单目3D目标检测——SMOKE 模型推理 | 可视化结果
本文分享SMOKE的模型推理,和可视化结果。以kitti数据集为例子,对训练完的模型进行推理,并可视化3D框的结果,画到图像中。
关于模型原理、搭建开发环境、模型训练,可以参考之前的博客:
【论文解读】SMOKE 单目相机 3D目标检测(CVPR2020)_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客_smoke 论文
CVPR2020 SMOKE 单目相机 3D目标检测【环境搭建篇】_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客
单目3D目标检测——SMOKE 环境搭建|模型训练_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客

一、模型训练
模型训练的轮数,建议参考官方的25000轮,然后获得模型训练产出:
last_checkpoint 指定模型权重路径
log.txt 记录训练过程的日志信息
model_0010000.pth 模型训练10000轮保持的权重
model_0018000.pth 模型训练18000轮保持的权重
model_final.pth 模型训练结束 保持的权重(25000轮)
当然可以调整训练的配置文件 configs/smoke_gn_vector.yaml
MAX_ITERATION,这里官网的训练轮数是25000次,训练完模型效果还行。
IMS_PER_BATCH,批量大小是32,显存没这么大,可以改小一些。
STEPS,是训练过程中,在多少轮时,保存模型的权重;默认是10000轮、18000轮,自行修改。
其它的根据任务情况,修改即可。
二、模型推理
在last_checkpoint 文件会指定模型推理权重路径,默认是:
./tools/logs/model_final.pth
可以根据权重的名称和路径,自行修改。
使用以下命令进行模型推理
python tools/plain_train_net.py --eval-only --config-file "configs/smoke_gn_vector.yaml"成功执行后,会在 tools/logs 目录中,生成一个inference目录,存放kitti testing的推理结果
000000.txt
000001.txt
......
007517.txt
三、可视化结果
首先观察inference目录的txt文件,以为000001.txt例
Car 0 0 0.47040000557899475 142.83970642089844 181.67050170898438 348.4837951660156 249.11219787597656 1.5202000141143799 1.6481000185012817 4.1107001304626465 -8.623299598693848 1.7422000169754028 17.326099395751953 0.00860000029206276 0.4050000011920929
Car 0 0 -1.8617000579833984 9.46560001373291 176.27439880371094 213.91610717773438 291.6900939941406 1.4990999698638916 1.6033999919891357 3.7634999752044678 -7.857800006866455 1.5611000061035156 11.27649974822998 -2.4702999591827393 0.40119999647140503
其实生成的结果,和kitii标签格式是一致的。
然后准备kitii testing的相机标定参数,实现可视化3D框的结果,画到图像中。代码的目录结构

其中dataset目录的结构如下:

我们需要存放calib 相机标定文件、imges_2 testing的图像、label_2 复制inference下的txt到里面。
主代码 kitti_3d_vis.py
# kitti_3d_vis.pyfrom __future__ import print_functionimport os
import sys
import cv2
import random
import os.path
import shutil
from PIL import Image
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = os.path.dirname(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'mayavi'))
from kitti_util import *def visualization():import mayavi.mlab as mlabdataset = kitti_object(r'./dataset/')path = r'./dataset/testing/label_2/'Save_Path = r'./save_3d_output/'files = os.listdir(path)for file in files:name = file.split('.')[0]save_path = Save_Path + name + '.png'data_idx = int(name)# Load data from datasetobjects = dataset.get_label_objects(data_idx)img = dataset.get_image(data_idx)img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)calib = dataset.get_calibration(data_idx)print(' ------------ save image with 3D bounding box ------- ')print('name:', name)show_image_with_boxes(img, objects, calib, save_path, True)if __name__=='__main__':visualization()依赖代码 kitti_util.py
# kitti_util.pyfrom __future__ import print_functionimport os
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = os.path.dirname(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'mayavi'))class kitti_object(object):def __init__(self, root_dir, split='testing'):self.root_dir = root_dirself.split = splitself.split_dir = os.path.join(root_dir, split)if split == 'training':self.num_samples = 7481elif split == 'testing':self.num_samples = 7518else:print('Unknown split: %s' % (split))exit(-1)self.image_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'image_2')self.calib_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'calib')self.label_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'label_2')def __len__(self):return self.num_samplesdef get_image(self, idx):assert(idx<self.num_samples) img_filename = os.path.join(self.image_dir, '%06d.png'%(idx))return load_image(img_filename)def get_calibration(self, idx):assert(idx<self.num_samples) calib_filename = os.path.join(self.calib_dir, '%06d.txt'%(idx))return Calibration(calib_filename)def get_label_objects(self, idx):# assert(idx<self.num_samples and self.split=='training') label_filename = os.path.join(self.label_dir, '%06d.txt'%(idx))return read_label(label_filename)def show_image_with_boxes(img, objects, calib, save_path, show3d=True):''' Show image with 2D bounding boxes '''img1 = np.copy(img) # for 2d bboximg2 = np.copy(img) # for 3d bboxfor obj in objects:if obj.type=='DontCare':continuecv2.rectangle(img1, (int(obj.xmin),int(obj.ymin)), (int(obj.xmax),int(obj.ymax)), (0,255,0), 2) # 画2D框box3d_pts_2d, box3d_pts_3d = compute_box_3d(obj, calib.P) # 获取3D框-图像(8*2)、3D框-相机坐标系(8*3)img2 = draw_projected_box3d(img2, box3d_pts_2d) # 在图像上画3D框if show3d:Image.fromarray(img2).save(save_path) # 保存带有3D框的图像# Image.fromarray(img2).show()else:Image.fromarray(img1).save(save_path) # 保存带有2D框的图像# Image.fromarray(img1).show()class Object3d(object):''' 3d object label '''def __init__(self, label_file_line):data = label_file_line.split(' ')data[1:] = [float(x) for x in data[1:]]# extract label, truncation, occlusionself.type = data[0] # 'Car', 'Pedestrian', ...self.truncation = data[1] # truncated pixel ratio [0..1]self.occlusion = int(data[2]) # 0=visible, 1=partly occluded, 2=fully occluded, 3=unknownself.alpha = data[3] # object observation angle [-pi..pi]# extract 2d bounding box in 0-based coordinatesself.xmin = data[4] # leftself.ymin = data[5] # topself.xmax = data[6] # rightself.ymax = data[7] # bottomself.box2d = np.array([self.xmin,self.ymin,self.xmax,self.ymax])# extract 3d bounding box informationself.h = data[8] # box heightself.w = data[9] # box widthself.l = data[10] # box length (in meters)self.t = (data[11],data[12],data[13]) # location (x,y,z) in camera coord.self.ry = data[14] # yaw angle (around Y-axis in camera coordinates) [-pi..pi]def print_object(self):print('Type, truncation, occlusion, alpha: %s, %d, %d, %f' % \(self.type, self.truncation, self.occlusion, self.alpha))print('2d bbox (x0,y0,x1,y1): %f, %f, %f, %f' % \(self.xmin, self.ymin, self.xmax, self.ymax))print('3d bbox h,w,l: %f, %f, %f' % \(self.h, self.w, self.l))print('3d bbox location, ry: (%f, %f, %f), %f' % \(self.t[0],self.t[1],self.t[2],self.ry))class Calibration(object):''' Calibration matrices and utils3d XYZ in <label>.txt are in rect camera coord.2d box xy are in image2 coordPoints in <lidar>.bin are in Velodyne coord.y_image2 = P^2_rect * x_recty_image2 = P^2_rect * R0_rect * Tr_velo_to_cam * x_velox_ref = Tr_velo_to_cam * x_velox_rect = R0_rect * x_refP^2_rect = [f^2_u, 0, c^2_u, -f^2_u b^2_x;0, f^2_v, c^2_v, -f^2_v b^2_y;0, 0, 1, 0]= K * [1|t]image2 coord:----> x-axis (u)||v y-axis (v)velodyne coord:front x, left y, up zrect/ref camera coord:right x, down y, front zRef (KITTI paper): http://www.cvlibs.net/publications/Geiger2013IJRR.pdfTODO(rqi): do matrix multiplication only once for each projection.'''def __init__(self, calib_filepath, from_video=False):if from_video:calibs = self.read_calib_from_video(calib_filepath)else:calibs = self.read_calib_file(calib_filepath)# Projection matrix from rect camera coord to image2 coordself.P = calibs['P2'] self.P = np.reshape(self.P, [3,4])# Rigid transform from Velodyne coord to