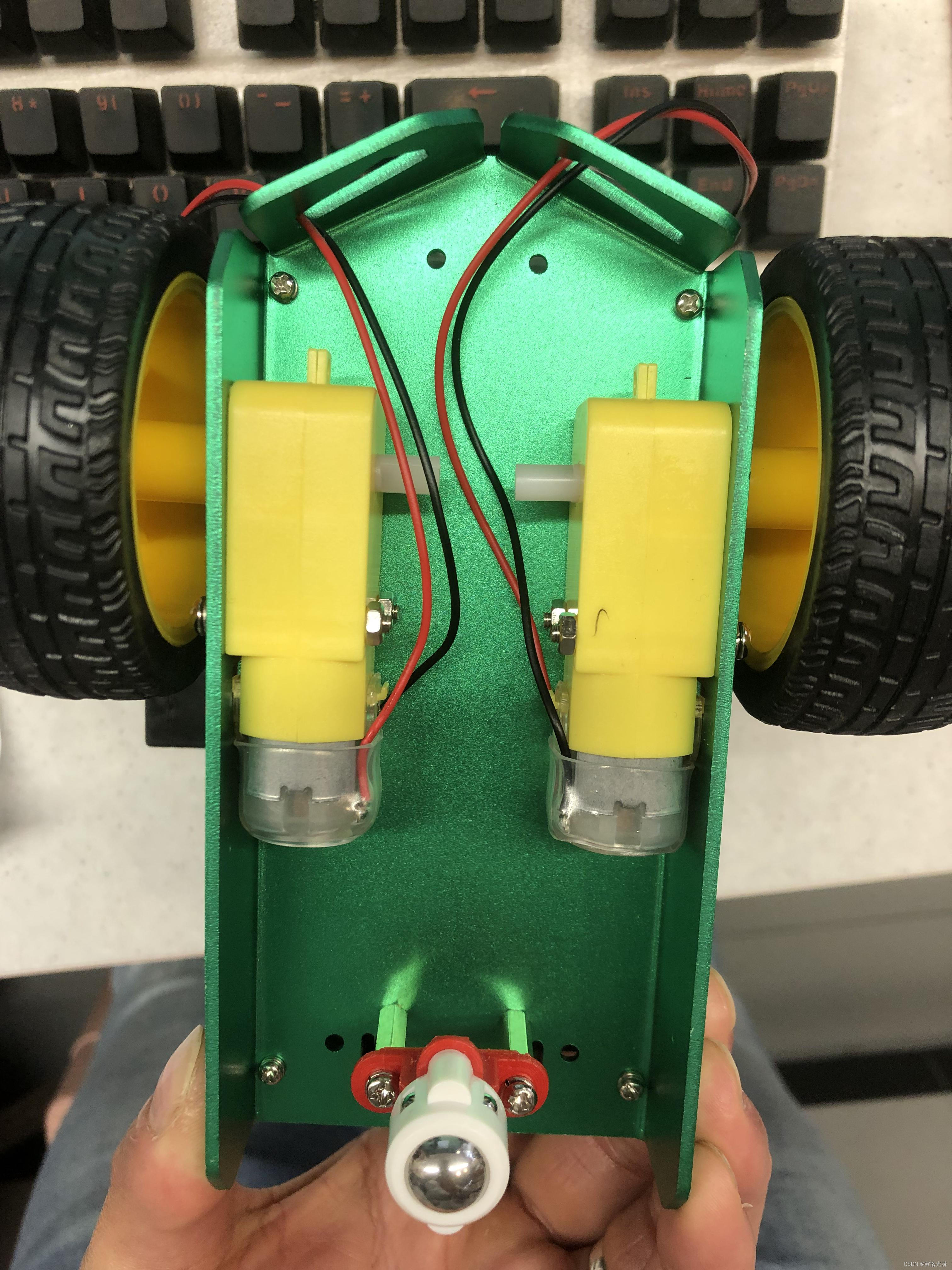
Jetson Nano驱动机器人的左右两路电机
基于Jetson Nano板子搭建一个无人车,少不了减速电机驱动轮子滚动,那如何驱动呢?
从Jetson.GPIO库文件来说,里面没有支持产生PWM的引脚,也就意味着Jetson nano没有硬件产生PWM的能力,所以我们不得不使用别的方法产生PWM完成驱动控制,而刚好STM8解决了这一问题并且节约了它有限的GPIO资源,我们借助STM8这款MCU作为协处理器,大大增强了Jetson nano的驱动能力,PWM的周期和占空比(在一个脉冲循环内,通电时间相对于总时间所占的比例)都完全可控。
我们来看下它的参数:
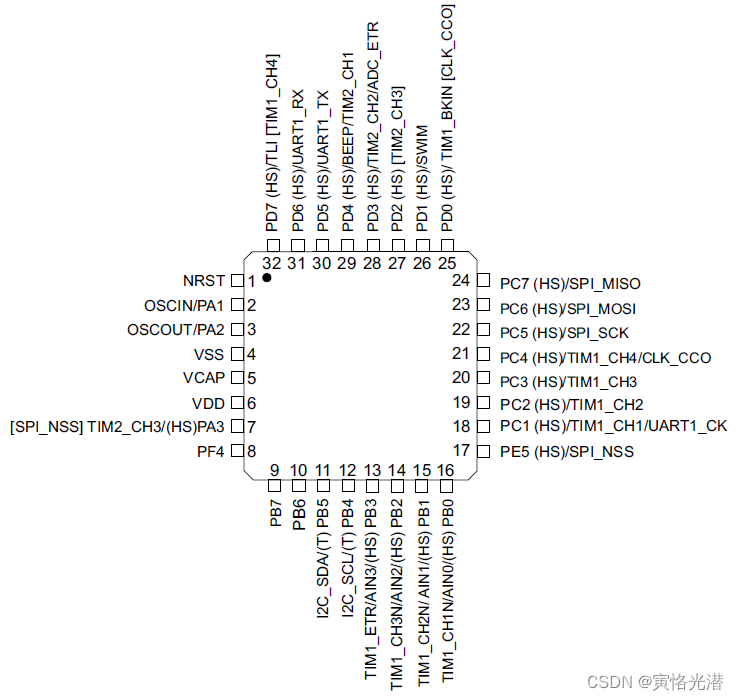
我们使用的是上图所示的QFN20封装的STM8,它主要参数特征如下:
1. I2C接口,支持多路PWM输出
2. 内置16MHz晶振,可不连接外部晶振,也可以连接外部晶振
3. 支持2.95V-5.5V电压,最大耐压值5.5V
4. 具有上电复位,以及软件复位等功能

