彻底理解链表(LinkedList)结构
目录
- 比较
- 操作
- 结构封装
- 单向链表
- 实现
- 面试题
- 循环链表
- 实现
- 双向链表
- 实现
链表(Linked List)是一种线性数据结构,由一组节点(Node)组成,每个节点包含两个部分:数据域(存储数据)和指针域(指向下一个节点的地址)。与数组不同,链表中的元素在内存中不是连续存储的,使用指针进行连接
-
链表类似于火车:有一个火车头,火车头会连接一个节点,节点上有乘客(类似于数据),并且这个节点会连接下一个节点,以此类推

-
实现栈和队列:链表结构非常适合实现这些数据结构。
-
LRU缓存:双向链表和哈希表结合实现。
-
操作系统进程管理:使用链表管理进程调度队列。
-
图和树结构:使用链表作为底层存储
比较
链表和数组一样,可以用于存储一系列的元素,但是链表和数组的实现机制完全不同
-
数组:
-
数组的创建通常需要申请一段连续的内存空间(一整块的内存),并且大小是固定的(大多数编程语言数组都是固定的)
-
当前数组不能满足容量需求时,需要扩容。 (一般情况下是申请一个更大的数组,比如2倍,然后将原数组中的元素复制过去)
-
在数组开头或中间位置插入数据的成本很高,需要进行大量元素的位移
-
-
链表:
-
链表中的元素在内存中不必是连续的空间,可以充分利用计算机的内存,实现灵活的内存动态管理
-
链表不必在创建时就确定大小,并且大小可以无限的延伸下去
-
链表在插入和删除数据时,时间复杂度可以达到O(1),相对数组效率高很多
-
链表访问任何一个位置的元素时,都需要从头开始访问。(无法跳过第一个元素访问任何一个元素)
-
链表无法通过下标直接访问元素,需要从头一个个访问,直到找到对应的元素
-
-
时间复杂度对比
-
在实际开发中,选择使用数组还是链表 需要根据具体应用场景来决定
-
如果数据量不大,且需要频繁随机 访问元素,使用数组可能会更好
-
如果数据量大,或者需要频繁插入 和删除元素,使用链表可能会更好

-
操作
-
append(element):向链表尾部添加一个新的项 -
travers():为了可以方便的看到链表上的每一个元素,我们实现一个遍历链表每一个元素的方法 -
insert(position,element):向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项 -
get(position):获取对应位置的元素 -
indexOf(element):返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素则返-1 -
update(position,element):修改某个位置的元素 -
removeAt(position):从链表的特定位置移除一项 -
remove(element):从链表中移除一项 -
peek():头的值 -
isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0则返回false -
size():链表的长度
结构封装
-
封装一个
Node类,用于封装每一个节点上的信息(包括值和指向下一个节点的引用),它是一个泛型类 -
封装一个
LinkedList类,用于表示我们的链表结构和操作 -
链表中我们保存三个属性,一个是链表的长度,一个是链表中第一个节点,这里也加最后一个节点,方便实现循环和双向链表
class Node<T> {value: T;next: Node<T>;constructor(value: T) {this.value = value;}
}export interface ILinkedList<T> {append(value: T): void;traverse(): void;insert(value: T, position: number): boolean;removeAt(position: number): T | null;get(position: number): T | null;update(value: T, position: number): boolean;indexOf(value: T): number;remove(value: T): T | null;isEmpty(): boolean;size(): number
}class LinkedList<T> implements ILinkedList<T> {head: Node<T> | null = null;tail: Node<T> | null = null;length: number = 0;append(value: T): void {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}traverse(): void {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}insert(value: T, position: number): boolean {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}removeAt(position: number): T | null {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}get(position: number): T | null {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}update(value: T, position: number): boolean {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}indexOf(value: T): number {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}remove(value: T): T | null {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}peek(value: T): T | undefined {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}isEmpty(): boolean {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}size(): number {throw new Error("Method not implemented.");}
}const linked = new LinkedList<string>();
console.log(linked.head); // null
单向链表

