霍夫曼编码 | 贪心算法 2
霍夫曼编码是一种无损数据压缩算法。其思想是为输入字符分配可变长度代码,分配代码的长度基于相应字符的频率。
分配给输入字符的可变长度代码是前缀代码,意味着代码(位序列)的分配方式是分配给一个字符的代码不是分配给任何其他字符的代码的前缀。这就是霍夫曼编码如何确保在解码生成的比特流时没有歧义。
让我们通过一个反例来理解前缀代码。设a、b、c、d四个字符,它们对应的变长码分别为00、01、0、1。这种编码会导致歧义,因为c的编码是a、b的编码前缀。如果压缩比特流是0001,解压输出可能是“cccd”或“ccb”或“acd”或“ab”。有关霍夫曼编码的应用,
霍夫曼编码主要有两大部分
- 从输入字符构建哈夫曼树。
- 遍历哈夫曼树并为字符分配代码。
算法:
用于构造最优前缀码的方法称为霍夫曼编码。
该算法以自下而上的方式构建树。我们可以用T来表示这棵树
让,|c| 是叶子的数量
|c| -1 是合并节点所需的操作数。Q 是构造二叉堆时可以使用的优先级队列。
Algorithm Huffman (c)
{n= |c| Q = c for i<-1 to n-1do{temp <- get node ()left (temp] Get_min (Q) right [temp] Get Min (Q)a = left [templ b = right [temp]F [temp]<- f[a] + [b]insert (Q, temp)}return Get_min (0)
}
构建哈夫曼树的步骤
输入是一组唯一字符及其出现频率,输出是哈夫曼树。
- 为每个唯一字符创建一个叶子节点,并构建一个所有叶子节点的最小堆(Min Heap用作优先队列。频率字段的值用于比较最小堆中的两个节点。最初,最不频繁的字符在根)
- 从最小堆中提取频率最小的两个节点。
- 创建一个新的内部节点,其频率等于两个节点频率的总和。将第一个提取的节点作为其左子节点,将另一个提取的节点作为其右子节点。将此节点添加到最小堆。
- 重复步骤#2 和#3,直到堆只包含一个节点。剩下的节点是根节点,树就完成了。
让我们通过一个例子来理解这个算法:
character Frequencya 5b 9c 12d 13e 16f 45
步骤 1.构建一个包含 6 个节点的最小堆,其中每个节点代表具有单个节点的树的根。
步骤 2从最小堆中提取两个最小频率节点。添加频率为 5 + 9 = 14 的新内部节点。
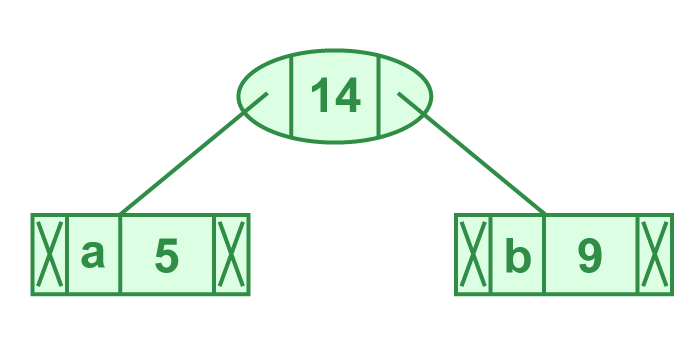
步骤 2 的图示
现在最小堆包含 5 个节点,其中 4 个节点是每个具有单个元素的树的根,一个堆节点是具有 3 个元素的树的根
character Frequencyc 12d 13Internal Node 14e 16f 45
第三步:从堆中提取两个最小频率节点。添加频率为 12 + 13 = 25 的新内部节点
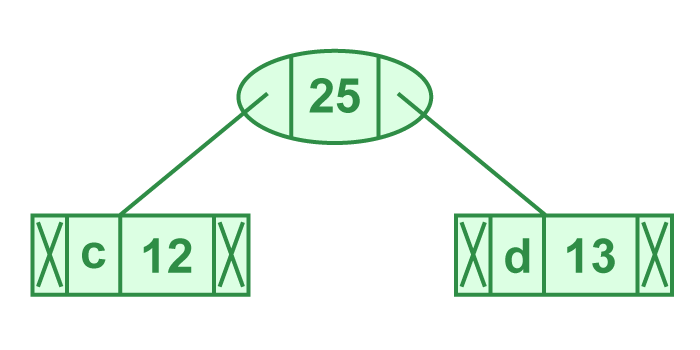
步骤 3 的图示
现在最小堆包含 4 个节点,其中 2 个节点是每个具有单个元素的树的根,两个堆节点是具有多个节点的树的根
character Frequency Internal Node 14e 16 Internal Node 25f 45
第四步:提取两个最小频率节点。添加频率为 14 + 16 = 30 的新内部节点
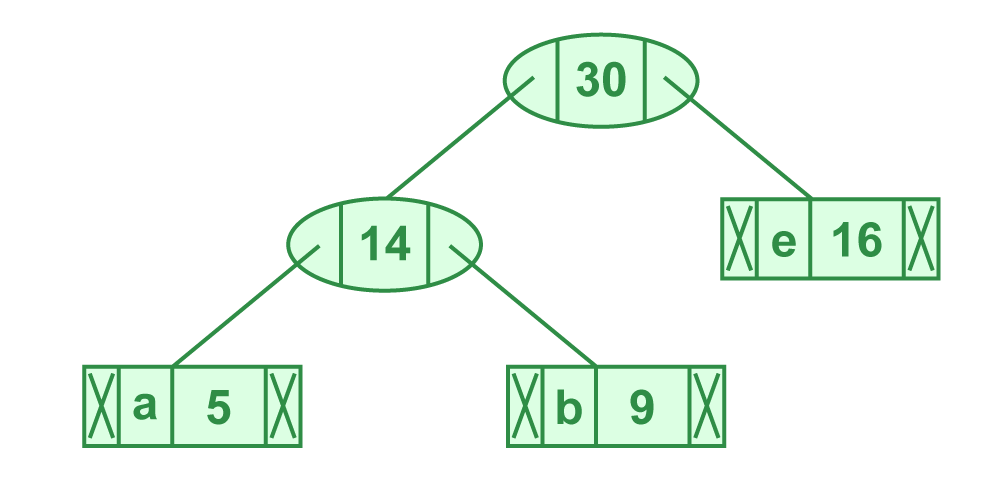
步骤 4 的图示
现在最小堆包含 3 个节点。
character Frequency Internal Node 25 Internal Node 30f 45
步骤5:提取两个最小频率节点。添加频率为 25 + 30 = 55 的新内部节点
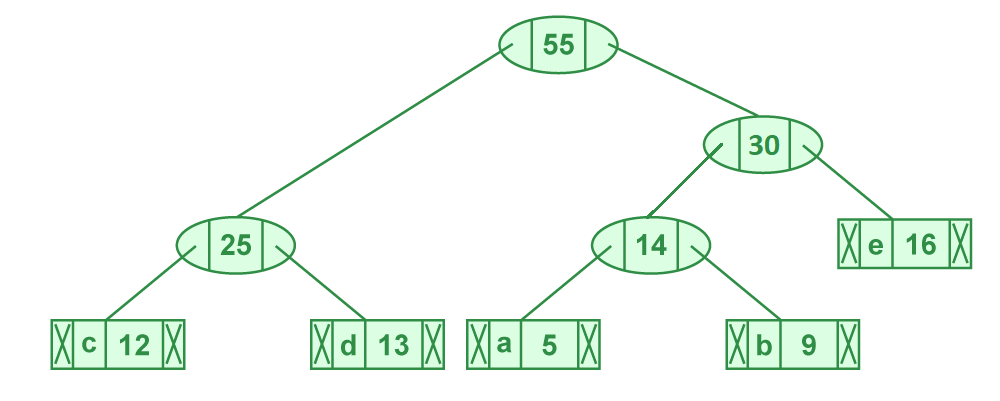
步骤 5 的图示
现在最小堆包含 2 个节点。
character Frequencyf 45 Internal Node 55
第六步:提取两个最小频率节点。添加频率为 45 + 55 = 100 的新内部节点
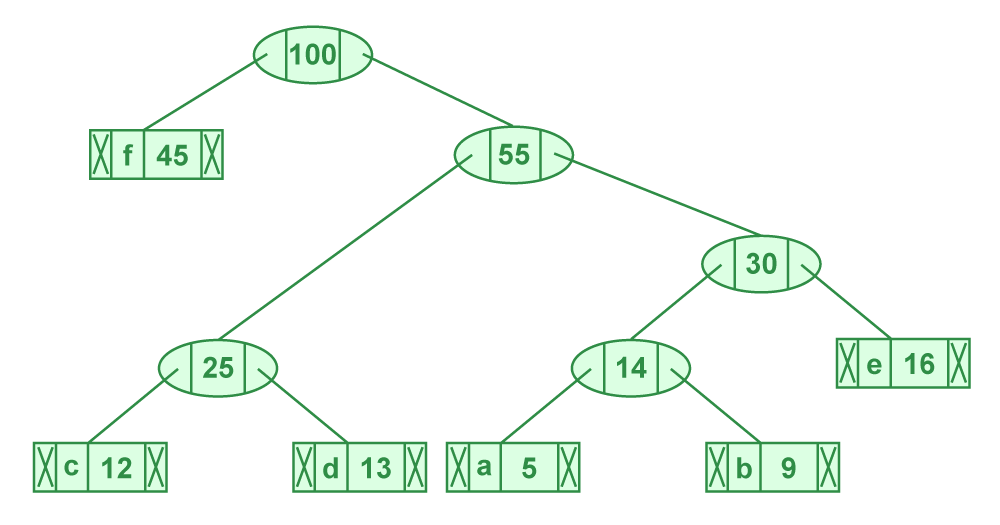
步骤 6 的图示
现在最小堆只包含一个节点。
character Frequency Internal Node 100
由于堆只包含一个节点,算法到此为止。
从哈夫曼树打印代码的步骤:
遍历从根开始形成的树。维护一个辅助数组。在移动到左孩子的同时,将 0 写入数组。在移动到右孩子的同时,将 1 写入数组。遇到叶节点时打印数组。
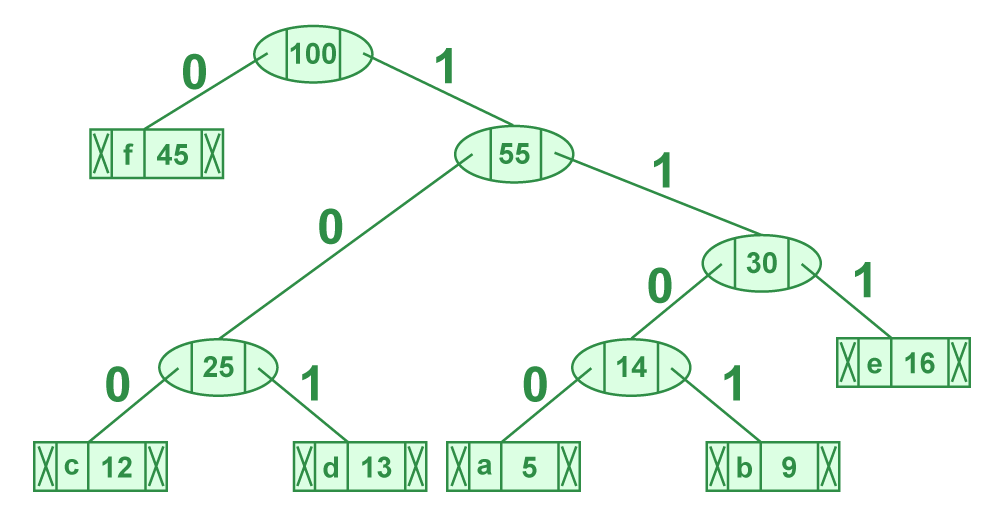
从 HuffmanTree 打印代码的步骤
代码如下:
character code-wordf 0c 100d 101a 1100b 1101e 111
下面是上述方法的实现:
// C++ program for Huffman Coding
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;// This constant can be avoided by explicitly
// calculating height of Huffman Tree
#define MAX_TREE_HT 100// A Huffman tree node
struct MinHeapNode {// One of the input characterschar data;// Frequency of the characterunsigned freq;// Left and right child of this nodestruct MinHeapNode *left, *right;
};// A Min Heap: Collection of
// min-heap (or Huffman tree) nodes
struct MinHeap {// Current size of min heapunsigned size;// capacity of min heapunsigned capacity;// Array of minheap node pointersstruct MinHeapNode** array;
};// A utility function allocate a new
// min heap node with given character
// and frequency of the character
struct MinHeapNode* newNode(char data, unsigned freq)
{struct MinHeapNode* temp = (struct MinHeapNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeapNode));temp->left = temp->right = NULL;temp->data = data;temp->freq = freq;return temp;
}// A utility function to create
// a min heap of given capacity
struct MinHeap* createMinHeap(unsigned capacity){struct MinHeap* minHeap= (struct MinHeap*)malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeap));// current size is 0minHeap->size = 0;minHeap->capacity = capacity;minHeap->array = (struct MinHeapNode**)malloc(minHeap->capacity * sizeof(struct MinHeapNode*));return minHeap;
}// A utility function to
// swap two min heap nodes
void swapMinHeapNode(struct MinHeapNode** a,struct MinHeapNode** b){struct MinHeapNode* t = *a;*a = *b;*b = t;
}// The standard minHeapify function.
void minHeapify(struct MinHeap* minHeap, int idx){int smallest = idx;int left = 2 * idx + 1;int right = 2 * idx + 2;if (left < minHeap->size&& minHeap->array[left]->freq< minHeap->array[smallest]->freq)smallest = left;if (right < minHeap->size&& minHeap->array[right]->freq< minHeap->array[smallest]->freq)smallest = right;if (smallest != idx) {swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->array[smallest],&minHeap->array[idx]);minHeapify(minHeap, smallest);}
}// A utility function to check
// if size of heap is 1 or not
int isSizeOne(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{return (minHeap->size == 1);
}// A standard function to extract
// minimum value node from heap
struct MinHeapNode* extractMin(struct MinHeap* minHeap){struct MinHeapNode* temp = minHeap->array[0];minHeap->array[0] = minHeap->array[minHeap->size - 1];--minHeap->size;minHeapify(minHeap, 0);return temp;
}// A utility function to insert
// a new node to Min Heap
void insertMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap,struct MinHeapNode* minHeapNode){++minHeap->size;int i = minHeap->size - 1;while (i&& minHeapNode->freq< minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2]->freq) {minHeap->array[i] = minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2];i = (i - 1) / 2;}minHeap->array[i] = minHeapNode;
}// A standard function to build min heap
void buildMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap){int n = minHeap->size - 1;int i;for (i = (n - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i)minHeapify(minHeap, i);
}// A utility function to print an array of size n
void printArr(int arr[], int n)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)cout << arr[i];cout << "\n";
