openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - quic-client-block.c
文章目录
- openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - quic-client-block.c
- 概述
- 笔记
- END
openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - quic-client-block.c
概述
在程序运行时, 要指定环境变量 SSL_CERT_FILE=rootcert.pem, 同时将rootcert.pem拷贝到工程目录下, 否则不好使
吐槽啊, 为啥不用命令行参数或者API参数传进来啊, 整啥环境变量啊, 看着膈应.
quic服务启动(openssl3.2 - quic服务的运行)时的命令行为 quicserver.exe -trace localhost 23456 servercert.pem serverkey.pem
本程序(quic客户端)命令行只能为 localhost 23456 才行
用 127.0.0.1 23456 不好使.
如果要单步调试, 得赶紧的. quic服务启动后, 如果30秒内没有客户端来, quic服务会退出, 这太不礼貌了…
只能跑一下, 听个响, 学不到东西.
这个demo, 是不是只想展示, openssl可以作为quic客户端程序的tls实现?
笔记
/*!
* \file quic-client-block.c
* \note openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - quic-client-block.c
* 在程序运行时, 要指定环境变量 SSL_CERT_FILE=rootcert.pem, 同时将rootcert.pem拷贝到工程目录下, 否则不好使
* 吐槽啊, 为啥不用命令行参数或者API参数传进来啊, 整啥环境变量啊, 看着膈应.
*
* quic服务启动时的命令行为 quicserver.exe -trace localhost 23456 servercert.pem serverkey.pem
本程序(quic客户端)命令行只能为 localhost 23456 才行
用 127.0.0.1 23456 不好使.如果要单步调试, 得赶紧的. quic服务启动后, 如果30秒内没有客户端来, quic服务会退出, 这太不礼貌了...
只能跑一下, 听个响, 学不到东西.这个demo, 是不是只想展示, openssl可以作为quic客户端程序的tls实现?
*//** Copyright 2023 The OpenSSL Project Authors. All Rights Reserved.** Licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (the "License"). You may not use* this file except in compliance with the License. You can obtain a copy* in the file LICENSE in the source distribution or at* https://www.openssl.org/source/license.html*//** NB: Changes to this file should also be reflected in* doc/man7/ossl-guide-quic-client-block.pod*/#include <string.h>/* Include the appropriate header file for SOCK_DGRAM */
#ifdef _WIN32 /* Windows */
# include <winsock2.h>
#else /* Linux/Unix */
# include <sys/socket.h>
#endif#include <openssl/bio.h>
#include <openssl/ssl.h>
#include <openssl/err.h>#include "my_openSSL_lib.h"/* Helper function to create a BIO connected to the server */
static BIO* create_socket_bio(const char* hostname, const char* port,int family, BIO_ADDR** peer_addr)
{int sock = -1;BIO_ADDRINFO* res;const BIO_ADDRINFO* ai = NULL;BIO* bio;/** Lookup IP address info for the server.*/if (!BIO_lookup_ex(hostname, port, BIO_LOOKUP_CLIENT, family, SOCK_DGRAM, 0,&res))return NULL;/** Loop through all the possible addresses for the server and find one* we can connect to.*/for (ai = res; ai != NULL; ai = BIO_ADDRINFO_next(ai)) {/** Create a UDP socket. We could equally use non-OpenSSL calls such* as "socket" here for this and the subsequent connect and close* functions. But for portability reasons and also so that we get* errors on the OpenSSL stack in the event of a failure we use* OpenSSL's versions of these functions.*/sock = BIO_socket(BIO_ADDRINFO_family(ai), SOCK_DGRAM, 0, 0);if (sock == -1)continue;/* Connect the socket to the server's address */if (!BIO_connect(sock, BIO_ADDRINFO_address(ai), 0)) {BIO_closesocket(sock);sock = -1;continue;}/* Set to nonblocking mode */if (!BIO_socket_nbio(sock, 1)) {BIO_closesocket(sock);sock = -1;continue;}break;}if (sock != -1) {*peer_addr = BIO_ADDR_dup(BIO_ADDRINFO_address(ai));if (*peer_addr == NULL) {BIO_closesocket(sock);return NULL;}}/* Free the address information resources we allocated earlier */BIO_ADDRINFO_free(res);/* If sock is -1 then we've been unable to connect to the server */if (sock == -1)return NULL;/* Create a BIO to wrap the socket */bio = BIO_new(BIO_s_datagram());if (bio == NULL) {BIO_closesocket(sock);return NULL;}/** Associate the newly created BIO with the underlying socket. By* passing BIO_CLOSE here the socket will be automatically closed when* the BIO is freed. Alternatively you can use BIO_NOCLOSE, in which* case you must close the socket explicitly when it is no longer* needed.*/BIO_set_fd(bio, sock, BIO_CLOSE);return bio;