reference camera coordself.V2C = calibs['Tr_velo_to_cam']self.V2C = np.reshape(self.V2C, [3,4])self.C2V = inverse_rigid_trans(self.V2C)# Rotation from reference camera coord to rect camera coordself.R0 = calibs['R0_rect']self.R0 = np.reshape(self.R0,[3,3])# Camera intrinsics and extrinsicsself.c_u = self.P[0,2]self.c_v = self.P[1,2]self.f_u = self.P[0,0]self.f_v = self.P[1,1]self.b_x = self.P[0,3]/(-self.f_u) # relative self.b_y = self.P[1,3]/(-self.f_v)def read_calib_file(self, filepath):''' Read in a calibration file and parse into a dictionary.'''data = {}with open(filepath, 'r') as f:for line in f.readlines():line = line.rstrip()if len(line)==0: continuekey, value = line.split(':', 1)# The only non-float values in these files are dates, which# we don't care about anywaytry:data[key] = np.array([float(x) for x in value.split()])except ValueError:passreturn datadef read_calib_from_video(self, calib_root_dir):''' Read calibration for camera 2 from video calib files.there are calib_cam_to_cam and calib_velo_to_cam under the calib_root_dir'''data = {}cam2cam = self.read_calib_file(os.path.join(calib_root_dir, 'calib_cam_to_cam.txt'))velo2cam = self.read_calib_file(os.path.join(calib_root_dir, 'calib_velo_to_cam.txt'))Tr_velo_to_cam = np.zeros((3,4))Tr_velo_to_cam[0:3,0:3] = np.reshape(velo2cam['R'], [3,3])Tr_velo_to_cam[:,3] = velo2cam['T']data['Tr_velo_to_cam'] = np.reshape(Tr_velo_to_cam, [12])data['R0_rect'] = cam2cam['R_rect_00']data['P2'] = cam2cam['P_rect_02']return datadef cart2hom(self, pts_3d):''' Input: nx3 points in CartesianOupput: nx4 points in Homogeneous by pending 1'''n = pts_3d.shape[0]pts_3d_hom = np.hstack((pts_3d, np.ones((n,1))))return pts_3d_hom# =========================== # ------- 3d to 3d ---------- # =========================== def project_velo_to_ref(self, pts_3d_velo):pts_3d_velo = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_velo) # nx4return np.dot(pts_3d_velo, np.transpose(self.V2C))def project_ref_to_velo(self, pts_3d_ref):pts_3d_ref = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_ref) # nx4return np.dot(pts_3d_ref, np.transpose(self.C2V))def project_rect_to_ref(self, pts_3d_rect):''' Input and Output are nx3 points '''return np.transpose(np.dot(np.linalg.inv(self.R0), np.transpose(pts_3d_rect)))def project_ref_to_rect(self, pts_3d_ref):''' Input and Output are nx3 points '''return np.transpose(np.dot(self.R0, np.transpose(pts_3d_ref)))def project_rect_to_velo(self, pts_3d_rect):''' Input: nx3 points in rect camera coord.Output: nx3 points in velodyne coord.''' pts_3d_ref = self.project_rect_to_ref(pts_3d_rect)return self.project_ref_to_velo(pts_3d_ref)def project_velo_to_rect(self, pts_3d_velo):pts_3d_ref = self.project_velo_to_ref(pts_3d_velo)return self.project_ref_to_rect(pts_3d_ref)def corners3d_to_img_boxes(self, corners3d):""":param corners3d: (N, 8, 3) corners in rect coordinate:return: boxes: (None, 4) [x1, y1, x2, y2] in rgb coordinate:return: boxes_corner: (None, 8) [xi, yi] in rgb coordinate"""sample_num = corners3d.shape[0]corners3d_hom = np.concatenate((corners3d, np.ones((sample_num, 8, 1))), axis=2) # (N, 8, 4)img_pts = np.matmul(corners3d_hom, self.P.T) # (N, 8, 3)x, y = img_pts[:, :, 0] / img_pts[:, :, 2], img_pts[:, :, 1] / img_pts[:, :, 2]x1, y1 = np.min(x, axis=1), np.min(y, axis=1)x2, y2 = np.max(x, axis=1), np.max(y, axis=1)boxes = np.concatenate((x1.reshape(-1, 1), y1.reshape(-1, 1), x2.reshape(-1, 1), y2.reshape(-1, 1)), axis=1)boxes_corner = np.concatenate((x.reshape(-1, 8, 1), y.reshape(-1, 8, 1)), axis=2)return boxes, boxes_corner# =========================== # ------- 3d to 2d ---------- # =========================== def project_rect_to_image(self, pts_3d_rect):''' Input: nx3 points in rect camera coord.Output: nx2 points in image2 coord.'''pts_3d_rect = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_rect)pts_2d = np.dot(pts_3d_rect, np.transpose(self.P)) # nx3pts_2d[:,0] /= pts_2d[:,2]pts_2d[:,1] /= pts_2d[:,2]return pts_2d[:,0:2]def project_velo_to_image(self, pts_3d_velo):''' Input: nx3 points in velodyne coord.Output: nx2 points in image2 coord.'''pts_3d_rect = self.project_velo_to_rect(pts_3d_velo)return self.project_rect_to_image(pts_3d_rect)# =========================== # ------- 2d to 3d ---------- # =========================== def project_image_to_rect(self, uv_depth):''' Input: nx3 first two channels are uv, 3rd channelis depth in rect camera coord.Output: nx3 points in rect camera coord.'''n = uv_depth.shape[0]x = ((uv_depth[:,0]-self.c_u)*uv_depth[:,2])/self.f_u + self.b_xy = ((uv_depth[:,1]-self.c_v)*uv_depth[:,2])/self.f_v + self.b_ypts_3d_rect = np.zeros((n,3))pts_3d_rect[:,0] = xpts_3d_rect[:,1] = ypts_3d_rect[:,2] = uv_depth[:,2]return pts_3d_rectdef project_image_to_velo(self, uv_depth):pts_3d_rect = self.project_image_to_rect(uv_depth)return self.project_rect_to_velo(pts_3d_rect)def rotx(t):''' 3D Rotation about the x-axis. '''c = np.cos(t)s = np.sin(t)return np.array([[1, 0, 0],[0, c, -s],[0, s, c]])def roty(t):''' Rotation about the y-axis. '''c = np.cos(t)s = np.sin(t)return np.array([[c, 0, s],[0, 1, 0],[-s, 0, c]])def rotz(t):''' Rotation about the z-axis. '''c = np.cos(t)s = np.sin(t)return np.array([[c, -s, 0],[s, c, 0],[0, 0, 1]])def transform_from_rot_trans(R, t):''' Transforation matrix from rotation matrix