设计跳表(动态设置节点高度)
最近学习redis的zset时候,又看到跳表的思想,突然对跳表的设置有了新的思考
这是19年设计的跳表,在leetcode的执行时间是200+ms
现在我对跳表有了新的想法
1、跳表的设计,类似二分查找,但是不是二分查找,比较像之前遇到的一个面试题,使用有限个数鸡蛋,确定鸡蛋易损程度
2、跳表无法在设计的时候,就达到完美状态,而是在操作过程中一直维护较完美状态(动态平衡)
基于以上想法,我开始重新进行跳表的设计,在leetCode执行时间为14ms
设计思路如下:
0、设计节点,节点有next和pre两个指针,且因为多层结构,所以是数组表达
1、设计多层数据结构,多层均为有序链表,其中第0层包含所有数值
2、初始时,只有一层结构,先设计为10层结构
3、新增数据时,如果发现步数(即执行next次数)过长(大于3倍层高),就进行抬升节点高度行为,即节点high值增加
2023-03-04有补充,看最下方
最初代码如下:
Node类
class Node {Node[] next = new Node[10];Node[] pre = new Node[10];//节点高度int high = 0;//节点值int value;//最近一次走到这个节点的步数int step = 0;//这个仅是为了后续show方法使用int k = 0;}
基础参数及构造器
//头节点Node head;int maxHigh = 0;//步数int step = 0;public Skiplist() {}
查询操作,不直接查是否有,而是查floor值后,与tagert进行比较,查floor作用是,复用
public boolean search(int target) {if (head == null) {return false;}if (head.value > target) {return false;}//查询Floorreturn searchFloor(head, maxHigh, target).value == target;
}private Node searchFloor(Node node, int high, int target) {//查到了if (node.value == target) {return node;}//已经最下层了if (high == -1) {return node;}//如果next值小于tagert,就进行next操作while (node.next[high] != null &&node.next[high].value <= target) {//步数增加step++;node = node.next[high];node.step = step;}//向下找return searchFloor(node, high - 1, target);
}
新增节点
public void add(int num) {if (head == null) {head = new Node();head.value = num;//没有head,好处理return;}if (num < head.value) {Node newHead = new Node();newHead.value = num;//比head还小,加上之后,充当新headsetNewHead(newHead, head);return;}step = 0;Node newNode = new Node();newNode.value = num;//找到floor,就加在floor后面Node node = searchFloor(head, maxHigh, num);setNext(node, newNode);if (step > 3 * maxHigh) {//需要抬高高度了,这个方法很重要,类似hashmap的扩容resize(newNode);}
}
先把几个简单的方法展示出来
private void setNext(Node pre, Node node) {int high = node.high;if (pre.next[high] == null) {pre.next[high] = node;node.pre[high] = pre;} else {Node next = pre.next[high];pre.next[high] = node;node.pre[high] = pre;node.next[high] = next;next.pre[high] = node;}}private void setNewHead(Node newHead, Node head) {newHead.high = head.high;for (int i = 0; i <= newHead.high; i++) {newHead.next[i] = head;head.pre[i] = newHead;}this.head = newHead;}
重点在resize
private void resize(Node node) {if (node.high == maxHigh) {//如果当前高度已经是最高高度了,将maxHigh增高maxHigh++;if (maxHigh == 10) {show();}node.high = maxHigh;head.high = maxHigh;head.next[maxHigh] = node;node.pre[maxHigh] = head;return;}//找前者Node pre = getMoreHighPre(node);//抬高高度node.high++;//加入节点(比如,开始加在0层,这时就记在1层)setNext(pre, node);//更新步数值node.step = pre.step + 1;//步数还大,继续增高if (node.step > 3 * (maxHigh + 1)) {resize(node);}}private Node getMoreHighPre(Node node) {int high = node.high;Node pre = node.pre[high];//找到高一层级的上一个节点while (pre.high == high) {pre = pre.pre[high];}return pre;}
删除操作
