LLVM学习笔记(64)
4.4.3.3.3. 设置寄存器类对类型的行为
1679行调用computeRegisterProperties()来计算寄存器类的衍生属性。TargetLoweringBase的容器RegisterTypeForVT、RegClassForVT以及NumRegistersForVT用于记录原生支持每个ValueType目标机器寄存器类的信息,即类型对应的寄存器类型、寄存器类别以及寄存器数量。前面每次调用addRegisterClass()时,就会设置上RegClassForVT中对应的项,因此1074~1087行确定需要一个以上寄存器来保存的类型。
1060 void TargetLoweringBase::computeRegisterProperties(
1061 const TargetRegisterInfo *TRI) {
1062 static_assert(MVT::LAST_VALUETYPE <= MVT::MAX_ALLOWED_VALUETYPE,
1063 "Too many value types for ValueTypeActions to hold!");
1064
1065 // Everything defaults to needing one register.
1066 for (unsigned i = 0; i != MVT::LAST_VALUETYPE; ++i) {
1067 NumRegistersForVT[i] = 1;
1068 RegisterTypeForVT[i] = TransformToType[i] = (MVT::SimpleValueType)i;
1069 }
1070 // ...except isVoid, which doesn't need any registers.
1071 NumRegistersForVT[MVT::isVoid] = 0;
1072
1073 // Find the largest integer register class.
1074 unsigned LargestIntReg = MVT::LAST_INTEGER_VALUETYPE;
1075 for (; RegClassForVT[LargestIntReg] == nullptr; --LargestIntReg)
1076 assert(LargestIntReg != MVT::i1 && "No integer registers defined!");
1077
1078 // Every integer value type larger than this largest register takes twice as
1079 // many registers to represent as the previous ValueType.
1080 for (unsigned ExpandedReg = LargestIntReg + 1;
1081 ExpandedReg <= MVT::LAST_INTEGER_VALUETYPE; ++ExpandedReg) {
1082 NumRegistersForVT[ExpandedReg] = 2*NumRegistersForVT[ExpandedReg-1];
1083 RegisterTypeForVT[ExpandedReg] = (MVT::SimpleValueType)LargestIntReg;
1084 TransformToType[ExpandedReg] = (MVT::SimpleValueType)(ExpandedReg - 1);
1085 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction((MVT::SimpleValueType)ExpandedReg,
1086 TypeExpandInteger);
1087 }
1088
1089 // Inspect all of the ValueType's smaller than the largest integer
1090 // register to see which ones need promotion.
1091 unsigned LegalIntReg = LargestIntReg;
1092 for (unsigned IntReg = LargestIntReg - 1;
1093 IntReg >= (unsigned)MVT::i1; --IntReg) {
1094 MVT IVT = (MVT::SimpleValueType)IntReg;
1095 if (isTypeLegal(IVT)) {
1096 LegalIntReg = IntReg;
1097 } else {
1098 RegisterTypeForVT[IntReg] = TransformToType[IntReg] =
1099 (const MVT::SimpleValueType)LegalIntReg;
1100 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(IVT, TypePromoteInteger);
1101 }
1102 }
1103
1104 // ppcf128 type is really two f64's.
1105 if (!isTypeLegal(MVT::ppcf128)) {
1106 if (isTypeLegal(MVT::f64)) {
1107 NumRegistersForVT[MVT::ppcf128] = 2*NumRegistersForVT[MVT::f64];
1108 RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::ppcf128] = MVT::f64;
1109 TransformToType[MVT::ppcf128] = MVT::f64;
1110 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(MVT::ppcf128, TypeExpandFloat);
1111 } else {
1112 NumRegistersForVT[MVT::ppcf128] = NumRegistersForVT[MVT::i128];
1113 RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::ppcf128] = RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::i128];
1114 TransformToType[MVT::ppcf128] = MVT::i128;
1115 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(MVT::ppcf128, TypeSoftenFloat);
1116 }
1117 }
1118
1119 // Decide how to handle f128. If the target does not have native f128 support,
1120 // expand it to i128 and we will be generating soft float library calls.
1121 if (!isTypeLegal(MVT::f128)) {
1122 NumRegistersForVT[MVT::f128] = NumRegistersForVT[MVT::i128];
1123 RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::f128] = RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::i128];
1124 TransformToType[MVT::f128] = MVT::i128;
