Summer School science communication project--Laptop Selection Suggestion
目录
Introduction
Audiance
Usage
CPU
What is a central processing unit (CPU)
Notable makers of CPUs
GPU
Graphics Card: GPU
The classifications of graphics cards
The brands of graphics cards
Dedicated Graphics Cards
GeForce MX Series:
GeForce RTX Series:
GeForce GTX Series:
MEMORY
Capacity
Frequency
Channels
Timing
Hard Drive
HARDWARE
Screen
Casing
Thermal management
Battery
Ports
Laptop Selection Categories
Ultrabooks
Business Laptops
Gaming Laptops
SUGGESTION
Introduction
Audiance
Includes beginners, students, gamers, professionals, AI researchers, and anyone with a need to purchase a computer.
Usage
Before buying a laptop, people often look for detailed guides and comparisons to understand which model best suits their needs, budget, and preferences. Our blog can provide some insights into different laptop specifications, brands, and features which can help readers identify the best options within their budget.
CPU
What is a central processing unit (CPU)
A central processing unit (CPU) is the primary functional component of a computer. The CPU is an assemblage of electronic circuitry that run a computer’s operating system and apps and manage a variety of other computer operations.
A CPU is, essentially, the active brain of the computer. The CPU is the invisible manager inside the computer where data input is transformed into information output. It stores and executes program instructions through its vast networks of circuitry.
Like the human brain, the CPU can multitask. This means it is also the part of the computer that simultaneously regulates the computer’s internal functions, oversees power consumption, allocates computing resources and interfaces with various apps, programs and networks.
A central processing unit (CPU) is the primary functional component of a computer. The CPU is an assemblage of electronic circuitry that run a computer’s operating system and apps and manage a variety of other computer operations.
A CPU is, essentially, the active brain of the computer. The CPU is the invisible manager inside the computer where data input is transformed into information output. It stores and executes program instructions through its vast networks of circuitry.
Like the human brain, the CPU can multitask. This means it is also the part of the computer that simultaneously regulates the computer’s internal functions, oversees power consumption, allocates computing resources and interfaces with various apps, programs and networks.

Notable makers of CPUs
It’s sometimes assumed that since CPU technology is well established, it must be stagnant. However, there’s considerable evidence of continued innovation at work as new products are constantly created, all of them trying to offer the best CPU (or microprocessor) possible. The following companies repeatedly demonstrate that effort:
- Advanced Micro Devices (AMD): AMD has manufactured Ryzen microprocessors since its 2017 founding. Notable AMD Ryzen products (e.g., Ryzen 7, Ryzen 9) have been prized by video gamers for dependably delivering high-speed game action, while the Ryzen 5 1600 processor has scored well with those working in software development.
- Intel: Intel has been a leading name in computer chip production for decades, having begun producing chips in 1975. Processors like the Intel Core i5 (introduced in 2009) have shown perfect compatibility with programs that require more processing power, such as video editing programs and software development programs.
Intel: Steady Strength
As a veteran manufacturer in the field of computer processors, Intel has always been known for its stable performance and reliability.
Its Core series processors are widely used in home computers and are divided into four sub-series: i3, i5, i7 and i9, covering the mid-to-low-end, mainstream, high-end and flagship markets.
Intel processors have strong single-core performance, low power consumption, and high stability, making them suitable for scenarios with high single-thread performance requirements, such as games.
GPU
Graphics Card: GPU
For gaming image-intensive or network training tasks, choosing the right graphics card is crucial. If you frequently work with video editing, play demanding games, or use software like Photoshop, you'll need a good graphics card. A higher-quality GPU will enhance image processing capabilities and better support the CPU, improving overall system performance.

The classifications of graphics cards
Laptop graphics cards are generally classified into integrated and dedicated types:
- Integrated Graphics (IGP): Also known as onboard graphics, these are usually built into the CPU and offer lower performance. However, they have lower power consumption.
- Dedicated Graphics: These are separate graphics cards with better performance than integrated graphics. They are installed in a dedicated slot, making it easier to replace or upgrade them.
The brands of graphics cards
The main brands are NVIDIA and AMD. Currently, dedicated laptop graphics cards are primarily from NVIDIA, so this article will focus on NVIDIA products.

