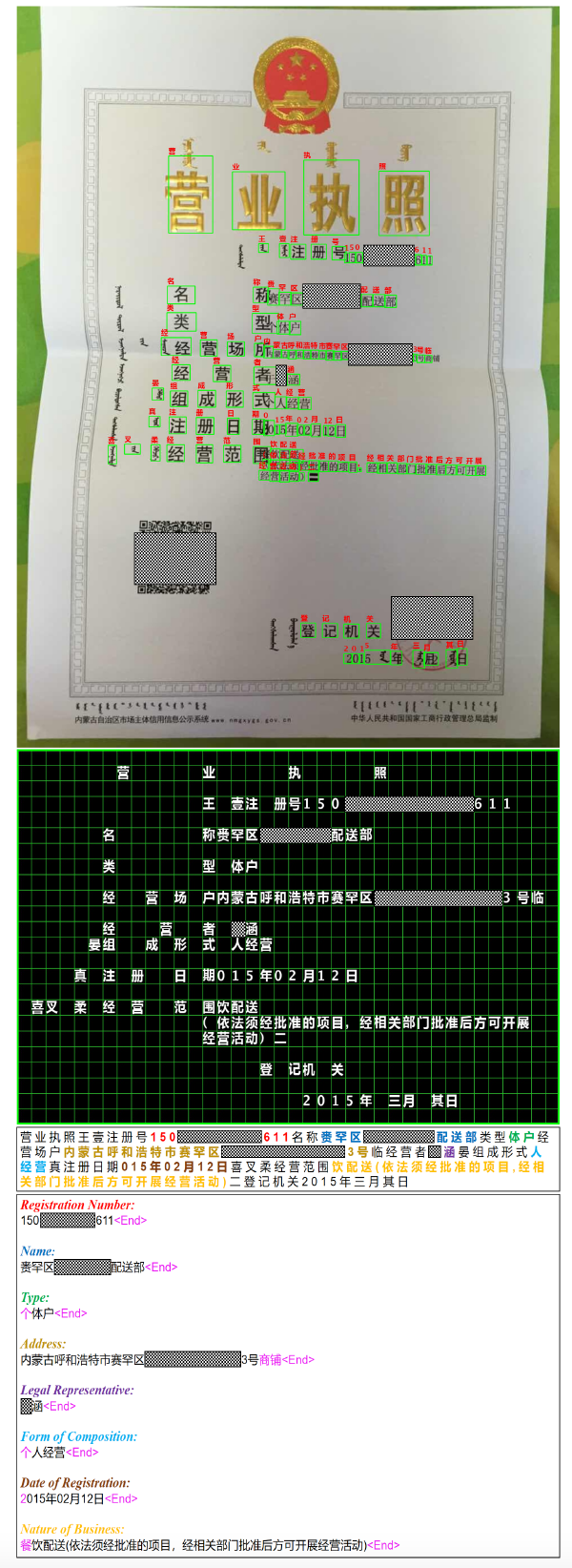
【数据结构初阶】栈与队列笔试题
前言
在我们学习了栈和队列之后,今天来通过几道练习题来巩固一下我们的知识。
题目一 用栈实现队列
题目链接:232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(Leetcode)