}/** Simple application to send a basic HTTP/1.0 request to a server and* print the response on the screen. Note that HTTP/1.0 over QUIC is* non-standard and will not typically be supported by real world servers. This* is for demonstration purposes only.*/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{SSL_CTX* ctx = NULL;SSL* ssl = NULL;BIO* bio = NULL;int res = EXIT_FAILURE;int ret;unsigned char alpn[] = { 8, 'h', 't', 't', 'p', '/', '1', '.', '0' };const char* request_start = "GET / HTTP/1.0\r\nConnection: close\r\nHost: ";const char* request_end = "\r\n\r\n";size_t written, readbytes;char buf[160];BIO_ADDR* peer_addr = NULL;char* hostname, * port;int argnext = 1;int ipv6 = 0;if (argc < 3) {printf("Usage: quic-client-block [-6] hostname port\n");goto end;}if (!strcmp(argv[argnext], "-6")) {if (argc < 4) {printf("Usage: quic-client-block [-6] hostname port\n");goto end;}ipv6 = 1;argnext++;}hostname = argv[argnext++];port = argv[argnext];/** Create an SSL_CTX which we can use to create SSL objects from. We* want an SSL_CTX for creating clients so we use* OSSL_QUIC_client_method() here.*/ctx = SSL_CTX_new(OSSL_QUIC_client_method());if (ctx == NULL) {printf("Failed to create the SSL_CTX\n");goto end;}/** Configure the client to abort the handshake if certificate* verification fails. Virtually all clients should do this unless you* really know what you are doing.*/SSL_CTX_set_verify(ctx, SSL_VERIFY_PEER, NULL);/* Use the default trusted certificate store */if (!SSL_CTX_set_default_verify_paths(ctx)) {printf("Failed to set the default trusted certificate store\n");goto end;}/* Create an SSL object to represent the TLS connection */ssl = SSL_new(ctx);if (ssl == NULL) {printf("Failed to create the SSL object\n");goto end;}/** Create the underlying transport socket/BIO and associate it with the* connection.*/bio = create_socket_bio(hostname, port, ipv6 ? AF_INET6 : AF_INET, &peer_addr);if (bio == NULL) {printf("Failed to crete the BIO\n");goto end;}SSL_set_bio(ssl, bio, bio);/** Tell the server during the handshake which hostname we are attempting* to connect to in case the server supports multiple hosts.*/if (!SSL_set_tlsext_host_name(ssl, hostname)) {printf("Failed to set the SNI hostname\n");goto end;}/** Ensure we check during certificate verification that the server has* supplied a certificate for the hostname that we were expecting.* Virtually all clients should do this unless you really know what you* are doing.*/if (!SSL_set1_host(ssl, hostname)) {printf("Failed to set the certificate verification hostname");goto end;}/* SSL_set_alpn_protos returns 0 for success! */if (SSL_set_alpn_protos(ssl, alpn, sizeof(alpn)) != 0) {printf("Failed to set the ALPN for the connection\n");goto end;}/* Set the IP address of the remote peer */if (!SSL_set1_initial_peer_addr(ssl, peer_addr)) {printf("Failed to set the initial peer address\n");goto end;}/*! 