Android Activity的启动器ActivityStarter入口
Activity启动器入口
Android的Activity的启动入口是在ActivityStarter类的execute(),在该方法里面继续调用executeRequest(Request request) ,相应的参数都设置在方法参数request中。代码挺长,分段现在看下它的实现,分段一:
/*** Executing activity start request and starts the journey of starting an activity. Here* begins with performing several preliminary checks. The normally activity launch flow will* go through {@link #startActivityUnchecked} to {@link #startActivityInner}.*/private int executeRequest(Request request) {if (TextUtils.isEmpty(request.reason)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Need to specify a reason.");}mLastStartReason = request.reason;mLastStartActivityTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis();mLastStartActivityRecord = null;final IApplicationThread caller = request.caller;Intent intent = request.intent;NeededUriGrants intentGrants = request.intentGrants;String resolvedType = request.resolvedType;ActivityInfo aInfo = request.activityInfo;ResolveInfo rInfo = request.resolveInfo;final IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession = request.voiceSession;final IBinder resultTo = request.resultTo;String resultWho = request.resultWho;int requestCode = request.requestCode;int callingPid = request.callingPid;int callingUid = request.callingUid;String callingPackage = request.callingPackage;String callingFeatureId = request.callingFeatureId;final int realCallingPid = request.realCallingPid;final int realCallingUid = request.realCallingUid;final int startFlags = request.startFlags;final SafeActivityOptions options = request.activityOptions;Task inTask = request.inTask;int err = ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;// Pull the optional Ephemeral Installer-only bundle out of the options early.final Bundle verificationBundle =options != null ? options.popAppVerificationBundle() : null;WindowProcessController callerApp = null;if (caller != null) {callerApp = mService.getProcessController(caller);if (callerApp != null) {callingPid = callerApp.getPid();callingUid = callerApp.mInfo.uid;} else {Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to find app for caller " + caller + " (pid=" + callingPid+ ") when starting: " + intent.toString());err = ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED;}}final int userId = aInfo != null && aInfo.applicationInfo != null? UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.applicationInfo.uid) : 0;if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {Slog.i(TAG, "START u" + userId + " {" + intent.toShortString(true, true, true, false)+ "} from uid " + callingUid);}ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null;ActivityRecord resultRecord = null;if (resultTo != null) {sourceRecord = mRootWindowContainer.isInAnyTask(resultTo);if (DEBUG_RESULTS) {Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS, "Will send result to " + resultTo + " " + sourceRecord);}if (sourceRecord != null) {if (requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing) {resultRecord = sourceRecord;}}}final int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();if ((launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT) != 0 && sourceRecord != null) {// Transfer the result target from the source activity to the new one being started,// including any failures.if (requestCode >= 0) {SafeActivityOptions.abort(options);return ActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT;}resultRecord = sourceRecord.resultTo;if (resultRecord != null && !resultRecord.isInRootTaskLocked()) {resultRecord = null;}resultWho = sourceRecord.resultWho;requestCode = sourceRecord.requestCode;sourceRecord.resultTo = null;if (resultRecord != null) {resultRecord.removeResultsLocked(sourceRecord, resultWho, requestCode);}if (sourceRecord.launchedFromUid == callingUid) {// The new activity is being launched from the same uid as the previous activity// in the flow, and asking to forward its result back to the previous. In this// case the activity is serving as a trampoline between the two, so we also want// to update its launchedFromPackage to be the same as the previous activity.// Note that this is safe, since we know these two packages come from the same// uid; the caller could just as well have supplied that same package name itself// . This specifially deals with the case of an intent picker/chooser being// launched in the app flow to redirect to an activity picked by the user, where// we want the final activity to consider it to have been launched by the// previous app activity.callingPackage = sourceRecord.launchedFromPackage;callingFeatureId = sourceRecord.launchedFromFeatureId;}}if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && intent.getComponent() == null) {// We couldn't find a class that can handle the given Intent.// That's the end of that!err = ActivityManager.START_INTENT_NOT_RESOLVED;}if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && aInfo == null) {// We couldn't find the specific class specified in the Intent.// Also the end of the line.err = ActivityManager.START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND;}if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && sourceRecord != null&& sourceRecord.getTask().voiceSession != null) {// If this activity is being launched as part of a voice session, we need to ensure// that it is safe to do so. If the upcoming activity will also be part of the voice// session, we can only launch it if it has explicitly said it supports the VOICE// category, or it is a part of the calling app.if ((launchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) == 0&& sourceRecord.info.applicationInfo.uid != aInfo.applicationInfo.uid) {try {intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_VOICE);if (!mService.getPackageManager().activitySupportsIntent(intent.getComponent(), intent, resolvedType)) {Slog.w(TAG, "Activity being started in current voice task does not support "+ "voice: " + intent);err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE;}} catch (RemoteException e) {Slog.w(TAG, "Failure checking voice capabilities", e);err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE;}}}if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && voiceSession != null) {// If the caller is starting a new voice session, just make sure the target// is actually allowing it to run this way.try {if (!mService.getPackageManager().activitySupportsIntent(intent.getComponent(),intent, resolvedType)) {Slog.w(TAG,"Activity being started in new voice task does not support: " + intent);err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE;}} catch (RemoteException e) {Slog.w(TAG, "Failure checking voice capabilities", e);err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE;}}final Task resultRootTask = resultRecord == null? null : resultRecord.getRootTask();if (err != START_SUCCESS) {if (resultRecord != null) {resultRecord.sendResult(INVALID_UID, resultWho, requestCode, RESULT_CANCELED,null /* data */, null /* dataGrants */);}SafeActivityOptions.abort(options);return err;}
