【C++】基于红黑树封装set和map


目录
- 前言
- 一、更高维度的泛型
- 二、模版参数
- 三、比较逻辑的重写
- 四、迭代器
- 4.1 const迭代器
- 4.2 ++重载
- 4.3 - -重载
- 五、完整代码
前言
前面我们介绍了set和map的底层细节,在上篇文章中也简单实现了红黑树,而我们知道set和map的底层就是依靠红黑树实现的,那么在本文我们将学习如何基于红黑树来封装出set和map。
本篇文章会带你深入理解C++的三大特性之一——封装。
封装屏蔽底层细节,提供统一访问方式。
一、更高维度的泛型
| 红黑树部分代码:
#pragma once#include <iostream>
using namespace std;enum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{pair<K, V> _kv;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv, Colour col = RED):_kv(kv), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _col(col){}
};template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:RBTree() = default;RBTree(const RBTree<K, V>& t){_root = _copy(t._root);}~RBTree(){_Destroy(_root);_root = nullptr;}RBTree<K, V>& operator=(RBTree<K, V> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}bool Find(const pair<K, V>& kv){Node* pcur = _root;while (pcur){if (kv.first < pcur->_kv.first){pcur = pcur->_left;}else if (kv.first > pcur->_kv.first){pcur = pcur->_right;}else{return true;}}return false;}bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){Node* pcur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;if (pcur == nullptr)//当前还没有节点{_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点必须是黑色的return true;}while (pcur){if (kv.first < pcur->_kv.first){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_left;}else if (kv.first > pcur->_kv.first){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_right;}else{return false;}}pcur = new Node(kv);if (kv.first < parent->_kv.first){parent->_left = pcur;}else{parent->_right = pcur;}pcur->_parent = parent;Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;Node* uncle = nullptr;//当父节点存在,且颜色为红,需要往上更新while (parent && parent->_col == RED){if (parent == grandfather->_left){uncle = grandfather->_right;}else{uncle = grandfather->_left;}if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)//情况一:u存在且为红{parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;if (grandfather->_parent == nullptr){grandfather->_col = BLACK;return true;}pcur = grandfather;parent = pcur->_parent;grandfather = parent->_parent;}else //情况二:u存在且为黑 / 情况三:u不存在{if (parent == grandfather->_left && pcur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_left && pcur == parent->_right){RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);pcur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_right && pcur == parent->_left){RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);pcur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_right && pcur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}return true;}
private:void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;subL->_right = parent;if (subLR){subLR->_parent = parent;}Node* parentparent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parentparent == nullptr){_root = subL;}else{if (parent == parentparent->_left){parentparent->_left = subL;}else{parentparent->_right = subL;}}subL->_parent = parentparent;}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL){subRL->_parent = parent;}subR->_left = parent;Node* parentparent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parentparent == nullptr){_root = subR;}else{if (parent == parentparent->_left){parentparent->_left = subR;}else{parentparent->_right = subR;}}subR->_parent = parentparent;}Node* _copy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}Node* newnode = new Node(root->_kv);newnode->_left = copy(root->_left);newnode->_right = copy(root->_right);return newnode;}void _Destroy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_Destroy(root->_left);_Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)//递归一定要有结束条件{return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;_InOrder(root->_right);}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};前面我们实现的红黑树存储的数据是键值对pair<K, V>,现在又需要基于红黑树封装出set和map,而我们知道set中存的是K,map中存的是pair<K, V>,它们数据类型不一样,那我们要拷贝两份红黑树的代码来分别封装set和map吗,如果真是这样那也太挫了。
我们可以想办法只用一个红黑树封装set和map,像这种使用不同类型在同一套代码中操作的需求,我们很容易就想到了模版。值得一说的是,我们实现的红黑树已经是一个类模版,不过这个类模版还不是太灵活,因为它存储类型是K还是pair<K, V>是写死的,并不能够做到完全泛型。
说到这里相信我们都想到了一个解决办法:把用于封装set和map的红黑树存储数据的类型也设计成一个模版参数,在实例化具体的类时根据传过去的值来确定是存储K还是pair<K, V>,而站在set和map层面它们肯定知道自己的数据类型。
RBTree.h:
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data, Colour col = RED): _data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _col(col){}
};template<class K, class T>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:RBTree() = default;RBTree(const RBTree<K, T>& t){_root = _copy(t._root);}~RBTree(){_Destroy(_root);_root = nullptr;}RBTree<K, T>& operator=(RBTree<K, T> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}//...
MySet.h:
namespace yjz
{template<class K>class set{public:private:RBTree<K, const K> _t;};
}
MyMap.h:
namespace yjz
{template<class K, class V>class map{public:private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>> _t;};
}
上面我们使红黑树节点模版类的模版参数仅用T来表示,当用set实例化红黑树类模版时,红黑树节点类模版参数T是K类型;当用map实例化红黑树类模版时,红黑树节点类模版参数T是pair<K, V>类型。这里相当于实现了一个更高一点维度的泛型。
二、模版参数
有同学可能注意到了,上面用红黑树封装set和map时传过去了两个参数。一个T类型不是就能确定是K还是pair<K, V>了嘛,为什么还要传过去一个K呢?而且像set传过去两个一模一样的K感觉很奇怪。其实这是为了满足红黑树一些接口的特点而不得不这样做。
bool Find(const K& key)
bool Insert(const T& data)
像上面的查找和插入操作,仅通过一个参数T还解决不了问题。对于插入操作如果是set就插入K,如果是map就插入pair<K, V>;但是对于查找操作不管是set还是map我们只能通过key查找,这是set和map的特点。 对于map来说是通过key找value,不能说骑驴找驴。
另外,这里的Find和Insert函数的返回值也需要改一改,Find函数应该返回节点的迭代器,Insert函数应该根据插入成功或失败返回相应的pair<iterator, bool>。
Iterator Find(const K& key)
{KeyOfT kot;Node* pcur = _root;while (pcur){if (key < kot(pcur->_data)){pcur = pcur->_left;}else if (key > kot(pcur->_data)){pcur = pcur->_right;}else{return Iterator(pcur, _root);}}return End();
}pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{KeyOfT kot;Node* pcur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;if (pcur == nullptr)//当前还没有节点{_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点必须是黑色的return make_pair(Iterator(_root, _root), true);}while (pcur){if (kot(data) < kot(pcur->_data)){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_left;}else if (kot(data) > kot(pcur->_data)){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_right;}else{return make_pair(Iterator(pcur, _root), false);}}pcur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = pcur;//记录新节点指针,旋转可能会更新pcurif (kot(data) < kot(parent->_data)){parent->_left = pcur;}else{parent->_right = pcur;}pcur->_parent = parent;Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;Node* uncle = nullptr;//当父节点存在,且颜色为红,需要往上更新while (parent && parent->_col == RED){if (parent == grandfather->_left){uncle = grandfather->_right;}else{uncle = grandfather->_left;}if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)//情况一:u存在且为红{parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;if (grandfather->_parent == nullptr){grandfather->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(Iterator(newnode, _root), true);}pcur = grandfather;parent = pcur->_parent;grandfather = parent->_parent;}else //情况二:u存在且为黑 / 情况三:u不存在{if (parent == grandfather->_left && pcur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_left && pcur == parent->_right){RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);pcur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_right && pcur == parent->_left){RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);pcur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_right && pcur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}return make_pair(Iterator(newnode, _root), true);
}
三、比较逻辑的重写
当我们修改了红黑树的模版参数,那它的底层实现也要做相应的修改。
例如,插入操作的部分代码:
//...while (pcur){if (data < pcur->data){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_left;}else if (data > pcur->data){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_right;}else{return false;}}
//...
同学们想一下,这里还能用data < pcur->data这种直接比较的方式吗?
当然是不可以的。如果是set还好说,key和key比较没问题;但是map就有问题了,因为我们知道pair<K, V>不是单纯的依据first比较的,来看下图中pair<K, V>的比较方式:

从上图我们可以看到second也加入了比较逻辑,这和我们期望的只依靠first比较是不符合的。
可能有同学想到了用仿函数,但是这里普通的仿函数还解决不了问题,因为仿函数的作用是让我们可以灵活的定制实际需求,而这里的问题是不能知道到底是K还是pair<K, V>。
这里我们就要想,我们期望的是:如果是set,就用key比较key;如果是map,就用first比较first。而站在红黑树的角度它是不知道接下来要实例化它的到底是set还是map的,那谁知道呢?当然是set和map他们自己知道嘛。
所以我们可以在set和map实例化红黑树时前,用仿函数提前把key和first取出来,这样在红黑树中比较时,通过回调的方式就能拿到我们想要的值。
这里我们再来回顾一下之前学的回调函数:回调函数不是由该函数的实现方直接调用,而是在待定的事件或条件发生时由另外的一方调用的,用于对该事件或条件进行响应。
MySet.h:
namespace yjz
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}
MyMap.h:
namespace yjz
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}
RBTree.h:
bool Insert(const T& data)
{KeyOfT kot;Node* pcur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;if (pcur == nullptr)//当前还没有节点{_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点必须是黑色的return true;}while (pcur){if (kot(data) < kot(pcur->_data)){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_left;}else if (kot(data) > kot(pcur->_data)){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_right;}else{return false;}}pcur = new Node(data);//...
四、迭代器

set和map的迭代器都是双向迭代器,既可以通过++操作符前进到下一个元素,也可以通过- -操作符回退到前一个元素。因为set和map的底层红黑树是二叉树,不能完成简单的++和- -,所以需要重载运算符。
这里我们先实现一下简单的构造、begin、end,以及*、->、==、!=的重载,最后再探讨++和- -的重载如何实现。
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;Node* _root;RBTreeIterator(Node* node, Node* root):_node(node),_root(root){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};
begin和end分别返回红黑树最左边节点的迭代器和最右边节点下一个空节点的迭代器。这里我们就暂且让end返回nullptr。(C++标准库中是借助哨兵节点解决end的。)

