SplayTree高分测试用例
测试用例结果展示
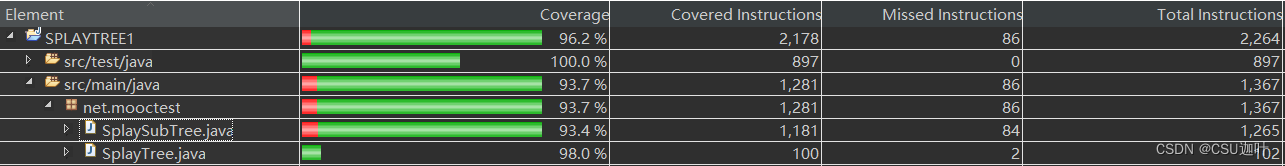
覆盖率
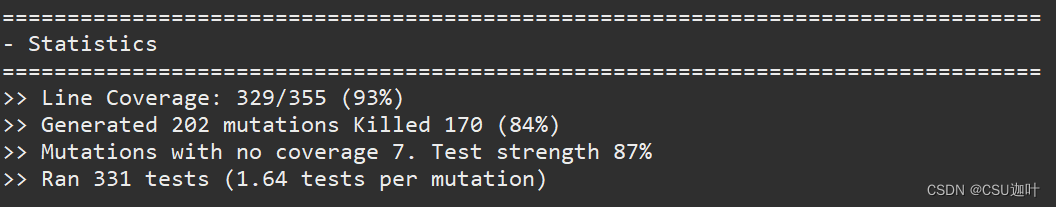
变异得分
测试注意点
- 从SplayTree测起,然后再测SubSplayTree,因为前者调用后者。
- SplaySubTree的remove方法大部分内容需要通过反射才能测到。
- value和index在SplayTree当中都不是唯一的。一个index可能对应多个value。
不足之处
- 没考虑到异常怎么接住。
- 对SplayTree这个数据结构的理解还很浅显。
测试文件MyTest.java
package net.mooctest;import static org.junit.Assert.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.Arrays;import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;public class MyTest {private Integer valArr[];private Integer remArr[];private Integer conArr[];private SplayTree<Integer> splayTree;private int howmanynumbers;private int removeCnt;private int containsCnt;@Beforepublic void initializeValArr() {this.howmanynumbers = 100;this.removeCnt = 0;this.containsCnt = 0;valArr = new Integer[howmanynumbers]; remArr = new Integer[howmanynumbers/7+1]; conArr = new Integer[howmanynumbers/9+1];for(int i=0;i<this.howmanynumbers;i++) {int val = (int)(Math.random()*100);
// System.out.println(val);valArr[i] = val;if(i%7==0) {remArr[this.removeCnt++] = val;}if(i%9==0) {conArr[this.containsCnt++] = val;}}}@Testpublic void testMain() {SplayTree.main(null);}// 测试remove和contains@Testpublic void test001() {splayTree = new SplayTree<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<this.howmanynumbers;i++) {splayTree.add(valArr[i]);assertNull(splayTree.root.join(splayTree.root));}assertNotNull(splayTree.root.add(null));assertEquals(howmanynumbers, splayTree.size());for(int i=0;i<this.removeCnt;i++) {int valToRemove = remArr[i];assertTrue(splayTree.contains(valToRemove));splayTree.remove(valToRemove);}assertEquals(howmanynumbers-removeCnt, splayTree.size());for(int i=0;i<this.containsCnt;i++) {int valToVarify = conArr[i];assertTrue(splayTree.contains(valToVarify));}}// 测试remove和contains@Testpublic void test002() {splayTree = new SplayTree<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<this.howmanynumbers;i++) {splayTree.add(valArr[i]);assertNull(splayTree.root.split(splayTree.root.getData()));}assertEquals(howmanynumbers, splayTree.size());for(int i=0;i<this.removeCnt;i++) {int valToRemove = remArr[i];assertTrue(splayTree.contains(valToRemove));splayTree.remove(valToRemove);}assertEquals(howmanynumbers-removeCnt, splayTree.size());for(int i=0;i<this.containsCnt;i++) {int valToVarify = conArr[i];assertTrue(splayTree.contains(valToVarify));}}// 测试get和indexOf// 不能再用随机生成的数据,因为随机数据很可能重复@Testpublic void test003() {splayTree = new SplayTree<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<this.howmanynumbers;i++) {splayTree.add(i*17);}assertEquals(howmanynumbers, splayTree.size());long idxArr[] = new long[howmanynumbers];for(int i=0;i<splayTree.size();i++) {idxArr[i] = splayTree.indexOf(i*17);}for(int i=0;i<splayTree.size();i++) {assertEquals(i*17, (int)splayTree.get(idxArr[i]));}assertNull(splayTree.get(-1));assertNull(splayTree.get(splayTree.size()+1));}//测试toString()@Testpublic void test004() {int primeArr[] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71 };splayTree = new SplayTree<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<primeArr.length;i++) {splayTree.add(primeArr[i]);}// System.out.println(splayTree.toString());
// String expectedStr = " data=2 left= null right null sz=1 cnt=1\n";
// assertEquals(expectedStr, splayTree.toString());String expectedStr = " data=71 left=67 right null sz=20 cnt=1\n" + " data=67 left=61 right null sz=19 cnt=1\n" + " data=61 left=59 right null sz=18 cnt=1\n" + " data=59 left=53 right null sz=17 cnt=1\n" + " data=53 left=47 right null sz=16 cnt=1\n" + " data=47 left=43 right null sz=15 cnt=1\n" + " data=43 left=41 right null sz=14 cnt=1\n" + " data=41 left=37 right null sz=13 cnt=1\n" + " data=37 left=31 right null sz=12 cnt=1\n" + " data=31 left=29 right null sz=11 cnt=1\n" + " data=29 left=23 right null sz=10 cnt=1\n" + " data=23 left=19 right null sz=9 cnt=1\n" + " data=19 left=17 right null sz=8 cnt=1\n" + " data=17 left=13 right null sz=7 cnt=1\n" + " data=13 left=11 right null sz=6 cnt=1\n" + " data=11 left=7 right null sz=5 cnt=1\n" + " data=7 left=5 right null sz=4 cnt=1\n" + " data=5 left=3 right null sz=3 cnt=1\n" + " data=3 left=2 right null sz=2 cnt=1\n" + " data=2 left= null right null sz=1 cnt=1\n";assertEquals(expectedStr, splayTree.toString());}//测试SplaySubTree--find@Test(timeout=4000)public void test005() {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(null);assertNull(splaySubTree.find(1));int primeArr[] = {2, 41, 5, 7, 67, 23, 11, 17, 19};for(int i=0;i<primeArr.length;i++) {splaySubTree = splaySubTree.add(primeArr[i]);}
// System.out.println(splaySubTree.toString());assertNull(splaySubTree.find(20));}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test006() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(0);int primeArr[] = {2, 41, 5, 7, 23, 11, 67, 17, 19};System.out.println(primeArr.length);for(int i=0;i<primeArr.length;i++) {splaySubTree = splaySubTree.add(primeArr[i]);}assertNotNull(splaySubTree.remove(20));assertEquals(primeArr.length+1,splaySubTree.remove(null).size());// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field countField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("count"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 countField.setAccessible(true); splaySubTree = splaySubTree.remove(7);// 访问私有属性 count 的值 int countValue = (int) countField.get(splaySubTree);
// System.out.println("countValue: " + countValue);assertEquals(0, countValue);
// System.out.println(splaySubTree.toString());splaySubTree = splaySubTree.remove(7);countValue = (int) countField.get(splaySubTree);
