【C++提高编程】C++全栈体系(二十七)
C++提高编程
第五章 STL- 常用算法
三、常用排序算法
算法简介:
sort//对容器内元素进行排序random_shuffle//洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序merge// 容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中reverse// 反转指定范围的元素
1. sort
功能描述:
- 对容器内元素进行排序
函数原型:
-
sort(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01() {vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);//sort默认从小到大排序sort(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;//从大到小排序sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*10 20 30 40 50 50 40 30 20 10
*/
总结: sort属于开发中最常用的算法之一,需熟练掌握
2. random_shuffle
功能描述:
- 洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
函数原型:
-
random_shuffle(iterator beg, iterator end);// 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));vector<int> v;for(int i = 0 ; i < 10;i++){v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;//打乱顺序random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 0 3 5 7 8 4 1 2 9
*/
总结: random_shuffle洗牌算法比较实用,使用时记得加随机数种子
3. merge
功能描述:
- 两个容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
函数原型:
-
merge(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);// 容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
// 注意: 两个容器必须是有序的
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 1);}vector<int> vtarget;//目标容器需要提前开辟空间vtarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());//合并 需要两个有序序列merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vtarget.begin());for_each(vtarget.begin(), vtarget.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 10
*/
总结: merge合并的两个容器必须的有序序列
4. reverse
功能描述:
- 将容器内元素进行反转
函数原型:
-
reverse(iterator beg, iterator end);// 反转指定范围的元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);cout << "反转前: " << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;cout << "反转后: " << endl;reverse(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*反转前: 10 30 50 20 40 反转后: 40 20 50 30 10
*/
总结: reverse反转区间内元素,面试题可能涉及到
四、常用拷贝和替换算法
算法简介:
copy// 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中replace// 将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素replace_if// 容器内指定范围满足条件的元素替换为新元素swap// 互换两个容器的元素
1. copy
功能描述:
- 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中
函数原型:
-
copy(iterator beg, iterator end, iterator dest);// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// dest 目标起始迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i + 1);}vector<int> v2;v2.resize(v1.size());copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
*/
总结: 利用copy算法在拷贝时,目标容器记得提前开辟空间
2. replace
功能描述:
- 将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素
函数原型:
-
replace(iterator beg, iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);// 将区间内旧元素 替换成 新元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// oldvalue 旧元素
// newvalue 新元素
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(20);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(20);cout << "替换前:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;//将容器中的20 替换成 2000cout << "替换后:" << endl;replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20, 2000);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*替换前:20 30 20 40 50 10 20 替换后:2000 30 2000 40 50 10 2000
*/
总结: replace会替换区间内满足条件的元素
3. replace_if
功能描述:
- 将区间内满足条件的元素,替换成指定元素
函数原型:
-
replace_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred, newvalue);// 按条件替换元素,满足条件的替换成指定元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _pred 谓词
// newvalue 替换的新元素
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};class ReplaceGreater30
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val >= 30;}};void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(20);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(20);cout << "替换前:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;//将容器中大于等于的30 替换成 3000cout << "替换后:" << endl;replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), ReplaceGreater30(), 3000);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*替换前:20 30 20 40 50 10 20 替换后:20 3000 20 3000 3000 10 20
*/
总结: replace_if按条件查找,可以利用仿函数灵活筛选满足的条件
4. swap
功能描述:
- 互换两个容器的元素
函数原型:
-
swap(container c1, container c2);// 互换两个容器的元素
// c1容器1
// c2容器2
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+100);}cout << "交换前: " << endl;for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;cout << "交换后: " << endl;swap(v1, v2);for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*交换前: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 交换后: 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
*/
总结: swap交换容器时,注意交换的容器要同种类型
五、常用算术生成算法
注意:
- 算术生成算法属于小型算法,使用时包含的头文件为
#include <numeric>
算法简介:
-
accumulate// 计算容器元素累计总和 -
fill// 向容器中添加元素
1. accumulate
功能描述:
- 计算区间内 容器元素累计总和
函数原型:
-
accumulate(iterator beg, iterator end, value);// 计算容器元素累计总和
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 起始值
示例:
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
void test01()
{vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {v.push_back(i);}int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);cout << "total = " << total << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*total = 5050
*/
总结: accumulate使用时头文件注意是 numeric,这个算法很实用
2. fill
功能描述:
- 向容器中填充指定的元素
函数原型:
-
fill(iterator beg, iterator end, value);// 向容器中填充元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 填充的值
示例:
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.resize(10);//填充fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
*/
总结: 利用fill可以将容器区间内元素填充为 指定的值
六、常用集合算法
算法简介:
-
set_intersection// 求两个容器的交集 -
set_union// 求两个容器的并集 -
set_difference// 求两个容器的差集
1. set_intersection
功能描述:
- 求两个容器的交集
函数原型:
-
set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);// 求两个集合的交集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+5);}vector<int> vTarget;//取两个里面较小的值给目标容器开辟空间vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*5 6 7 8 9
*/
总结:
- 求交集的两个集合必须的有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器中取小值
- set_intersection返回值既是交集中最后一个元素的位置
2. set_union
功能描述:
- 求两个集合的并集
函数原型:
-
set_union(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);// 求两个集合的并集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+5);}vector<int> vTarget;//取两个容器的和给目标容器开辟空间vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
*/
总结:
- 求并集的两个集合必须的有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要两个容器相加
- set_union返回值既是并集中最后一个元素的位置
3. set_difference
功能描述:
- 求两个集合的差集
函数原型:
-
set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);// 求两个集合的差集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+5);}vector<int> vTarget;//取两个里面较大的值给目标容器开辟空间vTarget.resize( max(v1.size() , v2.size()));//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址cout << "v1与v2的差集为: " << endl;vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;cout << "v2与v1的差集为: " << endl;itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}/*v1与v2的差集为: 0 1 2 3 4 v2与v1的差集为: 10 11 12 13 14
*/
总结:
- 求差集的两个集合必须的有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器取较大值
- set_difference返回值既是差集中最后一个元素的位置
相关文章:
)
【C++提高编程】C++全栈体系(二十七)
C提高编程 第五章 STL- 常用算法 三、常用排序算法 算法简介: sort //对容器内元素进行排序random_shuffle //洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序merge // 容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中reverse // 反转指定范围的元素 1. sort 功能描述&#…...