To help you choose, here’s an overview of NVIDIA’s naming conventions:
- Series Number: NVIDIA’s graphics cards are typically named with a series number, such as RTX 3080, where 30 represents the series and 80 indicates the performance tier within that series. Higher numbers generally denote better performance.
- Suffixes: Suffixes after the model number indicate specific variants, such as:
- Ti: Performance-enhanced version (e.g., RTX 3060 Ti).
- Super: Slightly improved performance version (e.g., RTX 2070 Super).
- Max-Q: Low-power version of the graphics card for laptops, suitable for thin and light laptops.
Dedicated Graphics Cards
-
GeForce MX Series:
- Target Users: Daily office tasks, ultra-portable users, lightweight graphic work.
- MX550: Provides better performance than integrated graphics, suitable for light graphic tasks and basic gaming.
- MX450: An older model, still suitable for budget-conscious users needing slightly better performance than integrated graphics.
- Thin and Light Laptops: Max-Q design graphics cards are suitable for users who want high performance in a thin and light laptop. These cards have lower power consumption and optimized cooling designs, balancing portability and performance.
- Gaming Laptops: For users prioritizing performance over portability, standard RTX graphics cards usually offer higher performance and better cooling management.
GeForce RTX Series:
- Target Users: Gamers, content creators, designers.
- RTX 4090, 4080, 4070 Ti: Top-tier graphics cards with the highest graphics processing power.
- RTX 3080, 3070: Offers good value for money, suitable for 2K or high frame rate 1080p gaming.
- RTX 3060 Ti, 3060: Mainstream cards, suitable for 1080p high settings games and some 2K games.
GeForce GTX Series:
- Target Users: Budget-conscious gamers and general users.
- GTX 1650, 1650 Ti: Commonly found in light gaming laptops, suitable for 1080p medium to high settings games.
- GTX 1660 Ti: Better performance than the GTX 1650 series, suitable for users with slightly higher performance needs.
MEMORY
The operation of a computer is much like a logistics system: when we start up the computer and open an application (such as a game), the application is typically stored on the hard drive. However, the processor doesn't directly read from the hard drive. Instead, the application is first loaded into memory. The processor then reads data from memory, and our interactions with the application are not directly sent to the hard drive. They are first transmitted to memory, which then communicates with the hard drive.
To help you better understand, you can think of the workings of computer memory as akin to a logistics system.

We users are like programs running on a computer. Memory acts as the courier, while the hard drive serves as the warehouse storing the packages (programs) we need. When we need a package, we don't go directly to the warehouse but rely on the courier to deliver it to us. Similarly, when we send a package, we don't go straight to the warehouse; instead, we contact the courier to come pick it up, and then it gets sent out from the warehouse.
Now, some might wonder: Why doesn't the processor connect directly to the hard drive and instead involve this memory "middleman"? Well, with the current speed of hard drives typically measured in MB, how could they compare to the speed of memory measured in GB?
Now let's talk about several key parameters of memory: capacity, frequency, channels, and timings.

Capacity
Memory capacity refers to the amount of data that a memory module can store. Continuing with the courier analogy, capacity is like the size of a courier's delivery vehicle. The larger the vehicle, the more packages it can deliver at once. In the context of computers, larger memory capacity allows for more programs to run simultaneously. This explains why many users experience lag when running multiple programs—the courier's delivery vehicle is too small, causing delays in delivering all the packages at once. It's better to buy more capacity within budget constraints, even if it means having more performance than needed. Currently, mainstream configurations typically include 16GB of memory. For gamers or those with high productivity demands (especially in design, editing, or modeling), it's advisable to go for 32GB or more. Also, after deciding on capacity, consider dual-channel configurations whenever possible, as mentioned earlier.
Frequency
Memory frequency refers to the clock speed of the memory, essentially its operating speed. Higher frequencies indicate faster data transfer rates. Using the courier analogy, this is like the speed of the courier's delivery vehicle. Would you prefer a courier on a bicycle or one in a car for faster deliveries? Obviously, the car, as it gets the packages to you more quickly. Currently, mainstream DDR4 memory frequencies include 3200, 3600, and 4000MHz; DDR5 includes 6000, 6400, and 6800MHz. Therefore, when purchasing memory, it's recommended not to buy DDR4 memory modules below 3200MHz in frequency or DDR5 modules below 6000MHz.
Channels
Memory channels refer to the physical connection pathways between memory modules and the memory controller on the motherboard. Multiple channels provide greater bandwidth, improving data transfer speeds. Using the courier analogy again, if two couriers can deliver the same number of packages, they will be faster than a single courier. Therefore, if possible, prioritize dual-channel or quad-channel configurations.
Timing
Memory timing refers to the access and response times of the memory. Lower timings indicate lower latency, meaning faster access and response times. This is akin to the courier's efficiency—the better their abilities, the more agile they are in delivering packages quickly to users. Memory timings are generally expressed on manufacturer websites as "CL-XX," where common DDR4 timings include CL14, CL16, CL18, and CL20. CL14 represents top-tier timing, CL16 is excellent, while CL18 and CL20 are common and ordinary timings. It's advisable not to purchase DDR4 memory with timings higher than CL20 or DDR5 memory with timings higher than CL38. High timings can lead to performance bottlenecks, indicating lower-quality memory chips.
To help you grasp these concepts better, here's a mind map for your reference:

Hard Drive
Capacity:
Generally speaking, the larger the capacity of a hard drive, the more files and data it can store, but the price will also be higher. If using a solid-state drive as a system drive to store a small amount of operating system and commonly used software, then 128GB or 256GB of capacity is usually sufficient; if you need to store a large number of files, games, or engage in professional tasks like image or video editing, then opting for a larger capacity (such as 1TB or 2TB) would be more suitable. If you are unsure about the capacity or prefer a one-time purchase, going for a larger capacity directly would be a better choice.
Flash Memory Chips:
The core of a solid-state drive lies in the flash memory chips, whose quality directly impacts user experience. They are mainly divided into four types: SLC, MLC, TLC, QLC.
SLC offers the fastest transfer speeds and longer lifespan, but it is very expensive and has small capacities, generally used in commercial or military settings and rarely found on the market.
MLC's performance and lifespan are second only to SLC, making it suitable for home use and data centers, although it has become rare in the market in recent years.
TLC is currently the mainstream in the solid-state drive market, offering a balanced mix of performance, lifespan, and price. The industry has now fully transitioned to consumer-grade and data center TLC chips. For consumers, choosing TLC is sufficient for daily gaming or office tasks, offering better value for money.
QLC is not yet mature, with lower read/write lifespans. Industry users and data centers completely avoid QLC. Furthermore, QLC is priced similarly to TLC but offers lackluster performance, making it not recommended. For everyday use, opting for TLC chips is the way to go.
Interfaces and Protocols Determine Speed:
Before purchasing a solid-state drive, it is important to first confirm the interface supported by your motherboard. Failure to do so could result in reduced speeds or even the drive being unusable. Common interfaces include SATA, M.2 (which has strong compatibility, supporting both SATA and NVMe channels), and PCIe interfaces.

The M.2 interface is further divided into M.2 SATA and M.2 NVMe, with M.2 NVMe supporting high-speed SSDs that utilize the NVMe protocol and run through the PCIe channel. Within M.2 NVMe solid-state drives, there are two interface protocols: PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0.
Currently, the theoretical maximum speed of the SATA bus is 600MB/s, while the PCIe 3.0 bus has a maximum speed of 4GB/s, and PCIe 4.0 reaches a maximum speed of 8GB/s. It can be said that M.2 NVMe SSDs, in terms of speed and performance, are more than twice as fast as standard SSDs using the SATA interface.
For those building a new computer, it is advisable to opt for an NVMe M.2 solid-state drive utilizing the PCIe 3.0 protocol. If the budget allows, consider upgrading to PCIe 4.0. In the case of upgrading an older computer (where the motherboard does not support M.2 interfaces), selecting a SATA solid-state drive is a viable option.
HARDWARE
Screen