}// Utility function to check if this node is leaf
int isLeaf(struct MinHeapNode* root){return !(root->left) && !(root->right);
}// Creates a min heap of capacity
// equal to size and inserts all character of
// data[] in min heap. Initially size of
// min heap is equal to capacity
struct MinHeap* createAndBuildMinHeap(char data[],int freq[], int size){struct MinHeap* minHeap = createMinHeap(size);for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)minHeap->array[i] = newNode(data[i], freq[i]);minHeap->size = size;buildMinHeap(minHeap);return minHeap;
}// The main function that builds Huffman tree
struct MinHeapNode* buildHuffmanTree(char data[],int freq[], int size){struct MinHeapNode *left, *right, *top;// Step 1: Create a min heap of capacity// equal to size. Initially, there are// modes equal to size.struct MinHeap* minHeap= createAndBuildMinHeap(data, freq, size);// Iterate while size of heap doesn't become 1while (!isSizeOne(minHeap)) {// Step 2: Extract the two minimum// freq items from min heapleft = extractMin(minHeap);right = extractMin(minHeap);// Step 3: Create a new internal// node with frequency equal to the// sum of the two nodes frequencies.// Make the two extracted node as// left and right children of this new node.// Add this node to the min heap// '$' is a special value for internal nodes, not// usedtop = newNode('$', left->freq + right->freq);top->left = left;top->right = right;insertMinHeap(minHeap, top);}// Step 4: The remaining node is the// root node and the tree is complete.return extractMin(minHeap);
}// Prints huffman codes from the root of Huffman Tree.
// It uses arr[] to store codes
void printCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, int arr[],int top){// Assign 0 to left edge and recurif (root->left) {arr[top] = 0;printCodes(root->left, arr, top + 1);}// Assign 1 to right edge and recurif (root->right) {arr[top] = 1;printCodes(root->right, arr, top + 1);}// If this is a leaf node, then// it contains one of the input// characters, print the character// and its code from arr[]if (isLeaf(root)) {cout << root->data << ": ";printArr(arr, top);}
}// The main function that builds a
// Huffman Tree and print codes by traversing
// the built Huffman Tree
void HuffmanCodes(char data[], int freq[], int size){// Construct Huffman Treestruct MinHeapNode* root= buildHuffmanTree(data, freq, size);// Print Huffman codes using// the Huffman tree built aboveint arr[MAX_TREE_HT], top = 0;printCodes(root, arr, top);
}// Driver code
int main()
{char arr[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };int freq[] = { 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45 };int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);HuffmanCodes(arr, freq, size);return 0;
}
// C++(STL) program for Huffman Coding with STL
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;// A Huffman tree node
struct MinHeapNode {// One of the input characterschar data;// Frequency of the characterunsigned freq;// Left and right childMinHeapNode *left, *right;MinHeapNode(char data, unsigned freq){left = right = NULL;this->data = data;this->freq = freq;}
};// For comparison of
// two heap nodes (needed in min heap)
struct compare {bool operator()(MinHeapNode* l, MinHeapNode* r){return (l->freq > r->freq);}
};// Prints huffman codes from
// the root of Huffman Tree.
void printCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, string str)
{if (!root)return;if (root->data != '$')cout << root->data << ": " << str << "\n";printCodes(root->left, str + "0");printCodes(root->right, str + "1");
}// The main function that builds a Huffman Tree and
// print codes by traversing the built Huffman Tree
void HuffmanCodes(char data[], int freq[], int size)
{struct MinHeapNode *left, *right, *top;// Create a min heap & inserts all characters of data[]priority_queue<MinHeapNode*, vector<MinHeapNode*>,compare>minHeap;for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)minHeap.push(new MinHeapNode(data[i], freq[i]));// Iterate while size of heap doesn't become 1while (minHeap.size() != 1) {// Extract the two minimum// freq items from min heapleft = minHeap.top();minHeap.pop();right = minHeap.top();minHeap.pop();// Create a new internal node with// frequency equal to the sum of the// two nodes frequencies. Make the// two extracted node as left and right children// of this new node. Add this node// to the min heap '$' is a special value// for internal nodes, not usedtop = new MinHeapNode('$',left->freq + right->freq);top->left = left;top->right = right;minHeap.push(top);}// Print Huffman codes using// the Huffman tree built aboveprintCodes(minHeap.top(), "");
}// Driver Code
int main()
{char arr[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };int freq[] = { 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45 };int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);HuffmanCodes(arr, freq, size);return 0;
}// This code is contributed by Aditya Goel
Output
f: 0 c: 100 d: 101 a: 1100 b: 1101 e: 111
时间复杂度: O(nlogn),其中 n 是唯一字符的数量。如果有 n 个节点,则调用 extractMin() 2*(n – 1) 次。extractMin() 在调用 minHeapify() 时需要 O(logn) 时间。因此,整体复杂度为 O(nlogn)。
如果输入数组已排序,则存在线性时间算法。我们很快就会在下一篇文章中讨论这个问题。
霍夫曼编码的应用:
- 它们用于传输传真和文本。
- 它们被传统的压缩格式使用,如 PKZIP、GZIP 等。
- JPEG、PNG 和 MP3 等多媒体编解码器使用霍夫曼编码(更准确地说是前缀代码)。
它在有一系列频繁出现的字符的情况下很有用。
相关文章:

霍夫曼编码 | 贪心算法 2
霍夫曼编码是一种无损数据压缩算法。其思想是为输入字符分配可变长度代码,分配代码的长度基于相应字符的频率。 分配给输入字符的可变长度代码是前缀代码,意味着代码(位序列)的分配方式是分配给一个字符的代码不是…...
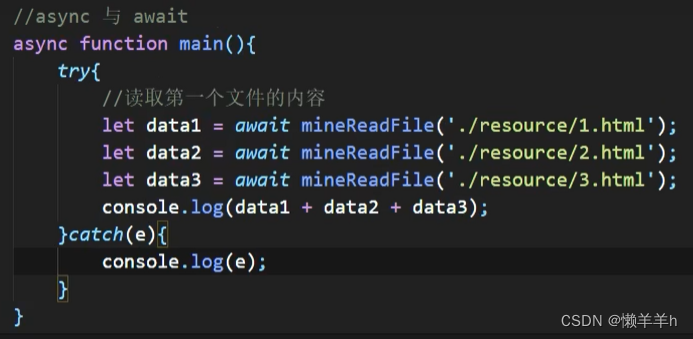
async 与 await
目录一、async函数二、await表达式三、async与await结合一、async函数 函数的返回值为promise对象promise对象的结果由async函数执行的返回值决定 async function main(){//1.如果返回的是一个非promise类型的数据,那么返回的就是成功的状态// return 521//2.如果…...

