【Coroutines】Full Understanding of Kotlinx.Corutines Framework
文章目录
- What is Corutines
- Difference between Corutine and Thread
- Fast Usage
- Suspend Function
- Advanced Usage of Coroutine
- Coroutine Essentials
- CoroutineContext
- CoroutineScope
- Predefined CoroutineScope
- Predefined Dispatchers
- Predefined CoroutineStart
- Job
- Create a Coroutine
- ContinuationInterceptor
- CoroutineExceptionHandler
What is Corutines
corutines is a modern way of async programming
a corutine is a async code block that supports suspend and resume
typically the code block looks like a synchronous block, but actually executed in async way
Difference between Corutine and Thread
both corutine and thread can achieve async works
for this point, they are the same, corutine can be regard as light-weight thread
but in fact, corutine is more a programming pattern, it cares how to write code easily
while thread is a hardware concept, it cares how cpu really works in concurrent situation
multiple corutines can run on same thread, also can run on different threads
corutines emphase how to write async code, while threads emphase the actual performance
corutines depend on threads, but it simplify traditional async programming with thread apis
Fast Usage
launch start a corutine to handle async work
step 2 will output before step 1 , because coroutine will not block code in host
import kotlinx.coroutines.*suspend fun main() {GlobalScope.launch {delay(1000L)println("step 1")}println("step 2")delay(999*1000L)
}
async start a corutine that have a return value
the return value which called deferred , can be used in other corutine
step 1 will output before step 2 this time, as corutine 2 will wait result of corutine 1
step 3 will still output before step 1
import kotlinx.coroutines.*suspend fun main() {val deferred = GlobalScope.async {delay(5000L)println("step 1")return@async 100}GlobalScope.launch {println("step 2 ${deferred.await()}")}println("step 3")delay(99000L)
}
Suspend Function
from demos above, we can see a keyword called suspend
suspend means that this function can hang up, and continue handling work in another place
suspend function can only be called from coroutine block, or other suspend functions
because only coroutine has the ability to suspend and resume, normal functions was not able to do this
behavior contrary to suspend is resume , which is often hidden under the mask of coroutines framework
Advanced Usage of Coroutine
there are many variant forms to use coroutines
you can launch a coroutine using kotlinx.coroutines library like this
import kotlinx.coroutines.*suspend fun main() {val parentJob = Job()val scope = CoroutineScope(parentJob)val dispatcher = Dispatchers.Defaultval start = CoroutineStart.LAZYval job = scope.launch(dispatcher, start) {println("coroutine by launch")}job.start()delay(999*1000L)
}
Coroutine Essentials
a coroutine contains may composed of many essentials
now, let’s introduce them one by one, please take patience here
- CoroutineContext : all essentials that determine how coroutine works
- CoroutineScope : offer a scope of current coroutine, determine which coroutine you are writting in
- CoroutineDispatcher : decide which thread coroutine work on
- CoroutineStart : decide when to execute coroutine block
- CoroutineExceptionHandler : how to handle exception when error occurs
- ContinuationInterceptor : intercept current coroutine, and create a new coroutine based on current
- most common implementation of ContinuationInterceptor is CoroutineDispatcher
- Job : present the task that coroutine handles, can be cancelled manually
- CoroutineName : give a name for current coroutine
CoroutineContext
CoroutineContext is the base class of most coroutine essential instances
coroutine context can be a single essential, or a collection of multiple essentials
context can be a standalone essential, also can hold some child essentials
likes a data struct below
class Context : Map<Key, Context>
a coroutine context can be added to another context, then form a new context contains both of them
if key is not contained in current context, add it, otherwise, replace it
val newCoroutineContext = currentContext + contextItem
coroutine essentials can be obtained from context through specific key
val job = context[Job]
val name = context[CoroutineName]
val dispather = context[CoroutineDispatcher]
val interceptor = context[ContinuationInterceptor]
val errorHandler = context[CoroutineExceptionHandler]
CoroutineContext has a direct child interface called CoroutineContext.Element
most classes are directly inherited from Element but not Context
they are actually the same thing
but Element emphas the class is intented to resolve specific requirement, not act as a collection
CoroutineScope
coroutine scope hold a coroutine context object named coroutineContext
coroutineContext holds all essentials for current coroutine
design intents of CoroutineScope can cover two aspects
