python: Sorting Algorithms
# encoding: utf-8
# 版权所有 2023 涂聚文有限公司
# 许可信息查看:Python Sorting Algorithms
# 描述: * https://www.programiz.com/dsa/counting-sort
# * https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sorting-algorithms/
# Author : geovindu,Geovin Du 涂聚文.
# IDE : PyCharm 2023.1 python 311
# Datetime : 2023/9/21 21:55
# User : geovindu
# Product : PyCharm
# Project : EssentialAlgorithms
# File : SortingAlgorithms.py
# explain : 学习import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import itertools
import math
import sys
import os
from typing import Listclass SortingAlgorithms(object):"""排序算法"""def BubbleSort(array:list):"""1。Bubble Sort冒泡排序法:param array int数组:return:"""# loop to access each array elementfor i in range(len(array)):# loop to compare array elementsfor j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1):# compare two adjacent elements# change > to < to sort in descending orderif array[j] > array[j + 1]:# swapping elements if elements# are not in the intended ordertemp = array[j]array[j] = array[j + 1]array[j + 1] = tempdef BubbleSort2(array:list):"""1。Bubble Sort冒泡排序法:param array int数组:return:"""# loop through each element of arrayfor i in range(len(array)):# keep track of swappingswapped = False# loop to compare array elementsfor j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1):# compare two adjacent elements# change > to < to sort in descending orderif array[j] > array[j + 1]:# swapping occurs if elements# are not in the intended ordertemp = array[j]array[j] = array[j + 1]array[j + 1] = tempswapped = True# no swapping means the array is already sorted# so no need for further comparisonif not swapped:breakdef SelectionSort(array:list):"""2 python Program for Selection Sort 选择排序:param array int数组:return:"""for i in range(len(array)):# Find the minimum element in remaining# unsorted arraymin_idx = ifor j in range(i+1, len(array)):if array[min_idx] > array[j]:min_idx = j# Swap the found minimum element with# the first elementarray[i], array[min_idx] = array[min_idx], array[i]def InsertionSort(array:list):"""3 Insertion Sort插入排序:param array int数组:return:"""# Traverse through 1 to len(arr)for i in range(1, len(array)):key = array[i]# Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are# greater than key, to one position ahead# of their current positionj = i - 1while j >= 0 and key < array[j]:array[j + 1] = array[j]j -= 1array[j + 1] = keydef Partition(array, low, high):""":param array int数组:param low::param high::return:"""# Choose the rightmost element as pivotpivot = array[high]# Pointer for greater elementi = low - 1# Traverse through all elements# compare each element with pivotfor j in range(low, high):if array[j] <= pivot:# If element smaller than pivot is found# swap it with the greater element pointed by ii = i + 1# Swapping element at i with element at j(array[i], array[j]) = (array[j], array[i])# Swap the pivot element with# the greater element specified by i(array[i + 1], array[high]) = (array[high], array[i + 1])# Return the position from where partition is donereturn i + 1def QuickSort(array, low, high):"""4 Quick Sort 快速排序:param array int数组:param low::param high::return:"""if low < high:# Find pivot element such that# element smaller than pivot are on the left# element greater than pivot are on the rightpi = SortingAlgorithms.Partition(array, low, high)# Recursive call on the left of pivotSortingAlgorithms.QuickSort(array, low, pi - 1)# Recursive call on the right of pivotSortingAlgorithms.QuickSort(array, pi + 1, high)def MergeSort(array:list):"""5 Merge Sort 合并/归并排序:param array int数组:return:"""if len(array) > 1:# Finding the mid of the arraymid = len(array) // 2# Dividing the array elementsL = array[:mid]# Into 2 halvesR = array[mid:]# Sorting the first halfSortingAlgorithms.MergeSort(L)# Sorting the second halfSortingAlgorithms.MergeSort(R)i = j = k = 0# Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[]while i < len(L) and j < len(R):if L[i] <= R[j]:array[k] = L[i]i += 1else:array[k] = R[j]j += 1k += 1# Checking if any element was leftwhile i < len(L):array[k] = L[i]i += 1k += 1while j < len(R):array[k] = R[j]j += 1k += 1def CountingSort(array:list,hight:int):"""6 Counting Sort 计数排序:param array int数组:param hight 最大的整数 如100,数组中必须小数此数的整数:return:"""size = len(array)output = [0] * size# Initialize count arraydcount = [0] * hight# Store the count of each elements in count arrayprint(size)for i in range(0, size):dcount[array[i]] += 1# Store the cummulative count 最大的数for i in range(1, hight):dcount[i] += dcount[i - 1]# Find the index of each element of the original array in count array# place the elements in output arrayi = size - 1while i >= 0:output[dcount[array[i]] - 1] = array[i]dcount[array[i]] -= 1i -= 1# Copy the sorted elements into original arrayfor i in range(0, size):array[i] = output[i]def CountingSortTo(array: List[int]):"""6 Counting Sort 计数排序:param:return:"""max = min = 0for i in array:if i < min:min = iif i > max:max = icount = [0] * (max - min + 1)for j in range(max - min + 1):count[j] = 0for index in array:count[index - min] += 1index = 0for a in range(max - min + 1):for c in range(count[a]):array[index] = a + minindex += 1def countingSort(array, exp1):""":param array:param exp1::return:"""n = len(array)# The output array elements that will have sorted arroutput = [0] * (n)# initialize count array as 0count = [0] * (10)# Store count of occurrences in count[]for i in range(0, n):index = array[i] // exp1count[index % 10] += 1# Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual# position of this digit in output arrayfor i in range(1, 10):count[i] += count[i - 1]# Build the output arrayi = n - 1while i >= 0:index = array[i] // exp1output[count[index % 10] - 1] = array[i]count[index % 10] -= 1i -= 1# Copying the output array to arr[],# so that arr now contains sorted numbersi = 0for i in range(0, len(array)):array[i] = output[i]def RadixSort(array:list):"""7 Radix Sort 基数排序:param array:return:"""# Find the maximum number to know number of digitsmax1 = max(array)# Do counting sort for every digit. Note that instead# of passing digit number, exp is passed. exp is 10^i# where i is current digit numberexp = 1while max1 / exp >= 1:SortingAlgorithms.countingSort(array, exp)exp *= 10def insertionSort(array:list):""":return:"""for i in range(1, len(array)):up = array[i]j = i - 1while j >= 0 and array[j] > up:array[j + 1] = array[j]j -= 1array[j + 1] = upreturn arraydef BucketSort(array):"""8 Bucket Sort 桶排序:param array:return:"""arr = []slot_num = 10 # 10 means 10 slots, each# slot's size is 0.1for i in range(slot_num):arr.append([])# Put array elements in different bucketsfor j in array:index_b = int(slot_num * j)arr[index_b].append(j)# Sort individual bucketsfor i in range(slot_num):arr[i] = SortingAlgorithms.insertionSort(arr[i])# concatenate the resultk = 0for i in range(slot_num):for j in range(len(arr[i])):array[k] = arr[i][j]k += 1return array# Bucket Sort in Pythondef BucketSortTo(array:list):"""8 Bucket Sort 桶排序:param array:return:"""bucket = []# Create empty bucketsfor i in range(len(array)):bucket.append([])# Insert elements into their respective bucketsfor j in array:index_b = int(10 * j)bucket[index_b].append(j)# Sort the elements of each bucketfor i in range(len(array)):bucket[i] = sorted(bucket[i])# Get the sorted elementsk = 0for i in range(len(array)):for j in range(len(bucket[i])):array[k] = bucket[i][j]k += 1return arraydef heapify(array:list, Nsize:int, index:int):""":param array 