<C++> set、map模拟实现
目录
一、适配器红黑树
二、红黑树再设计
1. 重新设计 RBTree 的模板参数
2. 仿函数模板参数
3. 正向迭代器
构造
operator*()
operator->()
operator!=()
operator++()
operator--()
正向迭代器代码
4. 反向迭代器
构造
operator*
operator->
operator++
operator--
operator!=
反向迭代器代码
5. 红黑树主体
begin()、end()、
rbegin()、rend()
insert 返回值
find返回值
STL标准库设计
6. 再设计后完整的RBTree代码
三、set、map封装
1. set基础封装
2. map基础封装
3. insert
4. map::operator[]
5. find
6. erase
7. 测试
一、适配器红黑树
STL在封装set、map时,直接适配了RBTree——红黑树,这里的红黑树相较上文我们的红黑树,这里实现了构造、拷贝构造、赋值运算符重载、析构、删除节点等函数
//枚举定义结点的颜色
enum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};//红黑树结点的定义
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{//三叉链RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;//存储的键值对pair<K, V> _kv;//结点的颜色int _col; //红/黑//构造函数RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _kv(kv), _col(RED){}
};//红黑树的实现
template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public://构造函数RBTree():_root(nullptr){}//拷贝构造RBTree(const RBTree<K, V>& t){_root = _Copy(t._root, nullptr);}//赋值运算符重载(现代写法)RBTree<K, V>& operator=(RBTree<K, V> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}//析构函数~RBTree(){_Destroy(_root);_root = nullptr;}//查找函数Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (key < cur->_kv.first) //key值小于该结点的值{cur = cur->_left; //在该结点的左子树当中查找}else if (key > cur->_kv.first) //key值大于该结点的值{cur = cur->_right; //在该结点的右子树当中查找}else //找到了目标结点{return cur; //返回该结点}}return nullptr; //查找失败}//插入函数pair<Node*, bool> Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (_root == nullptr) //若红黑树为空树,则插入结点直接作为根结点{_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK; //根结点必须是黑色return make_pair(_root, true); //插入成功}//1、按二叉搜索树的插入方法,找到待插入位置Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first) //待插入结点的key值小于当前结点的key值{//往该结点的左子树走parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first) //待插入结点的key值大于当前结点的key值{//往该结点的右子树走parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else //待插入结点的key值等于当前结点的key值{return make_pair(cur, false); //插入失败}}//2、将待插入结点插入到树中cur = new Node(kv); //根据所给值构造一个结点Node* newnode = cur; //记录新插入的结点(便于后序返回)if (kv.first < parent->_kv.first) //新结点的key值小于parent的key值{//插入到parent的左边parent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}else //新结点的key值大于parent的key值{//插入到parent的右边parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}//3、若插入结点的父结点是红色的,则需要对红黑树进行调整while (parent&&parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent; //parent是红色,则其父结点一定存在if (parent == grandfather->_left) //parent是grandfather的左孩子{Node* uncle = grandfather->_right; //uncle是grandfather的右孩子if (uncle&&uncle->_col == RED) //情况1:uncle存在且为红{//颜色调整parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else //情况2+情况3:uncle不存在 + uncle存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather); //右单旋//颜色调整grandfather->_col = RED;parent->_col = BLACK;}else //cur == parent->_right{RotateLR(grandfather); //左右双旋//颜色调整grandfather->_col = RED;cur->_col = BLACK;}break; //子树旋转后,该子树的根变成了黑色,无需继续往上进行处理}}else //parent是grandfather的右孩子{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left; //uncle是grandfather的左孩子if (uncle&&uncle->_col == RED) //情况1:uncle存在且为红{//颜色调整uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else //情况2+情况3:uncle不存在 + uncle存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_left){RotateRL(grandfather); //右左双旋//颜色调整cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else //cur == parent->_right{RotateL(grandfather); //左单旋//颜色调整grandfather->_col = RED;parent->_col = BLACK;}break; //子树旋转后,该子树的根变成了黑色,无需继续往上进行处理}}}_root->_col = BLACK; //根结点的颜色为黑色(可能被情况一变成了红色,需要变回黑色)return make_pair(newnode, true); //插入成功}//删除函数bool Erase(const K& key){//用于遍历二叉树Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;//用于标记实际的待删除结点及其父结点Node* delParentPos = nullptr;Node* delPos = nullptr;while (cur){if (key < cur->_kv.first) //所给key值小于当前结点的key值{//往该结点的左子树走parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (key > cur->_kv.first) //所给key值大于当前结点的key值{//往该结点的右子树走parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else //找到了待删除结点{if (cur->_left == nullptr) //待删除结点的左子树为空{if (cur == _root) //待删除结点是根结点{_root = _root->_right; //让根结点的右子树作为新的根结点if (_root){_root->_parent = nullptr;_root->_col = BLACK; //根结点为黑色}delete cur; //删除原根结点return true;}else{delParentPos = parent; //标记实际删除结点的父结点delPos = cur; //标记实际删除的结点}break; //进行红黑树的调整以及结点的实际删除}else if (cur->_right == nullptr) //待删除结点的右子树为空{if (cur == _root) //待删除结点是根结点{_root = _root->_left; //让根结点的左子树作为新的根结点if (_root){_root->_parent = nullptr;_root->_col = BLACK; //根结点为黑色}delete cur; //删除原根结点return true;}else{delParentPos = parent; //标记实际删除结点的父结点delPos = cur; //标记实际删除的结点}break; //进行红黑树的调整以及结点的实际删除}else //待删除结点的左右子树均不为空{//替换法删除//寻找待删除结点右子树当中key值最小的结点作为实际删除结点Node* minParent = cur;Node* minRight = cur->_right;while (minRight->_left){minParent = minRight;minRight = minRight->_left;}cur->_kv.first = minRight->_kv.first; //将待删除结点的key改为minRight的keycur->_kv.second = minRight->_kv.second; //将待删除结点的value改为minRight的valuedelParentPos = minParent; //标记实际删除结点的父结点delPos = minRight; //标记实际删除的结点break; //进行红黑树的调整以及结点的实际删除}}}if (delPos == nullptr) //delPos没有被修改过,说明没有找到待删除结点{return false;}//记录待删除结点及其父结点(用于后续实际删除)Node* del = delPos;Node* delP = delParentPos;//调整红黑树if (delPos->_col == BLACK) //删除的是黑色结点{if (delPos->_left) //待删除结点有一个红色的左孩子(不可能是黑色){delPos->_left->_col = BLACK; //将这个红色的左孩子变黑即可}else if (delPos->_right) //待删除结点有一个红色的右孩子(不可能是黑色){delPos->_right->_col = BLACK; //将这个红色的右孩子变黑即可}else //待删除结点的左右均为空{while (delPos != _root) //可能一直调整到根结点{if (delPos == delParentPos->_left) //待删除结点是其父结点的左孩子{Node* brother = delParentPos->_right; //兄弟结点是其父结点的右孩子//情况一:brother为红色if (brother->_col == RED){delParentPos->_col = RED;brother->_col = BLACK;RotateL(delParentPos);//需要继续处理brother = delParentPos->_right; //更新brother(否则在本循环中执行其他情况的代码会出错)}//情况二:brother为黑色,且其左右孩子都是黑色结点或为空if (((brother->_left == nullptr) || (brother->_left->_col == BLACK))&& ((brother->_right == nullptr) || (brother->_right->_col == BLACK))){brother->_col = RED;if (delParentPos->_col == RED){delParentPos->_col = BLACK;break;}//需要继续处理delPos = delParentPos;delParentPos = delPos->_parent;}else{//情况三:brother为黑色,且其左孩子是红色结点,右孩子是黑色结点或为空if ((brother->_right == nullptr) || (brother->_right->_col == BLACK)){brother->_left->_col = BLACK;brother->_col = RED;RotateR(brother);//需要继续处理brother = delParentPos->_right; //更新brother(否则执行下面情况四的代码会出错)}//情况四:brother为黑色,且其右孩子是红色结点brother->_col = delParentPos->_col;delParentPos->_col = BLACK;brother->_right->_col = BLACK;RotateL(delParentPos);break; //情况四执行完毕后调整一定结束}}else //delPos == delParentPos->_right //待删除结点是其父结点的左孩子{Node* brother = delParentPos->_left; //兄弟结点是其父结点的左孩子//情况一:brother为红色if (brother->_col == RED) //brother为红色{delParentPos->_col = RED;brother->_col = BLACK;RotateR(delParentPos);//需要继续处理brother = delParentPos->_left; //更新brother(否则在本循环中执行其他情况的代码会出错)}//情况二:brother为黑色,且其左右孩子都是黑色结点或为空if (((brother->_left == nullptr) || (brother->_left->_col == BLACK))&& ((brother->_right == nullptr) || (brother->_right->_col == BLACK))){brother->_col = RED;if (delParentPos->_col == RED){delParentPos->_col = BLACK;break;}//需要继续处理delPos = delParentPos;delParentPos = delPos->_parent;}else{//情况三:brother为黑色,且其右孩子是红色结点,左孩子是黑色结点或为空if ((brother->_left == nullptr) || (brother->_left->_col == BLACK)){brother->_right->_col = BLACK;brother->_col = RED;RotateL(brother);//需要继续处理brother = delParentPos->_left; //更新brother(否则执行下面情况四的代码会出错)}//情况四:brother为黑色,且其左孩子是红色结点brother->_col = delParentPos->_col;delParentPos->_col = BLACK;brother->_left->_col = BLACK;RotateR(delParentPos);break; //情况四执行完毕后调整一定结束}}}}}//进行实际删除if (del->_left == nullptr) //实际删除结点的左子树为空{if (del == delP->_left) //实际删除结点是其父结点的左孩子{delP->_left = del->_right;if (del->_right)del->_right->_parent = delP;}else //实际删除结点是其父结点的右孩子{delP->_right = del->_right;if (del->_right)del->_right->_parent = delP;}}else //实际删除结点的右子树为空{if (del == delP->_left) //实际删除结点是其父结点的左孩子{delP->_left = del->_left;if (del->_left)del->_left->_parent = delP;}else //实际删除结点是其父结点的右孩子{delP->_right = del->_left;if (del->_left)del->_left->_parent = delP;}}delete del; //实际删除结点return true;}private://拷贝树Node* _Copy(Node* root, Node* parent){if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_data);copyNode->_parent = parent;copyNode->_left = _Copy(root->_left, copyNode);copyNode->_right = _Copy(root->_right, copyNode);return copyNode;}//析构函数子函数void _Destroy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_Destroy(root->_left);_Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}//左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;//建立subRL与parent之间的联系parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;//建立parent与subR之间的联系subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;//建立subR与parentParent之间的联系if (parentParent == nullptr){_root = subR;_root->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == parentParent->_left){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = parentParent;}}//右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;//建立subLR与parent之间的联系parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;//建立parent与subL之间的联系subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;//建立subL与parentParent之间的联系if (parentParent == nullptr){_root = subL;_root->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == parentParent->_left){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}}//左右双旋void RotateLR(Node* parent){RotateL(parent->_left);RotateR(parent);}//右左双旋void RotateRL(Node* parent){RotateR(parent->_right);RotateL(parent);}Node* _root; //红黑树的根结点
};
二、红黑树再设计
1. 重新设计 RBTree 的模板参数
之前我们的RBTree模板参数是Key-Value模型,但此时我们不得不再考虑设计新的模板参数,因为STL中set、map都是适配红黑树,那么同一个RBTree模板如何同时适配set(Key模型)、map(Key-Value模型)呢?
template<class K, class T>
class RBTree
为什么要设计为K,T模板?
根据是set 还是 map,T有两种可能: key 或 pair<K, T>,所以我们需要第一个模板参数K,它绝对是Key。
设计成K,T是为了适配 find 、erase函数,因为 find 函数需要参数Key,如果以之前的模板参数设计,set调用时很方便,直接传递Key;而map只能传递pair键值对,那么 find 内部还要根据上层是set还是map,来解析传递的模板参数是裸露的Key还是在键值对中的Key,但是对于底层红黑树来说,它并不知道上层容器是map还是set,所以如果不修改模板参数,那么这无疑加重了红黑树中 find 的设计难度!
所以,set、map都后退一步,全都以统一的模板参数适配RBTree,set多传递一个模板参数Key、map将V修改为pair<K, V>,这样set、map就可以协调统一的适配RBTree,可以说set是跟着map “陪跑”,因为set、map共用的红黑树底层
- set容器:K和T都代表键值Key
- map容器:K代表键值Key,T代表由Key和Value构成的键值对
//set
RBTree<K, K> _t;//map
RBTree<K, pair<K, V>> _t;
在红黑树中 typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node,红黑树节点直接接收参数T,更改后代码如下:
//红黑树结点的定义
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{//三叉链RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;//存储的数据T _data;//结点的颜色int _col; //红/黑//构造函数RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _data(data), _col(RED){}
};
2. 仿函数模板参数
红黑树重新设计模板参数后,节点存储的是T类型,这个T即可能是Key,也可能是pair<Key, Value>键值对,那么如果在find函数内进行节点的Key大小比较时,如果正确获取Key用来比较大小呢?
底层红黑树的插入比较时,因为T的类型不确定,所以我们可以模仿list模拟实现时使用的仿函数,来比较大小,但是这里我们不直接在仿函数内比较大小,而是使用 KeyOfT 类,用它创建一个类对象,使用仿函数来获取 T 中 Key,而不是直接进行比较!