首先从类Request中取得对应值赋值给变量。
先将变量err设置为ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS。
caller是应用进程Java服务代理对象。如果它被设置过,通过mService.getProcessController(caller)得到对应的WindowProcessController对象,mService是ActivityTaskManagerService对象(它里面维护着它们俩的对应关系),如果它不为null,则将局部变量callingPid、callingUid设置为它的对应的值。如果mService中没有找到caller(不为null)对应的WindowProcessController对象,则会将err设置为ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED。
下面通过应用Uid(aInfo.applicationInfo.uid)得到用户id。
接下来sourceRecord和resultRecord和请求参数resultTo有关。resultTo是对应将启动Activity之后的应答发回到对应的Activity。在需要应答时,还和requestCode有关,需要将它设置为一个非负整数。所以下面通过resultTo得到sourceRecord,然后通过判断requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing之后,才给resultRecord赋值。
接下来是处理标识Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT的情况。
在sourceRecord不为null的情况下,如果设置了FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT标识,就不能设置requestCode,如果设置了requestCode(为非负数),就直接返回ActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT。
设置了FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT标识,是为了将结果转移到启动了sourceRecord的那个Activity。所以将resultRecord设置为sourceRecord.resultTo。如果resultRecord不在根任务的包括层级中,会将resultRecord = null。也会将resultWho、requestCode设置成sourceRecord的对应值。并将sourceRecord.resultTo = null。如果resultRecord != null,则将resultRecord中和sourceRecord、resultWho、requestCode相关的结果删除。如果sourceRecord的启动应用和当前要启动的应用相同,会将callingPackage、callingFeatureId设置为启动sourceRecord的包名和launchedFromFeatureId。
接下来判断如果intent.getComponent()为null,会将err设置为ActivityManager.START_INTENT_NOT_RESOLVED。代表没有找到对应的启动的类。
如果aInfo == null,代表也是没找到对应的类,将err设置为ActivityManager.START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND。
如果现在还没出错(err为ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS ),并且sourceRecord在一个语音交互任务(sourceRecord.getTask().voiceSession != null)中,需要检查新启动的Activity是否能支持。没有FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK标识,并且和sourceRecord不在同一个应用进程中,在该种条件先需要去检测。先给intent添加Intent.CATEGORY_VOICE的Category。下面是通过mService.getPackageManager().activitySupportsIntent()来检查的,最终是进入到PackageManagerService中去做检测的,这里主要检查的意思就是,启动的Activity是需要配置Intent.CATEGORY_VOICE的。如果检测没有通过,会将err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE。
如果目前需要启动一个语音交互任务,这里也是调用mService.getPackageManager().activitySupportsIntent()来检查的,不过它没有加Intent.CATEGORY_VOICE。这里也就是检查,它能运行。如果没通过检查,同样将err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE。
如果resultRecord不为null,会将它的根任务赋值给局部变量resultRootTask。
如果现在err != START_SUCCESS,则代表出错了,不需要往下执行了。如果此时resultRecord不为null,则调用它的sendResult方法,该方法主要做:如果状态为RESUMED,并且在应用进程中运行,则直接通知它。如果不是会将结果存在resultRecord中(它是ActivityRecord类,存在它的成员results中)。再处理一下options,之后就将错误代码返回。
继续往下看下分段二:
boolean abort = !mSupervisor.checkStartAnyActivityPermission(intent, aInfo, resultWho,requestCode, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, callingFeatureId,request.ignoreTargetSecurity, inTask != null, callerApp, resultRecord,resultRootTask);abort |= !mService.mIntentFirewall.checkStartActivity(intent, callingUid,callingPid, resolvedType, aInfo.applicationInfo);abort |= !mService.getPermissionPolicyInternal().checkStartActivity(intent, callingUid,callingPackage);boolean restrictedBgActivity = false;if (!abort) {try {Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER,"shouldAbortBackgroundActivityStart");restrictedBgActivity = shouldAbortBackgroundActivityStart(callingUid,callingPid, callingPackage, realCallingUid, realCallingPid, callerApp,request.originatingPendingIntent, request.allowBackgroundActivityStart,intent);} finally {Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);}}// Merge the two options bundles, while realCallerOptions takes precedence.ActivityOptions checkedOptions = options != null? options.getOptions(intent, aInfo, callerApp, mSupervisor) : null;if (request.allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup) {checkedOptions = mService.getActivityStartController().getPendingRemoteAnimationRegistry().overrideOptionsIfNeeded(callingPackage, checkedOptions);}if (mService.mController != null) {try {// The Intent we give to the watcher has the extra data stripped off, since it// can contain private information.Intent watchIntent = intent.cloneFilter();abort |= !mService.mController.activityStarting(watchIntent,aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName);} catch (RemoteException e) {mService.mController = null;}}mInterceptor.setStates(userId, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags, callingPackage,callingFeatureId);if (mInterceptor.intercept(intent, rInfo, aInfo, resolvedType, inTask, callingPid,callingUid, checkedOptions)) {// activity start was intercepted, e.g. because the target user is currently in quiet// mode (turn off work) or the target application is suspendedintent = mInterceptor.mIntent;rInfo = mInterceptor.mRInfo;aInfo = mInterceptor.mAInfo;resolvedType = mInterceptor.mResolvedType;inTask = mInterceptor.mInTask;callingPid = mInterceptor.mCallingPid;callingUid = mInterceptor.mCallingUid;checkedOptions = mInterceptor.mActivityOptions;// The interception target shouldn't get any permission grants// intended for the original destinationintentGrants = null;}if (abort) {if (resultRecord != null) {resultRecord.sendResult(INVALID_UID, resultWho, requestCode, RESULT_CANCELED,null /* data */, null /* dataGrants */);}// We pretend to the caller that it was really started, but they will just get a// cancel result.ActivityOptions.abort(checkedOptions);return START_ABORTED;}// If permissions need a review before any of the app components can run, we// launch the review activity and pass a pending intent to start the activity// we are to launching now after the review is completed.if (aInfo != null) {if (mService.getPackageManagerInternalLocked().isPermissionsReviewRequired(aInfo.packageName, userId)) {final IIntentSender target = mService.getIntentSenderLocked(ActivityManager.INTENT_SENDER_ACTIVITY, callingPackage, callingFeatureId,callingUid, userId, null, null, 0, new Intent[]{intent},new String[]{resolvedType}, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT| PendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOT, null);Intent newIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_REVIEW_PERMISSIONS);int flags = intent.getFlags();flags |= Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS;/** Prevent reuse of review activity: Each app needs their own review activity. By* default activities launched with NEW_TASK or NEW_DOCUMENT try to reuse activities* with the same launch parameters (extras are ignored). Hence to avoid possible* reuse force a new activity via the MULTIPLE_TASK flag.** Activities that are not launched with NEW_TASK or NEW_DOCUMENT are not re-used,* hence no need to add the flag in this case.