Iterator Begin()
{Node* leftMost = _root;while (leftMost && leftMost->_left){leftMost = leftMost->_left;}return Iterator(leftMost, _root);
}Iterator End()
{return Iterator(nullptr, _root);
}
4.1 const迭代器
除了普通迭代器,还需要const迭代器,const迭代器相较于普通迭代器主要是*和->的重载,为了复用普通迭代器,可以增加模版参数来提高泛型,这个在实现list迭代器中也有使用。
另外还有,set的key是不能修改的,map的key也不能修改,但value是可以修改的。既然如此,我们在pair<K, V>中K前面加上const,就能巧妙的解决这个问题。对于set也可以和map保持一致的做法。
MySet.h:
template<class K>
class set
{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};
public:typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}private:RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
MyMap.h:
template<class K, class V>
struct map
{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};
public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
RBTree.h:
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;Iterator Begin(){Node* leftMost = _root;while (leftMost && leftMost->_left){leftMost = leftMost->_left;}return Iterator(leftMost, _root);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr, _root);}ConstIterator Begin() const{Node* leftMost = _root;while (leftMost && leftMost->_left){leftMost = leftMost->_left;}return ConstIterator(leftMost, _root);}ConstIterator End() const{return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root);}RBTree() = default;RBTree(const RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>& t){_root = _copy(t._root);}~RBTree(){_Destroy(_root);_root = nullptr;}//...
4.2 ++重载
最后到了相对麻烦一点的++和- -重载,我们知道红黑树的遍历走的是中序,中序遍历是左子树、根节点、右子树,那如果通过++走到中序的下一个节点呢?

it当前指向8这个节点,按照中序遍历++应该指向11这个节点,因为左、根、右,所以++我们应该找当前节点的右节点,那么这时候就有两种情况,即右节点为空和右节点不为空。
上图情况一是右节点不为空,当右节点不为空时中序遍历的下一个节点并不一定就是当前节点的右孩子,而是当前节点右子树的最左节点。
情况二是右节点为空,右节点为空说明当前节点所在子树遍历完了,那当前节点所在子树遍历完了中序遍历下一个节点就是它的父亲吗?并不一定。接下来我们应该判断当前节点是它父亲的左孩子还是右孩子,如果是它父亲的右孩子,则说明它父亲所在子树也遍历完了,需要继续往上更新再做判断;如果是它父亲的左孩子,则下一个节点就是它的父亲。
Self& operator++()
{//1.当前节点右子树不为空if (_node->_right){Node* leftMost = _node->_right;while (leftMost && leftMost->_left){leftMost = leftMost->_left;}_node = leftMost;}else//2.当前节点右子树为空(当前节点所在子树访问完了){Node* pcur = _node;Node* parent = pcur->_parent;while (parent && pcur == parent->_right){pcur = parent;parent = pcur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;
}
4.3 - -重载