对于set,T 就是key;对于map,T是pair,所以要返回 pair 的 first
为什么不将仿函数功能复合,直接设计成比大小返回bool类型?
因为可能有指针等类型,不能按平常的比较来比较,并且在STL的set、map设计中,还有一个用户传递的模板参数compare,它的仿函数是专门用来比较的。
KeyOfT是红黑树内部用的,两个仿函数各干各的活。如果都交给一个仿函数,那么要排列组合设计很多种类型比较。
当底层红黑树需要进行两个结点之间键值的比较时,都会通过传入的仿函数来获取相应结点的键值,然后再进行比较,下面以红黑树的查找函数为例:
//查找函数
iterator Find(const K& key)
{KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (key < kot(cur->_data)) //key值小于该结点的值{cur = cur->_left; //在该结点的左子树当中查找}else if (key > kot(cur->_data)) //key值大于该结点的值{cur = cur->_right; //在该结点的右子树当中查找}else //找到了目标结点{return iterator(cur); //返回该结点}}return end(); //查找失败
}
3. 正向迭代器
构造
红黑树的迭代器封装红黑树节点指针即可(同list模拟实现,迭代器传入三个模板参数是为了更好的设计const迭代器)
//正向迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node; //结点的类型typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; //正向迭代器的类型Node* _node; //正向迭代器所封装结点的指针//构造函数__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node) //根据所给结点指针构造一个正向迭代器{}};
operator*()
当对正向迭代器进行解引用操作时,我们直接返回 对应结点数据的引用
Ref operator*()
{return _node->_data; //返回结点数据的引用
}
operator->()
当对正向迭代器进行->操作时,我们直接返回对应结点数据的指针
Ptr operator->()
{return &_node->_data; //返回结点数据的指针
}
operator!=()
operator重载!= 和 ==,比较时直接比较Node*即可(地址最容易比较是否相等)
//判断两个正向迭代器是否不同
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{return _node != s._node; //判断两个正向迭代器所封装的结点是否是同一个
}
//判断两个正向迭代器是否相同
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{return _node == s._node; //判断两个正向迭代器所封装的结点是否是同一个
}
迭代器设计最难的部分是迭代器的++和--,因为底层适配的是红黑树——非序列式容器,++或--是在树中移动!