软考高级信息系统项目管理师系列之三十九:项目集管理
软考高级信息系统项目管理师系列之三十九:项目集管理 一、项目集管理内容二、项目集管理基础概述1.项目集定义2.项目集活动3.项目集管理三、项目集的管理过程四、项目集治理1.项目集治理概述2.项目集指导委员会的职责3.项目集治理功能五、项目集生命周期1.项目集生命周期三个阶…...
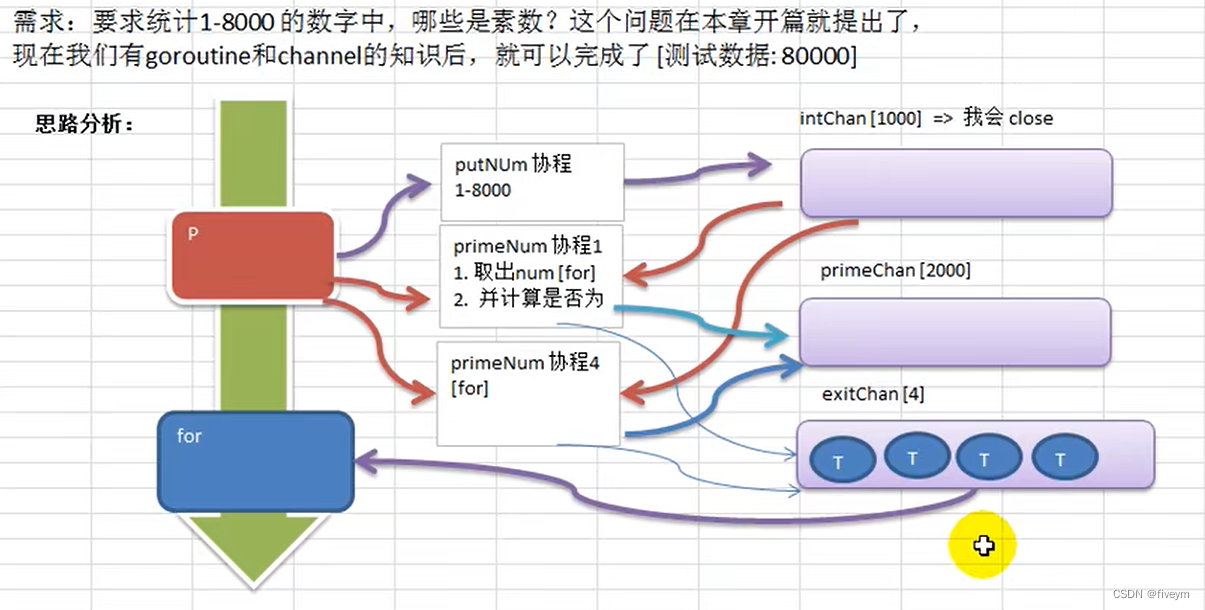
44-Golang中的channel
Golang中的channel为什么要使用channelchannel的介绍channel的基本使用定义/声明channel管道的遍历和关闭channel的关闭channel的遍历goroutine和channel结合应用实例1应用实例2案例注意事项为什么要使用channel 前面使用全局变量加锁同步来解决goroutine的通讯,但…...