// System.out.println("countValue: " + countValue); assertEquals(-1, countValue);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test007() {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test008() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field leftField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("left"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 leftField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);leftField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test009() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field rightField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("right"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 rightField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);rightField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test0010() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field leftField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("left");Field parentField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("parent"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 leftField.setAccessible(true); parentField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);leftField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree3 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(3);parentField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree3);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test0011() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field rightField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("right"); Field parentField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("parent"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 rightField.setAccessible(true); parentField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);rightField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree3 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(3);parentField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree3);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test0012() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field rightField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("right"); Field leftField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("left"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 rightField.setAccessible(true); leftField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);rightField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree3 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(3);leftField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree3);String expectedStr = " data=1 left=3 right=2 sz=1 cnt=1\n" + " data=3 left= null right null sz=1 cnt=1\n" + " data=2 left= null right null sz=1 cnt=1\n";assertEquals(expectedStr, splaySubTree.toString());}}
被测文件(1/2)SplayTree.java
package net.mooctest;import java.util.Arrays;public class SplayTree <T extends Comparable<T>> {SplaySubTree<T> root;public SplayTree(){root = new SplaySubTree<T>(null);}/*** @param index - of the node to search for.* @return - null if index<=0 or index>=size otherwise SubTree at index. */public T get(long index) {SplaySubTree<T> cT = root.get(index);if(cT==null)return null;cT.splay();root = cT;return cT.getData();}/*** @return - the number of nodes in the tree.*/public long size() { return root.size();}/*** @param node - to search for.* @return - the index of node. All nodes are ordered according to the compareTo(T) method.* */public long indexOf(T node) {long index = root.indexOf(node);get(index);return index;}/*** @param node - is added to the tree.* If node is null tree is unchanged.*/public void add(T node) {root = root.add(node);}/*** @param node - is removed from the tree.* If node is null tree is unchanged.*/public void remove(T node) {root = root.remove(node);}/*** @param node* @return*/public boolean contains(T node) {SplaySubTree<T> temp = root.find(node);if(temp!=null){temp.splay();root = temp;}return temp != null;}@Overridepublic String toString(){return root.toString();}public static void main(String[] args) {SplayTree<Integer> test = new SplayTree<Integer>();int howmanynumbers = 10000;for (int i = 0; i < howmanynumbers; i++) {int val = (int)(Math.random()*100);test.add(val);}System.out.println(test);}
}
被测文件(2/2)SubSplayTree.java
package net.mooctest;public class SplaySubTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {private T data;private SplaySubTree<T> left, right, parent;private long size; // number of nodes in treeprivate int count;/*** @param node* - If node==null then size will be 0 otherwise node will be in the* tree and size will be 1*/public SplaySubTree(T node) {data = node;if (node != null) {size = count = 1;}}public String toString() {String lft = "";String rght = "";String myData = " data=" + data;if (left != null) {myData += " left=" + left.data;lft = left.toString();} else {myData += " left= null";}if (right != null) {myData += " right=" + right.data;rght = right.toString();} else {myData += " right null";}myData += " sz="+size + " cnt="+count;return myData + "\n" + lft + rght;}public T getData() {return data;}/*** @param index* - of the node to search for.* @return - null if index<=0 or index>=size otherwise SubTree at index.*/public SplaySubTree<T> get(long index) {if (index > size || index < 0)return null;long cS = 1;SplaySubTree<T> cT = this;if (cT.left != null)cS += cT.left.size;while (cS != index) {if (cS > index) {cS--;cT = cT.left;if (cT != null && cT.right != null)cS -= cT.right.size;} else {cS++;cT = cT.right;if (cT != null && cT.left != null)cS += cT.left.size;}}return cT;}/*** @return - the number of nodes in the tree.*/public long size() {return size;}/*** @param node* - to search for.* @return - the index of node. All nodes are ordered according to the* compareTo(T) method.* */public long indexOf(T node) {if (node == null)return -1;long cI = 1;SplaySubTree<T> cT = this;if (cT.left != null)cI += cT.left.size;while (!cT.data.equals(node)) {if (cT.data.compareTo(node) > 0) {cI--;cT = cT.left;if (cT != null && cT.right != null)cI -= cT.right.size;} else {cI++;cT = cT.right;if (cT != null && cT.left != null)cI += cT.left.size;}if (cT == null)return -1;}return cI;}/*** @param node* - is added to the tree. If node is null tree is unchanged.* @return - New root of the tree.*/public SplaySubTree<T> add(T node) {if (node == null)return this;if (this.data == null)return new SplaySubTree<T>(node);SplaySubTree<T> current = this;SplaySubTree<T> child = null;if (this.data.compareTo(node) < 0)child = this.right;else if(this.data.compareTo(node)>0)child = this.left;while (child != null && current.data.compareTo(node)!=0) {current = child;if (current.data.compareTo(node) < 0)child = current.right;else if(current.data.compareTo(node)>0)child = current.left;}SplaySubTree<T> newNode = new SplaySubTree<T>(node);if (current.data.compareTo(node) < 0) {current.right = newNode;} else if(current.data.compareTo(node)>0){current.left = newNode;}else {current.size++;current.count++;newNode = current;current = newNode.parent;}newNode.parent = current;if (newNode.splay())return newNode;return this;}/*** @param node* - is removed from the tree. If node is null tree is unchanged.