1. Resolution: The resolution refers to the number of pixels arranged vertically and horizontally on a screen. For example, a common resolution for laptop screens is 1920x1080, which means there are 1920 pixels horizontally and 1080 pixels vertically. The more pixels a screen has, the more detailed the image will appear to the human eye. Common laptop screen resolutions include 1920x1080, 2560x1440, 2560x1600, 3840x2160, etc.
2. Color Gamut: The color gamut indicates the range of colors a screen can display. There are several standard color gamuts, including sRGB (Standard Red Green Blue), DCI-P3 (which includes more colors than sRGB, particularly in the red and green areas), and Adobe RGB (which encompasses a broader range of colors compared to sRGB, especially in the green and cyan regions).
3. Brightness: Brightness refers to the maximum light intensity of the screen. Common laptop screens have a brightness of around 300 nits, while some high-end screens can reach 400 or 500 nits. Screens with brightness over 400 nits provide better visibility in outdoor conditions. For users working outdoors or in bright environments, it is crucial to consider the screen's brightness specification.
4. Refresh Rate: Refresh rate indicates the number of frames displayed per second on the screen. A higher refresh rate provides smoother performance during gaming and web browsing. Common refresh rates for laptop screens include 60Hz, 90Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz, 300Hz, etc. Gamers should aim for a screen with at least a 120Hz refresh rate, while a 60Hz refresh rate is generally sufficient for daily office tasks. If the budget allows, higher refresh rates are preferable.
Casing
1. Plastic Casing:
ABS Plastic: Common in mid-range and lower-end laptops, it is cost-effective and provides basic protection but can easily show fingerprints.
Polycarbonate (PC): Stronger and more impact-resistant than ABS, typically used in mid-range to high-end laptops.
Polymer Composites: Made from high polymer materials and additives, usually more durable than regular plastics, commonly found in high-end models.
2. Metal Casing:
Aluminum Alloy: Lightweight and sturdy, often used in high-end laptops, with good heat dissipation properties.
Magnesium Alloy: Lighter and stronger than aluminum alloy, commonly found in high-end laptops.
Stainless Steel: Less common, but used in some specific models, offering higher durability and a premium feel.
3. Carbon Fiber Casing:
Carbon Fiber Composite: Extremely strong and lightweight, used in ultra-high-end or professional-grade laptops, providing excellent durability and portability.
Thermal management
Thermal management has a direct impact on the performance and overall experience of a laptop. Poor cooling can prevent the CPU and GPU from effectively dissipating heat, leading to thermal throttling. As a result, the CPU and GPU will reduce their performance to avoid overheating, causing noticeable lag.

1. Fan Cooling
Fan: Most laptops are equipped with internal fans to expel hot air from inside the laptop. The fan typically works in conjunction with a heatsink to aid in cooling.
Heatsink: The fan is usually paired with a heatsink (often made of aluminum or copper). The heatsink’s role is to increase the surface area for heat dissipation, making it more effective at transferring heat to the airflow generated by the fan.
2. Heat Pipes
Heat Pipe: A heat pipe is a sealed tube filled with a liquid that has good thermal conductivity. In the working principle of a heat pipe, the liquid evaporates at the hot part, transferring heat to the cooler part, where it then condenses, forming a cycle. This method effectively transfers heat from the heat source to the heatsink or fan.
3. Liquid Metal Cooling
Liquid Metal Thermal Paste: Liquid metal (such as gallium-indium alloy) has extremely high thermal conductivity and is used as a replacement for traditional thermal paste to enhance cooling efficiency. Liquid metal is commonly used in high-end laptops and workstations.
4. Thermal Pads
Thermal Pads: Thermal pads are soft materials used to fill gaps between the heat source and the heatsink, aiding in heat transfer. They are typically made from silicone or other thermal conductive materials.
Battery
1. Battery Types:
Lithium-Ion Battery (Li-ion): The most common type of laptop battery, known for its high energy density and long lifespan. Frequently used in Windows laptops.
Lithium-Polymer Battery (Li-Po): Lighter and thinner than lithium-ion batteries, allowing for various shapes and sizes, typically used in ultra-thin laptops. Common in Apple laptops.
2. Battery Capacity:
Capacity (mAh or Wh): The capacity of the battery determines the laptop's battery life. Higher capacity generally means longer battery life. Typical laptop battery capacities range from 30Wh to 100Wh.
3. Battery Lifespan:
Cycle Life: Refers to the number of charge and discharge cycles the battery can undergo before losing a significant percentage of its capacity. Most laptop batteries have a cycle life between 300 and 1000 cycles.
4. Battery Charging:
Fast Charging: Some laptops support fast charging technology, allowing for quicker charging within a shorter time frame.
USB-C Charging: An increasing number of laptops support charging through USB-C ports, simplifying the charging process and making chargers more universal.
Ports

