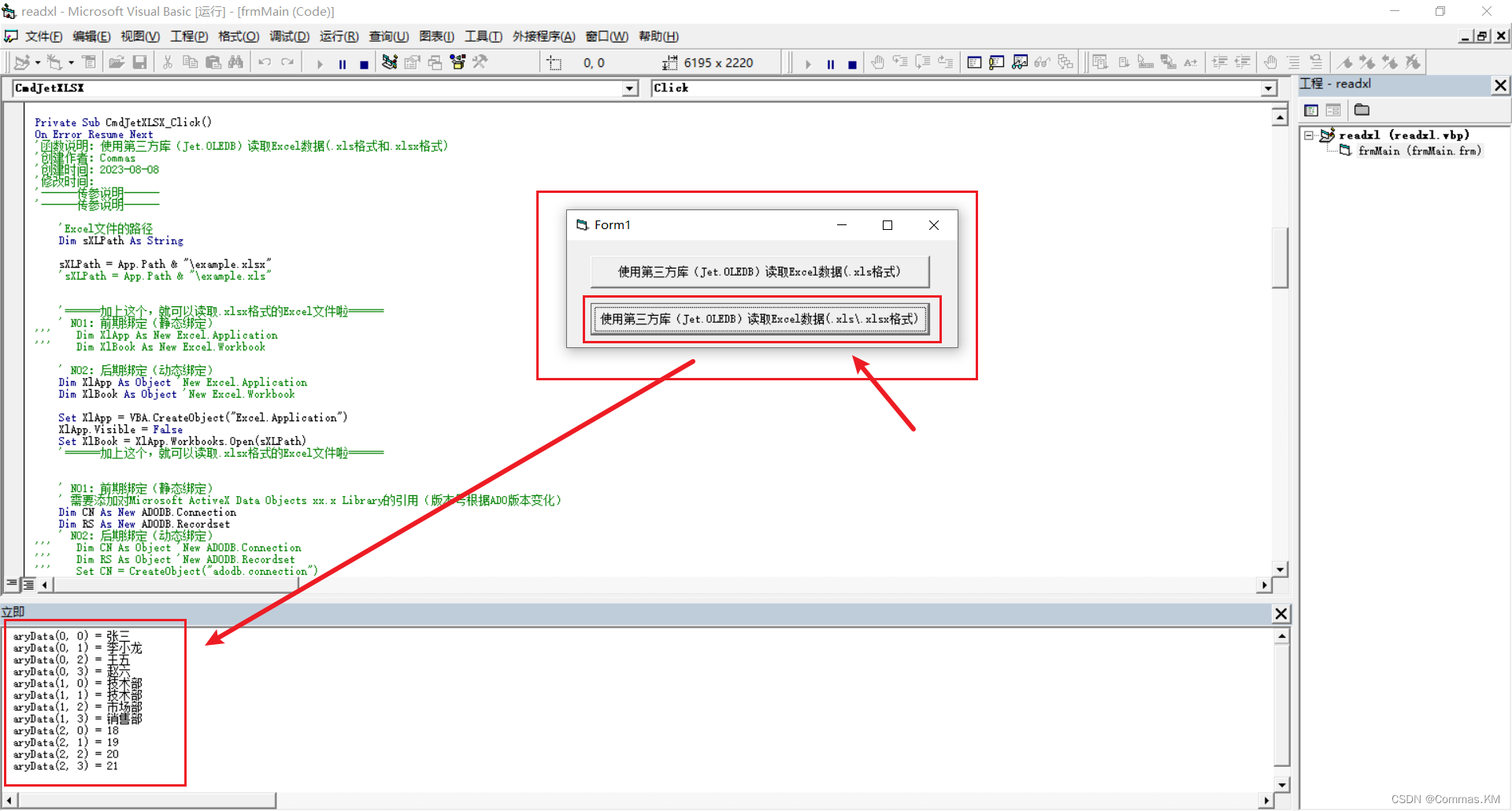
【VB6|第23期】原来Jet.OLEDB也可以读取新版.xlsx的Excel文件
日期:2023年8月11日 作者:Commas 签名:(ง •_•)ง 积跬步以致千里,积小流以成江海…… 注释:如果您觉得有所帮助,帮忙点个赞,也可以关注我,我们一起成长;如果有不对的地方…...