and translation vector. '''R = R.reshape(3, 3)t = t.reshape(3, 1)return np.vstack((np.hstack([R, t]), [0, 0, 0, 1]))def inverse_rigid_trans(Tr):''' Inverse a rigid body transform matrix (3x4 as [R|t])[R'|-R't; 0|1]'''inv_Tr = np.zeros_like(Tr) # 3x4inv_Tr[0:3,0:3] = np.transpose(Tr[0:3,0:3])inv_Tr[0:3,3] = np.dot(-np.transpose(Tr[0:3,0:3]), Tr[0:3,3])return inv_Trdef read_label(label_filename):lines = [line.rstrip() for line in open(label_filename)]objects = [Object3d(line) for line in lines]return objectsdef load_image(img_filename):return cv2.imread(img_filename)def load_velo_scan(velo_filename):scan = np.fromfile(velo_filename, dtype=np.float32)scan = scan.reshape((-1, 4))return scandef project_to_image(pts_3d, P):'''将3D坐标点投影到图像平面上,生成2D坐pts_3d是一个nx3的矩阵,包含了待投影的3D坐标点(每行一个点),P是相机的投影矩阵,通常是一个3x4的矩阵。函数返回一个nx2的矩阵,包含了投影到图像平面上的2D坐标点。'''''' Project 3d points to image plane.Usage: pts_2d = projectToImage(pts_3d, P)input: pts_3d: nx3 matrixP: 3x4 projection matrixoutput: pts_2d: nx2 matrixP(3x4) dot pts_3d_extended(4xn) = projected_pts_2d(3xn)=> normalize projected_pts_2d(2xn)<=> pts_3d_extended(nx4) dot P'(4x3) = projected_pts_2d(nx3)=> normalize projected_pts_2d(nx2)'''n = pts_3d.shape[0] # 获取3D点的数量pts_3d_extend = np.hstack((pts_3d, np.ones((n,1)))) # 将每个3D点的坐标扩展为齐次坐标形式(4D),通过在每个点的末尾添加1,创建了一个nx4的矩阵。# print(('pts_3d_extend shape: ', pts_3d_extend.shape))pts_2d = np.dot(pts_3d_extend, np.transpose(P)) # 将扩展的3D坐标点矩阵与投影矩阵P相乘,得到一个nx3的矩阵,其中每一行包含了3D点在图像平面上的投影坐标。每个点的坐标表示为[x, y, z]。pts_2d[:,0] /= pts_2d[:,2] # 将投影坐标中的x坐标除以z坐标,从而获得2D图像上的x坐标。pts_2d[:,1] /= pts_2d[:,2] # 将投影坐标中的y坐标除以z坐标,从而获得2D图像上的y坐标。return pts_2d[:,0:2] # 返回一个nx2的矩阵,其中包含了每个3D点在2D图像上的坐标。def compute_box_3d(obj, P):'''计算对象的3D边界框在图像平面上的投影输入: obj代表一个物体标签信息, P代表相机的投影矩阵-内参。输出: 返回两个值, corners_3d表示3D边界框在 相机坐标系 的8个角点的坐标-3D坐标。corners_2d表示3D边界框在 图像上 的8个角点的坐标-2D坐标。'''# compute rotational matrix around yaw axis# 计算一个绕Y轴旋转的旋转矩阵R,用于将3D坐标从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系。obj.ry是对象的偏航角R = roty(obj.ry) # 3d bounding box dimensions# 物体实际的长、宽、高l = obj.l;w = obj.w;h = obj.h;# 3d bounding box corners# 存储了3D边界框的8个角点相对于对象中心的坐标。这些坐标定义了3D边界框的形状。x_corners = [l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2,l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2];y_corners = [0,0,0,0,-h,-h,-h,-h];z_corners = [w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2,w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2];# rotate and translate 3d bounding box# 1、将3D边界框的角点坐标从对象坐标系转换到相机坐标系。它使用了旋转矩阵Rcorners_3d = np.dot(R, np.vstack([x_corners,y_corners,z_corners]))# 3D边界框的坐标进行平移corners_3d[0,:] = corners_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0];corners_3d[1,:] = corners_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1];corners_3d[2,:] = corners_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2];# 2、检查对象是否在相机前方,因为只有在相机前方的对象才会被绘制。# 如果对象的Z坐标(深度)小于0.1,就意味着对象在相机后方,那么corners_2d将被设置为None,函数将返回None。if np.any(corners_3d[2,:]<0.1):corners_2d = Nonereturn corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)# project the 3d bounding box into the image plane# 3、将相机坐标系下的3D边界框的角点,投影到图像平面上,得到它们在图像上的2D坐标。corners_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(corners_3d), P);return corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)def compute_orientation_3d(obj, P):''' Takes an object and a projection matrix (P) and projects the 3dobject orientation vector into the image plane.Returns:orientation_2d: (2,2) array in left image coord.orientation_3d: (2,3) array in in rect camera coord.'''# compute rotational matrix around yaw axisR = roty(obj.ry)# orientation in object coordinate systemorientation_3d = np.array([[0.0, obj.l],[0,0],[0,0]])# rotate and translate in camera coordinate system, project in imageorientation_3d = np.dot(R, orientation_3d)orientation_3d[0,:] = orientation_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0]orientation_3d[1,:] = orientation_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1]orientation_3d[2,:] = orientation_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2]# vector behind image plane?if np.any(orientation_3d[2,:]<0.1):orientation_2d = Nonereturn orientation_2d, np.transpose(orientation_3d)# project orientation into the image planeorientation_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(orientation_3d), P);return orientation_2d, np.transpose(orientation_3d)def draw_projected_box3d(image, qs, color=(0,60,255), thickness=2):'''qs: 包含8个3D边界框角点坐标的数组, 形状为(8, 2)。图像坐标下的3D框, 8个顶点坐标。'''''' Draw 3d bounding box in imageqs: (8,2) array of vertices for the 3d box in following order:1 -------- 0/| /|2 -------- 3 .| | | |. 5 -------- 4|/ |/6 -------- 7'''qs = qs.astype(np.int32) # 将输入的顶点坐标转换为整数类型,以便在图像上绘制。# 这个循环迭代4次,每次处理一个边界框的一条边。for k in range(0,4):# Ref: http://docs.enthought.com/mayavi/mayavi/auto/mlab_helper_functions.html# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制边界框的前四条边。i,j=k,(k+1)%4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制边界框的后四条边,与前四条边平行i,j=k+4,(k+1)%4 + 4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制连接前四条边和后四条边的边界框的边。i,j=k,k+4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)return image运行后会在save_3d_output中保存可视化的图像。
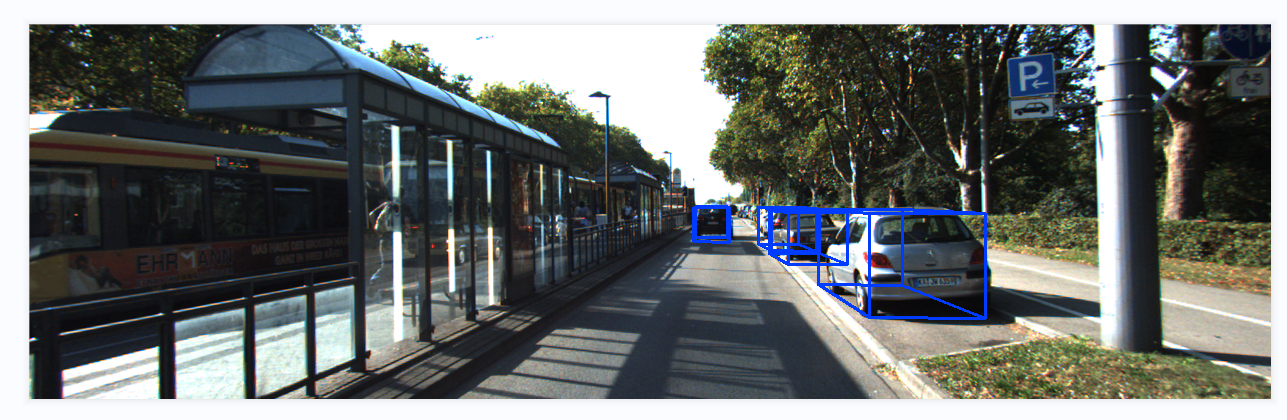
模型推理结果可视化效果:
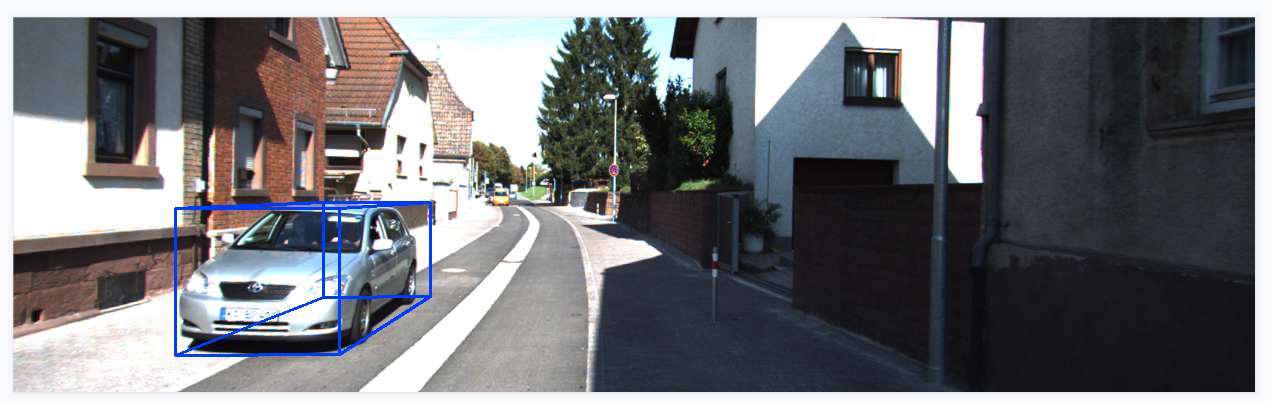
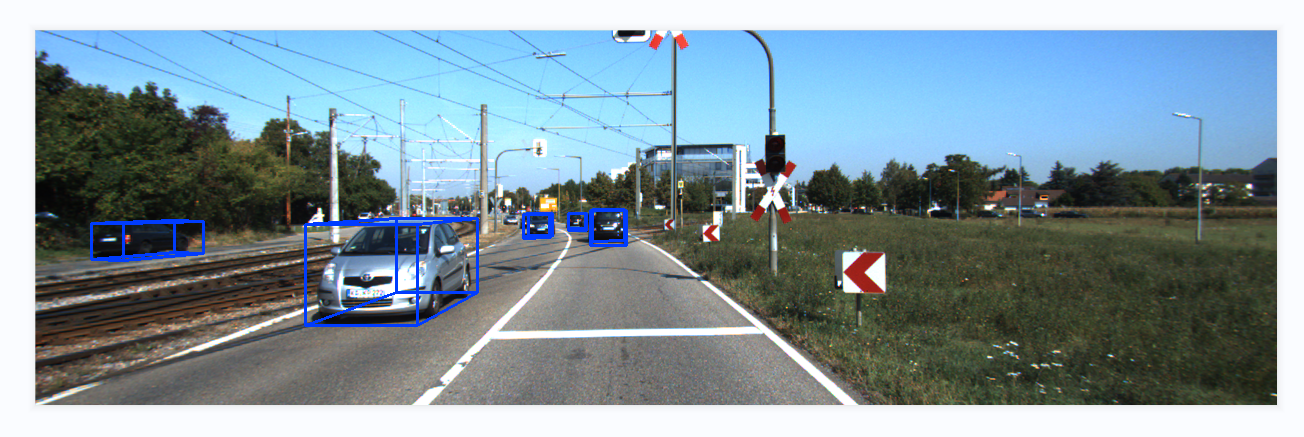