Common Port Types:
1. USB Ports:
USB 2.0: Provides a transfer speed of 480 Mbps.
USB 3.0/3.1/3.2: Offers faster data transfer speeds compared to USB 2.0, commonly used for high-performance peripherals. Transfer speed up to 5 Gbps.
2. HDMI:
HDMI: Used to connect the laptop to monitors, TVs, or projectors, supporting high-definition video and audio transmission.
3. Audio Ports:
Headphone/Microphone Jack: Typically a 3.5mm jack used for connecting headphones, microphones, or other audio devices.
3. Network Ports:
Ethernet (RJ-45): Used for wired network connections, commonly used in scenarios requiring stable network connections.
Wi-Fi: Wireless network interface; modern laptops support various Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) and Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax).
4. Power Ports:
Traditional Power Port: Used to connect the laptop to a power adapter.
Laptop Selection Categories
When looking to choose a cost-effective laptop, the first thing to consider is your primary use. Only by clarifying your functional needs can you find the corresponding type of laptop, and then select the one that you think is the best within that category.
Ultrabooks
Ultrabooks are compact and aesthetically pleasing, with screen sizes ranging from 14 to 15.6 inches and a weight not exceeding 2Kg. Due to their reduced size, there is no need to overly pursue performance and functionality. A moderate configuration can meet daily usage needs, but the key is that they are more portable for travel.

Business Laptops
Security and stability are the foundations of business laptops, ensuring the safety of users' data and improving work efficiency. They also require a simple and elegant appearance that fits the aesthetics of business people, with excellent portability. In terms of performance, they should be balanced, stable, safe, and user-friendly.[The business version is a little heavier than the thin version, more drop resistant to high temperatures, and has more space to add memory and hard disk

Gaming Laptops
These are laptops that focus on gaming performance and must have hardware configurations that meet certain gaming standards, such as high-performance CPUs, dedicated graphics cards, 2K resolution, and ultra-high refresh rate screens. Additionally, because gaming generates a lot of heat, their cooling performance is also crucial. Moreover, they also have strong productivity capabilities, providing better support for code programming and video editing.
【Can provide users with audio and video entertainment experience】

1.800-1000 euros is the purchase range of most people, if the unit price is more than 1500 euros, this laptop should be able to meet the appearance, performance, endurance, heat dissipation capacity. Even if it's a little weak, how weak is it
2. Demand budget first, demand second. When your budget is met, your needs will be met. It's like the boss asking why you don't take the initiative to work overtime: 3,000 yuan is the sale of labor, the sale of soul and dignity is not this price! There are also some bloggers who recommend the game book, and it is not entirely unreasonable. Games are not necessarily the best way to test computer performance, but they are the most intuitive way. It's really difficult to author: programmers reference:

SUGGESTION
Pre-Purchase Research: Before buying a laptop, people often look for detailed guides and comparisons to understand which model best suits their needs, budget, and preferences. A blog can provide insights into different laptop specifications, brands, and features.
Tech Reviews: Many people rely on blogs for reviews of the latest laptop models. These reviews can offer real-world performance assessments, pros and cons, and expert opinions, helping potential buyers make an informed decision.
Comparisons and Recommendations: Blogs can compare various laptops side-by-side, highlighting differences in performance, price, and features. This helps readers identify the best options within their budget.
Troubleshooting and Tips: After purchase, users might seek blogs for troubleshooting tips, maintenance advice, and ways to optimize their laptop's performance.
Trends and Innovations: Keeping up with the latest trends and innovations in laptop technology can be important for tech enthusiasts and professionals. Blogs often cover new developments and future trends in the laptop industry.
Join a community of tech enthusiasts and readers. Engage with our content, leave comments, and participate in discussions to share experiences and learn from others.
相关文章:

Summer School science communication project--Laptop Selection Suggestion
目录 Introduction Audiance Usage CPU What is a central processing unit (CPU) Notable makers of CPUs GPU Graphics Card: GPU The classifications of graphics cards The brands of graphics cards Dedicated Graphics Cards GeForce MX Series: GeForc…...

网络编程概念详解模拟回显客户端服务器
目录 1.网络中重要的概念 1)IP地址: 2)端口号: 3)协议 协议分层 OSI七层模型(教科书) TCP/IP五层模型 封装和分用 网络套接字 面试题:TCP/UDP的区别? UDP数据报套接字编程 模拟一个回…...
)
代码随想录第二十四天|动态规划(8)
目录 LeetCode 300. 最长递增子序列 LeetCode 674. 最长连续递增序列 LeetCode 718. 最长重复子数组 LeetCode 1143. 最长公共子序列 LeetCode 1035. 不相交的钱 LeetCode 53. 最大子序和 LeetCode 392. 判断子序列 总结 LeetCode 300. 最长递增子序列 题目链接&#…...