1125 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(MVT::f128, TypeSoftenFloat);
1126 }
1127
1128 // Decide how to handle f64. If the target does not have native f64 support,
1129 // expand it to i64 and we will be generating soft float library calls.
1130 if (!isTypeLegal(MVT::f64)) {
1131 NumRegistersForVT[MVT::f64] = NumRegistersForVT[MVT::i64];
1132 RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::f64] = RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::i64];
1133 TransformToType[MVT::f64] = MVT::i64;
1134 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(MVT::f64, TypeSoftenFloat);
1135 }
1136
1137 // Decide how to handle f32. If the target does not have native f32 support,
1138 // expand it to i32 and we will be generating soft float library calls.
1139 if (!isTypeLegal(MVT::f32)) {
1140 NumRegistersForVT[MVT::f32] = NumRegistersForVT[MVT::i32];
1141 RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::f32] = RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::i32];
1142 TransformToType[MVT::f32] = MVT::i32;
1143 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(MVT::f32, TypeSoftenFloat);
1144 }
1145
1146 // Decide how to handle f16. If the target does not have native f16 support,
1147 // promote it to f32, because there are no f16 library calls (except for
1148 // conversions).
1149 if (isTypeLegal(MVT::f32)) {
1150 NumRegistersForVT[MVT::f16] = NumRegistersForVT[MVT::f32];
1151 RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::f16] = RegisterTypeForVT[MVT::f32];
1152 TransformToType[MVT::f16] = MVT::f32;
1153 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(MVT::f16, TypePromoteFloat);
1154 }
容器TransformToType用于记录值类型间的提升或扩展关系。对于扩展类型,它包含了该扩展的一步(比如i64 -> i32),即使这个扩展要求多个步骤(比如i64 -> i16)。至于系统内在就支持的类型,容器会保存相同的类型(比如i32 -> i32)(1066行循环初始化)。注意,TransformToType与PromoteToType的含义是不同的。PromoteToType给出了对指定操作,指定类型所要提升到的类型。而TransformToType则是通用的提升规则(即PromoteToType给的是特例)。
与TransformToType伴随的容器ValueTypeActions则记录了该提升或扩展所需的操作,这些操作通过枚举类型LegalizeTypeAction来描述。
122 enum LegalizeTypeAction : uint8_t {
123 TypeLegal, // The target natively supports this type.
124 TypePromoteInteger, // Replace this integer with a larger one.
125 TypeExpandInteger, // Split this integer into two of half the size.
126 TypeSoftenFloat, // Convert this float to a same size integer type.
127 // if an operation is not supported in target HW.
128 TypeExpandFloat, // Split this float into two of half the size.
129 TypeScalarizeVector, // Replace this one-element vector with its element.
130 TypeSplitVector, // Split this vector into two of half the size.
131 TypeWidenVector, // This vector should be widened into a larger vector.
132 TypePromoteFloat // Replace this float with a larger one.
133 };
computeRegisterProperties()下半部分处理向量类型提升。1166行的getPreferredVectorAction(),如果类型是v32i1,支持AVX-512但不支持指令集,返回TypeSplitVector;如果开启了X86实验性的向量拓宽合法化,返回TypeWidenVector;如果该向量只包含一个元素,返回TypeScalarizeVector;否则返回TypePromoteInteger。
TargetLoweringBase::computeRegisterProperties(续)
1156 // Loop over all of the vector value types to see which need transformations.
1157 for (unsigned i = MVT::FIRST_VECTOR_VALUETYPE;
1158 i <= (unsigned)MVT::LAST_VECTOR_VALUETYPE; ++i) {
1159 MVT VT = (MVT::SimpleValueType) i;
1160 if (isTypeLegal(VT))
1161 continue;
1162
1163 MVT EltVT = VT.getVectorElementType();
1164 unsigned NElts = VT.getVectorNumElements();
1165 bool IsLegalWiderType = false;
1166 LegalizeTypeAction PreferredAction = getPreferredVectorAction(VT);
1167 switch (PreferredAction) {
1168 case TypePromoteInteger: {
1169 // Try to promote the elements of integer vectors. If no legal