MYSQL语句
在 Navicat Premium 里面test_database数据库 ,右击 “命令列界面..” 命令列界面 中 输入命令 查看所有的数据库 show databases; 选择数据库 -- use 数据库名; use test_database; 创建表 creat table 表名(字段名1 数据类型,字段名2 数据类型) -- 创建…...
C语言函数:内存函数memcpy()以及实现
C语言函数:内存函数memcpy() 引言: #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS#include <stdlib.h>int main() {int arr1[20] { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };int arr2[20] { 0 };strcpy(arr2, arr1);return 0; } strcpy函数:C语言函数:字…...
ArcGIS基础:栅格分区转矢量再裁剪面图层【重分类】【栅格转面】
如上所示,是一个原始的栅格数据(DEM),本操作将其转为矢量要素并裁剪另外的面图层 右键属性查看数据类型,可以发现此栅格数据属于【浮点型】,这里需要注意的是:栅格转为矢量数据时,必…...

vue尚品汇商城项目-day02【11.对axios二次封装+12.接口统一管理】
文章目录11.对axios二次封装11.1为什么需要进行二次封装axios?11.2在项目当中经常有API文件夹【axios】12.接口统一管理12.1跨域问题12.2接口统一管理12.3不同请求方式的src/api/index.js说明本人其他相关文章链接11.对axios二次封装 安装命令:cnpm inst…...
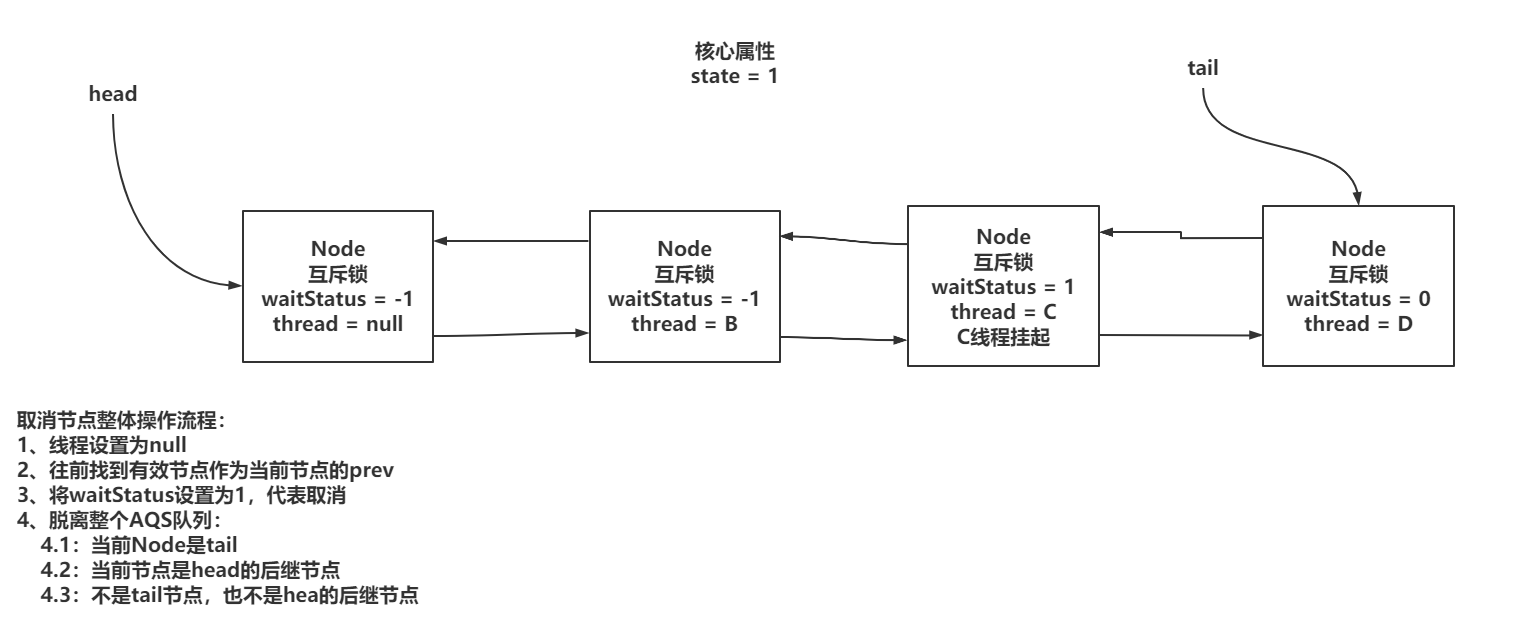
并发编程-2
1.锁的分类 1.1 可重入锁、不可重入锁 Java中提供的synchronized,ReentrantLock,ReentrantReadWriteLock都是可重入锁。 1.1.1重入: 当前线程获取到A锁,在获取之后尝试再次获取A锁是可以直接拿到的。 1.1.2不可重入ÿ…...

