5G NR gNB 逻辑架构及其功能拆分选项
5G NR gNB 逻辑架构及其功能拆分选项
- 中央单元 (CU) 和分布式单元功能拆分选项
- RAN 分体架构的优势
- 在哪里使用哪个拆分函数?
- 参考:
- 5G NR gNB Logical Architecture and It’s Functional Split Options
- Central Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit Functional Split Options
- Option 1 (RRC/PDCP, 1A-like split)
- Option 2 (PDCP/RLC split)
- Option 2-1 Split U-plane only (3C like split)
- Option 2-2
- Option 3 (High RLC/Low RLC Split)
- Option 3-1 Split based on ARQ
- Option 3-2 Split based on TX RLC and RX RLC
- Option 4 (RLC-MAC split)
- Option 5 (Intra MAC split)
- Option 6 (MAC-PHY split)
- Option 7 (Intra PHY split)
- Option 8 (PHY-RF split)
- Benefits of RAN Spilt Architecture
- Which split function to use where?
- Reference:
https://www.techplayon.com/5g-nr-gnb-logical-architecture-functional-split-options/
gNB 的逻辑架构如下图所示,包括中央单元 (CU) 和分布式单元 (DU)。Fs-C 和 Fs-U 通过 Fs 接口提供控制平面和用户平面连接。

在这种架构中,中央单元(CU)和分配单元(DU)可以定义如下。
中央单元 (CU):它是一个逻辑节点,包括 gNB 功能,例如用户数据传输、移动性控制、无线接入网络共享、定位、会话管理等,但不包括专门分配给 DU 的功能。CU 控制 DU 通过前传 (Fs) 接口的运行。中央单元 (CU) 也可以称为 BBU/REC/RCC/C-RAN/V-RAN
分布式单元 (DU):此逻辑节点包含 gNB 功能的子集,具体取决于功能拆分选项。其操作由 CU 控制。分布式单元 (DU) 也被称为 RRH/RRU/RE/RU 等其他名称。
中央单元 (CU) 和分布式单元功能拆分选项
作为新无线电(NR)研究项目的一部分,3GPP 开始研究中央单元和分布式单元之间的不同功能划分。在初始阶段,3GPP 以 LTE 协议栈作为讨论的基础,直到 RAN2 定义并冻结了新无线电(NR)的协议栈。他们提出了下图所示的大约 8 种可能选项。