1170 // promotion was found, fall through to the widen-vector method.
1171 for (unsigned nVT = i + 1; nVT <= MVT::LAST_VECTOR_VALUETYPE; ++nVT) {
1172 MVT SVT = (MVT::SimpleValueType) nVT;
1173 // Promote vectors of integers to vectors with the same number
1174 // of elements, with a wider element type.
1175 if (SVT.getScalarSizeInBits() > EltVT.getSizeInBits() &&
1176 SVT.getVectorNumElements() == NElts && isTypeLegal(SVT)) {
1177 TransformToType[i] = SVT;
1178 RegisterTypeForVT[i] = SVT;
1179 NumRegistersForVT[i] = 1;
1180 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(VT, TypePromoteInteger);
1181 IsLegalWiderType = true;
1182 break;
1183 }
1184 }
1185 if (IsLegalWiderType)
1186 break;
1187 LLVM_FALLTHROUGH;
1188 }
1189 case TypeWidenVector:
1190 // Try to widen the vector.
1191 for (unsigned nVT = i + 1; nVT <= MVT::LAST_VECTOR_VALUETYPE; ++nVT) {
1192 MVT SVT = (MVT::SimpleValueType) nVT;
1193 if (SVT.getVectorElementType() == EltVT
1194 && SVT.getVectorNumElements() > NElts && isTypeLegal(SVT)) {
1195 TransformToType[i] = SVT;
1196 RegisterTypeForVT[i] = SVT;
1197 NumRegistersForVT[i] = 1;
1198 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(VT, TypeWidenVector);
1199 IsLegalWiderType = true;
1200 break;
1201 }
1202 }
1203 if (IsLegalWiderType)
1204 break;
1205 LLVM_FALLTHROUGH;
1206
1207 case TypeSplitVector:
1208 case TypeScalarizeVector: {
1209 MVT IntermediateVT;
1210 MVT RegisterVT;
1211 unsigned NumIntermediates;
1212 NumRegistersForVT[i] = getVectorTypeBreakdownMVT(VT, IntermediateVT,
1213 NumIntermediates, RegisterVT, this);
1214 RegisterTypeForVT[i] = RegisterVT;
1215
1216 MVT NVT = VT.getPow2VectorType();
1217 if (NVT == VT) {
1218 // Type is already a power of 2. The default action is to split.
1219 TransformToType[i] = MVT::Other;
1220 if (PreferredAction == TypeScalarizeVector)
1221 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(VT, TypeScalarizeVector);
1222 else if (PreferredAction == TypeSplitVector)
1223 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(VT, TypeSplitVector);
1224 else
1225 // Set type action according to the number of elements.
1226 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(VT, NElts == 1 ? TypeScalarizeVector
1227 : TypeSplitVector);
1228 } else {
1229 TransformToType[i] = NVT;
1230 ValueTypeActions.setTypeAction(VT, TypeWidenVector);
1231 }
1232 break;
1233 }
1234 default:
1235 llvm_unreachable("Unknown vector legalization action!");
1236 }
1237 }
1238
1239 // Determine the 'representative' register class for each value type.
1240 // An representative register class is the largest (meaning one which is
1241 // not a sub-register class / subreg register class) legal register class for
1242 // a group of value types. For example, on i386, i8, i16, and i32
1243 // representative would be GR32; while on x86_64 it's GR64.
1244 for (unsigned i = 0; i != MVT::LAST_VALUETYPE; ++i) {
1245 const TargetRegisterClass* RRC;
1246 uint8_t Cost;
1247 std::tie(RRC, Cost) = findRepresentativeClass(TRI, (MVT::SimpleValueType)i);
1248 RepRegClassForVT[i] = RRC;
1249 RepRegClassCostForVT[i] = Cost;
1250 }
1251 }
注意1168行与1189行的case分支,如果1185行与1203行的条件语句不满足,它们将执行下一个case分支的语句。因此对扩展无望的类型,就会谋求分裂类型,即通过多个更小的向量类型来支持。对于TypeSplitVector操作,源向量类型必须是2幂次大小,getVectorTypeBreakdownMVT()获取可能的分裂类型,它的返回值是所需寄存器的个数。
856 static unsigned getVectorTypeBreakdownMVT(MVT VT, MVT &IntermediateVT,
857 unsigned &NumIntermediates,
858 MVT &RegisterVT,
859 TargetLoweringBase *TLI) {
860 // Figure out the right, legal destination reg to copy into.
861 unsigned NumElts = VT.getVectorNumElements();