operator++()
- 如果当前节点右子树不为空,++找右子树的最左节点,--找左子树的左右节点
- 如果当前结点的右子树为空,则
++操作后应该在该结点的祖先结点中,找到孩子不在父亲右的祖先
//前置++
Self operator++()
{if (_node->_right) //结点的右子树不为空{//寻找该结点右子树当中的最左结点Node* left = _node->_right;while (left->_left){left = left->_left;}_node = left; //++后变为该结点}else //结点的右子树为空{//寻找孩子不在父亲右的祖先Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent&&cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent; //++后变为该结点}return *this;
}
operator--()
- 如果当前结点的左子树不为空,则
--操作后应该找到其左子树当中的最右结点。 - 如果当前结点的左子树为空,则
--操作后应该在该结点的祖先结点中,找到孩子不在父亲左的祖先
//前置--
Self operator--()
{if (_node->_left) //结点的左子树不为空{//寻找该结点左子树当中的最右结点Node* right = _node->_left;while (right->_right){right = right->_right;}_node = right; //--后变为该结点}else //结点的左子树为空{//寻找孩子不在父亲左的祖先Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent&&cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent; //--后变为该结点}return *this;
}
正向迭代器代码
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;/*不管此时__TreeIterator是普通迭代器还是const迭代器,我们typedef的Iterator类型都是普通的迭代器*/typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;//成员变量Node* _node;//构造函数__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}//当__TreeIterator是const迭代器时,这里用普通迭代器构造const迭代器,这是一个构造函数//当_TreeIterator是普通迭代器时,这里用普通迭代器构造const迭代器,这是一个拷贝构造函数__TreeIterator(const Iterator& it):_node(it._node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator--(){//左子树不为空if (_node->_left){//找左子树的最右节点Node* subRight = _node->_left;while (subRight->_right){subRight = subRight->_right;}_node = subRight;}else //左子树为空,找孩子不在父亲左的祖先{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Self& operator++(){//如果右树不为空if (_node->_right){// 右树的最左节点(最小节点)Node* subLeft = _node->_right;while (subLeft->_left){subLeft = subLeft->_left;}_node = subLeft;}else //右树为空{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;// 找孩子是父亲左的那个祖先节点,就是下一个要访问的节点while (parent){if (cur == parent->_left) break;else{cur = cur->_parent;parent = parent->_parent;}}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{//拿地址来比较return _node == s._node;}};
4. 反向迭代器
在反向迭代器当中只有一个成员变量,那就是反向迭代器封装的正向迭代器。反向迭代器的中成员函数,都是通过调用正向迭代器对应的函数来完成相应功能的
构造
同list模拟实现,反向迭代器直接适配正向迭代器
#pragma oncetemplate<class Iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ReverseIterator
{typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self; //反向迭代器自身类型//封装普通迭代器Iterator _it;//构造ReverseIterator(Iterator it):_it(it){}};operator*
Ref operator* (){return *_it;}
operator->
Ptr operator->(){return _it.operator->();}
operator++
适配正向迭代器,直接--即可。
Self& operator++(){--_it;return *this;}
operator--
适配正向迭代器,直接++即可
Self& operator--(){++_it;return *this;}
注意:我们实现的都是前置的++或--
operator!=
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return _it != s._it;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return _it == s._it;}反向迭代器代码
#pragma oncetemplate<class Iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ReverseIterator
{typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self; //反向迭代器自身类型//封装普通迭代器Iterator _it;//构造ReverseIterator(Iterator it):_it(it){}Ref operator* (){return *_it;}Ptr operator->(){return _it.operator->();}Self& operator++(){--_it;return *this;}Self& operator--(){++_it;return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return _it != s._it;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return _it == s._it;}};
5. 红黑树主体
我们需要在红黑树的实现当中进行迭代器类型的typedef。需要注意的是,为了让外部能够使用typedef后的正向迭代器类型iterator,我们需要在public区域进行typedef
begin()、end()、
- begin函数返回中序序列当中第一个结点的正向迭代器,即最左结点。
- end函数返回中序序列当中最后一个结点下一个位置的正向迭代器,这里直接用空指针构造一个正向迭代器
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node; //结点的类型
public:typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){//寻找最左结点Node* left = _root;while (left&&left->_left){left = left->_left;}//返回最左结点的正向迭代器return iterator(left);}iterator end(){//返回由nullptr构造得到的正向迭代器(不严谨)return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* leftMin = _root;while (leftMin && leftMin->_left){leftMin = leftMin->_left;}return iterator(leftMin);}const_iterator end() const{return iterator(nullptr);}private:Node* _root; //红黑树的根结点
};
rbegin()、rend()
- rbegin函数返回中序序列当中最后一个结点的反向迭代器,即最右结点。
- rend函数返回中序序列当中第一个结点前一个位置的反向迭代器,这里直接用空指针构造一个反向迭代器。
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
struct RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;reverse_iterator rbegin(){Node* right = _root;while (right && right->_right){right = right->_right;}return reverse_iterator(iterator(right));}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(iterator(nullptr));}const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const{Node* right = _root;while (right && right->_right){right = right->_right;}return reverse_iterator(iterator(right));}const_reverse_iterator rend() const{return reverse_iterator(iterator(nullptr));}private:Node* _root; //红黑树的根结点
};
insert 返回值
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key);

- 如果插入成功,那么返回新插入的节点的迭代器与 true 构成的 pair
- 如果插入失败(相应的Key已经存在),那么返回已经存在的 Key 对应的节点迭代器与 false构成的pair
所以在红黑树主体部分,如果 insert 内部要返回 bool 类型时,我们 make_pair 返回 pair<iterator, bool>类型即可
//插入函数
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);}}cur = new Node(data);cur->_col = RED;Node* newnode = cur;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;// u存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // u不存在 或 存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_left){// g// p// cRotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// g// p// cRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else // parent == grandfather->_right{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;// u存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){// g// p// cRotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = RED;parent->_col = BLACK;}else{// g// p// cRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);
}find返回值

同理,在返回处 make_pair 即可。
注意:如果没找到需返回end()

iterator Find(const K& key)
{Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return iterator(cur);}}return end();
}STL标准库设计
上述所实现的迭代器是有缺陷的,因为理论上我们对end()位置的正向迭代器进行--操作后,应该得到最后一个结点的正向迭代器,但我们实现end()时,是直接返回由nullptr构造得到的正向迭代器的,因此上述实现的代码无法完成此操作。
下面我们来看看C++SLT库当中的实现逻辑:

C++STL库当中实现红黑树时,在红黑树的根结点处增加了一个头结点,该头结点的左指针指向红黑树当中的最左结点,右指针指向红黑树当中的最右结点,父指针指向红黑树的根结点。
在该结构下,实现begin()时,直接用头结点的左孩子构造一个正向迭代器即可,实现rbegin()时,直接用头结点的右孩子构造一个反向迭代器即可(实际是先用该结点构造一个正向迭代器,再用正向迭代器构造出反向迭代器),而实现end()和rend()时,直接用头结点构造出正向和反向迭代器即可。此后,通过对逻辑的控制,就可以实现end()进行--操作后得到最后一个结点的正向迭代器。
但实现该结构需要更改当前很多函数的逻辑,例如插入结点时,若插入到了红黑树最左结点的左边,或最右结点的右边,此时需要更新头结点左右指针的指向
6. 再设计后完整的RBTree代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include "ReverseIterator.h"
using namespace std;enum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;T _data;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _data(data), _col(RED){}
};// set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
// map->RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
struct RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* leftMin = _root;while (leftMin && leftMin->_left){leftMin = leftMin->_left;}return iterator(leftMin);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* leftMin = _root;while (leftMin && leftMin->_left){leftMin = leftMin->_left;}return iterator(leftMin);}const_iterator end() const{return iterator(nullptr);}reverse_iterator rbegin(){Node* right = _root;while (right && right->_right){right = right->_right;}return reverse_iterator(iterator(right));}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(iterator(nullptr));}const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const{Node* right = _root;while (right && right->_right){right = right->_right;}return reverse_iterator(iterator(right));}const_reverse_iterator rend() const{return reverse_iterator(iterator(nullptr));}//构造函数RBTree():_root(nullptr){}//拷贝构造RBTree(const RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>& t){_root = _Copy(t._root, nullptr);}//赋值运算符重载(现代写法)RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>& operator=(RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this; //支持连续赋值}//析构函数~RBTree(){_Destroy(_root);_root = nullptr;}iterator Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return iterator(cur);}}return end();}//插入函数pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);}}cur = new Node(data);cur->_col = RED;Node* newnode = cur;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;// u存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // u不存在 或 存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_left){// g// p// cRotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// g// p// cRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else // parent == grandfather->_right{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;// u存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){// g// p// cRotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = RED;parent->_col = BLACK;}else{// g// p// cRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);}//删除函数bool Erase(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;//用于遍历二叉树Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;//用于标记实际的待删除结点及其父结点Node* delParentPos = nullptr;Node* delPos = nullptr;while (cur){if (key < kot(cur->_data)) //所给key值小于当前结点的key值{//往该结点的左子树走parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (key > kot(cur->_data)) //所给key值大于当前结点的key值{//往该结点的右子树走parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else //找到了待删除结点{if (cur->_left == nullptr) //待删除结点的左子树为空{if (cur == _root) //待删除结点是根结点{_root = _root->_right; //让根结点的右子树作为新的根结点if (_root){_root->_parent = nullptr;_root->_col = BLACK; //根结点为黑色}delete cur; //删除原根结点return true;}else{delParentPos = parent; //标记实际删除结点的父结点delPos = cur; //标记实际删除的结点}break; //进行红黑树的调整以及结点的实际删除}else if (cur->_right == nullptr) //待删除结点的右子树为空{if (cur == _root) //待删除结点是根结点{_root = _root->_left; //让根结点的左子树作为新的根结点if (_root){_root->_parent = nullptr;_root->_col = BLACK; //根结点为黑色}delete cur; //删除原根结点return true;}else{delParentPos = parent; //标记实际删除结点的父结点delPos = cur; //标记实际删除的结点}break; //进行红黑树的调整以及结点的实际删除}else //待删除结点的左右子树均不为空{//替换法删除//寻找待删除结点右子树当中key值最小的结点作为实际删除结点Node* minParent = cur;Node* minRight = cur->_right;while (minRight->_left){minParent = minRight;minRight = minRight->_left;}cur->_data = minRight->_data; //将待删除结点的_data改为minRight的_datadelParentPos = minParent; //标记实际删除结点的父结点delPos = minRight; //标记实际删除的结点break; //进行红黑树的调整以及结点的实际删除}}}if (delPos == nullptr) //delPos没有被修改过,说明没有找到待删除结点{return false;}//记录待删除结点及其父结点(用于后续实际删除)Node* del = delPos;Node* delP = delParentPos;//调整红黑树if (delPos->_col == BLACK) //删除的是黑色结点{if (delPos->_left) //待删除结点有一个红色的左孩子(不可能是黑色){delPos->_left->_col = BLACK; //将这个红色的左孩子变黑即可}else if (delPos->_right) //待删除结点有一个红色的右孩子(不可能是黑色){delPos->_right->_col = BLACK; //将这个红色的右孩子变黑即可}else //待删除结点的左右均为空{while (delPos != _root) //可能一直调整到根结点{if (delPos == delParentPos->_left) //待删除结点是其父结点的左孩子{Node* brother = delParentPos->_right; //兄弟结点是其父结点的右孩子//情况一:brother为红色if (brother->_col == RED){delParentPos->_col = RED;brother->_col = BLACK;RotateL(delParentPos);//需要继续处理brother = delParentPos->_right; //更新brother(否则在本循环中执行其他情况的代码会出错)}//情况二:brother为黑色,且其左右孩子都是黑色结点或为空if (((brother->_left == nullptr) || (brother->_left->_col == BLACK))&& ((brother->_right == nullptr) || (brother->_right->_col == BLACK))){brother->_col = RED;if (delParentPos->_col == RED){delParentPos->_col = BLACK;break;}//需要继续处理delPos = delParentPos;delParentPos = delPos->_parent;}else{//情况三:brother为黑色,且其左孩子是红色结点,右孩子是黑色结点或为空if ((brother->_right == nullptr) || (brother->_right->_col == BLACK)){brother->_left->_col = BLACK;brother->_col = RED;RotateR(brother);//需要继续处理brother = delParentPos->_right; //更新brother(否则执行下面情况四的代码会出错)}//情况四:brother为黑色,且其右孩子是红色结点brother->_col = delParentPos->_col;delParentPos->_col = BLACK;brother->_right->_col = BLACK;RotateL(delParentPos);break; //情况四执行完毕后调整一定结束}}else //delPos == delParentPos->_right //待删除结点是其父结点的左孩子{Node* brother = delParentPos->_left; //兄弟结点是其父结点的左孩子//情况一:brother为红色if (brother->_col == RED) //brother为红色{delParentPos->_col = RED;brother->_col = BLACK;RotateR(delParentPos);//需要继续处理brother = delParentPos->_left; //更新brother(否则在本循环中执行其他情况的代码会出错)}//情况二:brother为黑色,且其左右孩子都是黑色结点或为空if (((brother->_left == nullptr) || (brother->_left->_col == BLACK))&& ((brother->_right == nullptr) || (brother->_right->_col == BLACK))){brother->_col = RED;if (delParentPos->_col == RED){delParentPos->_col = BLACK;break;}//需要继续处理delPos = delParentPos;delParentPos = delPos->_parent;}else{//情况三:brother为黑色,且其右孩子是红色结点,左孩子是黑色结点或为空if ((brother->_left == nullptr) || (brother->_left->_col == BLACK)){brother->_right->_col = BLACK;brother->_col = RED;RotateL(brother);//需要继续处理brother = delParentPos->_left; //更新brother(否则执行下面情况四的代码会出错)}//情况四:brother为黑色,且其左孩子是红色结点brother->_col = delParentPos->_col;delParentPos->_col = BLACK;brother->_left->_col = BLACK;RotateR(delParentPos);break; //情况四执行完毕后调整一定结束}}}}}//进行实际删除if (del->_left == nullptr) //实际删除结点的左子树为空{if (del == delP->_left) //实际删除结点是其父结点的左孩子{delP->_left = del->_right;if (del->_right)del->_right->_parent = delP;}else //实际删除结点是其父结点的右孩子{delP->_right = del->_right;if (del->_right)del->_right->_parent = delP;}}else //实际删除结点的右子树为空{if (del == delP->_left) //实际删除结点是其父结点的左孩子{delP->_left = del->_left;if (del->_left)del->_left->_parent = delP;}else //实际删除结点是其父结点的右孩子{delP->_right = del->_left;if (del->_left)del->_left->_parent = delP;}}delete del; //实际删除结点return true;}private://拷贝树Node* _Copy(Node* root, Node* parent){if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_data);copyNode->_parent = parent;copyNode->_left = _Copy(root->_left, copyNode);copyNode->_right = _Copy(root->_right, copyNode);return copyNode;}//析构函数子函数void _Destroy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_Destroy(root->_left);_Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}//左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){++_rotateCount;Node* cur = parent->_right;Node* curleft = cur->_left;parent->_right = curleft;if (curleft){curleft->_parent = parent;}cur->_left = parent;Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = cur;if (parent == _root){_root = cur;cur->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppnode->_left == parent){ppnode->_left = cur;}else{ppnode->_right = cur;}cur->_parent = ppnode;}}//右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){++_rotateCount;Node* cur = parent->_left;Node* curright = cur->_right;parent->_left = curright;if (curright)curright->_parent = parent;Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;cur->_right = parent;parent->_parent = cur;if (ppnode == nullptr){_root = cur;cur->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppnode->_left == parent){ppnode->_left = cur;}else{ppnode->_right = cur;}cur->_parent = ppnode;}}//检查红黑树颜色bool CheckColour(Node* root, int blacknum, int benchmark){if (root == nullptr){if (blacknum != benchmark)return false;return true;}if (root->_col == BLACK){++blacknum;}if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << root->_kv.first << "出现连续红色节点" << endl;return false;}return CheckColour(root->_left, blacknum, benchmark)&& CheckColour(root->_right, blacknum, benchmark);}bool IsBalance(){return IsBalance(_root);}bool IsBalance(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return true;if (root->_col != BLACK){return false;}// 基准值int benchmark = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK)++benchmark;cur = cur->_left;}return CheckColour(root, 0, benchmark);}int Height(){return Height(_root);}int Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;int leftHeight = Height(root->_left);int rightHeight = Height(root->_right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;}private:Node* _root = nullptr;public:int _rotateCount = 0;
};三、set、map封装
1. set基础封装
#include "RBTree.h"namespace my_set
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return _t.rbegin();}reverse_iterator rend(){return _t.rend();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){}void erase(const K& key){}iterator find(const K& key){}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}2. map基础封装
#include "RBTree.h"namespace my_map
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return _t.rbegin();}reverse_iterator rend(){return _t.rend();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){}V& operator[](const K& key){}void erase(const K& key){}iterator find(const K& key){}private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}3. insert
set:
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{return _t.Insert(key);
}set 的迭代器 typedef 了红黑树的 const_iterator
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
map:
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{return _t.Insert(kv);
}map 的 iterator 没有 typedef 红黑树的 const_iterator
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
编译:

问题的引发:在封装map的operator[] 函数时,需要用到insert函数的pair<iterator, bool>返回值,但是此时 set 的返回处出现问题
C2440 “return”: 无法从“std::pair<__TreeIterator<T,T &,T *>,bool>”转换为“std::pair<__TreeIterator<T,const T &,const T *>,bool>” 摸索:
set 底层适配 RBtree 结构 ,所以 set 的 insert 调用的是 RBTree 的 insert 函数,又 RBTree 的 insert 函数返回的是 pair<iterator, bool> 类型(这里的 iterator是红黑树返回的普通迭代器类型)

