【数据结构】双向链表 C++
一、什么是双向链表
1、定义
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。
双向链表的结构如图(图片来源于网络):
2、时空复杂度
双向链表的空间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 的,其时间复杂度如下:
| 操作 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| 遍历 | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
| 访问指定节点 | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) |
| 删除指定编号节点 | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
| 删除指定位置节点 | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) |
| 在指定编号的节点后插入节点 | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
| 在指定位置的节点后插入节点 | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) |
| 查询前驱、后继 | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) |
| 修改指定编号节点的值 | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
| 修改指定位置节点的值 | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) |
| 交换两个 list 容器 | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) |
二、双向链表的基本操作
1. 定义双向链表节点
每个节点有三个值:
val:存储每个节点的权值;last:指向每个节点的前面的第一个节点;next:指向每个节点的后面的第一个节点;
代码如下:
template<typename T>
struct ListNode{T value;ListNode<T>* last;ListNode<T>* next;ListNode():value(0){last=NULL,next=NULL;}ListNode(const T &x):value(x){last=NULL,next=NULL;}~ListNode(){value=0;delete last;delete next;}
};
2. 创建双向链表类
类里面包含两个节点和一个变量:
headnode:头节点,初始时前驱后继均为空,值为 − 1 -1 −1;endnode:尾节点,初始时前驱后继均为空,值为 − 1 -1 −1;listsize:记录双向链表的节点个数,不包含头尾节点;
代码如下:
template<typename T>
class list{private:unsigned listsize;ListNode<T>* headnode;ListNode<T>* endnode;
};
3. 初始化双向链表类
共有四种初始化方式:
list<类型名> a;:此时创建一个空的双向链表;list<类型名> a(n);:此时创建一个大小为 n n n 的双向链表,并将所有点的初始值赋为 0 0 0;list<类型名> a(n,m):此时创建一个大小为 n n n 的双向链表,并将所有点的初始值赋为 m m m;list<类型名> a={a1,a2,a3,...,an};:此时创建一个大小为 n n n 的双向链表,并将第 i i i 个节点的初始值赋为 a i a_i ai;
第一种初始化方式代码如下:
list():listsize(0){headnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);endnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);
}
第二种初始化方式代码如下:
list(const int &size_t):listsize(size_t) {headnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);endnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);ListNode<T>* now=headnode;for(int i=0;i<listsize;++i){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(0);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;now=now->next;}
}
第三种初始化方式代码如下:
list(const int &size_t,const int &val
):listsize(size_t){headnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);endnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);ListNode<T>* now=headnode;for(int i=0;i<listsize;++i){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;now=now->next;}
}
第四种初始化方式代码如下:
typedef std::initializer_list<T> lisval;
list(lisval vals){listsize=0;headnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);endnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);ListNode<T>* now=headnode;for(auto val:vals){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;now=now->next; ++listsize;}
}
3. 一些基础的函数
这些函数是除了加点删点之外最常见的几个函数。
-
size():获取链表的大小,返回一个 unsigned 值,表示当前链表中普通节点(非头尾节点)的个数。代码如下:
unsigned size() const {return listsize; } -
empty():返回当前链表是否为空,如果是,返回 true,否则返回 false。代码如下:
bool empty() const {return listsize==0; } -
begin():返回第一个普通节点。代码如下:
ListNode<T>* begin( ) const {return headnode->next; } -
end():返回尾指针。代码如下:
ListNode<T>* end( ) const {return endnode; } -
rbegin():返回最后一个普通节点。代码如下:
ListNode<T>* rbegin( ) const {return endnode->last; } -
rend():返回头指针。代码如下:
ListNode<T>* rend( ) const {return headnode; } -
front():返回第一个普通节点的值。代码如下:
T front() const {return begin()->value; } -
back():返回最后一个普通节点的值。代码如下:
T back() const {return rbegin()->value; } -
print():遍历并输出链表中每个普通节点的值,结尾换行。代码如下:
void print( ) const {if(empty()) return;ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;while(now->next!=NULL){printf("%d ",now->value);now=now->next;} putchar('\n'); } -
swap(list<类型名> &b):交换两个 list 容器,实际上是交换头尾指针和 l i s t s i z e listsize listsize。代码如下:
void swap(list<T> &b){ListNode<T>* temp;temp=headnode;headnode=b.headnode;b.headnode=temp;temp=endnode;endnode=b.endnode;b.endnode=temp;unsigned size_t=listsize;listsize=b.listsize;b.listsize=size_t; }
5. 插入节点
共四种方法,代码如下:
void push_back(const T &val