862 MVT EltTy = VT.getVectorElementType();
863
864 unsigned NumVectorRegs = 1;
865
866 // FIXME: We don't support non-power-of-2-sized vectors for now. Ideally we
867 // could break down into LHS/RHS like LegalizeDAG does.
868 if (!isPowerOf2_32(NumElts)) {
869 NumVectorRegs = NumElts;
870 NumElts = 1;
871 }
872
873 // Divide the input until we get to a supported size. This will always
874 // end with a scalar if the target doesn't support vectors.
875 while (NumElts > 1 && !TLI->isTypeLegal(MVT::getVectorVT(EltTy, NumElts))) {
876 NumElts >>= 1;
877 NumVectorRegs <<= 1;
878 }
879
880 NumIntermediates = NumVectorRegs;
881
882 MVT NewVT = MVT::getVectorVT(EltTy, NumElts);
883 if (!TLI->isTypeLegal(NewVT))
884 NewVT = EltTy;
885 IntermediateVT = NewVT;
886
887 unsigned NewVTSize = NewVT.getSizeInBits();
888
889 // Convert sizes such as i33 to i64.
890 if (!isPowerOf2_32(NewVTSize))
891 NewVTSize = NextPowerOf2(NewVTSize);
892
893 MVT DestVT = TLI->getRegisterType(NewVT);
894 RegisterVT = DestVT;
895 if (EVT(DestVT).bitsLT(NewVT)) // Value is expanded, e.g. i64 -> i16.
896 return NumVectorRegs*(NewVTSize/DestVT.getSizeInBits());
897
898 // Otherwise, promotion or legal types use the same number of registers as
899 // the vector decimated to the appropriate level.
900 return NumVectorRegs;
901 }
向量类型有一些限制,它元素的个数必须是2的幂。因此,如果要求的类型不是由2的幂个元素组成,就需要使用这么多个元素大小的类型来替换(868行条件)。如果这个检查通过了,那么在875行循环,我们每次将元素个数减半(换而言之寄存器数个数加倍),直到找到合法的向量类型为止。因此如果883行条件不满足,这意味着我们把元素个数降到1,也没找到合法的类型。那么以元素类型为出发点,在891行通过NextPowerOf2()向上查找大小为2次幂且最接近的类型。
在computeRegisterProperties()的1212与1214行通过NumRegistersForVT与RegisterTypeForVT记录下了getVectorTypeBreakdownMVT()给出的结果。在1216行,getPow2VectorType()返回大小为2次幂且最接近VT的上级类型,如果VT本身不是2次幂大小,就要提升到这个类型。
最后,在1244行循环,通过findRepresentativeClass()找出每个类型的代表寄存器。
1032 std::pair<const TargetRegisterClass *, uint8_t>
1033 TargetLoweringBase::findRepresentativeClass(const TargetRegisterInfo *TRI,
1034 MVT VT) const {
1035 const TargetRegisterClass *RC = RegClassForVT[VT.SimpleTy];
1036 if (!RC)
1037 return std::make_pair(RC, 0);
1038
1039 // Compute the set of all super-register classes.
1040 BitVector SuperRegRC(TRI->getNumRegClasses());
1041 for (SuperRegClassIterator RCI(RC, TRI); RCI.isValid(); ++RCI)
1042 SuperRegRC.setBitsInMask(RCI.getMask());
1043
1044 // Find the first legal register class with the largest spill size.
1045 const TargetRegisterClass *BestRC = RC;
1046 for (unsigned i : SuperRegRC.set_bits()) {
1047 const TargetRegisterClass *SuperRC = TRI->getRegClass(i);
1048 // We want the largest possible spill size.
1049 if (TRI->getSpillSize(*SuperRC) <= TRI->getSpillSize(*BestRC))
1050 continue;
1051 if (!isLegalRC(*TRI, *SuperRC))
1052 continue;
1053 BestRC = SuperRC;
1054 }
1055 return std::make_pair(BestRC, 1);
1056 }
1041行的SuperRegClassIterator是一个定制的迭代器,可以遍历一个指定寄存器类的上级寄存器。而容器SuperRegRC记录的就是这些上级寄存器类的序号。因此1046行循环就是查找最大的寄存器类,并连同使用代价返回它(这里代价总是1,它被调度器用来估算寄存器压力)。
从computeRegisterProperties()返回,X86TargetLowering构造函数完成剩下的配置就结束了。
相关文章:
)
LLVM学习笔记(64)
4.4.3.3.3. 设置寄存器类对类型的行为 1679行调用computeRegisterProperties()来计算寄存器类的衍生属性。TargetLoweringBase的容器RegisterTypeForVT、RegClassForVT以及NumRegistersForVT用于记录原生支持每个ValueType目标机器寄存器类的信息,即类型对应的寄存…...
深度学习TensorFlow2基础知识学习前半部分
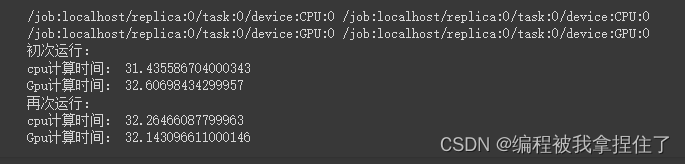
目录 测试TensorFlow是否支持GPU: 自动求导: 数据预处理 之 统一数组维度 定义变量和常量 训练模型的时候设备变量的设置 生成随机数据 交叉熵损失CE和均方误差函数MSE 全连接Dense层 维度变换reshape 增加或减小维度 数组合并 广播机制&#…...
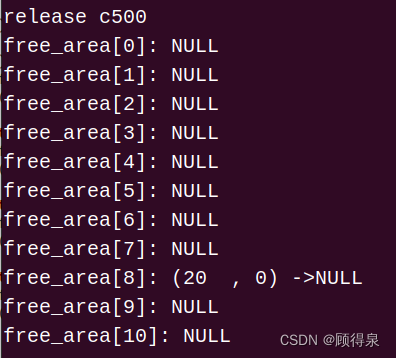
Linux系统---简易伙伴系统
顾得泉:个人主页 个人专栏:《Linux操作系统》 《C/C》 《LeedCode刷题》 键盘敲烂,年薪百万! 一、题目要求 1.采用C语言实现 2.伙伴系统采用free_area[11]数组来组织。要求伙伴内存最小为一个页面,页面大小为4KB…...

