【CPP】类和对象
1- Classes and Objects
Structures
- A struct in C is a type consisting of a sequence of data members
- Some functions/Statements are needed to operate the data members of an object of a struct type

不不小心操作错误,不小心越界
Classes
- You should be very careful to manipulated the data members in a struct object
- Can we improve struct to a better one ?
- Yes, it is
class! We can put some member functions in it
class Student
{private:static size_t student_total; // declaration only//inline static size_t student_total = 0; //C++17, definition outside isn't neededchar * name;int born;bool male; void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, sizeof(name));}
};
Student yu;
yu.setName("Yu");
firstclass.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>class Student
{public:char name[4];int born;bool male; void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, sizeof(name));}void setBorn(int b){born = b;}void setGender(bool isMale){male = isMale;}void printInfo(){std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;}
};int main()
{Student yu;yu.setName("Yu");yu.setBorn(2000);yu.setGender(true);yu.born = 2001; // it can also be manipulated directlyyu.printInfo();std::cout << "It's name is " << yu.name << std::endl; return 0;
}
Name: Yu
Born in 2001
Gender: Male
It's name is Yu
Access Specifiers
- You can protect data members by access specifier
private - Then data member can only be accessed by well designed member functions
access_attribute.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>class Student
{private:char name[4];int born;bool male; public:void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, sizeof(name));}void setBorn(int b){born = b;}void setGender(bool isMale){male = isMale;}void printInfo(){std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;}
};int main()
{Student yu;yu.setName("Yu");yu.setBorn(2000);yu.setGender(true);yu.born = 2001; // you cannot access a private memberyu.printInfo();return 0;
}
access-attribute.cpp:37:8: error: 'born' is a private member of 'Student'yu.born = 2001; // you cannot access a private member^
access-attribute.cpp:8:9: note: declared private hereint born;^
Member Functions
- A member function can be defined inside or outside class
- 如果在类内部实现函数则就是
inline函数
function.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>class Student
{private:char name[4];int born;bool male; public:void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, sizeof(name));}void setBorn(int b){born = b;}// the declarations, the definitions are out of the classvoid setGender(bool isMale);void printInfo();
};void Student::setGender(bool isMale)
{male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo()
{std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;
}int main()
{Student yu;yu.setName("Yu");yu.setBorn(2000);yu.setGender(true);yu.printInfo();return 0;
}
Name: Yu
Born in 2000
Gender: Male
File Structures
- The source code can be placed into multiple files
student.hpp
#pragma once#include <cstring>
class Student
{private:char name[4];int born;bool male; public:void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, sizeof(name));}void setBorn(int b){born = b;}// the declarations, the definitions are out of the classvoid setGender(bool isMale);void printInfo();
};student.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "student.hpp"void Student::setGender(bool isMale)
{male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo()
{std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;
}如果include <> 从编译器路径查找,如果是include "" 从编译器和当前目录找
main.cpp
#include "student.hpp"int main()
{Student yu;yu.setName("Yu");yu.setBorn(2000);yu.setGender(true);yu.printInfo();return 0;
}CMakeList.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12)project(persondemo)ADD_EXECUTABLE(persondemo main.cpp student.cpp)cd multi-files
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
./persondemo
Name: Yu
Born in 2000
Gender: Male
2-Constructors and Destructors
Constructors
- Different from
structin C, a constructor will be invoked when creating an object of aclass
(1) struct in C: allocate memory
(2) class in C++: allocate memory & invoke a constructor
- But, No constructor is defined explicitly in previous examples
(1) the compiler wil generate one with empty body
如果没有人为定义构造函数,则自动会有一个空的构造函数
- The same name with the class
- Have no return value
class Student
{private:char name[4];int born;bool male; public:Student(){name[0] = 0;born = 0;male = false;cout << "Constructor: Person()" << endl;}}Student(const char * initName, int initBorn, bool isMale){setName(initName);born = initBorn;male = isMale;cout << "Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)" << endl;}
}
- The members can also be initialized as follows
Student(const char * initName): born(0), male(true){setName(initName);cout << "Constructor: Person(const char*)" << endl;}
把成员变量born 初始化为0 , 把male 初始化为true
constructor.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>using namespace std;class Student
{private:char name[4];int born;bool male; public:Student(){name[0] = 0;born = 0;male = false;cout << "Constructor: Person()" << endl;}Student(const char * initName): born(0), male(true){setName(initName);cout << "Constructor: Person(const char*)" << endl;}Student(const char * initName, int initBorn, bool isMale){setName(initName);born = initBorn;male = isMale;cout << "Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)" << endl;}void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, sizeof(name));}void setBorn(int b){born = b;}// the declarations, the definitions are out of the classvoid setGender(bool isMale);void printInfo();
};void Student::setGender(bool isMale)
{male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo()
{std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;
}int main()
{Student yu;yu.printInfo();yu.setName("Yu");yu.setBorn(2000);yu.setGender(true);yu.printInfo();Student li("li");li.printInfo();Student xue = Student("XueQikun", 1962, true);//a question: what will happen since "XueQikun" has 4+ characters?xue.printInfo();Student * zhou = new Student("Zhou", 1991, false);zhou->printInfo();delete zhou;return 0;
}
Constructor: Person()
Name:
Born in 0
Gender: Female
Name: Yu
Born in 2000
Gender: Male
Constructor: Person(const char*)
Name: li
Born in 0
Gender: Male
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Name: XueQ�
Born in 1962
Gender: Male
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Name: Zhou�
Born in 1991
Gender: Female
Destructors
- The destructor will be invoked when the object is destroyed
- Be formed from the class name preceded by a tilde(~)
- Have no return value, no parameters
~Student(){cout << "To destroy object: " << name << endl;delete [] name;}
析构函数只能有一个
析构函数常做的事情:释放内存,关闭文件,断掉网络etc
destructor.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>using namespace std;class Student
{private:char * name;int born;bool male; public:Student(){name = new char[1024]{0};born = 0;male = false;cout << "Constructor: Person()" << endl;}Student(const char * initName, int initBorn, bool isMale){name = new char[1024];setName(initName);born = initBorn;male = isMale;cout << "Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)" << endl;}~Student(){cout << "To destroy object: " << name << endl;delete [] name;}void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, 1024);}void setBorn(int b){born = b;}// the declarations, the definitions are out of the classvoid setGender(bool isMale);void printInfo();
};void Student::setGender(bool isMale)
{male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo()
{std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;
}int main()
{{Student yu;yu.printInfo();yu.setName("Yu");yu.setBorn(2000);yu.setGender(true);yu.printInfo();}Student xue = Student("XueQikun", 1962, true);xue.printInfo();Student * zhou = new Student("Zhou", 1991, false);zhou->printInfo();delete zhou;return 0;
}
g++ destructor.cpp --std=c++11
Constructor: Person()
Name:
Born in 0
Gender: Female
Name: Yu
Born in 2000
Gender: Male
To destroy object: Yu
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Name: XueQikun
Born in 1962
Gender: Male
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Name: Zhou
Born in 1991
Gender: Female
To destroy object: Zhou
To destroy object: XueQikun
人工手动调用析构函数 delete zhou,作用域结束跳出也会自动调用析构函数
如果对于new 的对象不进行手动删除delete 则作用域结束也不会动态调用析构函数,造成内存泄漏
Student * class1 = new Student[3]{{"Tom", 2000, true},{"Bob", 2001, true},{"Amy", 2002, false},};
- What is the different between the following two lines?
delete class1;
delete [] class1;
array.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>using namespace std;class Student
{private:char * name;int born;bool male; public:Student(){name = new char[1024]{0};born = 0;male = false;cout << "Constructor: Person()" << endl;}Student(const char * initName, int initBorn, bool isMale){name = new char[1024];setName(initName);born = initBorn;male = isMale;cout << "Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)" << endl;}~Student(){cout << "To destroy object: " << name << endl;delete [] name;}void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, 1024);}void setBorn(int b){born = b;}// the declarations, the definitions are out of the classvoid setGender(bool isMale);void printInfo();
};void Student::setGender(bool isMale)
{male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo()
{std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;
}int main()
{Student * class1 = new Student[3]{{"Tom", 2000, true},{"Bob", 2001, true},{"Amy", 2002, false},};class1[1].printInfo();delete class1;delete []class1;return 0;
}
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Name: Bob
Born in 2001
Gender: Male
To destroy object: Tom
数组调用析构函数delete class1 , 只会调用第一个对象的析构函数,后面的对象不会被调用
数组调用析构函数 delete [] class1,则会调用全部对象的析构函数
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Name: Bob
Born in 2001
Gender: Male
To destroy object: Amy
To destroy object: Bob
To destroy object: Tom
3-this pointer
Why is this needed
- How does a member function know which name?
this Pointer
- All methods in a function have a
thispointer - It is set to the address of the object that invokes the method