实现
在下面实现各种方法时,我们会定义变量 previous 来保存前一个节点和 current 保存当前节点
-
各种方法实现都是通过操作变量来达到操作链表
-
这是因为变量实际上是链表中节点的引用,而不是节点的副本
-
链表的节点是对象,变量实际上指向的是链表中某个节点的内存地址(引用)
-
因此当我们修改变量时也会影响链表中的节点,这种机制使得我们能够轻松操作链表中的节点
-
部分方法图解如下:
-
append(element): 向链表表尾部追加数据链表为空,直接赋值为
head链表不为空,需要向其他节点后面追加节点

-
insert(position,element)添加到第一个位置,表示新添加的节点是头,需要将原来的头节点作为新节点的
next,head指向新节点添加到其他位置,需要先找到这个节点位置,通过循环向下找,并在这个过程中保存上一个节点和下一个节点,找到正确的位置后,将新节点的
next指向下一个节点,将上一个节点的next指向新的节点(步骤颠倒后续链表之间的连接就会断掉)
-
removeAt(position):从链表的特定位置移除一项移除第一项时,直接让
head指向第二项信息,第一项信息没有引用指向后面会被回收掉移除其他项的信息时,通过循环,找到正确的位置,将上一项的
next指向current项的next

-
-
完整代码如下: 抽取共同方法
export class Node<T> {value: T;next: Node<T> | null = null;constructor(value: T) {this.value = value;} }export interface ILinkedList<T> {append(value: T): void;traverse(): void;insert(value: T, position: number): boolean;removeAt(position: number): T | null;get(positon: number): T | null;update(value: T, position: number): boolean;indexOf(value: T): number;remove(value: T): T | null;peek(value: T): T | undefined;isEmpty(): boolean;size(): number; }export class LinkedList<T> implements ILinkedList<T> {// 使用protected也是为了让其子类继承时使用protected head: Node<T> | null = null;protected tail: Node<T> | null = null;protected length: number = 0;protected getNode(position: number): {previous: Node<T> | null;current: Node<T> | null;} {let index = 0;let previous: Node<T> | null = null;let current = this.head;while (index++ < position && current) {previous = current;current = current.next;}return { current, previous };}private isTail(node: Node<T>) {return this.tail === node;}/* 向链表表尾部追加数据 */append(value: T): void {const newNode = new Node(value);// 链表为空,直接赋值为headif (!this.head) {this.head = newNode;} else {// 链表不为空,循环找到尾部节点,让其next指向新节点完成追加// let current = this.head;// while (current.next) {// current = current.next;// }// current.next = newNode;this.tail!.next = newNode;}this.tail = newNode;this.length++;}/* 链表的遍历方法 */traverse(): void {let values: T[] = [];let current = this.head;while (current) {values.push(current.value);current = this.isTail(current) ? null : current.next; // 考虑循环链表的情况}if (this.head && this.tail!.next === this.head) {// 循环链表时values.push(this.head.value);}console.log(this.length, values.join(" -> "));}/* 向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项 */insert(value: T, position: number): boolean {// 1.越界的判断if (position < 0 && position > this.length) return false;// 2.根据value创建新的节点const newNode = new Node(value);let { previous, current } = this.getNode(position);// 头部插入if (position === 0) {newNode.next = this.head;this.head = newNode;} else {// 中尾部插入newNode.next = current;previous!.next = newNode;if (position === this.length) {// 尾部插入tail为新节点this.tail = newNode;}}this.length++;return true;}removeAt(position: number): T | null {// 1.越界的判断if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;let { current, previous } = this.getNode(position);if (position === 0) {this.head = current?.next ?? null;if (this.length === 1) {this.tail = null;}} else {previous!.next = current?.next ?? null;if (current === this.tail) {// 尾部删除tail为前一个节点this.tail = previous;}}this.length--;return current?.value ?? null;}// 获取方法get(position: number): T | null {// 越界问题if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;let { current } = this.getNode(position);return current?.value ?? null;}// 更新方法update(value: T, position: number): boolean {if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;// 获取对应位置的节点, 直接更新即可let { current } = this.getNode(position);current!.value = value;return true;}// 根据值, 获取对应位置的索引indexOf(value: T): number {let index = 0;let current = this.head;while (current) {if (current.value === value) return index;current = this.isTail(current) ? null : current.next; // 考虑循环链表的情况index++;}return -1;}// 删除方法: 根据value删除节点remove(value: T): T | null {const index = this.indexOf(value);return this.removeAt(index);}peek(): T | undefined {return this.head?.value;}// 判读单链表是否为空isEmpty(): boolean {return this.length === 0;}size(): number {return this.length;} }const linked = new LinkedList<string>(); linked.append("aaa"); linked.append("bbb"); linked.append("ccc"); linked.traverse(); // 3 aaa -> bbb -> ccclinked.insert("zzz", 0); linked.insert("ddd", 2); linked.insert("eee", 5); linked.traverse(); // 6 zzz -> aaa -> ddd -> bbb -> ccc -> eeeconsole.log(linked.removeAt(0)); // zzz console.log(linked.removeAt(1)); // ddd console.log(linked.removeAt(3)); // eee linked.traverse(); // 3 aaa -> bbb -> cccconsole.log(linked.get(0)); // aaa console.log(linked.get(1)); // bbb console.log(linked.get(2)); // ccc console.log(linked.get(3)); // nullconsole.log(linked.update("aa", 0)); // true console.log(linked.update("cc", 2)); // true console.log(linked.update("dd", 3)); // false linked.traverse(); // 3 aa -> bbb -> ccconsole.log(linked.indexOf("aa")); // 0 console.log(linked.indexOf("ccc")); // -1linked.remove("bbb"); linked.traverse(); // 2 aa -> ccconsole.log(linked.isEmpty()); // false
面试题
-
设计链表 https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-linked-list/description/ 上面代码已经完成