Redis使用Lua脚本
Lua脚本 redis可以支持lua脚本,可以使用lua脚本来将几个命令整合为一个整体来执行,这样可以使得多个命令原子操作,且可以减少网络开销 Lua的数据类型 Lua是一个动态类型的语言,一个变量可以存储任何类型的值,类型有&am…...

macos安装metal 加速版 pytorch
categories: [Python] tags: Python MacOS 写在前面 试试 m3 的 metal 加速效果如何 Mac computers with Apple silicon or AMD GPUsmacOS 12.3 or laterPython 3.7 or laterXcode command-line tools: xcode-select --install 安装 Python: conda-forge brew install minif…...

【学习笔记】lyndon分解
摘抄自quack的ppt。 这部分和 s a sa sa的关联比较大,可以加深对 s a sa sa的理解。 Part 1 如果字符串 s s s的字典序在 s s s以及 s s s的所有后缀中是最小的,则称 s s s是一个 lyndon \text{lyndon} lyndon串。 lyndon \text{lyndon} lyndon分解&a…...

21、命令执行
文章目录 一、命令执行概述1.1 基本定义1.2 原理1.3 两个条件1.4 命令执行漏洞产生的原因1.5 管道符号和通用命令符 二、远程命令执行2.1 远程命令执行相关函数2.2 远程命令执行漏洞的利用 三、系统命令执行3.1 相关函数3.2 系统命令执行漏洞利用 四、命令执行漏洞防御 一、命令…...
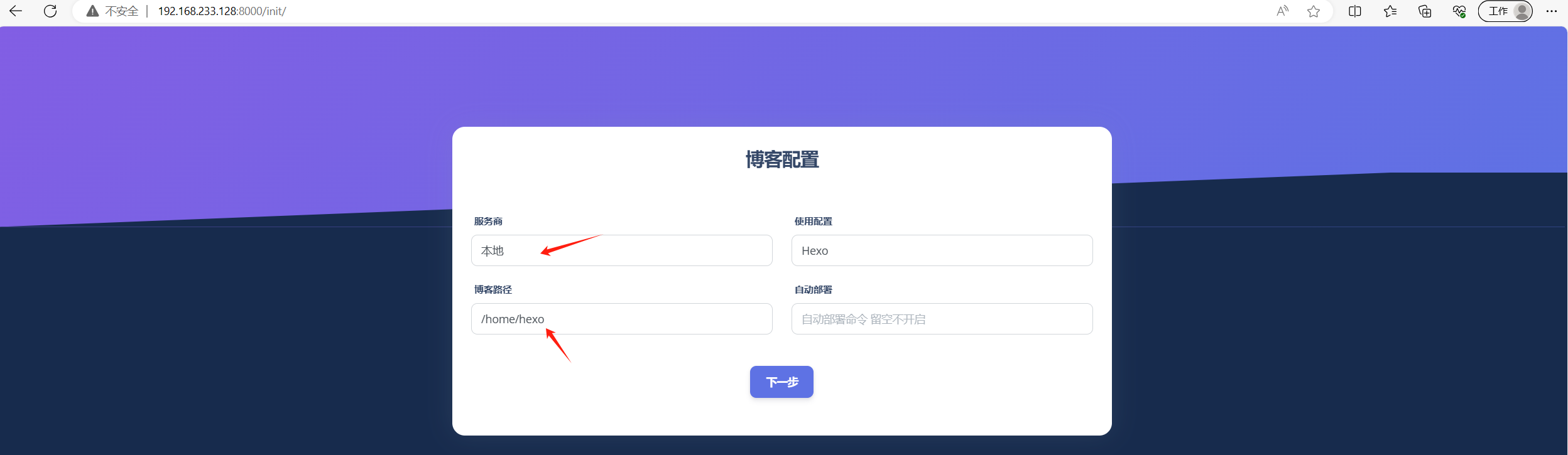
Qexo博客后台管理部署
Qexo博客后台管理部署 个人主页 个人博客 参考文档 https://www.oplog.cn/qexo/本地部署 采用本地Docker部署管理本地Hexo 下载代码包 若无法下载使用科学工具下载到本地在上传到服务器 wget https://github.com/Qexo/Qexo/archive/refs/tags/3.0.1.zip# 解压 unzip Qexo…...

最小生成树prim
最小生成树(三)Prim算法及存储结构_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 311 最小生成树 Prim 算法_哔哩哔哩_bilibili #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <set…...
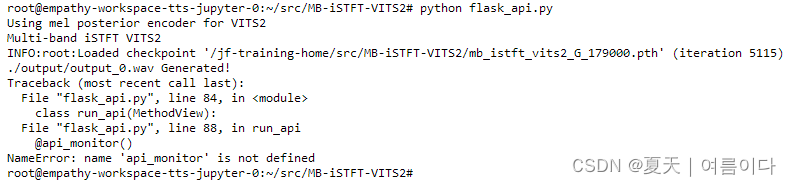
实用篇 | 一文学会人工智能中API的Flask编写(内含模板)
----------------------- 🎈API 相关直达 🎈-------------------------- 🚀Gradio: 实用篇 | 关于Gradio快速构建人工智能模型实现界面,你想知道的都在这里-CSDN博客 🚀Streamlit :实用篇 | 一文快速构建人工智能前端展…...
Si24R03—低功耗 SOC 芯片(集成RISC-V内核+2.4GHz无线收发器)
Si24R03是一款高度集成的低功耗SOC芯片,其集成了基于RISC-V核的低功耗MCU和工作在2.4GHz ISM频段的无线收发器模块。 MCU模块具有低功耗、Low Pin Count、宽电压工作范围,集成了13/14/15/16位精度的ADC、LVD、UART、SPI、I2C、TIMER、WUP、IWDG、RTC等丰…...

C# Winform 日志系统
目录 一、效果 1.刷新日志效果 2.单独日志的分类 3.保存日志的样式 二、概述 三、日志系统API 1.字段 Debug.IsScrolling Debug.Version Debug.LogMaxLen Debug.LogTitle Debug.IsConsoleShowLog 2.方法 Debug.Log(string) Debug.Log(string, params object[]) …...

【Java 基础】27 XML 解析
文章目录 1.SAX 解析器1)什么是 SAX2)SAX 工作流程初始化实现事件处理类解析 3)示例代码 2.DOM 解析器1)什么是 DOM2)DOM 工作流程初始化解析 XML 文档操作 DOM 树 3)示例代码 总结 在项目开发中࿰…...