this.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>using namespace std;class Student
{private:char * name;int born;bool male; public:Student(){name = new char[1024]{0};born = 0;male = false;cout << "Constructor: Person()" << endl;}Student(const char * name, int born, bool male){this->name = new char[1024];this->setName(name);this->born = born;this->male = male;cout << "Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)" << endl;}~Student(){cout << "To destroy object: " << name << endl;delete [] name;}void setName(const char * name){strncpy(this->name, name, 1024);}void setBorn(int born){this->born = born;}// the declarations, the definitions are out of the classvoid setGender(bool isMale);void printInfo();
};void Student::setGender(bool isMale)
{male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo()
{std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;
}int main()
{Student * class1 = new Student[3]{{"Tom", 2000, true},{"Bob", 2001, true},{"Amy", 2002, false},};class1[1].printInfo();delete []class1;return 0;
}
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
Name: Bob
Born in 2001
Gender: Male
To destroy object: Amy
To destroy object: Bob
To destroy object: Tom
4- const and static Members
const Variables
- statements for constants
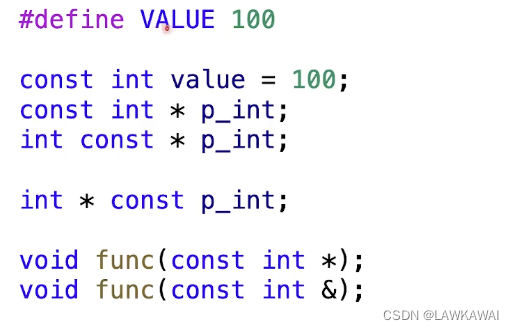
C++不推荐用 宏
const Members
constmember variables behavior similar with normal const variablesconstmember functions promise not to modify member variables
class Student
{private:const int BMI = 24;public:Student(){BMI = 25;//can it be modified?int getBorn() const{born++; //Can it be modified?return born;}
};
常量函数,const 放在后面,不然跟前面的const int相冲突。不可以修改成员变量,born 是不可以被修改的,保证不修改函数里的变量
const.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>using namespace std;class Student
{private:const int BMI = 24;char * name;int born;bool male; public:Student(){name = new char[1024]{0};born = 0;male = false;// BMI = 25;//can it be modified?cout << "Constructor: Person()" << endl;}Student(const char * name, int born, bool male){this->name = new char[1024];setName(name);this->born = born;this->male = male;cout << "Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)" << endl;}~Student(){cout << "To destroy object: " << name << endl;delete [] name;}void setName(const char * name){strncpy(this->name, name, 1024);}void setBorn(int born){this->born = born;}int getBorn() const{//born++; //Can it be modified?return born;}// the declarations, the definitions are out of the classvoid setGender(bool isMale);void printInfo();
};void Student::setGender(bool isMale)
{male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo()
{std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;
}int main()
{Student yu("Yu", 2000, true);cout << "yu.getBorn() = " << yu.getBorn() << endl;return 0;
}
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool)
yu.getBorn() = 2000
To destroy object: Yu
static members
staticmembers are not bound to class instances
class Student
{private:static size_t student_total; // declaration onlypublic:Student(){student_total++;}~Student(){student_total--;}static size_t getTotal() {return student_total;}
};// definition it here
size_t Student::student_total = 0; 静态成员不绑定在类对象上,只有一个
static.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>using namespace std;class Student
{private:static size_t student_total; // declaration only//inline static size_t student_total = 0; //C++17, definition outside isn't neededchar * name;int born;bool male; public:Student(){student_total++;name = new char[1024]{0};born = 0;male = false;cout << "Constructor: Person(): student_total = " << student_total << endl;}Student(const char * initName, int initBorn, bool isMale){student_total++;name = new char[1024];setName(initName);born = initBorn;male = isMale;cout << "Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool): student_total = " << student_total << endl;}~Student(){student_total--;cout << "To destroy object: " << name ;cout << ". Then " << student_total << " students are left" << endl;delete [] name;}void setName(const char * s){strncpy(name, s, 1024);}void setBorn(int b){born = b;}static size_t getTotal() {return student_total;}// the declarations, the definitions are out sof the classvoid setGender(bool isMale);void printInfo();
};void Student::setGender(bool isMale)
{male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo()
{std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;std::cout << "Born in " << born << std::endl;std::cout << "Gender: " << (male ? "Male" : "Female") << std::endl;
}size_t Student::student_total = 0; // definition it hereint main()
{cout << "---We have " << Student::getTotal() << " students---" << endl;Student * class1 = new Student[3]{{"Tom", 2000, true},{"Bob", 2001, true},{"Amy", 2002, false},};cout << "---We have " << Student::getTotal() << " students---" << endl;Student yu("Yu", 2000, true);cout << "---We have " << Student::getTotal() << " students---" << endl;class1[1].printInfo();delete []class1;cout << "---We have " << Student::getTotal() << " students---" << endl;return 0;
}
---We have 0 students---
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool): student_total = 1
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool): student_total = 2
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool): student_total = 3
---We have 3 students---
Constructor: Person(const char, int , bool): student_total = 4
---We have 4 students---
Name: Bob
Born in 2001
Gender: Male
To destroy object: Amy. Then 3 students are left
To destroy object: Bob. Then 2 students are left
To destroy object: Tom. Then 1 students are left
---We have 1 students---
To destroy object: Yu. Then 0 students are left
静态函数里面不可以修改非静态数据
相关文章:

【CPP】类和对象
1- Classes and Objects Structures A struct in C is a type consisting of a sequence of data membersSome functions/Statements are needed to operate the data members of an object of a struct type 不不小心操作错误,不小心越界 Classes You should b…...

【多线程面试题二十】、 如何实现互斥锁(mutex)?
文章底部有个人公众号:热爱技术的小郑。主要分享开发知识、学习资料、毕业设计指导等。有兴趣的可以关注一下。为何分享? 踩过的坑没必要让别人在再踩,自己复盘也能加深记忆。利己利人、所谓双赢。 面试官:如何实现互斥锁…...

hypercube背景设置为白色,绘制高光谱3D立方体
import scipy pip install wxpython PyOpenGL和Spectral需要本地安装 可参考链接https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43204333/article/details/119837870 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/Tiandailan/article/details/132719745?spm1001.2014.3001.5506Mouse Functions:left-cl…...
Visual Studio(VS)C++项目 管理第三方依赖库和目录设置
发现很多程序员存在这种做法:把项目依赖的第三方库的lib和dll放在项目目录下,或者复制到输出目录,因为每种配置都有不同的输出目录,所以要复制多份(至少包括Debug和Release两个输出目录),这些做…...

leetCode 2578. 最小和分割 + 排序 + 贪心 + 奇偶分组(构造最优解)
2578. 最小和分割 - 力扣(LeetCode) 给你一个正整数 num ,请你将它分割成两个非负整数 num1 和 num2 ,满足: num1 和 num2 直接连起来,得到 num 各数位的一个排列。 换句话说,num1 和 num2 中所…...