重载- -运算符和++类似,就是反过来而已。
假设当前节点的迭代器it,- -应该得到的是它的左孩子的迭代器,那这个时候也有两种情况,左孩子为空和左孩子不为空。
上图情况一是左孩子不为空,那- -得到的应该是其左子树的最右节点的迭代器;情况二是左孩子为空,左孩子为空说明当前节点所在子树遍历完了,如果当前节点是其父亲的左孩子,那说明其父亲所在子树也遍历完了,需要向上更新;如果当前节点是其父亲的右孩子,则- -得到的就是它的父亲。
值得注意的是,前面我们实现的end返回的是nullptr,而end返回的迭代器- -是要得到二叉树最右节点的迭代器的,显然我们这里的- -并不能实现,那我们就对这种情况做特殊处理。
如果当前指针为空,我们就通过_root来找到红黑树的最右节点。(这也是最开始在迭代器增加_root成员的原因。)
Self& operator--()
{//当迭代器是end()时特殊处理if (_node == nullptr){Node* rightMost = _root;while (rightMost && rightMost->_right){rightMost = rightMost->_right;}_node = rightMost;}//1.左子树不为空,找左子树最右节点else if (_node->_left){Node* rightMost = _node->_left;while (rightMost && rightMost->_right){rightMost = rightMost->_right;}_node = rightMost;}else//2.左子树为空,当前节点所在子树访问完了{Node* pcur = _node;Node* parent = pcur->_parent;while (parent && pcur == parent->_left){pcur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;
}
五、完整代码
RBTree.h:
#pragma once#include <iostream>
using namespace std;enum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data, Colour col = RED): _data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _col(col){}
};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;Node* _root;RBTreeIterator(Node* node, Node* root):_node(node),_root(root){}Self& operator++(){//1.当前节点右子树不为空if (_node->_right){Node* leftMost = _node->_right;while (leftMost && leftMost->_left){leftMost = leftMost->_left;}_node = leftMost;}else//2.当前节点右子树为空(当前节点所在子树访问完了){Node* pcur = _node;Node* parent = pcur->_parent;while (parent && pcur == parent->_right){pcur = parent;parent = pcur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Self& operator--(){//当迭代器是end()时特殊处理if (_node == nullptr){Node* rightMost = _root;while (rightMost && rightMost->_right){rightMost = rightMost->_right;}_node = rightMost;}//1.左子树不为空,找左子树最右节点else if (_node->_left){Node* rightMost = _node->_left;while (rightMost && rightMost->_right){rightMost = rightMost->_right;}_node = rightMost;}else//2.左子树为空,当前节点所在子树访问完了{Node* pcur = _node;Node* parent = pcur->_parent;while (parent && pcur == parent->_left){pcur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;RBTree() = default;RBTree(const RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>& t){_root = _copy(t._root);}~RBTree(){_Destroy(_root);_root = nullptr;}RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT>& operator=(RBTree<K, T, KeyOfT> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}Iterator Begin(){Node* leftMost = _root;while (leftMost && leftMost->_left){leftMost = leftMost->_left;}return Iterator(leftMost, _root);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr, _root);}ConstIterator Begin() const{Node* leftMost = _root;while (leftMost && leftMost->_left){leftMost = leftMost->_left;}return ConstIterator(leftMost, _root);}ConstIterator End() const{return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root);}Iterator Find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Node* pcur = _root;while (pcur){if (key < kot(pcur->_data)){pcur = pcur->_left;}else if (key > kot(pcur->_data)){pcur = pcur->_right;}else{return Iterator(pcur, _root);}}return End();}pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;Node* pcur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;if (pcur == nullptr)//当前还没有节点{_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点必须是黑色的return make_pair(Iterator(_root, _root), true);}while (pcur){if (kot(data) < kot(pcur->_data)){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_left;}else if (kot(data) > kot(pcur->_data)){parent = pcur;pcur = pcur->_right;}else{return make_pair(Iterator(pcur, _root), false);}}pcur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = pcur;//记录新节点指针,旋转可能会更新pcurif (kot(data) < kot(parent->_data)){parent->_left = pcur;}else{parent->_right = pcur;}pcur->_parent = parent;Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;Node* uncle = nullptr;//当父节点存在,且颜色为红,需要往上更新while (parent && parent->_col == RED){if (parent == grandfather->_left){uncle = grandfather->_right;}else{uncle = grandfather->_left;}if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)//情况一:u存在且为红{parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;if (grandfather->_parent == nullptr){grandfather->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(Iterator(newnode, _root), true);}pcur = grandfather;parent = pcur->_parent;grandfather = parent->_parent;}else //情况二:u存在且为黑 / 情况三:u不存在{if (parent == grandfather->_left && pcur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_left && pcur == parent->_right){RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);pcur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_right && pcur == parent->_left){RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);pcur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else if (parent == grandfather->_right && pcur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}return make_pair(Iterator(newnode, _root), true);}private:void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;subL->_right = parent;if (subLR){subLR->_parent = parent;}Node* parentparent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parentparent == nullptr){_root = subL;}else{if (parent == parentparent->_left){parentparent->_left = subL;}else{parentparent->_right = subL;}}subL->_parent = parentparent;}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL){subRL->_parent = parent;}subR->_left = parent;Node* parentparent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parentparent == nullptr){_root = subR;}else{if (parent == parentparent->_left){parentparent->_left = subR;}else{parentparent->_right = subR;}}subR->_parent = parentparent;}Node* _copy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}Node* newnode = new Node(root->_kv);newnode->_left = copy(root->_left);newnode->_right = copy(root->_right);return newnode;}void _Destroy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_Destroy(root->_left);_Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)//递归一定要有结束条件{return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;_InOrder(root->_right);}private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};
MySet.h:
#pragma once#include "RBTree.h"namespace yjz
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}iterator find(const K& key){return _t.Find(key);}private:RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};void Print(const set<int>& s){set<int>::iterator it = s.end();while (it != s.begin()){--it;cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;}void test_set(){set<int> s;int a[] = { 4,2,6,1,3,5,15,7,16,14 };for (auto e : a){s.insert(e);}for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;set<int>::iterator It = s.end();while (It != s.begin()){--It;cout << *It << " ";}cout << endl;Print(s);}
}
MyMap.h:
#pragma once#include "RBTree.h"namespace yjz
{template<class K, class V>struct map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.End();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}iterator find(const K& key){return _t.Find(key);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};void test_map(){map<string, string> m;m.insert({ "front", "前" });m.insert({ "behind", "后" });m.insert({ "left", "左" });m.insert({ "right", "右" });map<string, string>::iterator it = m.begin();m[it->first] = "前面";m["sort"] = "排序";m["string"];while (it != m.end()){//it->first += 'x';it->second += 'x';cout << it->first << "->" << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}
}
本篇文章的分享就到这里了,如果您觉得在本文有所收获,还请留下您的三连支持哦~

相关文章:

【C++】基于红黑树封装set和map
🚀个人主页:小羊 🚀所属专栏:C 很荣幸您能阅读我的文章,诚请评论指点,欢迎欢迎 ~ 目录 前言一、更高维度的泛型二、模版参数三、比较逻辑的重写四、迭代器4.1 const迭代器4.2 重载4.3 - -重载 五、完整代…...

24最新新手入门指南:Stable Diffusion!
前言 Stable Diffusion,一款新兴的开源AI绘画软件,正逐渐成为数字艺术家和爱好者的新宠。它的强大功能让用户能够轻松创造出令人印象深刻的数字艺术作品。 无论你是专业艺术家还是艺术新手,Stable Diffusion都为你提供了一个探索创造力的新…...

Java-基础
1. 导入模块不能纯粹的复制粘贴,要从new里导入,因为前者建立不了关联 2. 数组 String[] name{"张三","李四","王五"};int[] numsnew int[]{1,2,3};//二维String[][] names{{"张三","李四"},{"…...

二、后台管理系统布局菜单可拖动
前两天产品提出了一个需求,说后台管理系统的左边菜单的名称字数过多,遮挡了。希望能让客户能够看到全部的名称,给左侧菜单增加一个可拖动的功能,经过我的研究,这个功能最终也做出来了,先看效果,双击查看。 下面咱们进入实现步骤 第一步,找到文件。一般的项目中都存在l…...

socket和http区别
socket和http区别:1、主体不同;2、所处层次不同;3、连接状态不同;4、传输数据量不同;5、数据安全性不同;6、连接方式不同。其中,主体不同指的是socke是一个调用接口(API)…...