public boolean erase(int num) {if (head == null) {return false;}if (head.value == num) {if (head.next[0] != null && head.next[0].value == num) {//能不删head尽量不删headremoveNode(head.next[0]);} else {//只能删除headremoveHead();}return true;}//一样,找到对应节点Node node = searchFloor(head, maxHigh, num);if (node.value == num) {//移除removeNode(node);return true;}return false;}private void removeNode(Node node) {for (int i = 0; i <= node.high; i++) {//每一层,都要删除Node pre = node.pre[i];Node next = node.next[i];if (next == null) {//注意可能没有nextpre.next[i] = null;} else {pre.next[i] = next;next.pre[i] = pre;}}}private void removeHead() {//删除头节点,就是把老二当老大用if (head.next[0] == null) {head = null;}Node node = head.next[0];node.high = head.high;for (int i = 1; i <= maxHigh; i++) {if (head.next[i] != null && head.next[i] != node) {node.next[i] = head.next[i];head.next[i].pre[i] = node;}}head = node;}
以上代码执行后,leetCode执行时长为19ms,已经远快于19年的代码
但是,我发现了问题所在
因为数组高度有限,设置的高度为10,如果高度不够,就会出现数组越界,我尝试进行测试,写了show方法
private void show() {System.out.println("总数"+i+"为出现越界");System.out.println("0级,并设置k");head.k = 0;int k = 0;Node node = head;while (node != null) {node.k = k++;node = node.next[0];}for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(i + "级间隔:");node = head;Node next = node.next[i];while (next != null) {System.out.print(next.k - node.k + ",");node = next;next = node.next[i];}System.out.println();}}
结果如下
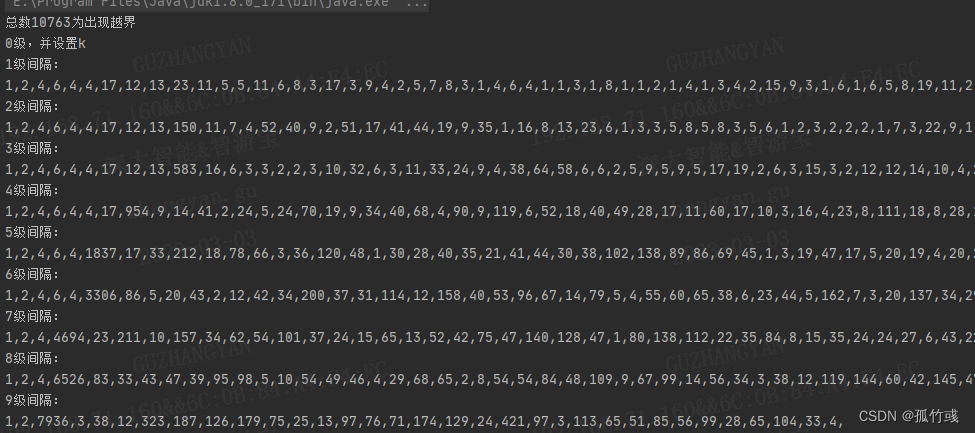
居然一万多数值之后就越界了,思考原因所在
应该是,抬高的node,不应该是插入的那个node,应该是node所在层次的中间node,调整接口如下
通过middleNode,找到需要抬高的node
private void resize(Node node) {if (node.high == maxHigh) {//最高层,这个可以接受maxHigh++;if (maxHigh == max) {show();}node.high = maxHigh;head.high = maxHigh;head.next[maxHigh] = node;node.pre[maxHigh] = head;return;}//找前人Node pre = getMoreHighPre(node);//不应该直接用node升级,应该用node区间的中间值node = middleNode(pre, node);node.high++;//加入节点setNext(pre, node);node.step = pre.step + 1;if (node.step > 3 * (maxHigh + 1)) {resize(node);}
}
寻找middleNode的代码如下
private Node middleNode(Node pre, Node node) {int high = node.high;if (pre.next[high + 1] == null) {return getLast(node);}Node next = pre.next[high + 1];int left = getLen(pre, node, node.high);int right = getLen(node, next, node.high);if (left == right) {return node;}if (left > right) {return left(node, (left - right) / 2);} else {return right(node, (right - left) / 2);}
}private int getLen(Node left, Node right, int high) {int step = 0;while (left != right) {left = left.next[high];step++;}return step;
}private Node left(Node node, int step) {if (step == 0) {return node;}return left(node.pre[node.high], step - 1);
}private Node right(Node node, int step) {if (step == 0) {return node;}return right(node.next[node.high], step - 1);
}private Node getLast(Node node) {int high = node.high;while (node.next[high] != null) {node = node.next[high];}return node;
}
同时发现,最左侧有一些数字极低值,优化setNewHead方法
private void setNewHead(Node newHead, Node head) {newHead.high = head.high;newHead.next[0] = head;head.pre[0] = newHead;head.high = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= newHead.high; i++) {Node next = head.next[i];if(next==null){break;}newHead.next[i] = next;next.pre[i] = newHead;}this.head = newHead;}
执行leetCode,14ms
使用show方法
结果如下:
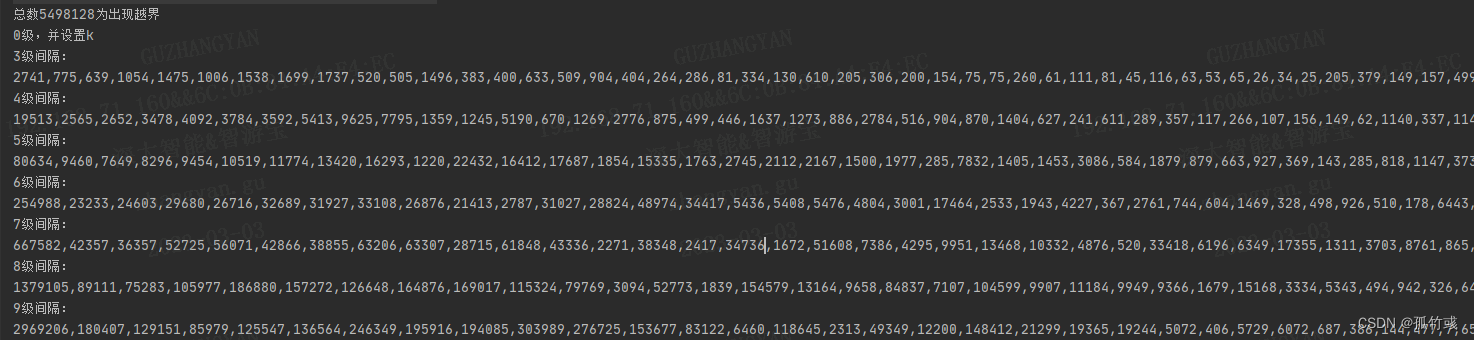
数据超过我的想象,百万级了
当然,这不是完美的跳表,比如我只在新增时,判断是否需要抬高(resize),查询时没有,可能出现某些节点运气不好,查询就是很慢
完整代码包括test在下方