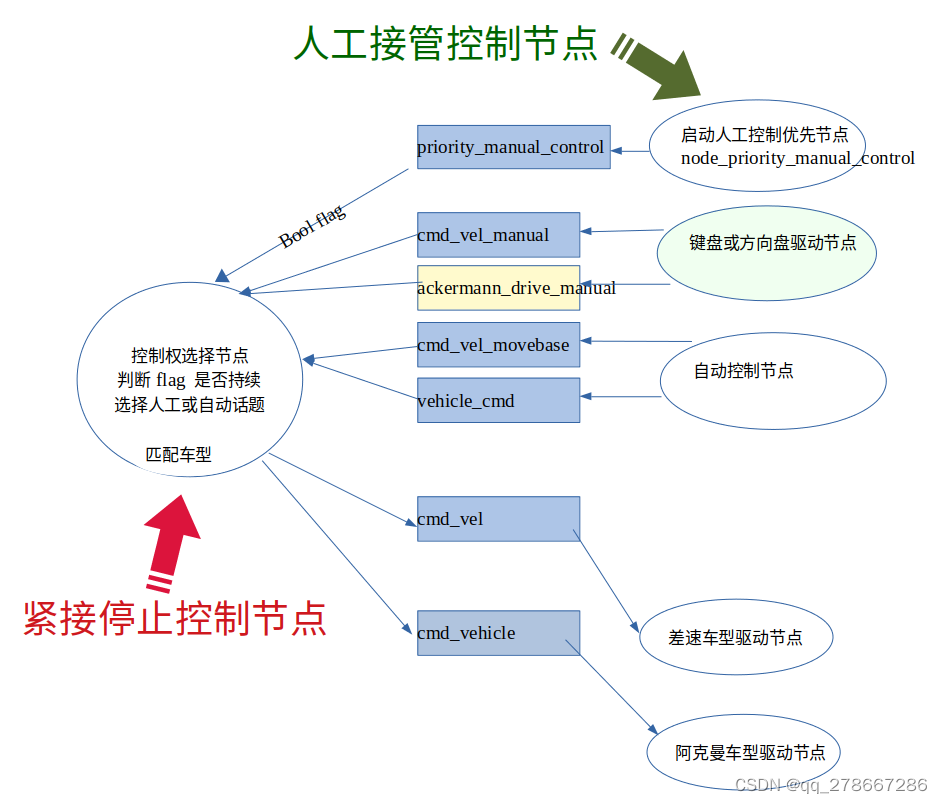
通过控制ros节点的启停,软实现人工控制和紧急停止功能的图示
通过控制ros节点的启停,软实现人工控制和紧急停止功能的图示 实现原理简介: 人工控制的节点: 键盘节点 方向盘节点 自动控制的节点: movebase 导航 autoware 等 底盘节点: 差速底盘 阿克曼底盘 控制节点࿱…...
面试热题(滑动窗口最大值)
给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。 返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。 输入:nums [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k 3 输出:[3,3,5,…...