地图服务 ArcGIS API for JavaScript基础用法全解析
地图服务 ArcGIS API for JavaScript基础用法全解析 前言 在接触ArcGIS之前,开发web在线地图时用过Leaflet来构建地图应用,作为一个轻量级的开源js库,在我使用下来Leaflet还有易懂易用的API文档,是个很不错的选择。在接触使用Ar…...
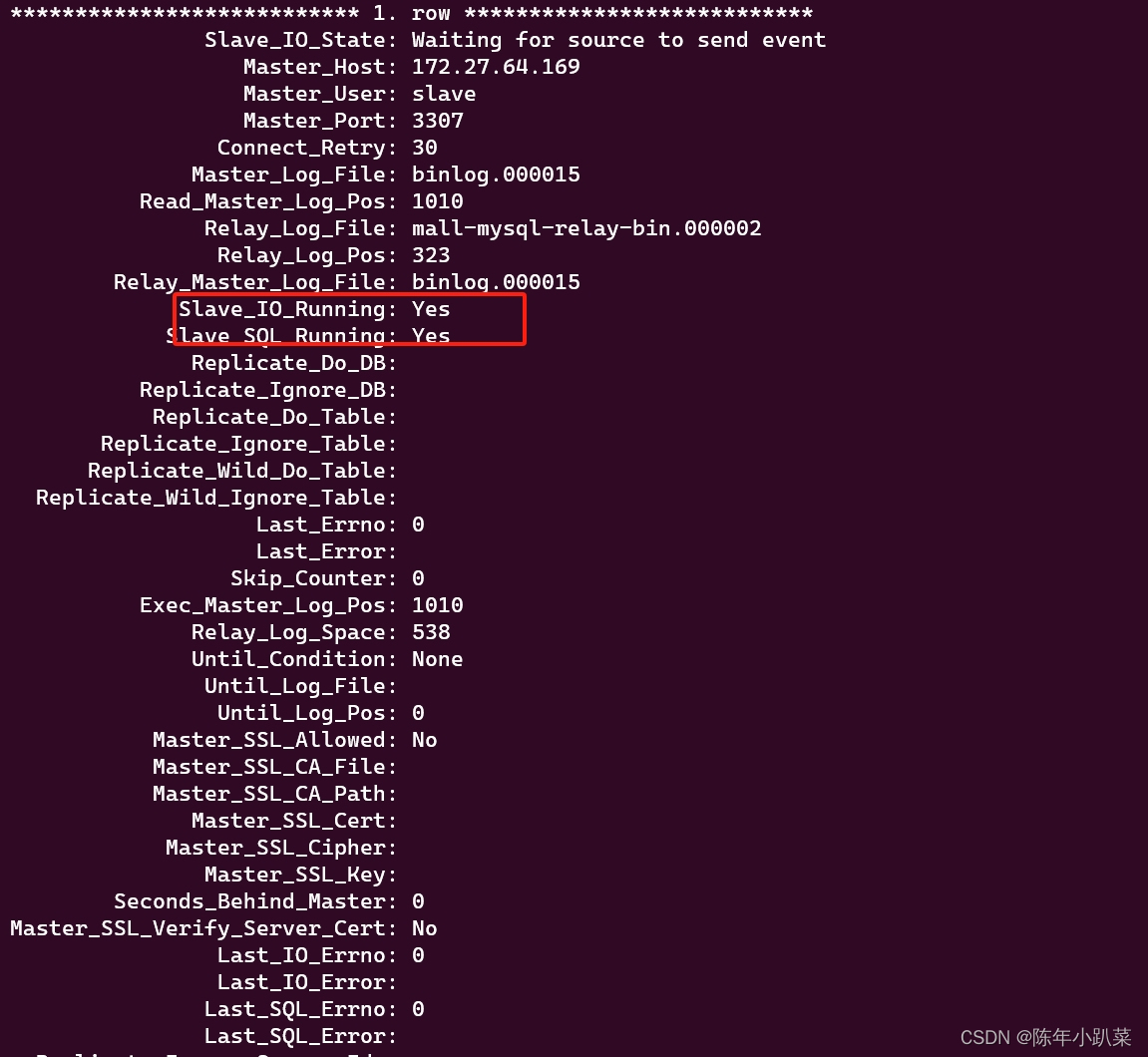
docker学习(八、mysql8.2主从复制遇到的问题)
在我配置主从复制的时候,遇到了一直connecting的问题。 起初可能是我ip配置的不对,slave_io_running一直connecting。(我的环境:windows中安装了wsl,是ubuntu环境的,在wsl中装了miniconda,mini…...
:表单验证)
React-hook-form-mui(三):表单验证
前言 在上一篇文章中,我们介绍了react-hook-form-mui的基础用法。本文将着重讲解表单验证功能。 react-hook-form-mui提供了丰富的表单验证功能,可以通过validation属性来设置表单验证规则。本文将详细介绍validation的三种实现方法,以及如何…...

【私域运营秘籍】4大用户调研方法,让你轻松掌握用户心理!
我们常说私域运营的核心是用户运营。根据二八法则,20%的超级用户贡献企业80%的利润。因此,企业应该根据用户的价值贡献来有针对性地进行运营。 然而,在实际的私域运营中,我们不仅需要找出贡献价值不同的用户,还可以从…...

2.8寸 ILI9341 TFTLCD 学习移植到STM32F103C8T6
2.8寸 ILI9341 TFTLCD 学习移植到STM32F103C8T6 文章目录 2.8寸 ILI9341 TFTLCD 学习移植到STM32F103C8T6前言第1章 LCD简介1.1 LCD硬件接口介绍 第2章 LCD指令介绍第3章 LCD 8080驱动方式3.1 8080写时序3.2 8080读时序 第4章 LCD 驱动代码部分4.1 修改代码部分4.2 代码工程下载…...

Java利用TCP实现简单的双人聊天
一、创建新项目 首先创建一个新的项目,并命名为聊天。然后创建包,创建两个类,客户端(SocketClient)和服务器端(SocketServer) 二、实现代码 客户端代码: package 聊天; import ja…...

软件压力测试的重要性与用途
在当今数字化的时代,软件已经成为几乎所有行业不可或缺的一部分。随着软件应用规模的增加和用户数量的上升,软件的性能变得尤为关键。为了确保软件在面对高并发和大负载时仍然能够保持稳定性和可靠性,软件压力测试变得至关重要。下面是软件压…...

