Android T 远程动画显示流程其二——动画的添加流程(更新中)
前言
接着上篇文章分析
Android T 远程动画显示流程其一
切入点——处理应用的显示过渡
下面,我们以从桌面点击一个应用启动的场景来分析远程动画的流程,窗口添加的流程见Android T WMS窗口相关流程
这里我们从AppTransitionController.handleAppTransitionReady方法开始跟踪代码流程
代码路径:framework/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/AppTransitionController.java
/*** Handle application transition for given display.*/void handleAppTransitionReady() {......//通过getTransitCompatType方法获取transit的值@TransitionOldType final int transit = getTransitCompatType(mDisplayContent.mAppTransition, mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps,mDisplayContent.mClosingApps, mDisplayContent.mChangingContainers,mWallpaperControllerLocked.getWallpaperTarget(), getOldWallpaper(),mDisplayContent.mSkipAppTransitionAnimation);......//方法收集正在打开 (mOpeningApps)、关闭 (mClosingApps) 和切换 (mChangingContainers) 的应用的activity类型//并将它们存储在 activityTypes 集合中。final ArraySet<Integer> activityTypes = collectActivityTypes(mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps,mDisplayContent.mClosingApps, mDisplayContent.mChangingContainers);//被用于查找与给定transit和activityTypes相关的 ActivityRecord//也就是我们当前打开的应用的ActivityRecordfinal ActivityRecord animLpActivity = findAnimLayoutParamsToken(transit, activityTypes,mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps, mDisplayContent.mClosingApps,mDisplayContent.mChangingContainers);//获取正在打开的应用列表 (mOpeningApps) 中的顶层应用。//ignoreHidden 参数设置为 false,意味着即使应用是隐藏的,也会被考虑在内final ActivityRecord topOpeningApp =getTopApp(mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps, false /* ignoreHidden */);//获取正在关闭的应用列表 (mClosingApps) 中的顶层应用final ActivityRecord topClosingApp =getTopApp(mDisplayContent.mClosingApps, false /* ignoreHidden */);//获取正在切换的应用列表 (mChangingContainers) 中的顶层应用//其取决于参数DisplayContent.mChangingContainers中是否有值/** 有三种情况会给DisplayContent.mChangingContainers中添加值1.{@link Task}在全屏和浮窗之间发生切换2.{@link TaskFragment}已组织好并且正在更改窗口边界3.{@link ActivityRecord}被重新分配到一个有组织的{@link TaskFragment}中**/final ActivityRecord topChangingApp =getTopApp(mDisplayContent.mChangingContainers, false /* ignoreHidden */);//从之前找到的animLpActivity(正在打开的应用的ActivityRecord)的窗口中获取布局参数final WindowManager.LayoutParams animLp = getAnimLp(animLpActivity);......try {/*1.1应用app transition动画(远程动画)*/applyAnimations(mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps, mDisplayContent.mClosingApps, transit,animLp, voiceInteraction);/*1.2.1处理closing activity可见性*/handleClosingApps();/*1.2.2处理opening actvity可见性*/handleOpeningApps();//处理用于处理正在切换的应用handleChangingApps(transit);//处理正在关闭或更改的容器handleClosingChangingContainers();//设置与最后一次应用过渡动画相关的信息appTransition.setLastAppTransition(transit, topOpeningApp,topClosingApp, topChangingApp);final int flags = appTransition.getTransitFlags();/*1.3播放远程动画*/layoutRedo = appTransition.goodToGo(transit, topOpeningApp);//处理非应用窗口的过渡动画handleNonAppWindowsInTransition(transit, flags);//执行动画回调appTransition.postAnimationCallback()} finally {mService.mSurfaceAnimationRunner.continueStartingAnimations();}......// This has changed the visibility of windows, so perform// a new layout to get them all up-to-date./*2.由于activity的可见性变更,将DisplayContent.mLayoutNeeded标志位置为true*/mDisplayContent.setLayoutNeeded();......}
这个方法主要处理这三件事:
1.处理activity的过渡动画(远程动画)
2.分别调用 handleClosingApps以及handleOpeningApps对要关闭的和要打开的Activity进行可见性更新。
3.调用AppTransition.goodToGo方法走播放远程动画流程。
4.由于activity的可见性变更,将DisplayContent.mLayoutNeeded设置为true,该标志位在DisplayContent.performLayoutNoTrace中用来判断是否对当前DisplayContent下的所有窗口进行刷新。
这里我们主要关注远程动画的流程,主要分为两个部分。
- 处理并创建远程动画流程
applyAnimations(mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps, mDisplayContent.mClosingApps, transit, animLp, voiceInteraction); - 播放显示远程动画流程
layoutRedo = appTransition.goodToGo(transit, topOpeningApp);
动画创建流程代码分析
applyAnimations(mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps, mDisplayContent.mClosingApps, transit, animLp, voiceInteraction);
基于一组ActivityRecord来应用动画,这些ActivityRecord表示正在进行切换的应用。
mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps, mDisplayContent.mClosingApps这两个参数分别代表正在打开和关闭的应用;
transit通过前面getTransitCompatType方法中获取,是TRANSIT_OLD_WALLPAPER_CLOSE(12);
animLp通过前面getAnimLp方法中获取,用于定义窗口的布局参数。这里就是代表正在打开的应用的ActivityRecord的窗口布局参数;
voiceInteraction:表示是否为语音交互。
处理并创建远程动画
代码路径:framework/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/AppTransitionController.java
/*** Apply an app transition animation based on a set of {@link ActivityRecord}** @param openingApps The list of opening apps to which an app transition animation applies.* @param closingApps The list of closing apps to which an app transition animation applies.* @param transit The current transition type.* @param animLp Layout parameters in which an app transition animation runs.* @param voiceInteraction {@code true} if one of the apps in this transition belongs to a voice* interaction session driving task.*/private void applyAnimations(ArraySet<ActivityRecord> openingApps,ArraySet<ActivityRecord> closingApps, @TransitionOldType int transit,LayoutParams animLp, boolean voiceInteraction) {//方法检查过渡类型是否未设置,或者打开和关闭的应用程序是否都为空。如果是,则方法直接返回,不执行任何动画。if (transit == WindowManager.TRANSIT_OLD_UNSET|| (openingApps.isEmpty() && closingApps.isEmpty())) {return;}//调用getAnimationTargets方法获取打开和关闭的应用的窗口容器(WindowContainer)final ArraySet<WindowContainer> openingWcs = getAnimationTargets(openingApps, closingApps, true /* visible */);final ArraySet<WindowContainer> closingWcs = getAnimationTargets(openingApps, closingApps, false /* visible */);//打开和关闭的窗口应用动画。这是通过调重载的applyAnimations方法完成的,传递相应的参数,如动画的目标、过渡类型等。applyAnimations(openingWcs, openingApps, transit, true /* visible */, animLp,voiceInteraction);applyAnimations(closingWcs, closingApps, transit, false /* visible */, animLp,voiceInteraction);//如果存在最近任务动画控制器(RecentsAnimationController),则发送任务出现任务final RecentsAnimationController rac = mService.getRecentsAnimationController();if (rac != null) {rac.sendTasksAppeared();}//遍历打开和关闭的应用,并设置mOverrideTaskTransition为falsefor (int i = 0; i < openingApps.size(); ++i) {openingApps.valueAtUnchecked(i).mOverrideTaskTransition = false;}for (int i = 0; i < closingApps.size(); ++i) {closingApps.valueAtUnchecked(i).mOverrideTaskTransition = false;}//如果存在辅助功能控制器(AccessibilityController)且有回调,则调用其onAppWindowTransition方法。final AccessibilityController accessibilityController =mDisplayContent.mWmService.mAccessibilityController;if (accessibilityController.hasCallbacks()) {accessibilityController.onAppWindowTransition(mDisplayContent.getDisplayId(), transit);}}
传递关键参数,处理应用程序窗口的打开和关闭动画。
通过getAnimationTargets方法获取当前打开和关闭的应用的容器,即ActivityRecord的容器。
最关键的方法是调用的applyAnimations方法:
applyAnimations(openingWcs, openingApps, transit, true /* visible */, animLp,voiceInteraction);applyAnimations(closingWcs, closingApps, transit, false /* visible */, animLp,voiceInteraction);
我们这里openingWcs和closingWcs实际上表示的是应用的容器,即Task;openingApps 和 closingApps就是前面传递的mDisplayContent.mOpeningApps, mDisplayContent.mClosingApps,分别代表正在打开和关闭的应用,也是挂在对应Task下面的ActivityRecord。并且传递了应用的可见性visible,true可见,false不可见。
因此在我们桌面点击打开应用的流程中,openingWcs实际上指的是应用的Task,openingApps是应用的ActivityRecord(其实就是应用的主界面),其可见性为true;closingWcs对应的是桌面的Task,closingApps是桌面的ActivityRecord,其可见性为false。
这也对应了我们前面创建动画图层的堆栈中所打印的,先创建了应用的动画图层,后创建桌面的动画图层。
注:
从这里开始后续流程执行了两次,第一次是打开的应用流程,第二次是关闭的应用流程(一个应用的启动,伴随这另一个应用的退出,浮窗等特殊场景除外)。
从桌面点击开启应用的场景来说,一次是启动的应用角度执行流程,另一次是桌面角度执行流程。
从代码逻辑上来说,唯一的不同点是传递的可见性的值不同。
这个方法调用的是重载的applyAnimations方法
获取需要做动画的容器
/*** Apply animation to the set of window containers.** @param wcs The list of {@link WindowContainer}s to which an app transition animation applies.* @param apps The list of {@link ActivityRecord}s being transitioning.* @param transit The current transition type.* @param visible {@code true} if the apps becomes visible, {@code false} if the apps becomes* invisible.* @param animLp Layout parameters in which an app transition animation runs.* @param voiceInteraction {@code true} if one of the apps in this transition belongs to a voice* interaction session driving task.*/private void applyAnimations(ArraySet<WindowContainer> wcs, ArraySet<ActivityRecord> apps,@TransitionOldType int transit, boolean visible, LayoutParams animLp,boolean voiceInteraction) {//获取窗口容器的数量final int wcsCount = wcs.size();//遍历每一个应用的窗口容器for (int i = 0; i < wcsCount; i++) {final WindowContainer wc = wcs.valueAt(i);// If app transition animation target is promoted to higher level, SurfaceAnimator// triggers WC#onAnimationFinished only on the promoted target. So we need to take care// of triggering AR#onAnimationFinished on each ActivityRecord which is a part of the// app transition.//对于每一个应用的窗口容器,检查正在进行切换的应用(apps)中哪些是该窗口容器的后代。//就比如应用的ActivityRecord是是应用的Task的后代final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> transitioningDescendants = new ArrayList<>();for (int j = 0; j < apps.size(); ++j) {final ActivityRecord app = apps.valueAt(j);//app如果是wc的后代,将其添加到一个列表中。if (app.isDescendantOf(wc)) {transitioningDescendants.add(app);}}//调用每个应用的窗口容器的applyAnimation方法,传入相应的参数//这些参数包含动画的布局、过渡类型、是否可见、是否有语音交互以及需要做动画的ActivityRecord应用的列表。wc.applyAnimation(animLp, transit, visible, voiceInteraction, transitioningDescendants);}}
入参含义:
wcs: 一个WindowContainer对象的集合,这些对象是需要应用动画的窗口容器。
apps: 一个ActivityRecord对象的集合,这些对象表示正在进行切换的应用程序。
transit: 当前的过渡类型,例如淡入淡出、滑动等。
visible: 一个布尔值,表示应用是否变为可见。
animLp: 布局参数,定义了动画运行时的布局。
voiceInteraction: 一个布尔值,表示是否有语音交互。
关键代码解读:
-
final WindowContainer wc = wcs.valueAt(i);获取窗口容器
wcs是前面传递过来的是Task,wc就是依次获取当前应用的Task和桌面Task。 -
transitioningDescendants存储的就是需要做动画的ActivityRecord。 -
传递动画参数
通过wc.applyAnimation(animLp, transit, visible, voiceInteraction, transitioningDescendants);方法,传递参数动画的布局、过渡类型、是否可见、是否有语音交互以及需要做动画的ActivityRecord应用的列表。