){ ++listsize;if(endnode->last==NULL){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;headnode->next=newnode;newnode->last=headnode;return;}ListNode<T>* pre=endnode->last;ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);pre->next=newnode;newnode->last=pre;newnode->next=endnode;endnode->last=newnode;
}
void push_front(const T &val
){ ++listsize;if(headnode->next==NULL){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;headnode->next=newnode;newnode->last=headnode;return;}ListNode<T>* suf=headnode->next;ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);headnode->next=newnode;newnode->last=headnode;newnode->next=suf;suf->last=newnode;
}
void insert(const T &pos,const T &val
){ int nowpos=0;if(pos==0){push_front(val);++listsize; return;} else if(pos>=listsize){push_back(val);++listsize; return;}ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;while(now->next!=NULL){++nowpos;if(nowpos==pos){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;newnode->next=suf;suf->last=newnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;++listsize; return;}now=now->next;}
}
void insert(ListNode<T>* now,const T &val
){if(now==endnode){push_back(val); return;}ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;newnode->next=suf;suf->last=newnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;++listsize; return;
}
6. 修改指定位置的值
两种方法,代码如下:
void reassign(const T &pos,const T &val
){if(pos>listsize) return;if(empty()||!pos) return;ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;int nowpos=0;while(now->next!=NULL){++nowpos;if(nowpos==pos){now->value=val;return;} now=now->next;}
}
void reassign(ListNode<T>* now,const int &val
) const {now->value=val;
}
7.删除节点
和插入一样,共有四种,代码如下:
void pop_back(){if(empty()) return;ListNode<T>* now=endnode->last;ListNode<T>* pre=now->last;if(pre==headnode){endnode->last=NULL;headnode->last=NULL;--listsize; return;}endnode->last=pre;pre->next=endnode;--listsize;
}
void pop_front(){if(empty()) return;ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;if(suf==endnode){endnode->last=NULL;headnode->last=NULL;--listsize; return;}headnode->next=suf;suf->last=headnode;--listsize;
}
void erase(const int &pos
) {if(pos>listsize) return;if(empty()||!pos) return;ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;int nowpos=0;while(now!=endnode){++nowpos;if(nowpos==pos){ListNode<T>* pre=now->last;ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;if(pre==headnode||suf==endnode){endnode->last=NULL;headnode->next=NULL;delete now;--listsize; return;}pre->next=suf;suf->last=pre;delete now;--listsize; return;}now=now->next;}
}
void erase(ListNode<T>* now
){ if(now==headnode) return;if(now==endnode) return;if(empty()) return;ListNode<T>* pre=now->last;ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;if(pre==headnode||suf==endnode){endnode->last=NULL;headnode->last=NULL;--listsize; return;}pre->next=suf;suf->last=pre;--listsize; return;
}
8. 注销双向链表类
遍历一遍,然后将每个节点都删除就可以了。
代码如下:
~list(){ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;while(now!=NULL){ListNode<T>* nxt=now->next;delete now;now=nxt;} delete headnode; listsize=0;
}
三、完整代码
我知道你们只看这个
码风丑陋,不喜勿喷
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<initializer_list>
namespace STL{template<typename T>struct ListNode{T value;ListNode<T>* last;ListNode<T>* next;ListNode():value({}){last=NULL,next=NULL;}ListNode(const T &x):value(x){last=NULL,next=NULL;}~ListNode(){// value={};last=NULL;next=NULL;}};template<typename T>class list{private:unsigned listsize;ListNode<T>* headnode;ListNode<T>* endnode;public:list():listsize(0){headnode=new ListNode<T>(T({-1}));endnode=new ListNode<T>(T({-1}));}list(const int &size_t):listsize(size_t) {headnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);endnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);ListNode<T>* now=headnode;for(int i=0;i<listsize;++i){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(0);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;now=now->next;}}list(const int &size_t,const int &val):listsize(size_t){headnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);endnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);ListNode<T>* now=headnode;for(int i=0;i<listsize;++i){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;now=now->next;}}typedef