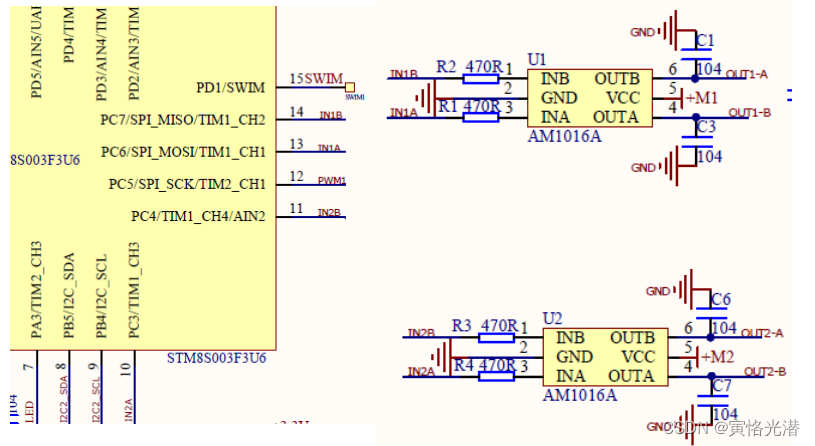
由上图三极管驱动的有源蜂鸣器电路,而三极管控制引脚接在协处理器可知,开启蜂鸣器只需要通过IIC给协处理器对应的指令即可,下面我们看到通讯协议:

在上一篇文章我们演示的蜂鸣器,我们通过IIC向协处理器(地址0x1B)的寄存器0x06发送1即可打开蜂鸣器,发送0即关闭蜂鸣器
bus.write_byte_data(0x1B,0x06,1或0)
同样的给出两路电机的电路图:
我们来实际驱动电机看下,这里电机控制部分用到了Jetbotmini的库:
from jetbotmini import Robot
import time
robot = Robot()print(dir(robot))
#['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setstate__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_add_notifiers', '_config_changed', '_cross_validation_lock', '_find_my_config', '_instance', '_load_config', '_log_default', '_notify_trait', '_register_validator', '_remove_notifiers', '_trait_default_generators', '_trait_notifiers', '_trait_validators', '_trait_values', '_walk_mro', 'add_traits', 'backward', 'class_config_rst_doc', 'class_config_section', 'class_get_help', 'class_get_trait_help', 'class_own_trait_events', 'class_own_traits', 'class_print_help', 'class_trait_names', 'class_traits', 'clear_instance', 'config', 'cross_validation_lock', 'forward', 'has_trait', 'hold_trait_notifications', 'i2c_bus', 'initialized', 'instance', 'left', 'left_motor', 'left_motor_alpha', 'left_motor_channel', 'log', 'motor_driver', 'notify_change', 'observe', 'on_trait_change', 'parent', 'right', 'right_motor', 'right_motor_alpha', 'right_motor_channel', 'section_names', 'set_motors', 'set_trait', 'setup_instance', 'stop', 'trait_events', 'trait_metadata', 'trait_names', 'traits', 'unobserve', 'unobserve_all', 'update_config']print(dir(robot.left_motor))
#['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setstate__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_add_notifiers', '_config_changed', '_cross_validation_lock', '_driver', '_find_my_config', '_load_config', '_motor', '_notify_trait', '_observe_value', '_register_validator', '_release', '_remove_notifiers', '_trait_default_generators', '_trait_notifiers', '_trait_validators', '_trait_values', '_write_value', 'add_traits', 'alpha', 'beta', 'class_config_rst_doc', 'class_config_section', 'class_get_help', 'class_get_trait_help', 'class_own_trait_events', 'class_own_traits', 'class_print_help', 'class_trait_names', 'class_traits', 'config', 'cross_validation_lock', 'has_trait', 'hold_trait_notifications', 'notify_change', 'observe', 'on_trait_change', 'parent', 'section_names', 'set_trait', 'setup_instance', 'trait_events', 'trait_metadata', 'trait_names', 'traits', 'unobserve', 'unobserve_all', 'update_config', 'value']#这个转速的范围是[0,1],不过我设置成0.1也没有转,设置成0.2及以上才转,不知道是不是电量不是很足的原因了。
robot.left_motor.value = 0.8
robot.right_motor.value = 0.8
#这样就可以让电机转动了,很简单,然后做停止电机的操作
robot.left_motor.value = 0
robot.right_motor.value = 0
#或者直接将robot停止也可以
#robot.stop()这段赋值左右马达的意思就是,控制电机速度的值的范围是0~1.0,即代表给出的PWM的占空比为0~100%,所以赋值为0,就是把输出给电机的PWM占空比设置为0,这样就关闭了电机
更多的robot实例方法可以自行查阅源码:
Help on Robot in module jetbotmini.robot object:class Robot(traitlets.config.configurable.SingletonConfigurable)| A configurable that only allows one instance.| | This class is for classes that should only have one instance of itself| or *any* subclass. To create and retrieve such a class use the| :meth:`SingletonConfigurable.instance` method.| | Method resolution order:| Robot| traitlets.config.configurable.SingletonConfigurable| traitlets.config.configurable.LoggingConfigurable| traitlets.config.configurable.Configurable| traitlets.traitlets.HasTraits| traitlets.traitlets.HasDescriptors| builtins.object| | Methods defined here:| | __init__(self, *args, **kwargs)| Create a configurable given a config config.| | Parameters| ----------| config : Config| If this is empty, default values are used. If config is a| :class:`Config` instance, it will be used to configure the| instance.| parent : Configurable instance, optional| The parent Configurable instance of this object.| | Notes| -----| Subclasses of Configurable must call the :meth:`__init__` method of| :class:`Configurable` *before* doing anything else and using| :func:`super`::| | class MyConfigurable(Configurable):| def __init__(self, config=None):| super(MyConfigurable, self).__init__(config=config)| # Then any other code you need to finish initialization.| | This ensures that instances will be configured properly.| | backward(self, speed=1.0)| | forward(self, speed=1.0, duration=None)| | left(self, speed=1.0)| | right(self, speed=1.0)| | set_motors(self, left_speed, right_speed)| | stop(self)| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Data descriptors defined here:| | i2c_bus| An int trait.| | left_motor| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.| | The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.| | Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute| | left_motor_alpha| A float trait.| | left_motor_channel| An int trait.| | right_motor| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.| | The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.| | Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute| | right_motor_alpha| A float trait.| | right_motor_channel| An int trait.| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Class methods inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.SingletonConfigurable:| | clear_instance() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| unset _instance for this class and singleton parents.| | initialized() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Has an instance been created?| | instance(*args, **kwargs) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Returns a global instance of this class.| | This method create a new instance if none have previously been created| and returns a previously created instance is one already exists.| | The arguments and keyword arguments passed to this method are passed| on to the :meth:`__init__` method of the class upon instantiation.| | Examples| --------| | Create a singleton class using instance, and retrieve it::| | >>> from traitlets.config.configurable import SingletonConfigurable| >>> class Foo(SingletonConfigurable): pass| >>> foo = Foo.instance()| >>> foo == Foo.instance()| True| | Create a subclass that is retrived using the base class instance::| | >>> class Bar(SingletonConfigurable): pass| >>> class Bam(Bar): pass| >>> bam = Bam.instance()| >>> bam == Bar.instance()| True| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Data descriptors inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.LoggingConfigurable:| | log| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.| | The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.| | Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Methods inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.Configurable:| | update_config(self, config)| Update config and load the new values| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Class methods inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.Configurable:| | class_config_rst_doc() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Generate rST documentation for this class' config options.| | Excludes traits defined on parent classes.| | class_config_section() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get the config class config section| | class_get_help(inst=None) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get the help string for this class in ReST format.| | If `inst` is given, it's current trait values will be used in place of| class defaults.| | class_get_trait_help(trait, inst=None) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get the help string for a single trait.| | If `inst` is given, it's current trait values will be used in place of| the class default.| | class_print_help(inst=None) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get the help string for a single trait and print it.| | section_names() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| return section names as a list| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Data descriptors inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.Configurable:| | config| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.