80/20法则
80/20法则(The 80/20 Rule)又称为帕累托法则(Pareto Principle)、二八定律、帕累托定律、最省力法则、不平衡原则、犹太法则、马特莱法则等一、什么是80/20法则80/20法则(The 80/20 Rule),又称为帕累托法则…...
)
计算机网络高频面试题(四)
一、什么是计算机网络 是一个将分散的、具有独立功能的计算机系统,通过通信设备与线路连接起来,由功能完善的软件实现资源共享和信息传递的系统 按分布范围,计算机网络里有局域网LAN和广域网WAN, 其中局域网的代表以太网,以及这…...
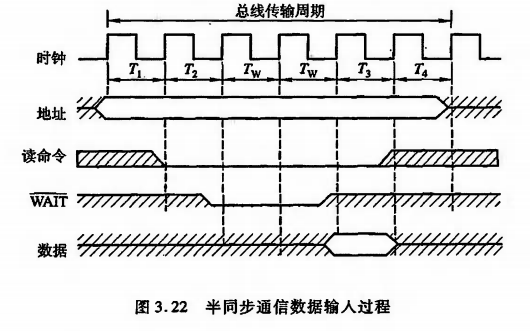
[计算机组成原理(唐朔飞 第2版)]第三章 系统总线(学习复习笔记)
3.1 总线的基本概念 计算机系统的五大部件之间的互连方式有两种 各部件之间使用单独的连线,称为分散连接将各部件连到一组公共信息传输线上,称为总线连接 总线是连接多个部件的信息传输线,是各部件共享的传输介质。 当多个部件与总线相连时&…...
| 机考必刷)
华为OD机试题 - 计算堆栈中的剩余数字(JavaScript)| 机考必刷
更多题库,搜索引擎搜 梦想橡皮擦华为OD 👑👑👑 更多华为OD题库,搜 梦想橡皮擦 华为OD 👑👑👑 更多华为机考题库,搜 梦想橡皮擦华为OD 👑👑👑 华为OD机试题 最近更新的博客使用说明本篇题解:计算堆栈中的剩余数字题目输入输出描述示例一输入输出说明示例二…...