- 选项 1(类似RRC/PCDP 1A 的拆分)
- 选项 2(PDCP/RLC 拆分,类似 3C 拆分)
- 选项 3(高 RLC/低 RLC分割,内部 RLC 分割)
- 选项 4(RLC-MAC 分离)
- 选项 5(MAC 内部拆分)
- 选项 6(MAC-PHY 分离)
- 选项 7(PHY 内部拆分)
- 选项 8(PHY-RF 分离)
选项 1(RRC/PDCP,类似 1A 的拆分):在此拆分选项中,RRC 位于中央单元,而 PDCP、RLC、MAC、物理层和 RF 保留在分布式单元中。因此,整个用户平面都在分布式单元中。
选项 2(PDCP/RLC 分离):由于 U 平面相似,选项 2 可能是类似 X2 的设计的基础,但某些功能可能不同,例如 C 平面,因为可能需要一些新程序。此选项有两种可能的变体。
选项 2-1 仅分割 U 平面(类似 3C 分割):在此分割选项中,RRC、PDCP 位于中央单元。RLC、MAC、物理层和 RF 位于分布式单元。
选项 2-2:在此拆分选项中,RRC、PDCP 位于中央单元中。RLC、MAC、物理层和 RF 位于分布式单元中。此外,可以通过将 CP 堆栈的 RRC 和 PDCP 以及 UP 堆栈的 PDCP 分离到不同的中央实体中来实现此选项。
选项 3(高 RLC/低 RLC 分割):在此选项中,根据实时/非实时功能分割采用两种方法,如下所示:
选项 3-1 基于 ARQ 的拆分
选项 3-2 根据 TX RLC 和 RX RLC 进行拆分
选项 3-1 基于 ARQ 的拆分
低RLC可能由分段功能组成;
高级RLC可能由ARQ和其他RLC功能组成;
此选项将 RLC 子层拆分为高级 RLC 和低级 RLC 子层,这样对于 RLC 确认模式操作,所有 RLC 功能都可以在位于中央单元的高级 RLC 子层上执行,而分段可以在位于分布式单元的低级 RLC 子层上执行。其中,高级 RLC 根据状态报告对 RLC PDU 进行分段,而低级 RLC 将 RLC PDU 分段到可用的 MAC PDU 资源中。
选项 3-2 根据 TX RLC 和 RX RLC 进行拆分
Low RLC可以由发送TM RLC实体、发送UM RLC实体、发送侧AM以及接收侧AM的路由功能组成,与下行传输有关。
高层RLC除了完成与上行传输相关的路由功能和RLC状态报告接收等功能外,还可以由接收TM RLC实体、接收UM RLC实体和接收AM侧实体组成。
选项 4(RLC-MAC 分离):在此分离选项中,RRC、PDCP 和 RLC 位于中央单元中。MAC、物理层和 RF 位于分布式单元中。
选项 5(MAC 内部拆分)
选项 5 假设以下分布:
RF、物理层和MAC层下部(Low-MAC)位于分布式单元中
MAC 层的较高部分 (High-MAC)、RLC 和 PDCP 位于中央单元
因此,通过将 MAC 层拆分为 2 个实体(例如 High-MAC 和 Low-MAC),MAC 层提供的服务和功能将位于中央单元 (CU)、分布式单元 (DU) 或两者中。下面给出了此类分布的示例。
在 High-MAC 子层中,High-MAC 子层的集中调度将负责多个 Low-MAC 子层的控制。它采取高层集中调度决策。High-MAC 子层中的小区间干扰协调将负责干扰协调方法,例如 JP/CS CoMP。
在 Low-MAC 子层中,Low-MAC 子层中的时间关键功能包括具有严格延迟要求的功能(例如 HARQ)或性能与延迟成比例的功能(例如来自 PHY 的无线信道和信号测量、随机访问控制)。它降低了前传接口的延迟要求。Low-MAC 子层中的无线特定功能可以执行与调度相关的信息处理和报告。它还可以测量/估计配置的操作或服务 UE 的统计数据上的活动,并定期或根据请求向 High-MAC 子层报告。
选项 6(MAC-PHY 分离): MAC 和上层位于中央单元 (CU)。PHY 层和 RF 位于 DU。CU 和 DU 之间的接口承载数据、配置和调度相关信息(例如 MCS、层映射、波束成形、天线配置、资源块分配等)和测量。
选项 7(PHY 内部分割):该选项有多种实现方式,包括允许独立获取 UL 和 DL 不同子选项优势的非对称选项。
此选项需要某种压缩技术来减少 DU 和 CU 之间的传输带宽要求。
在 UL 中,FFT 和 CP 移除位于 DU 中,对于两个子变体,7-1 和 7-2 如下所述。其余功能位于 CU 中。
在下行链路中,iFFT 和 CP 加法位于 DU 中,而 PHY 的其余部分位于 CU 中。
考虑到上述情况,此选项有三种子变体可用,如下所述
选项 7-1 在此选项中,UL、FFT、CP 移除和可能的 PRACH 过滤功能驻留在 DU 中,其余 PHY 功能驻留在 CU 中。在 DL 中,iFFT 和 CP 添加功能驻留在 DU 中,其余 PHY 功能驻留在 CU 中。
选项 7-2 在此选项中,UL、FFT、CP 移除、资源解映射和可能的预过滤功能驻留在 DU 中,其余 PHY 功能驻留在 CU 中。在 DL 中,iFFT、CP 添加、资源映射和预编码功能驻留在 DU 中,其余 PHY 功能驻留在 CU 中。
选项 7-3(仅适用于 DL):只有编码器驻留在 CU 中,其余 PHY 功能驻留在 DU 中。
选项 8(PHY-RF 分离):此选项允许分离 RF 层和 PHY 层。这种分离允许集中所有协议层级别的流程,从而实现 RAN 的紧密协调。这允许高效支持 CoMP、MIMO、负载平衡、移动性等功能。
RAN 分体架构的优势
具有在中央和分布式单元之间分割和移动新无线电 (NR) 功能的部署灵活性的架构的一些好处如下:
- 灵活的硬件实现允许可扩展且经济高效的解决方案
- 分离式架构(中央单元和分布式单元之间)可以协调性能特性、负载管理、实时性能优化,并支持 NFV/SDN
- 可配置的功能拆分可适应各种用例,例如传输中的可变延迟
在哪里使用哪个拆分函数?
如何划分架构中的新无线电 (NR) 功能取决于与无线电网络部署场景、约束和预期支持的服务相关的一些因素。这些因素的一些示例包括:
- 支持每个提供的服务的特定 QoS(例如低延迟、高吞吐量)
- 支持每个给定地理区域的特定用户密度和负载需求(这可能会影响 RAN 协调水平)
- 具有不同性能水平的可用性传输网络,从理想到非理想
- 应用程序类型,例如实时或非实时
- 无线电网络层的特色要求,例如 CA、eICIC、CoMP 等。
参考:
- 3GPP TR 38.801 无线接入架构和接口版本 14
5G NR gNB Logical Architecture and It’s Functional Split Options
The logical architecture of gNB is shown in figure below with Central Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit (DU). Fs-C and Fs-U provide control plane and user plane connectivity over Fs interface.