wc就是Task,其没有applyAnimation方法,向上找父类WindowContainer.applyAnimation方法调用。
判断是否应用动画,传递相关参数
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
/*** Applies the app transition animation according the given the layout properties in the* window hierarchy.** @param lp The layout parameters of the window.* @param transit The app transition type indicates what kind of transition to be applied.* @param enter Whether the app transition is entering transition or not.* @param isVoiceInteraction Whether the container is participating in voice interaction or not.* @param sources {@link ActivityRecord}s which causes this app transition animation.** @return {@code true} when the container applied the app transition, {@code false} if the* app transition is disabled or skipped.** @see #getAnimationAdapter*/boolean applyAnimation(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, @TransitionOldType int transit,boolean enter, boolean isVoiceInteraction,@Nullable ArrayList<WindowContainer> sources) {//判断是否禁用过渡动画if (mWmService.mDisableTransitionAnimation) {ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_APP_TRANSITIONS_ANIM,"applyAnimation: transition animation is disabled or skipped. "+ "container=%s", this);//取消当前动画cancelAnimation();return false;}// Only apply an animation if the display isn't frozen. If it is frozen, there is no reason// to animate and it can cause strange artifacts when we unfreeze the display if some// different animation is running.try {Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "WC#applyAnimation");//会判断是否有冻结,屏幕是否开启if (okToAnimate()) {ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_APP_TRANSITIONS_ANIM,"applyAnimation: transit=%s, enter=%b, wc=%s",AppTransition.appTransitionOldToString(transit), enter, this);//传递相关参数,创建AnimationAdapter和AnimationRunnerBuilder,准备启动动画applyAnimationUnchecked(lp, enter, transit, isVoiceInteraction, sources);} else {//取消当前动画cancelAnimation();}} finally {Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);}//检查指定的窗口容器是否正在进行动画return isAnimating();}
下面说说里面的几个关键点:
-
判断是否禁用过渡动画
mWmService.mDisableTransitionAnimation
这个变量是在WindowManagerService的构造方法中初始化的mDisableTransitionAnimation = context.getResources().getBoolean(com.android.internal.R.bool.config_disableTransitionAnimation);可以发现是读取
config_disableTransitionAnimation配置项
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/symbols.xml<java-symbol type="bool" name="config_disableTransitionAnimation" />定义了这个symbol
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/config.xml<!-- Flag to disable all transition animations --><bool name="config_disableTransitionAnimation">false</bool>定义了默认值为false,不禁用过渡动画
-
取消当前动画
cancelAnimation();void cancelAnimation() {//处理动画结束时的一些后续操作doAnimationFinished(mSurfaceAnimator.getAnimationType(), mSurfaceAnimator.getAnimation());//调用SurfaceAnimator.cancelAnimation方法来取消当前正在进行的动画mSurfaceAnimator.cancelAnimation();//调用unfreeze方法解除对显示的冻结状态,允许显示继续正常更新和渲染mSurfaceFreezer.unfreeze(getSyncTransaction());}doAnimationFinished方法在动画播放结束时处理回调逻辑中会调用到,具体见后面【动画移除流程】。
-
准备动画
applyAnimationUnchecked(lp, enter, transit, isVoiceInteraction, sources);
把前面传递的参数动画的布局、过渡类型、是否可见、是否有语音交互以及需要做动画的ActivityRecord应用的列表,再次传递到applyAnimationUnchecked方法中。
注意,这里调用的是Task中重写的applyAnimationUnchecked方法,而不是直接调用的WindowContainer中的applyAnimationUnchecked方法。
因为我们前面是通过前面AppTransitionController.applyAnimations中wc.applyAnimation(animLp, transit, visible, voiceInteraction, transitioningDescendants);调用过来的,因此此时的this指针指的是变量wc,即应用对应的Task。
后面细讲applyAnimationUnchecked方法。 -
检查动画
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.javafinal boolean isAnimating(int flags, int typesToCheck) {return getAnimatingContainer(flags, typesToCheck) != null;}flags用于确定要检查的动画类型和范围。
typesToCheck用于确定哪些类型的动画需要检查。
方法内部调用getAnimatingContainer方法来获取正在进行动画的窗口容器,并根据返回值判断是否存在符合条件和目标标志的动画。
如果返回值为 true,则说明存在符合条件的动画;如果返回值为 false,则说明不存在符合条件的动画。
处理最近任务状态的动画
applyAnimationUnchecked(lp, enter, transit, isVoiceInteraction, sources);
其中参数enter代表的其实就应用的可见性,从前面AppTransitionController.applyAnimations方法中逐步传递过来值有两个
applyAnimations(openingWcs, openingApps, transit, true /* visible */, animLp, voiceInteraction);
applyAnimations(closingWcs, closingApps, transit, false /* visible */, animLp, voiceInteraction);
启动的应用的可见性为true,桌面的可见性为false
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Task.java
@Overrideprotected void applyAnimationUnchecked(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, boolean enter,@TransitionOldType int transit, boolean isVoiceInteraction,@Nullable ArrayList<WindowContainer> sources) {//获取RecentsAnimationController//只有在最近任务中,切换到另一个应用时才会创建final RecentsAnimationController control = mWmService.getRecentsAnimationController();//RecentsAnimationController不为空if (control != null) {// We let the transition to be controlled by RecentsAnimation, and callback task's// RemoteAnimationTarget for remote runner to animate.//应用可见性为true,且当前activity不是桌面或者最近任务if (enter && !isActivityTypeHomeOrRecents()) {ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_RECENTS_ANIMATIONS,"applyAnimationUnchecked, control: %s, task: %s, transit: %s",control, asTask(), AppTransition.appTransitionOldToString(transit));//执行最近任务动画逻辑control.addTaskToTargets(this, (type, anim) -> {for (int i = 0; i < sources.size(); ++i) {sources.get(i).onAnimationFinished(type, anim);}});}//判断是否有返回手势} else if (mBackGestureStarted) {// Cancel playing transitions if a back navigation animation is in progress.// This bit is set by {@link BackNavigationController} when a back gesture is started.// It is used as a one-off transition overwrite that is cleared when the back gesture// is committed and triggers a transition, or when the gesture is cancelled.//返回手势mBackGestureStarted标志位置为falsemBackGestureStarted = false;//设置一个标志为true,表示应跳过应用的过渡动画。mDisplayContent.mSkipAppTransitionAnimation = true;ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_BACK_PREVIEW, "Skipping app transition animation. task=%s", this);} else {//调用父类WindowContainer的applyAnimationUnchecked方法super.applyAnimationUnchecked(lp, enter, transit, isVoiceInteraction, sources);}}
只有在最近任务中,切换到另一个应用时才会创建RecentsAnimationController,因此control的值为空。如果不为空,应用可见性为true,且当前activity不是桌面或者最近任务,则会进入到最近任务的动画处理逻辑。
我们在操作过程中也没有返回手势,因此mBackGestureStarted为false。
所以调用了父类WindowContainer的applyAnimationUnchecked方法。
获取AnimationAdapter并创建动画图层
接着前面super.applyAnimationUnchecked(lp, enter, transit, isVoiceInteraction, sources);进行分析
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
protected void applyAnimationUnchecked(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, boolean enter,@TransitionOldType int transit, boolean isVoiceInteraction,@Nullable ArrayList<WindowContainer> sources) {//获取当前Taskfinal Task task = asTask();//当前Task不为空,应用变为不可见状态,且应用Task不为桌面或者最近任务//可以理解为应用按home键回到桌面的场景if (task != null && !enter && !task.isActivityTypeHomeOrRecents()) {//对输入法相关insets做处理final InsetsControlTarget imeTarget = mDisplayContent.getImeTarget(IME_TARGET_LAYERING);final boolean isImeLayeringTarget = imeTarget != null && imeTarget.getWindow() != null&& imeTarget.getWindow().getTask() == task;// Attach and show the IME screenshot when the task is the IME target and performing// task closing transition to the next task.if (isImeLayeringTarget && AppTransition.isTaskCloseTransitOld(transit)) {mDisplayContent.showImeScreenshot();}}//创建AnimationAdapterfinal Pair<AnimationAdapter, AnimationAdapter> adapters = getAnimationAdapter(lp,transit, enter, isVoiceInteraction);//adapters.first指的是创建startBounds为空情况RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper的对象AnimationAdapter adapter = adapters.first;//adapters.second指的是创建startBounds不为空情况RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper的对象AnimationAdapter thumbnailAdapter = adapters.second;if (adapter != null) {if (sources != null) {//把需要做的动画的ActivityRecord添加到mSurfaceAnimationSourcesmSurfaceAnimationSources.addAll(sources);}//创建AnimationRunnerBuilderAnimationRunnerBuilder animationRunnerBuilder = new AnimationRunnerBuilder();//isTaskTransitOld方法中根据transit的值判断返回值,//从桌面启动应用时transit为12,表示TRANSIT_OLD_WALLPAPER_CLOSEif (isTaskTransitOld(transit)) {//设置过渡动画背景色animationRunnerBuilder.setTaskBackgroundColor(getTaskAnimationBackgroundColor());// TODO: Remove when we migrate to shell (b/202383002)//mTaskTransitionSpec不为nullif (mWmService.mTaskTransitionSpec != null) {//隐藏Insets溢出的部分animationRunnerBuilder.hideInsetSourceViewOverflows(mWmService.mTaskTransitionSpec.animationBoundInsets);}}// Check if the animation requests to show background color for Activity and embedded// TaskFragment.//获取当前Activity,但我们当前只有Task,因此为空final ActivityRecord activityRecord = asActivityRecord();//TaskFragment为Task父类,获取到了当前Taskfinal TaskFragment taskFragment = asTaskFragment();//设置过渡动动画背景色逻辑if (adapter.getShowBackground()// Check if it is Activity transition.&& ((activityRecord != null && isActivityTransitOld(transit))// Check if it is embedded TaskFragment transition.|| (taskFragment != null && taskFragment.isEmbedded()&& isTaskFragmentTransitOld(transit)))) {final @ColorInt int backgroundColorForTransition;if (adapter.getBackgroundColor() != 0) {// If available use the background color provided through getBackgroundColor// which if set originates from a call to overridePendingAppTransition.backgroundColorForTransition = adapter.getBackgroundColor();} else {......}animationRunnerBuilder.setTaskBackgroundColor(backgroundColorForTransition);}//进入创建动画图层逻辑animationRunnerBuilder.build().startAnimation(getPendingTransaction(), adapter, !isVisible(),ANIMATION_TYPE_APP_TRANSITION, thumbnailAdapter);//判断是否在动画中显示壁纸if (adapter.getShowWallpaper()) {//更新pendingLayoutChanges添加标志FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER,表示需要重新处理壁纸布局。getDisplayContent().pendingLayoutChanges |= FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER;}}}