自定义实现图片裁剪
要实现这个功能,首先需要创建一个自定义的View,然后在该View中绘制背景框和裁剪后的图片。以下是一个简单的实现: 1. 创建一个名为CustomImageView的自定义View类,继承自View: import android.content.Context; impor…...

开发语言工具编程系统化教程入门和初级专辑课程上线
开发语言工具编程系统化教程入门和初级专辑课程上线 学习编程捷径:(不论是正在学习编程的大学生,还是IT人士或者是编程爱好者,在学习编程的过程中用正确的学习方法 可以达到事半功倍的效果。对于初学者,可以通过下面…...
【Truffle】二、自定义合约测试
一、准备测试 上期我们自己安装部署了truffle,并且体验了测试用例的整个测试流程,实际开发中,我们可以对自己的合约进行测试。 我们首先先明白自定义合约测试需要几个文件 合约文件:既然要测试合约,肯定要有合约的源码…...
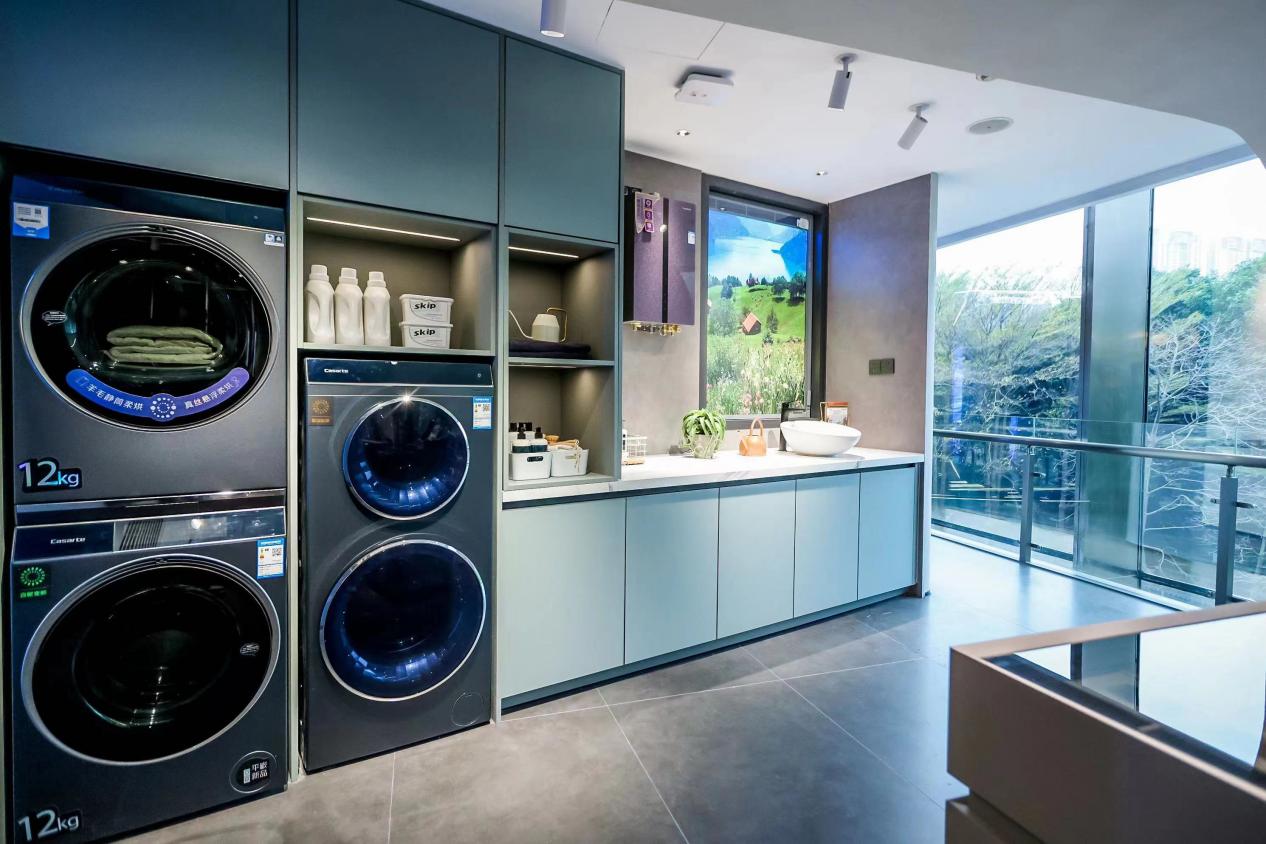

场景交易额超40亿,海尔智家三翼鸟开始收获
文 | 螳螂观察 作者 | 余一 随着双十一的到来,国内的消费情绪再次被点燃。在这类大促之下,品牌们就像一个个天体,不断引动着市场潮汐,期待自己能触发更大的“海潮效应”。 所谓“海潮效应”是指,海水因天体的引力而…...