高频面试之3Zookeeper
高频面试之3Zookeeper 文章目录 高频面试之3Zookeeper3.1 常用命令3.2 选举机制3.3 Zookeeper符合法则中哪两个?3.4 Zookeeper脑裂3.5 Zookeeper用来干嘛了 3.1 常用命令 ls、get、create、delete、deleteall3.2 选举机制 半数机制(过半机制࿰…...
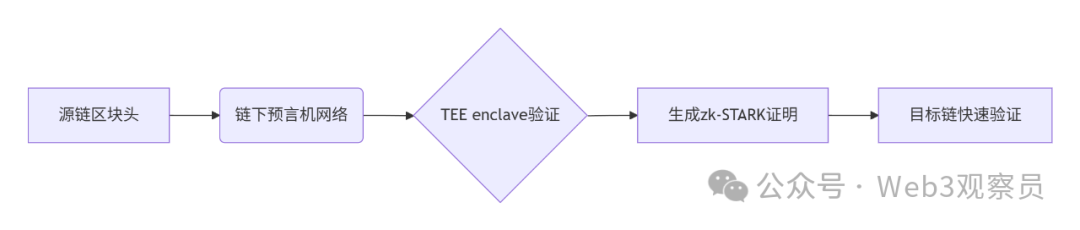
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案 ——构建下一代区块链互联网的技术基石 一、跨链架构的核心范式演进 1. 分层协议栈:模块化解耦设计 现代跨链系统采用分层协议栈实现灵活扩展(H2Cross架构): 适配层…...
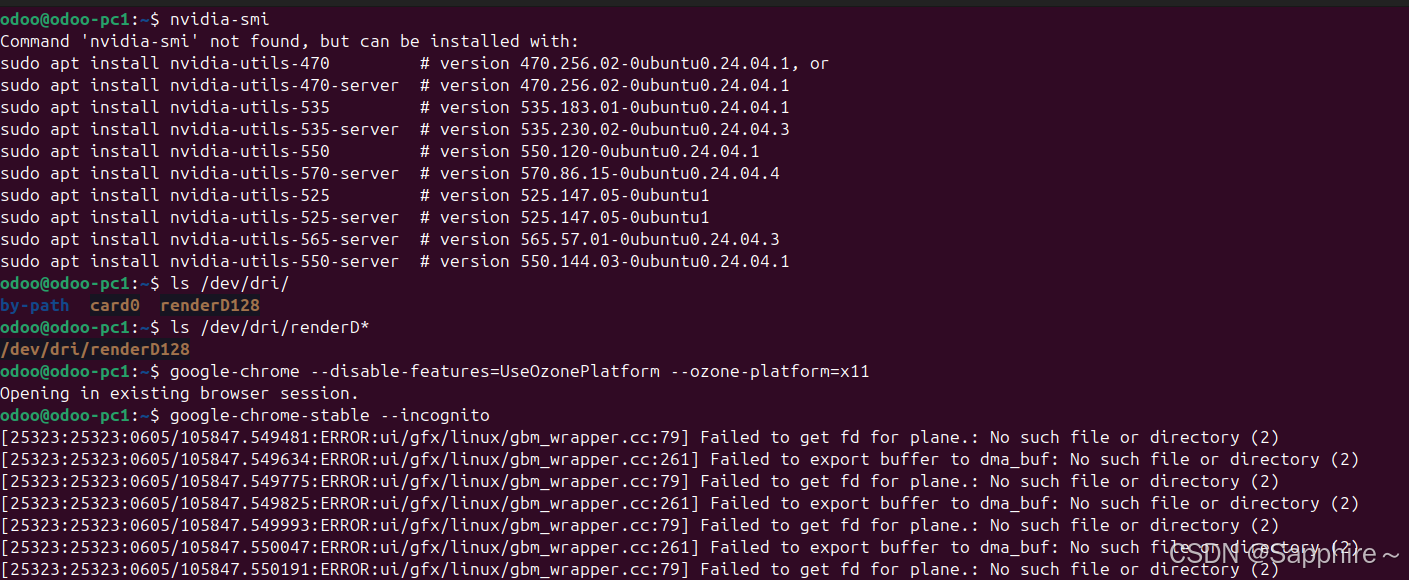
Linux-07 ubuntu 的 chrome 启动不了
文章目录 问题原因解决步骤一、卸载旧版chrome二、重新安装chorme三、启动不了,报错如下四、启动不了,解决如下 总结 问题原因 在应用中可以看到chrome,但是打不开(说明:原来的ubuntu系统出问题了,这个是备用的硬盘&a…...

【碎碎念】宝可梦 Mesh GO : 基于MESH网络的口袋妖怪 宝可梦GO游戏自组网系统
目录 游戏说明《宝可梦 Mesh GO》 —— 局域宝可梦探索Pokmon GO 类游戏核心理念应用场景Mesh 特性 宝可梦玩法融合设计游戏构想要素1. 地图探索(基于物理空间 广播范围)2. 野生宝可梦生成与广播3. 对战系统4. 道具与通信5. 延伸玩法 安全性设计 技术选…...