VB实现点爆炸效果
需在窗体放置以下 4 个控件,所有控件不用设置任何属性,均采用默认设置: ’ Picture1,Command1,Check1,Timer1 Option Explicit Dim I Dim ctD() As tyD, ctDs As Long, ctR As Single Private Type tyD x…...
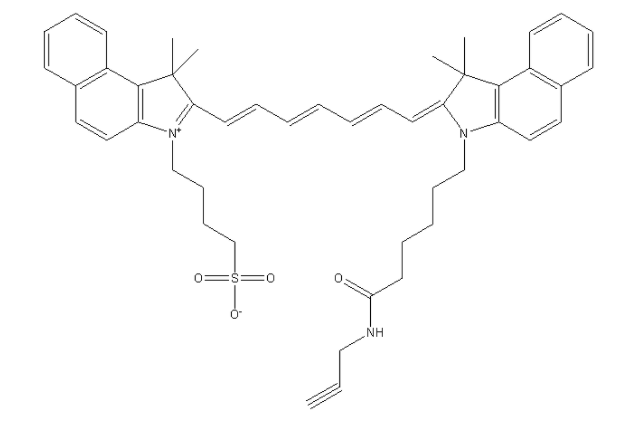
ICG-alkyne,吲哚菁绿-炔基结构式,实验室科研试剂,CAS号:1622335-41-4
ICG-alkyne,吲哚菁绿-炔基 中文名称:吲哚菁绿-炔基 CAS号:1622335-41-4 英文名称:ICG-alkyne 英文别名:ICG-alk 性状:绿色粉末 化学式:C48H53N3O4S 分子量:768.03 溶剂:溶于…...

【并发编程】volatile的原理我好像又懂了
文章目录优秀引用1、概述2、可见性保证2.1、什么是可见性2.2、例子举证2.3、结果解析3、有序性保证3.1、什么是有序性3.2、什么是重排序3.3、例子举证4、无法保证原子性4.1、什么是原子性4.2、例子举证5、内存屏障5.1、什么是内存屏障5.2、不同内存屏障的作用6、volatile和sync…...

【已更新实例】Java网络爬虫-HttpClient工具类
关于用Java进行爬虫的资料网上实在少之又少,但作为以一名对Java刚刚初窥门径建立好兴趣的学生怎么能静得下心用新学的Python去写,毕竟Java是世界上最好的语言嘛 (狗头)关于Java爬虫最受欢迎的一个框架Jsoup常常搭配HttpClient来使用,因为Jsou…...

7.2 向量的坐标
🙌作者简介:数学与计算机科学学院出身、在职高校高等数学专任教师,分享学习经验、生活、 努力成为像代码一样有逻辑的人! 🌙个人主页:阿芒的主页 ⭐ 高等数学专栏介绍:本专栏系统地梳理高等数学…...

公式编写1000问21-22
21.问: 求助——(周,日,60分钟,30分钟)MACD同时向上的公式怎么表达 答(知无不言): z:“macd.dea#week”; r:“macd.dea#day”; f:“macd.dea#min60”; f1:“macd.dea#min30”; rz:“macd.dea##week”; rr:“macd.dea##day”; rf:“…...

1041 考试座位号
每个 PAT 考生在参加考试时都会被分配两个座位号,一个是试机座位,一个是考试座位。正常情况下,考生在入场时先得到试机座位号码,入座进入试机状态后,系统会显示该考生的考试座位号码,考试时考生需要换到考试…...