编程-设计模式 3:单例模式
设计模式 3:单例模式 定义与目的 定义:单例模式确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点来访问该实例。目的:这种模式通常用于那些需要频繁访问且只需一个实例的对象,例如配置管理器、日志记录器等。 实现示例…...

Kaniko 构建 Docker 镜像
Kaniko 主要用于构建 Docker 镜像,而不是运行程序。它的主要用途是从 Dockerfile 构建容器镜像,但它并不负责运行容器或程序。以下是 Kaniko 的主要功能和局限性: 主要功能 构建镜像:Kaniko 从 Dockerfile 构建容器镜像。它通过…...

Javascript常见算法(每日两个)
合并两个有序链表 在JavaScript中,合并两个有序链表通常指的是将两个已经按照某种顺序(如升序或降序)排列的链表合并成一个新的有序链表。由于JavaScript本身不直接支持链表数据结构,我们通常会用对象或数组来模拟链表的行为。但…...
Spring -- 事务
Spring中事务的操作分为两类:(1)编程式事务 – 手动写代码操作事务(2)声明式事务 – 利用注解开启事务和提交事务 1. 编程式事务 准备Controller RestController RequestMapping("/user") public class UserInfoController {Autowiredprivate UserInfoService use…...
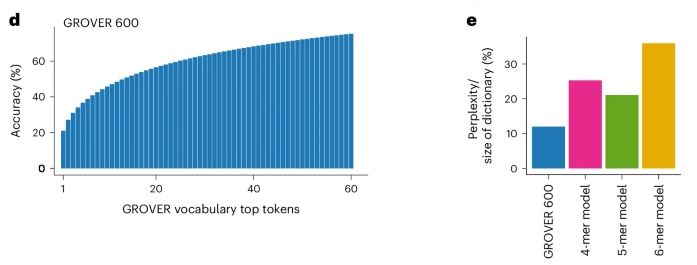
生命密码的破译者:AI如何学会读懂DNA语言?
引言 如果能像解读一本神秘的书籍那样,理解DNA的“语言”,将是多么令人兴奋的科学突破!如今,这正在逐步变为现实。科学家们训练出的AI模型GROVER正如一个勤奋的学生,学习着DNA的每一个“单词”和“语法”,…...

大数据信用报告查询哪家平台的比较好?
相信在搜索大数据信用的你,已经因为大数据信用不好受到了挫折,想详细了解一下自己的大数据信用,但是找遍了网络上的平台之后才发现,很多平台都只提供查询服务,想要找一个专业的平台查询和讲解很困难。下面本文就为大家…...

Java高级Day24-集合最后补充
75.HashTable 基本介绍: 存放元素的健值对 即K-V hashtable的键和值都不能为null,否则会抛出NullPointerException hashtable使用方法基本上和HashMap一样 hashtable是线程安全的,hashmap是线程不安全 扩容机制: 底层有数组…...

C++入门:C语言到C++的过渡
前言:C——为弥补C缺陷而生的语言 C起源于 1979 年,当时 Bjarne Stroustrup 在贝尔实验室工作,面对复杂软件开发任务,他感到 C 语言在表达能力、可维护性和可扩展性方面存在不足。 1983 年,Bjarne Stroustrup 在 C 语言…...

了解MVCC
概念 MVCC,全称Multi-Version Concurrency Control,即多版本并发控制,是一种并发控制的方法,维护一个数据的多个版本,使得读写操作没有冲突,快照读为MySQL实现MVCC提供了一个非阻塞读功能。MVCC的具体实现…...

WPF自定义控件的应用(DynamicResource的使用方法)
1 DynamicResource的使用方法 可以在字典文件 的抬头区写入数: <SolidColorBrush x:Key"PrimaryBackgroundColor" Color"#FFABAdB3"/><SolidColorBrush x:Key"TextBox.MouseOver.Border" Color"#FF7EB4EA"/>&l…...

Postgresql数据库密码忘记的解决
当您忘记PostgreSQL数据库的密码时,可以通过以下步骤来重置密码。这些步骤在Windows和Linux操作系统上大体相同,但具体操作路径和命令可能有所不同。 步骤一:找到并修改pg_hba.conf文件 定位安装目录: Windows:通常在PostgreSQL的安装目录下的data文件夹中。Linux:位置可…...