这道题难度不是很大,重要的是我们对结构认识的考察,由于这篇文章我们是通过C语言解决的,所以我们必须先去构造一个栈,并且可以进行栈的各种操作,最终实现队列的实现。
typedef int datetype;typedef struct Stack
{datetype* a;int capacity;int top;
}stack;
//初始化
void stackInit(stack* p);
//销毁
void stackDestroy(stack* p);
//入栈
void stackPush(stack* p, datetype x);
//出栈
void stackPop(stack* p);
//取栈顶数据
datetype stackTop(stack* p);
//数据个数
int stackSize(stack* p);
//判断是否为空
bool stackEmpty(stack* p);
bool isValid(char* s);
void stackInit(stack* p)
{assert(p);p->a = NULL;p->capacity = 0;p->top = 0;
}
void stackPush(stack* p,datetype x)
{assert(p);if (p->capacity == p->top){int newCapacity = p->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * p->capacity;datetype* tmp = (datetype*)realloc(p->a, newCapacity * sizeof(datetype));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc");exit(-1);}p->a = tmp;p->capacity=newCapacity;}p->a[p->top] = x;p->top++;
}void stackPop(stack* p)
{assert(p);assert(!stackEmpty(p));p->top--;
}void stackDestroy(stack* p)
{assert(p);if (p->capacity == 0)return;free(p->a);p->a = NULL;p->capacity = 0;p->top = 0;
}datetype stackTop(stack* p)
{assert(p);assert(!stackEmpty(p));return p->a[p->top-1];
}bool stackEmpty(stack* p)
{assert(p);return p->top==0;
}
int stackSize(stack* p)
{assert(p);return p->top;
}
//定义进行出数据和入数据的栈
typedef struct {stack pushST;stack popST;
} MyQueue;//创建队列,使用两个栈来实现
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue* tmp=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));stackInit(&tmp->pushST);stackInit(&tmp->popST);return tmp;
}
//直接将数据入pushST
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {stackPush(&obj->pushST,x);
}
//如过popST内不为空,直接输出数据,如果为空,将pushST数据都入到popST内
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {if(stackEmpty(&obj->popST)){while(!stackEmpty(&obj->pushST)){stackPush(&obj->popST,stackTop(&obj->pushST));stackPop(&obj->pushST);}}int front=stackTop(&obj->popST);stackPop(&obj->popST);return front;
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {if(stackEmpty(&obj->popST)){while(!stackEmpty(&obj->pushST)){stackPush(&obj->popST,stackTop(&obj->pushST));stackPop(&obj->pushST);}}return stackTop(&obj->popST);
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {return stackEmpty(&obj->pushST)&&stackEmpty(&obj->popST);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {stackDestroy(&obj->pushST);stackDestroy(&obj->popST);free(obj);obj=NULL;
}这道题我们使用两个栈,一个栈负责出数据,一个栈负责入数据,当入数据时,直接push即可,当出数据时,我们使用两个栈配合,使用栈先入先出的特点,将pushST的内容入到popST时,数据就已经变成了逆序,所以在popST栈内,直接出就可以实现队列的先入后出的功能。
题目二 用队列实现栈
题目链接:225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(Leetcode)

这道题与上道题类似,都是对结构的考察,使用队列先入先出的特点,通过两个队列之前出数据入数据后,可以实现栈的功能,当一个队列出队进入另外一个队列,只剩一个数据时,直接将这个数据出队列,两个队列互相配合,最终将所有数出队,实现栈的功能。
typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QueueNode;typedef struct Queue
{QueueNode* head;QueueNode* tail;// size_t _size;
}Queue;//void QueueInit(QueueNode** pphead, QueueNode** pptail);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;
}void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QueueNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur != NULL){QueueNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->head == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}
}void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);//if (pq->head == NULL)// return;assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;if (pq->head == NULL){pq->tail = NULL;}
}QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);int n = 0;QueueNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){++n;cur = cur->next;}return n;
}bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}typedef struct {Queue q1;Queue q2;
} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate() {MyStack* ret =(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&ret->q1);QueueInit(&ret->q2);return ret;
}//哪个队列不为空,就在哪个队列入数据
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);}else{QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);}
}
//找到为空和不为空的队列,将不为空的队列出为只剩一个数据,直接出这个数据
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {Queue* empty = &obj->q1;Queue* nonempty = &obj->q2;if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){empty = &obj->q2;nonempty = &obj->q1;}while(QueueSize(nonempty)>1){QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(nonempty));QueuePop(nonempty);}int ret=QueueFront(nonempty);QueuePop(nonempty);return ret;
}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){return QueueBack(&obj->q1);}else{return QueueBack(&obj->q2);}
}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}题目三 设计循环队列
题目链接:622. 设计循环队列 - 力扣(Leetcode)
我们之前实现队列是使用链表来实现的,当然也可以使用顺序表来实现,考虑到这道题循环队列的特殊结构,我们使用顺序表和链表两种方式来解决这个问题。