数组:param Nsize: 数组长度:param index: 索引号:return:"""largest = index # Initialize largest as rootl = 2 * index + 1 # left = 2*i + 1r = 2 * index + 2 # right = 2*i + 2# See if left child of root exists and is# greater than rootif l < Nsize and array[largest] < array[l]:largest = l# See if right child of root exists and is# greater than rootif r < Nsize and array[largest] < array[r]:largest = r# Change root, if neededif largest != index:array[index], array[largest] = array[largest], array[index] # swap# Heapify the root.SortingAlgorithms.heapify(array, Nsize, largest)# The main function to sort an array of given sizedef HeapSort(array:list):"""9 Heap Sort 堆排序:param array:return:"""Nsize = len(array)# Build a maxheap.for i in range(Nsize // 2 - 1, -1, -1):SortingAlgorithms.heapify(array, Nsize, i)# One by one extract elementsfor i in range(Nsize - 1, 0, -1):array[i], array[0] = array[0], array[i] # swapSortingAlgorithms.heapify(array, i, 0)def ShellSort(array:list):"""10 Shell Sort 希尔排序:param array 数组:return:"""# code herenszie=len(array)gap = nszie // 2while gap > 0:j = gap# Check the array in from left to right# Till the last possible index of jwhile j < nszie:i = j - gap # This will keep help in maintain gap valuewhile i >= 0:# If value on right side is already greater than left side value# We don't do swap else we swapif array[i + gap] > array[i]:breakelse:array[i + gap], array[i] = array[i], array[i + gap]i = i - gap # To check left side also# If the element present is greater than current elementj += 1gap = gap // 2def LinearSearch(array:list,fint:int):"""11 Linear Search线性搜索:param array 整数数组:param fint 要查找的数字:return:"""nsize=len(array)# Going through array sequenciallyfor i in range(0, nsize):if (array[i] == fint):return i #找到了return -1 #未找到def BinarySearch(array:list, x, low, high):"""12 Binary Search 二分查找:param x::param low::param high::return:"""if high >= low:mid = low + (high - low) // 2# If found at mid, then return itif array[mid] == x:return mid# Search the left halfelif array[mid] > x:return SortingAlgorithms.BinarySearch(array, x, low, mid - 1)# Search the right halfelse:return SortingAlgorithms.BinarySearch(array, x, mid + 1, high)else:return -1def BingoSort(array, size):""":param array:param size::return:"""# Finding the smallest element From the Arraybingo = min(array)# Finding the largest element from the Arraylargest = max(array)nextBingo = largestnextPos = 0while bingo < nextBingo:# Will keep the track of the element position to# shifted to their correct positionstartPos = nextPosfor i in range(startPos, size):if array[i] == bingo:array[i], array[nextPos] = array[nextPos], array[i]nextPos += 1# Here we are finding the next Bingo Element# for the next passelif array[i] < nextBingo:nextBingo = array[i]bingo = nextBingonextBingo = largest# encoding: utf-8
# 版权所有 2023 涂聚文有限公司
# 许可信息查看:
# 描述:
# Author : geovindu,Geovin Du 涂聚文.
# IDE : PyCharm 2023.1 python 311
# Datetime : 2023/9/21 22:00
# User : geovindu
# Product : PyCharm
# Project : EssentialAlgorithms
# File : SortingExample.py
# explain : 学习import ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithmsclass Example(object):""""实例"""def Bubble(self):"""1。Bubble Sort冒泡排序法:return:"""data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.BubbleSort(data)print('\n1 冒泡排序法 Bubble Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')for i in range(len(data)):print("%d" % data[i], end=" ")def Select(self):"""2 Selection Sort 选择排序:return:"""geovindu = [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.SelectionSort(geovindu)print("\n2 选择排序Selection Sorted ")for i in range(len(geovindu)):print("%d" % geovindu[i], end=" ")def Insert(self):"""3 Insertion Sort插入排序:return:"""arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6]ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.InsertionSort(arr)print("\n3 插入排序 Insertion Sorted ")for i in range(len(arr)):print("% d" % arr[i], end=" ")def Quick(self):"""4 Quick Sort 快速排序:return:"""array = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]N = len(array)# Function callChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.QuickSort(array, 0, N - 1)print("\n4 快速排序 Quick Sorted ")for x in array:print(x, end=" ")def Merge(self):"""5 Merge Sort 合并/归并排序:return:"""geovindu = [12, 11, 99, 13, 5, 6, 7,88,100]ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.MergeSort(geovindu)print("\n5 合并/归并排序 Merge Sorted ")for x in geovindu:print(x, end=" ")def Counting(self):"""6 Counting Sort 计数排序:return:"""geovindu = [17, 56, 71, 38, 61, 62, 48, 28, 57, 42]ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.CountingSortTo(geovindu)print("\n6 计数排序 Counting Sorted ")print(geovindu)for i in range(0,len(geovindu)):print("% d" % geovindu[i], end=" ")geovindu = [4, 55, 22, 98, 9, 43, 11]ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.CountingSort(geovindu, 100)print("\n6 计数排序 Counting Sorted ")for x in geovindu:print(x, end=" ")def Radix(self):"""7 Radix Sort 基数排序:return:"""geovindu = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66]print("\n7 基数排序 Radix Sorted ")# Function CallChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.RadixSort(geovindu)for i in range(len(geovindu)):print(geovindu[i], end=" ")def Bucket(self):"""8 Bucket Sort 桶排序:return:"""#geovindu = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66]geovindu = [0.897, 0.565, 0.656,0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434]print("\n8 桶排序 Bucket Sorted ")# Function Calldu=ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.BucketSort(geovindu)for i in range(len(du)):print(du[i], end=" ")def Heap(self):"""9 Heap Sort 堆排序:return:"""geovindu = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66]print("\n9 堆排序 Heap Sorted ")# Function CallChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.HeapSort(geovindu)for i in range(len(geovindu)):print(geovindu[i], end=" ")def Shell(self):"""10 Shell Sort 希尔排序:return:"""geovindu = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66]print("\n10 希尔排序 Shell Sorted ")# Function CallChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.ShellSort(geovindu)for i in range(len(geovindu)):print(geovindu[i], end=" ")def Linear(self):"""11 Linear Search 线性搜索:return:"""array = [2, 4, 8,0, 1, 9]x = 8n = len(array)result = ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.LinearSearch(array,x)print("\n11 线性搜索 Linear Search ")if (result == -1):print("Element not found")else:print("Element found at index: ", result)def Binary(self):"""12 Binary Search 二分查找:return:"""array = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]x = 4result = ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.BinarySearch(array, x, 0, len(array) - 1)print("\n12 二分查找 Binary Search ")if result != -1:print("Element is present at index " + str(result))else:print("Not found")def Bingo(self):"""13 Bingo Sort:return:"""arr = [5, 4, 8, 5, 4, 8, 5, 4, 4, 4]ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.BingoSort(arr, size=len(arr))print("\n13 Bingo Sorted ")for i in range(len(arr)):print(arr[i], end=" ")
调用:
exm=BLL.SortingExample.Example()exm.Bubble()exm.Select()exm.Insert()exm.Quick()exm.Merge()exm.Counting()exm.Radix()exm.Bucket()exm.Heap()exm.Shell()exm.Linear()exm.Binary()exm.Bingo()相关文章:

python: Sorting Algorithms
# encoding: utf-8 # 版权所有 2023 涂聚文有限公司 # 许可信息查看:Python Sorting Algorithms # 描述: * https://www.programiz.com/dsa/counting-sort # * https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sorting-algorithms/ # Author : geovindu,Geovin Du 涂…...