In this architecture, Central Unit (CU) and Distribution Unit (DU) can be defined as follows.
Central Unit (CU): It is a logical node that includes the gNB functions like Transfer of user data, Mobility control, Radio access network sharing, Positioning, Session Management etc., except those functions allocated exclusively to the DU. CU controls the operation of DUs over front-haul (Fs) interface. A central unit (CU) may also be known as BBU/REC/RCC/C-RAN/V-RAN
Distributed Unit (DU): This logical node includes a subset of the gNB functions, depending on the functional split option. Its operation is controlled by the CU. Distributed Unit (DU) also known with other names like RRH/RRU/RE/RU.
Central Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit Functional Split Options
As a part of study item for New Radio (NR), 3GPP started studying different functional splits between central and distributed units. For the initial phase, 3GPP has taken LTE protocol stack as a basis for the discussion, until RAN2 defines and freezes the protocol stack for New Radio (NR). They have proposed about 8 possible options shown in below figure.


- Option 1 (RRC/PCDP 1A-like split)
- Option 2 (PDCP/RLC Split 3C-like split)
- Option 3 (High RLC/Low RLC split, Intra RLC split)
- Option 4 (RLC-MAC split)
- Option 5 (Intra MAC split)
- Option 6 (MAC-PHY split)
- Option 7 (Intra PHY split)
- Option 8 (PHY-RF split)
Option 1 (RRC/PDCP, 1A-like split)
In this split option, RRC is in the central unit while PDCP, RLC, MAC, physical layer and RF are kept in the distributed unit. Thus the entire user plane is in the distributed unit.
Option 2 (PDCP/RLC split)
Option 2 may be a base for an X2-like design due to similarity on U-plane but some functionality may be different e.g. C-plane since some new procedures may be needed. There are two possible variants available in this option.
Option 2-1 Split U-plane only (3C like split)
In this split option, RRC, PDCP are in the central unit. RLC, MAC, physical layer and RF are in the distributed unit.
Option 2-2
In this split option, RRC, PDCP are in the central unit. RLC, MAC, physical layer and RF are in the distributed unit. In addition, this option can be achieved by separating the RRC and PDCP for the CP stack and the PDCP for the UP stack into different central entities.
Option 3 (High RLC/Low RLC Split)
In this option, two approaches are taken based on Real time/Non-Real time functions split which are as follows:
- Option 3-1 Split based on ARQ
- Option 3-2 Split based on TX RLC and RX RLC
Option 3-1 Split based on ARQ
- Low RLC may be composed of segmentation functions;
- High RLC may be composed of ARQ and other RLC functions;
This option splits the RLC sublayer into High RLC and Low RLC sublayers such that for RLC Acknowledge Mode operation, all RLC functions may be performed at the High RLC sublayer residing in the central unit, while the segmentation may be performed at the Low RLC sublayer residing in the distributed unit. Here, High RLC segments RLC PDU based on the status reports while Low RLC segments RLC PDU into the available MAC PDU resources.
Option 3-2 Split based on TX RLC and RX RLC
- Low RLC may be composed of transmitting TM RLC entity, transmitting UM RLC entity, a transmitting side of AM and the routing function of a receiving side of AM, which are related to downlink transmission.
- High RLC may be composed of receiving TM RLC entity, receiving UM RLC entity and a receiving side of AM except for the routing function and reception of RLC status reports, which are related to uplink transmission.
Option 4 (RLC-MAC split)
In this split option, RRC, PDCP, and RLC are in the central unit. MAC, physical layer, and RF are in the distributed unit.
Option 5 (Intra MAC split)
Option 5 assumes the following distribution:
- RF, physical layer and lower part of the MAC layer (Low-MAC) are in the Distributed Unit
- Higher part of the MAC layer (High-MAC), RLC and PDCP are in the Central Unit
Therefore, by splitting the MAC layer into 2 entities (e.g. High-MAC and Low-MAC), the services and functions provided by the MAC layer will be located in the Central Unit (CU), in the Distributed Unit (DU), or in both. An example of this kind distribution given below.