方法一:使用链表解决

首先定义每个结点的结构,再定义一个结构来存head,tail,数据个数size,最大容量capacity,当数据个数等于最大容量时,说明队列已满,当数据个数size为0时,说明队列为空。
typedef struct qNode
{int data;struct qNode* next;
}qNode;typedef struct {qNode* head;qNode* tail;int size;int capacity;
} MyCircularQueue;bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {MyCircularQueue* cq=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));cq->head=cq->tail=NULL;cq->capacity=k;cq->size=0;return cq;
}bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)){return false;}qNode* newNode=(qNode*)malloc(sizeof(qNode));newNode->data=value;newNode->next=NULL;if(obj->size==0){obj->head=obj->tail=newNode;}else{obj->tail->next=newNode;obj->tail=newNode;}obj->size++;return true;
}bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return false;}qNode* next=obj->head->next;free(obj->head);obj->head=next;obj->size--;return true;
}int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return -1;return obj->head->data;
}int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return -1;return obj->tail->data;
}bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {return !obj->size;
}bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {return obj->size==obj->capacity;
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){free(obj);return;}qNode* cur=obj->head;while(cur!=obj->tail){qNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(obj);obj=NULL;
}方法二:使用顺序表解决

使用顺序表,当head==tail时,说明队列为空,当head==tail+1时,说明队列为满。
typedef struct {int* a;int head;int tail;int capacity;
} MyCircularQueue;bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {MyCircularQueue* cq=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));cq->a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));cq->head=cq->tail=0;cq->capacity=k;return cq;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {return obj->head==obj->tail;
}bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {return (obj->tail+1)%(obj->capacity+1)==obj->head;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)){return false;}obj->a[obj->tail++]=value;obj->tail = obj->tail % (obj->capacity+1);return true;
}bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return false;}obj->head++;obj->head=obj->head%(obj->capacity+1);return true;
}int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return -1;return obj->a[obj->head];
}int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return -1;return obj->a[obj->tail];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {free(obj->a);free(obj);
}
总结
我们今天讲解了栈与队列的笔试题,希望可以得到大家的支持。
相关文章:

【数据结构初阶】栈与队列笔试题
前言在我们学习了栈和队列之后,今天来通过几道练习题来巩固一下我们的知识。题目一 用栈实现队列题目链接:232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(Leetcode)这道题难度不是很大,重要的是我们对结构认识的考察,由于这篇文…...
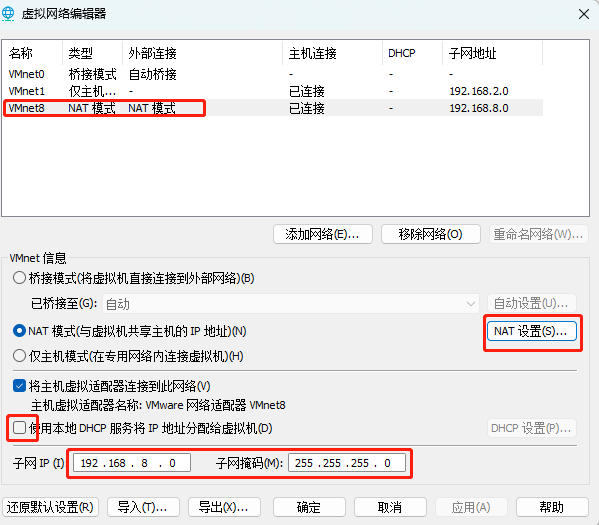
【Linux入门篇】操作系统安装、网络配置
目录 🍁Linux详解 🍂1.操作系统 🍂2.操作系统组成 🍂3.操作系统历史 🍂4.常见的Linux系统 🍂5.centos7下载 🍂6.安装centos7 🍁linux初始化配置 🍃1.虚拟机系统安装后操作…...