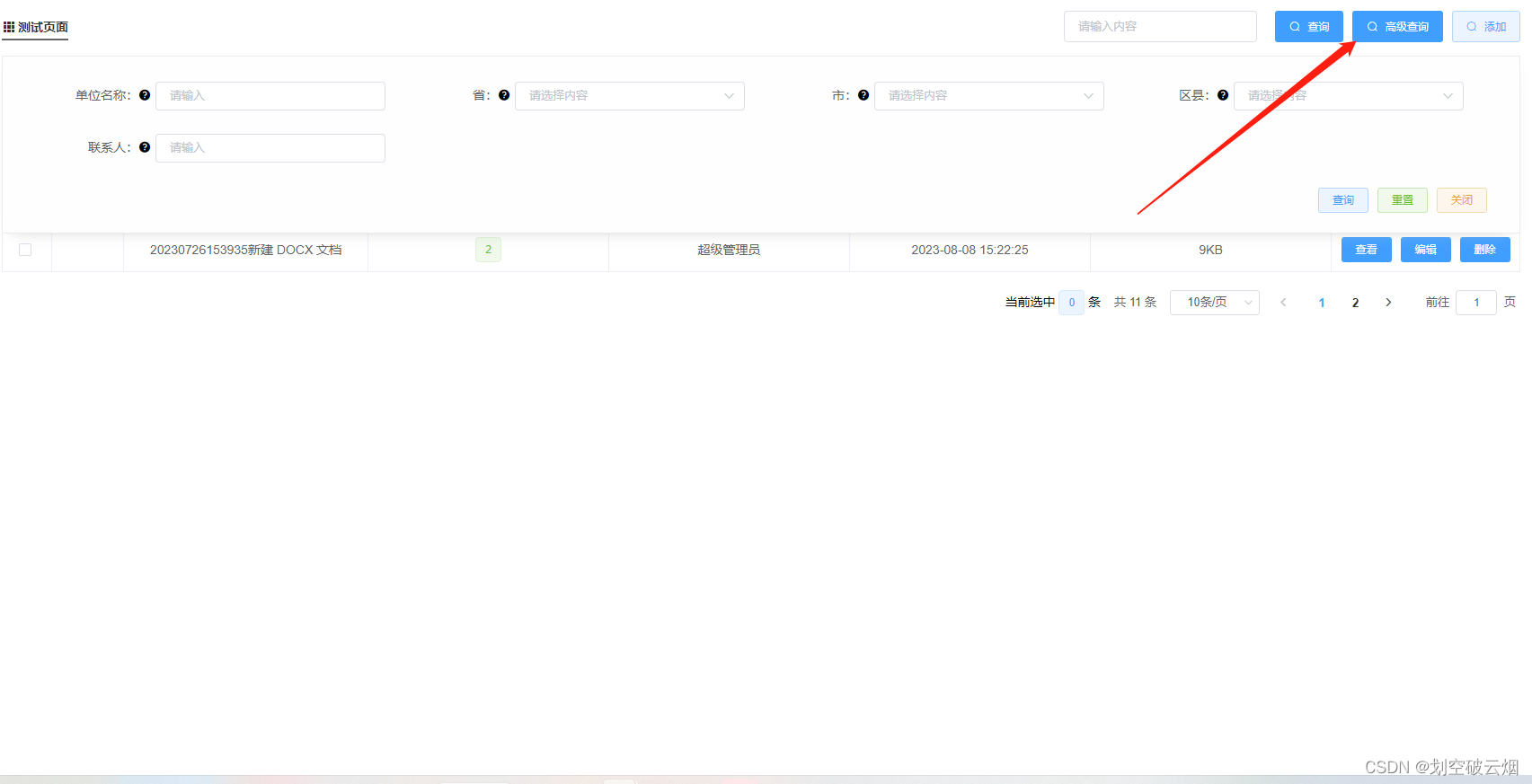
【代码】表格封装 + 高级查询 + 搜索 +分页器 (极简)
一、标题 查询条件按钮(Header) <!-- Header 标题搜索栏 --> <template><div><div class"header"><div class"h-left"><div class"title"><div class"desc-test">…...

ant.design 组件库中的 Tree 组件实现可搜索的树: React+and+ts
ant.design 组件库中的 Tree 组件实现可搜索的树,在这里我会详细介绍每个方法,以及容易踩坑的点。 效果图: 首先是要导入的文件 // React 自带的属性 import React, { useMemo, useState } from react; // antd 组件库中的,输入…...