到这就要将quic服务开起来, 否则连接失败 *//* Do the handshake with the server */if (SSL_connect(ssl) < 1) {printf("Failed to connect to the server\n");/** If the failure is due to a verification error we can get more* information about it from SSL_get_verify_result().*/if (SSL_get_verify_result(ssl) != X509_V_OK)printf("Verify error: %s\n",X509_verify_cert_error_string(SSL_get_verify_result(ssl)));goto end;}/* Write an HTTP GET request to the peer */if (!SSL_write_ex(ssl, request_start, strlen(request_start), &written)) {printf("Failed to write start of HTTP request\n");goto end;}if (!SSL_write_ex(ssl, hostname, strlen(hostname), &written)) {printf("Failed to write hostname in HTTP request\n");goto end;}if (!SSL_write_ex(ssl, request_end, strlen(request_end), &written)) {printf("Failed to write end of HTTP request\n");goto end;}/** Get up to sizeof(buf) bytes of the response. We keep reading until the* server closes the connection.*//*! 这前面, 给服务器发了3句话这下面循环, 然后将服务器回包读完, 就往下走了 */while (SSL_read_ex(ssl, buf, sizeof(buf), &readbytes)) {/** OpenSSL does not guarantee that the returned data is a string or* that it is NUL terminated so we use fwrite() to write the exact* number of bytes that we read. The data could be non-printable or* have NUL characters in the middle of it. For this simple example* we're going to print it to stdout anyway.*/fwrite(buf, 1, readbytes, stdout);}/* In case the response didn't finish with a newline we add one now */printf("\n");/** Check whether we finished the while loop above normally or as the* result of an error. The 0 argument to SSL_get_error() is the return* code we received from the SSL_read_ex() call. It must be 0 in order* to get here. Normal completion is indicated by SSL_ERROR_ZERO_RETURN. In* QUIC terms this means that the peer has sent FIN on the stream to* indicate that no further data will be sent.*/switch (SSL_get_error(ssl, 0)) {case SSL_ERROR_ZERO_RETURN:/* Normal completion of the stream *//*! 最后是从这里break的 */break;case SSL_ERROR_SSL:/** Some stream fatal error occurred. This could be because of a stream* reset - or some failure occurred on the underlying connection.*/switch (SSL_get_stream_read_state(ssl)) {case SSL_STREAM_STATE_RESET_REMOTE:printf("Stream reset occurred\n");/* The stream has been reset but the connection is still healthy. */break;case SSL_STREAM_STATE_CONN_CLOSED:printf("Connection closed\n");/* Connection is already closed. Skip SSL_shutdown() */goto end;default:printf("Unknown stream failure\n");break;}break;default:/* Some other unexpected error occurred */printf("Failed reading remaining data\n");break;}/** Repeatedly call SSL_shutdown() until the connection is fully* closed.*/do {ret = SSL_shutdown(ssl); // 关断ssl需要好久...if (ret < 0) {printf("Error shutting down: %d\n", ret);goto end;}} while (ret != 1);/* Success! */res = EXIT_SUCCESS;
end:/** If something bad happened then we will dump the contents of the* OpenSSL error stack to stderr. There might be some useful diagnostic* information there.*/if (res == EXIT_FAILURE)ERR_print_errors_fp(stderr);/** Free the resources we allocated. We do not free the BIO object here* because ownership of it was immediately transferred to the SSL object* via SSL_set_bio(). The BIO will be freed when we free the SSL object.*/SSL_free(ssl);SSL_CTX_free(ctx);BIO_ADDR_free(peer_addr);return res;
}END
相关文章:

openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - quic-client-block.c
文章目录 openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - quic-client-block.c概述笔记END openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - quic-client-block.c 概述 在程序运行时, 要指定环境变量 SSL_CERT_FILErootcert.pem, 同时将rootcert.pem拷贝到工程目录下, 否则不好使 吐槽啊, 为啥不…...

滑动窗口经典入门题-——长度最小子数组
文章目录 算法原理题目解析暴力枚举法的代码优化第一步初始化第二步right右移第三步left右移 滑动窗口法的代码 算法原理 滑动窗口是一种在序列(例如数组或链表)上解决问题的算法模式。它通常用于解决子数组或子字符串的问题,其中滑动窗口表示…...

AcGeMatrix2d::alignCoordSys一种实现方式
问题描述 此处为了简化问题,在2维空间中处理,按以下方式调用,AcGeMatrix2d::alignCoordSys是如何求出一个矩阵的呢,这里提供一个实现思路(但效率不保证好) AcGeMatrix2d matTrans AcGeMatrix2d::alignCo…...
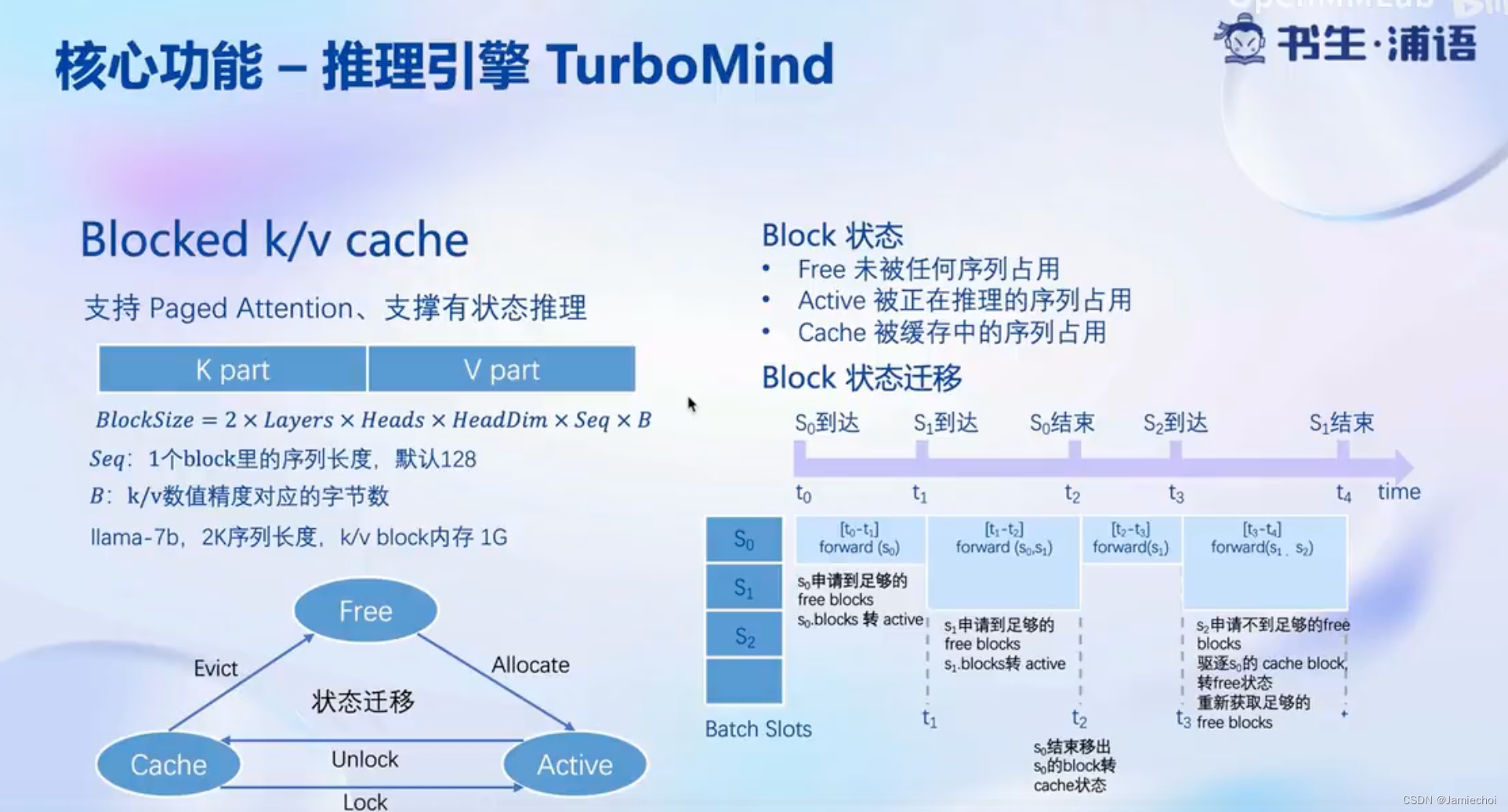
InternLM第5次课笔记
LMDeploy 大模型量化部署实践 1 大模型部署背景 2 LMDeploy简介 3 动手实践环节 https://github.com/InternLM/tutorial/blob/main/lmdeploy/lmdeploy.md 3...

2018年认证杯SPSSPRO杯数学建模D题(第一阶段)投篮的最佳出手点全过程文档及程序
2018年认证杯SPSSPRO杯数学建模 对于投篮最佳出手点的探究 D题 投篮的最佳出手点 原题再现: 影响投篮命中率的因素不仅仅有出手角度、球感、出手速度,还有出手点的选择。规范的投篮动作包含两膝微屈、重心落在两脚掌上、下肢蹬地发力、身体随之向前上…...
使用pdfbox 为 PDF 增加水印
使用pdfbox 为 PDF增加水印https://www.jylt.cc/#/detail?activityIndex2&idbd410851b0a72dad3105f9d50787f914 引入依赖 <dependency><groupId>org.apache.pdfbox</groupId><artifactId>pdfbox</artifactId><version>3.0.1</ve…...