分析完成~
相关文章:

单目3D目标检测——SMOKE 模型推理 | 可视化结果
本文分享SMOKE的模型推理,和可视化结果。以kitti数据集为例子,对训练完的模型进行推理,并可视化3D框的结果,画到图像中。 关于模型原理、搭建开发环境、模型训练,可以参考之前的博客: 【论文解读】SMOKE …...

C++智能指针shared_ptr使用详解
shared_ptr 是一个共享所有权的智能指针,允许多个指针指向同一个对象。 shared_ptr使用引用计数,每一个shared_ptr的拷贝都指向相同的内存。每使用它一次,内部的引用计数加1,每析构一次,内部的引用计数减1,减为0时,释放所指向的堆内存。shared_ptr内部的引用计数是…...
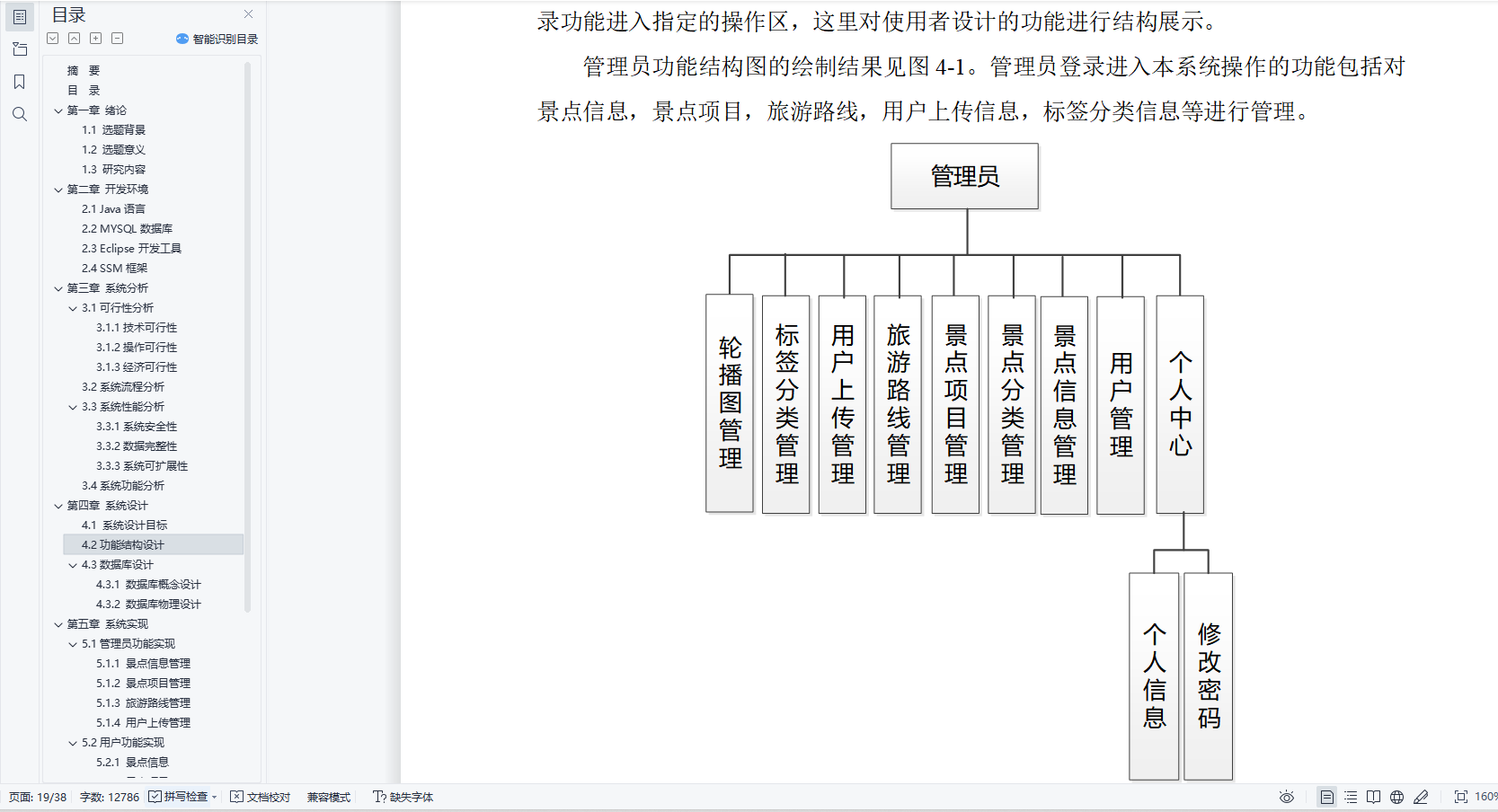
基于Java的个性化旅游攻略系统设计与实现(源码+lw+ppt+部署文档+视频讲解等)
文章目录 前言具体实现截图论文参考详细视频演示代码参考源码获取 前言 💗博主介绍:✌全网粉丝10W,CSDN特邀作者、博客专家、CSDN新星计划导师、全栈领域优质创作者,博客之星、掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java、小程序技…...

中国替代方案探索:替代谷歌企业邮箱的选择
“谷歌企业邮箱在中国有哪些替代方案?在中国市场上表现出色的企业邮箱有腾讯企业邮箱、网易企业邮箱、阿里企业邮箱以及适合外贸的Zoho Mail企业邮箱。” 在中国由于各种原因,包括网络安全、数据隐私保护以及与GFW(防火长城)等,谷歌企业邮箱并…...
Holographic MIMO Surfaces (HMIMOS)以及Reconfigurable Holographic Surface(RHS)仿真
这里写目录标题 Simulation setupchatgpt帮我总结代码总结:chatgpt生成的代码还是不靠谱:考虑把之前看的RHS中对于多用户的改成单用户全系MIMO与普通MIMO或者说RIS的区别到底是啥? Holographic MIMO Surfaces (HMIMOS)…...
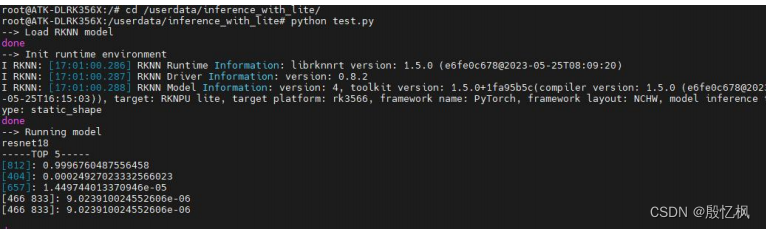
RK3568笔记一:RKNN开发环境搭建
若该文为原创文章,转载请注明原文出处。 由于对AI的好奇,想要学习如何部署AI,所以从RV1126到RK3568中过渡。 一、介绍 RK3568开发板使用的是正点原子新出的ATK-DLRK3568 开发板,主要是学习从训练到部署的全过程,并记…...