Linux系统编程之信号(上)
一、信号概念 信号就是软件中断。每当程序收到一个信号,都需要按指定的方法去处理。以下是UNIX系统的信号表。 其中core表示产生一个复制了该进程内存映像的core文件,它保存了程序现场,可以使用gdb来调试。 二、signal() signal()函数用于改…...

23.Netty源码之内置解码器
highlight: arduino-light Netty内置的解码器 在前两节课我们介绍了 TCP 拆包/粘包的问题,以及如何使用 Netty 实现自定义协议的编解码。可以看到,网络通信的底层实现,Netty 都已经帮我们封装好了,我们只需要扩展 ChannelHandler …...
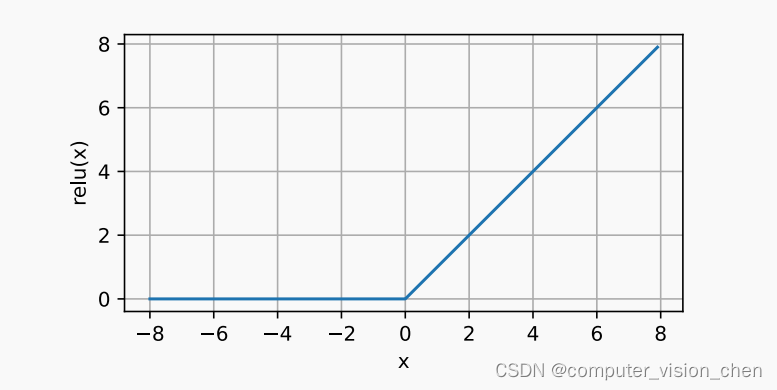
sigmoid ReLU 等激活函数总结
sigmoid ReLU sigoid和ReLU对比 1.sigmoid有梯度消失问题:当sigmoid的输出非常接近0或者1时,区域的梯度几乎为0,而ReLU在正区间的梯度总为1。如果Sigmoid没有正确初始化,它可能在正区间得到几乎为0的梯度。使模型无法有效训练。 …...

RabbitMQ 消息队列
文章目录 🍰有几个原因可以解释为什么要选择 RabbitMQ:🥩mq之间的对比🌽RabbitMQ vs Apache Kafka🌽RabbitMQ vs ActiveMQ🌽RabbitMQ vs RocketMQ🌽RabbitMQ vs Redis 🥩linux docke…...
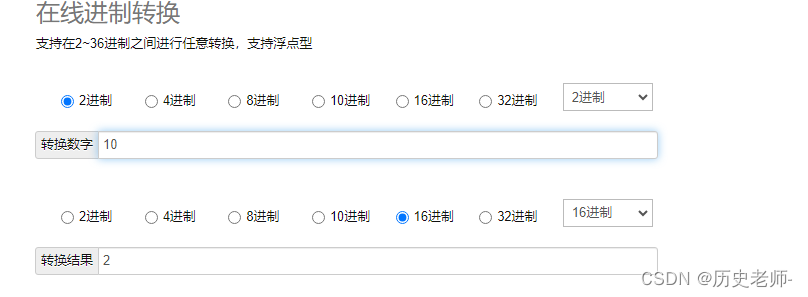
PHP实现在线进制转换器,10进制,2、4、8、16、32进制转换
1.接口文档 2.laravel实现代码 /*** 进制转换计算器* return \Illuminate\Http\JsonResponse*/public function binaryConvertCal(){$ten $this->request(ten);$two $this->request(two);$four $this->request(four);$eight $this->request(eight);$sixteen …...