Python 安装js环境
在终端执行下面的命令 npm install jsdom jsdom 是一个实现了 DOM API 的 JavaScript 环境,用于在 Node.js 中模拟浏览器的 DOM 环境。execjs 使用 jsdom 这个模块来执行 JavaScript 代码。所以在你的系统中,需要先安装并配置好 jsdom 模块,…...
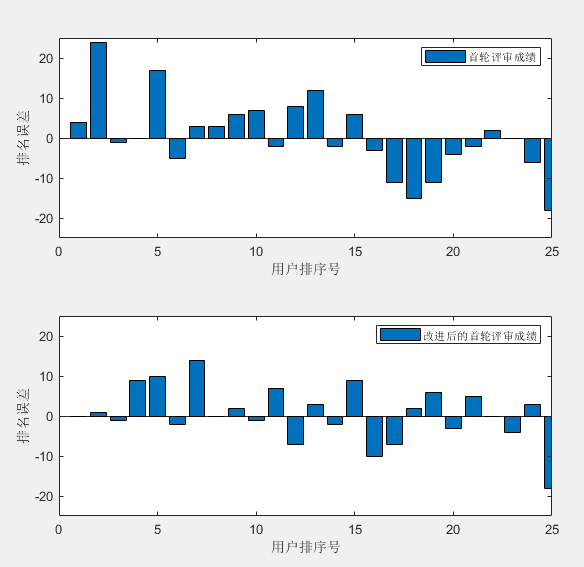
2023华为杯数模C题——大规模创新类竞赛评审方案研究
B题——大规模创新类竞赛评审方案研究 思路:采用数据分析等手段改进评分算法性能 完成情况(1-2问已经完成) 代码下载 问题一 在每个评审阶段,作品通常都是随机分发的,每份作品需要多位评委独立评审。为了增加不同评审专家所给成绩之间的可比…...
人工神经网络ANN:数学总结
一、内容 径向基函数(Radial basis function,RBF):一个取值仅依赖于到原点距离的实值函数,即。此外,也可以按到某一中心点c的距离来定义,即。 可以用于许多向函基数的和来逼近某一给定的函数&a…...
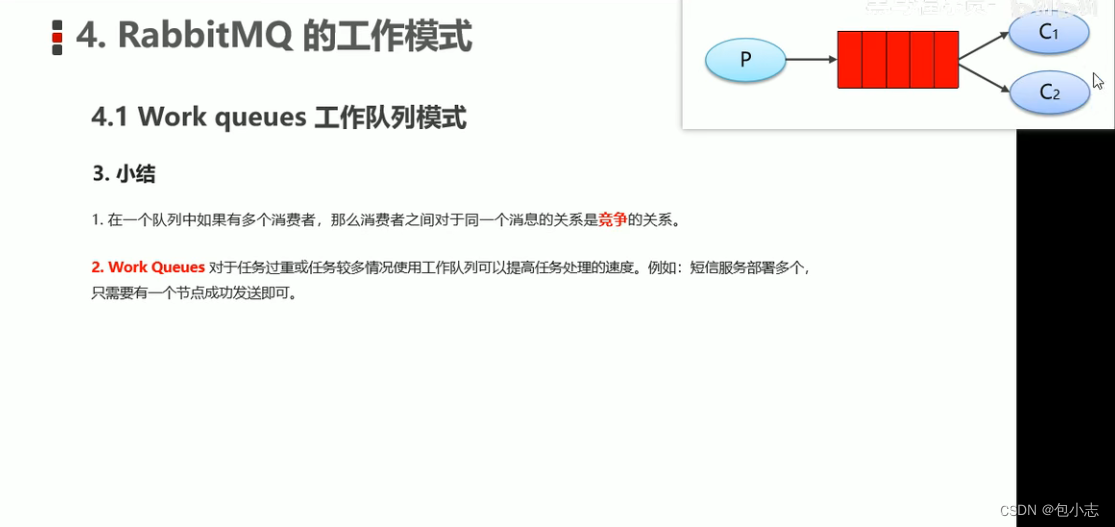
RabbitMQ的工作模式——WorkQueues
1.工作队列模式 生产者代码 public class Producer_WorkQueues1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {//1.创建连接工厂ConnectionFactory factory new ConnectionFactory();//2.设置参数factory.setHost("172.16.98.133&qu…...

AOJ 0531 坐标离散化
一、题目大意 在(0<x<w,0<y<h)的坐标系里有多个矩形,把区域分成了多个部分,我们需要针对找出被矩形分割的连通的区块数量。 二、解题思路 这个题目其实和学DFS时候那个找出连通的水洼是一样的。只是这个地图比较大,…...
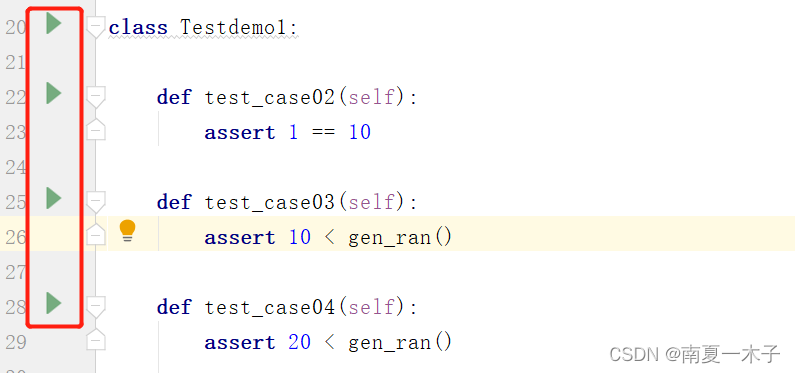
Python —— pytest框架
1、认识pytest框架 1、搭建自动化框架的思路与流程 1、搭建自动化测试框架的思路和流程,任意测试手段流程都是一致的:手工测试、自动化测试、工具测试 手工测试:熟悉业务 —— 写用例 —— 执行用例并记录结果 —— 生成测试报告自动化测试…...