众和策略可靠吗?股票扛杆怎么玩?
可靠 股票扛杆是一种出资战略,经过假贷资金来增加出资金额,从而进步出资收益。这种战略在股票商场中被广泛运用,但一起也伴随着一定的危险。在本文中,咱们将从多个视点来剖析股票扛杆怎么玩。 首要,扛杆出资的原理是…...
: Lost connection to MySQL server at ‘waiting)
解决连接Mysql出现ERROR 2013 (HY000): Lost connection to MySQL server at ‘waiting
在上一篇中解决Mysql ER_ACCESS_DENIED_ERROR: Access denied for user ‘root‘‘localhost‘ (using password: YES)-CSDN博客 写了mysql的密码报错问题,在执行 mysql -u root -p 出现了这个错误, ERROR 2013 (HY000): Lost connection to MySQL se…...

Hadoop YARN功能介绍--资源管理、调度任务
Hadoop YRAN介绍 YARN是一个通用资源管理系统平台和调度平台,可为上层应用提供统一的资源管理和 调度。 他的引入为集群在利用率、资源统一管理和数据共享等方面带来了好处。 1.资源管理系统 集群的硬件资源,和程序运行无关,比如内存、cu…...

从AlexNet到chatGPT的演进过程
一、演进 AlexNet(2012): AlexNet是深度学习领域的重要突破,包括5个卷积层和3个全连接层。使用ReLU激活函数和Dropout正则化,获得了ImageNet图像分类比赛的胜利。引入了GPU加速训练,大幅提高了深度神经网络…...

Unity如何实现bHaptics TrackSuit震动衣的SDK接入
前言 TrackSuit是bHaptisc公司旗下的一款震动衣,包括X16,X40等不同型号,是一款尖端的无线高级触觉背心,采用人体工程学设计,具有40个精确的触觉反馈点。通过无缝的跨平台支持和无限制、无滞后的游戏体验,增强您的VR冒险体验。用于PC或者VR游戏中高度还原真实射击触感。官…...
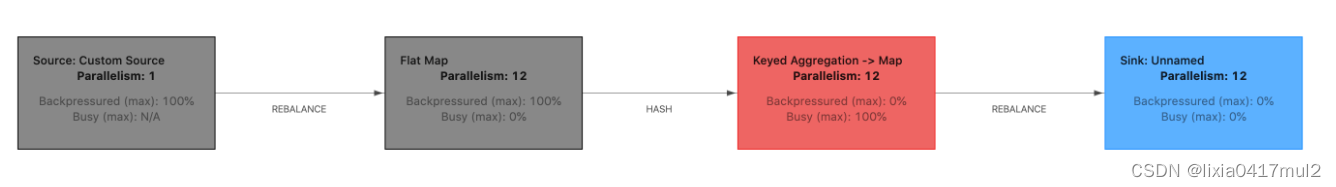
识别flink的反压源头
背景 flink中最常见的问题就是反压,这种情况下我们要正确的识别导致反压的真正的源头,本文就简单看下如何正确识别反压的源头 反压的源头 首先我们必须意识到现实中轻微的反压是没有必要去优化的,因为这种情况下是由于偶尔的流量峰值,Task…...

Spring是如何解决bean循环依赖的问题的
在Spring框架中,循环依赖是指两个或多个Bean之间相互依赖,形成了一个闭环的依赖关系。当存在循环依赖时,Bean的创建过程会陷入死循环,导致应用程序无法启动或出现异常。 说到循环依赖,首先我先说说bean的三级缓存 在S…...
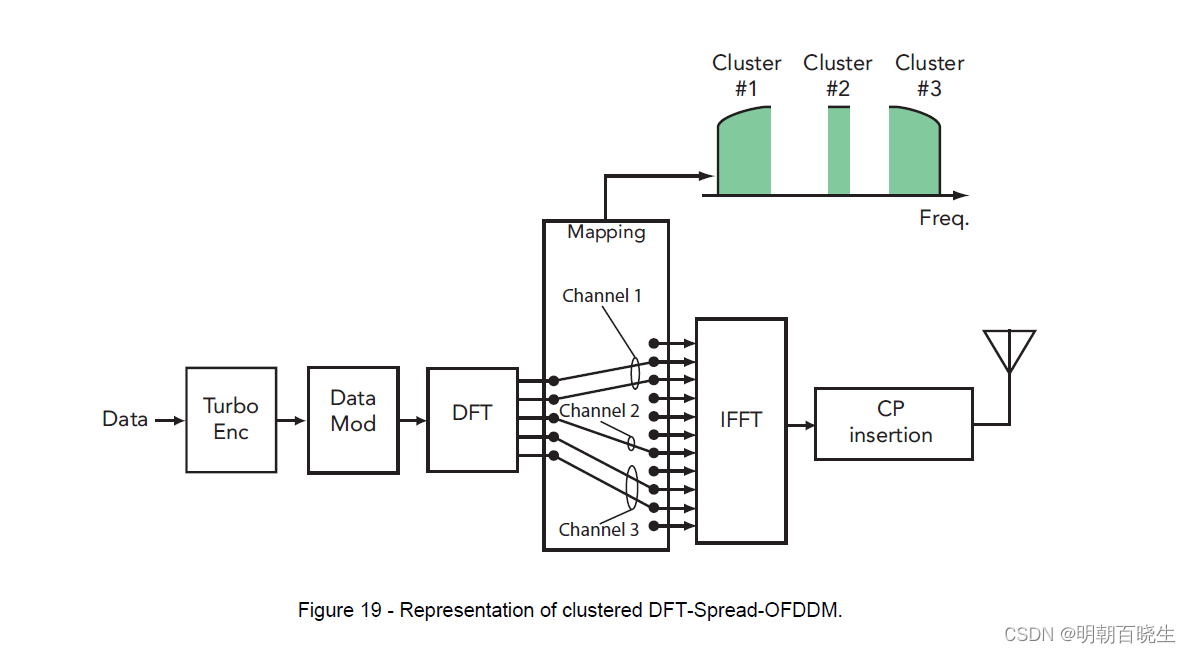
[移动通讯]【Carrier Aggregation-9】【 Radio Resource Control (RRC) Aspects】
前言: CA 分析辅助工具: UE Capabilities 目录: 总体流程 Radio Resource Control (RRC) Aspects SCell addition and removal Handover 一 总体流程 1.1 CA 总体流程 1.2 CA 和 NSA 区别 NSA 我理解也是一种特殊的CA 方案&…...