(注意:如果在 set.h 文件中,此时 pair 的 iterator 类型其实是 const_iterator 类型,因为我们是根据 STL 中的 set 设计来设计我们的 set ,STL 中 set 的 iterator 其实是 const_iterator 的 typedef,是为了保证set的key不被修改,因为底层红黑树节点是靠key来构建的,一旦key被修改,那么整个树的结构就会混乱无序)
所以 set 的 insert 在 return _t.Insert 时,在 pair 的构造函数的初始化列表处会发生普通迭代器构造 const 迭代器的过程
所以我们需要在红黑树迭代器类中再手写一个构造函数,参数是普通迭代器,用来支持普通迭代器向const迭代器转换
迭代器类中,默认生成的拷贝构造就已经够用了,因为成员变量类型是Node*,是内置类型,可以浅拷贝,那么为什么还要设计迭代器的拷贝构造?
其实这里并不是拷贝构造,而是重载构造函数。当 set 的 insert 返回时,我们先来看pair类的构造函数:
此时T1类型是const_iterator
template <class T1, class T2>
struct pair
{typedef T1 first_type;typedef T2 second_type;T1 first;T2 second;pair(): first(T1()) , second(T2()){}pair(const T1& a, const T2& b): first(a) 此时的参数a是普通iterator, second(b) first是const_iterator{}
};我们发现,在pair 的构造函数的初始化列表处,出现了以普通迭代器构造const迭代器的过程,而我们的迭代器此时并没有专门接收迭代器类型的构造函数
所以,我们要在红黑树的迭代器类中实现一个迭代器构造函数,支持从普通迭代器转为const迭代器功能
我们如何在一个const迭代器类中获得普通迭代器类型?
在迭代器类设计时,typedef一个普通迭代器即可
//不管此时__TreeIterator是普通迭代器还是const迭代器,//我们typedef的Iterator类型都是普通的迭代器typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
不管此时__TreeIterator 是普通迭代器还是 const 迭代器,我们 typedef 的 Iterator 类型都是普通的迭代器
//当__TreeIterator是const迭代器时,这里用普通迭代器构造const迭代器,这是一个构造函数//当_TreeIterator是普通迭代器时,这里用普通迭代器构造const迭代器,这是一个拷贝构造函数__TreeIterator(const Iterator& it):_node(it._node){}- 当 __TreeIterator 是const迭代器时,这里用普通迭代器构造const迭代器,这是一个构造函数,因为我们在迭代器类中已经写过构造函数了,所以还需要重载一个以迭代器为参数的构造函数
- 当 __TreeIterator 是普通迭代器时,这里用普通迭代器构造const迭代器,这是一个拷贝构造函数
4. map::operator[]
map::operator[]功能我们在map介绍时已经讲过了,返回 insert 返回的 iterator 的 second 数据的引用,即不管insert是否成功,我们都能获取Key的value的引用
V& operator[](const K& key)
{pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));iterator it = ret.first;return it->second;
}5. find
调用适配的红黑树的Find函数即可
iterator find(const K& key)
{return _t.Find(key);
}6. erase
调用适配的红黑树的Erase函数即可
void erase(const K& key)
{_t.Erase(key);
}7. 测试
#include <iostream>#include "MyMap.h"
#include "MySet.h"int main()
{//验证mapmy_map::map<int, int> m;m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));m.insert(make_pair(4, 4));m.insert(make_pair(3, 8));m.insert(make_pair(5, 1));my_map::map<int, int>::reverse_iterator mit = m.rbegin();while (mit != m.rend()){cout << mit->first << ":" << mit->second << endl;++mit;}cout << endl;m[1] = 100;m[99] = 120;m[3] = 4;for (const auto& e : m){cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;//验证setmy_set::set<int> s;s.insert(5);s.insert(15);s.insert(54);s.insert(23);s.insert(0);s.insert(9);s.insert(4);my_set::set<int>::iterator sit = s.begin();while (sit != s.end()){cout << *sit << " ";++sit;}cout << endl;for (const auto& e : s){cout << e << " ";}return 0;}

相关文章:

<C++> set、map模拟实现
目录 一、适配器红黑树 二、红黑树再设计 1. 重新设计 RBTree 的模板参数 2. 仿函数模板参数 3. 正向迭代器 构造 operator*() operator->() operator!() operator() operator--() 正向迭代器代码 4. 反向迭代器 构造 operator* operator-> operator operator-- operat…...

软考学习 数据结构 查找
1. 顺序查找(Sequential Search) 基本原理: 顺序查找是一种最简单、最直观的查找算法。它从数据集合的第一个元素开始,依次与目标元素进行比较,直到找到目标元素或遍历完所有元素为止。 适用条件: 适用…...