IP地址欺骗的危害与后果
IP地址欺骗,也被称为IP地址伪装或IP地址欺诈,是一种网络攻击技术,旨在伪装或隐藏攻击者的真实IP地址。尽管这种技术可能有一些合法的用途,例如保护用户的隐私或绕过地理位置限制,但它也经常被恶意黑客用于不法行为。本…...
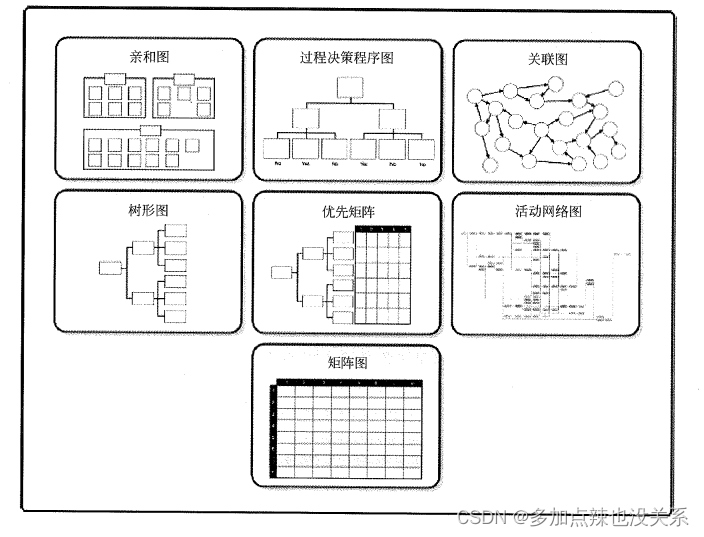
系统集成|第十章(笔记)
目录 第十章 质量管理10.1 项目质量管理概论10.2 主要过程10.2.1 规划质量管理10.2.2 实施质量保证10.2.3 质量控制 10.3 常见问题 上篇:第九章、成本管理 第十章 质量管理 10.1 项目质量管理概论 质量管理:指确定质量方针,质量目标和职责&a…...
配置)
Linux之perf(7)配置
Linux之perf(7)配置类命令 Author:Onceday Date:2023年9月23日 漫漫长路,才刚刚开始… 注:该文档内容采用了GPT4.0生成的回答,部分文本准确率可能存在问题。 参考文档: Tutorial - Perf Wiki (kernel.org)perf(1)…...
14:00面试,14:06就出来了,问的问题过于变态了。。。
从小厂出来,没想到在另一家公司又寄了。 到这家公司开始上班,加班是每天必不可少的,看在钱给的比较多的份上,就不太计较了。没想到5月一纸通知,所有人不准加班,加班费不仅没有了,薪资还要降40%…...
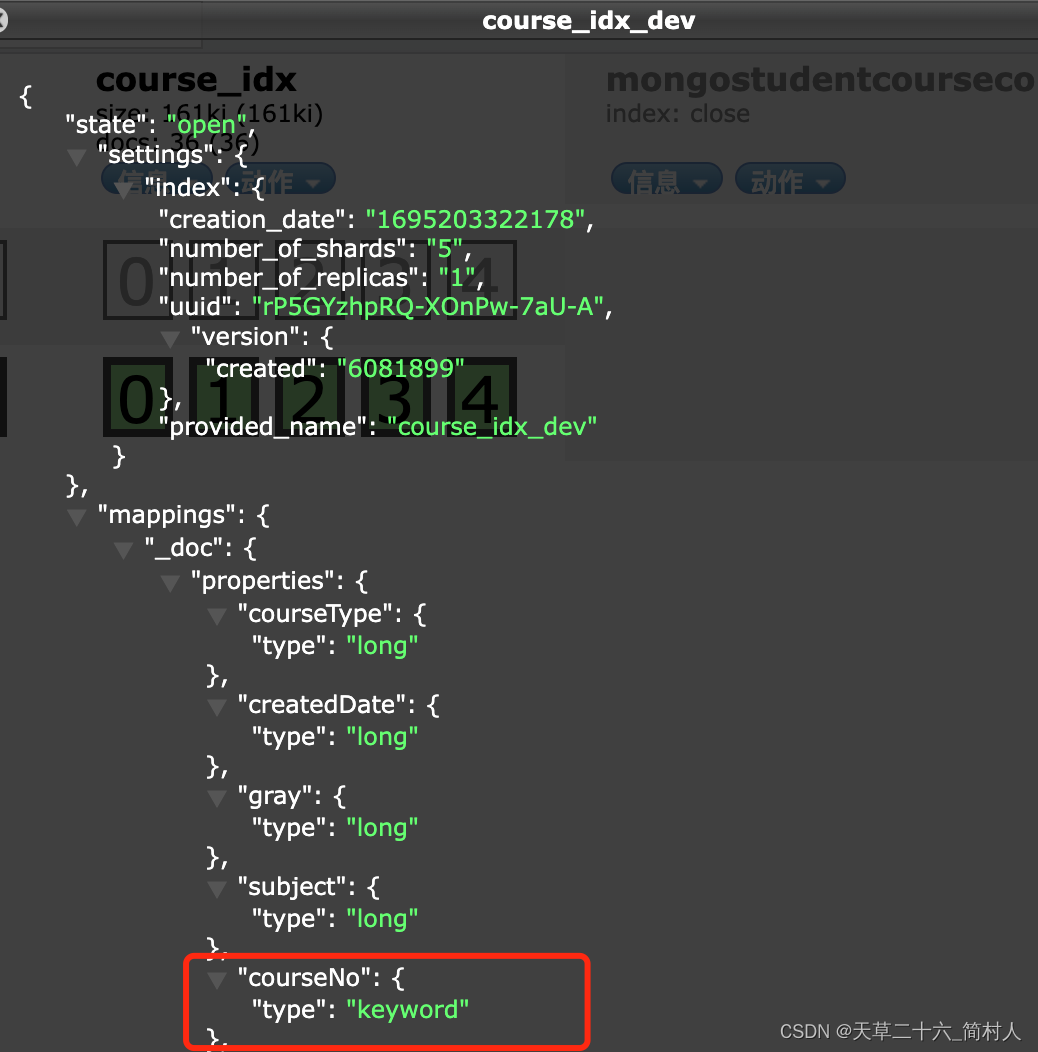
JPA的注解@Field指定为Keyword失败,导致查询不到数据
一、背景 使用 jpa 对es操作,查询条件不生效,需求是批量查询课程编号。说白了,就是一个In集合的查询。在es里,如果是精准匹配是termQuery,比如: queryBuilder.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery(“schoolId…...