-
删除链表中的节点 https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/description/

class ListNode {val: number;next: ListNode | null;constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;this.next = next === undefined ? null : next;} }function deleteNode(node: ListNode | null): void {node!.val = node!.next!.valnode!.next = node!.next!.next } -
反转链表 https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/

-
非递归实现:

class Node {val: number;next: ListNode | null;constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;this.next = next === undefined ? null : next;} } function reverseList(head: Node | null): Node | null {// 1.判断节点为null, 或者只要一个节点, 那么直接返回即可if (head === null || head.next === null) return head;let previous: Node | null = null;while (head) {const current: Node | null = head.next;head.next = previous;previous = head;head = current;}return previous; } -
递归实现:

function reverseList<T>(head: Node | null): Node | null {// 如果使用的是递归, 那么递归必须有结束条件if (head === null || head.next === null) return head;const newHead = reverseList(head?.next ?? null);head.next.next = head;head.next = null;return newHead; } let n = new Node(1); n.next = new Node(2); n.next.next = new Node(3); n.next.next.next = new Node(4); n.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);let current = reverseList(n); while (current) {console.log(current.value); // 5 4 3 2 1current = current.next; }
-
循环链表
循环链表(Circular Linked List)是一种特殊的链表结构,其中链表的最后一个节点指向链表的第一个节点,从而形成一个闭环。它的主要特性是任何一个节点都可以通过不断访问 next 指针回到起点节点,因此在循环链表中没有空指针这种终止条件

实现
-
方式一:从零去实现一个新的链表,包括其中所有的属性和方法
-
方式二:继承自之前封装的
LinkedList,只实现差异化的部分,我们使用这个方式 -
实现代码如下:实现
append、实现insert、实现removeAt、indexOf和traverse在写单向链表时判断了循环的情况不需要再重构import { LinkedList } from "./单向链表实现.ts";class CircularLinkedList<T> extends LinkedList<T> {append(value: T): void {super.append(value);this.tail!.next = this.head;}insert(value: T, position: number): boolean {const isSuccess = super.insert(value, position);if (isSuccess && (position === this.length - 1 || position === 0)) {// 如果插入成功 && (尾部插入 || 头部插入)都需要更新tail.nextthis.tail!.next = this.head;}return isSuccess;}removeAt(position: number): T | null {const value = super.removeAt(position);if (value &&this.tail &&(position === this.length - 1 || position === 0)) {// 如果删除成功 && tail != null &&(尾部删除 || 头部删除)都需要更新tail.nextthis.tail!.next = this.head;}return value;} }const linked = new CircularLinkedList<string>(); linked.append("aaa"); linked.append("bbb"); linked.append("ccc"); linked.traverse(); // 3 aaa -> bbb -> ccc -> aaalinked.insert("zzz", 0); linked.insert("ddd", 2); linked.insert("eee", 5); linked.traverse(); // zzz -> aaa -> ddd -> bbb -> ccc -> eee -> zzzconsole.log(linked.removeAt(0)); // zzz console.log(linked.removeAt(1)); // ddd console.log(linked.removeAt(3)); // eee linked.traverse(); // 3 aaa -> bbb -> ccc -> aaaconsole.log(linked.get(0)); // aaa console.log(linked.get(1)); // bbb console.log(linked.get(2)); // ccc console.log(linked.get(3)); // nullconsole.log(linked.update("aa", 0)); // true console.log(linked.update("cc", 2)); // true console.log(linked.update("dd", 3)); // false linked.traverse(); // 3 aa -> bbb -> cc -> aaconsole.log(linked.indexOf("aa")); // 0 console.log(linked.indexOf("ccc")); // -1linked.remove("bbb"); linked.traverse(); // 2 aa -> cc -> aaconsole.log(linked.isEmpty()); // false
双向链表
双向链表(Doubly Linked List)是一种数据结构,类似于单向链表,但每个节点包含两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,一个指向前一个节点