这个方法主要就是获取AnimationAdapter,创建对应的动画图层,我们下面主要讨论这两个点。
创建RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper实现AnimationAdapter接口
final Pair<AnimationAdapter, AnimationAdapter> adapters = getAnimationAdapter(lp,transit, enter, isVoiceInteraction);
调用的是WindowContainer中的getAnimationAdapter方法,传递了参数动画的布局、过渡类型、是否可见、是否有语音交互。
/*** Gets the {@link AnimationAdapter} according the given window layout properties in the window* hierarchy.** @return The return value will always contain two elements, one for normal animations and the* other for thumbnail animation, both can be {@code null}.* @See com.android.server.wm.RemoteAnimationController.RemoteAnimationRecord* @See LocalAnimationAdapter*/Pair<AnimationAdapter, AnimationAdapter> getAnimationAdapter(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp,@TransitionOldType int transit, boolean enter, boolean isVoiceInteraction) {final Pair<AnimationAdapter, AnimationAdapter> resultAdapters;//获取当前窗口的裁剪模式final int appRootTaskClipMode = getDisplayContent().mAppTransition.getAppRootTaskClipMode();// Separate position and size for use in animators.//获取屏幕大小,参数appRootTaskClipMode在这个方法中无实际意义final Rect screenBounds = getAnimationBounds(appRootTaskClipMode);//mTmpRect大小赋值为屏幕大小mTmpRect.set(screenBounds);//transit值为12,TRANSIT_OLD_WALLPAPER_CLOSE,不进入该流程if (this.asTask() != null && isTaskTransitOld(transit)) {this.asTask().adjustAnimationBoundsForTransition(mTmpRect);}//设置动画位置为左上角顶点(0, 0)getAnimationPosition(mTmpPoint);mTmpRect.offsetTo(0, 0);final AppTransition appTransition = getDisplayContent().mAppTransition;//创建RemoteAnimationControllerfinal RemoteAnimationController controller = appTransition.getRemoteAnimationController();//AppTransition.isChangeTransitOld(transit),transit值为12,返回false//enter 应用可见性,启动应用的可见性为true,桌面可见性为false//isChangingAppTransition(),判断当前应用是否切换过渡,//其取决于参数DisplayContent.mChangingContainers中是否有值/** 有三种情况会给DisplayContent.mChangingContainers中添加值1.{@link Task}在全屏和浮窗之间发生切换2.{@link TaskFragment}已组织好并且正在更改窗口边界3.{@link ActivityRecord}被重新分配到一个有组织的{@link TaskFragment}中**///这里我们isChangingAppTransition()值为false,即isChanging值为falsefinal boolean isChanging = AppTransition.isChangeTransitOld(transit) && enter&& isChangingAppTransition();// Delaying animation start isn't compatible with remote animations at all.//mSurfaceAnimator.isAnimationStartDelayed()判断动画是否延迟开启,//false表示不延迟,true表示延迟,我们这里值为falseif (controller != null && !mSurfaceAnimator.isAnimationStartDelayed()) {// Here we load App XML in order to read com.android.R.styleable#Animation_showBackdrop.boolean showBackdrop = false;// Optionally set backdrop color if App explicitly provides it through// {@link Activity#overridePendingTransition(int, int, int)}.@ColorInt int backdropColor = 0;//isFromActivityEmbedding(),返回的是RemoteAnimationController中的变量mIsActivityEmbedding//我们这里前面通过getRemoteAnimationController()创建RemoteAnimationController会对其赋值为false//因此下面流程不进行if (controller.isFromActivityEmbedding()) {......}//创建一个和mTmpRect相同大小和位置的矩阵final Rect localBounds = new Rect(mTmpRect);localBounds.offsetTo(mTmpPoint.x, mTmpPoint.y);final RemoteAnimationController.RemoteAnimationRecord adapters;//前面isChanging的值为false,因此!isChanging为true//enter 应用可见性,启动应用的可见性为true,桌面可见性为false//这里主要判断的是isClosingWhenResizing()方法的值,//这个值同样取决于参数DisplayContent.mChangingContainers中是否有值//这里我们isClosingWhenResizing()值为falseif (!isChanging && !enter && isClosingWhenResizing()) {// Container that is closing while resizing. Pass in the closing start bounds, so// the animation can start with the correct bounds, there won't be a snapshot.// Cleanup the mClosingChangingContainers so that when the animation is finished, it// will reset the surface.//调整大小时正在关闭的容器。传入关闭的开始边界,这样动画就可以从正确的边界开始,不会有快照。//清理mClosingChangingContainers,以便在动画完成时重置surface。final Rect closingStartBounds = getDisplayContent().mClosingChangingContainers.remove(this);adapters = controller.createRemoteAnimationRecord(this, mTmpPoint, localBounds, screenBounds, closingStartBounds,showBackdrop, false /* shouldCreateSnapshot */);} else {//isChanging为false,所以startBounds为nullfinal Rect startBounds = isChanging ? mSurfaceFreezer.mFreezeBounds : null;//创建RemoteAnimationRecord,之后创建RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper//RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper实现了AnimationAdapter接口adapters = controller.createRemoteAnimationRecord(this, mTmpPoint, localBounds, screenBounds, startBounds, showBackdrop);}if (backdropColor != 0) {adapters.setBackDropColor(backdropColor);}if (!isChanging) {//根据enter的值设置mMode的值adapters.setMode(enter? RemoteAnimationTarget.MODE_OPENING: RemoteAnimationTarget.MODE_CLOSING);}//RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper会根据startBounds变量是否为空进行不同的创建方式//startBounds变量为空的情况,保存到Pair类的first变量中//startBounds变量不为空的情况,保存到Pair类的second变量中resultAdapters = new Pair<>(adapters.mAdapter, adapters.mThumbnailAdapter);} else if (isChanging) {//创建的是LocalAnimationAdapter,非远程动画流程......} else {//创建的是LocalAnimationAdapter,非远程动画流程......}return resultAdapters;}
通过创建RemoteAnimationRecord来创建RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper
adapters = controller.createRemoteAnimationRecord(this, mTmpPoint, localBounds, screenBounds, startBounds, showBackdrop);
根据前面设置的参数我们可以知道传递的值分别为:
this指的是应用Task,以及桌面Task;
startBounds为 null ;mTmpPoint为(0,0) ;localBounds为屏幕分辨率的矩形; showBackdrop为false。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RemoteAnimationController.java
/*** Creates an animation record for each individual {@link WindowContainer}.** @param windowContainer The windows to animate.* @param position The position app bounds relative to its parent.* @param localBounds The bounds of the app relative to its parent.* @param endBounds The end bounds after the transition, in screen coordinates.* @param startBounds The start bounds before the transition, in screen coordinates.* @param showBackdrop To show background behind a window during animation.* @return The record representing animation(s) to run on the app.*/RemoteAnimationRecord createRemoteAnimationRecord(WindowContainer windowContainer,Point position, Rect localBounds, Rect endBounds, Rect startBounds,boolean showBackdrop) {return createRemoteAnimationRecord(windowContainer, position, localBounds, endBounds,startBounds, showBackdrop, startBounds != null /* shouldCreateSnapshot */);}/*** Creates an animation record for each individual {@link WindowContainer}.** @param windowContainer The windows to animate.* @param position The position app bounds relative to its parent.* @param localBounds The bounds of the app relative to its parent.* @param endBounds The end bounds after the transition, in screen coordinates.* @param startBounds The start bounds before the transition, in screen coordinates.* @param showBackdrop To show background behind a window during animation.* @param shouldCreateSnapshot Whether this target should create a snapshot animation.* @return The record representing animation(s) to run on the app.*/RemoteAnimationRecord createRemoteAnimationRecord(WindowContainer windowContainer,Point position, Rect localBounds, Rect endBounds, Rect startBounds,boolean showBackdrop, boolean shouldCreateSnapshot) {ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "createAnimationAdapter(): container=%s",windowContainer);final RemoteAnimationRecord adapters = new RemoteAnimationRecord(windowContainer, position,localBounds, endBounds, startBounds, showBackdrop, shouldCreateSnapshot);mPendingAnimations.add(adapters);return adapters;}
传递参数,创建RemoteAnimationRecord,其中shouldCreateSnapshot参数的值取决于startBounds是否为空,我们这里startBounds为空,所以shouldCreateSnapshot为false。
/*** Contains information about a remote-animation for one WindowContainer. This keeps track of,* potentially, multiple animating surfaces (AdapterWrappers) associated with one* Window/Transition. For example, a change transition has an adapter controller for the* main window and an adapter controlling the start-state snapshot.* <p>* This can be thought of as a bridge between the information that the remote animator sees (via* {@link RemoteAnimationTarget}) and what the server sees (the* {@link RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper}(s) interfacing with the moving surfaces).*/public class RemoteAnimationRecord {......RemoteAnimationRecord(WindowContainer windowContainer, Point endPos, Rect localBounds,Rect endBounds, @Nullable Rect startBounds, boolean showBackdrop,boolean shouldCreateSnapshot) {mWindowContainer = windowContainer;mShowBackdrop = showBackdrop;if (startBounds != null) {......} else {mAdapter = new RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper(this, endPos, localBounds, endBounds,new Rect(), mShowBackdrop);mStartBounds = null;}}......}
RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper会根据startBounds变量是否为空进行不同的创建方式,我们这里主要关注其为空的流程。
startBounds为空,走else流程
mAdapter = new RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper(this, endPos, localBounds, endBounds,new Rect(), mShowBackdrop);
这里通过new Rect()空矩阵(上下左右四点均为0),创建了一个startBounds
class RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper implements AnimationAdapter {......RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper(RemoteAnimationRecord record, Point position,Rect localBounds, Rect endBounds, Rect startBounds, boolean showBackdrop) {mRecord = record;mPosition.set(position.x, position.y);mLocalBounds = localBounds;mEndBounds.set(endBounds);mStartBounds.set(startBounds);mShowBackdrop = showBackdrop;}......