多线程带来的的风险-线程安全
多线程带来的的风险-线程安全 ~~ 多线程编程中,最难的地方,也是一个最重要的地方,还是一个最容易出错的地方,更是一个面试中特别爱考的地方.❤️❤️❤️ 线程安全的概念 万恶之源,罪魁祸首是多线程的抢占式执行,带来的随机性.~~😕😕&…...

Kafka 面试题
Kafka 面试题 Q:讲一下Kafka。 Kafka 入门一篇文章就够了 Kafka的简单理解 Q:消息队列,有哪些使用场景及用途? 解耦,削峰,限流。 Q:Kafka相对其他消息队列,有什么特点? 持久化:Kafka的持久化…...
离线部署 python 3.x 版本
文章目录 离线部署 python 3.x 版本1. 下载版本2. 上传到服务器3. 解压并安装4. 新建软连信息5. 注意事项 离线部署 python 3.x 版本 1. 下载版本 python 各版本下载地址 本次使用版本 Python-3.7.0a2.tgz # linux 可使用 wget 下载之后上传到所需服务器 wget https://www.py…...

Java 获取豆瓣电影TOP250
对于爬虫,Java并不是最擅长的,但是也可以实现,此次主要用到的包有hutool和jsoup。 hutool是一个Java工具包,它简化了Java的各种API操作,包括文件操作、类型转换、HTTP、日期处理、JSON处理、加密解密等。它的目标是使…...
)
笔试面试相关记录(5)
(1)不包含重复字符的最长子串的长度 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map>using namespace std;int getMaxLength(string& s) {int len s.size();map<char, int> mp;int max_len 0;int left 0;int i …...
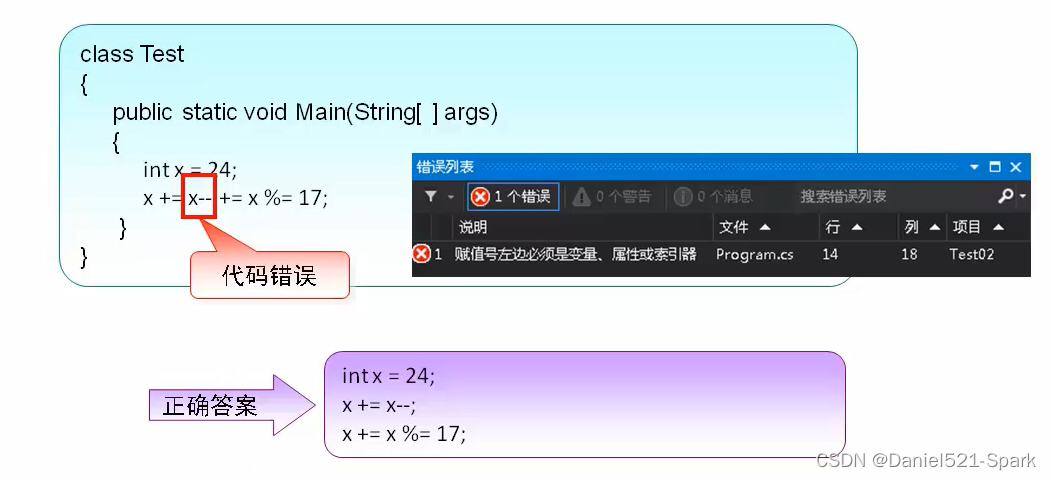
四、C#—变量,表达式,运算符(2)
🌻🌻 目录 一、表达式1.1 什么是表达式1.2 表达式的基本组成 二、运算符2.1 算术运算符2.1.1 使用 / 运算符时的注意事项2.1.2 使用%运算符时的注意事项 2.2 赋值运算符2.2.1 简单赋值运算符2.2.2 复合赋值运算符 2.3 关系运算符2.4 逻辑运算符2.4.1 逻辑…...
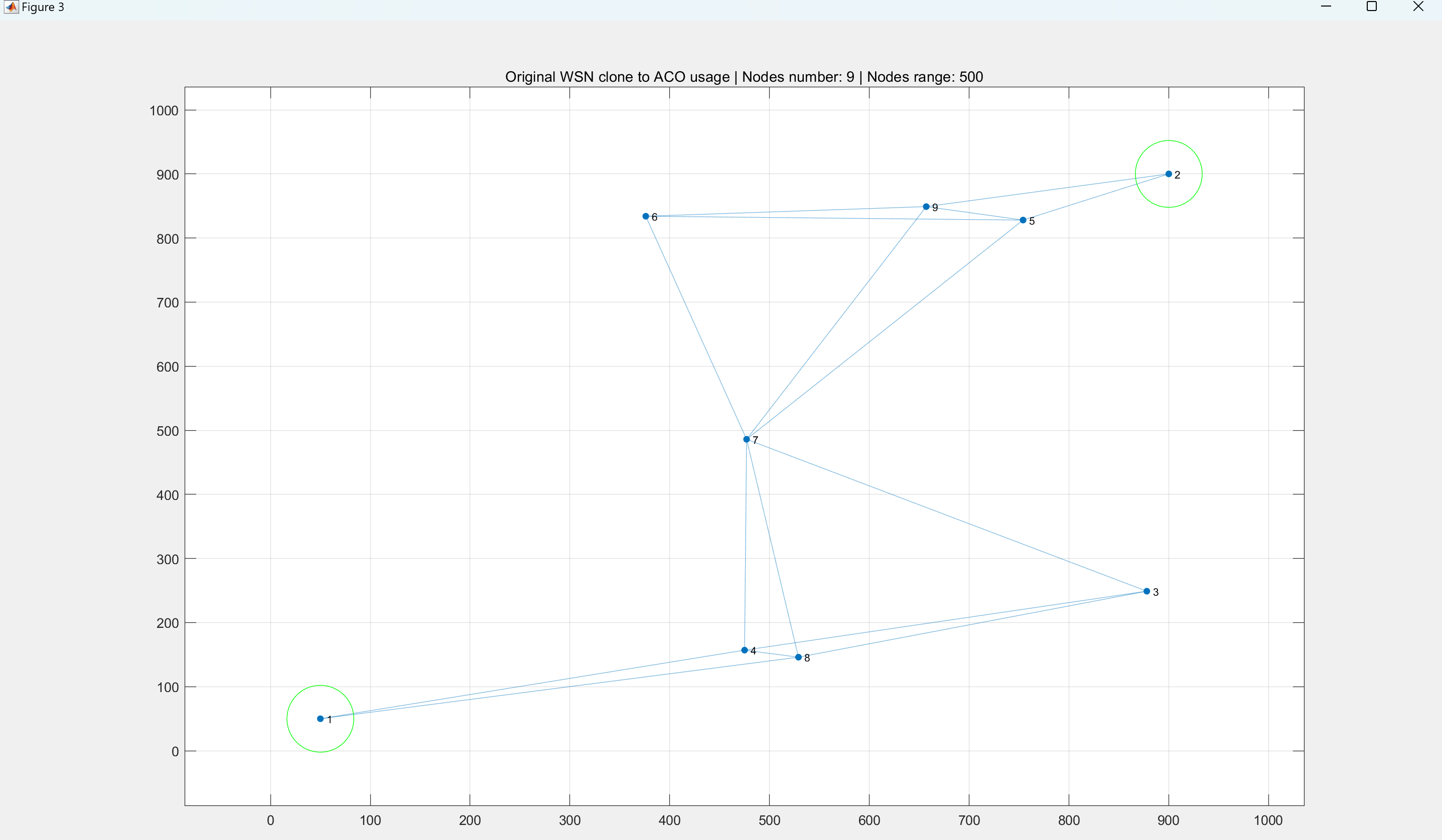
【WSN】基于蚁群算法的WSN路由协议(最短路径)消耗节点能量研究(Matlab代码实现)
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥 🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。 ⛳️座右铭&a…...