- hide internal functions of actual CoroutineImpl
- offer a block scope object to control current coroutine
coroutine scope can be cancelled, when scope is cancelled, coroutine is cancelled
in fact, coroutine scope cancell coroutine by delegate object obtained from coroutineContext[Job]
Predefined CoroutineScope
-
GlobalScope
an empty scope, cannot be cancelled, always available
-
LifecycleScope
bind with android LifecycleOwner, when lifecycle is destroyed, scope will be cancelled
-
ViewModelScope
bind with android ViewModel, when ViewModel is cancelled, scope will be cancelled
Predefined Dispatchers
-
Dispatchers.Default
post to default thread pool, designed to handle computation work
-
Dispatchers.IO
post to default thread pool, designed to handle computation work
-
Dispatchers.Main
post to ui thread, designed to handle ui work, implementation depend on platform adapter
-
Dispatchers.Unconfined
not change thread, execute immediately
there are some details we should concern
-
Dispatchers.Default and Dispatchers.IO share the same thread pool
but each thread has a flag, to indicate whether receive cpu-intensive-work or memory-intensive-work
-
when Dispatchers.Unconfined is continuously used in child coroutines
tasks will be post to event loop queue, maintained in current thread, to avoid StackOverflow error
Predefined CoroutineStart
CoroutineStart define the start strategy of coroutines
before introduce of those strategies, let’s understand differences between dispatch and execute first
execute means coroutine block is executed
dispatch means coroutine block is post to thread or task queue, but not executed yet
execute always happens behind dispatch
-
CoroutineStart.DEFAULT
dispatched immediately, can be cancelled before dispatch
-
CoroutineStart.ATOMIC
dispatched immediately, but cannot be cancelled until block suspended
-
CoroutineStart.LAZY
not dispatched, until start api is actively called, such as
startjoinawait -
CoroutineStart.UNDISPATCHED
executed immediately in current calling-stack, not dispatched, until block’s first suspend
CoroutineStart.DEFAULT and CoroutineStart.LAZY are the most common ways
while CoroutineStart.ATOMIC and CoroutineStart.UNDISPATCHED are design for special scenarios
Job
represent the task coroutine handles, returned when coroutine is created
can be used to start or cancel a coroutine, and query coroutine state
- start : start coroutine
- cancel : cancel coroutine
- join : join another coroutine and wait completed
- parent : get parent job
- isCancelled : query whether coroutine is cancelled
- isCompleted : query whether coroutine is completed
- invokeOnCompletion : set cancel or complete callback
Create a Coroutine
kotlinx.coroutines framework offers several ways to create coroutines
-
CoroutineScope.launch
create a coroutine, without blocking current calling stack
-
CoroutineScope.async
create a coroutine, with a
FutureResultcalledDeferredreturned, not blocking current calling stackvalue in Deferred can be got by
await, blocking current calling stack until value returned -
withContext(CoroutineContext, CoroutineScope.() -> R)
create a coroutine, with specified context, blocking current calling stack until block finished and value returned
-
CoroutineDispatcher.invoke(CoroutineScope.() -> R)
create a coroutine, with specified dispatcher, blocking current calling stack until block finished and value returned
in fact, this is a inline function, actually calls
withContext(dispatcher, block) -
runBlocking(CoroutineContext, CoroutineScope.() -> T)
create a coroutine, with specified context, blocking until block finished and value returned
this function will not only block calling stack, but also block current thread
it is designed to use suspend-style apis in non-suspend functions
only suggest using it in main function or unit test functions
-
coroutineScope(CoroutineScope.() -> R)
create a coroutine based on current coroutine context, equivalent to
withContext(coroutineContext, block) -
supervisorScope(CoroutineScope.() -> R)
like coroutineScope, but child coroutine’s exception won’t be delivered to parent coroutine
all coroutines will start automatically by default, unless you specify other start strategy
ContinuationInterceptor
interceptor can intercept current coroutine, and extend extra operations based on origin coroutine
taking Dispatcher as an example, it handles the same work as the origin coroutine, with a thread switch operation extended
CoroutineExceptionHandler
there are two chances can trigger exception
- error occurs, and exception is thrown
- error saved in result, and get result is called
there are several handlers can handle exception
- exception handler from parent coroutine
- exception handler from current coroutine
- exception handler from thread
how exception deliver between coroutine depends on many factors
it is a complex subject, we will talk about it in next blog
相关文章:

【Coroutines】Full Understanding of Kotlinx.Corutines Framework
文章目录 What is CorutinesDifference between Corutine and ThreadFast UsageSuspend FunctionAdvanced Usage of CoroutineCoroutine EssentialsCoroutineContextCoroutineScopePredefined CoroutineScopePredefined DispatchersPredefined CoroutineStartJobCreate a Corou…...

Python面向对象,实现图片处理案例,支持:高斯模糊、Canny边缘检测、反转边缘图像、生成手绘效果、调亮度......等等
实验图片如下: 命名为img1.jpg, 放在项目下新建文件夹images下 项目构造如下: app.py源码如下 import cv2 import os from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import numpy as npclass ImageProcessor:def __init__(self, image_path):self.image cv…...

SOLID - 依赖倒置原则(Dependency Inversion Principle)
SOLID - 依赖倒置原则(Dependency Inversion Principle) 定义 依赖倒置原则(Dependency Inversion Principle,DIP)是面向对象设计中的五大基本原则之一,通常缩写为SOLID中的D。DIP由Robert C. Martin提出&…...

【.NET 8 实战--孢子记账--从单体到微服务】--需求拆分与规划
在上一篇文章中我们收集了需求,并对需求进行了简单的分析和规划,但是对于开发人员来说,上一篇文章的需求还不够详细,并且没有形成计划。因此本篇文章将带领大家来拆分需求并规划开发里程碑。 一、详细需求列表 项目组进行了多次…...

在macOS的多任务处理环境中,如何平衡应用的性能与用户体验?这是否是一个复杂的优化问题?如何优化用户体验|多任务处理|用户体验|应用设计
目录 一 多任务处理与应用性能 1. macOS中的多任务处理机制 2. 性能优化的基本策略 二 用户体验的关键要素 1. 响应速度 2. 界面友好性 3. 功能的直观性 三 平衡性能与用户体验的策略 1. 资源管理 2. 优化数据加载 3. 使用合适的线程模型 4. 实时监测和调整 四 使…...
Vscode配置CC++编程环境的使用体验优化和补充说明
文章目录 快速编译运行👺code runner插件方案Code Runner Configuration 直接配置 相关指令和快捷键默认task配置和取消默认 配置文件补充介绍(可选 推荐阅读)😊使用vscode预置变量和环境变量环境变量的使用使用环境变量的好处环境变量可能引起的问题 检…...

十个方法杜绝CAD图纸泄密风险!2024年图纸防泄密指南!「必看」
随着信息技术的发展,CAD图纸的应用日益普遍,然而随之而来的图纸泄密风险也愈加严重。企业在提升效率的同时,更需重视信息安全。为此,本文将介绍十个有效的方法,帮助企业杜绝CAD图纸泄密风险,保障商业机密。…...