* @return - New root of the tree.*/public SplaySubTree<T> remove(T node) {if (node == null)return this;SplaySubTree<T> x = find(node);if (x == null)return this;if(x.data.equals(node)) {x.count--;x.size--;if(size>0) {x.splay();return x;}}// To delete a node x:// if x has no children remove it.if (x.left == null && x.right == null) {if (x.parent != null) {if (x.parent.left == x) {parent.left = null;} elseparent.right = null;} elsereturn new SplaySubTree(null);}// if x has one child remove x, and put the child in place of xif (x.left == null) {if (x.parent != null) {if (x.parent.left == x) {parent.left = x.right;x.right.parent = parent;x = x.right;} else {parent.right = x.right;x.right.parent = parent;x = x.right;}} else {x.right.parent = null;return x.right;}} else if (x.right == null) {if (x.parent != null) {if (x.parent.left == x) {parent.left = x.left;x.left.parent = parent;x = x.left;} else {parent.right = x.left;x.left.parent = parent;x = x.left;}} else {x.left.parent = null;return x.left;}} else {// if x has two children, swap its value with that of// the rightmost node of its left sub treeSplaySubTree<T> rmc = x.left;while (rmc.right != null)rmc = rmc.right;x.data = rmc.data;// Then remove that node instead.rmc.left.parent = rmc.parent;if (rmc.parent == x) {x.left = rmc.left;} else {rmc.parent.right = rmc.left;}x = rmc;}// After deletion, splay the parent of the removed node to the top of// the tree.x.splay();return x;}/*** @param other* @return*/public SplaySubTree<T> join(SplaySubTree<T> other) {return null;}/*** @param node* @return*/public SplaySubTree<T> split(T node) {return null;}/*** @param node* @return*/public SplaySubTree<T> find(T node) {SplaySubTree<T> current = this;if (this.data == null)return null;while (current != null) {if (node.equals(current.data))return current;if (node.compareTo(current.data) < 0)current = current.left;elsecurrent = current.right;}return current;}/*** Assuming this node is an interior or leaf node of a larger tree this method* moves this node up to the root balancing the tree in the process*/public boolean splay() {while (this.parent != null) {SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> g = p.parent;if (g == null && this == p.left) {zig();} else if (g == null && this == p.right) {zag();} else if (p.left == this && g.left == p) {zigzig();} else if (p.right == this && g.right == p) {zagzag();} else if (p.right == this && g.left == p) {zigzag();} else {zagzig();}}return true;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zig() {SplaySubTree<T> b = this.right;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;this.right = p;p.parent = this;p.left = b;if (b != null)b.parent = p;this.parent = null;p.size = p.count;if (p.right != null)p.size += p.right.size;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = p.size + this.count;if (this.left != null)this.size += this.left.size;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zag() {SplaySubTree<T> b = this.left;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;this.left = p;p.parent = this;p.right = b;if (b != null)b.parent = p;this.parent = null;p.size = p.count;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;if (p.left != null)p.size += p.left.size;this.size = p.size + this.count;if (this.right != null)this.size += this.right.size;}/*** This is a helper method used by zigzig, zagzag, zigzag, zagzig This "fixes"* the great grandparent*/private void fixGG(SplaySubTree<T> g) {SplaySubTree<T> gg = g.parent;if (gg != null) {if (g == gg.left)gg.left = this;if (g == gg.right)gg.right = this;}this.parent = gg;// might need to update size}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zigzig() {SplaySubTree<T> g = parent.parent;SplaySubTree<T> b = this.right;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> c = p.right;fixGG(g);if (b != null)b.parent = p;p.left = b;if (c != null)c.parent = g;g.left = c;g.parent = p;p.right = g;p.parent = this;this.right = p;g.size = g.count;if (c != null)g.size += c.size;if (g.right != null)g.size += g.right.size;p.size = p.count;if (g != null)p.size += g.size;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = p.size + this.count;if (this.left != null)this.size += this.left.size;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zagzag() {SplaySubTree<T> g = parent.parent;SplaySubTree<T> b = this.left;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> c = p.left;fixGG(g);if (b != null)b.parent = p;// above line throws java.lang.NullPointerExceptionp.right = b;if (c != null)c.parent = g;g.right = c;g.parent = p;p.left = g;p.parent = this;this.left = p;g.size = g.count;if (g.left != null)g.size += g.left.size;if (c != null)g.size += c.size;p.size = g.size + p.count;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = p.size + this.count;if (this.right != null)this.size += this.right.size;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zigzag() {SplaySubTree<T> g = parent.parent;SplaySubTree<T> b = this.left;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> c = this.right;fixGG(g);if (b != null)b.parent = p;p.right = b;if (c != null)c.parent = g;g.left = c;p.parent = this;this.left = p;g.parent = this;this.right = g;g.size = g.count;if (g.right != null)g.size += g.right.size;if (c != null)g.size += c.size;p.size = p.count;if (p.left != null)p.size += p.left.size;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = g.size + p.size + this.count;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zagzig() {SplaySubTree<T> g = parent.parent;SplaySubTree<T> b = this.right;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> c = this.left;fixGG(g);if (b != null)b.parent = p;p.left = b;if (c != null)c.parent = g;g.right = c;p.parent = this;this.right = p;g.parent = this;this.left = g;g.size = g.count;if (g.left != null)g.size += g.left.size;if (c != null)g.size += c.size;p.size = p.count;if (p.right != null)p.size += p.right.size;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = g.size + p.size + this.count;}}
相关文章:

SplayTree高分测试用例
测试用例结果展示 覆盖率 变异得分 测试注意点 从SplayTree测起,然后再测SubSplayTree,因为前者调用后者。SplaySubTree的remove方法大部分内容需要通过反射才能测到。value和index在SplayTree当中都不是唯一的。一个index可能对应多个value。 不足之…...

制作麒麟V10-server-sp2镜像
1.挂载iso 文件到目录 mount -o loop /xxx.iso /mnt 这样mnt 目录下会有iso 解压相关的文件 2.修改源文件内容 vim /etc/yum.repos.d/ kylin_x86_64.repo 将里面的所有的源enabled 都改成 0 并添加一个新的源 [ks10-local] name Kylin Linux Advanced Server 10 - Local base…...
2.docker镜像的导入导出
目录 概述docker 常用命令下载导出导入镜像结束 概述 docker 常用命令 本章节使用到的命令,总结在此,后面有使用案例。 命令作用docker images显示镜像docker rmi $(docker images -q)删除系统上所有的镜像docker rmi -f强制删除多个镜像 :…...

bs4介绍和遍历文档树、搜索文档树、案例:爬美女图片、 bs4其它用法、css选择器
bs4介绍和遍历文档树 BeautifulSoup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库,解析库 需要安装模块:pip install beautifulsoup4 使用 解析库可以使用 lxml,速度快(必须安装) 可以使用python内置的 # html…...
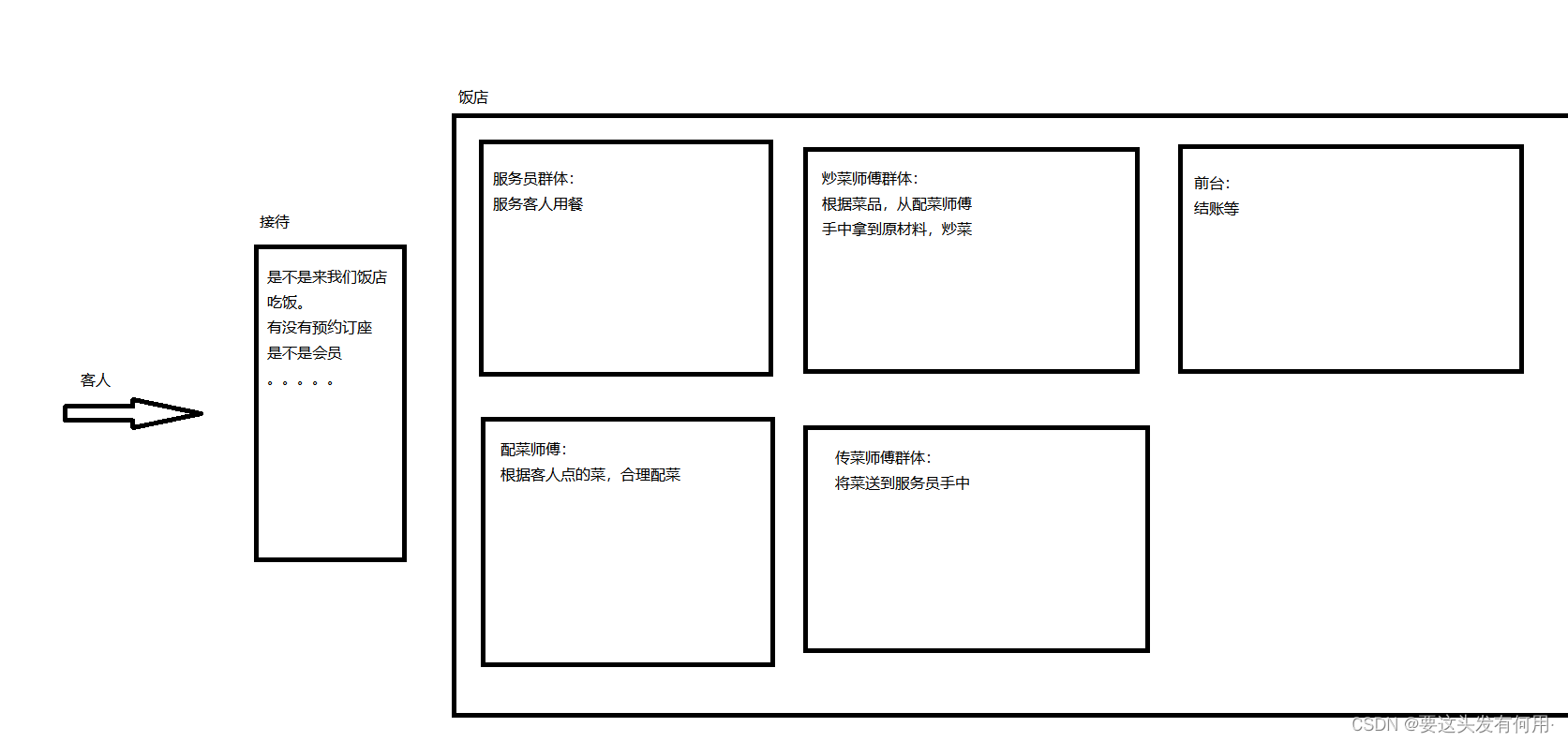
微服务-开篇-个人对微服务的理解
从吃饭说起 个人理解新事物的时候喜欢将天上飞的理念转换成平常生活中的实践,对比理解这些高大上的名词,才能让我们减少恐慌的同时加深理解。废话不多说,我们从吃饭开始说起,逐渐类比出微服务的思想。 (个人见解&…...