把传递的参数赋值给了RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper的成员变量。
这里我们的RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper实现了AnimationAdapter接口。
通过startAnimation方法创建动画图层
animationRunnerBuilder.build().startAnimation(getPendingTransaction(), adapter, !isVisible(),ANIMATION_TYPE_APP_TRANSITION, thumbnailAdapter);
getPendingTransaction():指的是一个事务。
adapter:是前面赋值AnimationAdapter adapter = adapters.first;,即创建的startBounds变量为空情况的RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper对象。
!isVisible():获取当前可见性后取反。应用当前可见性为false,即传递true;桌面当前可见性为true,即传递false。
ANIMATION_TYPE_APP_TRANSITION:过渡动画类型。
thumbnailAdapter:是前面赋值AnimationAdapter thumbnailAdapter = adapters.second;,即创建的startBounds变量不为空情况的RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper对象。
animationRunnerBuilder是AnimationRunnerBuilder对象,调用了其build方法中的startAnimation方法。我们这里调用的startAnimation方法是一个函数式接口。
private interface IAnimationStarter {void startAnimation(Transaction t, AnimationAdapter anim, boolean hidden,@AnimationType int type, @Nullable AnimationAdapter snapshotAnim);}
startAnimation方法的实现在AnimationRunnerBuilder中的build方法中return的 (Transaction t, AnimationAdapter adapter, boolean hidden, AnimationType int type, @Nullable AnimationAdapter snapshotAnim) -> {......}。
private class AnimationRunnerBuilder {/*** Runs when the surface stops animating*/private final List<Runnable> mOnAnimationFinished = new LinkedList<>();/*** Runs when the animation is cancelled but the surface is still animating*/private final List<Runnable> mOnAnimationCancelled = new LinkedList<>();......private IAnimationStarter build() {return (Transaction t, AnimationAdapter adapter, boolean hidden,@AnimationType int type, @Nullable AnimationAdapter snapshotAnim) -> {startAnimation(getPendingTransaction(), adapter, !isVisible(), type,(animType, anim) -> mOnAnimationFinished.forEach(Runnable::run),() -> mOnAnimationCancelled.forEach(Runnable::run), snapshotAnim);};}}
除了传递之前的参数之外,在return的(Transaction t, AnimationAdapter adapter, boolean hidden, AnimationType int type, @Nullable AnimationAdapter snapshotAnim) -> {......}中调用了startAnimation方法,传递了回调函数(animType, anim) -> mOnAnimationFinished.forEach(Runnable::run)和() -> mOnAnimationCancelled.forEach(Runnable::run),会执行mOnAnimationFinished和mOnAnimationCancelled这两个变量中的Runnable。
继续查看startAnimation方法
/*** Starts an animation on the container.** @param anim The animation to run.* @param hidden Whether our container is currently hidden. TODO This should use isVisible at* some point but the meaning is too weird to work for all containers.* @param type The type of animation defined as {@link AnimationType}.* @param animationFinishedCallback The callback being triggered when the animation finishes.* @param animationCancelledCallback The callback is triggered after the SurfaceAnimator sends a* cancel call to the underlying AnimationAdapter.* @param snapshotAnim The animation to run for the snapshot. {@code null} if there is no* snapshot.*/void startAnimation(Transaction t, AnimationAdapter anim, boolean hidden,@AnimationType int type,@Nullable OnAnimationFinishedCallback animationFinishedCallback,@Nullable Runnable animationCancelledCallback,@Nullable AnimationAdapter snapshotAnim) {ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ANIM, "Starting animation on %s: type=%d, anim=%s",this, type, anim);// TODO: This should use isVisible() but because isVisible has a really weird meaning at// the moment this doesn't work for all animatable window containers.mSurfaceAnimator.startAnimation(t, anim, hidden, type, animationFinishedCallback,animationCancelledCallback, snapshotAnim, mSurfaceFreezer);}
-
入参含义
t:这是一个对象,用于描述一系列的窗口操作,例如移动、调整大小、绘制等。这些操作在WMS中排队,并在适当的时机应用到窗口上。
anim:这是对动画进行封装的类。它包含了一些关于如何开始、更新和结束动画的信息。传递的也就是前面WindowContainer.getAnimationAdapter中创建startBounds变量为空情况的RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper对象。
hidden:这个布尔值表示窗口是否隐藏。如果窗口是隐藏的,那么就不会显示动画。前面传递的!isVisible()值为false。
type:这个整数代表了动画的类型。这里我们传递的是ANIMATION_TYPE_APP_TRANSITION,即图层上显示的app_transition。
animationFinishedCallback和animationCancelledCallback:这两个是回调函数,分别在动画完成和动画取消时被调用。
snapshotAnim:这个参数是给定动画的快照。如果参数为null,那么就表示没有快照。传递过来的是变量thumbnailAdapter,即startBounds变量不为空情况的RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper对象。 -
代码含义
关键的代码只有这一句mSurfaceAnimator.startAnimation(t, anim, hidden, type, animationFinishedCallback, animationCancelledCallback, snapshotAnim, mSurfaceFreezer);
这行代码调用了SurfaceAnimator的startAnimation方法来启动动画。SurfaceAnimator的作用主要是控制窗口动画,它是窗口动画的中控,通过操控mLeash对象来实现窗口的大小、位置、透明度等动画属性的改变。这个方法需要一系列参数,包括上面解释的所有参数,还有一个SurfaceFreezer对象mSurfaceFreezer,它可以在动画开始时冻结窗口的更新,以防止在动画过程中窗口的内容闪烁。
mSurfaceAnimator和mSurfaceFreezer是在WindowContainer的构造方法中初始化的class WindowContainer<E extends WindowContainer> extends ConfigurationContainer<E>implements Comparable<WindowContainer>, Animatable, SurfaceFreezer.Freezable,InsetsControlTarget {......WindowContainer(WindowManagerService wms) {mWmService = wms;mTransitionController = mWmService.mAtmService.getTransitionController();mPendingTransaction = wms.mTransactionFactory.get();mSyncTransaction = wms.mTransactionFactory.get();mSurfaceAnimator = new SurfaceAnimator(this, this::onAnimationFinished, wms);mSurfaceFreezer = new SurfaceFreezer(this, wms);}...... }
通过SurfaceAnimator中创建leash
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/SurfaceAnimator.java
/*** Starts an animation.** @param anim The object that bridges the controller, {@link SurfaceAnimator}, with the* component responsible for running the animation. It runs the animation with* {@link AnimationAdapter#startAnimation} once the hierarchy with* the Leash has been set up.* @param hidden Whether the container holding the child surfaces is currently visible or not.* This is important as it will start with the leash hidden or visible before* handing it to the component that is responsible to run the animation.* @param animationFinishedCallback The callback being triggered when the animation finishes.* @param animationCancelledCallback The callback is triggered after the SurfaceAnimator sends a* cancel call to the underlying AnimationAdapter.* @param snapshotAnim The animation to run for the snapshot. {@code null} if there is no* snapshot.*/void startAnimation(Transaction t, AnimationAdapter anim, boolean hidden,@AnimationType int type,@Nullable OnAnimationFinishedCallback animationFinishedCallback,@Nullable Runnable animationCancelledCallback,@Nullable AnimationAdapter snapshotAnim, @Nullable SurfaceFreezer freezer) {//开始新的动画之前,取消之前的动画//参数含义:t(是一个事务对象),true(表示动画正在重新启动),和true(表示向前取消)cancelAnimation(t, true /* restarting */, true /* forwardCancel */);//初始化参数,把WindowContainer.startAnimation中传递的参数赋值给对应变量mAnimation = anim;mAnimationType = type;mSurfaceAnimationFinishedCallback = animationFinishedCallback;mAnimationCancelledCallback = animationCancelledCallback;//获取当前窗口的SurfaceControlfinal SurfaceControl surface = mAnimatable.getSurfaceControl();//没有surface,则取消当前的动画if (surface == null) {Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to start animation, surface is null or no children.");cancelAnimation();return;}//调用SurfaceFreezer中takeLeashForAnimation()获取mLeash,但是SurfaceFreezer中没有被初始化,所以这里的mLeash还是为nullmLeash = freezer != null ? freezer.takeLeashForAnimation() : null;if (mLeash == null) {//创建mLeashmLeash = createAnimationLeash(mAnimatable, surface, t, type,mAnimatable.getSurfaceWidth(), mAnimatable.getSurfaceHeight(), 0 /* x */,0 /* y */, hidden, mService.mTransactionFactory);//创建动画“leash”后执行的一些操作,包括重置图层、重新分配图层以及重置Surface的位置mAnimatable.onAnimationLeashCreated(t, mLeash);}//处理动画开始时进行一些设置和准备工作mAnimatable.onLeashAnimationStarting(t, mLeash);if (mAnimationStartDelayed) {ProtoLog.i(WM_DEBUG_ANIM, "Animation start delayed for %s", mAnimatable);return;}//将leash传给AnimationAdaptermAnimation.startAnimation(mLeash, t, type, mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback);if (ProtoLogImpl.isEnabled(WM_DEBUG_ANIM)) {StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(sw);mAnimation.dump(pw, "");ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_ANIM, "Animation start for %s, anim=%s", mAnimatable, sw);}//获取一个快照,并使用该快照来执行动画,我们这里snapshotAnim为null,因此不涉及if (snapshotAnim != null) {mSnapshot = freezer.takeSnapshotForAnimation();if (mSnapshot == null) {Slog.e(TAG, "No snapshot target to start animation on for " + mAnimatable);return;}mSnapshot.startAnimation(t, snapshotAnim, type);}}
入参就是前面WindowContainer.startAnimation中传递的参数。
获取当前窗口的surface
final SurfaceControl surface = mAnimatable.getSurfaceControl();
mAnimatable是Animatable接口的对象,WindowContainer实现了Animatable接口。