- 优点:
-
可以从头到尾、也可以从尾到头进行遍历,灵活性更高
-
删除和插入操作时,不需要像单向链表那样只能从头遍历找到前一个节点
-
- 缺点:
-
每个节点需要额外的指针(
prev),会占用更多的存储空间 -
每次在插入或删除某个节点时,需要处理四个引用,实现起来要困难一些
-
实现
-
封装双向链表节点:需要进一步添加一个
prev属性,用于指向前一个节点 -
实现代码如下:因为差距较大重新实现
append、insert、removeAt,新增加prepend(在头部添加元素)、postTraverse(从尾部遍历所有节点)import { LinkedList, Node } from "./单向实现";class DoublyNode<T> extends Node<T> {next: DoublyNode<T> | null = null;prev: DoublyNode<T> | null = null; }class DoublyLinkedList<T> extends LinkedList<T> {protected head: DoublyNode<T> | null = null;protected tail: DoublyNode<T> | null = null;// 尾部追加元素append(value: T): void {const newNode = new DoublyNode(value);if (!this.head) {this.head = newNode;} else {this.tail!.next = newNode;// 不能将一个父类的对象, 赋值给一个子类的类型// 可以将一个子类的对象, 赋值给一个父类的类型(多态)newNode.prev = this.tail;}this.tail = newNode;this.length++;}// 插入元素insert(value: T, position: number): boolean {if (position < 0 && position > this.length) return false;if (position === 0) {this.prepend(value);} else if (position === this.length) {this.append(value);} else {const newNode = new DoublyNode(value);/* 使用 as 断言它是 DoublyNode<T> 类型,那么在后续代码中,TypeScript 会允许你访问 DoublyNode<T> 类型中的属性(例如 prev),即使这个属性在 Node<T> 类型中并未定义*/const current = this.getNode(position).current as DoublyNode<T>;newNode.next = current;newNode.prev = current.prev;current.prev!.next = newNode;current.prev = newNode;this.length++;}return true;}// 删除元素removeAt(position: number): T | null {if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;let current = this.head;if (position === 0) {if (this.length === 1) {this.head = null;this.tail = null;} else {this.head = this.head!.next;this.head!.prev = null;}} else if (position === this.length - 1) {current = this.tail;this.tail = this.tail!.prev;this.tail!.next = null;} else {current = this.getNode(position).current as DoublyNode<T>current!.next!.prev = current!.prev;current!.prev!.next = current!.next;}this.length--;return current?.value ?? null;}// 在头部添加元素prepend(value: T): boolean {const newNode = new DoublyNode(value);newNode.next = this.head;if (this.head) {this.head.prev = newNode;} else {this.tail = newNode;}this.head = newNode;this.length++;return true;}// 从尾部开始遍历所有节点postTraverse() {let values: T[] = [];let current = this.tail;while (current) {values.push(current.value);current = current.prev;}console.log(this.length, values.join(" <- "));} }const linked = new DoublyLinkedList<string>();linked.prepend("aaa"); linked.append("bbb"); linked.append("ccc"); linked.traverse(); // 3 aaa -> bbb -> ccc linked.postTraverse(); // 3 ccc <- bbb <- aaalinked.insert("zzz", 0); linked.insert("ddd", 2); linked.insert("eee", 5); linked.traverse(); // 6 zzz -> aaa -> ddd -> bbb -> ccc -> eeeconsole.log(linked.removeAt(0)); // zzz console.log(linked.removeAt(1)); // ddd console.log(linked.removeAt(3)); // eee linked.traverse(); // 3 aaa -> bbb -> cccconsole.log(linked.get(0)); // aaa console.log(linked.get(1)); // bbb console.log(linked.get(2)); // ccc console.log(linked.get(3)); // nullconsole.log(linked.update("aa", 0)); // true console.log(linked.update("cc", 2)); // true console.log(linked.update("dd", 3)); // false linked.traverse(); // 3 aa -> bbb -> ccconsole.log(linked.indexOf("aa")); // 0 console.log(linked.indexOf("ccc")); // -1linked.remove("bbb"); linked.traverse(); // 2 aa -> ccconsole.log(linked.isEmpty()); // false
相关文章:

彻底理解链表(LinkedList)结构
目录 比较操作结构封装单向链表实现面试题 循环链表实现 双向链表实现 链表(Linked List)是一种线性数据结构,由一组节点(Node)组成,每个节点包含两个部分:数据域(存储数据ÿ…...

TON 区块链开发的深入概述#TON链开发#DAPP开发#交易平台#NFT#Gamefi链游
区块链开发领域发展迅速,各种平台为开发人员提供不同的生态系统。其中一个更有趣且越来越相关的区块链是TON(开放网络)区块链。TON 区块链最初由 Telegram 构思,旨在提供快速、安全且可扩展的去中心化应用程序 (dApp)。凭借其独特…...

Hive专栏概述
Hive专栏概述 Hive“出身名门”,是最初由Facebook公司开发的数据仓库工具。它简单且容易上手,是深入学习Hadoop技术的一个很好的切入点。专栏内容包括:Hive的安装和配置,其核心组件和架构,Hive数据操作语言,…...

鼠标悬停后出现小提示框实现方法
大家在网页上会经常看到某些图标或文字,当鼠标悬停后会在四周某个位置出现一个简短的文字提示,这种提示分为两种,一种是提示固定的文字,例如放在qq图标上,会显示固定的文字“QQ”;第二种是显示鼠标所在标签…...

计算机视觉常用数据集Foggy Cityscapes的介绍、下载、转为YOLO格式进行训练
我在寻找Foggy Cityscapes数据集的时候花了一番功夫,因为官网下载需要用公司或学校邮箱邮箱注册账号,等待审核通过后才能进行下载数据集。并且一开始我也并不了解Foggy Cityscapes的格式和内容是什么样的,现在我弄明白后写下这篇文章…...

css中的样式穿透
1. >>> 操作符 <style scoped> /* 影响子组件的样式 */ .parent >>> .child {color: red; } </style>注意:>>> 操作符在某些预处理器(如Sass)中可能无法识别,因为它不是标准的CSS语法。 …...

MMCA:多模态动态权重更新,视觉定位新SOTA | ACM MM‘24 Oral
来源:晓飞的算法工程笔记 公众号,转载请注明出处 论文: Visual Grounding with Multi-modal Conditional Adaptation 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.04999论文代码:https://github.com/Mr-Bigworth/MMCA 创新点 提出了多模…...
)
linux同步执行命令脚本 (xcall)
linux同步执行命令脚本 (xcall) 1、在/usr/local/bin目录下 创建xcall文件 vim /usr/local/bin/xcall2、输入内容 #!/bin/bash # 获取控制台指令 判断指令是否为空 pcount$# if((pcount0)); thenecho "command can not be null !"exit fifor host in bigdata01 …...

opencv - py_imgproc - py_grabcut GrabCut 算法提取前景
文章目录 使用 GrabCut 算法进行交互式前景提取目标理论演示 使用 GrabCut 算法进行交互式前景提取 目标 在本章中 我们将了解 GrabCut 算法如何提取图像中的前景我们将为此创建一个交互式应用程序。 理论 GrabCut 算法由英国剑桥微软研究院的 Carsten Rother、Vladimir K…...