*/if ((flags & (FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT)) != 0) {flags |= Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK;}newIntent.setFlags(flags);newIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_PACKAGE_NAME, aInfo.packageName);newIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_INTENT, new IntentSender(target));if (resultRecord != null) {newIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_RESULT_NEEDED, true);}intent = newIntent;// The permissions review target shouldn't get any permission// grants intended for the original destinationintentGrants = null;resolvedType = null;callingUid = realCallingUid;callingPid = realCallingPid;rInfo = mSupervisor.resolveIntent(intent, resolvedType, userId, 0,computeResolveFilterUid(callingUid, realCallingUid, request.filterCallingUid));aInfo = mSupervisor.resolveActivity(intent, rInfo, startFlags,null /*profilerInfo*/);if (DEBUG_PERMISSIONS_REVIEW) {final Task focusedRootTask =mRootWindowContainer.getTopDisplayFocusedRootTask();Slog.i(TAG, "START u" + userId + " {" + intent.toShortString(true, true,true, false) + "} from uid " + callingUid + " on display "+ (focusedRootTask == null ? DEFAULT_DISPLAY: focusedRootTask.getDisplayId()));}}}
mSupervisor是ActivityTaskSupervisor对象,它的checkStartAnyActivityPermission方法主要是检查应用进程是否有START_ANY_ACTIVITY权限,如果取得,则返回true。如果没有获取到START_ANY_ACTIVITY权限,还会去检查待启动的Activity所需要的权限(如果存在)是否被应用拒绝、Action对应的权限是否被应用拒绝、如果被限制,则返回false。如果没有限制,也返回true。
mService.mIntentFirewall是IntentFirewall对象,看名字是Intent防火墙的意思。它的checkStartActivity方法是检查它的一些规则,如果不满足,这里会进行拦截,将abort设置为true。
mService.getPermissionPolicyInternal()是PermissionPolicyService类中的Internal对象。它主要检测Action为TelecomManager.ACTION_CHANGE_DEFAULT_DIALER和Telephony.Sms.Intents.ACTION_CHANGE_DEFAULT时,如果调用应用的目标SDK大于等于Q时,是拦截,不允许启动的。
在现在没有出现问题的情况下(abort为false),会调用shouldAbortBackgroundActivityStart方法来检查是否允许背景应用来启动Activity。并且将返回结果存储在变量restrictedBgActivity中。
接下来就是处理参数选项类options的getOptions()方法,它会检查其中的一些权限,并且它会合并它里面的选项,转为ActivityOptions类对象checkedOptions。
mService.mController在这里是一个观察者。这里是调用它的activityStarting方法通知它。
mInterceptor是ActivityStartInterceptor对象,它是一个启动拦截器。它在符合特定条件下,会进行拦截,改变对应的Intent和其他对应值,下面再跳转就是到拦截的界面了。mInterceptor.intercept()在符合拦截的情况下,是返回true的。在这个方法里面,会将mInterceptor对象的相应进行更改,下面就用它里面的对应值设置局部变量intent等。如果用户是在Quiet模式、应用被暂停、锁任务模式下应用不允许启动、启动的应用有有害警告时都会进行拦截。
接下来,如果abort为true,代表出现问题,需要终止,如果resultRecord不为null,将相应结果(RESULT_CANCELED,取消的结果)设置到里面,返回结果START_ABORTED。
接下来处理的是如果启动的Activity有review权限,则会启动这个review Activity。它会在review 完成之后,再启动目标Activity。这个权限是目标SDK在Build.VERSION_CODES.M之前才适用,新的权限模式不支持。最后这段代码,就是处理我说的这些。将目标Activity的启动Intent封装成IIntentSender对象,传递给review Activity。之后就是解析出来它的ResolveInfo对象、ActivityInfo对象。
继续往下看下分段三:
// If we have an ephemeral app, abort the process of launching the resolved intent.// Instead, launch the ephemeral installer. Once the installer is finished, it// starts either the intent we resolved here [on install error] or the ephemeral// app [on install success].if (rInfo != null && rInfo.auxiliaryInfo != null) {intent = createLaunchIntent(rInfo.auxiliaryInfo, request.ephemeralIntent,callingPackage, callingFeatureId, verificationBundle, resolvedType, userId);resolvedType = null;callingUid = realCallingUid;callingPid = realCallingPid;// The ephemeral installer shouldn't get any permission grants// intended for the original destinationintentGrants = null;aInfo = mSupervisor.resolveActivity(intent, rInfo, startFlags, null /*profilerInfo*/);}// TODO (b/187680964) Correcting the caller/pid/uid when start activity from shortcut// Pending intent launched from systemui also depends on caller appif (callerApp == null && realCallingPid > 0) {final WindowProcessController wpc = mService.mProcessMap.getProcess(realCallingPid);if (wpc != null) {callerApp = wpc;}}final ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord.Builder(mService).setCaller(callerApp).setLaunchedFromPid(callingPid).setLaunchedFromUid(callingUid).setLaunchedFromPackage(callingPackage).setLaunchedFromFeature(callingFeatureId).setIntent(intent).setResolvedType(resolvedType).setActivityInfo(aInfo).setConfiguration(mService.getGlobalConfiguration()).setResultTo(resultRecord).setResultWho(resultWho).setRequestCode(requestCode).setComponentSpecified(request.componentSpecified).setRootVoiceInteraction(voiceSession != null).setActivityOptions(checkedOptions).setSourceRecord(sourceRecord).build();mLastStartActivityRecord = r;if (r.appTimeTracker == null && sourceRecord != null) {// If the caller didn't specify an explicit time tracker, we want to continue// tracking under any it has.r.appTimeTracker = sourceRecord.appTimeTracker;}// Only allow app switching to be resumed if activity is not a restricted background// activity and target app is not home process, otherwise any background activity// started in background task can stop home button protection mode.// As the targeted app is not a home process and we don't need to wait for the 2nd// activity to be started to resume app switching, we can just enable app switching// directly.WindowProcessController homeProcess = mService.mHomeProcess;boolean isHomeProcess = homeProcess != null&& aInfo.applicationInfo.uid == homeProcess.mUid;if (!restrictedBgActivity && !isHomeProcess) {mService.resumeAppSwitches();}mLastStartActivityResult = startActivityUnchecked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession,request.voiceInteractor, startFlags, true /* doResume */, checkedOptions, inTask,restrictedBgActivity, intentGrants);if (request.outActivity != null) {request.outActivity[0] = mLastStartActivityRecord;}return mLastStartActivityResult;}
rInfo.auxiliaryInfo是和安装Instant应用有关,如果启动的是Instant应用,则会启动Instant安装者。
接着下面处理的是从快捷方式启动Activity的情况,这种情况下,callerApp == null,realCallingPid > 0,所以取出realCallingPid对应的应用,赋值给callerApp 。
接下来就是构建ActivityRecord对象,它是应用端Activity在系统框架层中对应的对象。它的创建是采用了建造者模式。里面用到的变量,前面大多都涉及到了,这里不详细说了。
创建完之后,将创建的对象赋值给mLastStartActivityRecord。
r.appTimeTracker是用来跟踪用户使用应用时间,如果没有设置它,则将它设置为sourceRecord对象(它不为null的情况下)的appTimeTracker。
如果不是背景应用启动Activity并且启动的Activity不是Launcher进程,可以直接使APP切换开关打开。看着注释的解释是,背景应用如果是APP切换开关打开,会停止Home按键的保护模式。启动的Activity如果在Launcher进程中,需要等待Activity启动之后,才能打开APP切换开关。
再接下来就是调用startActivityUnchecked方法来启动Activity了。并将结果存储在mLastStartActivityResult中。
request.outActivity不为null,会将它设置为启动的ActivityRecord对象mLastStartActivityRecord。
最后将结果返回。
可见该方法主要就是做了一些检查,主要是一些权限和拦截的处理。
executeRequest(Request request)的代码说完了,Activity启动的代码是在方法startActivityUnchecked方法中,所以,我们继续看它的实现。
检查之后的startActivityUnchecked方法
看一下startActivityUnchecked方法的实现:
/*** Start an activity while most of preliminary checks has been done and caller has been* confirmed that holds necessary permissions to do so.* Here also ensures that the starting activity is removed if the start wasn't successful.*/private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, Task inTask,boolean restrictedBgActivity, NeededUriGrants intentGrants) {int result = START_CANCELED;final Task startedActivityRootTask;// Create a transition now to record the original intent of actions taken within// startActivityInner. Otherwise, logic in startActivityInner could start a different// transition based on a sub-action.// Only do the create here (and defer requestStart) since startActivityInner might abort.final Transition newTransition = (!mService.getTransitionController().isCollecting()&& mService.getTransitionController().getTransitionPlayer() != null)? mService.getTransitionController().createTransition(TRANSIT_OPEN) : null;IRemoteTransition remoteTransition = r.takeRemoteTransition();if (newTransition != null && remoteTransition != null) {newTransition.setRemoteTransition(remoteTransition);}mService.getTransitionController().collect(r);try {mService.deferWindowLayout();Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "startActivityInner");result = startActivityInner(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,startFlags, doResume, options, inTask, restrictedBgActivity, intentGrants);} finally {Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);startedActivityRootTask = handleStartResult(r, result);mService.continueWindowLayout();mSupervisor.mUserLeaving = false;// Transition housekeepingif (!ActivityManager.isStartResultSuccessful(result)) {if (newTransition != null) {newTransition.abort();}} else {if (!mAvoidMoveToFront && mDoResume&& mRootWindowContainer.hasVisibleWindowAboveButDoesNotOwnNotificationShade(r.launchedFromUid)) {// If the UID launching the activity has a visible window on top of the// notification shade and it's launching an activity that's going to be at the// front, we should move the shade out of the way so the user can see it.// We want to avoid the case where the activity is launched on top of a// background task which is not moved to the front.StatusBarManagerInternal statusBar = mService.getStatusBarManagerInternal();if (statusBar != null) {// This results in a async call since the interface is one-waystatusBar.collapsePanels();}}if (result == START_SUCCESS || result == START_TASK_TO_FRONT) {// The activity is started new rather than just brought forward, so record// it as an existence change.mService.getTransitionController().collectExistenceChange(r);}if (newTransition != null) {mService.getTransitionController().requestStartTransition(newTransition,mTargetTask, remoteTransition);} else {// Make the collecting transition wait until this request is ready.mService.getTransitionController().setReady(false);}}}postStartActivityProcessing(r, result, startedActivityRootTask);return result;}
Transition和Activity的转场动画相关,调用mService.getTransitionController()的collect®方法将ActivityRecord对象收集到转换中。
接着mService.deferWindowLayout()是延迟窗口布局。
调用startActivityInner()方法,实现启动Activity。
handleStartResult(r, result)是处理启动的结果,如果启动成功,会返回它的RootTask。
mService.continueWindowLayout()是恢复窗口布局。
mSupervisor.mUserLeaving是一个状态,如果用户没有明确设定FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_USER_ACTION标识,在前面startActivityInner()方法中,mSupervisor.mUserLeaving会被设置为true,这样会在Activity执行onPause之前,通知用户离开方法onUserLeaveHint()。执行完毕之后,在这里将它设置为false。
如果启动Activity的结果不是成功的状态,如果前面创建的newTransition不为null,设置它的abort状态。
如果是启动成功,在不是避免移到前面的条件下,如果启动的应用在通知栏打开的上层有打开窗口,这里将通知栏关闭。
接下来是处理转场相关。如果返回结果为START_SUCCESS或START_TASK_TO_FRONT的情况下,这里将启动的ActivityRecord对象的改变状态记录下来(Activity打开或关闭)。START_SUCCESS代表正常启动一个Activity,START_TASK_TO_FRONT是一种什么情况呢?它代表Activity已经在任务栈中,并且将任务栈挪到根任务的最前端,包括根任务也会移动到TaskDisplayArea对象的最前端(这里根任务和任务有可能是同一个)。还有一个返回值为START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP,它则是代表在任务栈顶上和被启动的Activity是相同的,不需要再次启动一个新的。
如果newTransition是在这里新创建的,这里就开始请求开始。如果不是,则是等待,直到请求是准备好。
最后是调用postStartActivityProcessing方法。它是处理启动Activity之后的工作。
startActivityInner()方法
接下来看看startActivityInner()方法:
/*** Start an activity and determine if the activity should be adding to the top of an existing* task or delivered new intent to an existing activity. Also manipulating the activity task* onto requested or valid root-task/display.** Note: This method should only be called from {@link #startActivityUnchecked}.*/// TODO(b/152429287): Make it easier to exercise code paths through startActivityInner@VisibleForTestingint startActivityInner(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, Task inTask,boolean restrictedBgActivity, NeededUriGrants intentGrants) {setInitialState(r, options, inTask, doResume, startFlags, sourceRecord, voiceSession,voiceInteractor, restrictedBgActivity);computeLaunchingTaskFlags();computeSourceRootTask();mIntent.setFlags(mLaunchFlags);final Task reusedTask = getReusableTask();// If requested, freeze the task listif (mOptions != null && mOptions.freezeRecentTasksReordering()&& mSupervisor.mRecentTasks.isCallerRecents(r.launchedFromUid)&& !mSupervisor.mRecentTasks.isFreezeTaskListReorderingSet()) {mFrozeTaskList = true;mSupervisor.mRecentTasks.setFreezeTaskListReordering();}// Compute if there is an existing task that should be used for.final Task targetTask = reusedTask != null ? reusedTask : computeTargetTask();final boolean newTask = targetTask == null;mTargetTask = targetTask;computeLaunchParams(r, sourceRecord, targetTask);// Check if starting activity on given task or on a new task is allowed.int startResult = isAllowedToStart(r, newTask, targetTask);if (startResult != START_SUCCESS) {return startResult;}final ActivityRecord targetTaskTop = newTask? null : targetTask.getTopNonFinishingActivity();if (targetTaskTop != null) {// Recycle the target task for this launch.startResult = recycleTask(targetTask, targetTaskTop, reusedTask, intentGrants);if (startResult != START_SUCCESS) {return startResult;}} else {mAddingToTask = true;}// If the activity being launched is the same as the one currently at the top, then// we need to check if it should only be launched once.final Task topRootTask = mPreferredTaskDisplayArea.getFocusedRootTask();if (topRootTask != null) {startResult = deliverToCurrentTopIfNeeded(topRootTask, intentGrants);if (startResult != START_SUCCESS) {return startResult;}}if (mTargetRootTask == null) {mTargetRootTask = getLaunchRootTask(mStartActivity, mLaunchFlags, targetTask, mOptions);}if (newTask) {final Task taskToAffiliate = (mLaunchTaskBehind && mSourceRecord != null)? mSourceRecord.getTask() : null;setNewTask(taskToAffiliate);} else if (mAddingToTask) {addOrReparentStartingActivity(targetTask, "adding to task");}if (!mAvoidMoveToFront && mDoResume) {mTargetRootTask.getRootTask().moveToFront("reuseOrNewTask", targetTask);if (mOptions != null) {if (mOptions.getTaskAlwaysOnTop()) {mTargetRootTask.setAlwaysOnTop(true);}}if (!mTargetRootTask.isTopRootTaskInDisplayArea() && mService.mInternal.isDreaming()) {// Launching underneath dream activity (fullscreen, always-on-top). Run the launch-// -behind transition so the Activity gets created and starts in visible state.mLaunchTaskBehind = true;r.mLaunchTaskBehind = true;}}mService.mUgmInternal.grantUriPermissionUncheckedFromIntent(intentGrants,mStartActivity.getUriPermissionsLocked());if (mStartActivity.resultTo != null && mStartActivity.resultTo.info != null) {// we need to resolve resultTo to a uid as grantImplicitAccess deals explicitly in UIDsfinal PackageManagerInternal pmInternal =mService.getPackageManagerInternalLocked();final int resultToUid = pmInternal.getPackageUid(mStartActivity.resultTo.info.packageName, 0 /* flags */,mStartActivity.mUserId);pmInternal.grantImplicitAccess(mStartActivity.mUserId, mIntent,UserHandle.getAppId(mStartActivity.info.applicationInfo.uid) /*recipient*/,resultToUid /*visible*/, true /*direct*/);}if (newTask) {EventLogTags.writeWmCreateTask(mStartActivity.mUserId,mStartActivity.getTask().mTaskId);}mStartActivity.