算法:974.和可以被K整除的子数组
题目 链接:leetcode链接 思路分析(前缀和 同余定理) 首先,我们要了解一下什么是同余定理 同余定理: 如果(a - b)/ p k …… 0 则 a % p b % p 证明我写在草稿纸上,如下图: 初…...

QD1-P8 HTML 格式化标签(font、pre、b、strong、i、u、del、s、sub、sup)
本节学习:HTML 格式化标签。 本节视频 www.bilibili.com/video/BV1n64y1U7oj?p8 一、font 标签 用途:定义文本的字体大小、颜色和 face(字体类型)。 示例 <!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta cha…...

红米Turbo 3工程固件预览 修复底层 体验原生态系统 默认开启diag端口
红米Turbo 3机型代码:peridot 国外版本:POCO F6 用于以下型号的小米机型:24069RA21C, 24069PC21G, 24069PC21I。搭载1.5K OLED屏、骁龙8s处理器、5000mAh电池+90W快充、5000万像素主摄。 通过博文了解 1💝💝💝-----此机型工程固件的资源刷写注意事项 2💝💝�…...

sql的调优指南及高级sql技巧
SQL调优是优化数据库性能的重要手段,涉及编写高效的SQL查询、合理设计索引、优化数据库结构等。以下是一些SQL调优指南和高级技巧: SQL调优指南 选择合适的查询方式: **避免使用SELECT ***:仅选择所需的列,减少数据传…...

生成式专题的第一节课---GAN图像生成
一、GAN的起源与发展 1.GAN的起源 GAN (生成式对抗网络)诞生于 2014 年,由 Ian Goodfellow 提出,是用于生成数据的深度学习模型,创新点是对抗性训练,即生成器与判别器的竞争关系,为图像生成、…...

中科星图GVE(案例)——AI实现建筑用地变化前后对比情况
目录 简介 函数 gve.Services.AI.ConstructionLandChangeExtraction(image1,image2) 代码 结果 知识星球 机器学习 简介 AI可以通过分析卫星图像、航拍影像或其他地理信息数据,实现建筑用地变化前后对比。以下是一种可能的实现方法: 数据获取&am…...

Spring Boot中获取application.yml中属性的几种方式
在Spring Boot应用程序中,可以通过多种方式从application.yml文件中获取配置属性。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 使用Value注解 你可以使用Value注解将application.yml中的属性注入到Spring管理的bean中。 application.yml app:name: MySpringBootAppve…...

YOLO11改进 | 注意力机制 | 结合静态和动态上下文信息的注意力机制
秋招面试专栏推荐 :深度学习算法工程师面试问题总结【百面算法工程师】——点击即可跳转 💡💡💡本专栏所有程序均经过测试,可成功执行💡💡💡 上下文Transformer(CoT&…...

Python中函数的使用方法
1 问题 在python的学习中,一个相同的程序可能会有多种不同的代码输入方式,那么函数这种方式是否方便快捷呢?今天我们来简单介绍函数的部分使用方法。 2 方法 定义函数:代码清单1Def function name (arguments):return result在上面…...