设计模式 - 行为型模式:策略模式(概述 | 案例实现 | 优缺点 | 使用场景)
目录 一、行为型模式 1.1、策略模式 1.1.1、概论 1.1.2、案例实现 1.1.3、优缺点 1.1.4、使用场景 一、行为型模式 1.1、策略模式 1.1.1、概论 策略模式设计的每一个算法都封装了起来,使他们可以相互替换,通过一个对象委派不同的算法给相应的客户…...
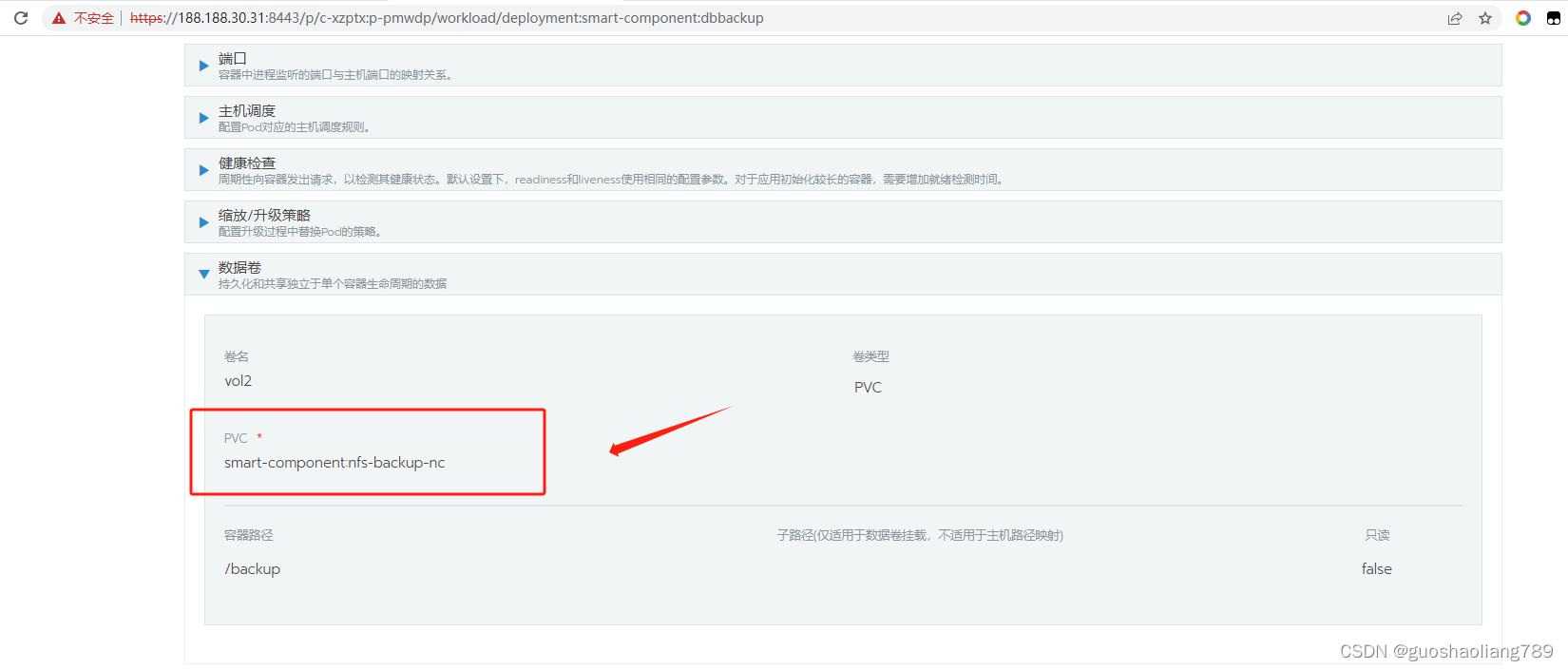
rancher部署pv、pvc、离线部署nfs
(1)NFS离线安装 使用nfs配置两台机器共享目录 假设两台机器188.188.30.32(服务端)、188.188.30.31(客户端)配置nfs 1.在可以联网的机器上下载rpm安装包 yum -y install nfs-utils --downloadonly --dow…...

视频拍摄教程分享
(1)新片场:静物美食视频拍摄(22.76GB) 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1uj6wcPXGw-ztLQ1cdyogTA 提取码:929z(永久有效) (2)新片场:《孙晓迪分镜头脚本》掌握10种类型商业广告创作思…...

IP组成,分类,子网划分
一、基本概念 IP地址是指互联网协议地址,IP地址是IP协议提供的一种统一的地址格式,他为互联网上的每一个网络和每一台主机分配了一个逻辑地址,以此来屏蔽物理地址的差异,每个ip地址由网络地址和主机地址两个部分组成,网…...

Python视频剪辑-Moviepy视频内容变换技术
在视频编辑中,内容变换是个不能忽视的环节。这不仅仅是关于视频的方向、颜色或者大小,更多的是关于如何让视频内容更具创造性和吸引力。接下来将深入探讨如何使用MoviePy库进行高级的视频内容变换。 文章目录 视频内容变换函数剪辑逆时针旋转指定的角度或弧度像素的RGB值各取…...