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.WM_CREATE_ACTIVITY, mStartActivity.getTask());mTargetRootTask.mLastPausedActivity = null;mRootWindowContainer.startPowerModeLaunchIfNeeded(false /* forceSend */, mStartActivity);mTargetRootTask.startActivityLocked(mStartActivity,topRootTask != null ? topRootTask.getTopNonFinishingActivity() : null, newTask,mKeepCurTransition, mOptions, sourceRecord);if (mDoResume) {final ActivityRecord topTaskActivity =mStartActivity.getTask().topRunningActivityLocked();if (!mTargetRootTask.isTopActivityFocusable()|| (topTaskActivity != null && topTaskActivity.isTaskOverlay()&& mStartActivity != topTaskActivity)) {// If the activity is not focusable, we can't resume it, but still would like to// make sure it becomes visible as it starts (this will also trigger entry// animation). An example of this are PIP activities.// Also, we don't want to resume activities in a task that currently has an overlay// as the starting activity just needs to be in the visible paused state until the// over is removed.// Passing {@code null} as the start parameter ensures all activities are made// visible.mTargetRootTask.ensureActivitiesVisible(null /* starting */,0 /* configChanges */, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);// Go ahead and tell window manager to execute app transition for this activity// since the app transition will not be triggered through the resume channel.mTargetRootTask.mDisplayContent.executeAppTransition();} else {// If the target root-task was not previously focusable (previous top running// activity on that root-task was not visible) then any prior calls to move the// root-task to the will not update the focused root-task. If starting the new// activity now allows the task root-task to be focusable, then ensure that we// now update the focused root-task accordingly.if (mTargetRootTask.isTopActivityFocusable()&& !mRootWindowContainer.isTopDisplayFocusedRootTask(mTargetRootTask)) {mTargetRootTask.moveToFront("startActivityInner");}mRootWindowContainer.resumeFocusedTasksTopActivities(mTargetRootTask, mStartActivity, mOptions, mTransientLaunch);}}mRootWindowContainer.updateUserRootTask(mStartActivity.mUserId, mTargetRootTask);// Update the recent tasks list immediately when the activity startsmSupervisor.mRecentTasks.add(mStartActivity.getTask());mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(mStartActivity.getTask(),mPreferredWindowingMode, mPreferredTaskDisplayArea, mTargetRootTask);return START_SUCCESS;}
setInitialState()主要用来初始化ActivityStarter对象的成员变量,
computeLaunchingTaskFlags()是用来计算启动任务的标识mLaunchFlags。这里注意的一点是,在没指定Task的情况下,如果启动的Activity模式是LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE或LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK,会给mLaunchFlags添加FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK标识。
computeSourceRootTask()是用来得到源根任务mSourceRootTask。
接下来将mLaunchFlags设置到mIntent中。
getReusableTask()得到新启动Activity应该添加进的Task。主要处理启动标识FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK标识,还有启动模式为LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE、LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK的情况,这样得到包含对应Activity的Task。
接下来,如果设置参数里面请求冻结任务链,设置冻结任务链属性。
targetTask是启动的Activity使用的Task,它可能存在,也可能不存在,需要创建。这里如果上面得到的reusedTask不为null,就使用它;如果他为null,再通过computeTargetTask()计算得到。computeTargetTask()会在有FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK标识的情况下,返回null。代表需要新建Task。computeTargetTask()在其他的情况下,如果启动Activity不为null,就返回它的Task。如果指定Task,就使用指定Task。
如果targetTask为null,则代表需要新建Task。
给成员变量mTargetTask赋值。
computeLaunchParams用来计算成员变量mLaunchParams。
isAllowedToStart()用来判断是否允许启动Activity。它主要用来判断ACTIVITY_TYPE_HOME类型Activity能否在显示屏上启动、后台启动的Activity是否终止、是否违法锁任务模式。如果返回的结果不为START_SUCCESS,则返回对应结果。
下面如果目标Task不为null,则得到目标Task上面的不为finishing的ActivityRecord targetTaskTop。
如果目标Task上的不为finishing的ActivityRecord targetTaskTop不为null,则调用recycleTask()处理。注意,这里的targetTaskTop可不见得就是启动的Activity,像SINGLE_TASK模式启动的Activity,它所属的任务栈里在它上面可能存在其他的Activity。recycleTask主要是对于目标Task的重用处理。如果目标Task的根Task不是当前获取焦点的根Task,它会将目标Task的根Task移动到最前面。处理启动的标识,在这里,它可能会将Task里面的Activity给去除(对应启动SingleTask的Activity,它的实现是由complyActivityFlags()实现)。它还决定是在Task顶端添加Activity还是将Task放到最前端。如果是在Task顶端添加Activity,它会将成员变量mAddingToTask设置为true。
注意,如果recycleTask()返回的结果不为START_SUCCESS,则不会再往下执行,直接返回对应的结果。这里返回START_SUCCESS也即在Task顶端添加Activity。它会继续向下处理。像我们平时启动模式为SingleTask、SingleInstance的Activity,并且已经存在Task的情况下,就不会继续向下执行了。
如果目标Task上的不为finishing的ActivityRecord targetTaskTop为null,则将变量mAddingToTask = true,代表需要将Activity添加到Task中。
接下来,是判断启动的Activity是否和当前Task最顶的Activity是不是相同,如果相同,检查是不是需要重新启动一个新的Activity。下面的deliverToCurrentTopIfNeeded(topRootTask, intentGrants)就是做这个事情的。像我们平时启动模式为SingleTop的Activity就是在这里处理的。如果不用新启动Activity,返回START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP。
再接下来,如果mTargetRootTask为null的话,通过getLaunchRootTask()方法来获得。getLaunchRootTask()如果不能得到目前存在的Task,它会新建一个Task。
下面继续是新建Task(newTask决定),还是将Activity添加到Task中(mAddingToTask决定)。如果是新建Task,在新建之后,还需要将Activity添加到Task中的最顶端。在这里由于上一步可能通过getLaunchRootTask()新建了RootTask,在这里也可能是使用的上一步新建的RootTask。如果不需要新建Task,只是将Activity加入到Task中,这里是调用addOrReparentStartingActivity(targetTask, “adding to task”)完成的。
下面,如果mAvoidMoveToFront为false,代表将任务移动到前面。mDoResume为true,代表需要将Activity启动。这里会调用根Task的moveToFront()将任务移动到前面。
下面是检测Uri权限。
如果启动Activity之后,返回结果给对应Activity存在(mStartActivity.resultTo != null)。这里获取返回接收者应用对启动应用的可见性。
下面继续将mTargetRootTask.mLastPausedActivity = null。
mTargetRootTask.startActivityLocked()主要是将Activity放置到Task的最上端。然后显示应用的StartingWindow。
mDoResume代表需要恢复Activity。
得到启动Activity的所在任务的最顶端可以运行的Activity topTaskActivity。
如果根任务的顶端Activity不是可以取得焦点的或者任务的顶端有一个遮罩并且不是启动的Activity,这样的情况下,也不恢复Activity,只是让它可见。
除了上面那两种情况下,就需要恢复Activity。还是检查如果根任务不是顶端获取焦点的根任务,需要将它挪到最前端。接着就调用mRootWindowContainer.resumeFocusedTasksTopActivities()来恢复目标Activity的执行。在它里面会执行根Task的resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked()方法。由于在前面已经将Activity添加到Task的最顶端,所以这里就会将之前的处于Resumed状态的Activity给暂停,然后将新添加的Activity启动,并且将它状态改成Resumed。
接下来调用mRootWindowContainer.updateUserRootTask()方法来更新对应用户的根Task。
会将启动的Activity的Task添加到mSupervisor.mRecentTasks中。
接着调用mSupervisor的handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded()方法来处理不是可变大小的Task。
最后返回结果START_SUCCESS。
总结
这里是启动Activity的实现。
首先是需要执行一系列检查,主要是权限和拦截的处理。
接着处理主要分可以重用的Task,还是新建Task。对于可以重用的Task,还是要区分里面是否已经存在Activity实例(SingleTask、SingleInstance、SingleTop模式的Activity)进行处理。
最后会将满足条件的Activty启动起来。
相关文章:

Android Activity的启动器ActivityStarter入口
Activity启动器入口 Android的Activity的启动入口是在ActivityStarter类的execute(),在该方法里面继续调用executeRequest(Request request) ,相应的参数都设置在方法参数request中。代码挺长,分段现在看下它的实现,分段一&#x…...

Python深度学习算法介绍
一、引言 深度学习是机器学习的一个重要分支,它通过构建多层神经网络结构,自动从数据中学习特征表示,从而实现对复杂模式的识别和预测。Python作为一门强大的编程语言,凭借其简洁易读的语法和丰富的库支持,成为深度学…...

关于sqlalchemy的使用
关于sqlalchemy的使用 说明一、sqlachemy总体使用思路二、安装与创建库、连结库三、创建表、增加数据四、查询记录五、更新或删除六、关联表定义七、一对多关联查询八、映射类定义与添加记录 说明 本教程所需软件及库python3.10、sqlalchemy安装与创建库、连结库创建表、增加数…...
利用LLMs准确预测旋转机械(如轴承)的剩余使用寿命(RUL)
研究背景 研究问题:如何准确预测旋转机械(如轴承)的剩余使用寿命(RUL),这对于设备可靠性和减少工业系统中的意外故障至关重要。研究难点:该问题的研究难点包括:训练和测试阶段数据分布不一致、长期RUL预测的泛化能力有限。相关工作:现有工作主要包括基于模型的方法、数…...