h264 视频流中添加目标检测的位置、类型信息到SEI帧
在 H.264 视频编码中,SEI(Supplemental Enhancement Information)消息用于传输额外的、非编码的数据,例如目标检测的信息。SEI 数据可以嵌入到 H.264 流中,以在解码过程中传递这些附加信息。 一、步骤 确定 SEI 类型&…...
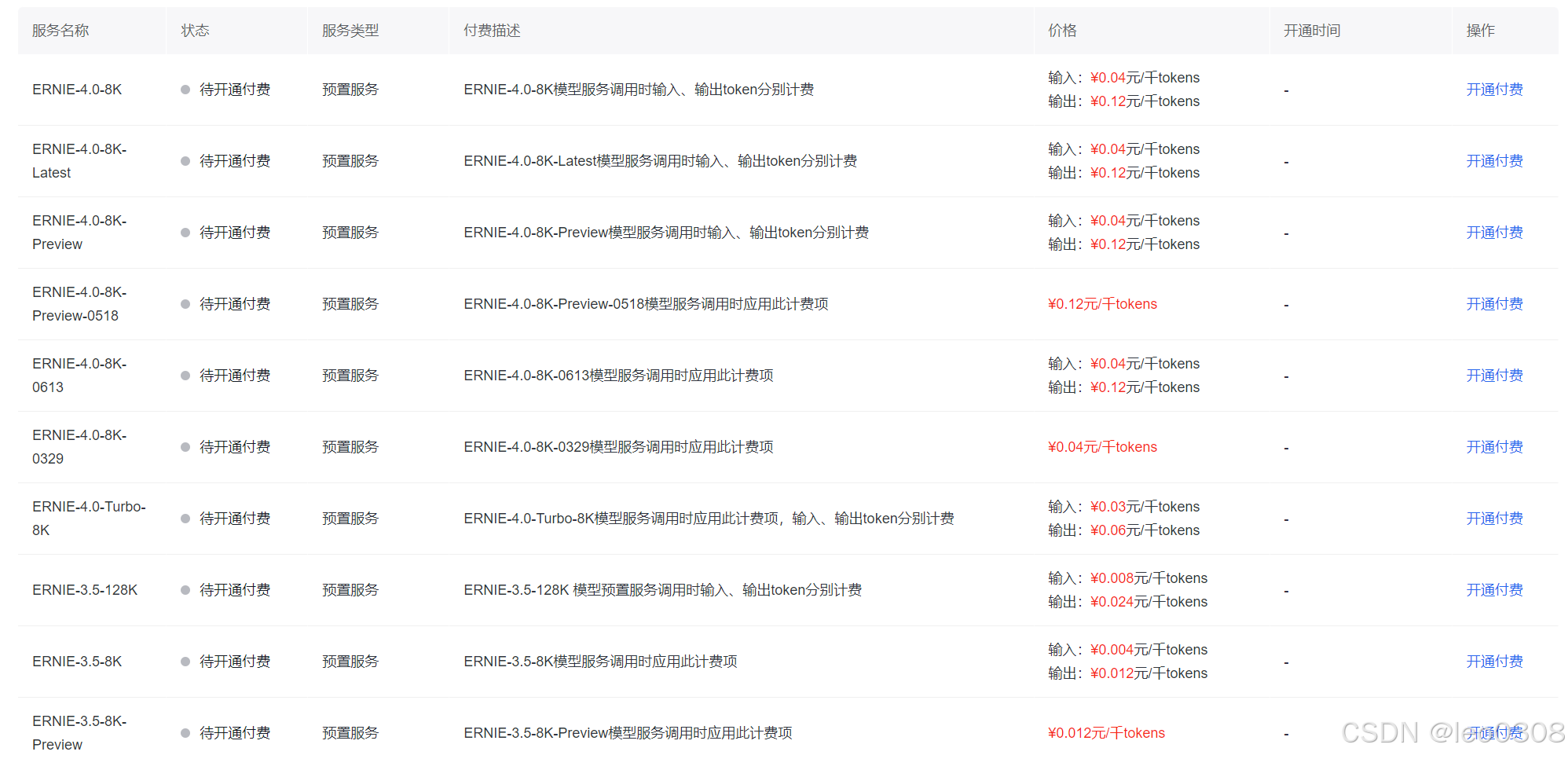
大模型api谁家更便宜
1 openai 可点此链接查询价格:https://openai.com/api/pricing/ 2 百度 可点此链接查询价格:https://console.bce.baidu.com/qianfan/chargemanage/list 需要注意,百度千帆平台上还提供其他家的模型调用服务, 如llama, yi-34b等…...
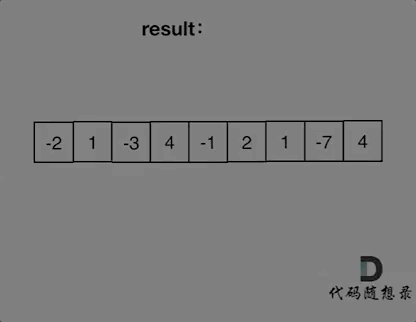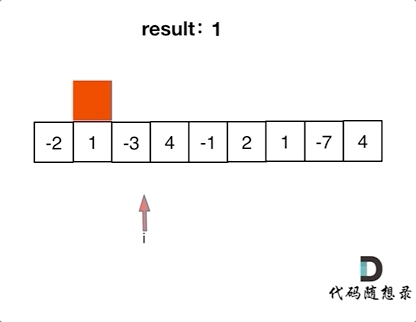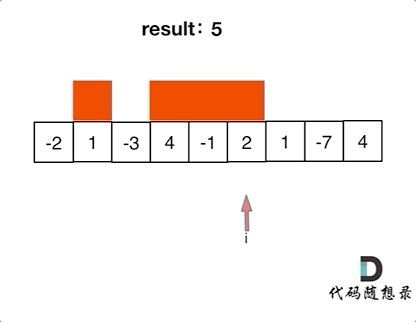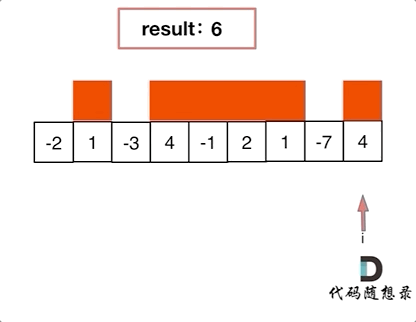
代码随想录算法训练营第二十三天| 455. 分发饼干、376. 摆动序列、53. 最大子序和
今日内容 贪心理论基础Leetcode. 455 分发饼干Leetcode. 376 摆动序列Leetcode. 53 最大子序和 贪心理论基础 贪心算法的本质就是选择每一阶段的最优,达到全局上的最优。 贪心算法和之前学到的所有方法相比,它没有固定的使用套路,也没有固…...
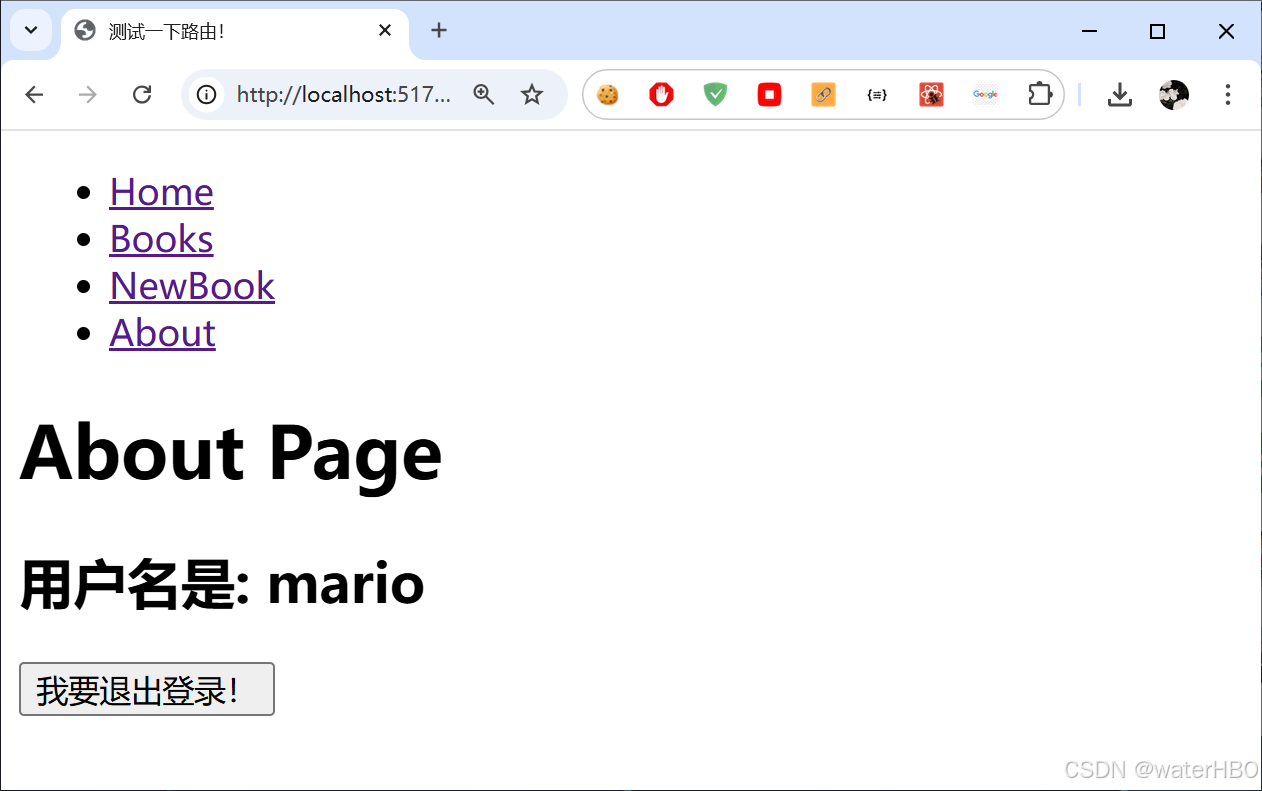
react js 路由 Router
完整的项目,我已经上传了 资料链接 起因, 目的: 路由, 这部分很难。 原因是, 多个组件,进行交互,复杂度比较高。 我看的视频教程 1. 初步使用 安装: npm install react-router-dom 修改 index.js/ 或是 main.js 把 App, 用 BrowserRouter 包裹起来 2. Navigate 点击…...
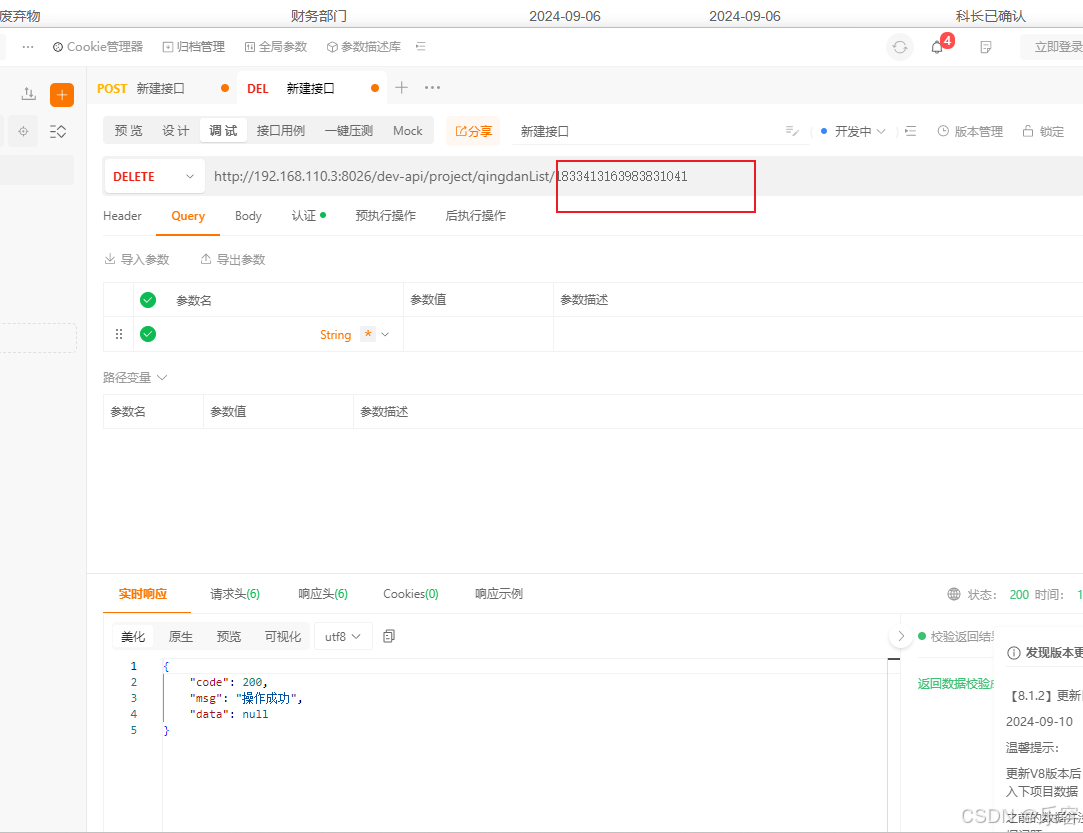
AplPost使用
请求get 方法 1,添加token 2,填写get 的参数 2,post方法 把对象的形式直接复制到row里面 3,delete方法 可以直接后面拼接参数...
【Qt】Qt与Html网页进行数据交互
前言:此项目使用达梦数据库,以Qt制作服务器,Html制作网页客户端界面,可以通过任意浏览器访问。 1、Qt与网页进行数据交互 1.1、第一步:准备qwebchannel.js文件 直接在qt的安装路径里复制即可 1.2、第二步…...

教师节特辑:AI绘制的卡通人物,致敬最可爱的人
【编号:9】教师节到了,今天我要分享一组由AI绘制的教师节主题卡通人物插画,每一幅都充满了对老师的敬意和爱戴。让我们一起用这些可爱的卡通形象,向辛勤的园丁们致敬! 🎓【教师形象】 这…...
SprinBoot+Vue智慧农业专家远程指导系统的设计与实现
目录 1 项目介绍2 项目截图3 核心代码3.1 Controller3.2 Service3.3 Dao3.4 application.yml3.5 SpringbootApplication3.5 Vue 4 数据库表设计5 文档参考6 计算机毕设选题推荐7 源码获取 1 项目介绍 博主个人介绍:CSDN认证博客专家,CSDN平台Java领域优质…...