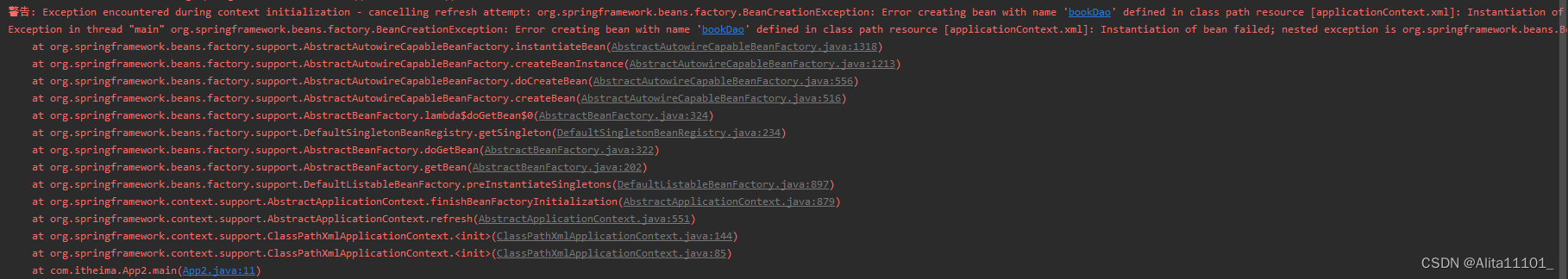
报错 | Spring报错详解
Spring报错详解 一、前言二、报错提示三、分层解读1.最下面一层Caused by2.上一层Caused by3.最上层Caused by 四、总结五、解决方案 一、前言 本文主要是记录在初次学习Spring时遇到报错后的解读以及解决方案 二、报错提示 三、分层解读 遇到报错的时候,我们需要…...

PHP最简单自定义自己的框架数据库封装调用(五)
1、实现效果调用实现数据增删改查封装 2、index.php 入口定义数据库账号密码 <?php//定义当前请求模块 define("MODULE",index);//定义数据库 define(DB_HOST,localhost);//数据库地址 define(DB_DATABASE,aaa);//数据库 define(DB_USER,root);//数据库账号 def…...

使用Redis来实现点赞功能的基本思路
使用Redis来实现点赞功能是一种高效的选择,因为Redis是一个内存数据库,适用于处理高并发的数据操作。以下是一个基本的点赞功能在Redis中的设计示例: 假设我们有一个文章或帖子,用户可以对其进行点赞,取消点赞&#x…...
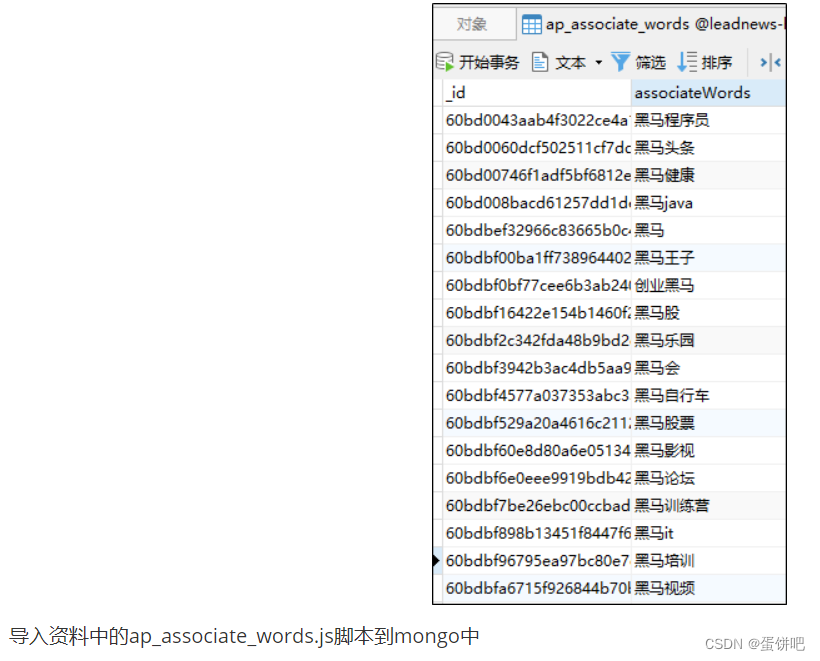
【黑马头条之app端文章搜索ES-MongoDB】
本笔记内容为黑马头条项目的app端文章搜索部分 目录 一、今日内容介绍 1、App端搜索-效果图 2、今日内容 二、搭建ElasticSearch环境 1、拉取镜像 2、创建容器 3、配置中文分词器 ik 4、使用postman测试 三、app端文章搜索 1、需求分析 2、思路分析 3、创建索引和…...