深度学习 PyTorch 中 18 种数据增强策略与实现
深度学习pytorch之简单方法自定义9类卷积即插即用 数据增强通过对训练数据进行多种变换,增加数据的多样性,它帮助我们提高模型的鲁棒性,并减少过拟合的风险。PyTorch 提供torchvision.transforms 模块丰富的数据增强操作,我们可以…...

视觉图像处理
在MATLAB中进行视觉图像处理仿真通常涉及图像增强、滤波、分割、特征提取等操作。以下是一个分步指南和示例代码,帮助您快速入门: 1. MATLAB图像处理基础步骤 1.1 读取和显示图像 % 读取图像(替换为实际文件路径) img = imread(lena.jpg); % 显示原图 figure; subplot(2…...

深度学习与普通神经网络有何区别?
深度学习与普通神经网络的主要区别体现在以下几个方面: 一、结构复杂度 普通神经网络:通常指浅层结构,层数较少,一般为2-3层,包括输入层、一个或多个隐藏层、输出层。深度学习:强调通过5层以上的深度架构…...

Vue3、vue学习笔记
<!-- Vue3 --> 1、Vue项目搭建 npm init vuelatest cd 文件目录 npm i npm run dev // npm run _ 这个在package.json中查看scripts /* vue_study\.vscode可删 // vue_study\src\components也可删除(基本语法,不使用组件) */ // vue_study\.vscode\lau…...

python中C#类库调用+调试方法~~~
因为开发需要,我们经常会用C#来写一些库供python调用,但是在使用过程中难免会碰到一些问题,需要我们抽丝剥茧来解决~~~ 首先,我们在python中要想调用C#(基于.net)的dll,需要安装一个库,它就是 pythonnet …...

L33.【LeetCode笔记】循环队列(数组解法)
目录 1.题目 2.分析 方法1:链表 尝试使用单向循环链表模拟 插入节点 解决方法1:开辟(k1)个节点 解决方法2:使用变量size记录队列元素个数 获取队尾元素 其他函数的实现说明 方法2:数组 重要点:指针越界的解决方法 方法1:单独判断 方法2:取模 3.数组代码的逐步实现…...

css实现元素垂直居中显示的7种方式
文章目录 * [【一】知道居中元素的宽高](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41305441/article/details/89886846#_1) [absolute 负margin](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41305441/article/details/89886846#absolute__margin_2) [absolute margin auto](https://blog.csdn.net…...

【Python】Django 中的算法应用与实现
Django 中的算法应用与实现 在 Django 开发中,算法的应用可以极大地扩展 Web 应用的功能和性能。从简单的数据处理到复杂的机器学习模型,Django 都可以作为一个强大的后端框架来支持这些算法的实现。本文将介绍几种常见的算法及其在 Django 中的使用方法…...

Docker 运行 GPUStack 的详细教程
GPUStack GPUStack 是一个用于运行 AI 模型的开源 GPU 集群管理器。它具有广泛的硬件兼容性,支持多种品牌的 GPU,并能在 Apple MacBook、Windows PC 和 Linux 服务器上运行。GPUStack 支持各种 AI 模型,包括大型语言模型(LLMs&am…...
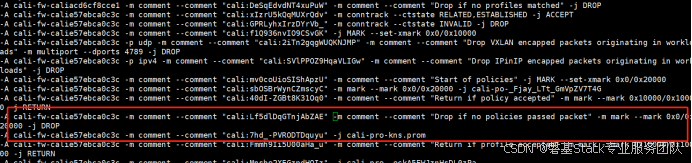
Kubernetes中的 iptables 规则介绍
#作者:邓伟 文章目录 一、Kubernetes 网络模型概述二、iptables 基础知识三、Kubernetes 中的 iptables 应用四、查看和调试 iptables 规则五、总结 在 Kubernetes 集群中,iptables 是一个核心组件, 用于实现服务发现和网络策略。iptables 通…...
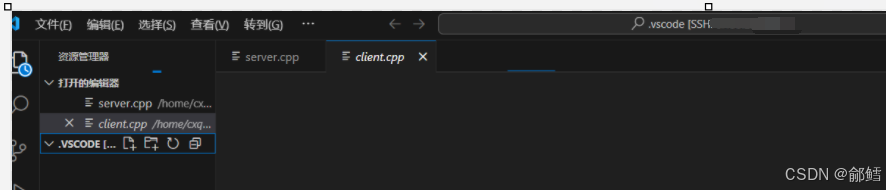
解决VScode 连接不上问题
问题 :VScode 连接不上 解决方案: 1、手动杀死VS Code服务器进程,然后重新尝试登录 打开xshell ,远程连接服务器 ,查看vscode的进程 ,然后全部杀掉 [cxqiZwz9fjj2ssnshikw14avaZ ~]$ ps ajx | grep vsc…...

AI 驱动的软件测试革命:从自动化到智能化的进阶之路
🚀引言:软件测试的智能化转型浪潮 在数字化转型加速的今天,软件产品的迭代速度与复杂度呈指数级增长。传统软件测试依赖人工编写用例、执行测试的模式,已难以应对快速交付与高质量要求的双重挑战。人工智能技术的突破为测试领域注…...
【Java代码审计 | 第六篇】XSS防范
文章目录 XSS防范使用HTML转义使用Content Security Policy (CSP)输入验证使用安全的库和框架避免直接使用用户输入构建JavaScript代码 XSS防范 使用HTML转义 在输出用户输入时,对特殊字符进行转义,防止它们被解释为HTML或JavaScript代码。 例如&…...

Android WebSocket工具类:重连、心跳、消息队列一站式解决方案
依赖库 使用 OkHttp 的WebSocket支持。 在 build.gradle 中添加依赖: implementation com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:4.9.3WebSocket工具类实现 import okhttp3.*; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.Looper; import android.util.Log;import java.ut…...