机器学习算法-集成学习
概念 集成学习是一种机器学习方法,它通过构建并结合多个机器学习器(基学习器)来完成学习任务。集成学习的潜在思想是即便某一个弱分类器得到了错误的预测,其他的弱分类器也可以将错误纠正回来。集成学习通常被视为一种元算法&…...

LINUX入门篇【4】开发篇--开发工具vim的使用
前言: 从这一篇开始,我们将正式进入使用LINUX进行写程序和开发的阶段,可以说,由此开始,我们才开始真正去使用LINUX。 介绍工具: 1.LINUX软件包管理器yum: 1.yum的介绍: 在LINUX…...

代码随想录算法训练营Day 50 || 309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期、714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期 力扣题目链接 给定一个整数数组,其中第 i 个元素代表了第 i 天的股票价格 。 设计一个算法计算出最大利润。在满足以下约束条件下,你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票): 你不能同时…...

【C语言】【数据结构】【环形链表判断是否带环并返回进环节点】有数学推导加图解
1.判断是否带环: 用快慢指针 slow指针一次走一步,fast指针一次走两步 当两个指针相遇时,链表带环;两个指针不能相遇时,当fast走到倒数第一个节点或为空时,跳出循环返回空指针。 那么slow指针一次走一步&a…...
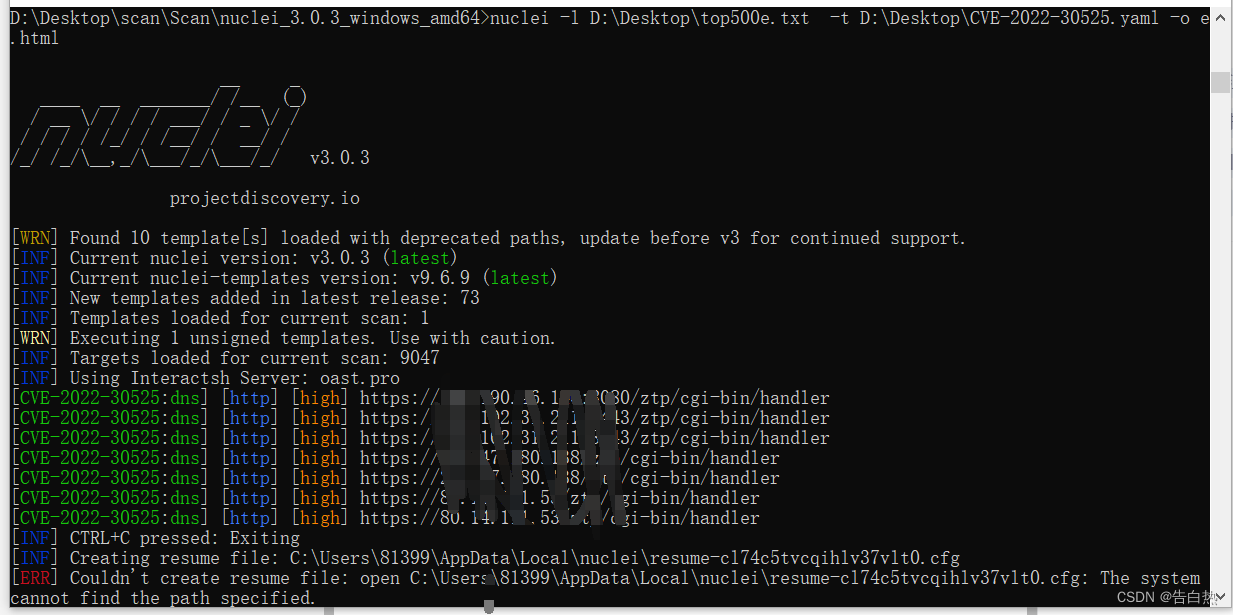
漏洞扫描-nuclei-poc编写
0x00 nuclei Nuclei是一款基于YAML语法模板的开发的定制化快速漏洞扫描器。它使用Go语言开发,具有很强的可配置性、可扩展性和易用性。 提供TCP、DNS、HTTP、FILE 等各类协议的扫描,通过强大且灵活的模板,可以使用Nuclei模拟各种安全检查。 …...