Nginx安装以及LVS-DR集群搭建
Nginx安装 1.环境准备 yum insatall -y make gcc gcc-c pcre-devel #pcre-devel -- pcre库 #安装openssl-devel yum install -y openssl-devel 2.tar安装包 3.解压软件包并创建软连接 tar -xf nginx-1.22.0.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ ln -s /usr/local/nginx-1.22.0/ /usr/local…...
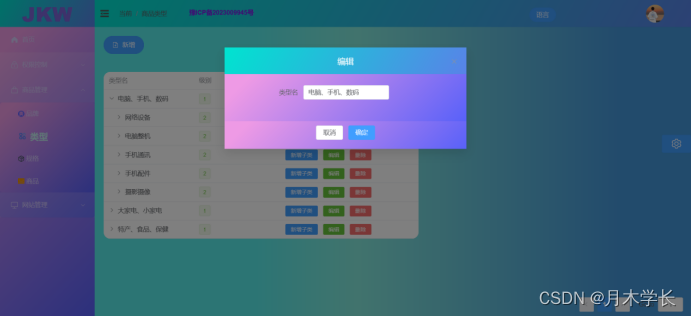
后端开发9.商品类型模块
概述 简介 商品类型我设计的复杂了点,设计了多级类型 效果图 数据库设计...

spring框架自带的http工具RestTemplate用法
1. RestTemplate是什么? RestTemplate是由Spring框架提供的一个可用于应用中调用rest服务的类它简化了与http服务的通信方式。 RestTemplate是一个执行HTTP请求的同步阻塞式工具类,它仅仅只是在 HTTP 客户端库(例如 JDK HttpURLConnection&a…...
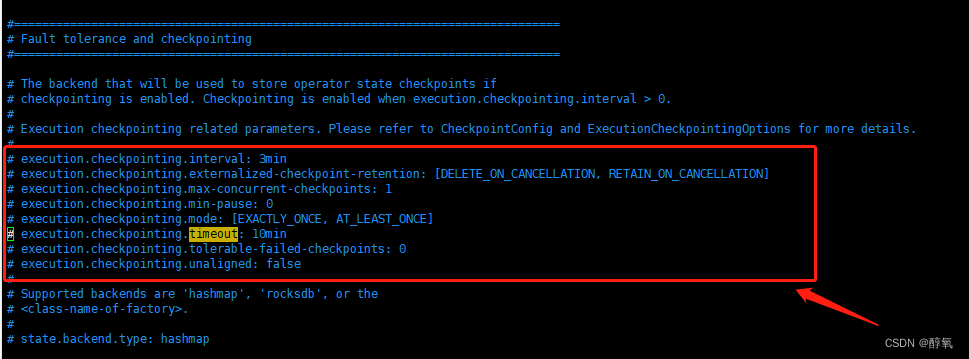
【flink】Checkpoint expired before completing.
使用flink同步数据出现错误Checkpoint expired before completing. 11:32:34,455 WARN org.apache.flink.runtime.checkpoint.CheckpointFailureManager [Checkpoint Timer] - Failed to trigger or complete checkpoint 4 for job 1b1d41031ea45d15bdb3324004c2d749. (2 con…...