遨游智能终端赋能“危急特”场景,力推北斗技术规模化应用!
随着《北斗规模应用三年行动计划(2023-2025)》的发布,北京、湖北、重庆等多地出台北斗支持政策,北斗系统正稳步迈向“安全可控,泛在融合,开放兼容,服务全球”的发展目标。遨游通讯紧跟国家战略步…...
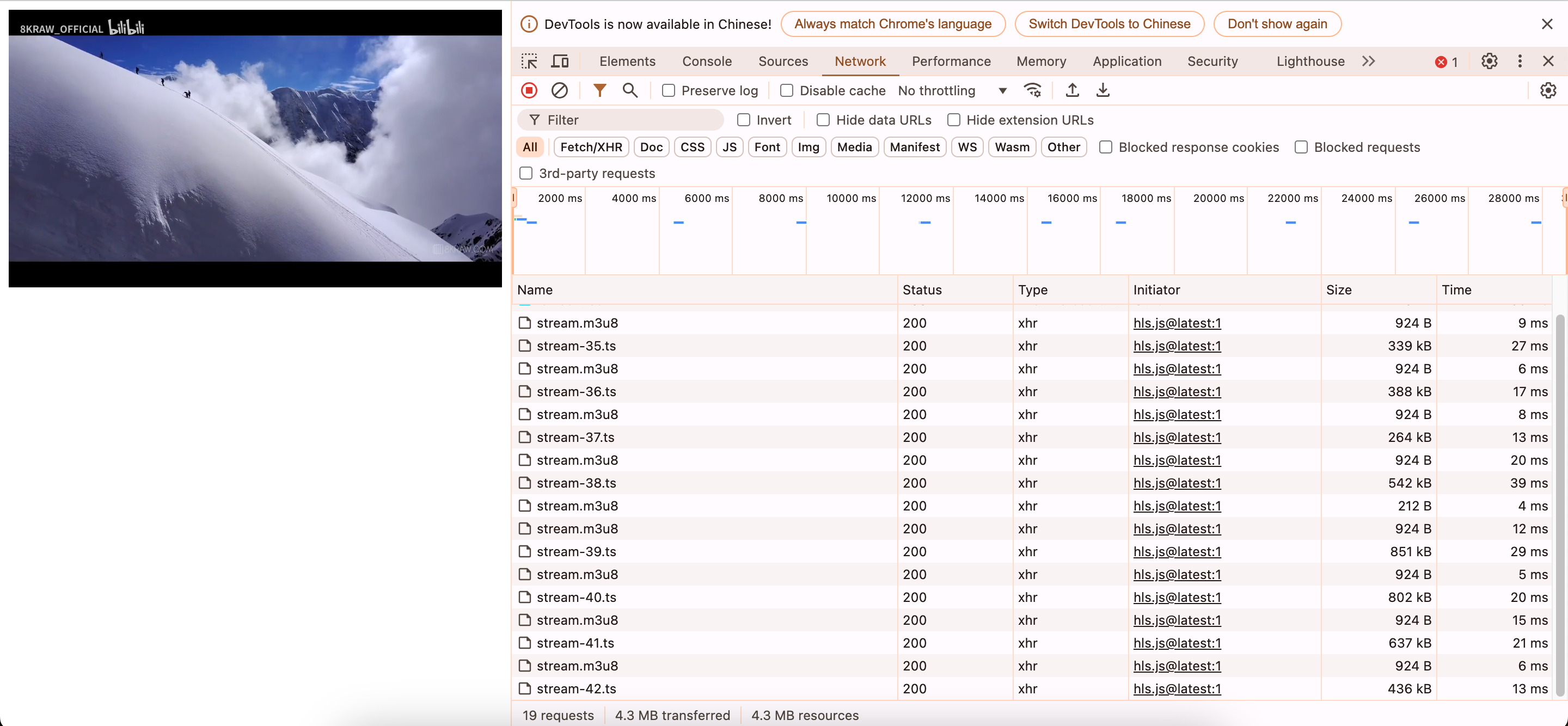
构建流媒体管道:利用 Docker 部署 Nginx-RTMP 从 FFmpeg RTMP 推流到 HLS 播放的完整流程
最近要实现一个类似导播台的功能,于是我先用 FFmpeg 实现一个参考对照的 Demo,我将其整理为一篇文章,方便后续大家或者和自己参考! 1、软件工具介绍 本次部署相关软件 / 工具如下: FFmpeg:全称是 Fast Fo…...

【汇编语言】寄存器(CPU工作原理)(六)—— 修改CS,IP的指令以及代码段
文章目录 前言1. 修改CS、IP的指令2. 问题分析:CPU运行的流程3. 代码段小结结语 前言 📌 汇编语言是很多相关课程(如数据结构、操作系统、微机原理)的重要基础。但仅仅从课程的角度出发就太片面了,其实学习汇编语言可以深入理解计…...

机器学习与神经网络:从技术前沿到诺贝尔奖的跨越与未来展望
近日,2024年诺贝尔物理学奖颁发给了机器学习与神经网络领域的研究者,这是历史上首次出现这样的情况。这项奖项原本只授予对自然现象和物质的物理学研究作出重大贡献的科学家,如今却将全球范围内对机器学习和神经网络的研究和开发作为了一种能…...

java 洛谷题单【数据结构1-2】二叉树
P4715 【深基16.例1】淘汰赛 解题思路 半区分配:将前半部分国家分配到左半区,后半部分国家分配到右半区,分别找到两个半区的最强国家。决赛和亚军确定:最后比较两个半区最强国家的能力值,失败者即为亚军,输…...

项目优化内容及实战
文章目录 事前思考Prometheus 普罗米修斯概述架构安装及使用 Grafana可视化数据库读写分离实战1-PrometheusGrafanaspringboot 事前思考 需要了解清楚:需要从哪些角度去分析实现?使用了缓存,就需要把缓存命中率数据进行收集;使用…...

【OSG学习笔记】Day 18: 碰撞检测与物理交互
物理引擎(Physics Engine) 物理引擎 是一种通过计算机模拟物理规律(如力学、碰撞、重力、流体动力学等)的软件工具或库。 它的核心目标是在虚拟环境中逼真地模拟物体的运动和交互,广泛应用于 游戏开发、动画制作、虚…...
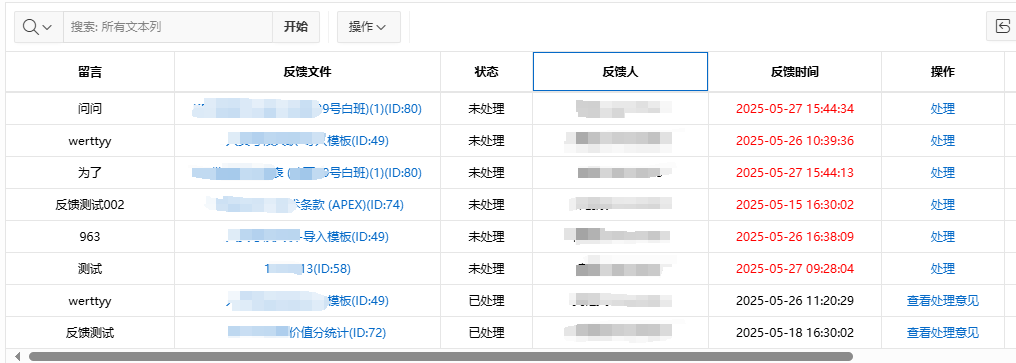
【Oracle APEX开发小技巧12】
有如下需求: 有一个问题反馈页面,要实现在apex页面展示能直观看到反馈时间超过7天未处理的数据,方便管理员及时处理反馈。 我的方法:直接将逻辑写在SQL中,这样可以直接在页面展示 完整代码: SELECTSF.FE…...
)
Spring Boot 实现流式响应(兼容 2.7.x)
在实际开发中,我们可能会遇到一些流式数据处理的场景,比如接收来自上游接口的 Server-Sent Events(SSE) 或 流式 JSON 内容,并将其原样中转给前端页面或客户端。这种情况下,传统的 RestTemplate 缓存机制会…...