public class TiaoBIaoNewTest {static int i =0;public static void main(String[] args) {Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist();Random random = new Random();for (i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {skiplist.add(random.nextInt());}System.out.println();}static class Skiplist {static int max = 10;class Node {Node[] next = new Node[max];Node[] pre = new Node[max];int high = 0;int value;//最近一次走到这个节点的步数int step = 0;int k = 0;}Node head;int maxHigh = 0;//1)先分割0级public Skiplist() {}public boolean search(int target) {if (head == null) {return false;}if (head.value > target) {return false;}Node node = searchFloor(head, maxHigh, target);return node.value == target;}int step = 0;private Node searchFloor(Node node, int high, int target) {if (node.value == target) {return node;}if (high == -1) {return node;}while (node.next[high] != null &&node.next[high].value <= target) {step++;node = node.next[high];node.step = step;}return searchFloor(node, high - 1, target);}public void add(int num) {if (head == null) {head = new Node();head.value = num;return;}if (num < head.value) {Node newHead = new Node();newHead.value = num;setNewHead(newHead, head);return;}step = 0;Node newNode = new Node();newNode.value = num;Node node = searchFloor(head, maxHigh, num);setNext(node, newNode);if (step > 3 * maxHigh) {resize(newNode);}}private void setNewHead(Node newHead, Node head) {newHead.high = head.high;newHead.next[0] = head;head.pre[0] = newHead;head.high = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= newHead.high; i++) {Node next = head.next[i];if(next==null){break;}newHead.next[i] = next;next.pre[i] = newHead;}this.head = newHead;}public boolean erase(int num) {if (head == null) {return false;}if (head.value == num) {if (head.next[0] != null && head.next[0].value == num) {removeNode(head.next[0]);} else {removeHead();}return true;}Node node = searchFloor(head, maxHigh, num);if (node.value == num) {removeNode(node);return true;}return false;}private void removeNode(Node node) {for (int i = 0; i <= node.high; i++) {Node pre = node.pre[i];Node next = node.next[i];if (next == null) {pre.next[i] = null;} else {pre.next[i] = next;next.pre[i] = pre;}}}private void removeHead() {if (head.next[0] == null) {head = null;}Node node = head.next[0];node.high = head.high;for (int i = 1; i <= maxHigh; i++) {if (head.next[i] != null && head.next[i] != node) {node.next[i] = head.next[i];head.next[i].pre[i] = node;}}head = node;}private void resize(Node node) {if (node.high == maxHigh) {//最高层,这个可以接受maxHigh++;if (maxHigh == max) {show();}node.high = maxHigh;head.high = maxHigh;head.next[maxHigh] = node;node.pre[maxHigh] = head;return;}//找前人Node pre = getMoreHighPre(node);//不应该直接用node升级,应该用node区间的中间值node = middleNode(pre, node);node.high++;//加入节点setNext(pre, node);node.step = pre.step + 1;if (node.step > 3 * (maxHigh + 1)) {resize(node);}}private Node middleNode(Node pre, Node node) {int high = node.high;if (pre.next[high + 1] == null) {return getLast(node);}Node next = pre.next[high + 1];int left = getLen(pre, node, node.high);int right = getLen(node, next, node.high);if (left == right) {return node;}if (left > right) {return left(node, (left - right) / 2);} else {return right(node, (right - left) / 2);}}private int getLen(Node left, Node right, int high) {int step = 0;while (left != right) {left = left.next[high];step++;}return step;}private Node left(Node node, int step) {if (step == 0) {return node;}return left(node.pre[node.high], step - 1);}private Node right(Node node, int step) {if (step == 0) {return node;}return right(node.next[node.high], step - 1);}private Node getLast(Node node) {int high = node.high;while (node.next[high] != null) {node = node.next[high];}return node;}private Node getMoreHighPre(Node node) {int high = node.high;Node pre = node.pre[high];while (pre.high == high) {pre = pre.pre[high];}return pre;}private void setNext(Node pre, Node node) {int high = node.high;if (pre.next[high] == null) {pre.next[high] = node;node.pre[high] = pre;} else {Node next = pre.next[high];pre.next[high] = node;node.pre[high] = pre;node.next[high] = next;next.pre[high] = node;}}private void show() {System.out.println("总数"+i+"为出现越界");System.out.println("0级,并设置k");head.k = 0;int k = 0;Node node = head;while (node != null) {node.k = k++;node = node.next[0];}for (int i = 3; i < max; i++) {System.out.println(i + "级间隔:");node = head;Node next = node.next[i];while (next != null) {System.out.print(next.k - node.k + ",");node = next;next = node.next[i];}System.out.println();}}@Overridepublic String toString() {String s = "";Node node = head;while (node != null) {s += node.value + ",";node = node.next[0];}return s;}}
}
2023-03-04补充
今日验证每个节点的搜索路径,验证结果如下:
总数5445676为出现越界
0级,并设置k
9级最大step:33
8级最大step:35
7级最大step:35
6级最大step:35
5级最大step:35
4级最大step:36
3级最大step:38
2级最大step:39
1级最大step:44
0级最大step:58
平均step24.20 总数6749752为出现越界
0级,并设置k
9级最大step:31
8级最大step:32
7级最大step:34
6级最大step:34
5级最大step:36
4级最大step:37
3级最大step:39
2级最大step:45
1级最大step:47
0级最大step:59
平均step24.38总数5829201为出现越界
0级,并设置k
9级最大step:32
8级最大step:33
7级最大step:35
6级最大step:35
5级最大step:37
4级最大step:38
3级最大step:41
2级最大step:46
1级最大step:49
0级最大step:62
平均step24.40
最大step也只是60左右,之所以不是30,之前也说了,是因为没有对查询操作进行提高判断操作(加了判断,有可能反而导致查询减慢),个人也觉得没必要,平均的查询步骤是24
进行局部修改,当出现待提高node的左相邻节点,本身高度就够情况下,提高左节点(防止较低层级节点密集)
如下
private void resize(Node node) {if (node.high == maxHigh) {//最高层,这个可以接受maxHigh++;if (maxHigh == max) {show();}node.high = maxHigh;head.high = maxHigh;head.next[maxHigh] = node;node.pre[maxHigh] = head;return;}//找前人Node pre = getMoreHighPre(node);//不应该直接用node升级,应该用node区间的中间值node = middleNode(pre, node);if(pre.next[node.high]==node){//升自己不如升preresize(pre);return;}node.high++;//加入节点setNext(pre, node);node.step = pre.step + 1;if (node.step > 3 * (maxHigh + 1)) {resize(node);}}
验证结果如下:
总数11386207为出现越界
0级,并设置k
9级最大step:32
8级最大step:32
7级最大step:36
6级最大step:37
5级最大step:38
4级最大step:39
3级最大step:41
2级最大step:42
1级最大step:52
0级最大step:62
平均step24.78总数13122318为出现越界
0级,并设置k
9级最大step:30
8级最大step:32
7级最大step:37
6级最大step:38
5级最大step:39
4级最大step:41
3级最大step:42
2级最大step:43
1级最大step:49
0级最大step:63
平均step25.30 总数11352711为出现越界
0级,并设置k
9级最大step:28
8级最大step:30
7级最大step:31
6级最大step:32
5级最大step:35
4级最大step:37
3级最大step:39
2级最大step:42
1级最大step:46
0级最大step:59
平均step25.09
最大步骤没有明显增加,平均步骤从24+增加至25+,查询会些许减慢,但是可容纳数据量,从600w左右,提升至1000w以上,提升明显
以上只是个人实现的跳表,肯定会有问题,欢迎大家一起讨论
相关文章:

设计跳表(动态设置节点高度)
最近学习redis的zset时候,又看到跳表的思想,突然对跳表的设置有了新的思考 这是19年设计的跳表,在leetcode的执行时间是200ms 现在我对跳表有了新的想法 1、跳表的设计,类似二分查找,但是不是二分查找,比较…...