std::initializer_list<T> lisval;list(lisval vals){listsize=0;headnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);endnode=new ListNode<T>(-1);ListNode<T>* now=headnode;for(auto val:vals){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;now=now->next; ++listsize;}}unsigned size() const {return listsize;}bool empty() const {return listsize==0;}ListNode<T>* begin() const {return headnode->next;}ListNode<T>* end() const {return endnode;}ListNode<T>* rbegin() const {return endnode->last;}ListNode<T>* rend() const {return headnode;}T front() const {return begin()->value;}T back() const {return rbegin()->value;}void print() const {if(empty()) return;ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;while(now->next!=NULL){printf("%lld ",now->value);now=now->next;} putchar('\n');}void push_back(const T &val){ ++listsize;if(endnode->last==NULL){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;headnode->next=newnode;newnode->last=headnode;return;}ListNode<T>* pre=endnode->last;ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);pre->next=newnode;newnode->last=pre;newnode->next=endnode;endnode->last=newnode;}void push_front(const T &val){ ++listsize;if(headnode->next==NULL){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);endnode->last=newnode;newnode->next=endnode;headnode->next=newnode;newnode->last=headnode;return;}ListNode<T>* suf=headnode->next;ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);headnode->next=newnode;newnode->last=headnode;newnode->next=suf;suf->last=newnode;}void insert(const T &pos,const T &val){ int nowpos=0;if(pos==0){push_front(val);++listsize; return;} else if(pos>=listsize){push_back(val);++listsize; return;}ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;while(now->next!=NULL){++nowpos;if(nowpos==pos){ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;newnode->next=suf;suf->last=newnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;++listsize; return;}now=now->next;}}void insert(ListNode<T>* now,const T &val){if(now==endnode){push_back(val); return;}ListNode<T>* newnode=new ListNode<T>(val);ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;newnode->next=suf;suf->last=newnode;newnode->last=now;now->next=newnode;++listsize; return;}void reassign(const T &pos,const T &val){if(pos>listsize) return;if(empty()||!pos) return;ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;int nowpos=0;while(now->next!=NULL){++nowpos;if(nowpos==pos){now->value=val;return;} now=now->next;}}void reassign(ListNode<T>* now,const int &val) const {now->value=val;}void pop_back(){if(empty()) return;ListNode<T>* now=endnode->last;ListNode<T>* pre=now->last;if(pre==headnode){endnode->last=NULL;headnode->next=NULL;delete now;--listsize; return;}endnode->last=pre;pre->next=endnode;delete now;--listsize;}void pop_front(){if(empty()) return;ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;if(suf==endnode){endnode->last=NULL;headnode->next=NULL;delete now;--listsize; return;}headnode->next=suf;suf->last=headnode;delete now;--listsize;}void erase(const int &pos) {if(pos>listsize) return;if(empty()||!pos) return;ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;int nowpos=0;while(now!=endnode){++nowpos;if(nowpos==pos){ListNode<T>* pre=now->last;ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;if(pre==headnode||suf==endnode){endnode->last=NULL;headnode->next=NULL;delete now;--listsize; return;}pre->next=suf;suf->last=pre;delete now;--listsize; return;}now=now->next;}}void erase(ListNode<T>* now){ if(now==headnode) return;if(now==endnode) return;if(empty()) return;ListNode<T>* pre=now->last;ListNode<T>* suf=now->next;if(pre==headnode||suf==endnode){endnode->last=NULL;headnode->last=NULL;delete now;--listsize; return;}pre->next=suf;suf->last=pre;delete now;--listsize; return;}void swap(list<T> &b){ListNode<T>* temp;temp=headnode;headnode=b.headnode;b.headnode=temp;temp=endnode;endnode=b.endnode;b.endnode=temp;unsigned size_t=listsize;listsize=b.listsize;b.listsize=size_t;}~list(){ListNode<T>* now=headnode->next;while(now!=NULL){ListNode<T>* nxt=now->next;delete now;now=nxt;} delete headnode;listsize=0;}};
}
using STL::list;signed main(){system("pause");
}
给个赞再走吧
相关文章:

【数据结构】双向链表 C++
一、什么是双向链表 1、定义 双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。 双…...
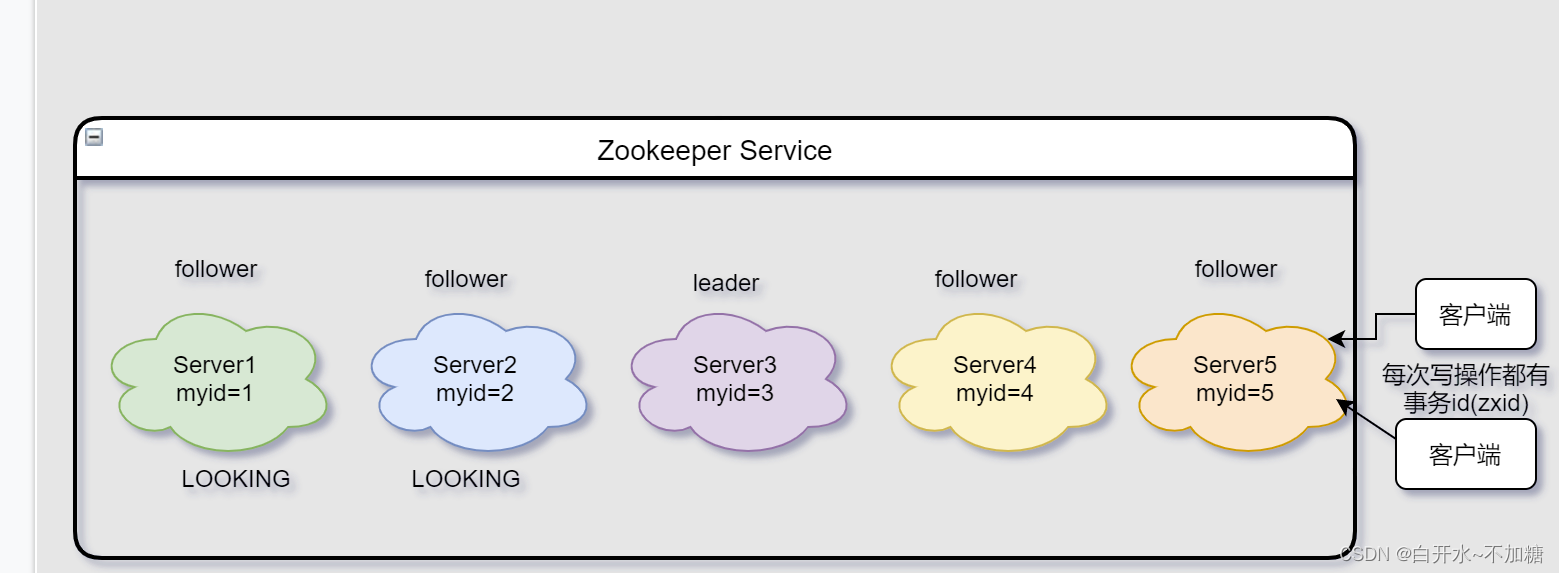
消息队列之-----------------zookeeper机制
目录 一、ZooKeeper是什么 二、ZooKeeper的工作机制 三、ZooKeeper特点 四、ZooKeeper数据结构 五、ZooKeeper应用场景 5.1统一命名服务 5.2统一配置管理 5.3统一集群管理 5.4服务器动态上下线 5.5软负载均衡 六、ZooKeeper的选举机制 6.1第一次启动选举机制 6.2非…...
第十届蓝桥杯大赛个人赛省赛(软件类) CC++ 研究生组2.0
A立方和 #include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main(){int n, t, flag, x;long long ans 0;for(int i 1; i < 2019; i){t i;flag 0;while(t && !flag){x t % 10;if(x 2 || x 0 || x 1 || x 9) flag 1;t / 10;}if(fl…...
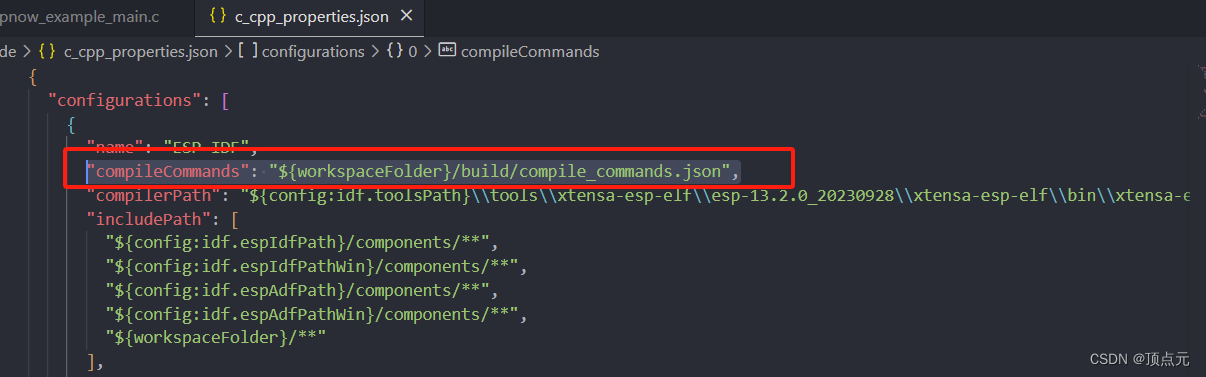
vscode开发ESP32问题记录
vscode 开发ESP32问题记录 1. 解决vscode中的波浪线警告 1. 解决vscode中的波浪线警告 参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fucingman/article/details/134404485 首先可以通过vscode 中的IDF插件生成模板工程,这样会自动创建.vscode文件夹中的一些json配…...
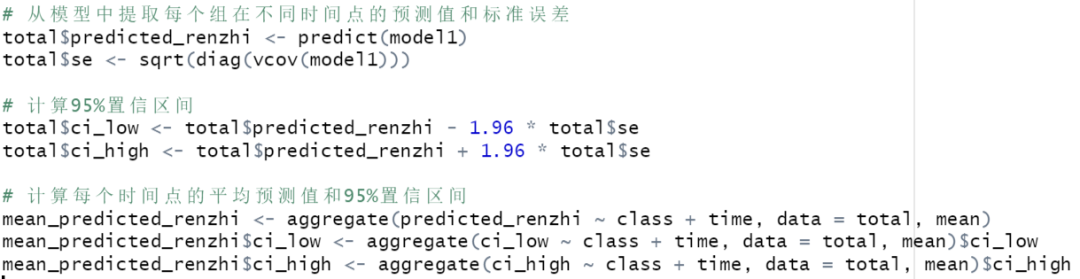
R语言复现:轨迹增长模型发表二区文章 | 潜变量模型系列(2)
培训通知 Nhanes数据库数据挖掘,快速发表发文的利器,你来试试吧!欢迎报名郑老师团队统计课程,4.20直播。 案例分享 2022年9月,中国四川大学学者在《Journal of Psychosomatic Research》(二区,I…...