Flink SQL 基础操作
Flink SQL是建立在Apache Flink之上的SQL处理引擎,它允许用户以SQL的方式处理流数据和批数据。以下是一些Flink SQL的基础操作: 一、环境准备 1.启动flink集群 ./start-cluster.sh启动sql-client ./sql-client.sh二、数据源定义 创建表(…...

海思AE模块Lines_per_500ms参数的意义
基础知识 1秒(S)1000毫秒(ms)1000_000微妙(s)1000_000_000纳秒(ns) 1GHz1000Mhz1000_000KHz1000_000_000Hz 1Hz1/s 抗频闪原理 海思AE模块参数中有一个LinesPer500ms的参数,意思为500ms对应的曝光行数。此个参数和抗频闪有关。 我们知道: 50HZ…...

【代码随想录】区间和——前缀和方法
本博文为《代码随想录》学习笔记,原文链接:代码随想录 题目 原题链接:58. 区间和(第九期模拟笔试) 题目描述 给定一个整数数组 Array,请计算该数组在每个指定区间内元素的总和。 输入描述 第一行输入为…...

Bug 解决 | 前端项目无法正确安装依赖?
目录 1、网络问题 2、权限问题 3、版本冲突 4、缓存问题 5、依赖配置错误 6、系统环境问题 前端项目和后端项目一样,都需要用到很多第三方的类库依赖。目前基本上我们主流的前端项目都使用 Npm、Yarn 等包管理工具来管理项目依赖,正常情况下通过执…...

【mysql 第四篇章】bin log 的作用是啥呢?
一、redo Log 介绍 redo log 是一种偏向物理性质的重做日志,因为他里面记录类似的这样的东西,“对那个数据也中的什么记录,做了个什么修改”。它是 InnoDB 存储引擎特有的东西。 二、bin Log 日志 bin log 叫做归档日志,它里面…...

Linux 操作系统:基于环形队列的生产者消费者模型
Linux 操作系统:基于环形队列的生产者消费者模型 一、前言二、大致框架二、P操作、V操作三、生产者生产数据四、生产者获取数据五、代码测试六、所有代码 一、前言 环形队列采用数组模拟,用模运算来模拟环状特性。和基于阻塞队列的生产者消费者模型不同的…...

华为云AI开发平台ModelArts
华为云ModelArts:重塑AI开发流程的“智能引擎”与“创新加速器”! 在人工智能浪潮席卷全球的2025年,企业拥抱AI的意愿空前高涨,但技术门槛高、流程复杂、资源投入巨大的现实,却让许多创新构想止步于实验室。数据科学家…...

【杂谈】-递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战
递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战 文章目录 递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战1、自我改进型人工智能的崛起2、人工智能如何挑战人类监管?3、确保人工智能受控的策略4、人类在人工智能发展中的角色5、平衡自主性与控制力6、总结与…...
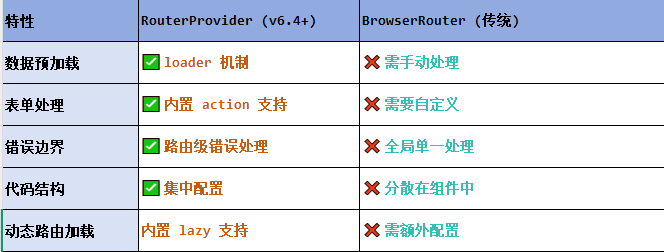
React第五十七节 Router中RouterProvider使用详解及注意事项
前言 在 React Router v6.4 中,RouterProvider 是一个核心组件,用于提供基于数据路由(data routers)的新型路由方案。 它替代了传统的 <BrowserRouter>,支持更强大的数据加载和操作功能(如 loader 和…...
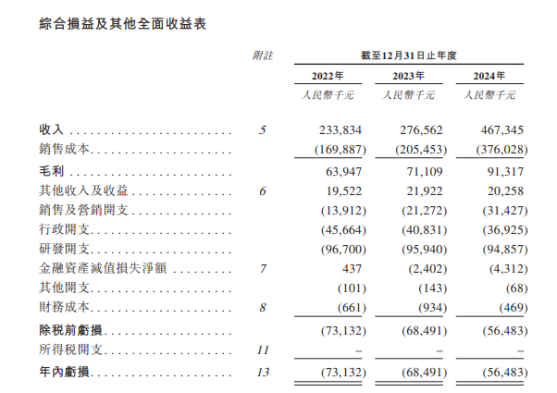
从深圳崛起的“机器之眼”:赴港乐动机器人的万亿赛道赶考路
进入2025年以来,尽管围绕人形机器人、具身智能等机器人赛道的质疑声不断,但全球市场热度依然高涨,入局者持续增加。 以国内市场为例,天眼查专业版数据显示,截至5月底,我国现存在业、存续状态的机器人相关企…...