Selenium:找不到对应的网页元素?常见的一些坑
目录 1. 用Xpath查找数据时无法直接获取节点属性 2. 使用了WebDriverWait以后仍然无法找到元素 2.1. 分辨率原因 2.2. 需要滚动页面 2.3. 由于其他元素的遮挡 1. 用Xpath查找数据时无法直接获取节点属性 通常在我们使用xpath时,可以使用class的方式直接获取节…...
flex布局优化(两端对齐,从左至右)
文章目录前言方式一 nth-child方式二 gap属性方式三 设置margin左右两边为负值总结前言 flex布局是前端常用的布局方式之一,但在使用过程中,我们总是感觉不太方便,因为日常开发中,大多数时候,我们想要的效果是这样的 …...
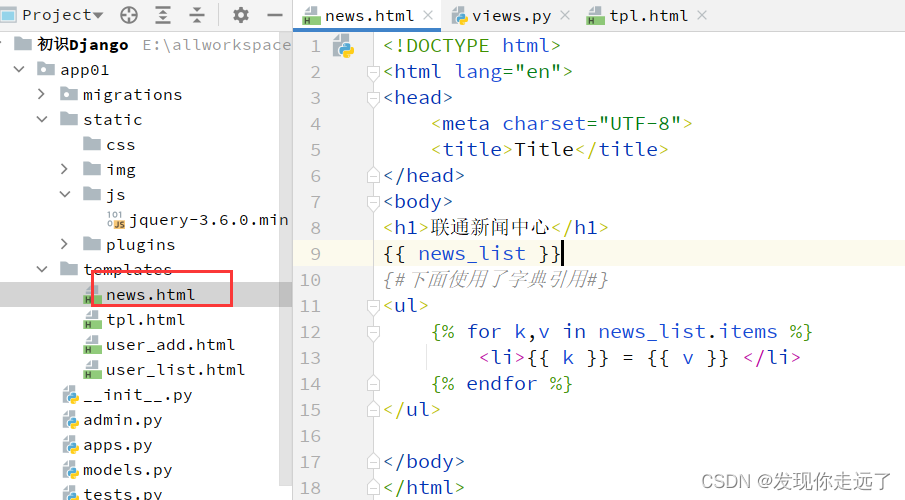
【Django 网页Web开发】03. 初识Django(保姆级图文)
目录1. 命令行创建与pycharm创建的区别2. 项目结构信息2.1 项目结构2.2 项目app结构2.3 快速查看项目结构树3. 创建并注册app3.1 创建app3.2 注册app4. 编写URL与视图的对应关系5. 编写视图文件6. 启动项目7. 写多个页面8. templates模板的使用8.1 编写html文件8.3 导入html文件…...

KubeSphere All in one安装配置手册
KubeSphere All in one安装配置手册 1. 初始化 1.1 配置apt源 # vi /etc/apt/sources.list deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiversedeb…...

Spring Boot 核心配置文件
Spring Boot 核心配置文件1、application.properties2、application.yml使用建议3、常用配置项服务器配置数据库配置日志配置其他配置4、配置文件的加载顺序5、配置文件的占位符6、配置文件的动态刷新7、配置文件的属性分组定义属性分组绑定属性分组使用属性分组总结Spring Boo…...
个人小站折腾后记
个人小站折腾后记 🏠个人主页:shark-Gao 🧑个人简介:大家好,我是shark-Gao,一个想要与大家共同进步的男人😉😉 🎉目前状况:23届毕业生,目前在某…...