【数据结构】顺序表的实现——动态分配
🎈个人主页:豌豆射手^ 🎉欢迎 👍点赞✍评论⭐收藏 🤗收录专栏:数据结构 🤝希望本文对您有所裨益,如有不足之处,欢迎在评论区提出指正,让我们共同学习、交流进…...

3.3.k8s搭建-rancher RKE2
目录 RKE2介绍 k8s集群搭建 搭建k8s集群 下载离线包 部署rke2-server 部署rke2-agent 部署helm 部署rancher RKE2介绍 RKE2,也称为 RKE Government,是 Rancher 的下一代 Kubernetes 发行版。 官网地址:Introduction | RKE2 k8s集群搭…...
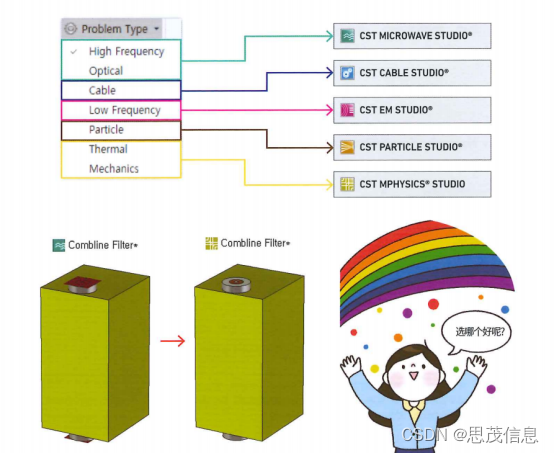
CST电磁仿真软件的设置变更与问题【官方教程】
保存结果的Result Navigator 积累的结果一目了然! 用户界面上的Result Navigator 在一个仿真工程中更改变量取值进行仿真分析或者改变设置进行仿真分析时,之前的1DResult会不会消失呢? 1D Result:CST中1D Result指的是Y值取决…...
保研线性代数复习3
一.基底(Basis) 1.什么是生成集(Generating Set)?什么是张成空间(Span)? 存在向量空间V(V,,*),和向量集(xi是所说的列向量ÿ…...