基于神经辐射场(Neural Radiance Fileds, NeRF)的三维重建- 简介(1)
Nerf简介 Nerf(neural Radiance Fileds) 为2020年ICCV上提出的一个基于隐式表达的三维重建方法,使用2D的 Posed Imageds 来生成(表达)复杂的三维场景。现在越来越多的研究人员开始关注这个潜力巨大的领域,也…...
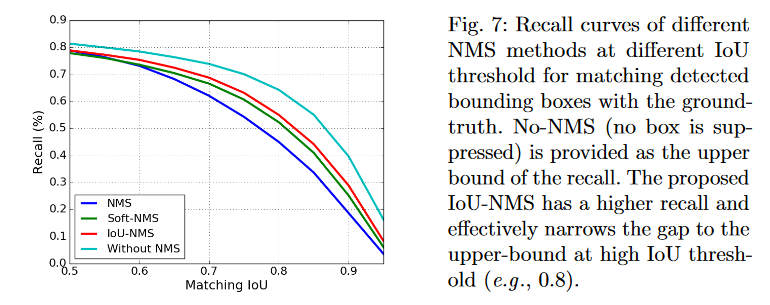
【AI面试】NMS 与 Soft NMS 的辨析
往期文章: AI/CV面试,直达目录汇总【AI面试】L1 loss、L2 loss和Smooth L1 Loss,L1正则化和L2正则化 一、NMS 非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression,NMS),并不是深度学习时期,目标…...
一文让你彻底理解Linux内核多线程(互斥锁、条件变量、读写锁、自旋锁、信号量)
一、互斥锁(同步) 在多任务操作系统中,同时运行的多个任务可能都需要使用同一种资源。这个过程有点类似于,公司部门里,我在使用着打印机打印东西的同时(还没有打印完),别人刚好也在…...
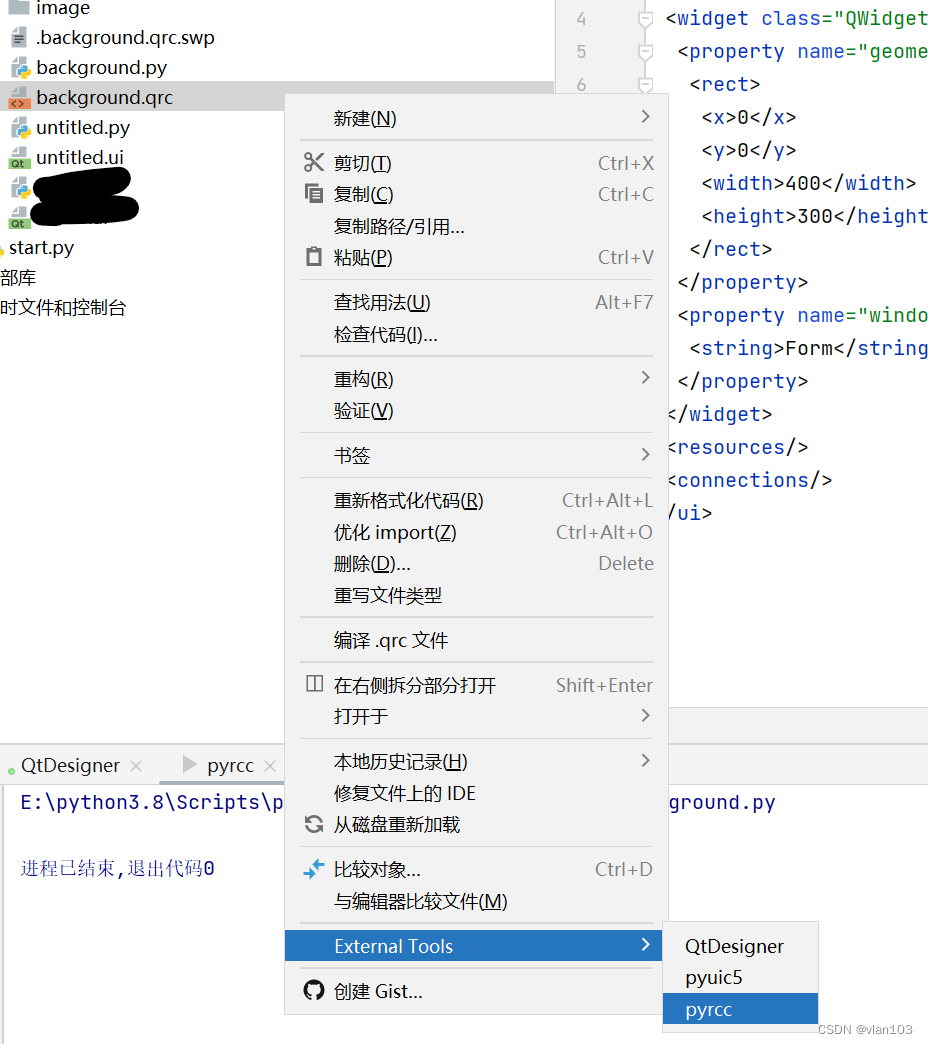
利用python写一个gui小公举--环境搭建
文章目录背景搭建环境安装必要库添加工具快捷方式检验背景 在实习过程中遇到一个问题,某项目是通过python代码实现的,而且需要一直修改参数实现功能,过程有些繁琐。虽然师兄用PHP study搭了一个网站用于查看结果,但是还是过于繁琐…...