2023年3月北京/广州/杭州/深圳数据治理工程师认证DAMA-CDGA/CDGP
DAMA认证为数据管理专业人士提供职业目标晋升规划,彰显了职业发展里程碑及发展阶梯定义,帮助数据管理从业人士获得企业数字化转型战略下的必备职业能力,促进开展工作实践应用及实际问题解决,形成企业所需的新数字经济下的核心职业…...
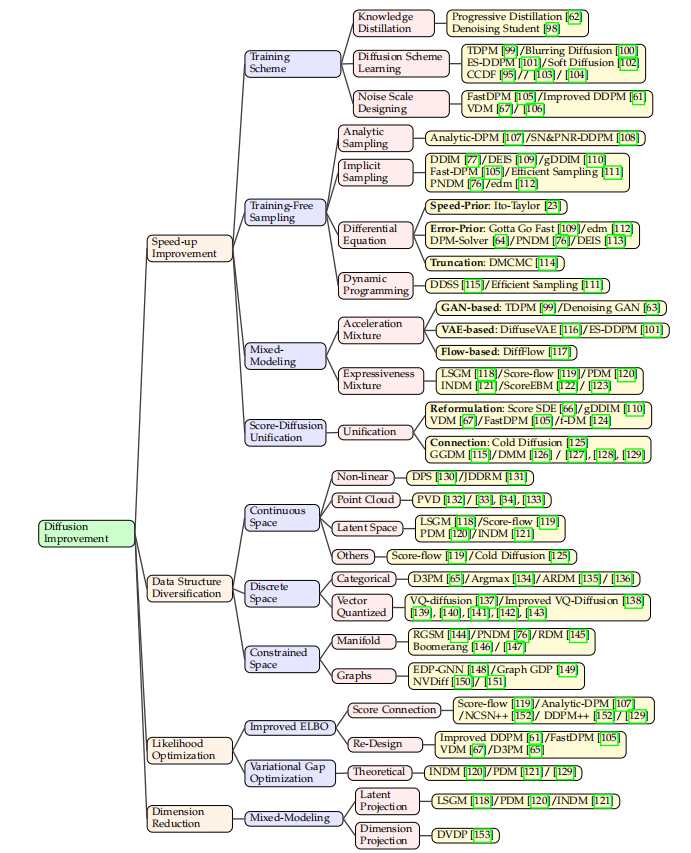
【AICG】2、扩散模型 | 到底什么是扩散模型?
文章目录一、什么是扩散模型二、扩散模型相关定义2.1 符号和定义2.2 问题规范化三、可以提升的点参考论文:A Survey on Generative Diffusion Model github:https://github.com/chq1155/A-Survey-on-Generative-Diffusion-Model 一、什么是扩散模型 已…...