6.【CPP】Date类的实现
Date.h #pragma once using namespace std; #include<iostream>class Date {friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d); public://构造函数会被频繁调用,放在类…...
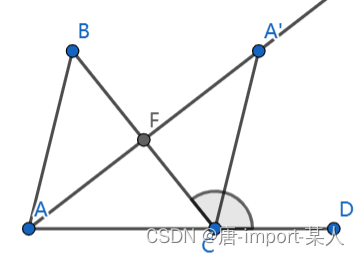
三角形任意一外角大于不相邻的任意一内角
一.代数证明 ∵ 对与△ A C B 中 ∠ c 外接三角形是 ∠ B C D ∵对与△ACB中∠c外接三角形是∠BCD ∵对与△ACB中∠c外接三角形是∠BCD ∴ ∠ B C D π − ∠ C ∴∠BCD\pi-∠C ∴∠BCDπ−∠C ∵ ∠ A ∠ B ∠ C π ∵∠A∠B∠C\pi ∵∠A∠B∠Cπ ∴ ∠ B C D ∠ A ∠…...

【Spring Boot 3】【Redis】集成Lettuce
【Spring Boot 3】【Redis】集成Lettuce 背景介绍开发环境开发步骤及源码工程目录结构总结背景 软件开发是一门实践性科学,对大多数人来说,学习一种新技术不是一开始就去深究其原理,而是先从做出一个可工作的DEMO入手。但在我个人学习和工作经历中,每次学习新技术总是要花…...
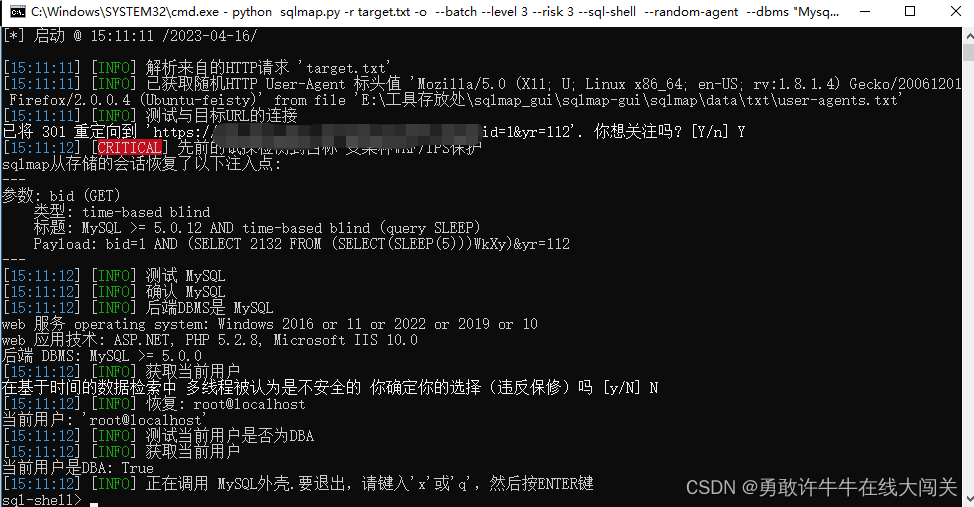
【SQL注入】SQLMAP v1.7.11.1 汉化版
下载链接 【SQL注入】SQLMAP v1.7.11.1 汉化版 简介 SQLMAP是一款开源的自动化SQL注入工具,用于扫描和利用Web应用程序中的SQL注入漏洞。它在安全测试领域被广泛应用,可用于检测和利用SQL注入漏洞,以验证应用程序的安全性。 SQL注入是一种…...
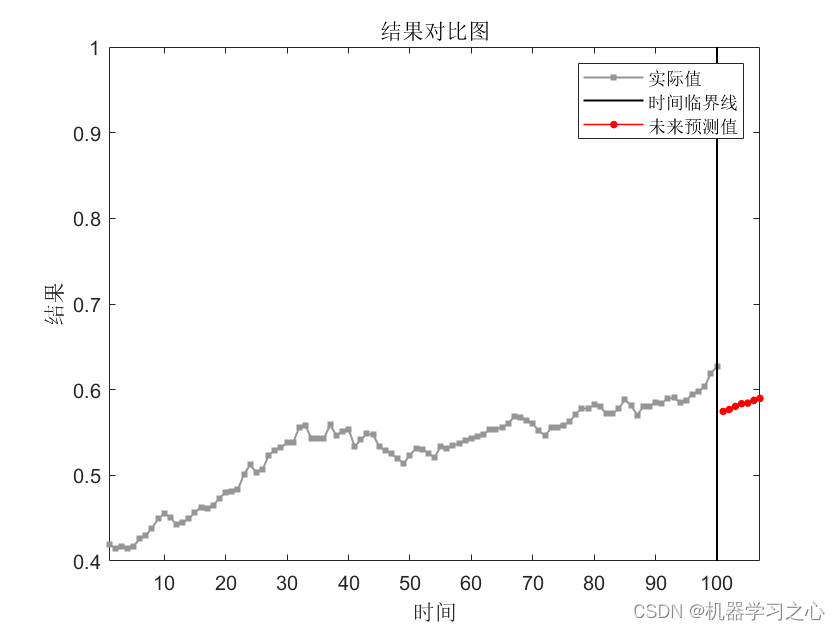
时序预测 | MATLAB实现GRNN广义回归神经网络时间序列未来多步预测(程序含详细预测步骤)
时序预测 | MATLAB实现GRNN广义回归神经网络时间序列未来多步预测(程序含详细预测步骤) 目录 时序预测 | MATLAB实现GRNN广义回归神经网络时间序列未来多步预测(程序含详细预测步骤)预测效果基本介绍程序设计参考资料预测效果 基本介绍 MATLAB实现GRNN广义回归神经网络时间序列…...