| | The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.| | Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute| | parent| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.| | The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.| | Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Methods inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasTraits:| | __getstate__(self)| | __setstate__(self, state)| | add_traits(self, **traits)| Dynamically add trait attributes to the HasTraits instance.| | has_trait(self, name)| Returns True if the object has a trait with the specified name.| | hold_trait_notifications(self)| Context manager for bundling trait change notifications and cross| validation.| | Use this when doing multiple trait assignments (init, config), to avoid| race conditions in trait notifiers requesting other trait values.| All trait notifications will fire after all values have been assigned.| | notify_change(self, change)| | observe(self, handler, names=traitlets.All, type='change')| Setup a handler to be called when a trait changes.| | This is used to setup dynamic notifications of trait changes.| | Parameters| ----------| handler : callable| A callable that is called when a trait changes. Its| signature should be ``handler(change)``, where ``change`` is a| dictionary. The change dictionary at least holds a 'type' key.| * ``type``: the type of notification.| Other keys may be passed depending on the value of 'type'. In the| case where type is 'change', we also have the following keys:| * ``owner`` : the HasTraits instance| * ``old`` : the old value of the modified trait attribute| * ``new`` : the new value of the modified trait attribute| * ``name`` : the name of the modified trait attribute.| names : list, str, All| If names is All, the handler will apply to all traits. If a list| of str, handler will apply to all names in the list. If a| str, the handler will apply just to that name.| type : str, All (default: 'change')| The type of notification to filter by. If equal to All, then all| notifications are passed to the observe handler.| | on_trait_change(self, handler=None, name=None, remove=False)| DEPRECATED: Setup a handler to be called when a trait changes.| | This is used to setup dynamic notifications of trait changes.| | Static handlers can be created by creating methods on a HasTraits| subclass with the naming convention '_[traitname]_changed'. Thus,| to create static handler for the trait 'a', create the method| _a_changed(self, name, old, new) (fewer arguments can be used, see| below).| | If `remove` is True and `handler` is not specified, all change| handlers for the specified name are uninstalled.| | Parameters| ----------| handler : callable, None| A callable that is called when a trait changes. Its| signature can be handler(), handler(name), handler(name, new),| handler(name, old, new), or handler(name, old, new, self).| name : list, str, None| If None, the handler will apply to all traits. If a list| of str, handler will apply to all names in the list. If a| str, the handler will apply just to that name.| remove : bool| If False (the default), then install the handler. If True| then unintall it.| | set_trait(self, name, value)| Forcibly sets trait attribute, including read-only attributes.| | setup_instance(self, *args, **kwargs)| This is called **before** self.__init__ is called.| | trait_metadata(self, traitname, key, default=None)| Get metadata values for trait by key.| | trait_names(self, **metadata)| Get a list of all the names of this class' traits.| | traits(self, **metadata)| Get a ``dict`` of all the traits of this class. The dictionary| is keyed on the name and the values are the TraitType objects.| | The TraitTypes returned don't know anything about the values| that the various HasTrait's instances are holding.| | The metadata kwargs allow functions to be passed in which| filter traits based on metadata values. The functions should| take a single value as an argument and return a boolean. If| any function returns False, then the trait is not included in| the output. If a metadata key doesn't exist, None will be passed| to the function.| | unobserve(self, handler, names=traitlets.All, type='change')| Remove a trait change handler.| | This is used to unregister handlers to trait change notifications.| | Parameters| ----------| handler : callable| The callable called when a trait attribute changes.| names : list, str, All (default: All)| The names of the traits for which the specified handler should be| uninstalled. If names is All, the specified handler is uninstalled| from the list of notifiers corresponding to all changes.| type : str or All (default: 'change')| The type of notification to filter by. If All, the specified handler| is uninstalled from the list of notifiers corresponding to all types.| | unobserve_all(self, name=traitlets.All)| Remove trait change handlers of any type for the specified name.| If name is not specified, removes all trait notifiers.| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Class methods inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasTraits:| | class_own_trait_events(name) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get a dict of all event handlers defined on this class, not a parent.| | Works like ``event_handlers``, except for excluding traits from parents.| | class_own_traits(**metadata) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get a dict of all the traitlets defined on this class, not a parent.| | Works like `class_traits`, except for excluding traits from parents.| | class_trait_names(**metadata) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get a list of all the names of this class' traits.| | This method is just like the :meth:`trait_names` method,| but is unbound.| | class_traits(**metadata) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get a ``dict`` of all the traits of this class. The dictionary| is keyed on the name and the values are the TraitType objects.| | This method is just like the :meth:`traits` method, but is unbound.| | The TraitTypes returned don't know anything about the values| that the various HasTrait's instances are holding.| | The metadata kwargs allow functions to be passed in which| filter traits based on metadata values. The functions should| take a single value as an argument and return a boolean. If| any function returns False, then the trait is not included in| the output. If a metadata key doesn't exist, None will be passed| to the function.| | trait_events(name=None) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits| Get a ``dict`` of all the event handlers of this class.| | Parameters| ----------| name: str (default: None)| The name of a trait of this class. If name is ``None`` then all| the event handlers of this class will be returned instead.| | Returns| -------| The event handlers associated with a trait name, or all event handlers.| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Data descriptors inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasTraits:| | cross_validation_lock| A contextmanager for running a block with our cross validation lock set| to True.| | At the end of the block, the lock's value is restored to its value| prior to entering the block.| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Static methods inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasDescriptors:| | __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs)| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.| | ----------------------------------------------------------------------| Data descriptors inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasDescriptors:| | __dict__| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)| | __weakref__| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
相关文章:
Jetson Nano驱动机器人的左右两路电机
基于Jetson Nano板子搭建一个无人车,少不了减速电机驱动轮子滚动,那如何驱动呢?从Jetson.GPIO库文件来说,里面没有支持产生PWM的引脚,也就意味着Jetson nano没有硬件产生PWM的能力,所以我们不得不使用别的方…...