英飞凌Tricore实战系列02_ENDINIT属性看门狗原理及应用
目录 1.概述2.ENDINIT功能及使用2.1 ENDINIT属性2.2 改写受ENDINIT保护寄存器的步骤3. Tricore 看门狗介绍及使用3.1 看门狗系统介绍3.1.1 安全看门狗介绍3.1.2 CPU看门狗介绍3.2 看门狗模式介绍3.2.1 Time-out模式3.2.2 正常模式(Normal Mode)3.2.3 禁用模式(Disabled Mode…...

Java Number类
Java Number 类是一个抽象类,它是所有数字类的基类。Java 中的数字类包括 Byte、Short、Integer、Long、Float 和 Double,它们都继承自 Number 类。Java Number 类提供了一些常用的方法,可以用于将数字类型转换为不同的格式,以及进…...
C++构造和析构
欢迎来观看温柔了岁月.c的博客 目前 设有C学习专栏 C语言项目专栏 数据结构与算法专栏 目前主要更新C学习专栏,C语言项目专栏不定时更新 待C专栏完毕,会陆续更新C项目专栏和数据结构与算法专栏 一周主要三更,星期三,星期五&#x…...
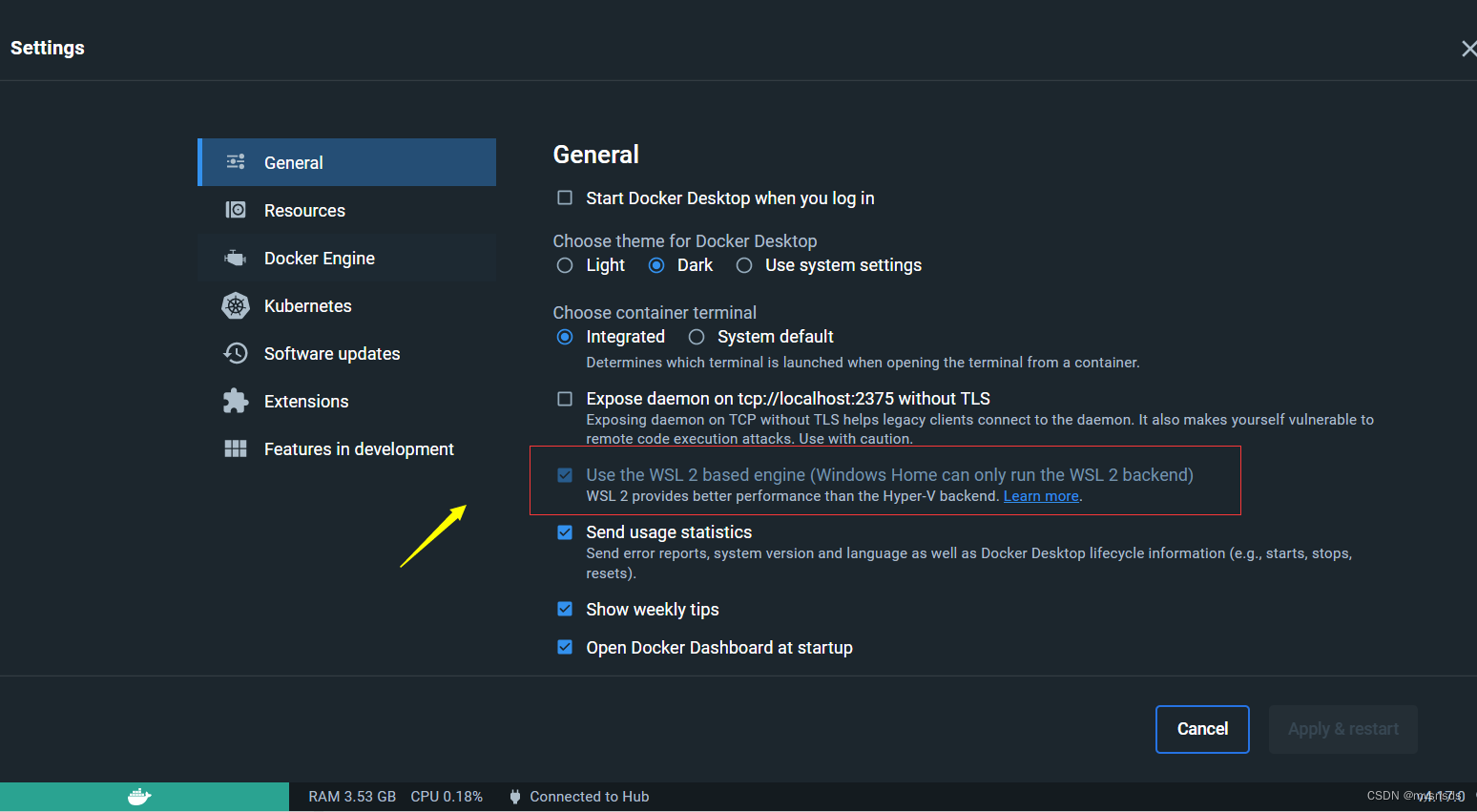
docker安装即docker连接mysql(window)
一 安装docker 1.什么是docker Docker容器与虚拟机类似,但二者在原理上不同。容器是将操作系统层虚拟化,虚拟机则是虚拟化硬件,因此容器更具有便携性、高效地利用服务器。 2.WSL2 WSL,即Windows Subsystem on Linux,中…...