长期戴耳机的危害有哪些?戴哪种耳机不伤耳朵听力?
长期佩戴耳机可能会出现听力下降、耳道感染等危害。 听力下降:长时间戴耳机可能会导致耳道内的声音过大,容易对耳膜造成一定的刺激,容易出现听力下降的情况。 耳道感染:长时间戴耳机,耳道长期处于封闭潮湿的情况下&a…...

C++中的预处理
一.预定义符号 1.__FILE__进行编译的源文件 2.__LINE__文件当前的行号 3.__DATE__文件被编译的日期 4.__TIME文件被编译的时间 5.__STDC__如果编译器遵循ANSIC,其值为1,否则未定义 二.#define 基本语法:#define 名字 内容 eg.define M 1 经#define定义的常量时不经过…...
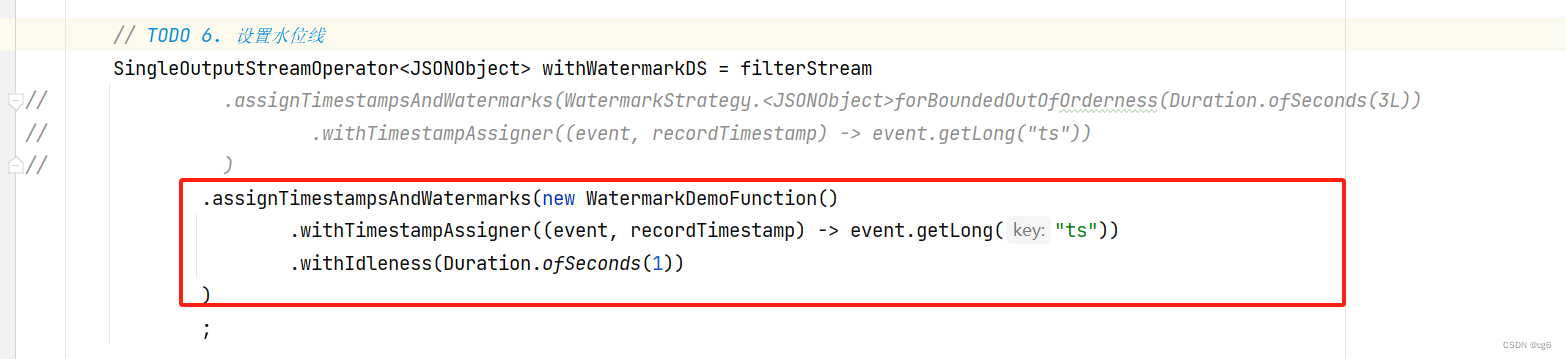
flink 最后一个窗口一直没有新数据,窗口不关闭问题
flink 最后一个窗口一直没有新数据,窗口不关闭问题 自定义实现 WatermarkStrategy接口 自定义实现 WatermarkStrategy接口 窗口类型:滚动窗口 代码: public static class WatermarkDemoFunction implements WatermarkStrategy<JSONObject…...
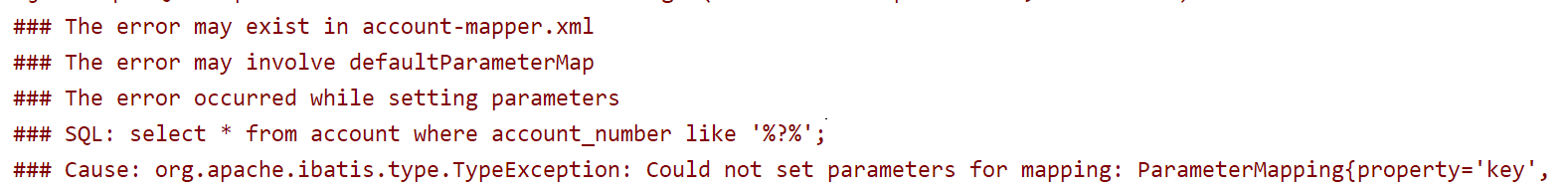
mybatis----小细节
1、起别名 在MyBatis中,<typeAliases>元素用于定义类型别名,它可以将Java类名映射为一个更简短的别名,这样在映射文件中可以直接使用别名而不需要完整的类名。 下面是一个示例: 在mybatis核心配置文件中配置typeAliases标…...