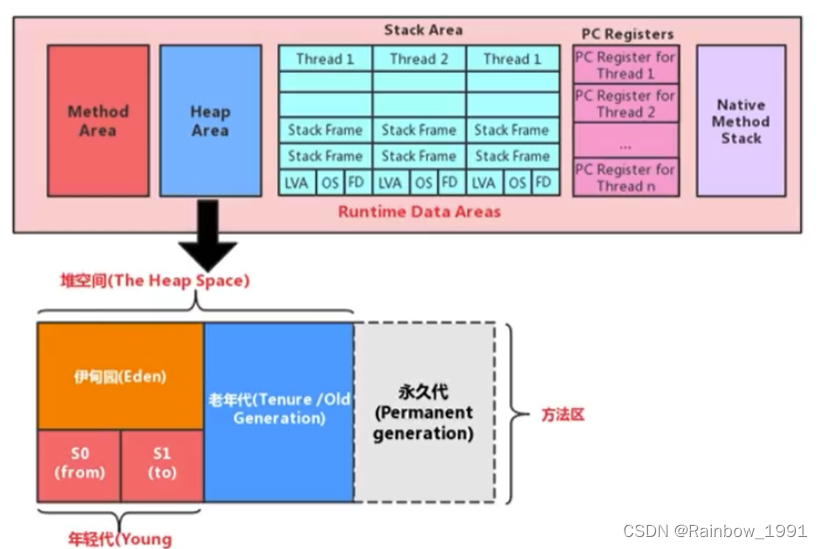
JVM的内存分配及垃圾回收
内存分配 在了解Java的内存管理前,需要知道JVM中的内存分配。 栈 存储局部变量。在方法的定义中或在方法中声明的变量为局部变量;栈内存中的数据在该方法结束(返回或抛出异常或方法体运行到最后)时自动释放栈中存放的数据结构为…...
)
椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)
一、ECC算法概述 椭圆曲线密码学(Elliptic Curve Cryptography)是基于椭圆曲线数学理论的公钥密码系统,由Neal Koblitz和Victor Miller在1985年独立提出。相比RSA,ECC在相同安全强度下密钥更短(256位ECC ≈ 3072位RSA…...
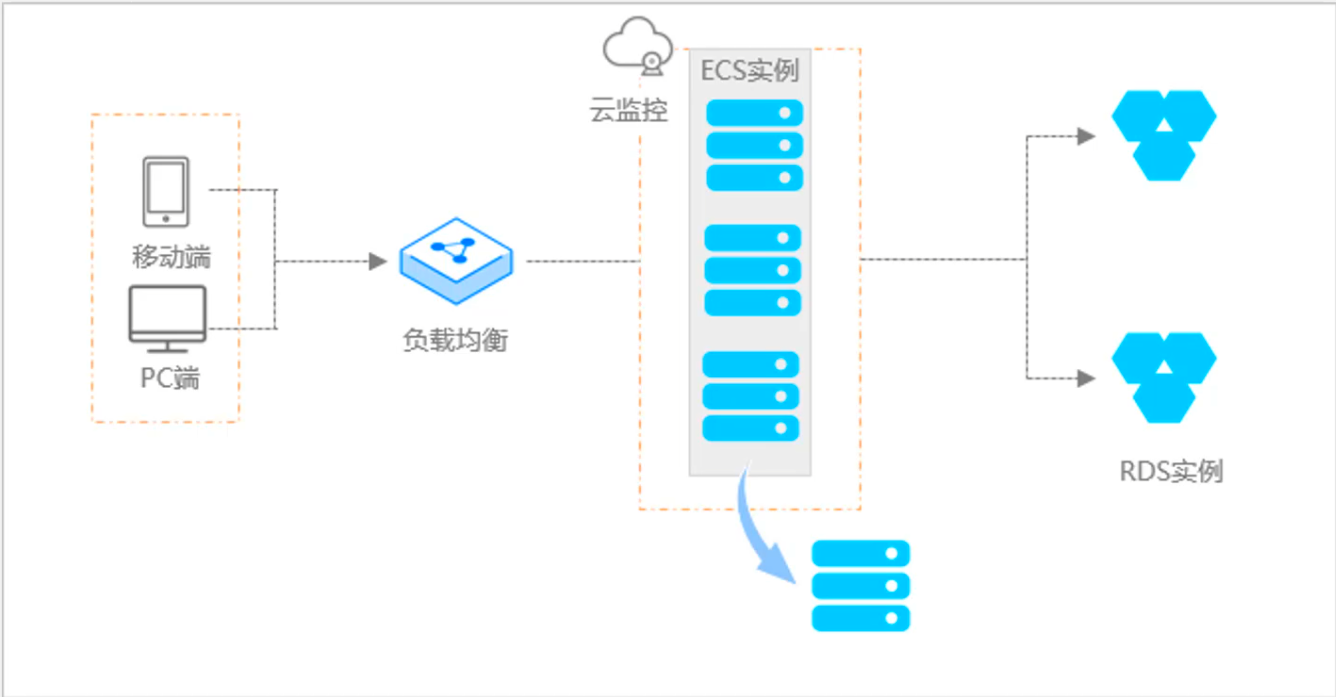
阿里云ACP云计算备考笔记 (5)——弹性伸缩
目录 第一章 概述 第二章 弹性伸缩简介 1、弹性伸缩 2、垂直伸缩 3、优势 4、应用场景 ① 无规律的业务量波动 ② 有规律的业务量波动 ③ 无明显业务量波动 ④ 混合型业务 ⑤ 消息通知 ⑥ 生命周期挂钩 ⑦ 自定义方式 ⑧ 滚的升级 5、使用限制 第三章 主要定义 …...