从零开始学Spring Boot系列-集成MyBatis-Plus
在Spring Boot应用开发中,MyBatis-Plus是一个强大且易于使用的MyBatis增强工具,它提供了很多实用的功能,如代码生成器、条件构造器、分页插件等,极大地简化了MyBatis的使用和配置。本篇文章将指导大家如何在Spring Boot项目中集成…...

【云原生篇】k8s之Deployment详解
Kubernetes 的 Deployment 是一种管理声明式更新的资源对象,它允许你描述应用的期望状态,并由 Deployment 控制器自动将当前状态改变为期望状态。Deployment 主要用于无状态应用的部署和扩展,但也可以用于有状态应用。 核心功能 自动化部署…...
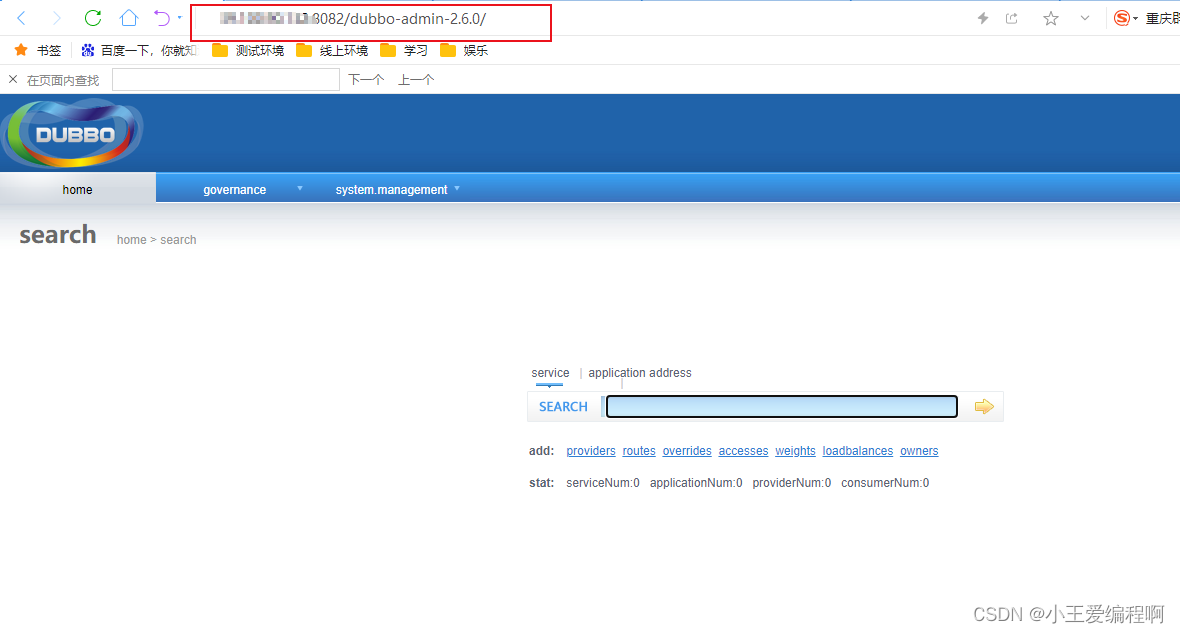
linux安装dubboAdmin
1.环境准备: jdk-8u391-linux-x64apache-maven-3.9.6apache-tomcat-8.5.100 2.安装注册中心zookeeper zookeeper的安装看我的另一篇文章,安装完成后保持启动状态 linux安装Zookeeper的详细步骤-CSDN博客 3.安装dubboadmin 源码下载地址:R…...

Android 系统编译 and 应用裁剪
平台应用编译 平台应用demo的Android.mk写法: LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir) include $(CLEAR_VARS)LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional# Only compile source java files in this apk. LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(call all-java-files-under, src)LOCAL_PACKAGE_NAME := TestLOCAL_CER…...
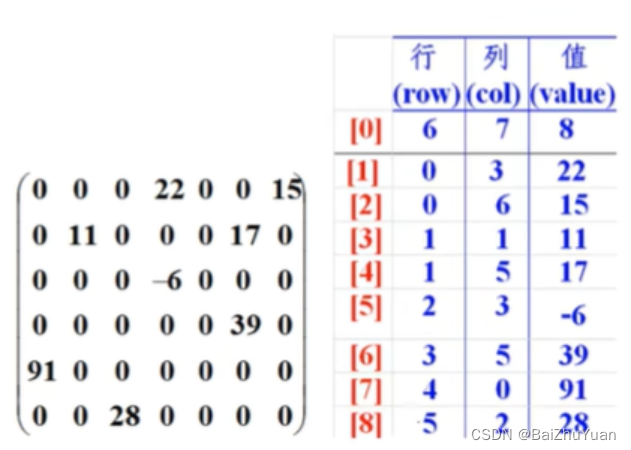
java数组.day16(冒泡排序,稀疏数组)
冒泡排序 冒泡排序无疑是最为出名的排序算法之一,总共有八大排序! 冒泡的代码还是相当简单的,两层循环,外层冒泡轮数,里层依次比较,江湖中人人尽皆知。 我们看到嵌套循环,应该立马就可以得出这个算法的时…...
vue+springboot多角色登录
①前端编写 将Homeview修改为manager Manager: <template><div><el-container><!-- 侧边栏 --><el-aside :width"asideWidth" style"min-height: 100vh; background-color: #001529"><div style"h…...

使用 ADB 查找应用名称和活动名称,并启动指定页面
知识点和难题: 查找应用名称和活动名称: 使用 ADB 命令 adb shell dumpsys window | findstr mCurrentFocus 可以查找当前设备上活动的应用名称和活动名称。 保存输出结果: 将命令的输出结果保存到文件中,方便后续使用。 启动指…...

LangChain - 文档转换
文章目录 一、文档转换器 & 文本拆分器文本拆分器 二、开始使用文本拆分器三、按字符进行拆分四、代码分割 (Split code)1、PythonTextSplitter2、JS3、Markdown4、Latex5、HTML6、Solidity 五、MarkdownHeaderTextSplitter1、动机2、Use case 六、递归按字符分割七、按tok…...

【C++】STL--list
目录 list的介绍 list的使用 list的构造 list iterator的使用 list capacity list modifiers list的迭代器失效 list模拟实现 list的介绍 1. list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。 2. list的底层是双向…...