解密Oracle数据库引擎:揭开数据存储的神秘面纱
目录 1、介绍Oracle数据库引擎 1.1 什么是Oracle数据库引擎 1.2 Oracle数据库引擎的作用和功能 1.3 Oracle数据库引擎的历史和发展 2、Oracle数据库引擎的体系结构 2.1 Oracle数据库实例的组成部分 2.2 Oracle数据库引擎的层次结构 2.3 Oracle数据库引擎的关键组件 3、…...

「HDLBits题解」Karnaugh Map to Circuit
本专栏的目的是分享可以通过HDLBits仿真的Verilog代码 以提供参考 各位可同时参考我的代码和官方题解代码 或许会有所收益 相关资料:卡诺图化简法-CSDN博客 题目链接:Kmap1 - HDLBits module top_module(input a,input b,input c,output out );assig…...
由于找不到d3dcompiler_43.dll缺失,无法打开软件的解决方法分享
d3dcompiler43.dll是什么文件?为什么会出现丢失的情况?又该如何解决呢?本文将详细介绍d3dcompiler43.dll的作用和影响,并提供6个有效的解决方法。 一、d3dcompiler43.dll是什么文件? d3dcompiler43.dll是DirectX SDK…...
现阶段Python和Java哪个更吃香?
现阶段Python和Java哪个更吃香? 在开始前我有一些资料,是我根据网友给的问题精心整理了一份「Java的资料从专业入门到高级教程」, 点个关注在评论区回复“888”之后私信回复“888”,全部无偿共享给大家!!&…...
基于DNA的密码学和隐写术综述
摘要 本文全面调研了不同的脱氧核糖核酸(DNA)-基于密码学和隐写术技术。基于DNA的密码学是一个新兴领域,利用DNA分子的大规模并行性和巨大的存储容量来编码和解码信息。近年来,由于其相对传统密码学方法的潜在优势,如高存储容量、低错误率和对环境因素的抗性,该领域引起…...

Vim 调用外部命令学习笔记
Vim 外部命令集成完全指南 文章目录 Vim 外部命令集成完全指南核心概念理解命令语法解析语法对比 常用外部命令详解文本排序与去重文本筛选与搜索高级 grep 搜索技巧文本替换与编辑字符处理高级文本处理编程语言处理其他实用命令 范围操作示例指定行范围处理复合命令示例 实用技…...
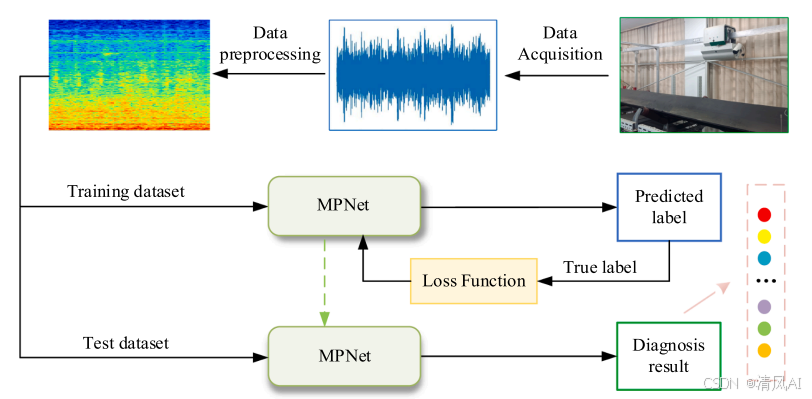
MPNet:旋转机械轻量化故障诊断模型详解python代码复现
目录 一、问题背景与挑战 二、MPNet核心架构 2.1 多分支特征融合模块(MBFM) 2.2 残差注意力金字塔模块(RAPM) 2.2.1 空间金字塔注意力(SPA) 2.2.2 金字塔残差块(PRBlock) 2.3 分类器设计 三、关键技术突破 3.1 多尺度特征融合 3.2 轻量化设计策略 3.3 抗噪声…...

vscode里如何用git
打开vs终端执行如下: 1 初始化 Git 仓库(如果尚未初始化) git init 2 添加文件到 Git 仓库 git add . 3 使用 git commit 命令来提交你的更改。确保在提交时加上一个有用的消息。 git commit -m "备注信息" 4 …...

css实现圆环展示百分比,根据值动态展示所占比例
代码如下 <view class""><view class"circle-chart"><view v-if"!!num" class"pie-item" :style"{background: conic-gradient(var(--one-color) 0%,#E9E6F1 ${num}%),}"></view><view v-else …...