SpringBoot 自动配置
Condition 自定义条件: 定义条件类:自定义类实现Condition接口,重写 matches 方法,在 matches 方法中进行逻辑判断,返回boolean值 。 matches 方法两个参数: context:上下文对象,可…...
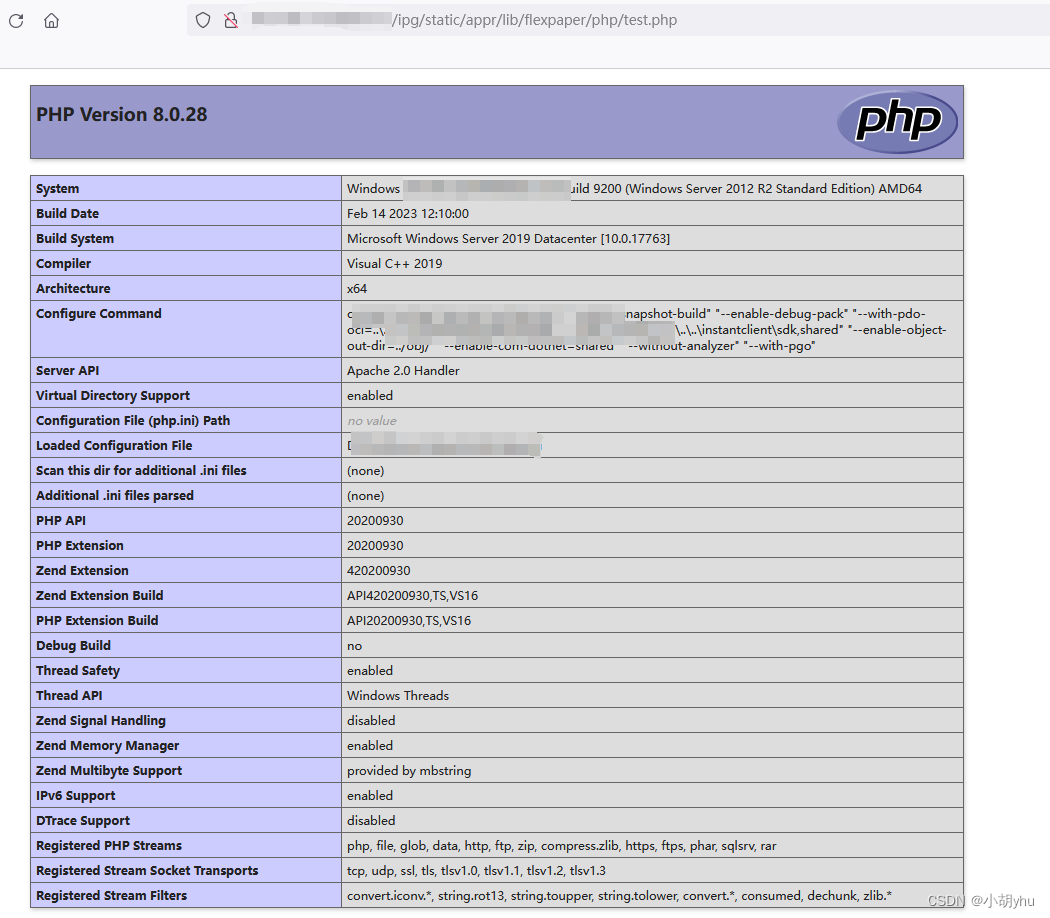
IP-guard WebServer 远程命令执行漏洞
IP-guard WebServer 远程命令执行漏洞 免责声明漏洞描述漏洞影响漏洞危害网络测绘Fofa: app"ip-guard" 漏洞复现1. 构造poc2. 访问文件3. 执行命令 免责声明 仅用于技术交流,目的是向相关安全人员展示漏洞利用方式,以便更好地提高网络安全意识和技术水平。 任何人不…...
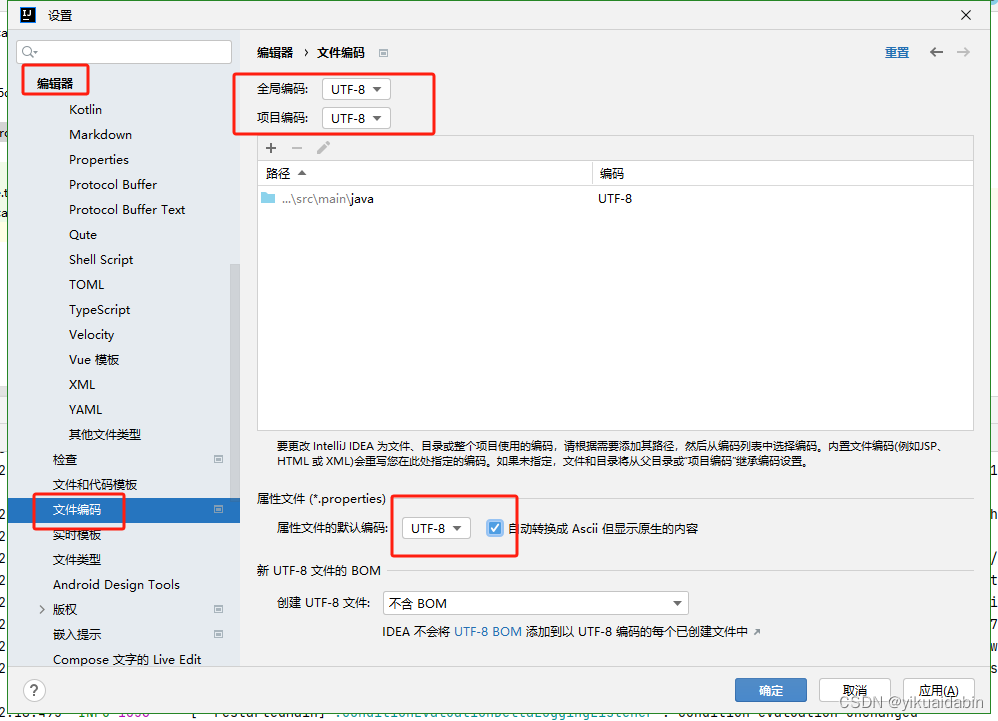
每次重启完IDEA,application.properties文件里的中文变成?
出现这种情况,在IDEA打开Settings-->Editor-->File Encodings 然后,你需要将问号改为你需要的汉字。 重启IDEA,再次查看你的.properties文件就会发现再没有变成问号了...
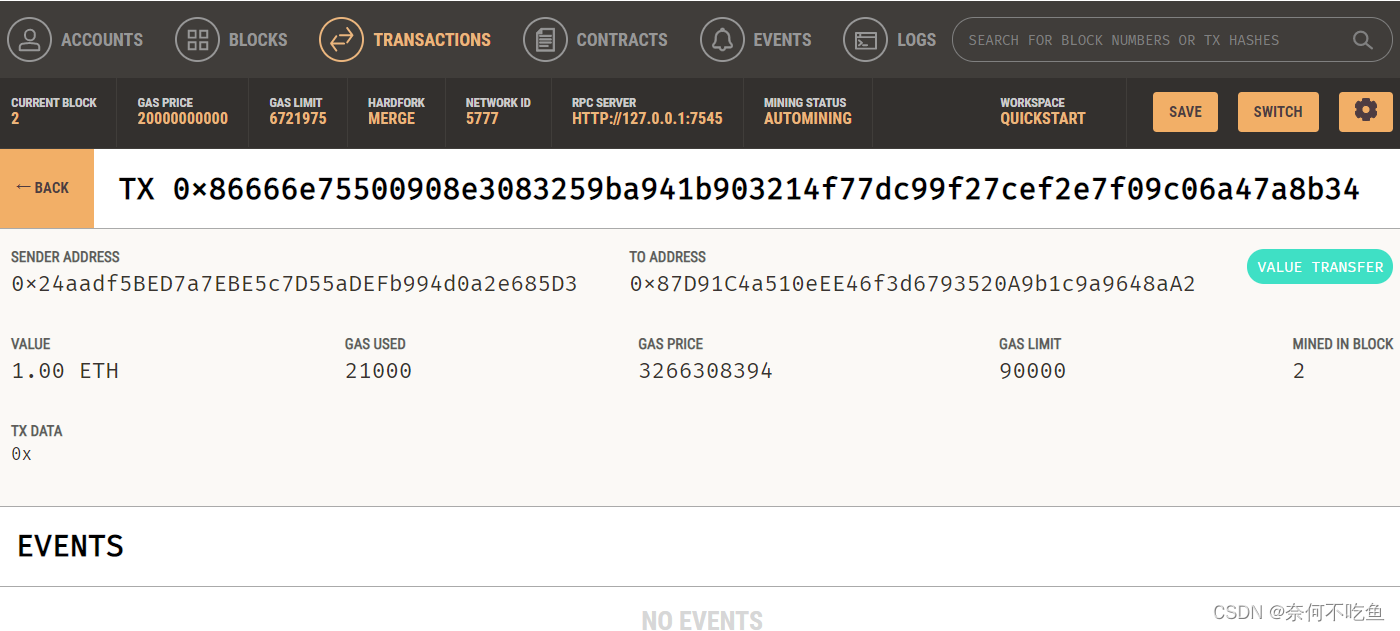
【Truffle】四、通过Ganache部署连接
目录 一、下载安装 Ganache: 二、在本地部署truffle 三、配置ganache连接truffle 四、交易发送 除了用Truffle Develop,还可以选择使用 Ganache, 这是一个桌面应用,他同样会创建一个个人模拟的区块链。 对于刚接触以太坊的同学来说&#x…...
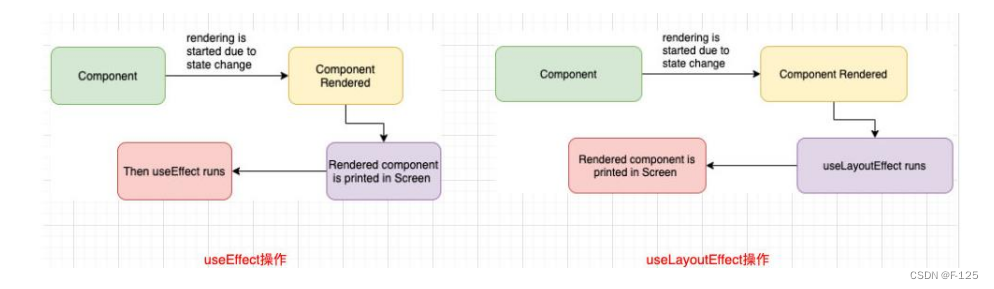
React 其他常用Hooks
1. useImperativeHandle 在react中父组件可以通过forwardRef将ref转发到子组件;子组件拿到父组件创建的ref,绑定到自己的某个元素; forwardRef的做法本身没有什么问题,但是我们是将子组件的DOM直接暴露给了父组件,某下…...
将 ONLYOFFICE 文档编辑器与 С# 群件平台集成
在本文中,我们会向您展示 ONLYOFFICE 文档编辑器与其自有的协作平台集成。 ONLYOFFICE 是一款开源办公套件,包括文本文档、电子表格和演示文稿编辑器。这款套件支持用户通过文档编辑组件扩展第三方 web 应用的功能,可直接在应用的界面中使用。…...