万字解析Linux内核调试之动态追踪
文章介绍几种常用的内核动态追踪技术,对 ftrace、perf 及 eBPF 的使用方法进行案例说明。 1、什么是动态追踪 动态追踪技术,是通过探针机制来采集内核或者应用程序的运行信息,从而可以不用修改内核或应用程序的代码,就获得调试信…...
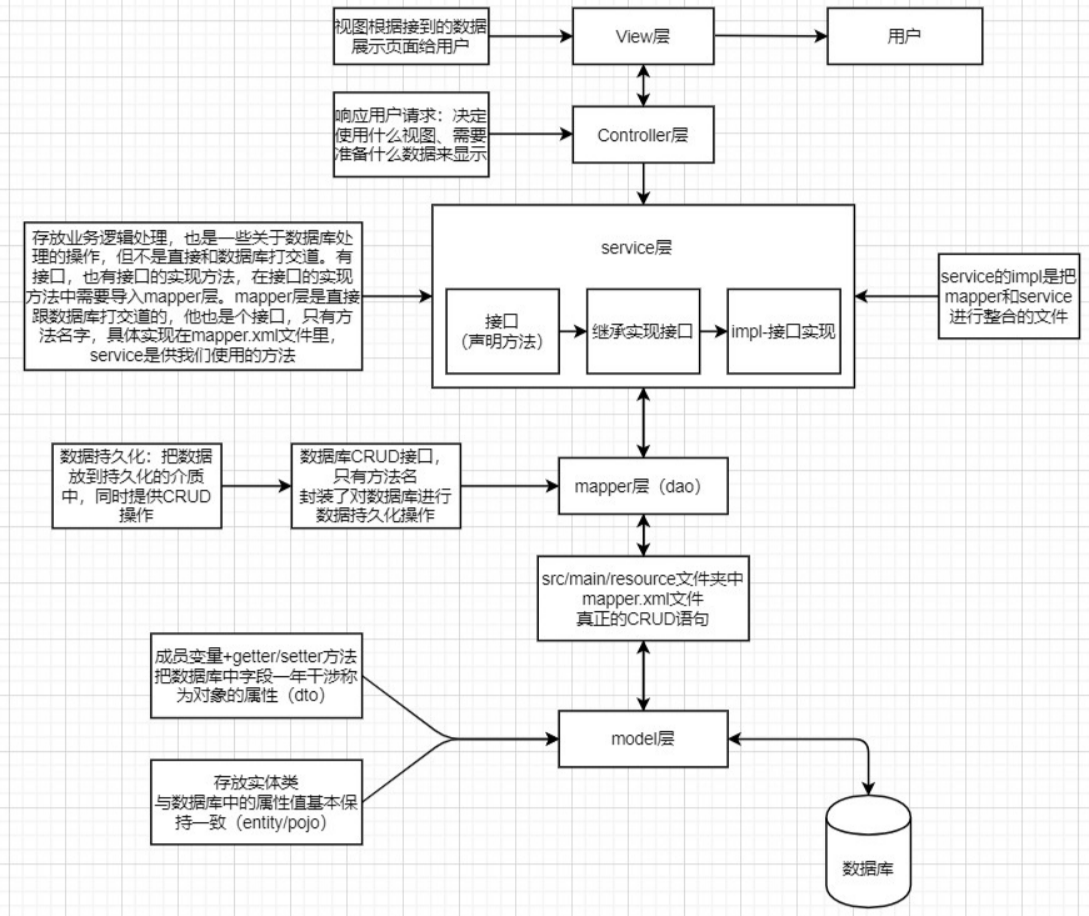
Spring Boot 各层作用与联系
目录 1 Entity 层 2 DAO 层 3 Service 层 4 Controller 层 Spring Boot 各层之间的联系: controller 层-----> service 层(接口->接口实现类) -----> dao 层的.mapper 文件 -----> 和 mapper 层里的.xml 文件对应 1 Entity 层 实体层,…...
苦中作乐---竞赛刷题(15分-20分题库)
(一)概述 (Ⅰ)彩票是幸运的 (Ⅱ)AI 英文问答程序 ( Ⅲ ) 胎压检测 (二)题目 Ⅰ 彩票的号码有 6 位数字,若一张彩票的前 3 位上的数之和等于后 3 …...
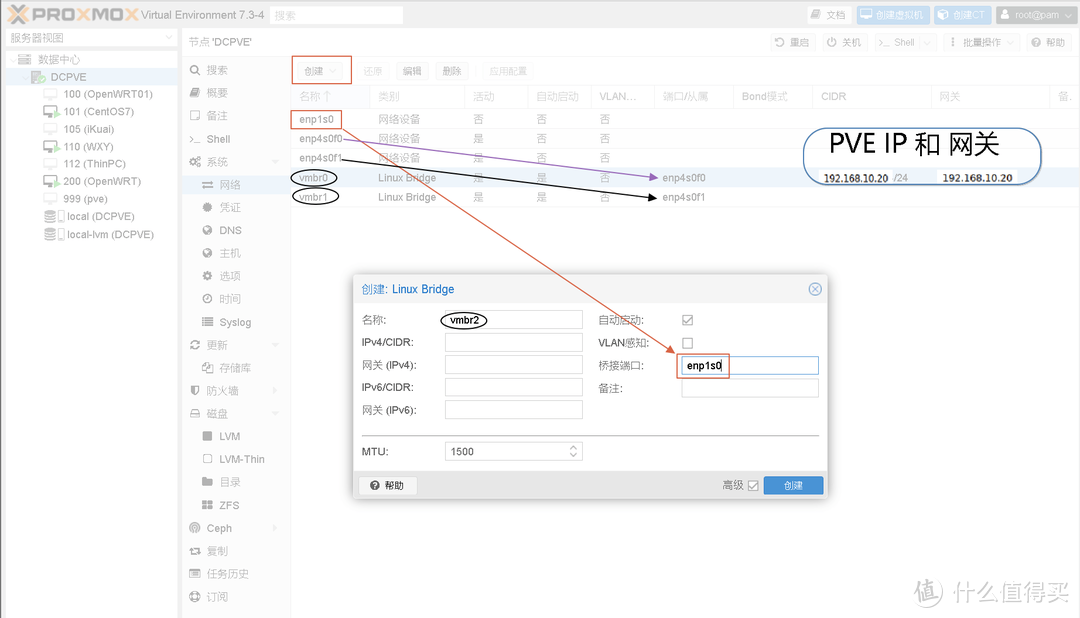
超详细,多图,PVE安装以及简单设置教程(个人记录)
前言: - 写这个的目的是因为本人健忘所以做个记录以便日后再折腾时查阅,。 - 本人笔拙如有选词,错字,语法,标点错误请忽视,大概率知道了也不会修改,本人能看懂就好。 - 内容仅适用于本人的使用环境,不同…...