WebService简单入门
1. JAX-WS发布WebService 创建web工程 创建simple包,和server、client两个子包。正常情况下server和client应该是两个项目,这里我们只是演示效果,所以简化写到一个项目中: 1.1 创建服务类Server package simple.server;import ja…...
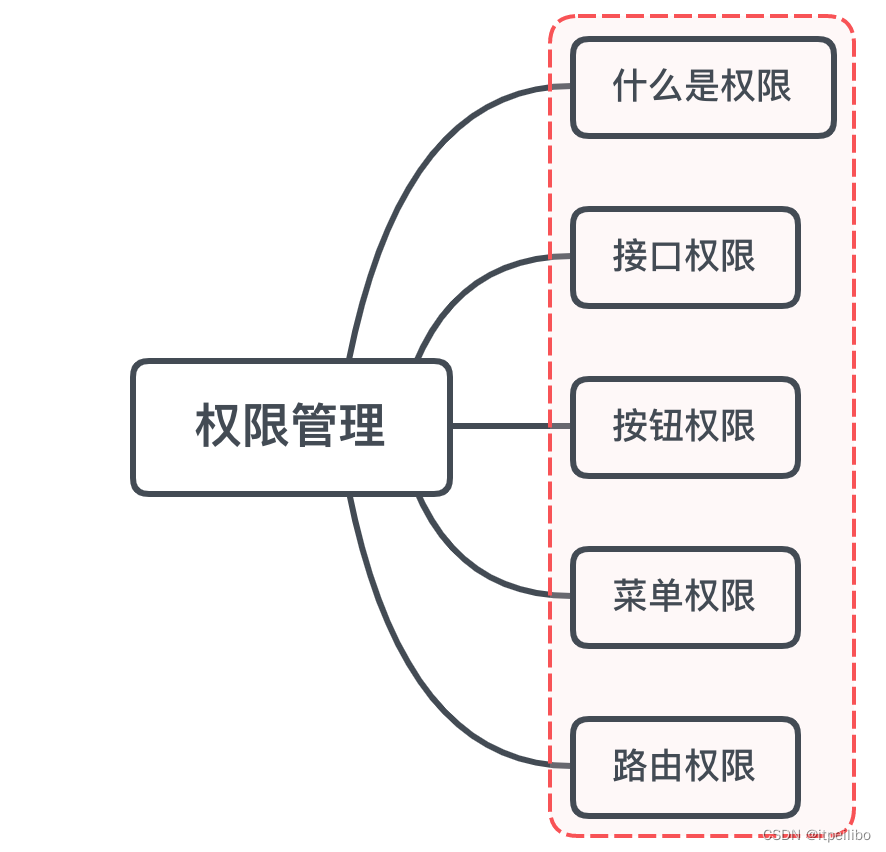
「Vue面试题」vue要做权限管理该怎么做?如果控制到按钮级别的权限怎么做?
文章目录一、是什么二、如何做接口权限路由权限控制菜单权限方案一方案二按钮权限方案一方案二小结参考文章一、是什么 权限是对特定资源的访问许可,所谓权限控制,也就是确保用户只能访问到被分配的资源 而前端权限归根结底是请求的发起权,…...
Docker部署springcloud项目(清晰明了)
概述 最近在想做个cloud项目,gitee上找了个模板项目,后端使用到 Nacos、Gateway、Security等技术,需要到 Docker 容器部署,在此总结一下,若有不足之处,望大佬们可以指出。 什么是 Docker Docker 使用 Google 公司推…...
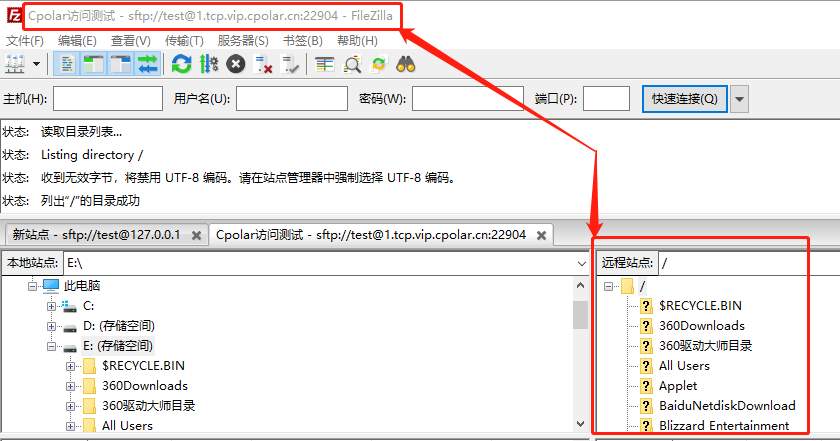
搭建SFTP服务安全共享文件,实现在外远程访问「内网穿透」
文章目录1.前言2.本地SFTP服务器搭建2.1.SFTP软件的下载和安装2.2.配置SFTP站点2.3.Cpolar下载和安装3.SFTP服务器的发布3.1.Cpolar云端设置3.2.Cpolar本地设置4.公网访问测试5.结语1.前言 现在的网络发达,个人电脑容量快速上升,想要保存的数据资料也越…...
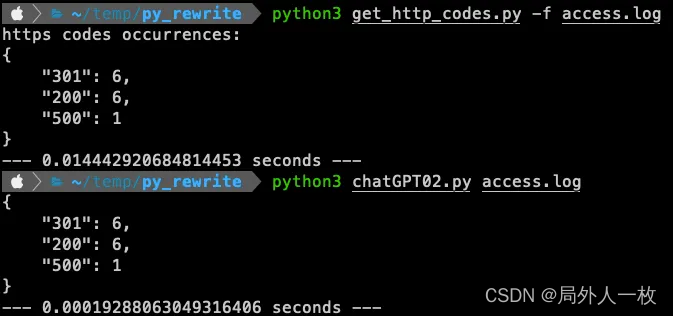
ChatGPT优化Python代码的小技巧
使用 chatGPT 优化代码并降低运行时的云成本 许多开发人员说“过早的优化是万恶之源”。 这句话的来源归功于Donald Knuth。在他的书《计算机编程的艺术》中,他写道: “真正的问题是,程序员在错误的时间和错误的地方花费了太多时间来担心效率…...
Stm32-使用TB6612驱动电机及编码器测速
这里写目录标题起因一、电机及编码器的参数二、硬件三、接线四、驱动电机1、TB6612电机驱动2、定时器的PWM模式驱动电机五、编码器测速1、定时器的编码器接口模式2、定时器编码器模式测速的原理3、编码器模式的配置4、编码器模式相关代码5、测速方法六、相关问题以及解答1、编码…...