故障预测与健康管理(PHM)的由来以及当前面临的挑战
故障预测与健康管理(PHM)作为一项关键技术,旨在帮助企业在事故发生之前较长时间内实现故障预测与健康管理,达到“治未病”的效果。PHM的发展源于对设备可靠性和安全性的追求,以及对预测性维护的需求。然而,…...

【ChatGPT瀑布到水母】AI 在驱动软件研发的革新与实践
这里写目录标题 前言内容简介作者简介专家推荐读者对象目录直播预告 前言 计算机技术的发展和互联网的普及,使信息处理和传输变得更加高效,极大地改变了金融、商业、教育、娱乐等领域的运作方式。数据分析、人工智能和云计算等新兴技术,也在不…...

【Django】项目模型
Django的基本命令 django-admin 命令含义startproject启动Django项目startapp启动Django应用check检查项目完整性runserver本地运行项目shell进入Django项目的Python Shell环境test 进行Django用例测试makemigrations创建模型变更的迁移文件migrate执行makemigrations…...
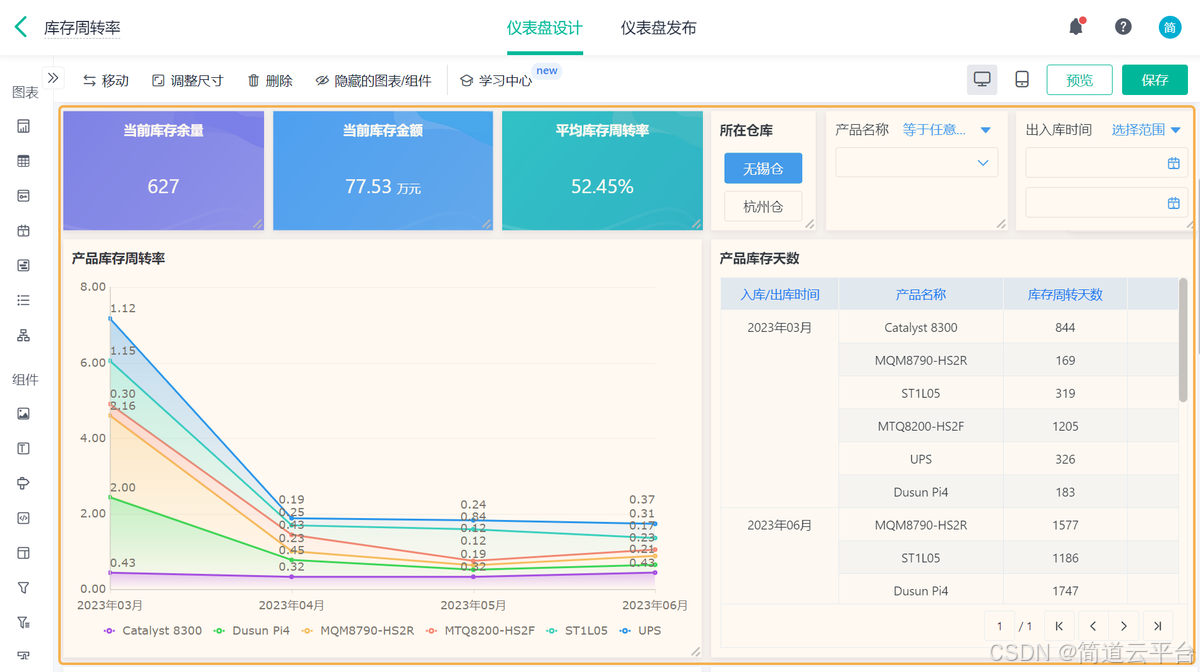
什么是库存周转?如何用进销存系统提高库存周转率?
你可能听说过这样一句话: “利润不是赚出来的,是管出来的。” 尤其是在制造业、批发零售、电商这类“货堆成山”的行业,很多企业看着销售不错,账上却没钱、利润也不见了,一翻库存才发现: 一堆卖不动的旧货…...

【配置 YOLOX 用于按目录分类的图片数据集】
现在的图标点选越来越多,如何一步解决,采用 YOLOX 目标检测模式则可以轻松解决 要在 YOLOX 中使用按目录分类的图片数据集(每个目录代表一个类别,目录下是该类别的所有图片),你需要进行以下配置步骤&#x…...