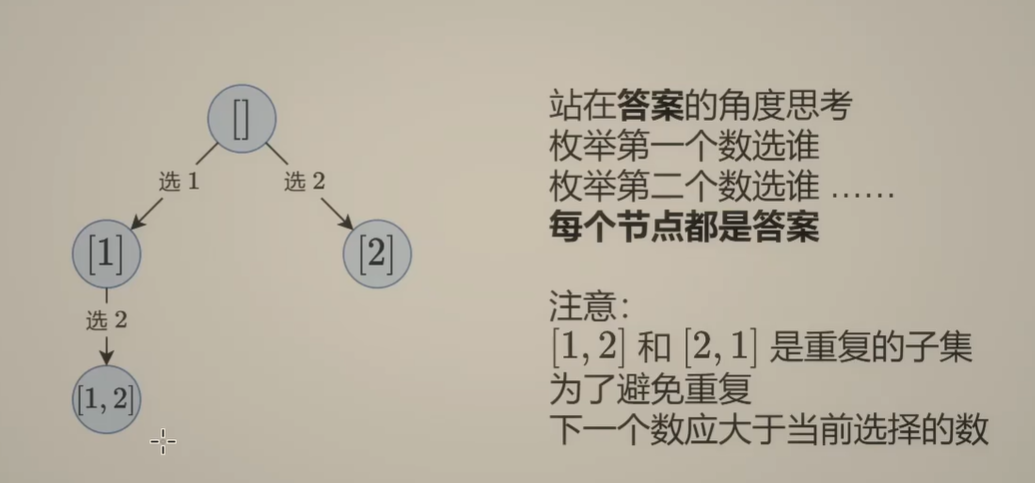
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...

java调用dll出现unsatisfiedLinkError以及JNA和JNI的区别
UnsatisfiedLinkError 在对接硬件设备中,我们会遇到使用 java 调用 dll文件 的情况,此时大概率出现UnsatisfiedLinkError链接错误,原因可能有如下几种 类名错误包名错误方法名参数错误使用 JNI 协议调用,结果 dll 未实现 JNI 协…...
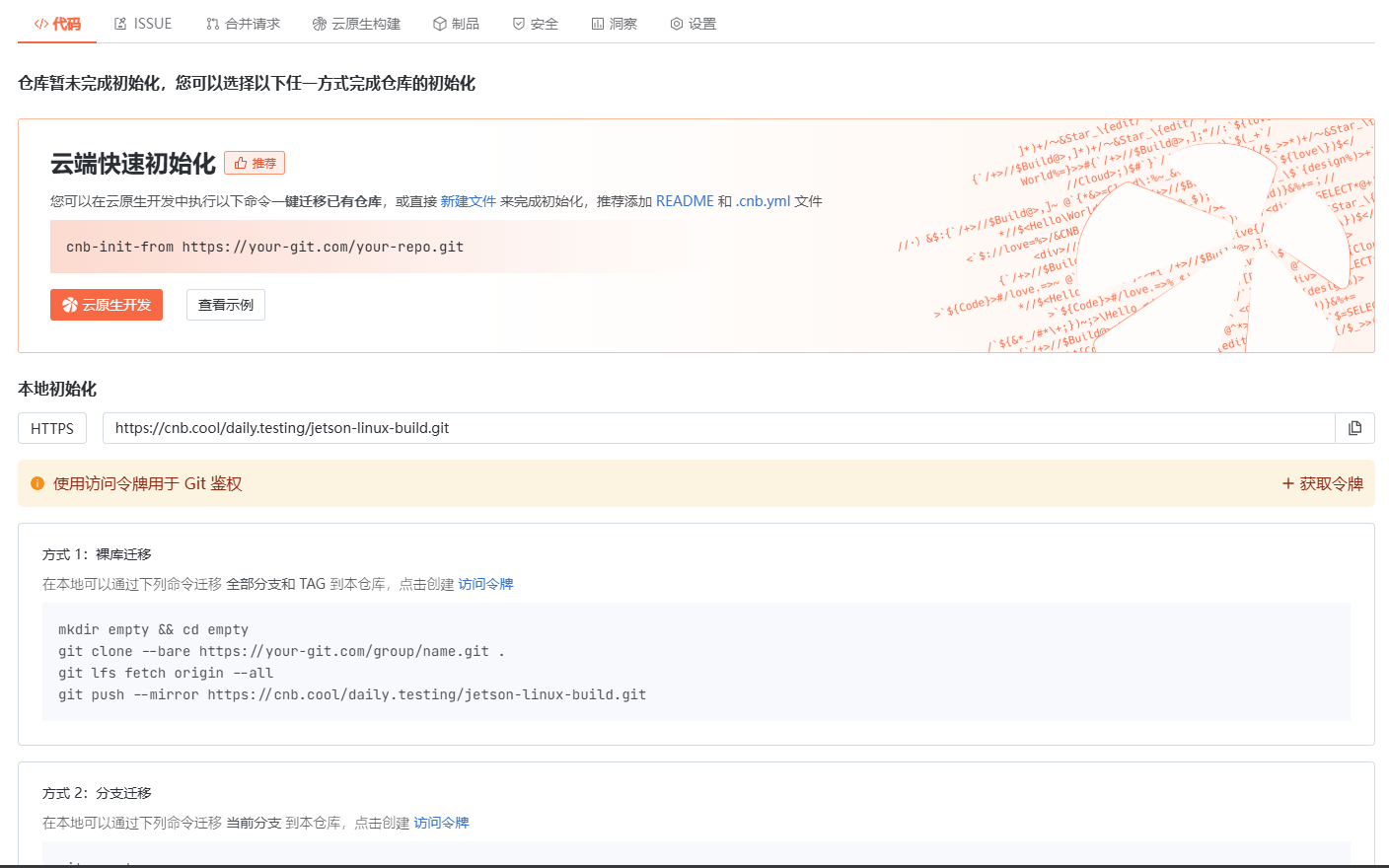
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境 引言 临时运维一个古董项目,无文档,无环境,无交接人,俗称三无。 运行设备的环境老,本地环境版本高,ssh不过去。正好最近对 腾讯出品的云原生 cnb 感兴趣&…...