二. CUDA编程入门-双线性插值计算
目录 前言0. 简述1. 执行一下我们的第十个CUDA程序2. Bilinear interpolation3. 代码分析总结参考 前言 自动驾驶之心推出的 《CUDA与TensorRT部署实战课程》,链接。记录下个人学习笔记,仅供自己参考 Note:关于 CUDA 加速双线程插值的内容博主…...

实时计算平台设计方案:913-基于100G光口的DSP+FPGA实时计算平台
基于100G光口的DSPFPGA实时计算平台 一、产品概述 基于以太网接口的实时数据智能计算一直应用于互联网、网络安全、大数据交换的场景。以DSPFPGA的方案,体现了基于硬件计算的独特性能,区别于X86GPU的计算方案,保留了高带宽特性&…...
使用VSCode开发Django指南
使用VSCode开发Django指南 一、概述 Django 是一个高级 Python 框架,专为快速、安全和可扩展的 Web 开发而设计。Django 包含对 URL 路由、页面模板和数据处理的丰富支持。 本文将创建一个简单的 Django 应用,其中包含三个使用通用基本模板的页面。在此…...

多场景 OkHttpClient 管理器 - Android 网络通信解决方案
下面是一个完整的 Android 实现,展示如何创建和管理多个 OkHttpClient 实例,分别用于长连接、普通 HTTP 请求和文件下载场景。 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android"http://schemas…...
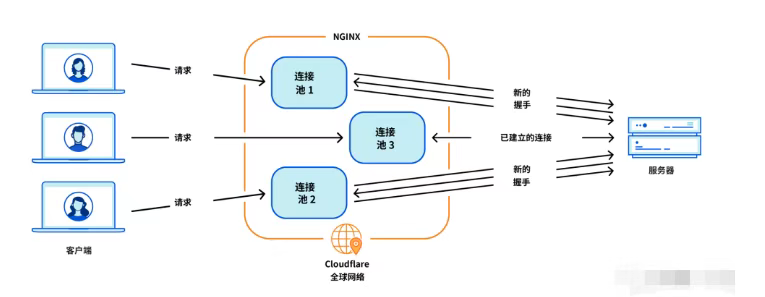
Cloudflare 从 Nginx 到 Pingora:性能、效率与安全的全面升级
在互联网的快速发展中,高性能、高效率和高安全性的网络服务成为了各大互联网基础设施提供商的核心追求。Cloudflare 作为全球领先的互联网安全和基础设施公司,近期做出了一个重大技术决策:弃用长期使用的 Nginx,转而采用其内部开发…...

基于Docker Compose部署Java微服务项目
一. 创建根项目 根项目(父项目)主要用于依赖管理 一些需要注意的点: 打包方式需要为 pom<modules>里需要注册子模块不要引入maven的打包插件,否则打包时会出问题 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8…...
基础光照(Basic Lighting))
C++.OpenGL (10/64)基础光照(Basic Lighting)
基础光照(Basic Lighting) 冯氏光照模型(Phong Lighting Model) #mermaid-svg-GLdskXwWINxNGHso {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg-GLdskXwWINxNGHso .error-icon{fill:#552222;}#mermaid-svg-GLd…...
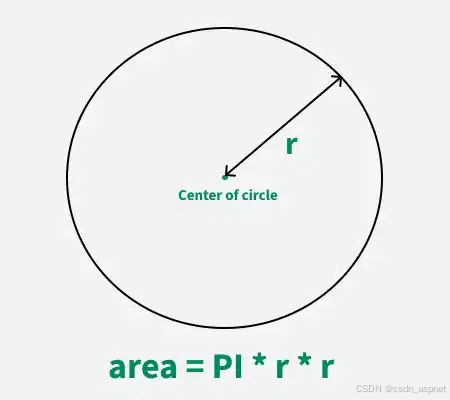
C++ 求圆面积的程序(Program to find area of a circle)
给定半径r,求圆的面积。圆的面积应精确到小数点后5位。 例子: 输入:r 5 输出:78.53982 解释:由于面积 PI * r * r 3.14159265358979323846 * 5 * 5 78.53982,因为我们只保留小数点后 5 位数字。 输…...