如何通过openssl生成公钥和私钥?
1、生成RSA秘钥的方法 生成RSA秘钥的方法: openssl genrsa -des3 -out privkey.pem 2048 注:建议用2048位秘钥,少于此可能会不安全或很快将不安全。 这个命令会生成一个2048位的秘钥,同时有一个des3方法加密的密码,…...
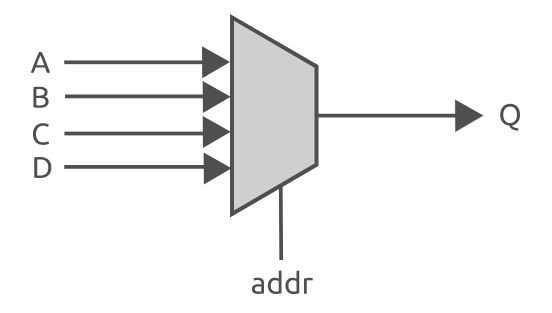
Verilog的If语句和Case语句
这篇文章将讨论 verilog 中两个最常用的结构----if语句和case语句。在之前的文章中学习了如何使用过程块(例如always块)来编写按顺序执行的verilog 代码。此外还可以在过程块中使用许多语句----统称为顺序语句,如case 语句和 if 语句。这篇文…...

HJ31 单词倒排
描述 对字符串中的所有单词进行倒排。 说明: 1、构成单词的字符只有26个大写或小写英文字母; 2、非构成单词的字符均视为单词间隔符; 3、要求倒排后的单词间隔符以一个空格表示;如果原字符串中相邻单词间有多个间隔符时…...
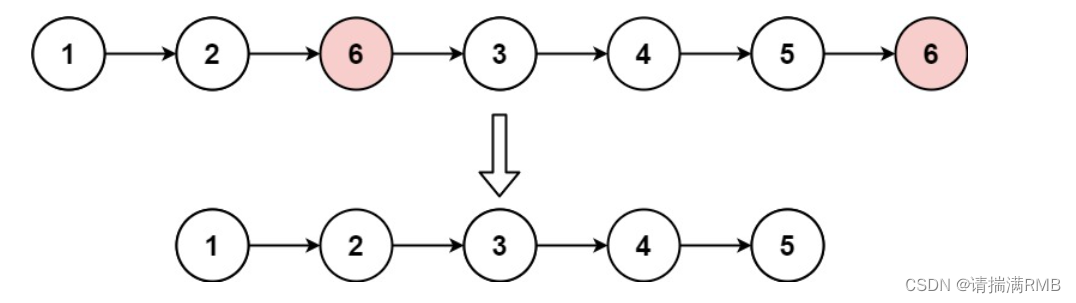
leetcode——203.移除链表元素
文章目录🐨1.题目🪅2.解法1-头节点迭代🌿2.1 思路🌿2.2 代码实现🦆3. 解法2-创建新链表🎏3.1 思路🎏3.2 代码实现🐐4. 题目链接🐨1.题目 给你一个链表的头节点head和一个…...
GPT-4来袭:开启人工智能新时代
文章目录介绍GPT4 模型演示示例示例 1示例 2示例 3示例 4示例 5最后Reference介绍 2023年3月15日,OpenAI公司正式发布了先进的自然语言处理模型GPT-4,前不久发布的GPT-3.5模型只能理解文字的语言模型,而新发布的GPT4则是多模态模型ÿ…...
芯微电子IPO终止:业绩开始大幅下滑,王日新、王苟新兄弟不同命
近日,深圳证券交易所披露的信息显示,黄山芯微电子股份有限公司(下称“芯微电子”)申请撤回发行上市申请文件。因此,深圳证券交易所决定终止对其首次公开发行股票并在创业板上市的审核。 据贝多财经了解,芯…...
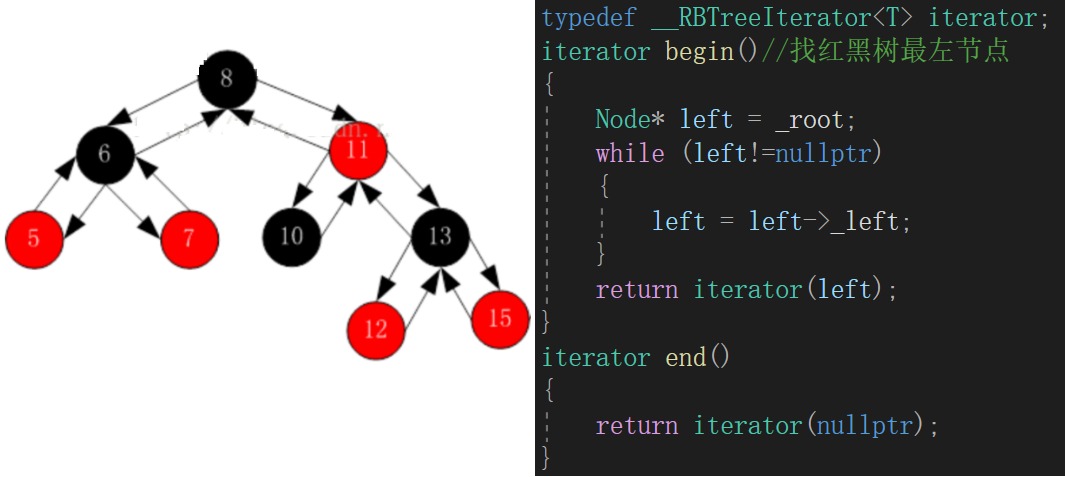
【C++】用手搓的红黑树手搓set和map
目录 一、set/map的底层结构 1、set/map的源码 2、利用模板区分set/map 3、利用仿函数控制比较大小 二、set/map的迭代器(红黑树的迭代器) 1、红黑树的begin、end迭代器 2、红黑树迭代器的operator 3、红黑树迭代器的operator-- 三、set的const…...