茴子的写法:关于JAVA中的函数传递语法糖:lambda
解决的问题:Java中实现函数传递。 在Java编程的实践过程中,有一些场景,我们希望能够将函数传递进去,不同的函数实现代表着不同的策略,这在JDK8以前,需要定义一个接口,这个接口中定义这个函数方…...

动态规划刷题记录(2)
今天的三个题目属于模板题,可能将来会遇见它们的变形应用。 1、最长上升子序列问题 这道题目的关键就在于我们的状态定义,我们定义:f(i)表示长度为i的子序列的末尾最大值。意思就是,比如一个子序列为:1,4,5࿰…...
)
2023年广东省网络安全竞赛——Web 渗透测试解析(超级详细)
任务一:Web 渗透测试 任务环境说明: √ 服务器场景:Server03 √ 服务器场景操作系统:未知(关闭连接) 通过本地 PC 中的渗透测试平台 Kali 对靶机进行 WEB 渗透,找到页面内的文件上传漏洞并且尝试进行上传攻击,将文件上传成功后的页面回显字符串作为Flag 提交(如:…...
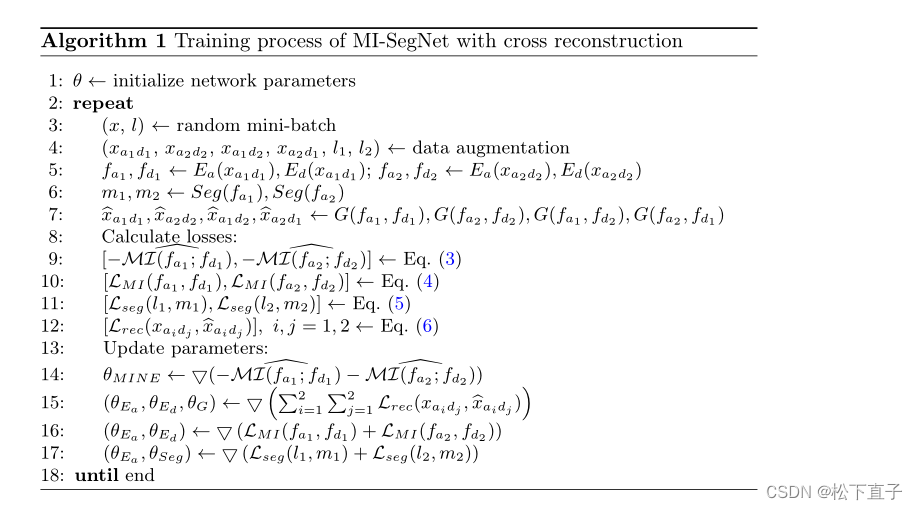
MI-SegNet阅读笔记
MI-SegNet: Mutual Information-Based US Segmentation for Unseen Domain Generalization 摘要 解决医学成像泛化能力提出了一种新的基于互信息(MI)的框架MI- segnet分离解剖结构和领域特征采用两个编码器提取相关特征:两个特征映射中出现的任何MI都将受到惩罚&a…...

十、MyBatis分页插件
1.分页插件实现的步骤 ①在pom.xml添加依赖 <dependency><groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId><artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId><version>5.2.0</version> </dependency>②配置分页插件 mybatis-config.xml 在MyB…...