认识vue2脚手架
1.认识脚手架结构 使用VSCode将vue项目打开: package.json:包的说明书(包的名字,包的版本,依赖哪些库)。该文件里有webpack的短命令: serve(启动内置服务器) build命令…...
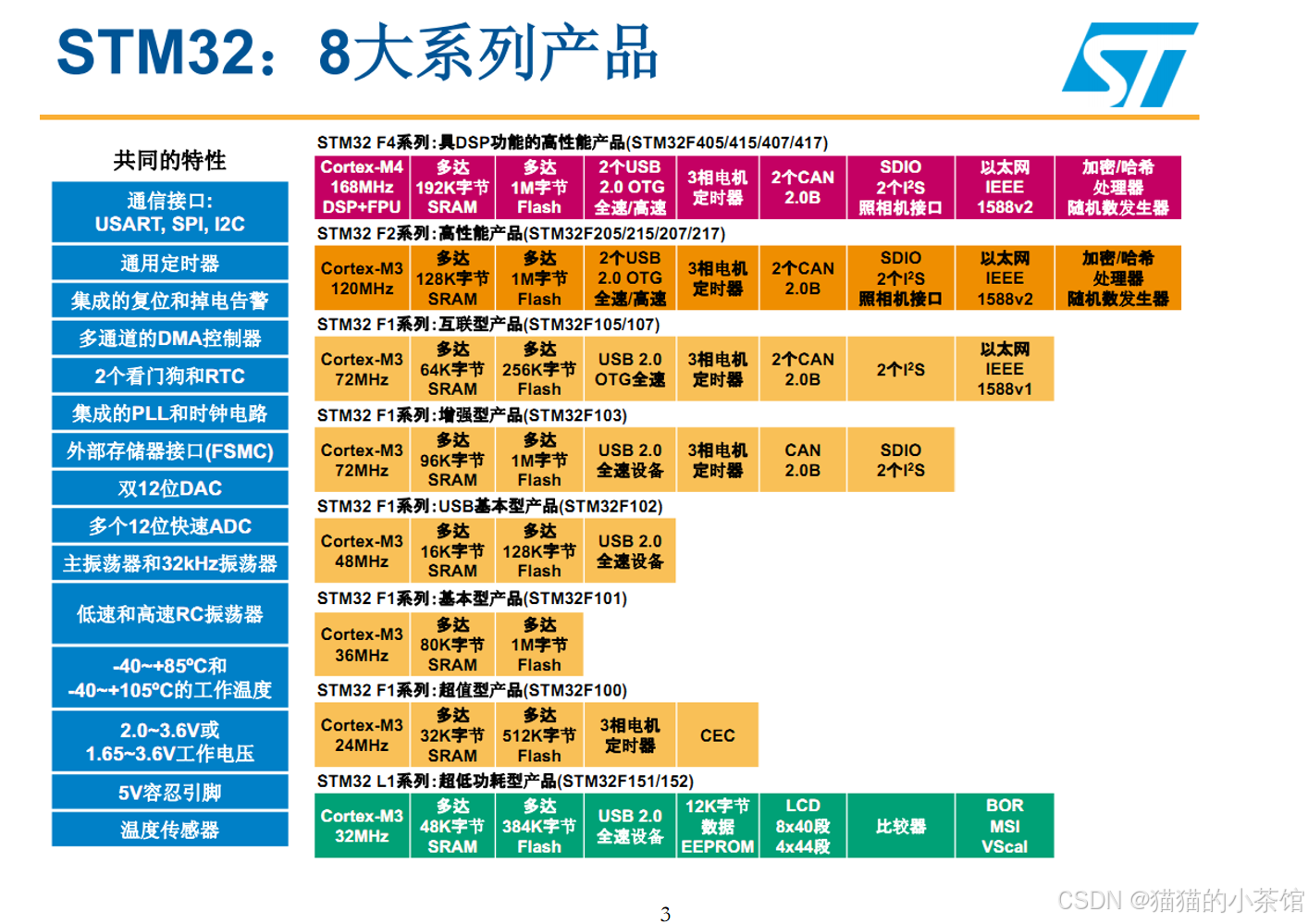
【STM32】STM32系列产品以及新手入门的STM32F103
📢 STM32F103xC/D/E 系列是一款高性能、低功耗的 32 位 MCU,适用于工业、汽车、消费电子等领域;基于 ARM Cortex-M3,主频最高 72MHz,支持 512KB Flash、64KB SRAM,适合复杂嵌入式应用,提供丰富的…...

基于距离变化能量开销动态调整的WSN低功耗拓扑控制开销算法matlab仿真
目录 1.程序功能描述 2.测试软件版本以及运行结果展示 3.核心程序 4.算法仿真参数 5.算法理论概述 6.参考文献 7.完整程序 1.程序功能描述 通过动态调整节点通信的能量开销,平衡网络负载,延长WSN生命周期。具体通过建立基于距离的能量消耗模型&am…...
最新SpringBoot+SpringCloud+Nacos微服务框架分享
文章目录 前言一、服务规划二、架构核心1.cloud的pom2.gateway的异常handler3.gateway的filter4、admin的pom5、admin的登录核心 三、code-helper分享总结 前言 最近有个活蛮赶的,根据Excel列的需求预估的工时直接打骨折,不要问我为什么,主要…...

C# SqlSugar:依赖注入与仓储模式实践
C# SqlSugar:依赖注入与仓储模式实践 在 C# 的应用开发中,数据库操作是必不可少的环节。为了让数据访问层更加简洁、高效且易于维护,许多开发者会选择成熟的 ORM(对象关系映射)框架,SqlSugar 就是其中备受…...

高防服务器能够抵御哪些网络攻击呢?
高防服务器作为一种有着高度防御能力的服务器,可以帮助网站应对分布式拒绝服务攻击,有效识别和清理一些恶意的网络流量,为用户提供安全且稳定的网络环境,那么,高防服务器一般都可以抵御哪些网络攻击呢?下面…...
-HIve数据分析)
大数据学习(132)-HIve数据分析
🍋🍋大数据学习🍋🍋 🔥系列专栏: 👑哲学语录: 用力所能及,改变世界。 💖如果觉得博主的文章还不错的话,请点赞👍收藏⭐️留言Ǵ…...

稳定币的深度剖析与展望
一、引言 在当今数字化浪潮席卷全球的时代,加密货币作为一种新兴的金融现象,正以前所未有的速度改变着我们对传统货币和金融体系的认知。然而,加密货币市场的高度波动性却成为了其广泛应用和普及的一大障碍。在这样的背景下,稳定…...

rnn判断string中第一次出现a的下标
# coding:utf8 import torch import torch.nn as nn import numpy as np import random import json""" 基于pytorch的网络编写 实现一个RNN网络完成多分类任务 判断字符 a 第一次出现在字符串中的位置 """class TorchModel(nn.Module):def __in…...

【Java学习笔记】BigInteger 和 BigDecimal 类
BigInteger 和 BigDecimal 类 二者共有的常见方法 方法功能add加subtract减multiply乘divide除 注意点:传参类型必须是类对象 一、BigInteger 1. 作用:适合保存比较大的整型数 2. 使用说明 创建BigInteger对象 传入字符串 3. 代码示例 import j…...

蓝桥杯 冶炼金属
原题目链接 🔧 冶炼金属转换率推测题解 📜 原题描述 小蓝有一个神奇的炉子用于将普通金属 O O O 冶炼成为一种特殊金属 X X X。这个炉子有一个属性叫转换率 V V V,是一个正整数,表示每 V V V 个普通金属 O O O 可以冶炼出 …...

基于Java Swing的电子通讯录设计与实现:附系统托盘功能代码详解
JAVASQL电子通讯录带系统托盘 一、系统概述 本电子通讯录系统采用Java Swing开发桌面应用,结合SQLite数据库实现联系人管理功能,并集成系统托盘功能提升用户体验。系统支持联系人的增删改查、分组管理、搜索过滤等功能,同时可以最小化到系统…...