聊一聊接口测试的意义有哪些?
目录 一、隔离性 & 早期测试 二、保障系统集成质量 三、验证业务逻辑的核心层 四、提升测试效率与覆盖度 五、系统稳定性的守护者 六、驱动团队协作与契约管理 七、性能与扩展性的前置评估 八、持续交付的核心支撑 接口测试的意义可以从四个维度展开,首…...
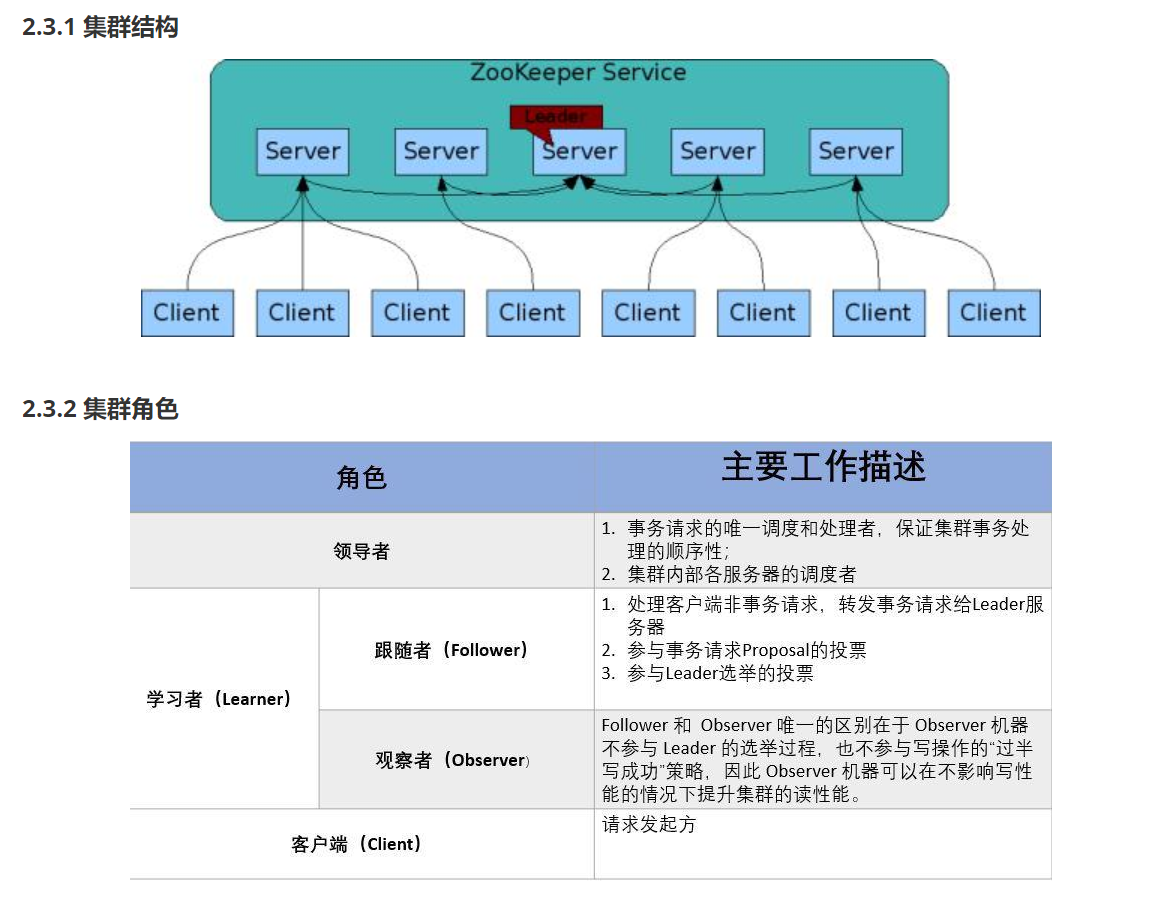
HDFS分布式存储 zookeeper
hadoop介绍 狭义上hadoop是指apache的一款开源软件 用java语言实现开源框架,允许使用简单的变成模型跨计算机对大型集群进行分布式处理(1.海量的数据存储 2.海量数据的计算)Hadoop核心组件 hdfs(分布式文件存储系统)&a…...