EasyCVR平台国标GB28181协议设备接入时,可支持过滤通道类型
EasyCVR基于云边端智能协同架构,能支持海量视频的轻量化接入与集中汇聚管理,平台可支持多协议接入,包括市场主流标准协议与厂家私有协议及SDK,如:国标GB28181、RTMP、RTSP/Onvif、海康Ehome、海康SDK、宇视SDK等&#…...
玩转git的第1章节:git的理论以及操作规则
一 git原理 1.1 git的操作原理 上图是Git与提交有关的三个命令对应的操作: Add命令是把文件从IDE的工作目录添加到本地仓库的stage区, Commit命令把stage区的暂存文件提交到当前分支的仓库,并清空stage区。 Push命令把本地仓库的提交同步…...

【新2023Q2模拟题JAVA】华为OD机试 - 二叉树层次遍历
最近更新的博客 华为od 2023 | 什么是华为od,od 薪资待遇,od机试题清单华为OD机试真题大全,用 Python 解华为机试题 | 机试宝典【华为OD机试】全流程解析+经验分享,题型分享,防作弊指南华为od机试,独家整理 已参加机试人员的实战技巧本篇题解:二叉树层次遍历 题目 有一棵…...

轻松拿结果-第三部分 同欲 -第六章 有凝聚力才有战斗力
第三部分 同欲 “上下同欲者胜”,同结果、共承担,不仅是打造销售铁军军魂的必要条件,也能让成员们对每个结果负责,更好更快实现目标。 第六章 有凝聚力才有战斗力 管理者有担当才能上下齐心 苦劳是自己的,功劳是团队的 做管理者,就要做好承受苦劳奉献功劳的心理准备 学…...
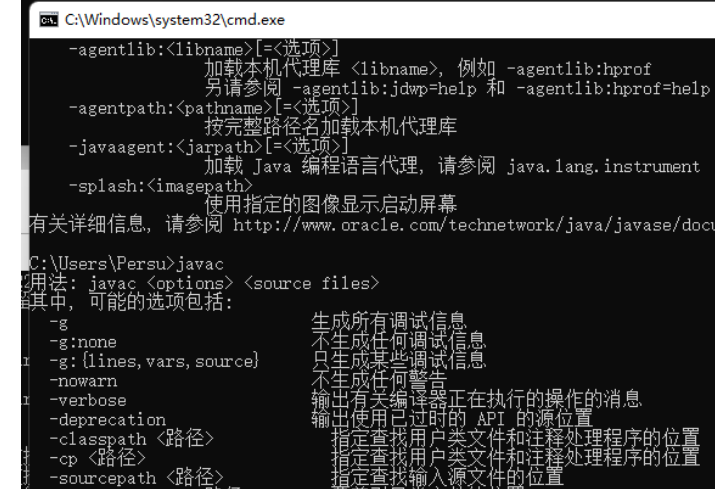
python/java环境配置
环境变量放一起 python: 1.首先下载Python Python下载地址:Download Python | Python.org downloads ---windows -- 64 2.安装Python 下面两个,然后自定义,全选 可以把前4个选上 3.环境配置 1)搜高级系统设置 2…...
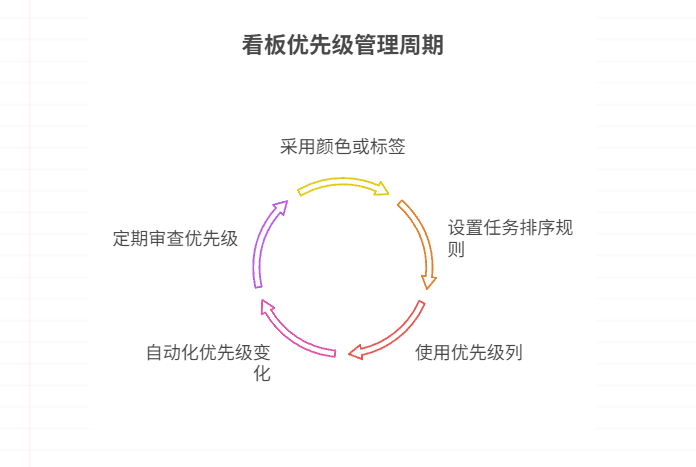
如何在看板中体现优先级变化
在看板中有效体现优先级变化的关键措施包括:采用颜色或标签标识优先级、设置任务排序规则、使用独立的优先级列或泳道、结合自动化规则同步优先级变化、建立定期的优先级审查流程。其中,设置任务排序规则尤其重要,因为它让看板视觉上直观地体…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院查看报告小程序
一、开发环境准备 工具安装: 下载安装DevEco Studio 4.0(支持HarmonyOS 5)配置HarmonyOS SDK 5.0确保Node.js版本≥14 项目初始化: ohpm init harmony/hospital-report-app 二、核心功能模块实现 1. 报告列表…...