技术干货|HyperMesh CFD功能详解:虚拟风洞 Part 1
虚拟风洞VWT 从2023版本开始,虚拟风洞VWT(Virtual Wind Tunnel)模块合并到HyperMesh CFD中。 用户在VWT模块中完成LBM求解器ultraFluidX的前处理设置,导出参数文件XML和模型文件STL,并在GPU服务器上提交计算。 VWT目前…...
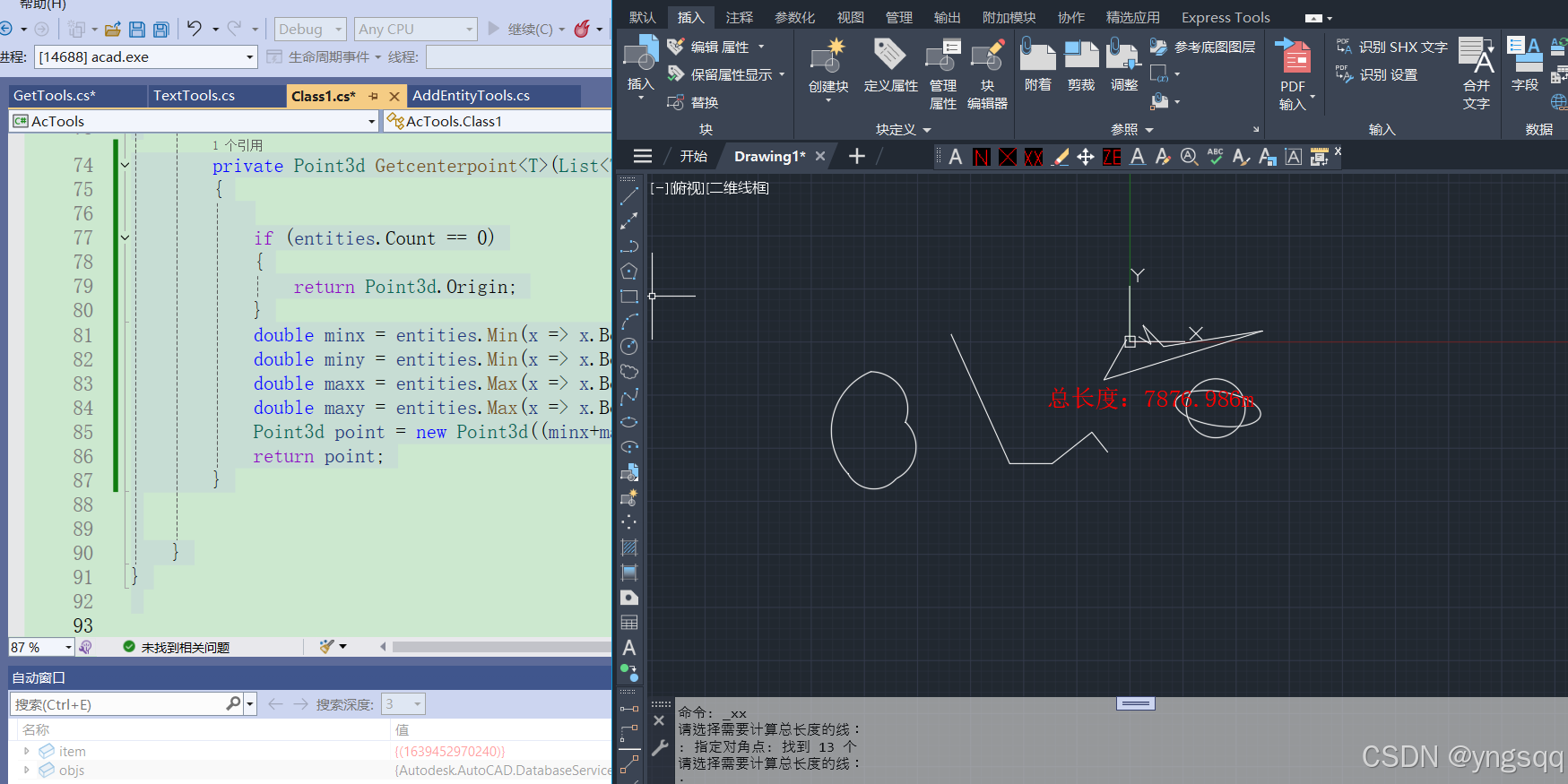
022集——统计多条线的总长度(CAD—C#二次开发入门)
如下图所示,选择多条线并统计长度: c#中不包含直接获取curve曲线长度 属性,需用如下方法:curve.GetDistanceAtParameter(item.EndParam) 附部分代码如下: using Autodesk.AutoCAD.ApplicationServices; using Autode…...

大模型重要技术系列三:高效推理
接上一篇高效训练,这一篇汇总下高效推理的方法。高效推理的两个主要优化目标是低延迟(快速得到推理结果)和高吞吐量(能同时处理很多请求),同时还要尽可能地少用资源(算力、存储、网络带宽&#…...

Android 刘海屏适配指南
如果您不希望您的内容与刘海区域重叠, 以确保您的内容不会与状态栏及 导航栏。如果您要呈现在刘海区域中,请使用 WindowInsetsCompat.getDisplayCutout() 检索 DisplayCutout 对象 包含每个刘海屏的安全边衬区和边界框。借助这些 API 您需要检查视频内容…...