- In High-MAC sublayer the centralized scheduling in the High-MAC sublayer will be in charge of the control of multiple Low-MAC sublayers. It takes high-level centralized scheduling decision. The inter-cell interference coordination in the High-MAC sublayer will be in charge of interference coordination methods such as JP/CS CoMP.
- In Low-MAC sublayer the time-critical functions in the Low-MAC sublayer include the functions with stringent delay requirements (e.g. HARQ) or the functions where performance is proportional to latency (e.g. radio channel and signal measurements from PHY, random access control). It reduces the delay requirements on the fronthaul interface. Radio specific functions in the Low-MAC sublayer can for perform scheduling-related information processing and be reporting. It can also measure/estimate the activities on the configured operations or the served UE’s statistics and report periodically or as requested to the High-MAC sublayer.
Option 6 (MAC-PHY split)
The MAC and upper layers are in the central unit (CU). PHY layer and RF are in the DU. The interface between the CU and DUs carries data, configuration, and scheduling-related information (e.g. MCS, Layer Mapping, Beamforming, Antenna Configuration, resource block allocation, etc.) and measurements.
Option 7 (Intra PHY split)
Multiple realizations of this option are possible, including asymmetrical options which allow obtaining benefits of different sub-options for UL and DL independently.
This option requires some kind of compression technique to reduce transport bandwidth requirements between the DU and CU.
- In the UL, FFT, and CP removal reside in the DU and for the two sub-variants, 7-1 and 7-2 are described below. Remaining functions reside in the CU.
- In the downlink, iFFT and CP addition reside in the DU and the rest of the PHY resides in the CU.
Considering above there are three sub-variant available for this option described as below
Option 7-1 In this option the UL, FFT, CP removal and possibly PRACH filtering functions reside in the DU, the rest of PHY functions reside in the CU. In the DL, iFFT and CP addition functions reside in the DU, the rest of PHY functions reside in the CU.
Option 7-2 In this option the UL, FFT, CP removal, resource de-mapping and possibly pre-filtering functions reside in the DU, the rest of PHY functions reside in the CU. In the DL, iFFT, CP addition, resource mapping and precoding functions reside in the DU, the rest of PHY functions reside in the CU.
Option 7-3 (Only for DL): Only the encoder resides in the CU, and the rest of PHY functions reside in the DU.
Option 8 (PHY-RF split)
This option allows to separate the RF and the PHY layer. This split permit centralization of processes at all protocol layer levels, resulting in very tight coordination of the RAN. This allows efficient support of functions such as CoMP, MIMO, load balancing, mobility.
Benefits of RAN Spilt Architecture
Some of the benefits of an architecture with the deployment flexibility to split and move New Radio (NR) functions between central and distributed units are below:
- Flexible HW implementations allows scalable cost-effective solutions
- A split architecture (between central and distributed units) allows for coordination for performance features, load management, real-time performance optimization, and enables NFV/SDN
- Configurable functional splits enables adaptation to various use cases, such as variable latency on transport
Which split function to use where?
The choice of how to split New Radio (NR) functions in the architecture depends on some factors related to radio network deployment scenarios, constraints and intended supported services. Some examples of such factors are:
- Support of specific QoS per offered services (e.g. low latency, high throughput)
- Support of specific user density and load demand per given geographical area (which may influence the level of RAN coordination)
- Availability transport networks with different performance levels, from ideal to non-ideal
- Application type e.g. Real-time or Non- Real Time
- Features requirement at Radio Network level e.g. CA, eICIC, CoMP etc.
Reference:
- 3GPP TR 38.801 Radio Access Architecture and Interfaces Release 14
相关文章:

5G NR gNB 逻辑架构及其功能拆分选项
5G NR gNB 逻辑架构及其功能拆分选项 中央单元 (CU) 和分布式单元功能拆分选项RAN 分体架构的优势在哪里使用哪个拆分函数?参考: 5G NR gNB Logical Architecture and It’s Functional Split OptionsCentral Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit Functional…...

PyQt入门指南四十六 性能优化策略
在PyQt应用程序中,性能优化是一个重要的考虑因素,尤其是在处理大型数据集或复杂图形界面时。以下是一些常见的性能优化策略: 1. 使用延迟加载(Lazy Loading) 延迟加载是一种优化技术,只在需要时加载资源。…...

【RMA】基于知识注入和模糊学习的多模态歧义分析
abstract 多模态情感分析(MSA)利用互补的多模态特征来预测情感极性,主要涉及语言、视觉和音频三种模态。现有的多模态融合方法主要考虑不同模态的互补性,而忽略了模态之间的冲突所导致的歧义(即文本模态预测积极情绪&…...
CulturalBench :一个旨在评估大型语言模型在全球不同文化背景下知识掌握情况的基准测试数据集
2024-10-04,为了提升大型语言模型在不同文化背景下的实用性,华盛顿大学、艾伦人工智能研究所等机构联合创建了CulturalBench。这个数据集包含1,227个由人类编写和验证的问题,覆盖了包括被边缘化地区在内的45个全球区域。CulturalBench的推出&…...

Git 入门篇(一)
前言 操作系统:win11 64位 与gitee搭配使用 Git 入门篇(一) Git 入门篇(二) Git 入门篇(三) 目录 git下载、安装与配置 下载 安装 配置 git下载、安装与配置 下载 官网:git-…...

一个灵活且功能强大的动画库 Popmotion
一个灵活且功能强大的动画库 Popmotion 什么是 Popmotion? Popmotion 是一个强大的 JavaScript 动画库,提供了一系列简洁的 API,方便开发者创建流畅的动画效果。它支持不同类型的动画,包括 CSS 动画、SVG 动画和 DOM 动画&#…...

如何解决传统能源企业后备人才不足、人才规划缺失问题
如何解决传统能源企业后备人才不足、人才规划缺失问题 很多传统能源企业都面临着老员工逐渐退休,新员工还没有培养起来的问题,缺乏提前对人力资源规划的意识,导致当企业要开展新业务时或者老员工离职的时候,缺乏合适的人选。特别…...

PDF模板制作与填充(Java)
1.PDF模板制作 准备原始模板 准备一个原始PDF模板,可以编辑好Word,预留出要填充的部分,再转换成PDF格式。 设置表单域 用任意PDF编辑器打开PDF模板文件,设置表单域,下面以WPS为例: 拖动文本域到需要填充的…...

LeetCode题练习与总结:迷你语法分析器--385
一、题目描述 给定一个字符串 s 表示一个整数嵌套列表,实现一个解析它的语法分析器并返回解析的结果 NestedInteger 。 列表中的每个元素只可能是整数或整数嵌套列表 示例 1: 输入:s "324", 输出:324 解释ÿ…...