【JS】常用js方法
1、判断是否是数组、字符串等方法a instanceof ba是你需要判断的数据b是判断的类型//直接判断原型 var a [1,5,8] var b 123456console.log(a instanceof Array)//true console.log(a instanceof String)//falseconsole.log(b instanceof String)//true2、分割字符串a.split(…...
Android---动态权限申请
目录 权限分类 动态权限核心函数 简易实现案例 完整代码 Google 在 Android 6.0 开始引入了权限申请机制,将所有权限分成了正常权限和危险权限。App 每次在使用危险权限时需要动态的申请并得到用户的授权才能使用。 权限分类 系统权限分为两类:正常…...

【Linux】环境变量(基本概念 常见环境变量 测试PATH 环境变量相关命令)
文章目录环境变量基本概念常见环境变量测试PATH别的环境变量通过系统调用获取或设置环境变量环境变量相关命令export: 设置一个新的环境变量set: 显示本地定义的shell变量和环境变量unset: 清除环境变量通过代码如何获取环境变量环境变量 基本概念 环境变量(environment vari…...
安全牛+瑞数信息:《数据安全管控平台应用指南》报告共同发布
随着《中华人民共和国网络安全法》《中华人民共和国数据安全法》《中华人民共和国个人信息保护法》和《关键信息基础设施安全保护条例》“三法一条例”的陆续发布,从国家、社会与个人已经逐步形成了加强数据安全保护的态势。 2023年1月中旬,工业和信息化…...
【洛谷刷题】蓝桥杯专题突破-深度优先搜索-dfs(6)
目录 写在前面: 题目:P1683 入门 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn) 题目描述: 输入格式: 输出格式: 输入样例: 输出样例: 解题思路: 代码: AC &a…...
论文解读TCPN
一、简要介绍视觉信息提取(VIE)近年来受到了越来越多的关注。现有的方法通常首先将光学字符识别(OCR)结果组织成纯文本,然后利用标记级实体注释作为监督来训练序列标记模型。但是,它花费大量的注释成本&…...