高等数学——多元函数微分学
文章目录多元函数微分学多元函数的极限多元函数的连续性偏导数定义高阶偏导数全微分定义全微分存在的必要条件全微分存在的充分条件多元函数的微分法复合函数微分法隐函数微分法多元函数的极值与最值无约束极值条件极值及拉格朗日乘数法最大值最小值二重积分概念性质计算利用直…...
一文打通Sleuth+Zipkin 服务链路追踪
1、为什么用 微服务架构是一个分布式架构,它按业务划分服务单元,一个分布式系统往往有很多个服务单元。由于服务单元数量众多,业务的复杂性,如果出现了错误和异常,很难去定位。主要体现在,一个请求可能需要…...
牛客刷题第一弹
1.异常处理 都是Throwable的子类: ①.Exception(异常):是程序本身可以处理的异常。 ②.Error(错误): 是程序无法处理的错误。这些错误表示故障发生于虚拟机自身、或者发生在虚拟机试图执行应用时,一般不需…...
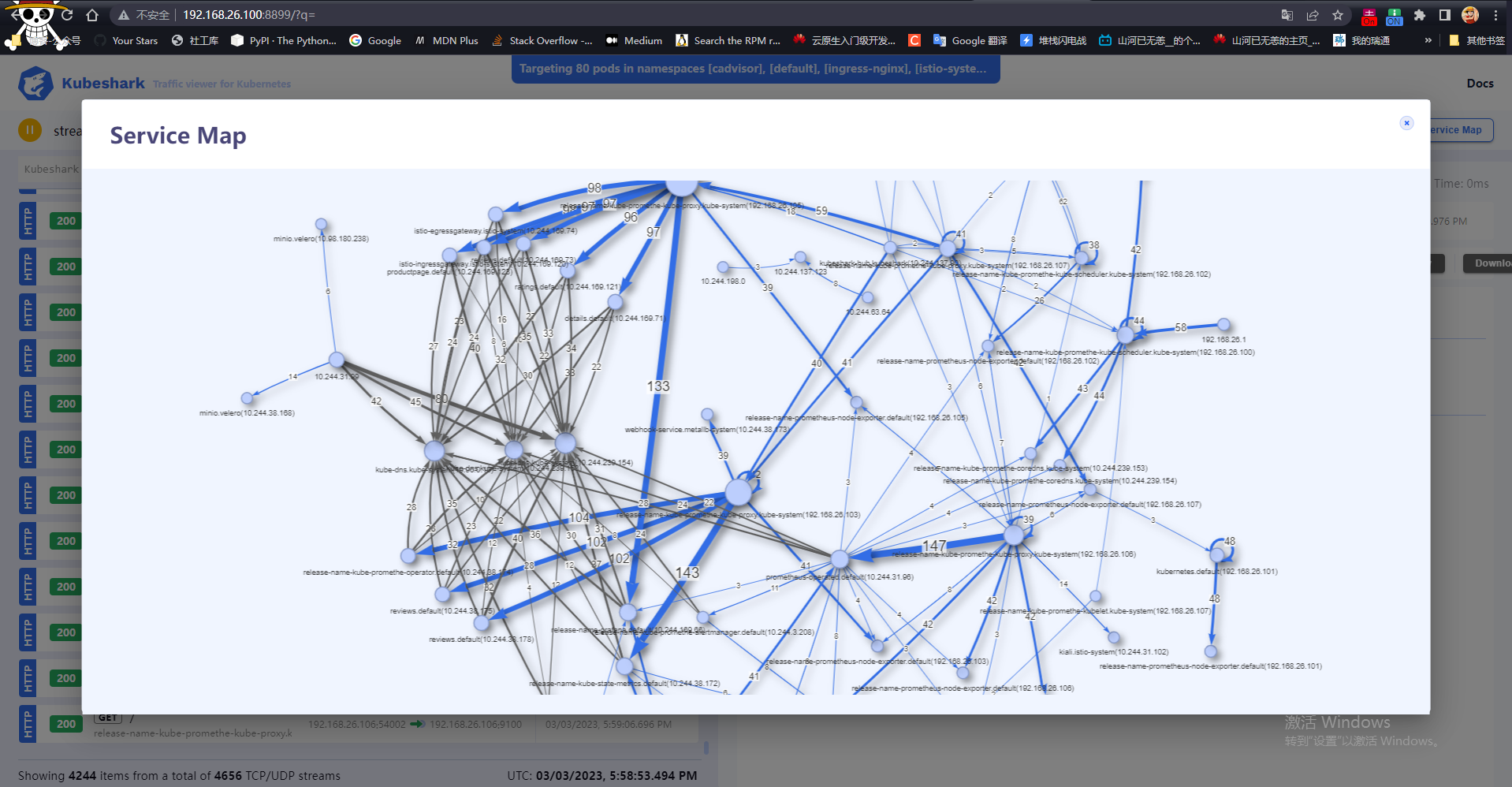
K8s:通过 Kubeshark 体验 大白鲨(Wireshark)/TCPDump 监控 Kubernetes 集群
写在前面 分享一个 k8s 集群流量查看器很轻量的一个工具,监控方便博文内容涉及: Kubeshark 简单介绍Windows、Linux 下载运行监控DemoKubeshark 特性功能介绍 理解不足小伙伴帮忙指正 对每个人而言,真正的职责只有一个:找到自我。…...

(LeetCode 每日一题) 3442. 奇偶频次间的最大差值 I (哈希、字符串)
题目:3442. 奇偶频次间的最大差值 I 思路 :哈希,时间复杂度0(n)。 用哈希表来记录每个字符串中字符的分布情况,哈希表这里用数组即可实现。 C版本: class Solution { public:int maxDifference(string s) {int a[26]…...

Vue记事本应用实现教程
文章目录 1. 项目介绍2. 开发环境准备3. 设计应用界面4. 创建Vue实例和数据模型5. 实现记事本功能5.1 添加新记事项5.2 删除记事项5.3 清空所有记事 6. 添加样式7. 功能扩展:显示创建时间8. 功能扩展:记事项搜索9. 完整代码10. Vue知识点解析10.1 数据绑…...
:OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下))
脑机新手指南(八):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下)
一、数据处理与分析实战 (一)实时滤波与参数调整 基础滤波操作 60Hz 工频滤波:勾选界面右侧 “60Hz” 复选框,可有效抑制电网干扰(适用于北美地区,欧洲用户可调整为 50Hz)。 平滑处理&…...