在WindowContainer构造方法中初始化mSurfaceAnimator = new SurfaceAnimator(this, this::onAnimationFinished, wms);
而SurfaceAnimator的构造方法是
SurfaceAnimator(Animatable animatable,@Nullable OnAnimationFinishedCallback staticAnimationFinishedCallback,WindowManagerService service) {mAnimatable = animatable;mService = service;mStaticAnimationFinishedCallback = staticAnimationFinishedCallback;mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback = getFinishedCallback(staticAnimationFinishedCallback);}
也就是说实际上是把this赋值给了mAnimatable,因此mAnimatable就代表了当前的窗口。
从前面的代码可以看出远程动画涉及到打开的应用和关闭的应用,这两个应用的动画。
applyAnimations(openingWcs, openingApps, transit, true /* visible */, animLp,voiceInteraction);applyAnimations(closingWcs, closingApps, transit, false /* visible */, animLp,voiceInteraction);
即我们这里第一次获取当前窗口mAnimatable时,代表的是正在打开的应用,即应用Task;第二次获取的则是桌面,即桌面Task。
获取Leash
mLeash = freezer != null ? freezer.takeLeashForAnimation() : null;
根据freezer是否为null来确定mLeash的值,我们这里freezer是从WindowContainer.startAnimation方法中传递过来的mSurfaceFreezer,这个变量在WindowContainer的构造方法中初始化mSurfaceFreezer = new SurfaceFreezer(this, wms);,因此mSurfaceFreezer不为null,即freezer不为null,freezer != null 为true,所以走freezer.takeLeashForAnimation()
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/SurfaceFreezer.java
SurfaceControl mLeash;/*** Used by {@link SurfaceAnimator}. This "transfers" the leash to be used for animation.* By transferring the leash, this will no longer try to clean-up the leash when finished.*/SurfaceControl takeLeashForAnimation() {SurfaceControl out = mLeash;mLeash = null;return out;}
mLeash在SurfaceFreezer类中并没有初始化,因此我们的mLeash值为null,所以out的值同样为null,最终SurfaceAnimator类中的mLeash获取到的值为null
创建Leash
mLeash为null,使用createAnimationLeash方法创建Leash
mLeash = createAnimationLeash(mAnimatable, surface, t, type,mAnimatable.getSurfaceWidth(), mAnimatable.getSurfaceHeight(), 0 /* x */,0 /* y */, hidden, mService.mTransactionFactory);
入参含义
mAnimatable:当前窗口。
surface:当前窗口的surface。
t:一个事务对象,用于执行一系列操作。
type:动画类型。
mAnimatable.getSurfaceWidth()、mAnimatable.getSurfaceHeight():窗口surface尺寸的参数。
0 /* x */、 0 /* y */:坐标位置
hidden:一个布尔值,表示是否隐藏。
mService.mTransactionFactory:一个事务工厂对象,用于创建新的事务。
SurfaceAnimator.createAnimationLeash()
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/SurfaceAnimator.java
static SurfaceControl createAnimationLeash(Animatable animatable, SurfaceControl surface,Transaction t, @AnimationType int type, int width, int height, int x, int y,boolean hidden, Supplier<Transaction> transactionFactory) {/* log add start*/Slog.i("WindowManager:","createAnimationLeash type = " + animationTypeToString(type) , new Exception());/* log add end*/ProtoLog.i(WM_DEBUG_ANIM, "Reparenting to leash for %s", animatable);//通过SurfaceControl.Builder创建leashfinal SurfaceControl.Builder builder = animatable.makeAnimationLeash().setParent(animatable.getAnimationLeashParent()).setName(surface + " - animation-leash of " + animationTypeToString(type))// TODO(b/151665759) Defer reparent calls// We want the leash to be visible immediately because the transaction which shows// the leash may be deferred but the reparent will not. This will cause the leashed// surface to be invisible until the deferred transaction is applied. If this// doesn't work, you will can see the 2/3 button nav bar flicker during seamless// rotation..setHidden(hidden).setEffectLayer().setCallsite("SurfaceAnimator.createAnimationLeash");//通过前面的SurfaceControl.Builder创建leashfinal SurfaceControl leash = builder.build();//其他属性设置t.setWindowCrop(leash, width, height);t.setPosition(leash, x, y);t.show(leash);t.setAlpha(leash, hidden ? 0 : 1);//当前窗口的surface重新绑定到新创建的leash上t.reparent(surface, leash);return leash;}
传递当前窗口animatable,为其和其父节点之间添加surface。第一次创建的是正在打开的应用的动画,第二次是桌面关闭时的动画。
下面我们解读一下,leash是如何创建并加入其中的
通过SurfaceControl.Builder创建leash
-
animatable.makeAnimationLeash()
代码路径: frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.javapublic Builder makeAnimationLeash() {return makeSurface().setContainerLayer();}创建一个图层作为容器layer
-
setParent(animatable.getAnimationLeashParent())
这段代码我们分成两个部分来看,即setParent()和getAnimationLeashParent()
1.setParent()
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/SurfaceControl.java/*** Set a parent surface for our new SurfaceControl.** Child surfaces are constrained to the onscreen region of their parent.* Furthermore they stack relatively in Z order, and inherit the transformation* of the parent.** @param parent The parent control.*/@NonNullpublic Builder setParent(@Nullable SurfaceControl parent) {mParent = parent;return this;}这个段代码很简单,就是给当前SurfaceControl设置一个父SurfaceControl。
2.getAnimationLeashParent()
代码路径: frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java@Overridepublic SurfaceControl getAnimationLeashParent() {return getParentSurfaceControl();}/** @return The SurfaceControl parent for this containers SurfaceControl.* The SurfaceControl must be valid if non-null.*/@Overridepublic SurfaceControl getParentSurfaceControl() {final WindowContainer parent = getParent();if (parent == null) {return null;}return parent.getSurfaceControl();}/*** @return The SurfaceControl for this container.* The SurfaceControl must be valid if non-null.*/@Overridepublic SurfaceControl getSurfaceControl() {return mSurfaceControl;}简单来说,就是获取当前窗口父SurfaceControl。
那么合起来
setParent(animatable.getAnimationLeashParent())的意思就是,把当前新创建的SurfaceControl(leash)的父亲设置为当前窗口父亲的SurfaceControl。
即此时leash图层和当前窗口应用Task的父亲均是DefaultTaskDsiplayArea,两人还在当兄弟。
简图如下:
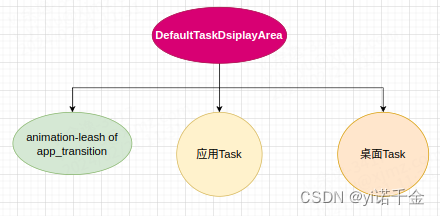
此时创建的是应用Task的动画,桌面Task的动画尚未创建,待应用Task动画创建完成后,才会去走正在关闭的应用(桌面)的动画逻辑。
桌面Task是一直挂在DefaultTaskDsiplayArea上的,这里我们先不关注桌面Task节点。 -
setEffectLayer()
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/SurfaceControl.java/*** Indicate whether an 'EffectLayer' is to be constructed.** An effect layer behaves like a container layer by default but it can support* color fill, shadows and/or blur. These layers will not have an associated buffer.* When created, this layer has no effects set and will be transparent but the caller* can render an effect by calling:* - {@link Transaction#setColor(SurfaceControl, float[])}* - {@link Transaction#setBackgroundBlurRadius(SurfaceControl, int)}* - {@link Transaction#setShadowRadius(SurfaceControl, float)}** @hide*/public Builder setEffectLayer() {mFlags |= NO_COLOR_FILL;//清空缓冲区设置unsetBufferSize();return setFlags(FX_SURFACE_EFFECT, FX_SURFACE_MASK);}设置为EffectLayer。它是一种特殊类型的SurfaceControl层,它默认表现得像一个容器层,但可以支持颜色填充、阴影和/或模糊效果。
这个EffectLayer主要就是用于实现一些视觉效果。
默认的注释里面也说明可以使用这些方法来渲染一个效果:
Transaction#setColor(SurfaceControl, float[]):使用给定的颜色数组设置该层的颜色。
Transaction#setBackgroundBlurRadius(SurfaceControl, int):设置背景模糊的半径。
Transaction#setShadowRadius(SurfaceControl, float):设置阴影的半径。
final SurfaceControl leash = builder.build();
最后通过build()方法创建leash
当前窗口的surface重新绑定到新创建的leash上
t.reparent(surface, leash);
这里的surface指的就是从前面传递的当前窗口的SurfaceControl。
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/SurfaceControl.java
/*** Re-parents a given layer to a new parent. Children inherit transform (position, scaling)* crop, visibility, and Z-ordering from their parents, as if the children were pixels within the* parent Surface.** @param sc The SurfaceControl to reparent* @param newParent The new parent for the given control.* @return This Transaction*/@NonNullpublic Transaction reparent(@NonNull SurfaceControl sc,@Nullable SurfaceControl newParent) {//检查传入的SurfaceControl对象是否满足某些预设条件checkPreconditions(sc);long otherObject = 0;if (newParent != null) {//检查新父对象是否被释放。如果已经被释放,那么它会抛出异常。newParent.checkNotReleased();//新父对象不为null且未被释放,那么将新父对象的Native对象赋值给otherObject。otherObject = newParent.mNativeObject;}//传入了三个参数:1.当前对象的Native对象 2.被重新设置父对象的SurfaceControl的Native对象 3.新父对象的Native对象。//用于实现重新设置父对象的具体操作。nativeReparent(mNativeObject, sc.mNativeObject, otherObject);//把被重新设置父对象的SurfaceControl和新父对象存储到mReparentedSurfaces这个map中。mReparentedSurfaces.put(sc, newParent);return this;}
@NonNull SurfaceControl sc: 表示要被重新设置父对象的SurfaceControl对象。这个参数不能为null。
@Nullable SurfaceControl newParent: 表示新的父SurfaceControl对象。可以为null,表示没有新的父对象。
这个方法主要就是把当前窗口的SurfaceControl的父亲,修改为leash。
mReparentedSurfaces是ArrayMap对象,以键值对的形式临时存储父子关系,key值存储SurfaceControl对象,value为其父SurfaceControl对象。
即此时leash图层变成了当前窗口应用Task图层的父亲,如简易图所示:
曾经我们是兄弟,如今我是你爸爸~
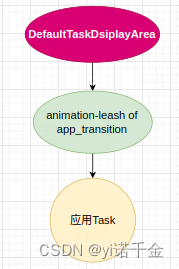
需要注意的是,Task和DefaultTaskDsiplayArea容器之前的关系并未改变,创建leash图层的过程只是改变的是surface之间的关系。
即leash图层是DefaultTaskDsiplayArea图层的父亲,Task的图层是leash图层的父亲,但是Task的父亲仍然是DefaultTaskDsiplayArea。
实际关系情况如下图所示:
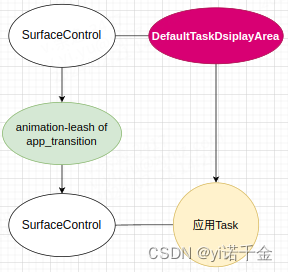
所以DefaultTaskDsiplayArea和leash实际上是表面父子,leash和Task也是表面父子