HMM-维特比算法
HMM-维特比算法(viterbi)HMM回顾隐马科夫链解法:维特比算法(Viterbi)HMM回顾 最终的公式可以解释主要分为两个部分: P(xi|yi),发射概率,字面意思是从一个词性中发射/生成出某一个单…...
【C++初阶】2. 类和对象_1
1. 面向过程和面向对象的初步认识 2. 类的引入 C语言结构体中只能定义变量,在C中,结构体内不仅可以定义变量,也可以定义函数。比如: 之前在数据结构初阶中,用C语言方式实现的栈,结构体中只能定义变量&#…...

kotlin把函数作为参数转递给另一个函数
kotlin把函数作为参数转递给另一个函数 fun say(s: String, foo: (String) -> Unit) {print("hello")foo(s) }fun hi(str: String) {println(str) }fun main(args: Array<String>) {say("hello", ::hi) } 输出: hellohello...
海思嵌入式开发-005-OpenHarmony源码编译问题
海思嵌入式开发-005-OpenHarmony源码编译问题一、问题描述二、解决方案2.1解决原理2.2获取OpenHarmony 3.1.1 Release源码2.3最后解决问题,编译成功。一、问题描述 按照链接拉取master源码,出现如下问题,打开build.log文件 提示相应位置的文…...
指针的进阶续(笔试题强化练习)
写在前面:在上次我们学习了指针的相关类型的知识,对指针家族的成员基本有了了解,这次让我们跟着一些题目来练习和补充一些知识,这有助于我们强化理解这些知识。 话不多说,我们马上开始: 1.指针和数组的笔…...

一个供参考的计算机的学习路线
本文是介绍如何成为一个Geek,一个真正的计算机高手。 适合有成为IT领域技术大牛的人参考。 写给大一新生和所有向深耕IT领域的人,避免走一些弯路。 仅代表个人想法,供批判性参考。 第一门入门的必备功课-语法与算法 什么是计算机?…...
React(五):受控组件、高阶组件、Portals、Fragment、CSS的编写方式
React(五)一、受控组件1.什么是受控组件(v-model)2.收集表单数据:input和单选框3.收集表单数据:下拉框二、非受控组件三、高阶组件1.什么是高阶组件2.高阶组件的应用13.高阶组件的应用2-注入Context4.高阶组件的应用3-登录鉴权5.高…...
MATLAB——系统环境
MATLAB概述MATLAB的发展MATLAB:MATrix LABoratory1980年前后,Cleve Moler教授编写的Linpack 和Eispack的接口程序。1984年,MATLAB第1版(DOS版)1992年,MATLAB4.0版1994年,MATLAB 4.2版1997年,MATLAB 5.0版1999年&#x…...

2 GateWay工作流程+GateWay搭建
GateWay工作流程GateWay搭建 核心流程图如下: 核心概念: 客户端向 Spring Cloud Gateway 发出请求。如果Gateway Handler Mapping确定请求与路由匹配,则将其发送到Gateway Web Handler 处理程序。此处理程序通过特定于请求的Fliter链运行请求…...

【微信小程序】富文本rich-text的图片预览效果的几种方法
前言 使用原生小程序开发,实现在富文本rich-text中的图片预览效果的几种方法对比。 1.正则wx.previewImage(有明显不足) 一个不需要用额外组件或插件的方法: 思路:使用正则把图片的url进行剖离出来,push…...

通信网络-Socket、Java中的网络支持、多线程服务器
前言 通信网络-Socket、Java中的网络支持、多线程服务器 场景:使用java网络创建一个聊天室 博客地址:芒果橙的个人博客 文章目录前言通信网络-SocketTCP/IPTCP/IP 模型端口Java中的网络支持概念1. InetAddress2. URL3. Socket4. Datagram多线程服务器应用…...