微信小程序服务通知
项目中用到了小程序的服务消息通知,通知订单状态信息,下边就是整理的一下代码,放到项目中,把项目的小程序appid和小程序的secret写进去,直接运行即可 提前申请好小程序服务信息通知短信模板,代码需要用到模…...

Ubuntu使用Qt虚拟键盘,支持中英文切换
前言 最近领导给了个需求,希望将web嵌入到客户端里面,做一个客户端外壳,可以控制程序的启动、停止、重启,并且可以调出键盘在触摸屏上使用(我们的程序虽然是BS架构,但程序还是运行在本地工控机上的),我…...

泰州农商行
该文章用于测试,暴露面检测服务 1595116111115951161112159511611131595116111415951161115159511611161595116111715951161118159511611191595116112015951161121159511611221595116112315951161124159511611251595116112615951161127159511611281595116112915951…...

扫雷(C语言)
目录 前言 一、前提知识 二、扫雷游戏编写 2.2 test文件基本逻辑 2.2.1菜单编写 2.2.2game函数的逻辑 2.2.2.1定义两个数组 2.2.2.2两个数组数组的初始化 2.2.2.3打印棋盘 2.2.2.4布置雷 2.2.2.5排查雷 2.2.2.6获取坐标附近雷的数量 2.2.2.7什么时候…...

【实践功能记录8】使用UseElementSize实现表格高度自适应
一、关于 UseElementSize UseElementSize 是一个 Vue 组合式 API 的实用工具,通常用于获取 DOM 元素的尺寸信息,例如宽度、高度等。它通常与 v-slot 一起使用,以便在模板中直接访问这些尺寸信息。 地址:https://vueuse.org/core/u…...

SMO算法 公式推导
min α 1 2 ∑ i 1 N ∑ j 1 N α i α j y i y j K ( x i ⋅ x j ) − ∑ i 1 N α i s.t. ∑ i 1 N α i y i 0 0 ≤ α i ≤ C , i 1 , 2 , ⋯ , N (9-69) \begin{aligned} & \min_{\alpha} \quad \frac{1}{2} \sum_{i1}^{N} \sum_{j1}^{N} \alpha_i \alpha_j…...

nodejs包管理器pnpm
简介 通常在nodejs项目中我们使用npm或者yarn做为默认的包管理器,但是pnpm的出现让我们的包管理器有了更多的选择,pnpm相比npm具有以下优势: 速度更快,pnpm在安装依赖时,会将依赖包缓存到全局目录,下次安…...
【postman】工具下载安装
postman作用 postman用于测试http协议接口,无论是开发, 还是测试人员, 都有必要学习使用postman来测试接口, 用起来非常方便。 环境安装 postman 可以直接在chrome 上安装插件,当然大部分的同学是没法连接到谷歌商店的,我们可以在电脑本地…...

Java_Springboot核心配置详解
Spring Boot以其简洁、高效和约定优于配置的理念,极大地简化了Java应用的开发流程。在Spring Boot中,核心配置是应用启动和运行的基础。本文将详细介绍Spring Boot中的两种配置文件格式、基础注解的配置方式、自定义配置以及多环境配置。 一、Spring Bo…...
【力扣数据库知识手册笔记】索引
索引 索引的优缺点 优点1. 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。2. 可以加快数据的检索速度(创建索引的主要原因)。3. 可以加速表和表之间的连接,实现数据的参考完整性。4. 可以在查询过程中,…...

系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询优化策略
系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询分表策略 背景Solution --- 分表 背景 使用audit log实现Audi Trail功能 Audit Trail范围: 六个月数据量: 每秒5-7条audi log,共计7千万 – 1亿条数据需要实现全文检索按照时间倒序因为license问题,不能使用ELK只能使用…...

MVC 数据库
MVC 数据库 引言 在软件开发领域,Model-View-Controller(MVC)是一种流行的软件架构模式,它将应用程序分为三个核心组件:模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)。这种模式有助于提高代码的可维护性和可扩展性。本文将深入探讨MVC架构与数据库之间的关系,以…...
详解:相对定位 绝对定位 固定定位)
css的定位(position)详解:相对定位 绝对定位 固定定位
在 CSS 中,元素的定位通过 position 属性控制,共有 5 种定位模式:static(静态定位)、relative(相对定位)、absolute(绝对定位)、fixed(固定定位)和…...