ChatGPT多模态命名实体识别
ChatGPT多模态命名实体识别 ChatGPT辅助细化知识增强!一、研究背景二、模型结构和代码任务流程第一阶段:辅助精炼知识启发式生成第二阶段:基于…...
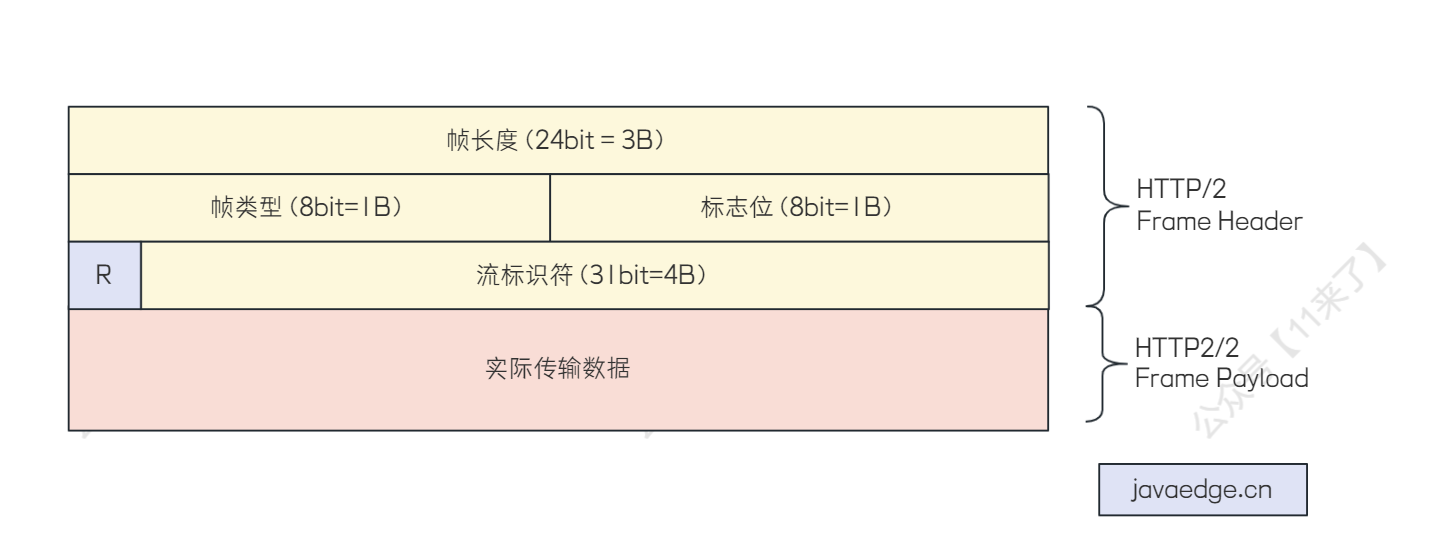
04-Dubbo的通信协议
04-Dubbo的通信协议 Dubbo 支持的通信协议 Dubbo 框架提供了自定义的高性能 RPC 通信协议: 基于 TCP 的 Dubbo2 协议 基于 HTTP/2 的 Triple 协议 Dubbo 框架是不和任何通信协议绑定的,对通信协议的支持非常灵活,支持任意的第三方协议&#x…...

开源数据库 - mysql - innodb源码阅读 - 线程启动
线程启动源码 /** Start up the InnoDB service threads which are independent of DDL recovery.*/void srv_start_threads() {if (!srv_read_only_mode) {/* Before 8.0, it was master thread that was doing periodicalcheckpoints (every 7s). Since 8.0, it is the log …...

在美团外卖上抢券 Python来实现
在美团外卖上抢券的 Python 实现 在如今的互联网时代,自动化脚本已经成为了许多用户生活中不可或缺的工具。尤其是在购物、抢券等场景中,自动化脚本能够帮助我们节省大量的时间和精力。今天,我们将一起探索如何使用 Python 编写一个简单的脚…...