系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询优化策略
系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询分表策略 背景Solution --- 分表 背景 使用audit log实现Audi Trail功能 Audit Trail范围: 六个月数据量: 每秒5-7条audi log,共计7千万 – 1亿条数据需要实现全文检索按照时间倒序因为license问题,不能使用ELK只能使用…...

【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat
目录 【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat工具概述安装方式核心功能基础用法进阶操作实战案例面试题场景生产场景 注意事项 【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat 工具概述 iostat(I/O Statistics)是Linux系统下用于监视系统输入输出设备和CPU使…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院挂号小程序
一、开发准备 环境搭建: 安装DevEco Studio 3.0或更高版本配置HarmonyOS SDK申请开发者账号 项目创建: File > New > Create Project > Application (选择"Empty Ability") 二、核心功能实现 1. 医院科室展示 /…...
 自用)
css3笔记 (1) 自用
outline: none 用于移除元素获得焦点时默认的轮廓线 broder:0 用于移除边框 font-size:0 用于设置字体不显示 list-style: none 消除<li> 标签默认样式 margin: xx auto 版心居中 width:100% 通栏 vertical-align 作用于行内元素 / 表格单元格ÿ…...

大学生职业发展与就业创业指导教学评价
这里是引用 作为软工2203/2204班的学生,我们非常感谢您在《大学生职业发展与就业创业指导》课程中的悉心教导。这门课程对我们即将面临实习和就业的工科学生来说至关重要,而您认真负责的教学态度,让课程的每一部分都充满了实用价值。 尤其让我…...