Unity WebGL交互通信
Unity 调用 H5 本文使用的 unity 版本为:2021.3.3 1.在unity中通过c#的特性DllImport导出外部实现函数 [DllImport("__Internal")]private static extern void callJsString(string param);[DllImport("__Internal")]private static extern vo…...

王道考研之数据结构
数据结构系列 提示:这里可以添加系列文章的所有文章的目录,目录需要自己手动添加 数据结构 数据结构系列1.线性表1.1 线性表的定义和相关概念1.2 线性表的创销 增删查改 判空表长打印 2.顺序表2.1 顺序表定义和相关概念2.2 顺序表的静态实现2.3 顺序表的…...

实习冲刺Day17
算法题 x的平方根 69. x 的平方根 - 力扣(LeetCode) class Solution { public:int mySqrt(int x) {long left 0,right x;//定义左右边界//数值取的大longlong类型while (left < right) {long mid (right-left1)/2left;//定义中间节点if ((mid *…...

我自己nodejs练手时常用的一些库基础用法
我自己在使用nodejs以及前端实战练习时常用的一些库的基本使用 1.bcrypt //注册账号时,给密码加密 password是前端传过来的密码,hashPassword是存到数据库中的密码 const bcrypt require(bcrypt) const hashPassword bcrypt.hash(password,10) //登…...

岛屿数量问题
给一个0 1矩阵,1代表是陆地,0代表海洋, 如果两个1相邻,那么这两个1属于同一个岛。我们只考虑上下左右为相邻。 岛屿问题: 相邻陆地可以组成一个岛屿(相邻:上下左右) 判断岛屿个数。 C 解决方案 #include &…...

智能制造基础- TPM(全面生产维护)
TPM 前言一、TPM二、TPM实施步骤三、 消除主要问题3.1 实施指南3.2 如何进行“主要问题”的消除? 四、自主维护4.1 实施指南4.2 主要工作内容4.3 如何进行“自主维护“ 五、计划维护5.1 实施指南5.2 如何实施计划维护 六、TPM 适当的 设备 设计5.1 实施指南5.2 如何…...
---- 模板概览与类模板(4))
C++学习笔记----11、模块、头文件及各种主题(一)---- 模板概览与类模板(4)
2.2.2、显式实例化 有危险存在于有些类模板成员函数的编译错误,在隐式实例化时没有注意到。未被使用的类模板成员函数也可能包含语法错误,因为它们不会被编译到。这会使得检测代码的语法错误很困难。可以强制编译器生成所有成员函数的代码,vi…...

【力扣热题100】[Java版] 刷题笔记-160. 相交链表
题目:160. 相交链表 给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。 图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交: 题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。 注意…...

多线程和线程同步复习
多线程和线程同步复习 进程线程区别创建线程线程退出线程回收全局写法传参写法 线程分离线程同步同步方式 互斥锁互斥锁进行线程同步 死锁读写锁api细说读写锁进行线程同步 条件变量生产者消费者案例问题解答加强版生产者消费者 总结信号量信号量实现生产者消费者同步-->一个…...