OceanBase 数据库入门知识
🙈作者简介:练习时长两年半的Java up主 🙉个人主页:程序员老茶 🙊 ps:点赞👍是免费的,却可以让写博客的作者开兴好久好久😎 📚系列专栏:Java全栈,…...
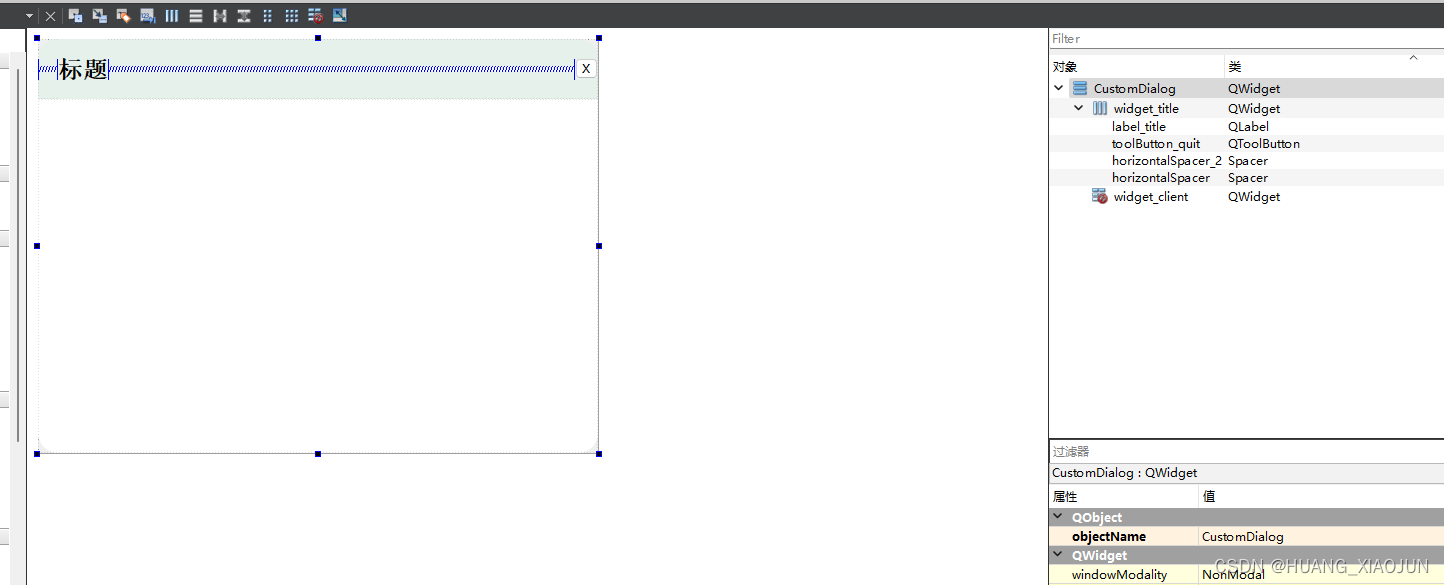
自定义无边框窗口
效果: 可拖动拉伸 ui:设计如下 样式表:在ui CustomDialog 里设置的 #widget_title{background: #E6F1EB;border-top-left-radius: 20px;border-top-right-radius: 20px;}#widget_client{background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);border-bottom…...
【网络安全 --- kali2023安装】超详细的kali2023安装教程(提供镜像资源)
如果你还没有安装vmware 虚拟机,请参考下面博客安装 【网络安全 --- 工具安装】VMware 16.0 详细安装过程(提供资源)-CSDN博客【网络安全 --- 工具安装】VMware 16.0 详细安装过程(提供资源)https://blog.csdn.net/m0…...
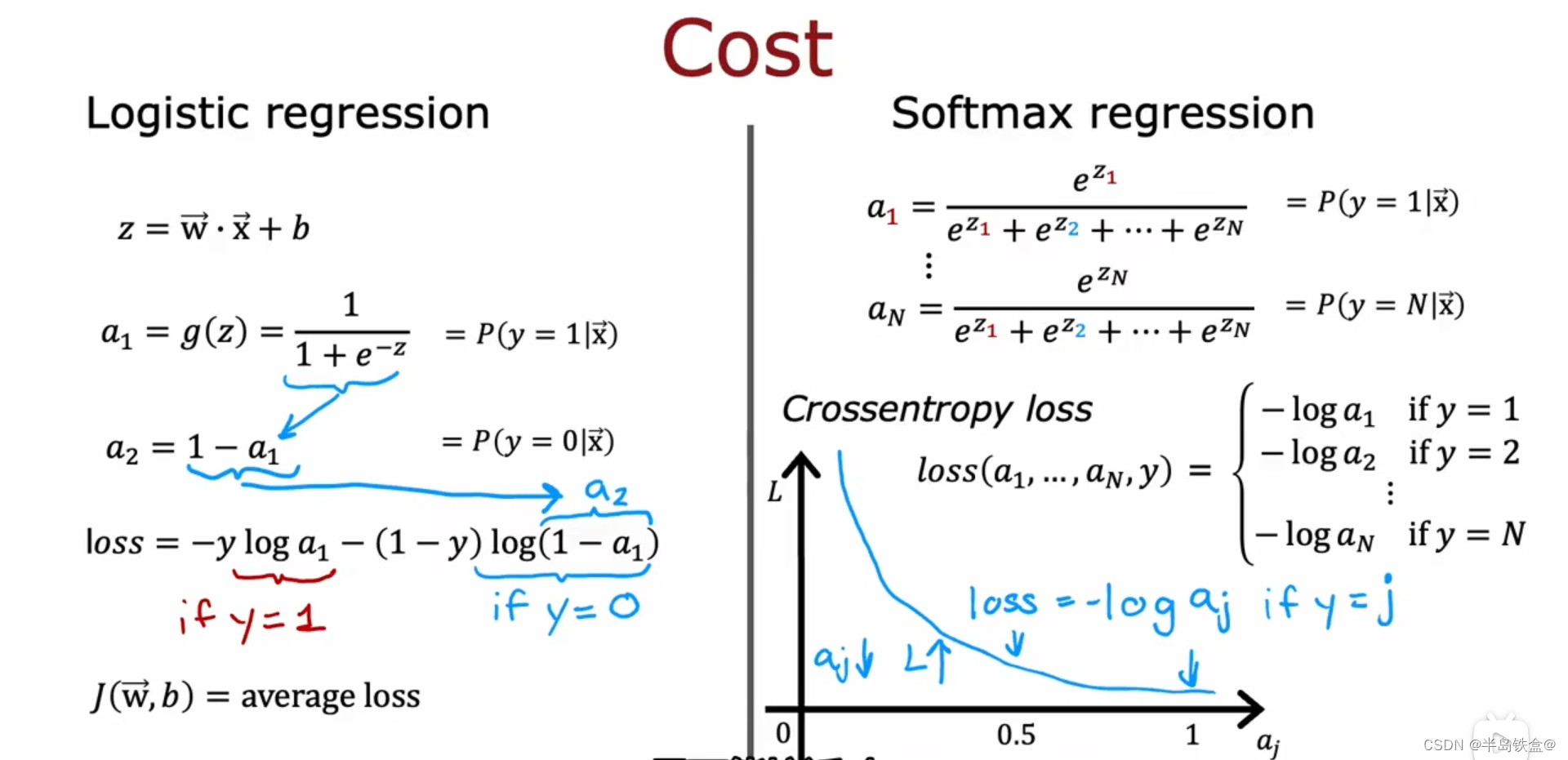
机器学习笔记(二)
过拟合 如下图左边,模型出现了过拟合现象 为了解决过拟合现象, 其中一个做法是多收集数据,如右图。 第二种做法是减少模型的特征数量,即x 第三种做法是正则化 正则化就是减少x前面的参数 w的数值, 不用消除x 正则化的梯度下降如下, 因为只是缩小了w的值,而 b的值保持不变 …...
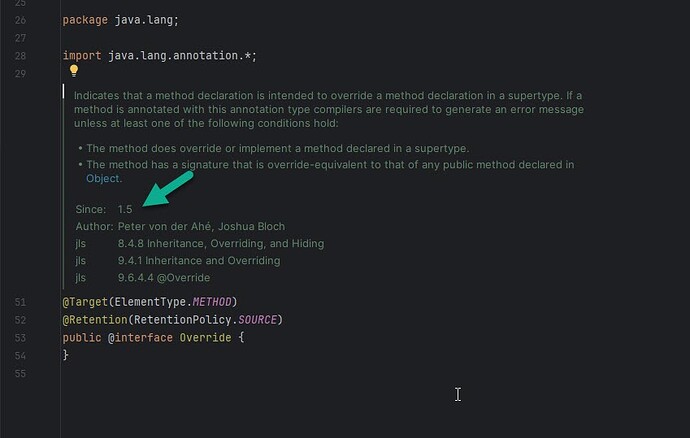
Java @Override 注解
在代码中,你可能会看到大量的 Override 注解。 这个注解简单来说就是让编译器去读的,能够避免你在写代码的时候犯一些低级的拼写错误。 Java Override 注解用来指定方法重写(Override),只能修饰方法并且只能用于方法…...

