理解Android中不同的Context
作者:两日的blog
Context是什么,有什么用
在Android开发中,Context是一个抽象类,它是Android应用程序环境的一部分。它提供了访问应用程序资源和执行各种操作的接口。可以说,Context是Android应用程序与系统环境进行交互的桥梁。
Context的作用包括:
- 访问应用程序资源:通过
Context,可以获取应用程序的资源,如字符串、布局文件、图像等。这些资源可以在应用程序的各个组件中使用,例如Activity、Service、BroadcastReceiver等。 - 启动组件:通过
Context,可以启动其他组件,如启动Activity、启动Service、发送广播等。它提供了访问系统服务的能力,如启动其他应用程序、发送系统广播等。 - 获取应用程序的上下文:通过
Context,可以获取应用程序的上下文,如获取ApplicationContext,用于在整个应用程序中共享数据或执行全局操作。 - 访问系统服务:通过
Context,可以访问各种系统服务,如获取系统级的服务(如传感器服务、位置服务)、访问设备功能(如摄像头、存储器)、执行网络操作等。 - 访问应用程序的文件:通过
Context对象,可以获取应用程序的文件目录,创建、读取、写入和删除文件等操作。 - 处理资源生命周期:通过
Context,可以管理应用程序资源的生命周期,如创建、销毁对象、注册和注销监听器等。它提供了一种机制,确保资源的正确使用和释放,避免内存泄漏等问题。
public abstract AssetManager getAssets();/*** Returns a Resources instance for the application's package.* <p>* <strong>Note:</strong> Implementations of this method should return* a Resources instance that is consistent with the AssetManager instance* returned by {@link #getAssets()}. For example, they should share the* same {@link Configuration} object.** @return a Resources instance for the application's package* @see #getAssets()*/
public abstract Resources getResources();/** Return PackageManager instance to find global package information. */
public abstract PackageManager getPackageManager();/** Return a ContentResolver instance for your application's package. */
public abstract ContentResolver getContentResolver();/*** Return the Looper for the main thread of the current process. This is* the thread used to dispatch calls to application components (activities,* services, etc).* <p>* By definition, this method returns the same result as would be obtained* by calling {@link Looper#getMainLooper() Looper.getMainLooper()}.* </p>** @return The main looper.*/
public abstract Looper getMainLooper();/*** Return an {@link Executor} that will run enqueued tasks on the main* thread associated with this context. This is the thread used to dispatch* calls to application components (activities, services, etc).*/
public Executor getMainExecutor() {// This is pretty inefficient, which is why ContextImpl overrides itreturn new HandlerExecutor(new Handler(getMainLooper()));
}public abstract Context getApplicationContext();public final CharSequence getText(@StringRes int resId) {return getResources().getText(resId);
}/*** Returns a localized string from the application's package's* default string table.** @param resId Resource id for the string* @return The string data associated with the resource, stripped of styled* text information.*/
@NonNull
public final String getString(@StringRes int resId) {return getResources().getString(resId);
}/*** Returns a localized formatted string from the application's package's* default string table, substituting the format arguments as defined in* {@link java.util.Formatter} and {@link java.lang.String#format}.** @param resId Resource id for the format string* @param formatArgs The format arguments that will be used for* substitution.* @return The string data associated with the resource, formatted and* stripped of styled text information.*/
@NonNull
public final String getString(@StringRes int resId, Object... formatArgs) {return getResources().getString(resId, formatArgs);
}/*** Returns a color associated with a particular resource ID and styled for* the current theme.** @param id The desired resource identifier, as generated by the aapt* tool. This integer encodes the package, type, and resource* entry. The value 0 is an invalid identifier.* @return A single color value in the form 0xAARRGGBB.* @throws android.content.res.Resources.NotFoundException if the given ID* does not exist.*/
@ColorInt
public final int getColor(@ColorRes int id) {return getResources().getColor(id, getTheme());
}/*** Returns a drawable object associated with a particular resource ID and* styled for the current theme.** @param id The desired resource identifier, as generated by the aapt* tool. This integer encodes the package, type, and resource* entry. The value 0 is an invalid identifier.* @return An object that can be used to draw this resource.* @throws android.content.res.Resources.NotFoundException if the given ID* does not exist.*/
@Nullable
public final Drawable getDrawable(@DrawableRes int id) {return getResources().getDrawable(id, getTheme());
}/*** Returns a color state list associated with a particular resource ID and* styled for the current theme.** @param id The desired resource identifier, as generated by the aapt* tool. This integer encodes the package, type, and resource* entry. The value 0 is an invalid identifier.* @return A color state list.* @throws android.content.res.Resources.NotFoundException if the given ID* does not exist.*/