Python ROS2【机器人中间件框架】 简介
销量过万TEEIS德国护膝夏天用薄款 优惠券冠生园 百花蜂蜜428g 挤压瓶纯蜂蜜巨奇严选 鞋子除臭剂360ml 多芬身体磨砂膏280g健70%-75%酒精消毒棉片湿巾1418cm 80片/袋3袋大包清洁食品用消毒 优惠券AIMORNY52朵红玫瑰永生香皂花同城配送非鲜花七夕情人节生日礼物送女友 热卖妙洁棉…...
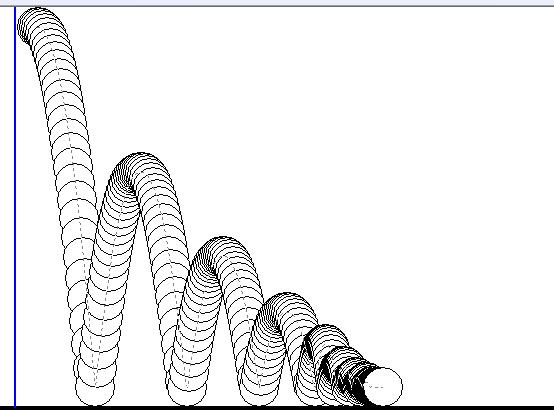
MFC 抛体运动模拟:常见问题解决与界面美化
在 MFC 中开发抛体运动模拟程序时,我们常遇到 轨迹残留、无效刷新、视觉单调、物理逻辑瑕疵 等问题。本文将针对这些痛点,详细解析原因并提供解决方案,同时兼顾界面美化,让模拟效果更专业、更高效。 问题一:历史轨迹与小球残影残留 现象 小球运动后,历史位置的 “残影”…...
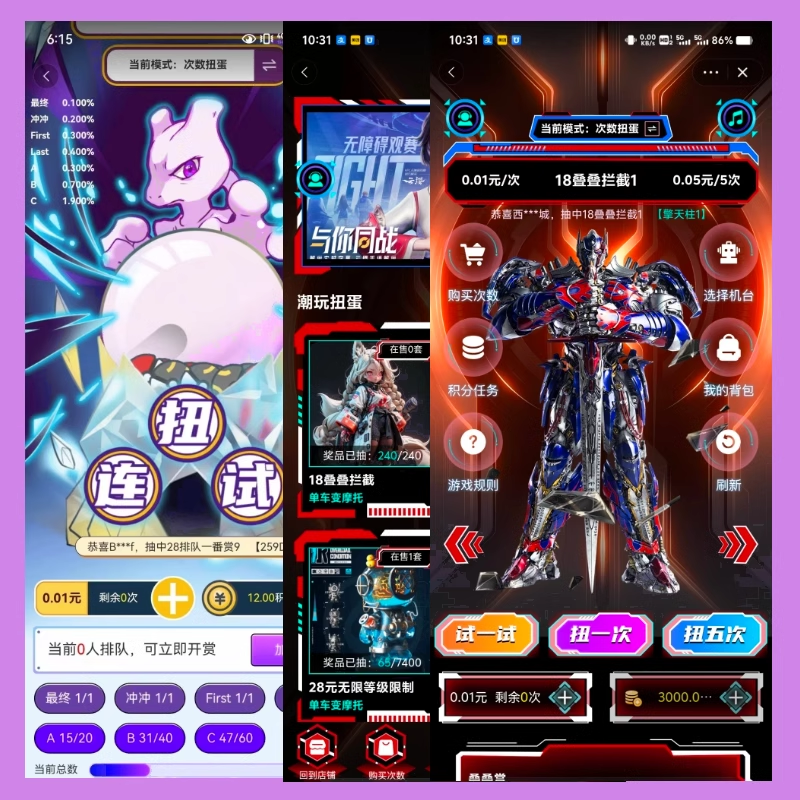
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统开发:打造互动性强的购物平台
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统的开发,旨在打造一个互动性强的购物平台,让用户在购物的同时,能够享受到更多的乐趣和惊喜。 淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统拥有丰富的互动功能。用户可以通过虚拟摇杆操作扭蛋机,实现旋转、抽拉等动作,增…...
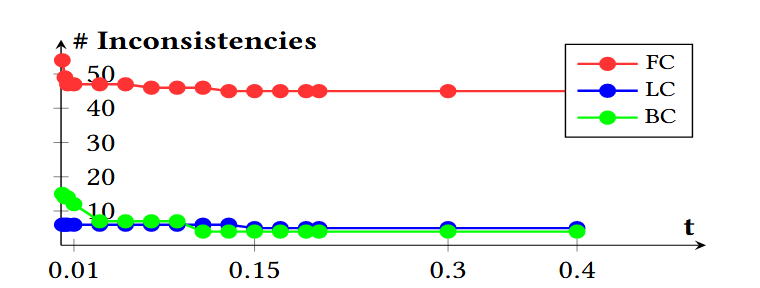
论文阅读笔记——Muffin: Testing Deep Learning Libraries via Neural Architecture Fuzzing
Muffin 论文 现有方法 CRADLE 和 LEMON,依赖模型推理阶段输出进行差分测试,但在训练阶段是不可行的,因为训练阶段直到最后才有固定输出,中间过程是不断变化的。API 库覆盖低,因为各个 API 都是在各种具体场景下使用。…...

实战三:开发网页端界面完成黑白视频转为彩色视频
一、需求描述 设计一个简单的视频上色应用,用户可以通过网页界面上传黑白视频,系统会自动将其转换为彩色视频。整个过程对用户来说非常简单直观,不需要了解技术细节。 效果图 二、实现思路 总体思路: 用户通过Gradio界面上…...