376. Wiggle Subsequence
376. Wiggle Subsequence 代码 class Solution { public:int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int>& nums) {int n nums.size();int res 1;int prediff 0;int curdiff 0;for(int i 0;i < n-1;i){curdiff nums[i1] - nums[i];if( (prediff > 0 && curdif…...

学习STC51单片机31(芯片为STC89C52RCRC)OLED显示屏1
每日一言 生活的美好,总是藏在那些你咬牙坚持的日子里。 硬件:OLED 以后要用到OLED的时候找到这个文件 OLED的设备地址 SSD1306"SSD" 是品牌缩写,"1306" 是产品编号。 驱动 OLED 屏幕的 IIC 总线数据传输格式 示意图 …...
可以参考以下方法:)
根据万维钢·精英日课6的内容,使用AI(2025)可以参考以下方法:
根据万维钢精英日课6的内容,使用AI(2025)可以参考以下方法: 四个洞见 模型已经比人聪明:以ChatGPT o3为代表的AI非常强大,能运用高级理论解释道理、引用最新学术论文,生成对顶尖科学家都有用的…...
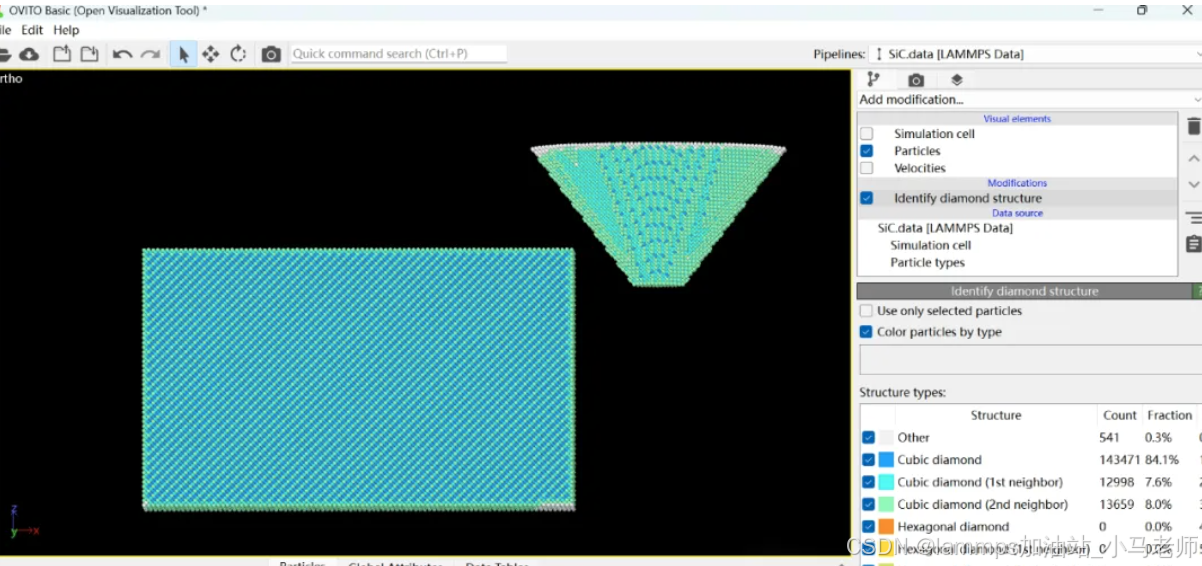
Python Ovito统计金刚石结构数量
大家好,我是小马老师。 本文介绍python ovito方法统计金刚石结构的方法。 Ovito Identify diamond structure命令可以识别和统计金刚石结构,但是无法直接输出结构的变化情况。 本文使用python调用ovito包的方法,可以持续统计各步的金刚石结构,具体代码如下: from ovito…...