Mac下Android Studio扫描根目录卡死问题记录
环境信息 操作系统: macOS 15.5 (Apple M2芯片)Android Studio版本: Meerkat Feature Drop | 2024.3.2 Patch 1 (Build #AI-243.26053.27.2432.13536105, 2025年5月22日构建) 问题现象 在项目开发过程中,提示一个依赖外部头文件的cpp源文件需要同步,点…...
关键领域软件测试的突围之路:如何破解安全与效率的平衡难题
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,软件系统已成为国家关键领域的核心战斗力。不同于普通商业软件,这些承载着国家安全使命的软件系统面临着前所未有的质量挑战——如何在确保绝对安全的前提下,实现高效测试与快速迭代?这一命题正考验着…...
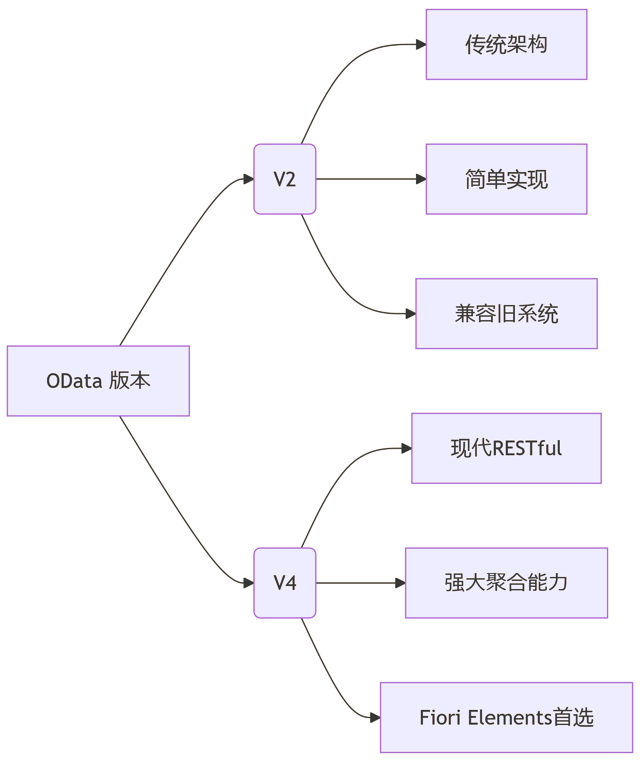
SAP学习笔记 - 开发26 - 前端Fiori开发 OData V2 和 V4 的差异 (Deepseek整理)
上一章用到了V2 的概念,其实 Fiori当中还有 V4,咱们这一章来总结一下 V2 和 V4。 SAP学习笔记 - 开发25 - 前端Fiori开发 Remote OData Service(使用远端Odata服务),代理中间件(ui5-middleware-simpleproxy)-CSDN博客…...

学习一下用鸿蒙DevEco Studio HarmonyOS5实现百度地图
在鸿蒙(HarmonyOS5)中集成百度地图,可以通过以下步骤和技术方案实现。结合鸿蒙的分布式能力和百度地图的API,可以构建跨设备的定位、导航和地图展示功能。 1. 鸿蒙环境准备 开发工具:下载安装 De…...

Python 高效图像帧提取与视频编码:实战指南
Python 高效图像帧提取与视频编码:实战指南 在音视频处理领域,图像帧提取与视频编码是基础但极具挑战性的任务。Python 结合强大的第三方库(如 OpenCV、FFmpeg、PyAV),可以高效处理视频流,实现快速帧提取、压缩编码等关键功能。本文将深入介绍如何优化这些流程,提高处理…...
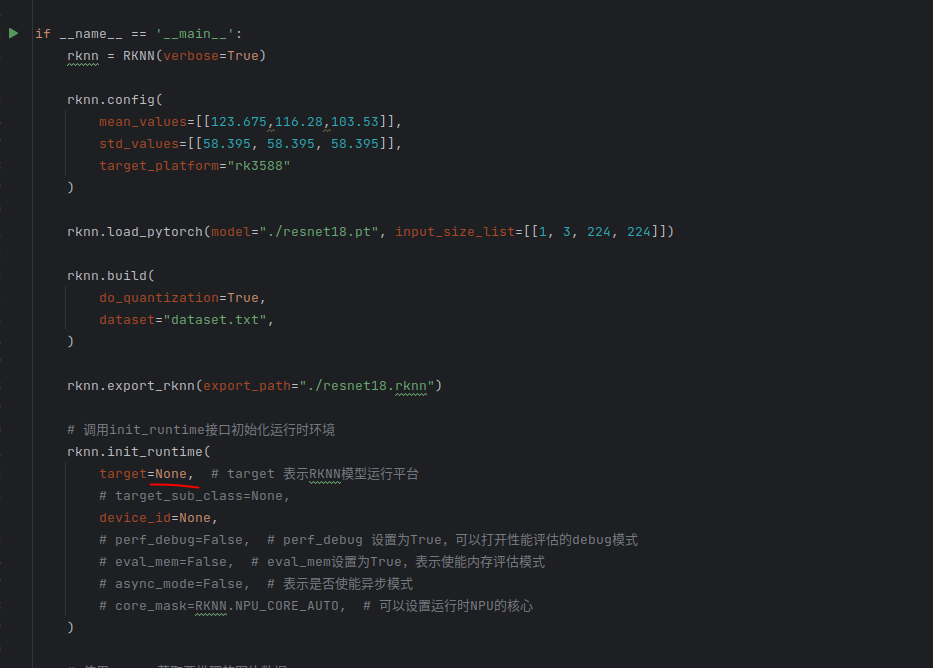
rknn toolkit2搭建和推理
安装Miniconda Miniconda - Anaconda Miniconda 选择一个 新的 版本 ,不用和RKNN的python版本保持一致 使用 ./xxx.sh进行安装 下面配置一下载源 # 清华大学源(最常用) conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn…...