【C++】空指针弃NULL用nullptr
空指针(null pointer)不指向任何对象,在试图使用一个指针之前代码可以首先检查它是否为空。声明空指针的3种方法: int* p1 NULL; int* p2 nullptr; int* p3 0; 在C语言中常用NULL生成空指针,NULL是一个宏…...
【selenium学习】数据驱动测试
数据驱动在 unittest 中,使用读取数据文件来实现参数化可以吗?当然可以。这里以读取 CSV文件为例。创建一个 baidu_data.csv 文件,如图所示:文件第一列为测试用例名称,第二例为搜索的关键字。接下来创建 test_baidu_da…...

嵌入式硬件电路设计的基本技巧
目录 1 分模块 2 标注关键参数 3 电阻/电容/电感/磁珠的注释 4 可维修性 5 BOM表归一化 6 电源和地的符号 7 测试点 8 网络标号 9 容错性/兼容性 10 NC、NF 11 版本变更 12 悬空引脚 13 可扩展性 14 防呆 15 信号的流向 16 PCB走线建议 17 不使用\表示取反 不…...

Spring MVC 图片的上传和下载
✅作者简介:2022年博客新星 第八。热爱国学的Java后端开发者,修心和技术同步精进。 🍎个人主页:Java Fans的博客 🍊个人信条:不迁怒,不贰过。小知识,大智慧。 💞当前专栏…...
远程工具神器之MobaXterm (小白必看)
目录 1、介绍 2、ssh连接详解过程 3、特点 1、介绍 带有 X11 服务器、选项卡式 SSH 客户端、网络工具等的 Windows 增强型终端。 MobaXterm 是您远程计算的终极工具箱。在单个Windows应用程序中,它提供了大量功能,这些功能是为程序员,网站管…...
VRIK+Unity XR Interaction Toolkit 实现VR上半身的追踪(附带VRM模型导入Unity方法和手腕扭曲的解决方法)
文章目录📕第一步:配置 OpenXR XR Interaction Toolkit 的开发环境📕第二步:导入人物模型⭐VRM 模型导入 Unity 的方法📕第三步:配置 VRIK⭐给模型加上 VRIK 组件⭐将模型的头部和手部的位置作为 VR 追踪目…...
【C++进阶】map的介绍和使用