关于 WASM:1. WASM 基础原理
一、WASM 简介 1.1 WebAssembly 是什么? WebAssembly(WASM) 是一种能在现代浏览器中高效运行的二进制指令格式,它不是传统的编程语言,而是一种 低级字节码格式,可由高级语言(如 C、C、Rust&am…...

docker 部署发现spring.profiles.active 问题
报错: org.springframework.boot.context.config.InvalidConfigDataPropertyException: Property spring.profiles.active imported from location class path resource [application-test.yml] is invalid in a profile specific resource [origin: class path re…...
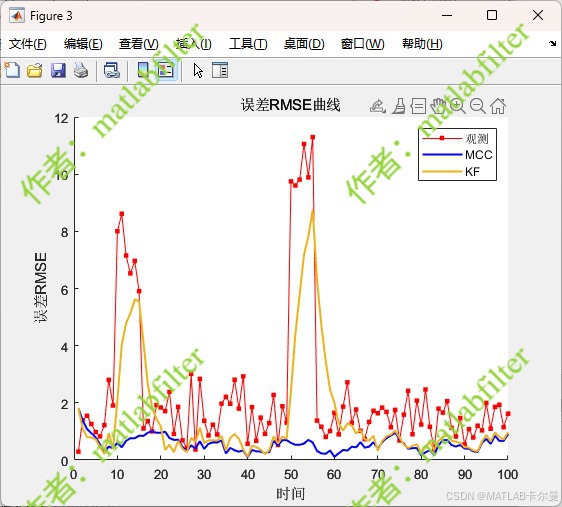
【MATLAB代码】基于最大相关熵准则(MCC)的三维鲁棒卡尔曼滤波算法(MCC-KF),附源代码|订阅专栏后可直接查看
文章所述的代码实现了基于最大相关熵准则(MCC)的三维鲁棒卡尔曼滤波算法(MCC-KF),针对传感器观测数据中存在的脉冲型异常噪声问题,通过非线性加权机制提升滤波器的抗干扰能力。代码通过对比传统KF与MCC-KF在含异常值场景下的表现,验证了后者在状态估计鲁棒性方面的显著优…...
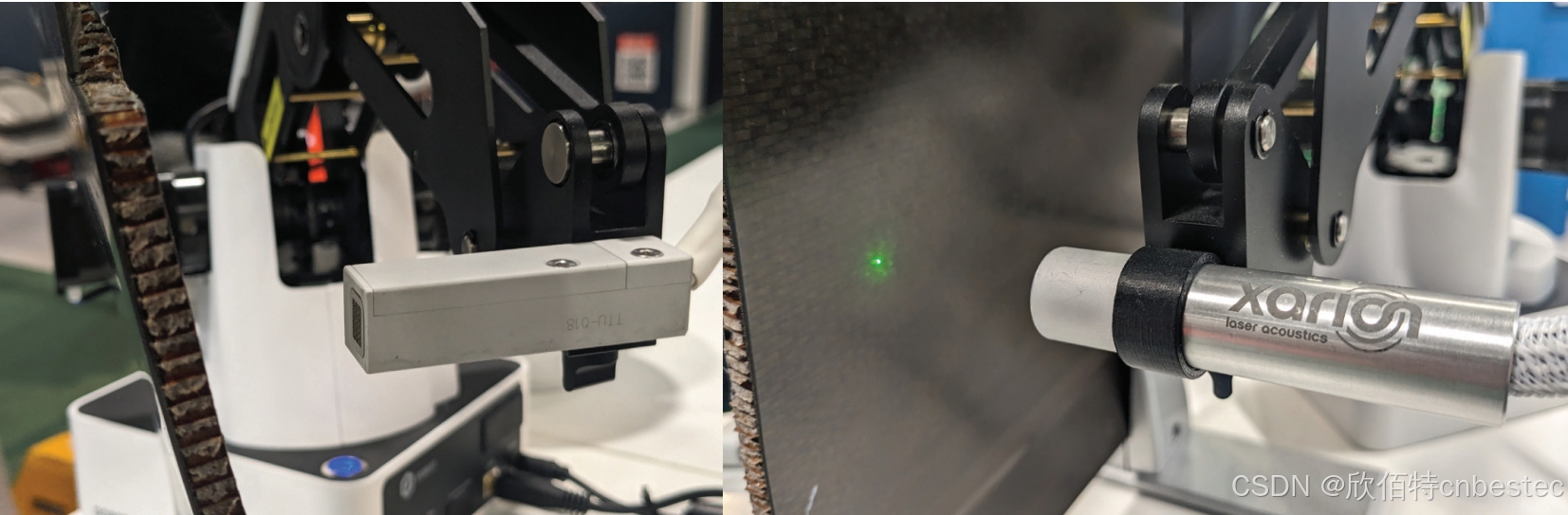

解析奥地利 XARION激光超声检测系统:无膜光学麦克风 + 无耦合剂的技术协同优势及多元应用
在工业制造领域,无损检测(NDT)的精度与效率直接影响产品质量与生产安全。奥地利 XARION开发的激光超声精密检测系统,以非接触式光学麦克风技术为核心,打破传统检测瓶颈,为半导体、航空航天、汽车制造等行业提供了高灵敏…...