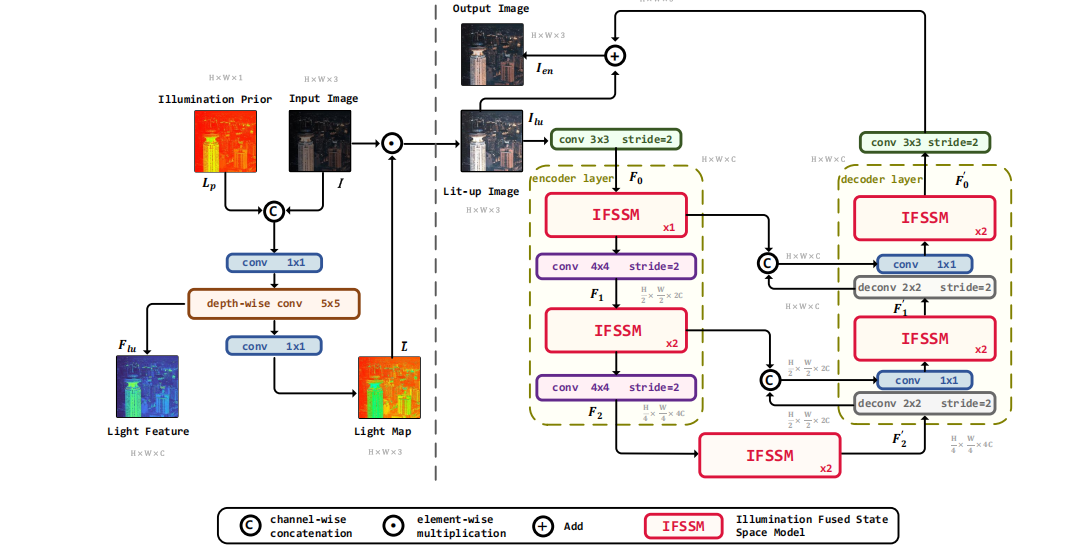
深度学习水论文:mamba+图像增强
🧀当前视觉领域对高效长序列建模需求激增,对Mamba图像增强这方向的研究自然也逐渐火热。原因在于其高效长程建模,以及动态计算优势,在图像质量提升和细节恢复方面有难以替代的作用。 🧀因此短时间内,就有不…...
【C++特殊工具与技术】优化内存分配(一):C++中的内存分配
目录 一、C 内存的基本概念 1.1 内存的物理与逻辑结构 1.2 C 程序的内存区域划分 二、栈内存分配 2.1 栈内存的特点 2.2 栈内存分配示例 三、堆内存分配 3.1 new和delete操作符 4.2 内存泄漏与悬空指针问题 4.3 new和delete的重载 四、智能指针…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中使用DevEco Studio实现企业微信功能
1. 开发环境准备 安装DevEco Studio 3.1: 从华为开发者官网下载最新版DevEco Studio安装HarmonyOS 5.0 SDK 项目配置: // module.json5 {"module": {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permis…...
给网站添加live2d看板娘
给网站添加live2d看板娘 参考文献: stevenjoezhang/live2d-widget: 把萌萌哒的看板娘抱回家 (ノ≧∇≦)ノ | Live2D widget for web platformEikanya/Live2d-model: Live2d model collectionzenghongtu/live2d-model-assets 前言 网站环境如下,文章也主…...
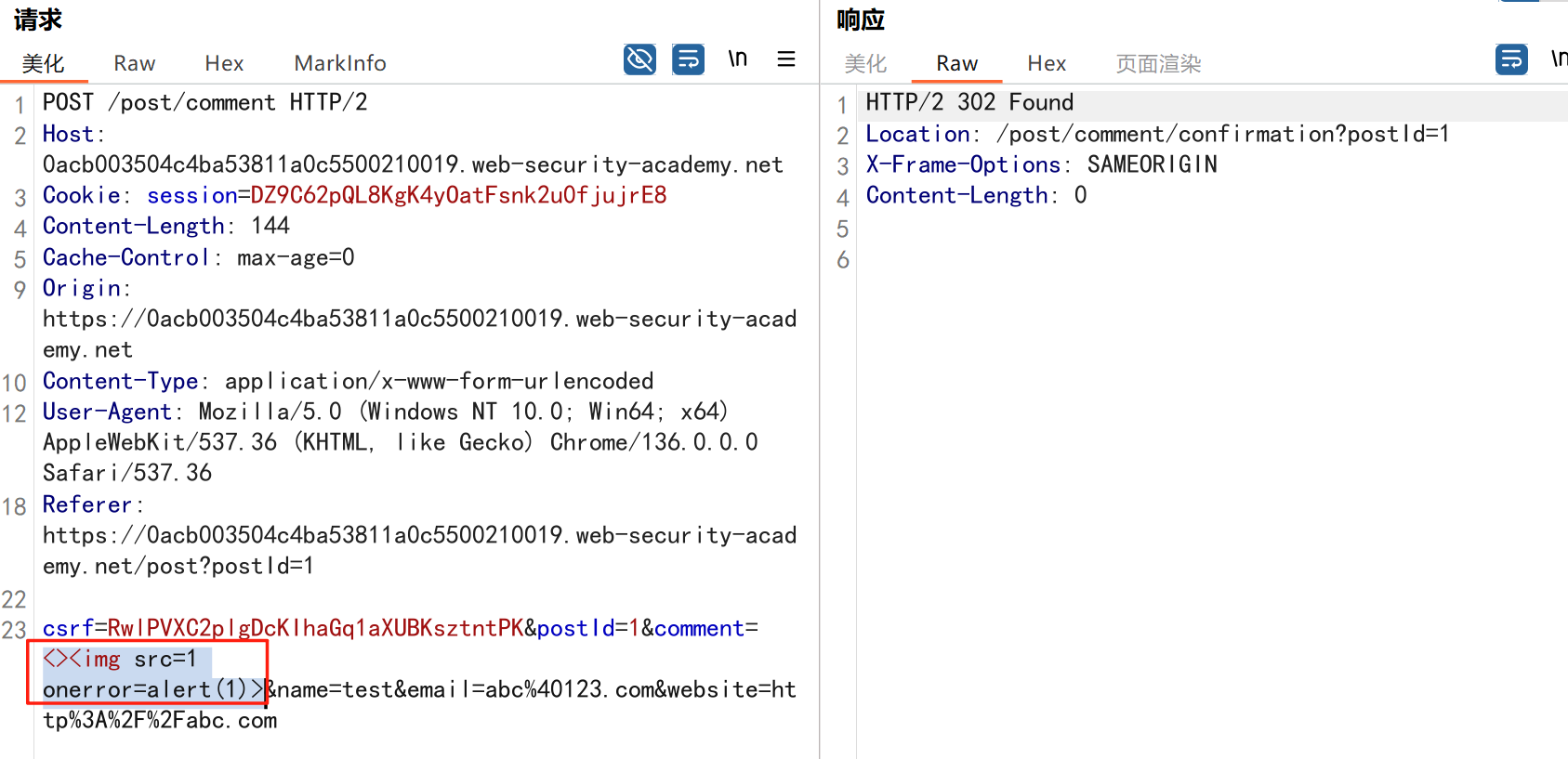
渗透实战PortSwigger靶场:lab13存储型DOM XSS详解
进来是需要留言的,先用做简单的 html 标签测试 发现面的</h1>不见了 数据包中找到了一个loadCommentsWithVulnerableEscapeHtml.js 他是把用户输入的<>进行 html 编码,输入的<>当成字符串处理回显到页面中,看来只是把用户输…...