使用电脑时提示msvcp140.dll丢失的5个解决方法
“计算机中msvcp140.dll丢失的5个解决方法”。在我们日常使用电脑的过程中,有时会遇到一些错误提示,其中之一就是“msvcp140.dll丢失”。那么,什么是msvcp140.dll呢?它的作用是什么?丢失它会对电脑产生什么影响呢&…...

VR全景如何应用在房产行业,VR看房有哪些优势
导语: 在如今的数字时代,虚拟现实(VR)技术的迅猛发展为许多行业带来了福音,特别是在房产楼盘行业中。通过利用VR全景技术,开发商和销售人员可以为客户提供沉浸式的楼盘浏览体验,从而带来诸多优…...

11月份 四川汽车托运报价已经上线
中国人不骗中国人!! 国庆小长假的高峰期过后 放假综合症的你还没痊愈吧 今天给大家整理了9条最新线路 广州到四川的托运单价便宜到💥 核算下来不过几毛钱💰 相比起自驾的漫长和疲惫🚗 托运不得不说真的很省事 - 赠送保险 很多客户第一次运车 …...
springcloud图书借阅管理系统源码
开发说明: jdk1.8,mysql5.7,nodejs,idea,nodejs,vscode springcloud springboot mybatis vue elementui 功能介绍: 用户端: 登录注册 首页显示搜索图书,轮播图&…...

Docker 离线安装指南
参考文章 1、确认操作系统类型及内核版本 Docker依赖于Linux内核的一些特性,不同版本的Docker对内核版本有不同要求。例如,Docker 17.06及之后的版本通常需要Linux内核3.10及以上版本,Docker17.09及更高版本对应Linux内核4.9.x及更高版本。…...

<6>-MySQL表的增删查改
目录 一,create(创建表) 二,retrieve(查询表) 1,select列 2,where条件 三,update(更新表) 四,delete(删除表…...