Python竞赛环境搭建全攻略
Python环境搭建竞赛技术文章大纲 竞赛背景与意义 竞赛的目的与价值Python在竞赛中的应用场景环境搭建对竞赛效率的影响 竞赛环境需求分析 常见竞赛类型(算法、数据分析、机器学习等)不同竞赛对Python版本及库的要求硬件与操作系统的兼容性问题 Pyth…...
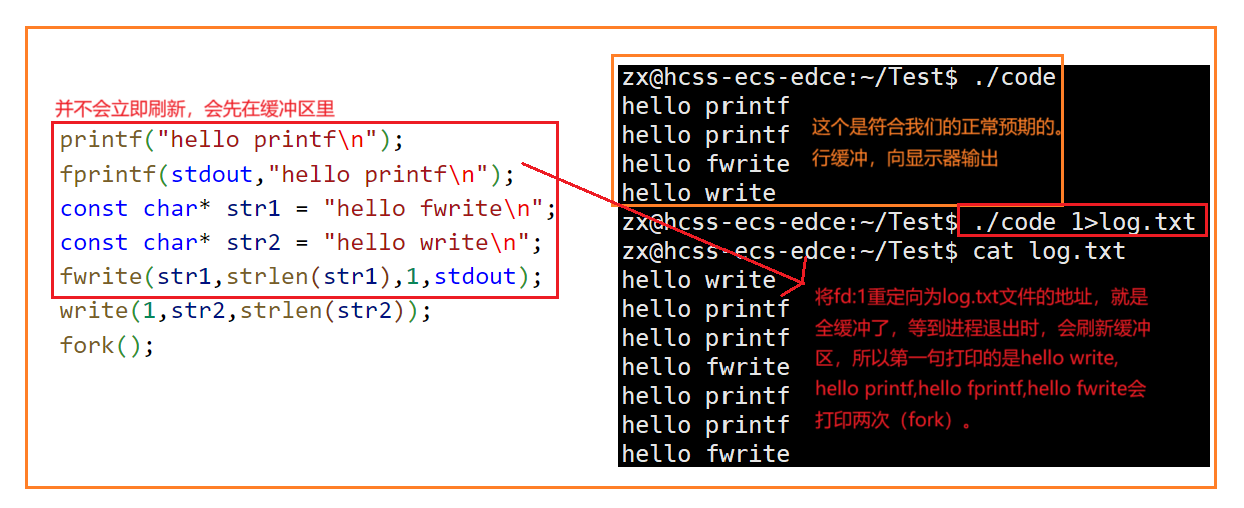
Linux中《基础IO》详细介绍
目录 理解"文件"狭义理解广义理解文件操作的归类认知系统角度文件类别 回顾C文件接口打开文件写文件读文件稍作修改,实现简单cat命令 输出信息到显示器,你有哪些方法stdin & stdout & stderr打开文件的方式 系统⽂件I/O⼀种传递标志位…...
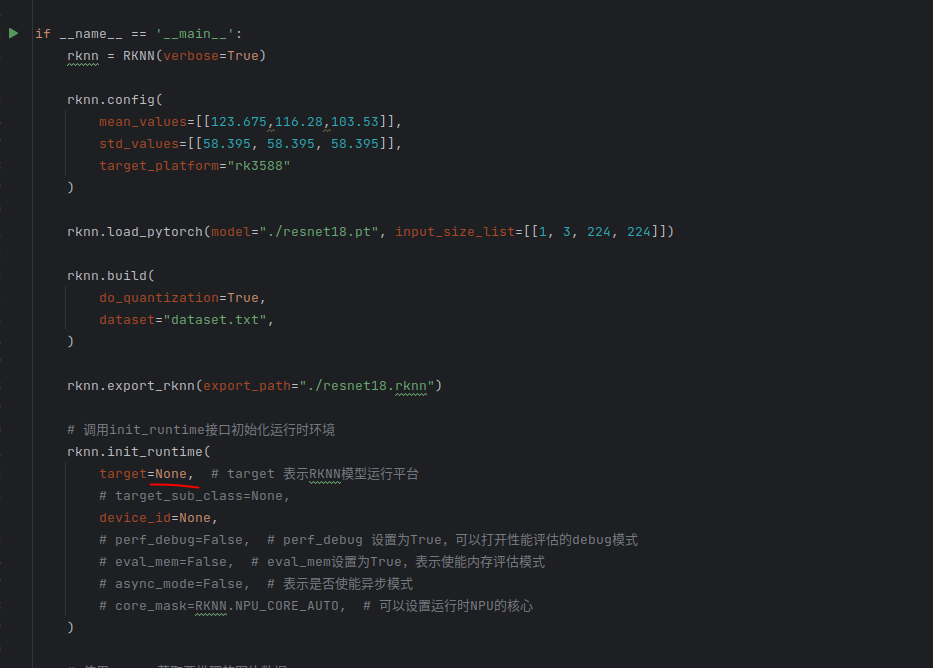
rknn toolkit2搭建和推理
安装Miniconda Miniconda - Anaconda Miniconda 选择一个 新的 版本 ,不用和RKNN的python版本保持一致 使用 ./xxx.sh进行安装 下面配置一下载源 # 清华大学源(最常用) conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn…...