智能在线客服平台:数字化时代企业连接用户的 AI 中枢
随着互联网技术的飞速发展,消费者期望能够随时随地与企业进行交流。在线客服平台作为连接企业与客户的重要桥梁,不仅优化了客户体验,还提升了企业的服务效率和市场竞争力。本文将探讨在线客服平台的重要性、技术进展、实际应用,并…...
1.3 VSCode安装与环境配置
进入网址Visual Studio Code - Code Editing. Redefined下载.deb文件,然后打开终端,进入下载文件夹,键入命令 sudo dpkg -i code_1.100.3-1748872405_amd64.deb 在终端键入命令code即启动vscode 需要安装插件列表 1.Chinese简化 2.ros …...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...
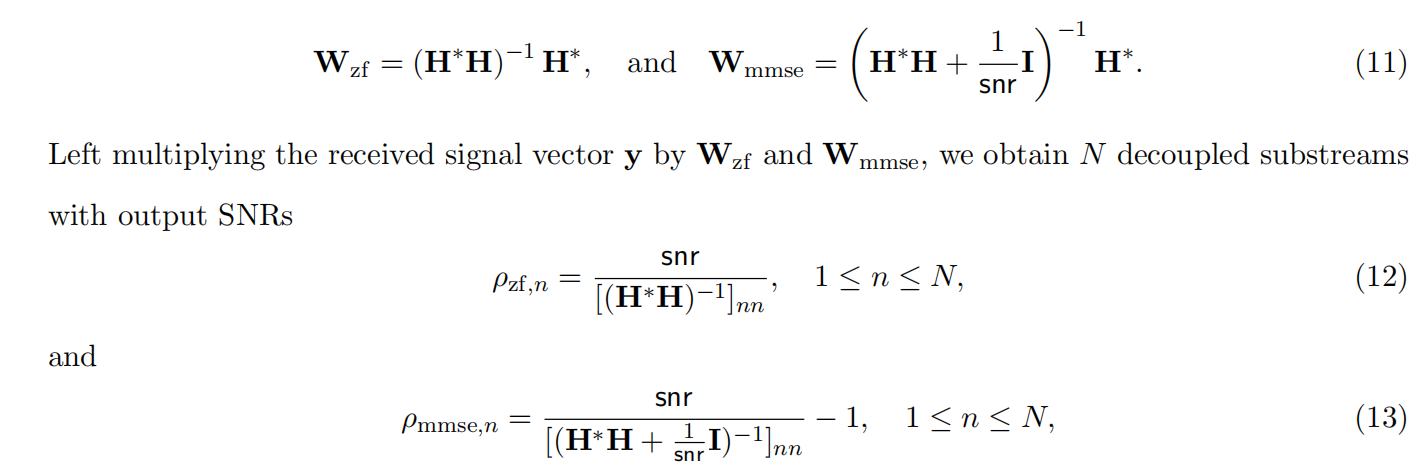
均衡后的SNRSINR
本文主要摘自参考文献中的前两篇,相关文献中经常会出现MIMO检测后的SINR不过一直没有找到相关数学推到过程,其中文献[1]中给出了相关原理在此仅做记录。 1. 系统模型 复信道模型 n t n_t nt 根发送天线, n r n_r nr 根接收天线的 MIMO 系…...
)
Typeerror: cannot read properties of undefined (reading ‘XXX‘)
最近需要在离线机器上运行软件,所以得把软件用docker打包起来,大部分功能都没问题,出了一个奇怪的事情。同样的代码,在本机上用vscode可以运行起来,但是打包之后在docker里出现了问题。使用的是dialog组件,…...
给网站添加live2d看板娘
给网站添加live2d看板娘 参考文献: stevenjoezhang/live2d-widget: 把萌萌哒的看板娘抱回家 (ノ≧∇≦)ノ | Live2D widget for web platformEikanya/Live2d-model: Live2d model collectionzenghongtu/live2d-model-assets 前言 网站环境如下,文章也主…...