Oracle查询表空间大小
1 查询数据库中所有的表空间以及表空间所占空间的大小 SELECTtablespace_name,sum( bytes ) / 1024 / 1024 FROMdba_data_files GROUP BYtablespace_name; 2 Oracle查询表空间大小及每个表所占空间的大小 SELECTtablespace_name,file_id,file_name,round( bytes / ( 1024 …...
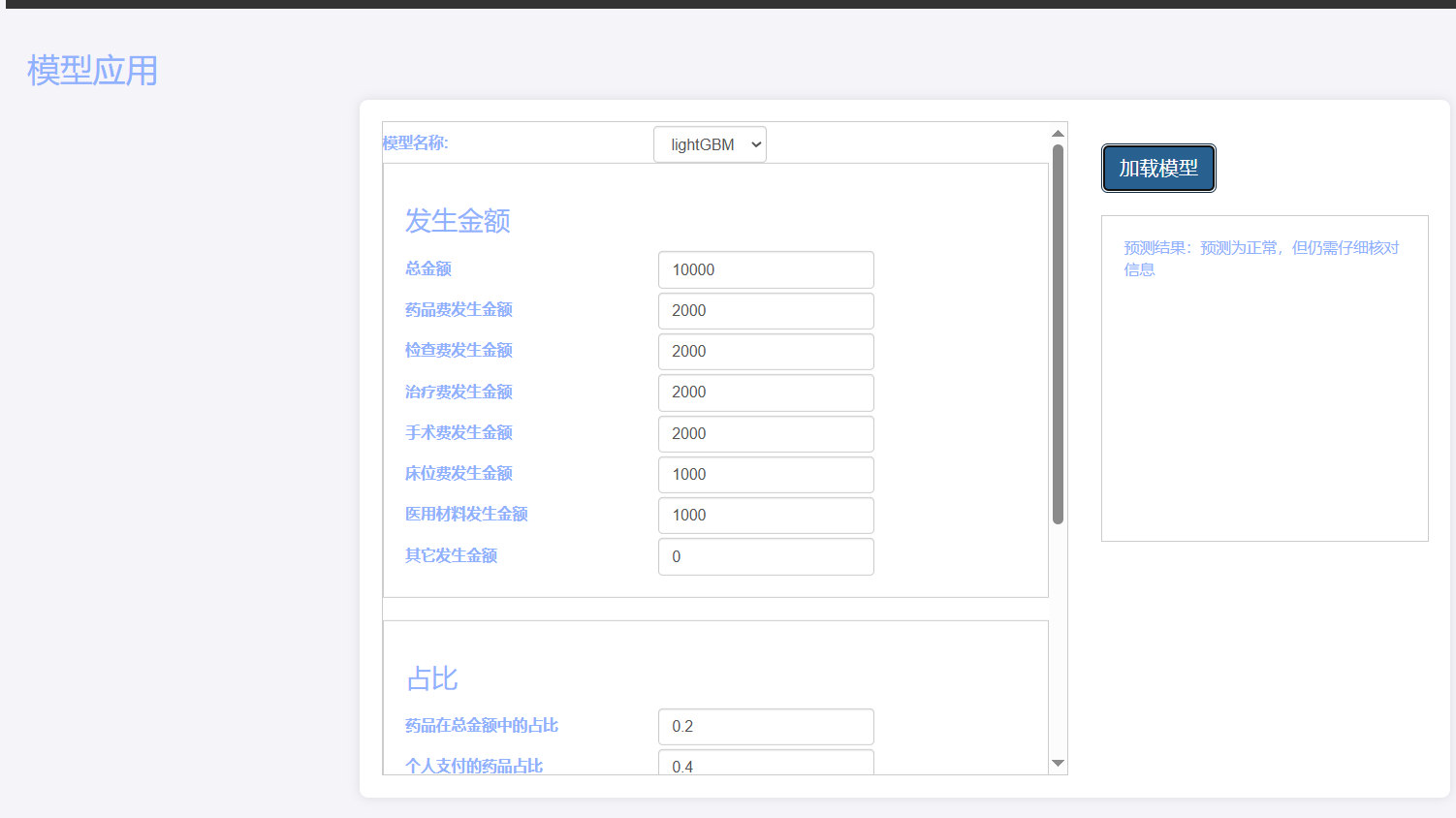
基于Flask实现的医疗保险欺诈识别监测模型
基于Flask实现的医疗保险欺诈识别监测模型 项目截图 项目简介 社会医疗保险是国家通过立法形式强制实施,由雇主和个人按一定比例缴纳保险费,建立社会医疗保险基金,支付雇员医疗费用的一种医疗保险制度, 它是促进社会文明和进步的…...