代码随想录刷题day30
1、零钱兑换II 给你一个整数数组 coins 表示不同面额的硬币,另给一个整数 amount 表示总金额。 请你计算并返回可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。如果任何硬币组合都无法凑出总金额,返回 0 。 假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。 题目数据保证结果符合 32 位带…...
推荐 github 项目:GeminiImageApp(图片生成方向,可以做一定的素材)
推荐 github 项目:GeminiImageApp(图片生成方向,可以做一定的素材) 这个项目能干嘛? 使用 gemini 2.0 的 api 和 google 其他的 api 来做衍生处理 简化和优化了文生图和图生图的行为(我的最主要) 并且有一些目标检测和切割(我用不到) 视频和 imagefx 因为没 a…...
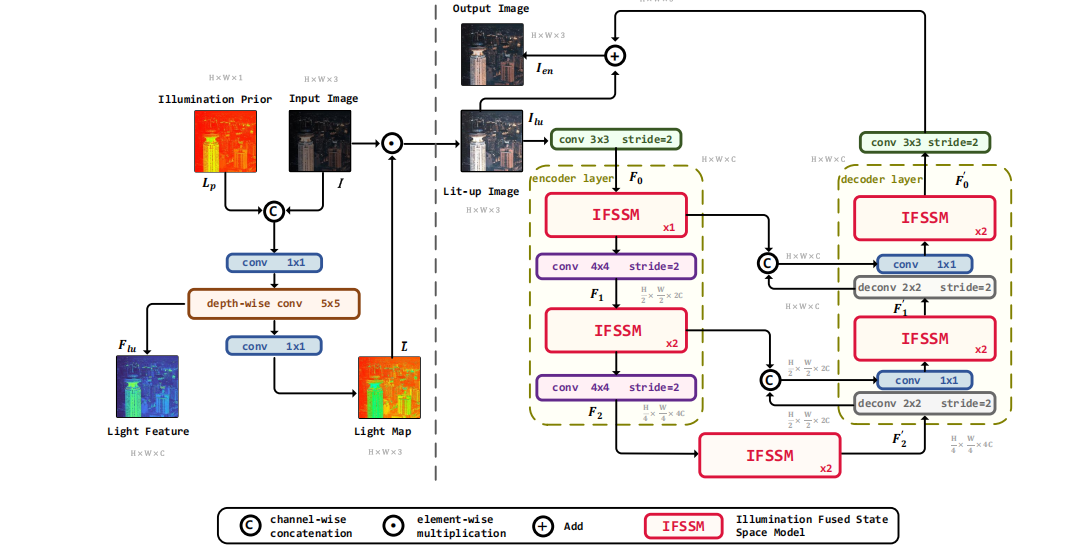
深度学习水论文:mamba+图像增强
🧀当前视觉领域对高效长序列建模需求激增,对Mamba图像增强这方向的研究自然也逐渐火热。原因在于其高效长程建模,以及动态计算优势,在图像质量提升和细节恢复方面有难以替代的作用。 🧀因此短时间内,就有不…...

Python+ZeroMQ实战:智能车辆状态监控与模拟模式自动切换
目录 关键点 技术实现1 技术实现2 摘要: 本文将介绍如何利用Python和ZeroMQ消息队列构建一个智能车辆状态监控系统。系统能够根据时间策略自动切换驾驶模式(自动驾驶、人工驾驶、远程驾驶、主动安全),并通过实时消息推送更新车…...
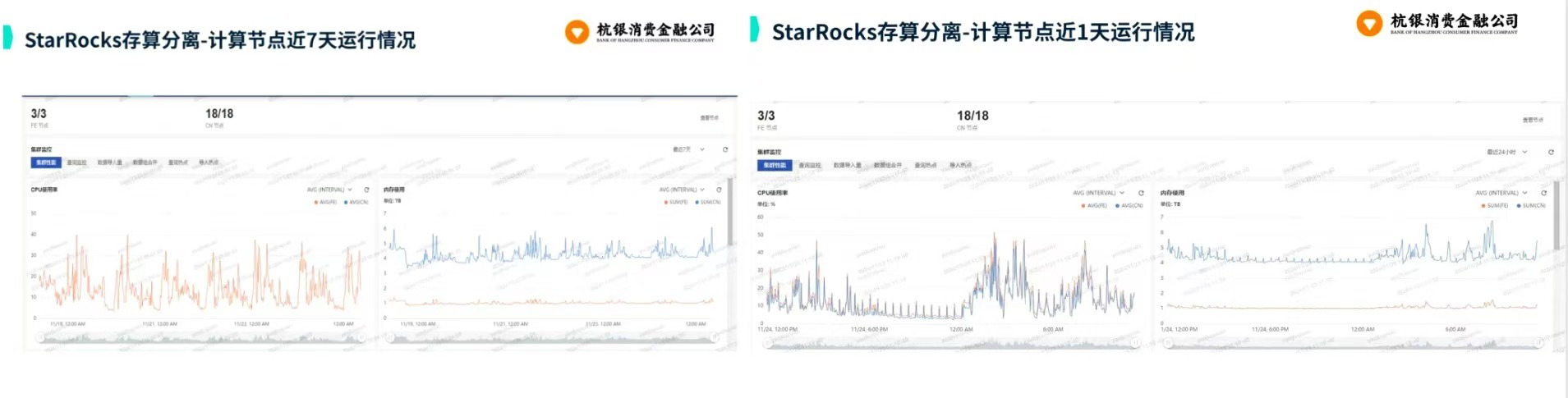
从 GreenPlum 到镜舟数据库:杭银消费金融湖仓一体转型实践
作者:吴岐诗,杭银消费金融大数据应用开发工程师 本文整理自杭银消费金融大数据应用开发工程师在StarRocks Summit Asia 2024的分享 引言:融合数据湖与数仓的创新之路 在数字金融时代,数据已成为金融机构的核心竞争力。杭银消费金…...

什么是VR全景技术
VR全景技术,全称为虚拟现实全景技术,是通过计算机图像模拟生成三维空间中的虚拟世界,使用户能够在该虚拟世界中进行全方位、无死角的观察和交互的技术。VR全景技术模拟人在真实空间中的视觉体验,结合图文、3D、音视频等多媒体元素…...