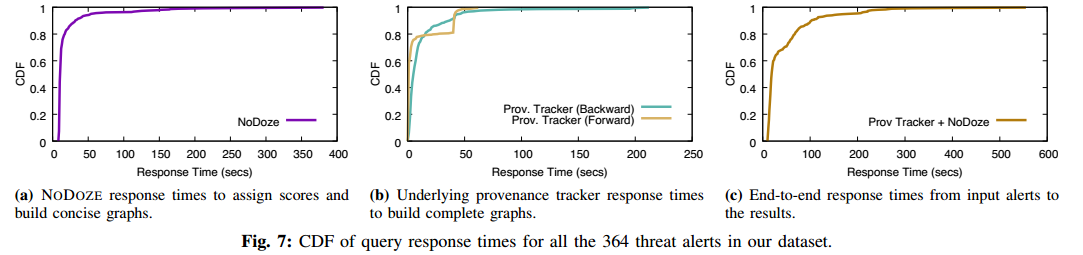
【论文阅读】NoDoze:使用自动来源分类对抗威胁警报疲劳(NDSS-2019)
NODOZE: Combatting Threat Alert Fatigue with Automated Provenance Triage 伊利诺伊大学芝加哥分校 Hassan W U, Guo S, Li D, et al. Nodoze: Combatting threat alert fatigue with automated provenance triage[C]//network and distributed systems security symposium.…...
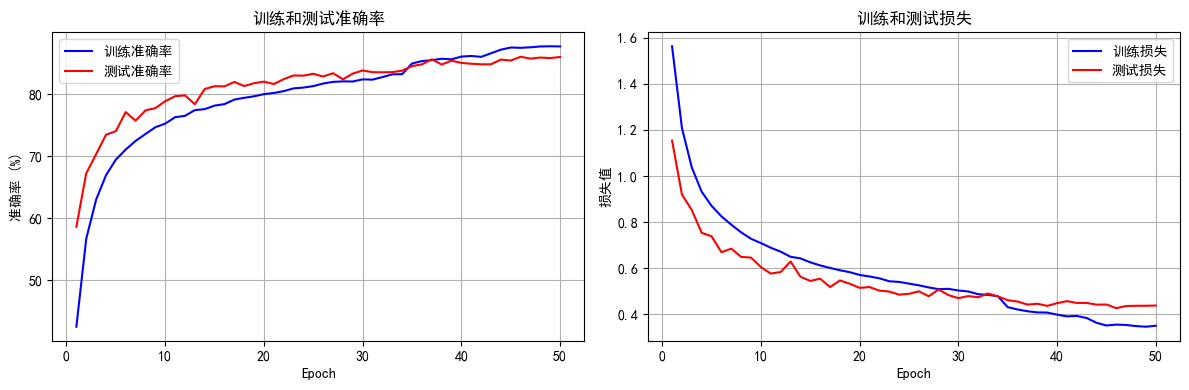
python打卡day49
知识点回顾: 通道注意力模块复习空间注意力模块CBAM的定义 作业:尝试对今天的模型检查参数数目,并用tensorboard查看训练过程 import torch import torch.nn as nn# 定义通道注意力 class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):def __init__(self,…...
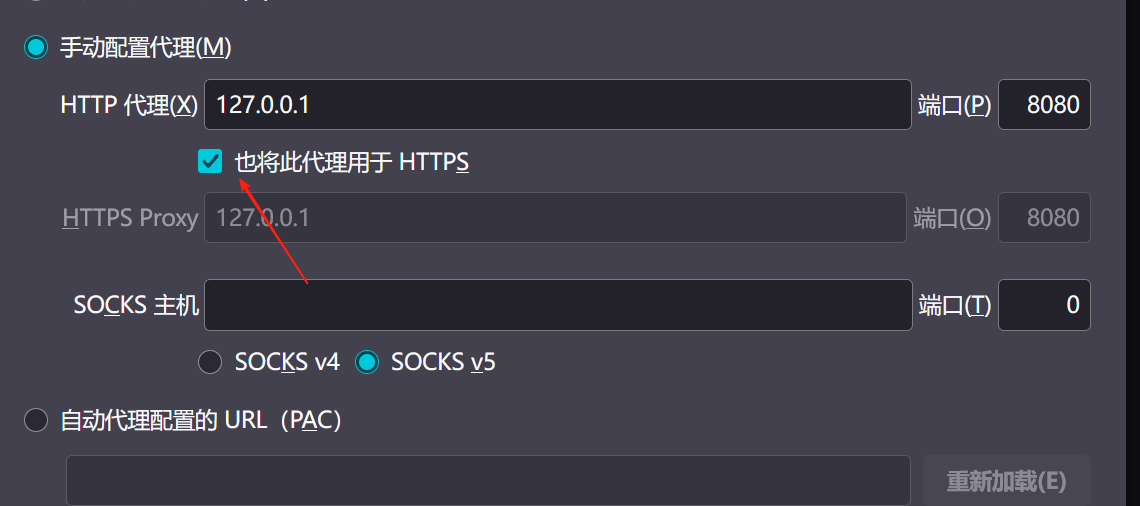
【2025年】解决Burpsuite抓不到https包的问题
环境:windows11 burpsuite:2025.5 在抓取https网站时,burpsuite抓取不到https数据包,只显示: 解决该问题只需如下三个步骤: 1、浏览器中访问 http://burp 2、下载 CA certificate 证书 3、在设置--隐私与安全--…...