【ONLYOFFICE 文档 8.2 版本深度测评】功能革新与用户体验的双重飞跃
引言 在数字化办公的浪潮中,ONLYOFFICE 文档以其强大的在线协作功能和全面的办公套件解决方案,赢得了全球用户的青睐。随着 8.2 版本的发布,ONLYOFFICE 再次证明了其在办公软件领域的创新能力和技术实力。 一.协作编辑 PDF:团队合…...

npm入门教程18:npm发布npm包
一、准备工作 注册npm账号: 前往npm官网注册一个账号。注册过程中需要填写个人信息,并完成邮箱验证。 安装Node.js和npm: 确保你的计算机上已安装Node.js和npm。Node.js的安装包中通常包含了npm。你可以通过运行node -v和npm -v命令来检查它…...

VueSSR详解 VueServerRenderer Nutx
SSR Vue中的SSR(Server-Side Rendering,服务器端渲染)是一种将页面的渲染工作从客户端转移到服务器端的技术。以下是对Vue中SSR的详细解释: 一、SSR的工作原理 在传统的客户端渲染(CSR)中,页面的…...

构建您自己的 RAG 应用程序:使用 Ollama、Python 和 ChromaDB 在本地设置 LLM 的分步指南
在数据隐私至关重要的时代,建立自己的本地语言模型 (LLM) 为公司和个人都提供了至关重要的解决方案。本教程旨在指导您完成使用 Ollama、Python 3 和 ChromaDB 创建自定义聊天机器人的过程,所有这些机器人都托管在您的系统本地。以…...

谷歌浏览器安装axure插件
1.在生成静态原型页面的路径下,找到resources\chrome\axure-chrome-extension.crx,这就是需要的插件了。 2.将axure-chrome-extension.crx重命名成axure-chrome-extension.zip然后解压到指定的文件夹(这个文件夹不能删除, 例如解压到了扩展程…...

Java唯一键实现方案
数据唯一性 1、生成UUID1.1 代码中实现1.2 数据库中实现优点缺点 2、数据库递增主键优点 3、数据库递增序列3.1 创建序列3.2 使用序列优点缺点 在Java项目开发中,对数据的唯一性要求,业务数据入库的时候保持单表只有一条记录,因此对记录中要求…...

opencv - py_imgproc - py_canny Canny边缘检测
文章目录 Canny 边缘检测目标理论OpenCV 中的 Canny 边缘检测其他资源 Canny 边缘检测 目标 在本章中,我们将学习 Canny 边缘检测的概念用于该目的的 OpenCV 函数:cv.Canny() 理论 Canny 边缘检测是一种流行的边缘检测算法。它由 John F. Canny 于1…...

【大模型RAG】拍照搜题技术架构速览:三层管道、两级检索、兜底大模型
摘要 拍照搜题系统采用“三层管道(多模态 OCR → 语义检索 → 答案渲染)、两级检索(倒排 BM25 向量 HNSW)并以大语言模型兜底”的整体框架: 多模态 OCR 层 将题目图片经过超分、去噪、倾斜校正后,分别用…...

逻辑回归:给不确定性划界的分类大师
想象你是一名医生。面对患者的检查报告(肿瘤大小、血液指标),你需要做出一个**决定性判断**:恶性还是良性?这种“非黑即白”的抉择,正是**逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)** 的战场&a…...

云启出海,智联未来|阿里云网络「企业出海」系列客户沙龙上海站圆满落地
借阿里云中企出海大会的东风,以**「云启出海,智联未来|打造安全可靠的出海云网络引擎」为主题的阿里云企业出海客户沙龙云网络&安全专场于5.28日下午在上海顺利举办,现场吸引了来自携程、小红书、米哈游、哔哩哔哩、波克城市、…...