Opencv中的addweighted函数
一.addweighted函数作用 addweighted()是OpenCV库中用于图像处理的函数,主要功能是将两个输入图像(尺寸和类型相同)按照指定的权重进行加权叠加(图像融合),并添加一个标量值&#x…...

汽车生产虚拟实训中的技能提升与生产优化
在制造业蓬勃发展的大背景下,虚拟教学实训宛如一颗璀璨的新星,正发挥着不可或缺且日益凸显的关键作用,源源不断地为企业的稳健前行与创新发展注入磅礴强大的动力。就以汽车制造企业这一极具代表性的行业主体为例,汽车生产线上各类…...

React Native在HarmonyOS 5.0阅读类应用开发中的实践
一、技术选型背景 随着HarmonyOS 5.0对Web兼容层的增强,React Native作为跨平台框架可通过重新编译ArkTS组件实现85%以上的代码复用率。阅读类应用具有UI复杂度低、数据流清晰的特点。 二、核心实现方案 1. 环境配置 (1)使用React Native…...

多模态大语言模型arxiv论文略读(108)
CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文标题:CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文作者:Sayna Ebrahimi, Sercan O. Arik, Tejas Nama, Tomas Pfister ➡️ 研究机构: Google Cloud AI Re…...
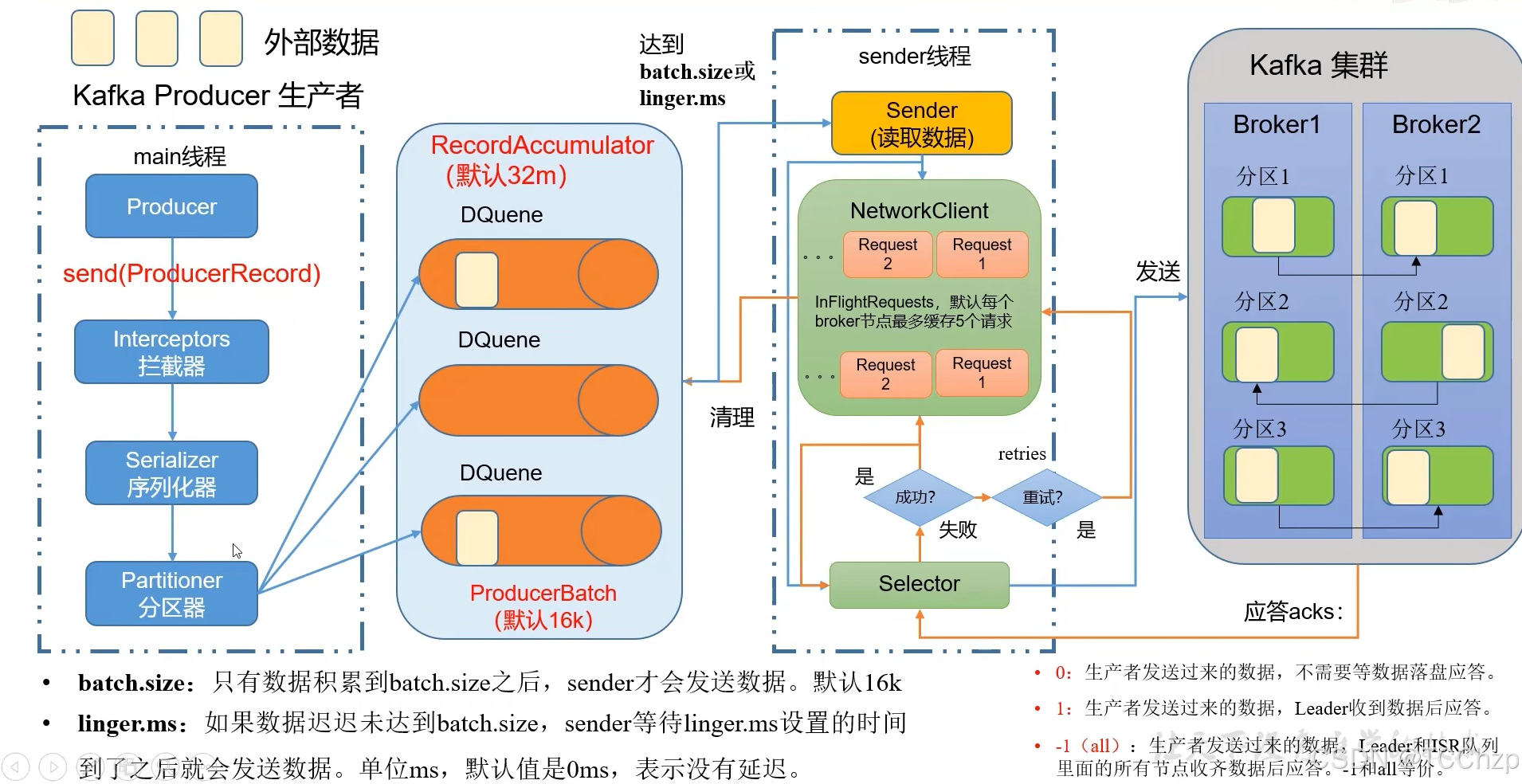
Kafka入门-生产者
生产者 生产者发送流程: 延迟时间为0ms时,也就意味着每当有数据就会直接发送 异步发送API 异步发送和同步发送的不同在于:异步发送不需要等待结果,同步发送必须等待结果才能进行下一步发送。 普通异步发送 首先导入所需的k…...