关键领域软件测试的突围之路:如何破解安全与效率的平衡难题
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,软件系统已成为国家关键领域的核心战斗力。不同于普通商业软件,这些承载着国家安全使命的软件系统面临着前所未有的质量挑战——如何在确保绝对安全的前提下,实现高效测试与快速迭代?这一命题正考验着…...

苹果AI眼镜:从“工具”到“社交姿态”的范式革命——重新定义AI交互入口的未来机会
在2025年的AI硬件浪潮中,苹果AI眼镜(Apple Glasses)正在引发一场关于“人机交互形态”的深度思考。它并非简单地替代AirPods或Apple Watch,而是开辟了一个全新的、日常可接受的AI入口。其核心价值不在于功能的堆叠,而在于如何通过形态设计打破社交壁垒,成为用户“全天佩戴…...

Scrapy-Redis分布式爬虫架构的可扩展性与容错性增强:基于微服务与容器化的解决方案
在大数据时代,海量数据的采集与处理成为企业和研究机构获取信息的关键环节。Scrapy-Redis作为一种经典的分布式爬虫架构,在处理大规模数据抓取任务时展现出强大的能力。然而,随着业务规模的不断扩大和数据抓取需求的日益复杂,传统…...
)
华为OD最新机试真题-数组组成的最小数字-OD统一考试(B卷)
题目描述 给定一个整型数组,请从该数组中选择3个元素 组成最小数字并输出 (如果数组长度小于3,则选择数组中所有元素来组成最小数字)。 输入描述 行用半角逗号分割的字符串记录的整型数组,0<数组长度<= 100,0<整数的取值范围<= 10000。 输出描述 由3个元素组成…...
:工厂方法模式、单例模式和生成器模式)
上位机开发过程中的设计模式体会(1):工厂方法模式、单例模式和生成器模式
简介 在我的 QT/C 开发工作中,合理运用设计模式极大地提高了代码的可维护性和可扩展性。本文将分享我在实际项目中应用的三种创造型模式:工厂方法模式、单例模式和生成器模式。 1. 工厂模式 (Factory Pattern) 应用场景 在我的 QT 项目中曾经有一个需…...

CppCon 2015 学习:Time Programming Fundamentals
Civil Time 公历时间 特点: 共 6 个字段: Year(年)Month(月)Day(日)Hour(小时)Minute(分钟)Second(秒) 表示…...

在Zenodo下载文件 用到googlecolab googledrive
方法:Figshare/Zenodo上的数据/文件下载不下来?尝试利用Google Colab :https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1898503078782674027 参考: 通过Colab&谷歌云下载Figshare数据,超级实用!!࿰…...
Copilot for Xcode (iOS的 AI辅助编程)
Copilot for Xcode 简介Copilot下载与安装 体验环境要求下载最新的安装包安装登录系统权限设置 AI辅助编程生成注释代码补全简单需求代码生成辅助编程行间代码生成注释联想 代码生成 总结 简介 尝试使用了Copilot,它能根据上下文补全代码,快速生成常用…...