leash的surface调整
mAnimatable.onAnimationLeashCreated(t, mLeash);
入参是一个事务(用于操作窗口系统的底层API)和一个SurfaceControl对象(表示一个可以控制和操作Surface的接口)
把创建好的mLeash传递到onAnimationLeashCreated方法中,做一些Surface调整操作。
该方法实现在WindowContainer中。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
void reassignLayer(Transaction t) {final WindowContainer parent = getParent();if (parent != null) {parent.assignChildLayers(t);}}void resetSurfacePositionForAnimationLeash(Transaction t) {t.setPosition(mSurfaceControl, 0, 0);final SurfaceControl.Transaction syncTransaction = getSyncTransaction();if (t != syncTransaction) {// Avoid restoring to old position if the sync transaction is applied later.syncTransaction.setPosition(mSurfaceControl, 0, 0);}mLastSurfacePosition.set(0, 0);}@Overridepublic void onAnimationLeashCreated(Transaction t, SurfaceControl leash) {mLastLayer = -1;mAnimationLeash = leash;reassignLayer(t);// Leash is now responsible for position, so set our position to 0.resetSurfacePositionForAnimationLeash(t);}
这段代码主要用于在创建新的leash时,重置动画目标的位置,并初始化一些动画相关的状态。同时,可能还用于重新分配或者设置子容器的图层。
首先,在新的动画(leash)被创建时被调用。在这个方法中,首先将mLastLayer(可能表示上一个图层或者上一个动画目标)设置为-1,然后保存传入的leash到mAnimationLeash(后面removeLeash流程中会用到mAnimationLeash)。
之后,调用reassignLayer(t)方法,这个方法获取这个视图的父容器,如果父容器存在,那么就调用父容器的assignChildLayers(t)方法(用于调整其所有child的z-order)。
最后,为了确保leash现在位置的控制,调用resetSurfacePositionForAnimationLeash(t)方法将Surface的位置重置为(0,0),重置界面元素的位置以便进行动画。
注:Z-order也被称为深度顺序(depth order)或Z轴顺序,它用于确定图层(Layers)在屏幕上的堆叠顺序。简单来说,Z-order就是图层在Z轴上的位置,Z轴位置越低,图层越在底层,Z轴位置越高,图层越在顶层。
处理动画开始时进行一些设置和准备工作
mAnimatable.onLeashAnimationStarting(t, mLeash);
入参同样是一个事务(用于操作窗口系统的底层API)和一个SurfaceControl对象(表示一个可以控制和操作Surface的接口)
onLeashAnimationStarting方法是在ActivityRecord中实现的。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityRecord.java
@Overridepublic void onLeashAnimationStarting(Transaction t, SurfaceControl leash) {if (mAnimatingActivityRegistry != null) {//1.将正在启动或者有动画效果的Activity添加到列表中,以便于管理和控制这些Activity的动画效果。mAnimatingActivityRegistry.notifyStarting(this);}// If the animation needs to be cropped then an animation bounds layer is created as a// child of the root pinned task or animation layer. The leash is then reparented to this// new layer.//2.否需要创建一个动画边界层if (mNeedsAnimationBoundsLayer) {//设置临时矩形为空mTmpRect.setEmpty();//调用方法检查当前的活动转移是否在任务内部。//如果是,则获取任务的边界到临时矩形mTmpRect。如果不是,则获取RootTask的边界。if (getDisplayContent().mAppTransitionController.isTransitWithinTask(getTransit(), task)) {task.getBounds(mTmpRect);} else {final Task rootTask = getRootTask();if (rootTask == null) {return;}// Set clip rect to root task bounds.rootTask.getBounds(mTmpRect);}//创建动画边界层mAnimationBoundsLayer = createAnimationBoundsLayer(t);// Crop to root task bounds.//设置leash的层为0//leash将被放置在Z轴的最底层,如果有其他层级的SurfaceControl对象,它们将会覆盖在leash之上。t.setLayer(leash, 0);//并设置AnimationBoundsLayer的层为上一个层的值,保证leash在AnimationBoundsLayer下面t.setLayer(mAnimationBoundsLayer, getLastLayer());// Reparent leash to animation bounds layer.//重新将leash的父节点设置为动画边界层。t.reparent(leash, mAnimationBoundsLayer);}}private SurfaceControl createAnimationBoundsLayer(Transaction t) {ProtoLog.i(WM_DEBUG_APP_TRANSITIONS_ANIM, "Creating animation bounds layer");final SurfaceControl.Builder builder = makeAnimationLeash()//给AnimationBoundsLayer设置父节点为Leash的父节点//即把动画边界层的父节点设置为windowToken.setParent(getAnimationLeashParent()).setName(getSurfaceControl() + " - animation-bounds").setCallsite("ActivityRecord.createAnimationBoundsLayer");final SurfaceControl boundsLayer = builder.build();t.show(boundsLayer);return boundsLayer;}
这个方法其实主要就是做了两件事:
1.根据mAnimatingActivityRegistry的值判断,是否需要把有动画效果的Activity添加到列表中
2.根据mNeedsAnimationBoundsLayer的值判断,否需要创建一个动画边界层
createAnimationBoundsLayer就是创建了一个SurfaceControl。
getLastLayer()用于返回当前窗口的最高(或最后)层级。假设我们有一个窗口管理系统中,窗口的层级从0开始编号。当一个新窗口创建时,它可能被赋予层级0。然后,如果这个新窗口被另一个窗口覆盖,那么新窗口的层级可能会更新为1,依此类推。
通过使用AnimationBoundsLayer,可以定义一个矩形区域,该区域可以作为动画的边界。当动画开始时,它只在该定义的区域内显示,不会超出这个边界。AnimationBoundsLayer的主要作用是限制动画的显示区域,以确保动画不会影响到应用程序的其他部分。
将leash传给RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper,执行动画
mAnimation.startAnimation(mLeash, t, type, mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback);
mAnimation是AnimationAdapter接口的对象,调用其startAnimation方法,传递mLeash(动画)、t(事务)、type(动画类型)和mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback(回调函数)。
mAnimation的值是前面WindowContainer.startAnimation传递的anim,这个anim实际上就是传递的也就是前面WindowContainer.getAnimationAdapter中创建startBounds变量为空情况的RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper对象。因此这里调用接口AnimationAdapter的方法startAnimation正是在RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper中实现的。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RemoteAnimationController.java
@Overridepublic void startAnimation(SurfaceControl animationLeash, Transaction t,@AnimationType int type, @NonNull OnAnimationFinishedCallback finishCallback) {ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "startAnimation");//设置动画的起始位置和窗口裁剪区域if (mStartBounds.isEmpty()) {// Restore position and stack crop until client has a chance to modify it.t.setPosition(animationLeash, mPosition.x, mPosition.y);t.setWindowCrop(animationLeash, mEndBounds.width(), mEndBounds.height());} else {// Offset the change animation leash to the relative start position in parent.// (mPosition) is the relative end position in parent container.// (mStartBounds - mEndBounds) is the position difference between start and end.// (mPosition + mStartBounds - mEndBounds) will be the relative start position.t.setPosition(animationLeash, mPosition.x + mStartBounds.left - mEndBounds.left,mPosition.y + mStartBounds.top - mEndBounds.top);t.setWindowCrop(animationLeash, mStartBounds.width(), mStartBounds.height());}//保存动画图层到mCapturedLeashmCapturedLeash = animationLeash;//当动画完成时的回调函数 finishCallback保存到mCapturedFinishCallback。mCapturedFinishCallback = finishCallback;//保存动画类型mAnimationType = type;}
这个方法的主要目的是根据提供的起始和结束边界来设置动画的起始位置和窗口裁剪区域,并保存相关信息到RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper的成员变量中,以供后续使用。
启动并显示动画流程
layoutRedo = appTransition.goodToGo(transit, topOpeningApp);
在最开始的AppTransitionController.handleAppTransitionReady方法中调用AppTransition.goodToGo方法开始启动并显示动画的流程。
入参同样都是在handleAppTransitionReady方法中初始化的:
参数transit的值通过getTransitCompatType方法中获取,是TRANSIT_OLD_WALLPAPER_CLOSE(12);
参数topOpeningApp指的是正在打开的应用列表 (mOpeningApps) 中的顶层应用,即应用Task对应的ActivityRecord,也就是我们在桌面启动的应用的ActivityRecord。
判断是否需要重新进行布局,RemoteAnimationController状态
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/AppTransitionController.java
/*** @return bit-map of WindowManagerPolicy#FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_* to indicate whether another* layout pass needs to be done*/int goodToGo(@TransitionOldType int transit, ActivityRecord topOpeningApp) {mNextAppTransitionFlags = 0;mNextAppTransitionRequests.clear();setAppTransitionState(APP_STATE_RUNNING);//如果topOpeningApp不为空,即应用ActivityRecord不为空,//那么获取其ActivityRecord的容器,即应用Taskfinal WindowContainer wc =topOpeningApp != null ? topOpeningApp.getAnimatingContainer() : null;//应用ActivityRecord不为空,获取AnimationAdapter,即RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapperfinal AnimationAdapter topOpeningAnim = wc != null ? wc.getAnimation() : null;//通知所有的AppTransitionListener,应用过渡动画即将开始//根据其返回值判断是否需要重新进行布局//我们这里所有的调用AppTransitionListener的redoLayout返回值都0//即redoLayout返回值都0int redoLayout = notifyAppTransitionStartingLocked(AppTransition.isKeyguardGoingAwayTransitOld(transit),AppTransition.isKeyguardOccludeTransitOld(transit),topOpeningAnim != null ? topOpeningAnim.getDurationHint() : 0,topOpeningAnim != null? topOpeningAnim.getStatusBarTransitionsStartTime(): SystemClock.uptimeMillis(),AnimationAdapter.STATUS_BAR_TRANSITION_DURATION);//mRemoteAnimationController不为空if (mRemoteAnimationController != null) {mRemoteAnimationController.goodToGo(transit);}//如果mRemoteAnimationController为空//transit值为TRANSIT_OLD_WALLPAPER_CLOSE//topOpeningAnim,应用ActivityRecord不为空时else if ((isTaskOpenTransitOld(transit) || transit == TRANSIT_OLD_WALLPAPER_CLOSE)&& topOpeningAnim != null) {//shouldAttachNavBarToAppDuringTransition(),在动画过渡期间将导航栏附加到应用程序//getRecentsAnimationController(),RecentsAnimationController为空if (mDisplayContent.getDisplayPolicy().shouldAttachNavBarToAppDuringTransition()&& mService.getRecentsAnimationController() == null) {//创建一个新的NavBarFadeAnimationControllerfinal NavBarFadeAnimationController controller =new NavBarFadeAnimationController(mDisplayContent);// For remote animation case, the nav bar fades out and in is controlled by the// remote side. For non-remote animation case, we play the fade out/in animation// here. We play the nav bar fade-out animation when the app transition animation// starts and play the fade-in animation sequentially once the fade-out is finished.//使用fadeOutAndInSequentially方法使其淡出并淡入controller.fadeOutAndInSequentially(topOpeningAnim.getDurationHint(),null /* fadeOutParent */, topOpeningApp.getSurfaceControl());}}return redoLayout;}