贝式计算的 AI4S 观察:使用机器学习对世界进行感知与推演,最大魅力在于横向扩展的有效性
「传统研究方法高度依赖于科研人员自身的特征和问题定义能力,通常采用小数据,在泛化能力和拓展能力上存疑。而 AI 研究方法则需要引入大规模、高质量数据,并采用机器学习进行特征抽取,这使得产生的科研结果在真实世界的问题中非常…...
容器化技术入门:Docker详解
💓 博客主页:瑕疵的CSDN主页 📝 Gitee主页:瑕疵的gitee主页 ⏩ 文章专栏:《热点资讯》 容器化技术入门:Docker详解 容器化技术入门:Docker详解 容器化技术入门:Docker详解 引言 Doc…...
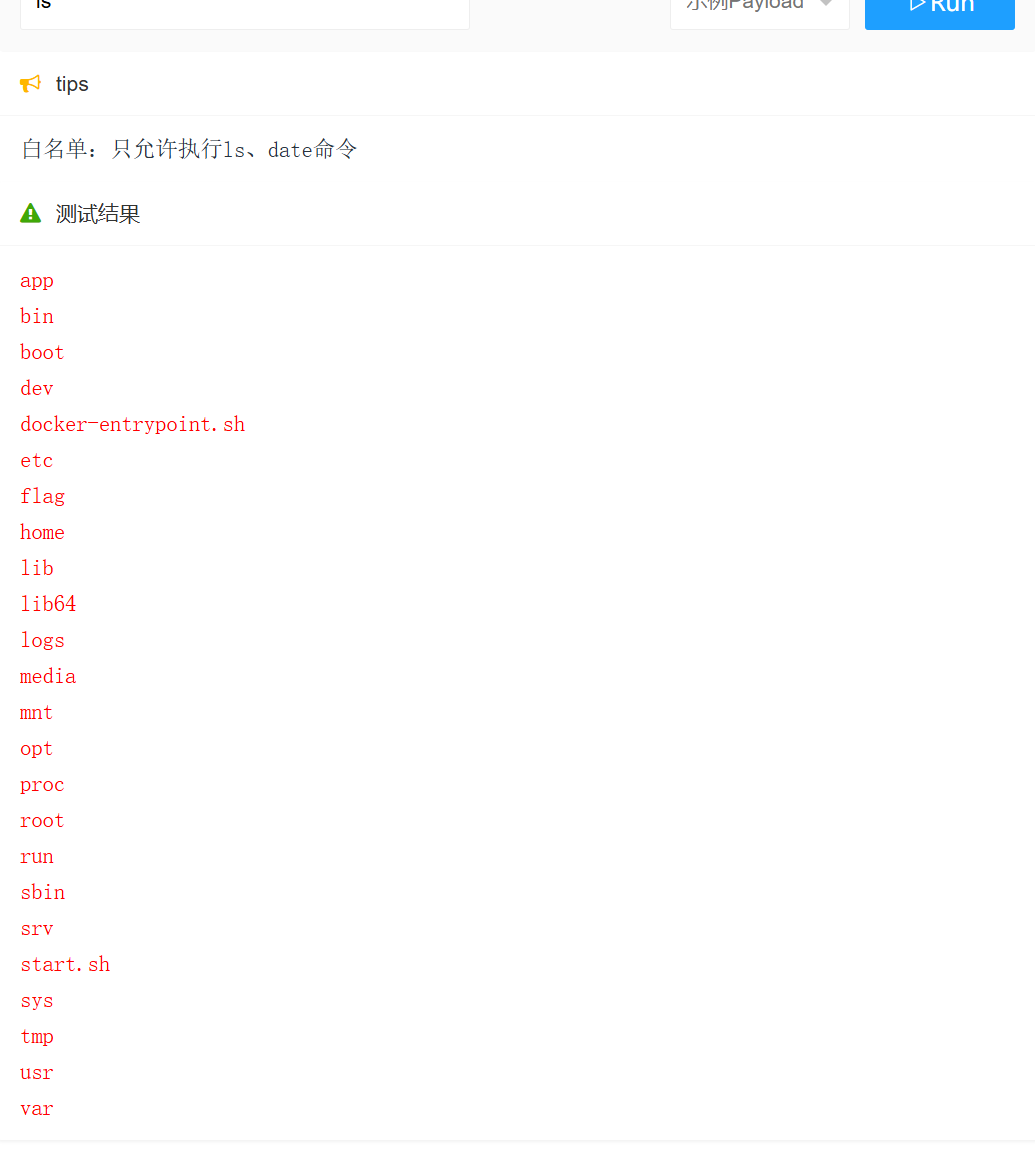
JavaSec-RCE
简介 RCE(Remote Code Execution),可以分为:命令注入(Command Injection)、代码注入(Code Injection) 代码注入 1.漏洞场景:Groovy代码注入 Groovy是一种基于JVM的动态语言,语法简洁,支持闭包、动态类型和Java互操作性,…...
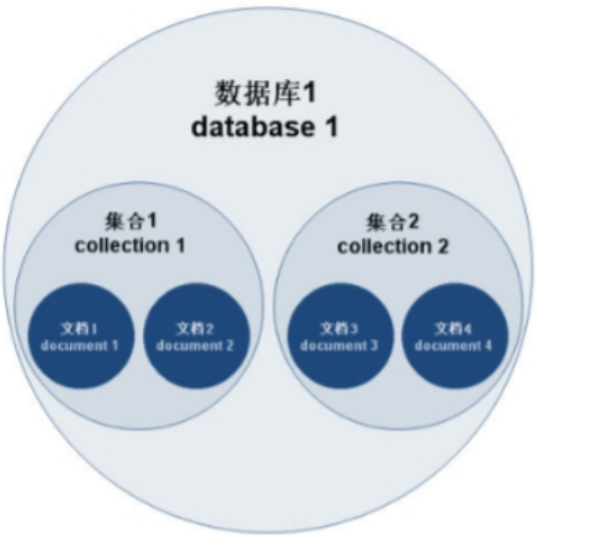
MongoDB学习和应用(高效的非关系型数据库)
一丶 MongoDB简介 对于社交类软件的功能,我们需要对它的功能特点进行分析: 数据量会随着用户数增大而增大读多写少价值较低非好友看不到其动态信息地理位置的查询… 针对以上特点进行分析各大存储工具: mysql:关系型数据库&am…...