用rabbitMq 怎么处理“延迟消息队列”?
延迟消息队列是一种允许消息在发送后等待一段时间,然后再被消费的机制。这种机制通常用于需要延迟处理的应用场景,如定时任务、消息重试、消息调度等。在 RabbitMQ 中,实现延迟消息队列需要使用一些额外的组件和技术,因为 RabbitM…...

不常见的JS加密分析
前言 今天发现一个很少见的JS加密代码,他由一段十分少见的环境检测逻辑,修改一个字符都会被检测到,十分神奇,今天献上。 源代码 let hiJsJiami;!function(){const Zg3GArray.prototype.slice.call(arguments);return eval(&…...

TCP原理特性详解
文章目录 可靠传输机制1.确认应答2.超时重传2.连接管理1.三次握手2.四次挥手 传输效率1.滑动窗口2.流量控制3.拥塞控制4.延时应答5.捎带应答 面向字节流粘包问题 TCP异常情况 可靠传输机制 可靠性:即发送方知道数据是发送成功了,还是失败了。 1.确认应答…...

什么是懒加载,JS如何实现懒加载,在php中如何去实现懒加载
懒加载(Lazy Loading)是一种前端优化技术,用于推迟加载页面中的某些资源(如图片、脚本、样式等),直到用户需要访问或者接近该资源时才进行加载。这可以减少初始页面加载时间,并提高页面性能和用…...

STM32+rt-thread判断是否联网
一、根据NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP位判断 static bool is_conncected(void) {struct netdev *dev RT_NULL;dev netdev_get_first_by_flags(NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP);if (dev RT_NULL){printf("wait netdev internet up...");return false;}else{printf("loc…...

三分算法与DeepSeek辅助证明是单峰函数
前置 单峰函数有唯一的最大值,最大值左侧的数值严格单调递增,最大值右侧的数值严格单调递减。 单谷函数有唯一的最小值,最小值左侧的数值严格单调递减,最小值右侧的数值严格单调递增。 三分的本质 三分和二分一样都是通过不断缩…...

libfmt: 现代C++的格式化工具库介绍与酷炫功能
libfmt: 现代C的格式化工具库介绍与酷炫功能 libfmt 是一个开源的C格式化库,提供了高效、安全的文本格式化功能,是C20中引入的std::format的基础实现。它比传统的printf和iostream更安全、更灵活、性能更好。 基本介绍 主要特点 类型安全:…...

SQL Server 触发器调用存储过程实现发送 HTTP 请求
文章目录 需求分析解决第 1 步:前置条件,启用 OLE 自动化方式 1:使用 SQL 实现启用 OLE 自动化方式 2:Sql Server 2005启动OLE自动化方式 3:Sql Server 2008启动OLE自动化第 2 步:创建存储过程第 3 步:创建触发器扩展 - 如何调试?第 1 步:登录 SQL Server 2008第 2 步…...

GraphRAG优化新思路-开源的ROGRAG框架
目前的如微软开源的GraphRAG的工作流程都较为复杂,难以孤立地评估各个组件的贡献,传统的检索方法在处理复杂推理任务时可能不够有效,特别是在需要理解实体间关系或多跳知识的情况下。先说结论,看完后感觉这个框架性能上不会比Grap…...

拟合问题处理
在机器学习中,核心任务通常围绕模型训练和性能提升展开,但你提到的 “优化训练数据解决过拟合” 和 “提升泛化性能解决欠拟合” 需要结合更准确的概念进行梳理。以下是对机器学习核心任务的系统复习和修正: 一、机器学习的核心任务框架 机…...

前端工具库lodash与lodash-es区别详解
lodash 和 lodash-es 是同一工具库的两个不同版本,核心功能完全一致,主要区别在于模块化格式和优化方式,适合不同的开发环境。以下是详细对比: 1. 模块化格式 lodash 使用 CommonJS 模块格式(require/module.exports&a…...

Spring是如何实现无代理对象的循环依赖
无代理对象的循环依赖 什么是循环依赖解决方案实现方式测试验证 引入代理对象的影响创建代理对象问题分析 源码见:mini-spring 什么是循环依赖 循环依赖是指在对象创建过程中,两个或多个对象相互依赖,导致创建过程陷入死循环。以下通过一个简…...

CSS(2)
文章目录 Emmet语法快速生成HTML结构语法 Snipaste快速生成CSS样式语法快速格式化代码 快捷键(VScode)CSS 的复合选择器什么是复合选择器交集选择器后代选择器(重要)子选择器(重要)并集选择器(重要)**链接伪类选择器**focus伪类选…...

【RabbitMQ】- Channel和Delivery Tag机制
在 RabbitMQ 的消费者代码中,Channel 和 tag 参数的存在是为了实现消息确认机制(Acknowledgment)和精细化的消息控制。 Channel 参数 作用 Channel 是 AMQP 协议的核心操作接口,通过它可以直接与 RabbitMQ 交互: 手…...