文章目录map的介绍map的模板参数介绍map的容器介绍map重要容器接口的介绍及使用构造函数增删查改迭代器的使用map的介绍 map是关联容器,它按照特定的次序(按照key来比较)存储由键值key和值value组合而成的元素。在map中,键值key通常用于排序和惟一地标识…...
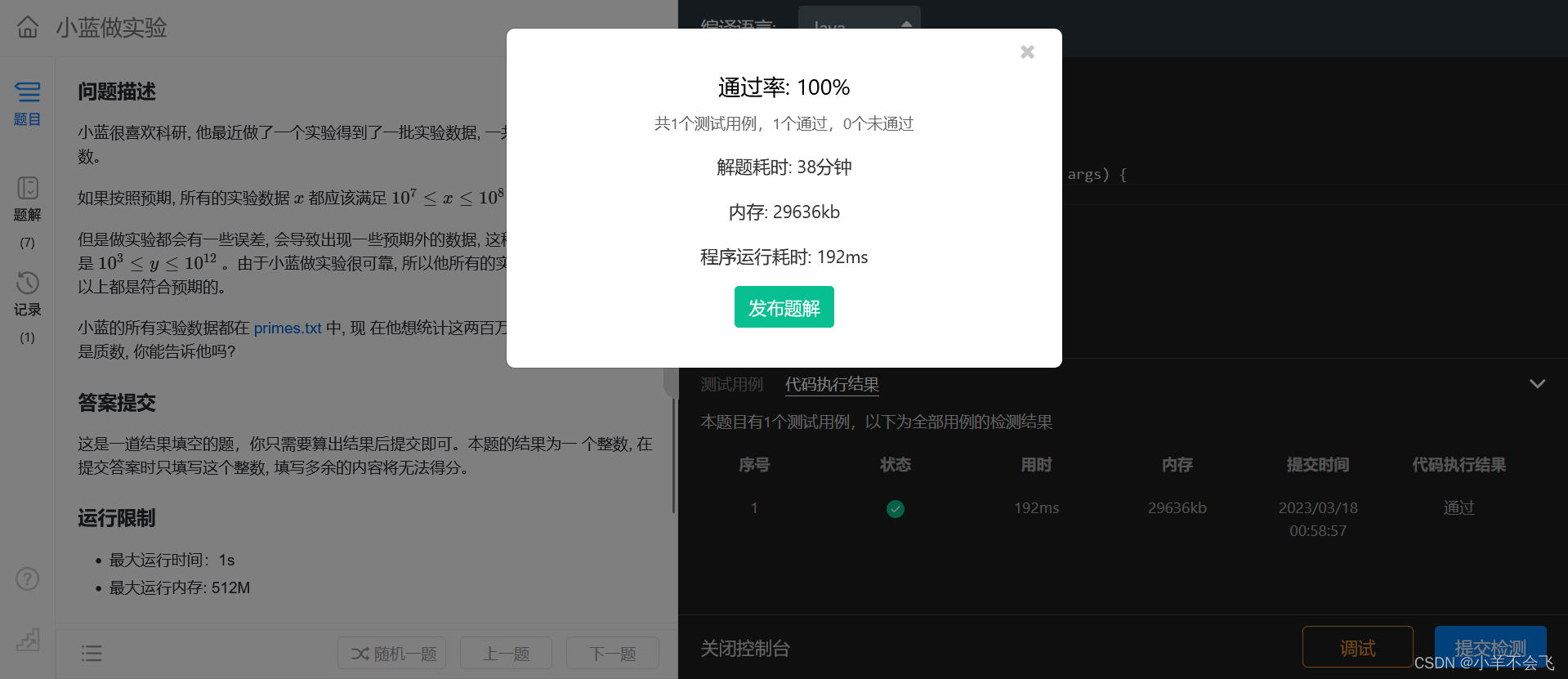
第十四届蓝桥杯三月真题刷题训练——第 15 天
目录 第 1 题:斐波那契与7 问题描述 答案提交 运行限制 代码: 第 2 题:小蓝做实验 问题描述 答案提交 运行限制 代码: 第 1 题:斐波那契与7 问题描述 斐波那契数列的递推公式为: FnFn−1Fn−2, 其中 F1F21…...

HTML5是什么?怎么学习HTML5?
HTML5 是什么?HTML5是什么?相信这个问题并不容易回答,大多数人对于HTML5的概念仅仅是听说过而已,非要让他说出个所以然来,结果只能让你失望。相比普及了近十四年的HTML4来说,HTML5带来的震撼其实丝毫不亚于…...

个人算法题精简导航整理(精炼汇总,含知识点、模板题、题单)
文章目录前言导航注意事项技巧类自定义Pair排序N维数组转一维位运算状态压缩算法基础枚举 √指数型枚举排列型枚举组合型枚举模拟 √日期天数问题:平年闰年情况递归&分治 √贪心 √货仓选址-模板题排序 √归并排序前缀和&差分 √前缀和差分(一维…...

Mac 和 Win,到底用哪个系统学编程?
今天来聊一个老生常谈的问题,学编程时到底选择什么操作系统?Mac、Windows,还是别的什么。。 作为一个每种操作系统都用过很多年的程序员,我会结合我自己的经历来给大家一些参考和建议。 接下来先分别聊聊每种操作系统的优点和不…...
文心一言---中国版的“ChatGPT”狂飙的机会或许要出现了
⭐️我叫忆_恒心,一名喜欢书写博客的在读研究生👨🎓。 如果觉得本文能帮到您,麻烦点个赞👍呗! 近期会不断在专栏里进行更新讲解博客~~~ 有什么问题的小伙伴 欢迎留言提问欧,喜欢的小伙伴给个三…...
)
uniapp 对接腾讯云IM群组成员管理(增删改查)
UniApp 实战:腾讯云IM群组成员管理(增删改查) 一、前言 在社交类App开发中,群组成员管理是核心功能之一。本文将基于UniApp框架,结合腾讯云IM SDK,详细讲解如何实现群组成员的增删改查全流程。 权限校验…...