我们RemoteAnimationController已经创建,所以mRemoteAnimationController != null为true,进入该流程mRemoteAnimationController.goodToGo(transit);,调用RemoteAnimationController的goodToGo方法,传递的参数值为TRANSIT_OLD_WALLPAPER_CLOSE
准备开始动画
/*** Called when the transition is ready to be started, and all leashes have been set up.*/void goodToGo(@WindowManager.TransitionOldType int transit) {ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "goodToGo()");if (mCanceled) {ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS,"goodToGo(): Animation canceled already");onAnimationFinished();invokeAnimationCancelled("already_cancelled");return;}// Scale the timeout with the animator scale the controlling app is using.mHandler.postDelayed(mTimeoutRunnable,(long) (TIMEOUT_MS * mService.getCurrentAnimatorScale()));mFinishedCallback = new FinishedCallback(this);// Create the app targetsfinal RemoteAnimationTarget[] appTargets = createAppAnimations();if (appTargets.length == 0 && !AppTransition.isKeyguardOccludeTransitOld(transit)) {// Keyguard occlude transition can be executed before the occluding activity becomes// visible. Even in this case, KeyguardService expects to receive binder call, so we// don't cancel remote animation.ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS,"goodToGo(): No apps to animate, mPendingAnimations=%d",mPendingAnimations.size());onAnimationFinished();invokeAnimationCancelled("no_app_targets");return;}if (mOnRemoteAnimationReady != null) {mOnRemoteAnimationReady.run();mOnRemoteAnimationReady = null;}// Create the remote wallpaper animation targets (if any)final RemoteAnimationTarget[] wallpaperTargets = createWallpaperAnimations();// Create the remote non app animation targets (if any)final RemoteAnimationTarget[] nonAppTargets = createNonAppWindowAnimations(transit);mService.mAnimator.addAfterPrepareSurfacesRunnable(() -> {try {linkToDeathOfRunner();Slog.i("RemoteAnimationController","goodToGo mRemoteAnimationAdapter.getRunner():"+mRemoteAnimationAdapter.getRunner());ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "goodToGo(): onAnimationStart,"+ " transit=%s, apps=%d, wallpapers=%d, nonApps=%d",AppTransition.appTransitionOldToString(transit), appTargets.length,wallpaperTargets.length, nonAppTargets.length);mRemoteAnimationAdapter.getRunner().onAnimationStart(transit, appTargets,wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets, mFinishedCallback);} catch (RemoteException e) {Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to start remote animation", e);onAnimationFinished();}if (ProtoLogImpl.isEnabled(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS)) {ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "startAnimation(): Notify animation start:");writeStartDebugStatement();}});setRunningRemoteAnimation(true);}
动画移除流程
处理和响应动画完成的逻辑
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
private void doAnimationFinished(@AnimationType int type, AnimationAdapter anim) {for (int i = 0; i < mSurfaceAnimationSources.size(); ++i) {//mSurfaceAnimationSources中每个容器,做对应的onAnimationFinishedmSurfaceAnimationSources.valueAt(i).onAnimationFinished(type, anim);}//清除动画源列表mSurfaceAnimationSources.clear();if (mDisplayContent != null) {//调用DisplayContent的onWindowAnimationFinished方法//从当前源码上看,主要是针对输入法相关做了一些操作mDisplayContent.onWindowAnimationFinished(this, type);}}/*** Called when an animation has finished running.*/protected void onAnimationFinished(@AnimationType int type, AnimationAdapter anim) {//主要用于 清空 mSurfaceAnimationSources 列表doAnimationFinished(type, anim);//WindowManagerService中实现onAnimationFinished()//用于唤醒所有等待mGlobalLock对象的线程,确保多个线程能够正确地执行任务mWmService.onAnimationFinished();//将 mNeedsZBoost 设置为 false,表示不再需要Z轴增强mNeedsZBoost = false;}
我们这里mSurfaceAnimationSources是保存的是需要做动画的ActivityRecord,mSurfaceAnimationSources的值是在applyAnimationUnchecked方法中添加的。
mSurfaceAnimationSources.valueAt(i).onAnimationFinished(type, anim);调用了不同容器onAnimationFinished方法,在ActivityRecord和WindowState中都重写了这个方法。我们这里是远程动画,主要调用的就是ActivityRecord中重写的onAnimationFinished方法。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityRecord.java
@Overrideprotected void onAnimationFinished(@AnimationType int type, AnimationAdapter anim) {super.onAnimationFinished(type, anim);Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "AR#onAnimationFinished");mTransit = TRANSIT_OLD_UNSET;mTransitFlags = 0;setAppLayoutChanges(FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_ANIM | FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER,"ActivityRecord");clearThumbnail();setClientVisible(isVisible() || mVisibleRequested);getDisplayContent().computeImeTargetIfNeeded(this);ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ANIM, "Animation done in %s"+ ": reportedVisible=%b okToDisplay=%b okToAnimate=%b startingDisplayed=%b",this, reportedVisible, okToDisplay(), okToAnimate(),isStartingWindowDisplayed());// clean up thumbnail windowif (mThumbnail != null) {mThumbnail.destroy();mThumbnail = null;}// WindowState.onExitAnimationDone might modify the children list, so make a copy and then// traverse the copy.final ArrayList<WindowState> children = new ArrayList<>(mChildren);children.forEach(WindowState::onExitAnimationDone);// The starting window could transfer to another activity after app transition started, in// that case the latest top activity might not receive exit animation done callback if the// starting window didn't applied exit animation success. Notify animation finish to the// starting window if needed.if (task != null && startingMoved) {final WindowState transferredStarting = task.getWindow(w ->w.mAttrs.type == TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING);if (transferredStarting != null && transferredStarting.mAnimatingExit&& !transferredStarting.isSelfAnimating(0 /* flags */,ANIMATION_TYPE_WINDOW_ANIMATION)) {transferredStarting.onExitAnimationDone();}}getDisplayContent().mAppTransition.notifyAppTransitionFinishedLocked(token);scheduleAnimation();// Schedule to handle the stopping and finishing activities which the animation is done// because the activities which were animating have not been stopped yet.mTaskSupervisor.scheduleProcessStoppingAndFinishingActivitiesIfNeeded();Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);}
相关文章:

Android T 远程动画显示流程其二——动画的添加流程(更新中)
前言 接着上篇文章分析 Android T 远程动画显示流程其一 切入点——处理应用的显示过渡 下面,我们以从桌面点击一个应用启动的场景来分析远程动画的流程,窗口添加的流程见Android T WMS窗口相关流程 这里我们从AppTransitionController.handleAppTran…...

Pytorch-SGD算法解析
关注B站可以观看更多实战教学视频:肆十二-的个人空间-肆十二-个人主页-哔哩哔哩视频 (bilibili.com) SGD,即随机梯度下降(Stochastic Gradient Descent),是机器学习中用于优化目标函数的迭代方法,特别是在处…...

物联网土壤传感器简介
物联网土壤传感器简介 物联网土壤传感器的工作原理基于多种物理、化学和生物原理,通过感应器等组成部件将土壤中的特征数据转化为电信号,从而进行采集、处理和输出。这些传感器主要包括土壤湿度传感器、土壤温度传感器、土壤酸碱度传感器和土壤颗粒物传…...
)
MySQL索引面试题(高频)
文章目录 前言什么时候需要(不需要))使用索引?有哪些优化索引的方法前缀索引优化索引覆盖优化索引失效场景 总结 前言 今天来讲一讲 MySQL 索引的高频面试题。主要是针对前一篇文章 MySQL索引入门(一文搞定)进行查漏补…...

SouthLeetCode-打卡24年02月第2周
SouthLeetCode-打卡24年02月第2周 // Date : 2024/02/05 ~ 2024/02/11 039.有效的字母异位词 (1) 题目描述 039#LeetCode.242.简单题目链接#Monday2024/02/05 给定两个字符串 *s* 和 *t* ,编写一个函数来判断 *t* 是否是 *s* 的字母异位词。 **注意࿱…...

Rust CallBack的几种写法
模拟常用的几种函数调用CallBack的写法。测试调用都放在函数t6_call_back_task中。我正在学习Rust,有不对或者欠缺的地方,欢迎交流指正 type Callback std::sync::Arc<dyn Fn() Send Sync>; type CallbackReturnVal std::sync::Arc<dyn Fn…...

Redis突现拒绝连接问题处理总结
一、问题回顾 项目突然报异常 [INFO] 2024-02-20 10:09:43.116 i.l.core.protocol.ConnectionWatchdog [171]: Reconnecting, last destination was 192.168.0.231:6379 [WARN] 2024-02-20 10:09:43.120 i.l.core.protocol.ConnectionWatchdog [151]: Cannot reconnect…...

css中选择器的优先级
CSS 的优先级是由选择器的特指度(Specificity)和重要性(Importance)决定的,以下是优先级规则: 特指度: ID 选择器 (#id): 每个ID选择器计为100。 类选择器 (.class)、属性选择器 ([attr]) 和伪…...
心得)
python3字符串内建方法split()心得
python3字符串内建方法split()心得 概念 用指定分隔符(默认是任何空白字符)将字符串拆分成列表。 语法 string.split(separator.max) 参数1.split(参数2,参数3) 参数1:string 字符串,需要被拆分的字符串。 参数2&a…...

html的列表标签
列表标签 列表在html里面经常会用到的,主要使用来布局的,使其整齐好看. 无序列表 无序列表[重要]: ul ,li 示例代码1: 对应的效果: 无序列表的属性 属性值描述typedisc,square,…...
【Pytorch深度学习开发实践学习】B站刘二大人课程笔记整理lecture04反向传播
lecture04反向传播 课程网址 Pytorch深度学习实践 部分课件内容: import torchx_data [1.0,2.0,3.0] y_data [2.0,4.0,6.0] w torch.tensor([1.0]) w.requires_grad Truedef forward(x):return x*wdef loss(x,y):y_pred forward(x)return (y_pred-y)**2…...
PyTorch使用Tricks:学习率衰减 !!