AI大模型行业专题报告:大模型发展迈入爆发期,开启AI新纪元
大规模语言模型(Large Language Models,LLM)泛指具有超大规模参数或者经过超大规模数据训练所得到的语言模型。与传统语言模型相比,大语言模型的构建过程涉及到更为复杂的训练方法,进而展现出了强大的自然语言理解能力…...
FLV 格式详解资料整理,关键帧格式解析写入库等等
FLV 是一种比较简单的视频封装格式。大致可以分为 FLV 文件头,Metadata元数据,然后一系列的音视频数据。 资料够多: FLV格式解析图 知乎用户 Linux服务器研究 画了一张格式解析图,比较全,但默认背景是白色ÿ…...

《深度学习》OpenCV 高阶 图像直方图、掩码图像 参数解析及案例实现
目录 一、图像直方图 1、什么是图像直方图 2、作用 1)分析图像的亮度分布 2)判断图像的对比度 3)检测图像的亮度和色彩偏移 4)图像增强和调整 5)阈值分割 3、举例 二、直方图用法 1、函数用法 2、参数解析…...

coredump-N: stack 消耗完之后,用户自定义信号处理有些问题 sigaltstack
https://mzhan017.blog.csdn.net/article/details/129401531 在上面一篇是关于stack耗尽的一个小程序例子。 https://www.man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/sigaltstack.2.html 这里提到一个问题,就是如果栈被用光了,这个时候SIGSEGV的用户自定义的handler处理可能就没有空间进…...

数据库有关c语言
数据库的概念 SQL(Structured Query Language)是一种专门用来与数据库进行交互的编程语言,它允许用户查询、更新和管理关系型数据库中的数据。关系型数据库是基于表(Table)的数据库,其中表由行(…...
【网页播放器】播放自己喜欢的音乐
// 错误处理 window.onerror function(message, source, lineno, colno, error) {console.error("An error occurred:", message, "at", source, ":", lineno);return true; };// 检查 particlesJS 是否已定义 if (typeof particlesJS ! undefi…...
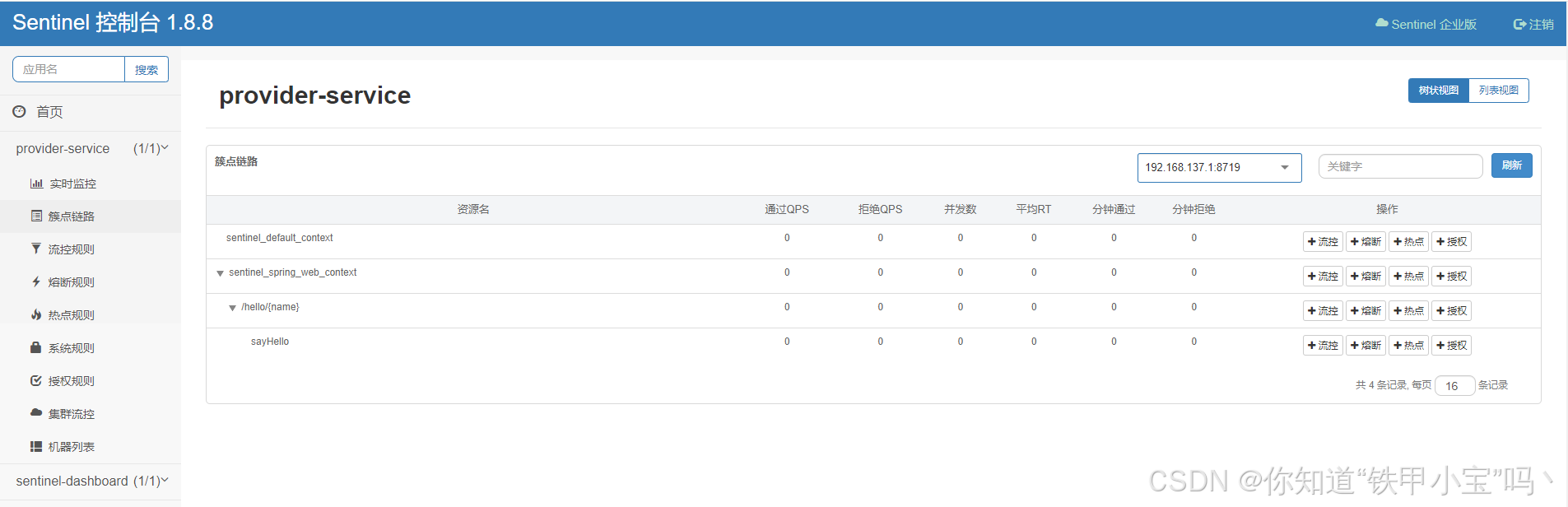
【第27章】Spring Cloud之适配Sentinel
文章目录 前言一、准备1. 引入依赖2. 配置控制台信息 二、定义资源1. Controller2. Service3. ServiceImpl 三、访问控制台1. 发起请求2. 访问控制台 总结 前言 Spring Cloud Alibaba 默认为 Sentinel 整合了 Servlet、RestTemplate、FeignClient 和 Spring WebFlux。Sentinel…...
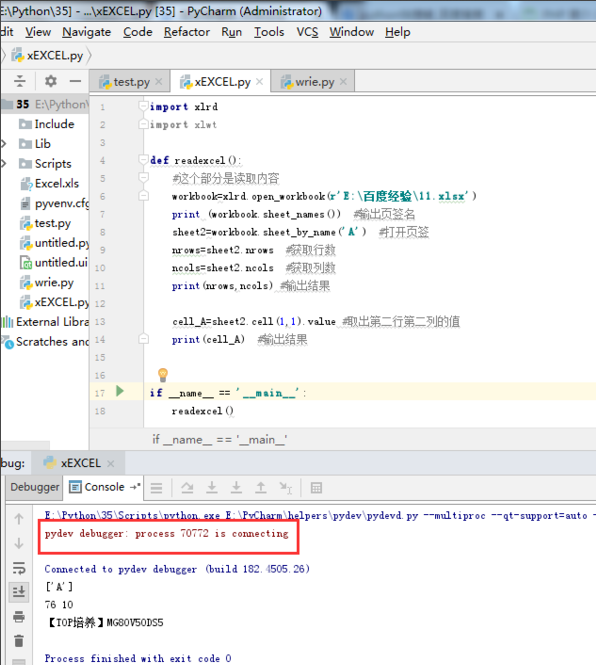
怎么debug python
1、打开pycharm,新建一个python程序,命名为excel.py。 2、编写代码。 3、点击菜单栏中的“Run”,在下拉菜单中选择“debug excel.py”或者“Debug...”,这两个功能是一样的,都是调试功能。 4、调试快捷键:C…...
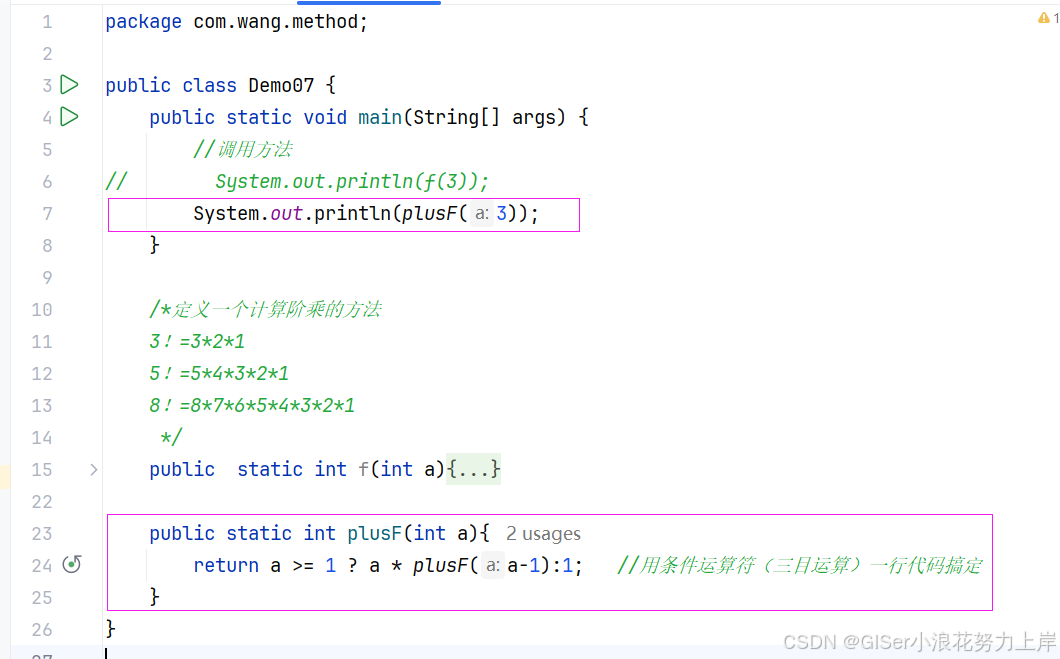
Java 递归
目录 1.A方法调用B方法,很容易理解! 2.递归:A方法调用A方法,就是自己调用自己! 3. 递归的优点: 4. 递归结构包括两个部分: 5. 递归的三个阶段 6. 递归的缺点&#…...