高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景
高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景 高危文件识别旨在检测可能导致安全威胁的文件,如包含恶意代码、敏感数据或欺诈内容的文档,在企业协同办公环境中(如Teams、Google Workspace)尤为重要。结合大模型技术&…...

python如何将word的doc另存为docx
将 DOCX 文件另存为 DOCX 格式(Python 实现) 在 Python 中,你可以使用 python-docx 库来操作 Word 文档。不过需要注意的是,.doc 是旧的 Word 格式,而 .docx 是新的基于 XML 的格式。python-docx 只能处理 .docx 格式…...
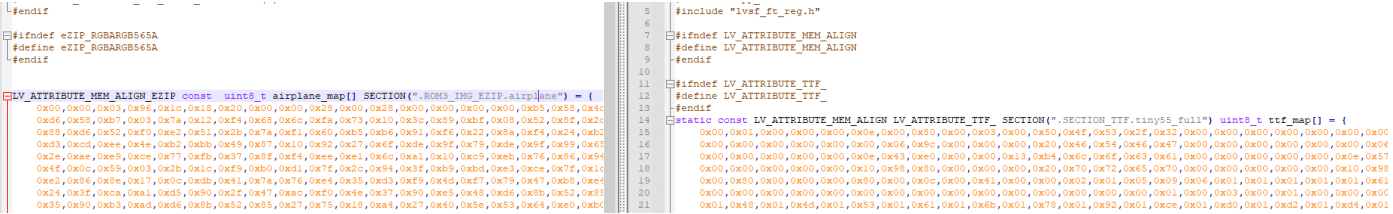
SiFli 52把Imagie图片,Font字体资源放在指定位置,编译成指定img.bin和font.bin的问题
分区配置 (ptab.json) img 属性介绍: img 属性指定分区存放的 image 名称,指定的 image 名称必须是当前工程生成的 binary 。 如果 binary 有多个文件,则以 proj_name:binary_name 格式指定文件名, proj_name 为工程 名&…...

十九、【用户管理与权限 - 篇一】后端基础:用户列表与角色模型的初步构建
【用户管理与权限 - 篇一】后端基础:用户列表与角色模型的初步构建 前言准备工作第一部分:回顾 Django 内置的 `User` 模型第二部分:设计并创建 `Role` 和 `UserProfile` 模型第三部分:创建 Serializers第四部分:创建 ViewSets第五部分:注册 API 路由第六部分:后端初步测…...
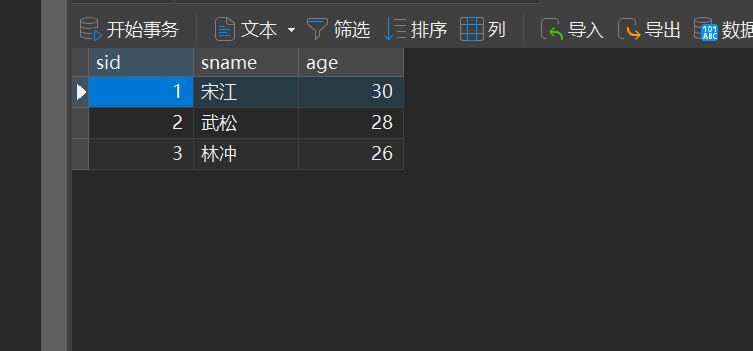
MySQL的pymysql操作
本章是MySQL的最后一章,MySQL到此完结,下一站Hadoop!!! 这章很简单,完整代码在最后,详细讲解之前python课程里面也有,感兴趣的可以往前找一下 一、查询操作 我们需要打开pycharm …...

Windows 下端口占用排查与释放全攻略
Windows 下端口占用排查与释放全攻略 在开发和运维过程中,经常会遇到端口被占用的问题(如 8080、3306 等常用端口)。本文将详细介绍如何通过命令行和图形化界面快速定位并释放被占用的端口,帮助你高效解决此类问题。 一、准…...

小智AI+MCP
什么是小智AI和MCP 如果还不清楚的先看往期文章 手搓小智AI聊天机器人 MCP 深度解析:AI 的USB接口 如何使用小智MCP 1.刷支持mcp的小智固件 2.下载官方MCP的示例代码 Github:https://github.com/78/mcp-calculator 安这个步骤执行 其中MCP_ENDPOI…...
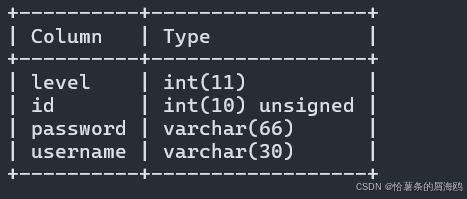
SQL注入篇-sqlmap的配置和使用
在之前的皮卡丘靶场第五期SQL注入的内容中我们谈到了sqlmap,但是由于很多朋友看不了解命令行格式,所以是纯手动获取数据库信息的 接下来我们就用sqlmap来进行皮卡丘靶场的sql注入学习,链接:https://wwhc.lanzoue.com/ifJY32ybh6vc…...
ubuntu中安装conda的后遗症
缘由: 在编译rk3588的sdk时,遇到编译buildroot失败,提示如下: 提示缺失expect,但是实测相关工具是在的,如下显示: 然后查找借助各个ai工具,重新安装相关的工具,依然无解。 解决&am…...