文章目录 前言 1、指数衰减 2、固定步长衰减 3、多步长衰减 4、余弦退火衰减 5、自适应学习率衰减 6、自定义函数实现学习率调整:不同层不同的学习率 前言 在训练神经网络时,如果学习率过大,优化算法可能会在最优解附近震荡而无法收敛&#x…...
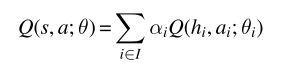
10MARL深度强化学习 Value Decomposition in Common-Reward Games
文章目录 前言1、价值分解的研究现状2、Individual-Global-Max Property3、Linear and Monotonic Value Decomposition3.1线性值分解3.2 单调值分解 前言 中心化价值函数能够缓解一些多智能体强化学习当中的问题,如非平稳性、局部可观测、信用分配与均衡选择等问题…...

2 Nacos适配达梦数据库实现方案
1、修改源代码方式 Nacos 原生是不支持达梦数据库的,所以就要想办法让它 “支持”,因为是开源软件,我们可以从源码入手,在流行的 1.x 、2.x 或最新版本代码的基本上进行修改。 主要涉及到以下内容的修改: com/alibaba/nacos/persistence/datasource/ExternalDataS...
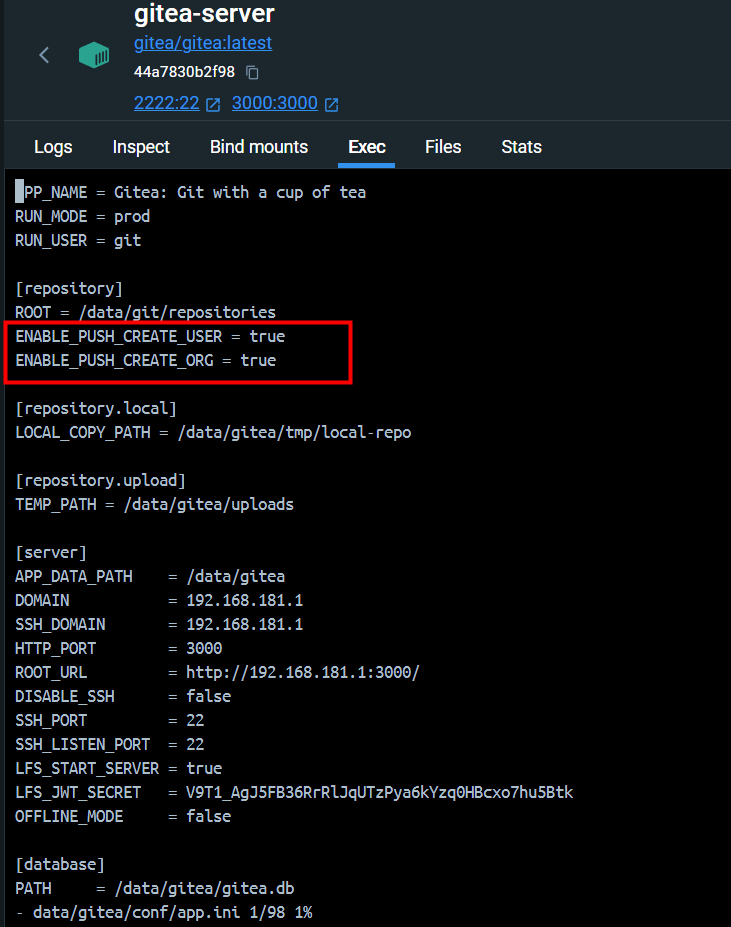
【Gitea】配置 Push To Create
引 在 Git 代码管理工具使用过程中,经常需要将一个文件夹作为仓库上传到一个未创建的代码仓库。如果 Git 服务端使用的是 Gitea,通常会推送失败。 PS D:\tmp\git-test> git remote add origin http://192.1.1.1:3000/root/git-test.git PS D:\tmp\g…...
)
关于postgresql数据库单独设置某个用户日志级别(日志审计)
前言: 很多时候我们想让数据库日志打印详细一点,但是又担心会对数据库本身产生一些不可控的影响,还会担心数据库产生的庞大的日志导致主机资源不太够用的影响。那么今天我们就通过讲解给单个用户设置 log_statement来解决以上这些问题。 注…...
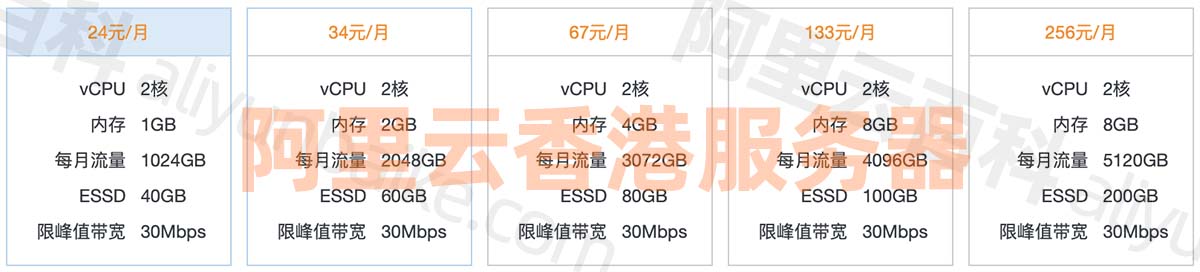
阿里云ECS香港服务器性能强大、cn2高速网络租用价格表
阿里云香港服务器中国香港数据中心网络线路类型BGP多线精品,中国电信CN2高速网络高质量、大规格BGP带宽,运营商精品公网直连中国内地,时延更低,优化海外回中国内地流量的公网线路,可以提高国际业务访问质量。阿里云服务…...
实战打靶集锦-025-HackInOS
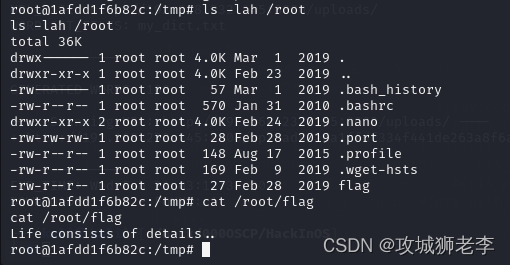
文章目录 1. 主机发现2. 端口扫描3. 服务枚举4. 服务探查5. 提权5.1 枚举系统信息5.2 探索一下passwd5.3 枚举可执行文件5.4 查看capabilities位5.5 目录探索5.6 枚举定时任务5.7 Linpeas提权 靶机地址:https://download.vulnhub.com/hackinos/HackInOS.ova 1. 主机…...
.forEach()和list.forEach()的区别)
list.stream().forEach()和list.forEach()的区别
list.stream().forEach() 和 list.forEach() 在 Java 中都是用于遍历集合元素的方法,但它们在使用场景和功能上有所不同: list.forEach(): 是从 Java 8 开始引入到 java.util.List 接口的标准方法。直接对列表进行迭代,它采用内部…...
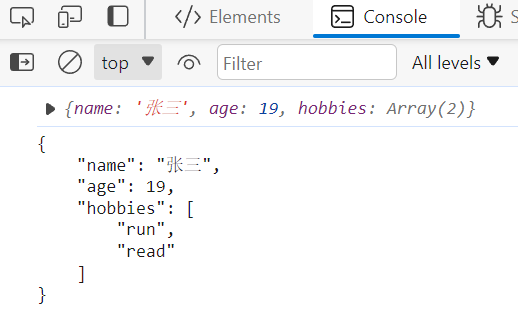
JS基础之JSON对象
JS基础之JSON对象 目录 JS基础之JSON对象对象转JSON字符串JSON转JS对象 对象转JSON字符串 JSON.stringify(value,replacer,space) value:要转换的JS对象 replacer:(可选)用于过滤和转换结果的函数或数组 space:(可选)指定缩进量 // 创建JS对象 let date {name:"张三…...
接口测试中缓存处理策略
在接口测试中,缓存处理策略是一个关键环节,直接影响测试结果的准确性和可靠性。合理的缓存处理策略能够确保测试环境的一致性,避免因缓存数据导致的测试偏差。以下是接口测试中常见的缓存处理策略及其详细说明: 一、缓存处理的核…...

conda相比python好处
Conda 作为 Python 的环境和包管理工具,相比原生 Python 生态(如 pip 虚拟环境)有许多独特优势,尤其在多项目管理、依赖处理和跨平台兼容性等方面表现更优。以下是 Conda 的核心好处: 一、一站式环境管理:…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...

MODBUS TCP转CANopen 技术赋能高效协同作业
在现代工业自动化领域,MODBUS TCP和CANopen两种通讯协议因其稳定性和高效性被广泛应用于各种设备和系统中。而随着科技的不断进步,这两种通讯协议也正在被逐步融合,形成了一种新型的通讯方式——开疆智能MODBUS TCP转CANopen网关KJ-TCPC-CANP…...
)
【RockeMQ】第2节|RocketMQ快速实战以及核⼼概念详解(二)
升级Dledger高可用集群 一、主从架构的不足与Dledger的定位 主从架构缺陷 数据备份依赖Slave节点,但无自动故障转移能力,Master宕机后需人工切换,期间消息可能无法读取。Slave仅存储数据,无法主动升级为Master响应请求ÿ…...

蓝桥杯3498 01串的熵
问题描述 对于一个长度为 23333333的 01 串, 如果其信息熵为 11625907.5798, 且 0 出现次数比 1 少, 那么这个 01 串中 0 出现了多少次? #include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std;int n 23333333;int main() {//枚举 0 出现的次数//因…...

Hive 存储格式深度解析:从 TextFile 到 ORC,如何选对数据存储方案?
在大数据处理领域,Hive 作为 Hadoop 生态中重要的数据仓库工具,其存储格式的选择直接影响数据存储成本、查询效率和计算资源消耗。面对 TextFile、SequenceFile、Parquet、RCFile、ORC 等多种存储格式,很多开发者常常陷入选择困境。本文将从底…...

音视频——I2S 协议详解
I2S 协议详解 I2S (Inter-IC Sound) 协议是一种串行总线协议,专门用于在数字音频设备之间传输数字音频数据。它由飞利浦(Philips)公司开发,以其简单、高效和广泛的兼容性而闻名。 1. 信号线 I2S 协议通常使用三根或四根信号线&a…...
Unity UGUI Button事件流程
场景结构 测试代码 public class TestBtn : MonoBehaviour {void Start(){var btn GetComponent<Button>();btn.onClick.AddListener(OnClick);}private void OnClick(){Debug.Log("666");}}当添加事件时 // 实例化一个ButtonClickedEvent的事件 [Formerl…...
android RelativeLayout布局
<?xml version"1.0" encoding"utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width"match_parent"android:layout_height"match_parent"android:gravity&…...