XCTF-web-easyupload
试了试php,php7,pht,phtml等,都没有用 尝试.user.ini 抓包修改将.user.ini修改为jpg图片 在上传一个123.jpg 用蚁剑连接,得到flag...

.Net框架,除了EF还有很多很多......
文章目录 1. 引言2. Dapper2.1 概述与设计原理2.2 核心功能与代码示例基本查询多映射查询存储过程调用 2.3 性能优化原理2.4 适用场景 3. NHibernate3.1 概述与架构设计3.2 映射配置示例Fluent映射XML映射 3.3 查询示例HQL查询Criteria APILINQ提供程序 3.4 高级特性3.5 适用场…...
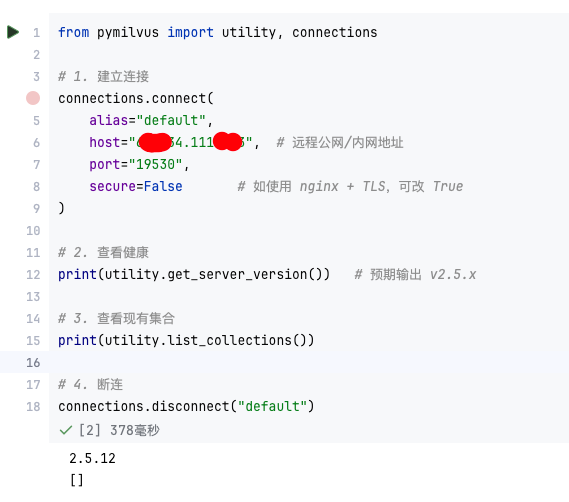
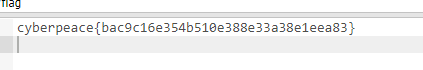
【大模型RAG】Docker 一键部署 Milvus 完整攻略
本文概要 Milvus 2.5 Stand-alone 版可通过 Docker 在几分钟内完成安装;只需暴露 19530(gRPC)与 9091(HTTP/WebUI)两个端口,即可让本地电脑通过 PyMilvus 或浏览器访问远程 Linux 服务器上的 Milvus。下面…...

学习STC51单片机31(芯片为STC89C52RCRC)OLED显示屏1
每日一言 生活的美好,总是藏在那些你咬牙坚持的日子里。 硬件:OLED 以后要用到OLED的时候找到这个文件 OLED的设备地址 SSD1306"SSD" 是品牌缩写,"1306" 是产品编号。 驱动 OLED 屏幕的 IIC 总线数据传输格式 示意图 …...

学校时钟系统,标准考场时钟系统,AI亮相2025高考,赛思时钟系统为教育公平筑起“精准防线”
2025年#高考 将在近日拉开帷幕,#AI 监考一度冲上热搜。当AI深度融入高考,#时间同步 不再是辅助功能,而是决定AI监考系统成败的“生命线”。 AI亮相2025高考,40种异常行为0.5秒精准识别 2025年高考即将拉开帷幕,江西、…...
Mobile ALOHA全身模仿学习
一、题目 Mobile ALOHA:通过低成本全身远程操作学习双手移动操作 传统模仿学习(Imitation Learning)缺点:聚焦与桌面操作,缺乏通用任务所需的移动性和灵活性 本论文优点:(1)在ALOHA…...
关键领域软件测试的突围之路:如何破解安全与效率的平衡难题
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,软件系统已成为国家关键领域的核心战斗力。不同于普通商业软件,这些承载着国家安全使命的软件系统面临着前所未有的质量挑战——如何在确保绝对安全的前提下,实现高效测试与快速迭代?这一命题正考验着…...
深度学习习题2
1.如果增加神经网络的宽度,精确度会增加到一个特定阈值后,便开始降低。造成这一现象的可能原因是什么? A、即使增加卷积核的数量,只有少部分的核会被用作预测 B、当卷积核数量增加时,神经网络的预测能力会降低 C、当卷…...
算法岗面试经验分享-大模型篇
文章目录 A 基础语言模型A.1 TransformerA.2 Bert B 大语言模型结构B.1 GPTB.2 LLamaB.3 ChatGLMB.4 Qwen C 大语言模型微调C.1 Fine-tuningC.2 Adapter-tuningC.3 Prefix-tuningC.4 P-tuningC.5 LoRA A 基础语言模型 A.1 Transformer (1)资源 论文&a…...

招商蛇口 | 执笔CID,启幕低密生活新境
作为中国城市生长的力量,招商蛇口以“美好生活承载者”为使命,深耕全球111座城市,以央企担当匠造时代理想人居。从深圳湾的开拓基因到西安高新CID的战略落子,招商蛇口始终与城市发展同频共振,以建筑诠释对土地与生活的…...