OPENCV形态学基础之二腐蚀
一.腐蚀的原理 (图1) 数学表达式:dst(x,y) erode(src(x,y)) min(x,y)src(xx,yy) 腐蚀也是图像形态学的基本功能之一,腐蚀跟膨胀属于反向操作,膨胀是把图像图像变大,而腐蚀就是把图像变小。腐蚀后的图像变小变暗淡。 腐蚀…...
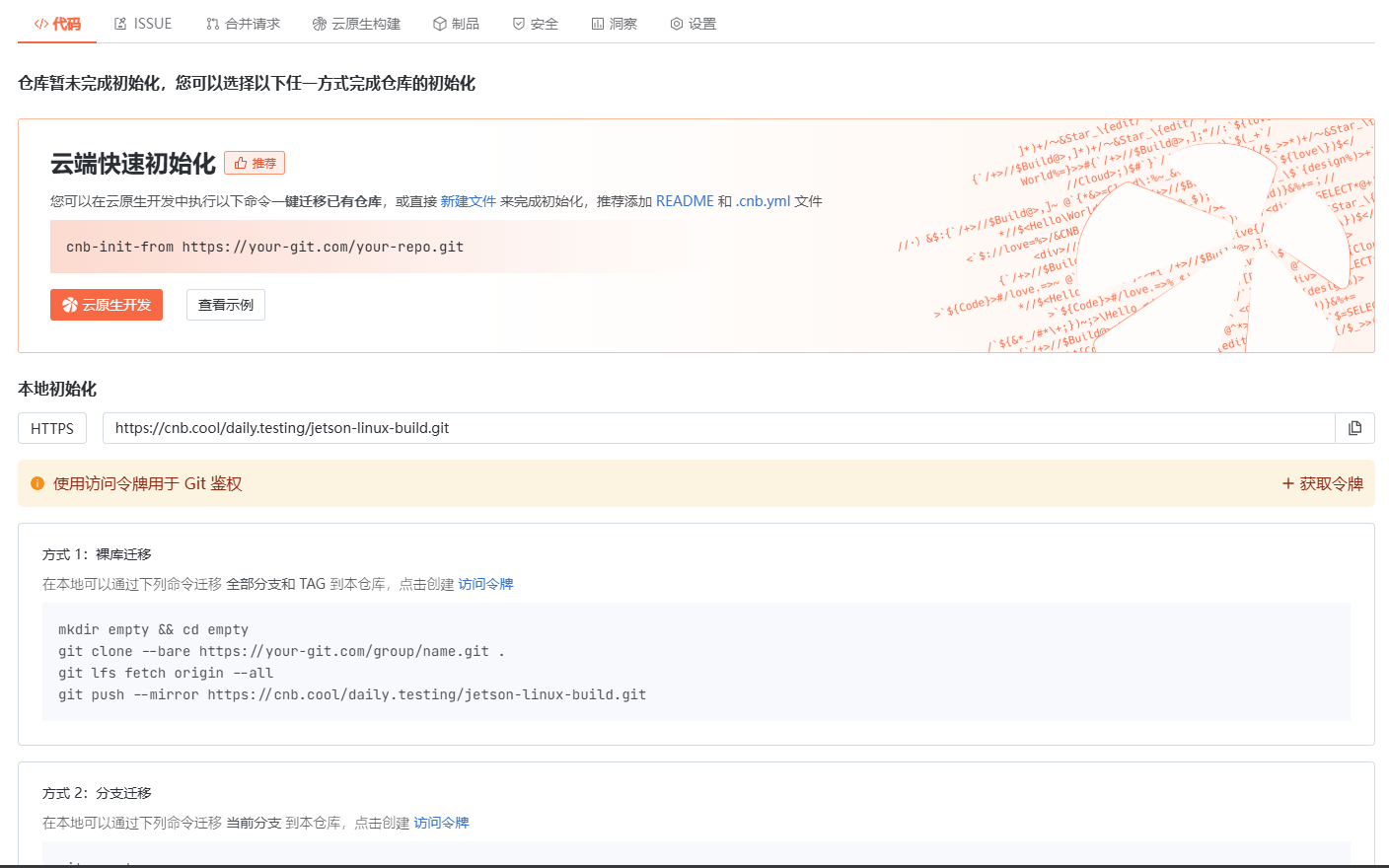
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境 引言 临时运维一个古董项目,无文档,无环境,无交接人,俗称三无。 运行设备的环境老,本地环境版本高,ssh不过去。正好最近对 腾讯出品的云原生 cnb 感兴趣&…...
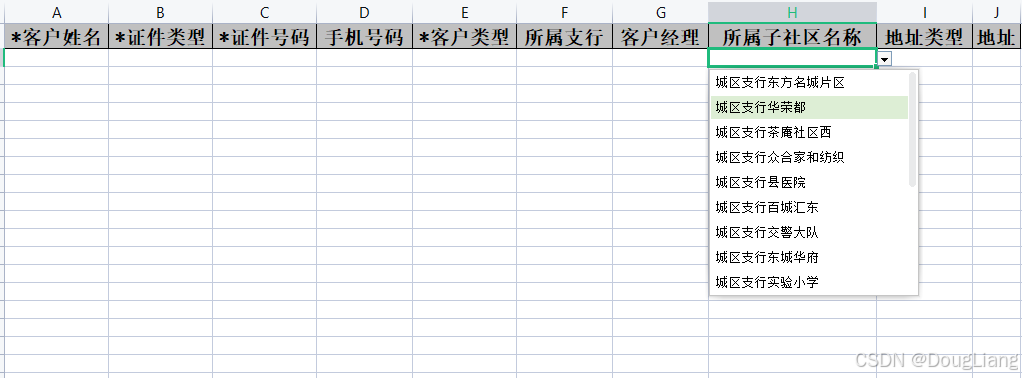
关于easyexcel动态下拉选问题处理
前些日子突然碰到一个问题,说是客户的导入文件模版想支持部分导入内容的下拉选,于是我就找了easyexcel官网寻找解决方案,并没有找到合适的方案,没办法只能自己动手并分享出来,针对Java生成Excel下拉菜单时因选项过多导…...

从零开始了解数据采集(二十八)——制造业数字孪生
近年来,我国的工业领域正经历一场前所未有的数字化变革,从“双碳目标”到工业互联网平台的推广,国家政策和市场需求共同推动了制造业的升级。在这场变革中,数字孪生技术成为备受关注的关键工具,它不仅让企业“看见”设…...

密码学基础——SM4算法
博客主页:christine-rr-CSDN博客 专栏主页:密码学 📌 【今日更新】📌 对称密码算法——SM4 目录 一、国密SM系列算法概述 二、SM4算法 2.1算法背景 2.2算法特点 2.3 基本部件 2.3.1 S盒 2.3.2 非线性变换 编辑…...

医疗AI模型可解释性编程研究:基于SHAP、LIME与Anchor
1 医疗树模型与可解释人工智能基础 医疗领域的人工智能应用正迅速从理论研究转向临床实践,在这一过程中,模型可解释性已成为确保AI系统被医疗专业人员接受和信任的关键因素。基于树模型的集成算法(如RandomForest、XGBoost、LightGBM)因其卓越的预测性能和相对良好的解释性…...

P10909 [蓝桥杯 2024 国 B] 立定跳远
# P10909 [蓝桥杯 2024 国 B] 立定跳远 ## 题目描述 在运动会上,小明从数轴的原点开始向正方向立定跳远。项目设置了 $n$ 个检查点 $a_1, a_2, \cdots , a_n$ 且 $a_i \ge a_{i−1} > 0$。小明必须先后跳跃到每个检查点上且只能跳跃到检查点上。同时࿰…...