Swift 协议扩展精进之路:解决 CoreData 托管实体子类的类型不匹配问题(下)
概述 在 Swift 开发语言中,各位秃头小码农们可以充分利用语法本身所带来的便利去劈荆斩棘。我们还可以恣意利用泛型、协议关联类型和协议扩展来进一步简化和优化我们复杂的代码需求。 不过,在涉及到多个子类派生于基类进行多态模拟的场景下,…...
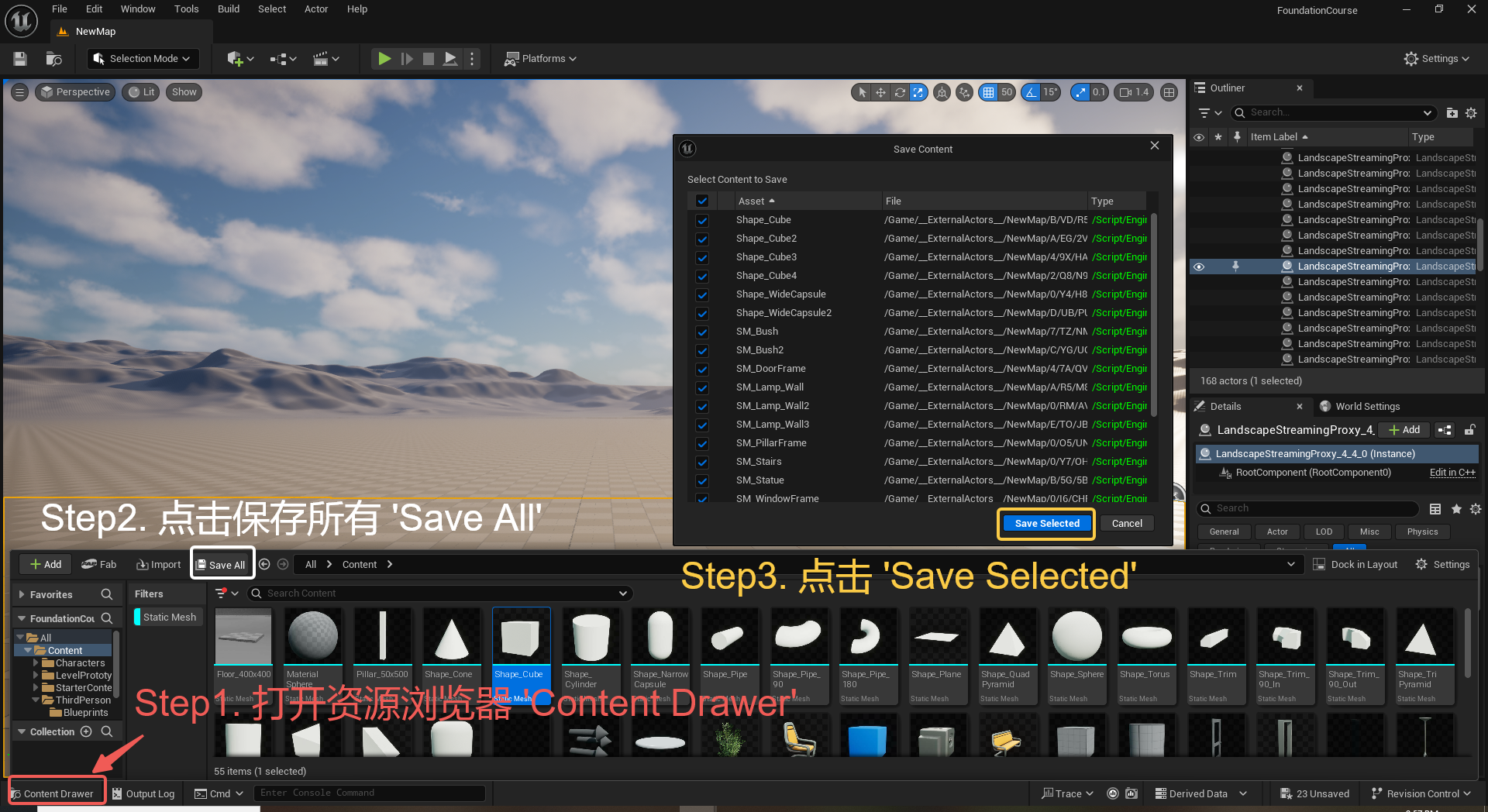
UE5 学习系列(三)创建和移动物体
这篇博客是该系列的第三篇,是在之前两篇博客的基础上展开,主要介绍如何在操作界面中创建和拖动物体,这篇博客跟随的视频链接如下: B 站视频:s03-创建和移动物体 如果你不打算开之前的博客并且对UE5 比较熟的话按照以…...
YSYX学习记录(八)
C语言,练习0: 先创建一个文件夹,我用的是物理机: 安装build-essential 练习1: 我注释掉了 #include <stdio.h> 出现下面错误 在你的文本编辑器中打开ex1文件,随机修改或删除一部分,之后…...

连锁超市冷库节能解决方案:如何实现超市降本增效
在连锁超市冷库运营中,高能耗、设备损耗快、人工管理低效等问题长期困扰企业。御控冷库节能解决方案通过智能控制化霜、按需化霜、实时监控、故障诊断、自动预警、远程控制开关六大核心技术,实现年省电费15%-60%,且不改动原有装备、安装快捷、…...

对WWDC 2025 Keynote 内容的预测
借助我们以往对苹果公司发展路径的深入研究经验,以及大语言模型的分析能力,我们系统梳理了多年来苹果 WWDC 主题演讲的规律。在 WWDC 2025 即将揭幕之际,我们让 ChatGPT 对今年的 Keynote 内容进行了一个初步预测,聊作存档。等到明…...

unix/linux,sudo,其发展历程详细时间线、由来、历史背景
sudo 的诞生和演化,本身就是一部 Unix/Linux 系统管理哲学变迁的微缩史。来,让我们拨开时间的迷雾,一同探寻 sudo 那波澜壮阔(也颇为实用主义)的发展历程。 历史背景:su的时代与困境 ( 20 世纪 70 年代 - 80 年代初) 在 sudo 出现之前,Unix 系统管理员和需要特权操作的…...

06 Deep learning神经网络编程基础 激活函数 --吴恩达
深度学习激活函数详解 一、核心作用 引入非线性:使神经网络可学习复杂模式控制输出范围:如Sigmoid将输出限制在(0,1)梯度传递:影响反向传播的稳定性二、常见类型及数学表达 Sigmoid σ ( x ) = 1 1 +...
)
是否存在路径(FIFOBB算法)
题目描述 一个具有 n 个顶点e条边的无向图,该图顶点的编号依次为0到n-1且不存在顶点与自身相连的边。请使用FIFOBB算法编写程序,确定是否存在从顶点 source到顶点 destination的路径。 输入 第一行两个整数,分别表示n 和 e 的值(1…...