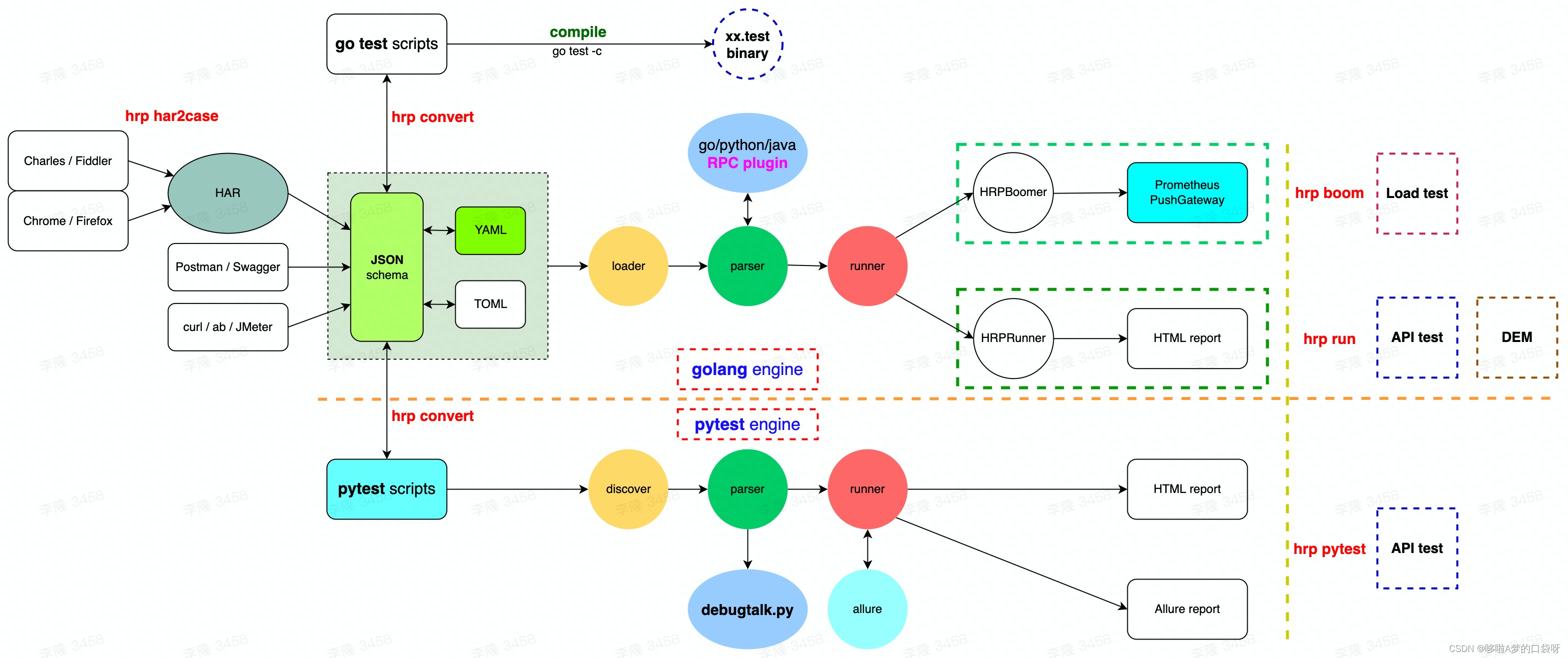
接口自动化测试:HttpRunner基础
相关文档 HttpRunner V3.x中文文档 HttpRunner 用户指南 使用HttpRunner 3.x实现接口自动化测试 HttpRunner介绍 HttpRunner 是一个开源的 API 测试工具,支持 HTTP(S)/HTTP2/WebSocket/RPC 等网络协议,涵盖接口测试、性能测试、数字体验监测等测试类型…...
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统开发:打造互动性强的购物平台
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统的开发,旨在打造一个互动性强的购物平台,让用户在购物的同时,能够享受到更多的乐趣和惊喜。 淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统拥有丰富的互动功能。用户可以通过虚拟摇杆操作扭蛋机,实现旋转、抽拉等动作,增…...

SQL Server 触发器调用存储过程实现发送 HTTP 请求
文章目录 需求分析解决第 1 步:前置条件,启用 OLE 自动化方式 1:使用 SQL 实现启用 OLE 自动化方式 2:Sql Server 2005启动OLE自动化方式 3:Sql Server 2008启动OLE自动化第 2 步:创建存储过程第 3 步:创建触发器扩展 - 如何调试?第 1 步:登录 SQL Server 2008第 2 步…...