蓝桥杯 2024 15届国赛 A组 儿童节快乐
P10576 [蓝桥杯 2024 国 A] 儿童节快乐 题目描述 五彩斑斓的气球在蓝天下悠然飘荡,轻快的音乐在耳边持续回荡,小朋友们手牵着手一同畅快欢笑。在这样一片安乐祥和的氛围下,六一来了。 今天是六一儿童节,小蓝老师为了让大家在节…...

Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信
文章目录 Linux C语言网络编程详细入门教程:如何一步步实现TCP服务端与客户端通信前言一、网络通信基础概念二、服务端与客户端的完整流程图解三、每一步的详细讲解和代码示例1. 创建Socket(服务端和客户端都要)2. 绑定本地地址和端口&#x…...

2025季度云服务器排行榜
在全球云服务器市场,各厂商的排名和地位并非一成不变,而是由其独特的优势、战略布局和市场适应性共同决定的。以下是根据2025年市场趋势,对主要云服务器厂商在排行榜中占据重要位置的原因和优势进行深度分析: 一、全球“三巨头”…...
短视频矩阵系统文案创作功能开发实践,定制化开发
在短视频行业迅猛发展的当下,企业和个人创作者为了扩大影响力、提升传播效果,纷纷采用短视频矩阵运营策略,同时管理多个平台、多个账号的内容发布。然而,频繁的文案创作需求让运营者疲于应对,如何高效产出高质量文案成…...

动态 Web 开发技术入门篇
一、HTTP 协议核心 1.1 HTTP 基础 协议全称 :HyperText Transfer Protocol(超文本传输协议) 默认端口 :HTTP 使用 80 端口,HTTPS 使用 443 端口。 请求方法 : GET :用于获取资源,…...

【SSH疑难排查】轻松解决新版OpenSSH连接旧服务器的“no matching...“系列算法协商失败问题
【SSH疑难排查】轻松解决新版OpenSSH连接旧服务器的"no matching..."系列算法协商失败问题 摘要: 近期,在使用较新版本的OpenSSH客户端连接老旧SSH服务器时,会遇到 "no matching key exchange method found", "n…...

实战设计模式之模板方法模式
概述 模板方法模式定义了一个操作中的算法骨架,并将某些步骤延迟到子类中实现。模板方法使得子类可以在不改变算法结构的前提下,重新定义算法中的某些步骤。简单来说,就是在一个方法中定义了要执行的步骤顺序或算法框架,但允许子类…...
32单片机——基本定时器
STM32F103有众多的定时器,其中包括2个基本定时器(TIM6和TIM7)、4个通用定时器(TIM2~TIM5)、2个高级控制定时器(TIM1和TIM8),这些定时器彼此完全独立,不共享任何资源 1、定…...