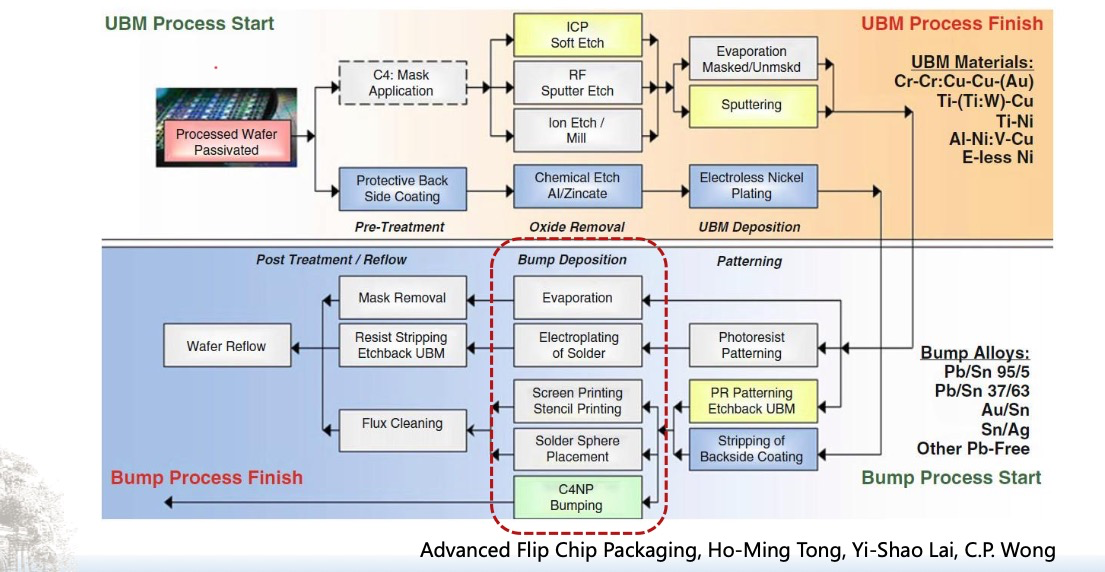
倒装芯片凸点成型工艺
UBM(Under Bump Metallization)与Bump(焊球)形成工艺流程。我们可以将整张流程图分为三大阶段来理解: 🔧 一、UBM(Under Bump Metallization)工艺流程(黄色区域ÿ…...

React核心概念:State是什么?如何用useState管理组件自己的数据?
系列回顾: 在上一篇《React入门第一步》中,我们已经成功创建并运行了第一个React项目。我们学会了用Vite初始化项目,并修改了App.jsx组件,让页面显示出我们想要的文字。但是,那个页面是“死”的,它只是静态…...

【多线程初阶】单例模式 指令重排序问题
文章目录 1.单例模式1)饿汉模式2)懒汉模式①.单线程版本②.多线程版本 2.分析单例模式里的线程安全问题1)饿汉模式2)懒汉模式懒汉模式是如何出现线程安全问题的 3.解决问题进一步优化加锁导致的执行效率优化预防内存可见性问题 4.解决指令重排序问题 1.单例模式 单例模式确保某…...