第25节 Node.js 断言测试
Node.js的assert模块主要用于编写程序的单元测试时使用,通过断言可以提早发现和排查出错误。 稳定性: 5 - 锁定 这个模块可用于应用的单元测试,通过 require(assert) 可以使用这个模块。 assert.fail(actual, expected, message, operator) 使用参数…...
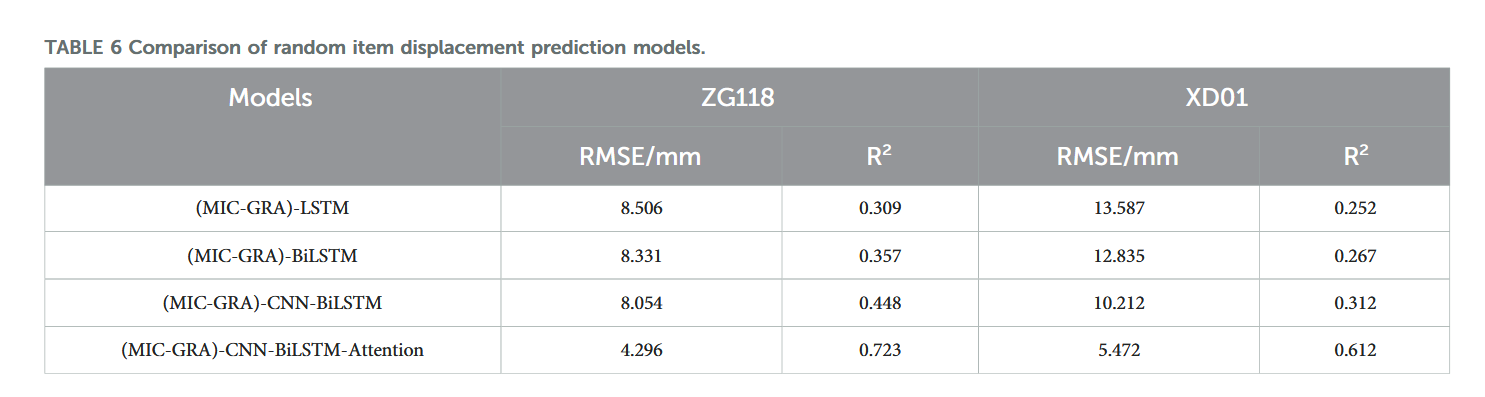
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...

Python ROS2【机器人中间件框架】 简介
销量过万TEEIS德国护膝夏天用薄款 优惠券冠生园 百花蜂蜜428g 挤压瓶纯蜂蜜巨奇严选 鞋子除臭剂360ml 多芬身体磨砂膏280g健70%-75%酒精消毒棉片湿巾1418cm 80片/袋3袋大包清洁食品用消毒 优惠券AIMORNY52朵红玫瑰永生香皂花同城配送非鲜花七夕情人节生日礼物送女友 热卖妙洁棉…...

Java求职者面试指南:计算机基础与源码原理深度解析
Java求职者面试指南:计算机基础与源码原理深度解析 第一轮提问:基础概念问题 1. 请解释什么是进程和线程的区别? 面试官:进程是程序的一次执行过程,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位;而线程是进程中的…...
免费数学几何作图web平台
光锐软件免费数学工具,maths,数学制图,数学作图,几何作图,几何,AR开发,AR教育,增强现实,软件公司,XR,MR,VR,虚拟仿真,虚拟现实,混合现实,教育科技产品,职业模拟培训,高保真VR场景,结构互动课件,元宇宙http://xaglare.c…...

elementUI点击浏览table所选行数据查看文档
项目场景: table按照要求特定的数据变成按钮可以点击 解决方案: <el-table-columnprop"mlname"label"名称"align"center"width"180"><template slot-scope"scope"><el-buttonv-if&qu…...
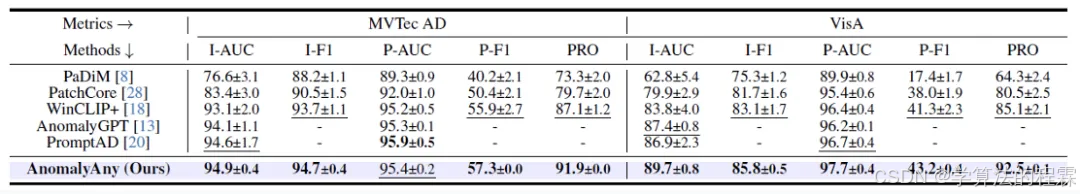
CVPR2025重磅突破:AnomalyAny框架实现单样本生成逼真异常数据,破解视觉检测瓶颈!
本文介绍了一种名为AnomalyAny的创新框架,该方法利用Stable Diffusion的强大生成能力,仅需单个正常样本和文本描述,即可生成逼真且多样化的异常样本,有效解决了视觉异常检测中异常样本稀缺的难题,为工业质检、医疗影像…...