获取业务库的schema信息导出成数据字典
获取业务库的schema信息导出成数据字典 场景:需要获取业务库的schema信息导出成数据字典,以下为获取oracle与mysql数据库的schema信息语句 --获取oracle库schema信息 selecttt1.owner as t_owner,tt1.table_name,tt1.column_name,tt1.data_type,tt1.dat…...
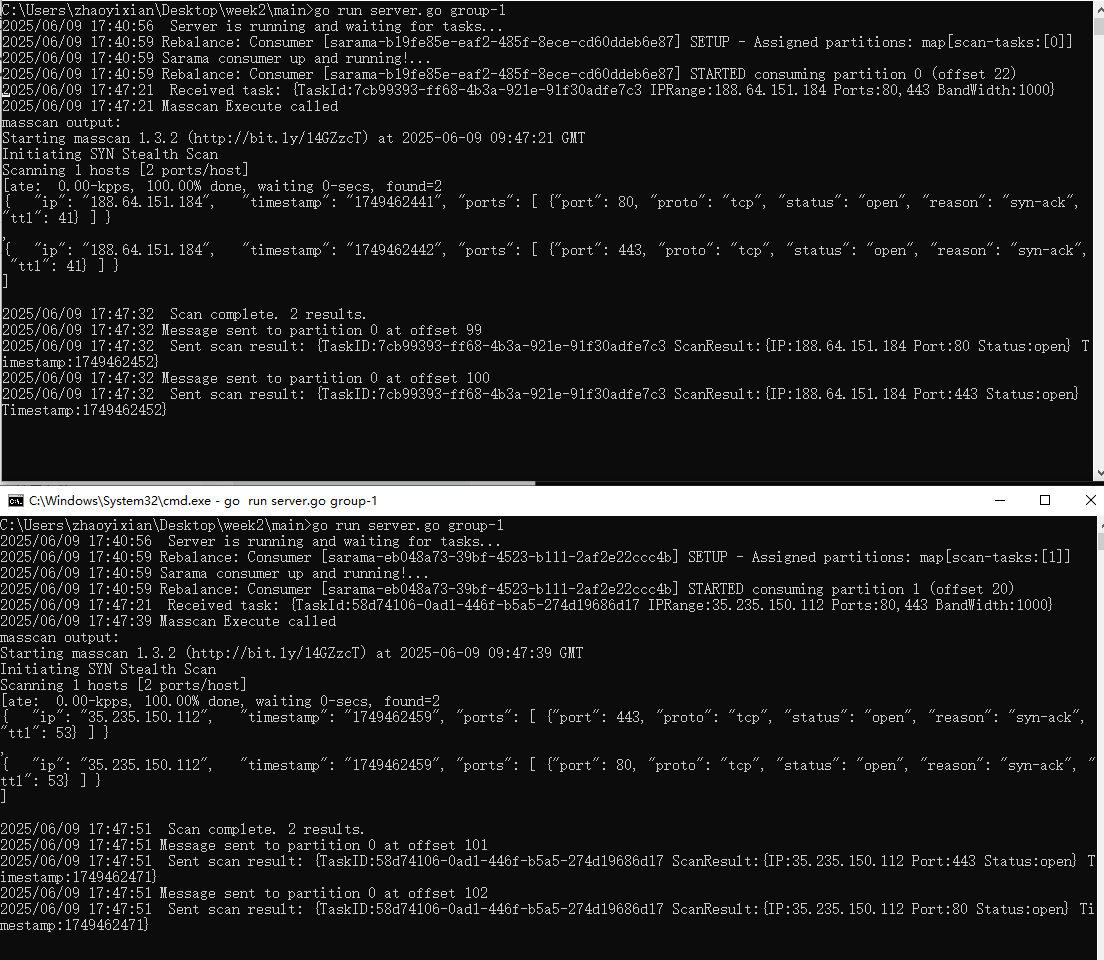
【kafka】Golang实现分布式Masscan任务调度系统
要求: 输出两个程序,一个命令行程序(命令行参数用flag)和一个服务端程序。 命令行程序支持通过命令行参数配置下发IP或IP段、端口、扫描带宽,然后将消息推送到kafka里面。 服务端程序: 从kafka消费者接收…...
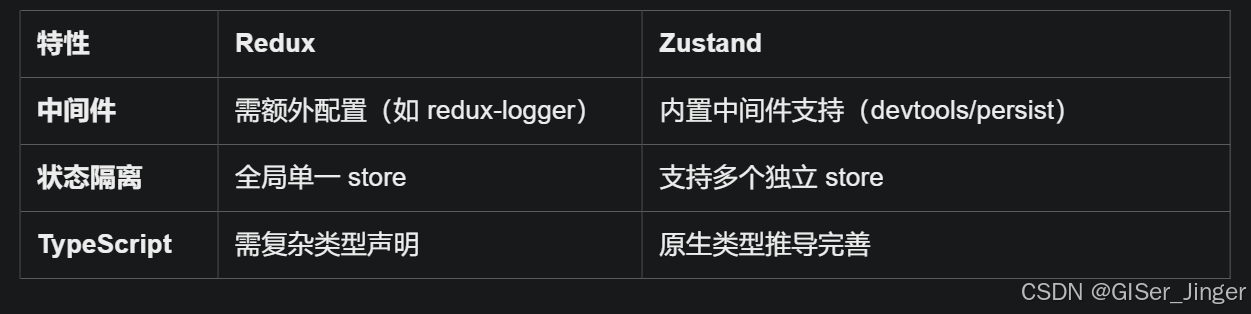
Zustand 状态管理库:极简而强大的解决方案
Zustand 是一个轻量级、快速和可扩展的状态管理库,特别适合 React 应用。它以简洁的 API 和高效的性能解决了 Redux 等状态管理方案中的繁琐问题。 核心优势对比 基本使用指南 1. 创建 Store // store.js import create from zustandconst useStore create((set)…...
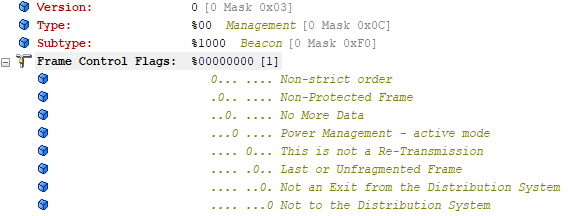
【WiFi帧结构】
文章目录 帧结构MAC头部管理帧 帧结构 Wi-Fi的帧分为三部分组成:MAC头部frame bodyFCS,其中MAC是固定格式的,frame body是可变长度。 MAC头部有frame control,duration,address1,address2,addre…...

Java 8 Stream API 入门到实践详解
一、告别 for 循环! 传统痛点: Java 8 之前,集合操作离不开冗长的 for 循环和匿名类。例如,过滤列表中的偶数: List<Integer> list Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); List<Integer> evens new ArrayList…...

.Net框架,除了EF还有很多很多......
文章目录 1. 引言2. Dapper2.1 概述与设计原理2.2 核心功能与代码示例基本查询多映射查询存储过程调用 2.3 性能优化原理2.4 适用场景 3. NHibernate3.1 概述与架构设计3.2 映射配置示例Fluent映射XML映射 3.3 查询示例HQL查询Criteria APILINQ提供程序 3.4 高级特性3.5 适用场…...

OkHttp 中实现断点续传 demo
在 OkHttp 中实现断点续传主要通过以下步骤完成,核心是利用 HTTP 协议的 Range 请求头指定下载范围: 实现原理 Range 请求头:向服务器请求文件的特定字节范围(如 Range: bytes1024-) 本地文件记录:保存已…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院查看报告小程序
一、开发环境准备 工具安装: 下载安装DevEco Studio 4.0(支持HarmonyOS 5)配置HarmonyOS SDK 5.0确保Node.js版本≥14 项目初始化: ohpm init harmony/hospital-report-app 二、核心功能模块实现 1. 报告列表…...
相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?)
Redis的发布订阅模式与专业的 MQ(如 Kafka, RabbitMQ)相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?
Redis 的发布订阅(Pub/Sub)模式与专业的 MQ(Message Queue)如 Kafka、RabbitMQ 进行比较,核心的权衡点在于:简单与速度 vs. 可靠与功能。 下面我们详细展开对比。 Redis Pub/Sub 的核心特点 它是一个发后…...

CSS设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整
width: fit-content 是 CSS 中的一个属性值,用于设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整,确保宽度刚好容纳内容而不会超出。 效果对比 默认情况(width: auto): 块级元素(如 <div>)会占满父容器…...

回溯算法学习
一、电话号码的字母组合 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;import javax.management.loading.PrivateClassLoader;public class letterCombinations {private static final String[] KEYPAD {"", //0"", //1"abc", //2"…...