Cesium1.95中高性能加载1500个点
一、基本方式: 图标使用.png比.svg性能要好 <template><div id"cesiumContainer"></div><div class"toolbar"><button id"resetButton">重新生成点</button><span id"countDisplay&qu…...

渲染学进阶内容——模型
最近在写模组的时候发现渲染器里面离不开模型的定义,在渲染的第二篇文章中简单的讲解了一下关于模型部分的内容,其实不管是方块还是方块实体,都离不开模型的内容 🧱 一、CubeListBuilder 功能解析 CubeListBuilder 是 Minecraft Java 版模型系统的核心构建器,用于动态创…...
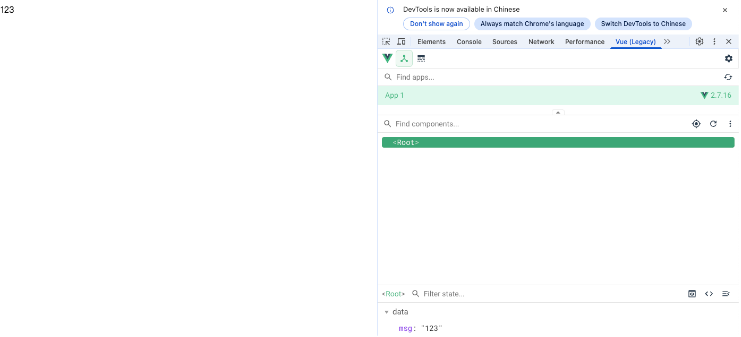
Vue2 第一节_Vue2上手_插值表达式{{}}_访问数据和修改数据_Vue开发者工具
文章目录 1.Vue2上手-如何创建一个Vue实例,进行初始化渲染2. 插值表达式{{}}3. 访问数据和修改数据4. vue响应式5. Vue开发者工具--方便调试 1.Vue2上手-如何创建一个Vue实例,进行初始化渲染 准备容器引包创建Vue实例 new Vue()指定配置项 ->渲染数据 准备一个容器,例如: …...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中使用DevEco Studio实现录音机应用
1. 项目配置与权限设置 1.1 配置module.json5 {"module": {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permission.MICROPHONE","reason": "录音需要麦克风权限"},{"name": "ohos.permission.WRITE…...
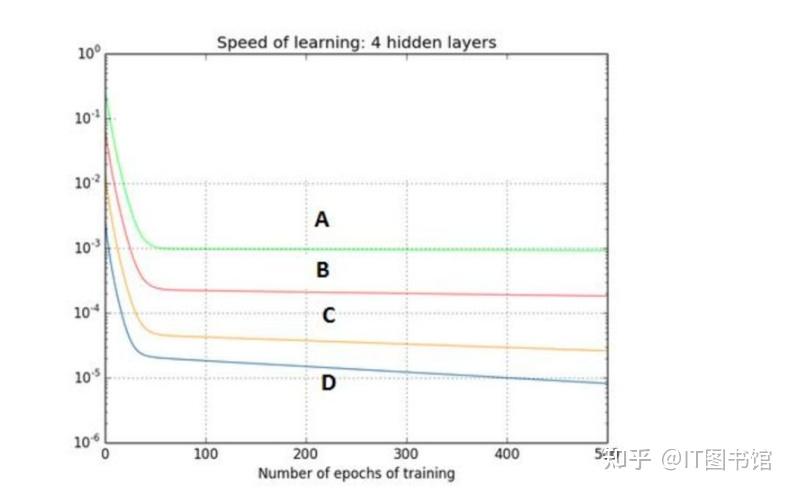
深度学习习题2
1.如果增加神经网络的宽度,精确度会增加到一个特定阈值后,便开始降低。造成这一现象的可能原因是什么? A、即使增加卷积核的数量,只有少部分的核会被用作预测 B、当卷积核数量增加时,神经网络的预测能力会降低 C、当卷…...