@NonNull
public final ColorStateList getColorStateList(@ColorRes int id) {return getResources().getColorStateList(id, getTheme());
}/*** Set the base theme for this context. Note that this should be called* before any views are instantiated in the Context (for example before* calling {@link android.app.Activity#setContentView} or* {@link android.view.LayoutInflater#inflate}).** @param resid The style resource describing the theme.*/
public abstract void setTheme(@StyleRes int resid);/** @hide Needed for some internal implementation... not public because* you can't assume this actually means anything. */
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public int getThemeResId() {return 0;
}/*** Return the Theme object associated with this Context.*/
@ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(deepExport = true)
public abstract Resources.Theme getTheme();/*** Retrieve styled attribute information in this Context's theme. See* {@link android.content.res.Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributes(int[])}* for more information.** @see android.content.res.Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributes(int[])*/
@NonNull
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(@NonNull @StyleableRes int[] attrs) {return getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs);
}/*** Retrieve styled attribute information in this Context's theme. See* {@link android.content.res.Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributes(int, int[])}* for more information.** @see android.content.res.Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributes(int, int[])*/
@NonNull
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(@StyleRes int resid,@NonNull @StyleableRes int[] attrs) throws Resources.NotFoundException {return getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(resid, attrs);
}/*** Retrieve styled attribute information in this Context's theme. See* {@link android.content.res.Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet, int[], int, int)}* for more information.** @see android.content.res.Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet, int[], int, int)*/
@NonNull
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(@Nullable AttributeSet set, @NonNull @StyleableRes int[] attrs) {return getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(set, attrs, 0, 0);
}/*** Retrieve styled attribute information in this Context's theme. See* {@link android.content.res.Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet, int[], int, int)}* for more information.** @see android.content.res.Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet, int[], int, int)*/
@NonNull
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(@Nullable AttributeSet set,@NonNull @StyleableRes int[] attrs, @AttrRes int defStyleAttr,@StyleRes int defStyleRes) {return getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(set, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
总之,Context在Android开发中具有重要的作用,它提供了访问应用程序资源、启动组件、访问系统服务以及处理资源生命周期的能力。开发者可以使用Context来实现各种应用程序功能和与系统环境的交互。
Context有哪些
Context 本身是一个抽象类,主要实现类为 ContextImpl,另外有子类 ContextWrapper 和 ContextThemeWrapper,另外还有其他由上述三个类引申出来的Context类,Application/Service/Activity,他们的继承关系如下:

ContextImpl/ContextWrapper/ContextThemeWrapper的区别
| ContextImpl | ContextWrapper | ContextThemeWrapper |
|---|---|---|
ContextImpl是Context的主要实现类,它提供了大部分Context的基本功能和行为。它是Android框架中真正的上下文实现类,用于处理应用程序的资源访问、组件启动、文件操作和系统服务等操作。 | ContextWrapper是一个包装类,用于对现有的Context对象进行包装或修改其功能。它是Context的一个间接子类,可以通过继承ContextWrapper类来扩展Context的功能,例如添加自定义的行为或修改Context的行为。 | ContextThemeWrapper:ContextThemeWrapper是Context的另一个包装类,它继承自ContextWrapper类。与ContextWrapper类似,ContextThemeWrapper也是用于包装现有的Context对象,但它还提供了自己的主题资源。通过ContextThemeWrapper,可以为特定的上下文设置不同的主题,以实现界面的样式和外观的变化。 |
ContextImpl
上文说到,Context本身是一个抽象类,主要的实现类就是ContextImpl,即Context的那些功能都是在ContexImpl中实现的,即ContextImpl实际承担着提供应用程序资源访问、组件启动和系统服务等功能的责任。
public class ContextImpl extends Context {private Resources mResources;private Theme mTheme;void setResources(Resources r) {if (r instanceof CompatResources) {((CompatResources) r).setContext(this);}mResources = r;}@Overridepublic Resources getResources() {return mResources;}@Overridepublic void setTheme(int resId) {synchronized (mSync) {if (mThemeResource != resId) {mThemeResource = resId;initializeTheme();}}}public Resources.Theme getTheme() {synchronized (mSync) {if (mTheme != null) {return mTheme;}mThemeResource = Resources.selectDefaultTheme(mThemeResource,getOuterContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion);initializeTheme();return mTheme;}}private void initializeTheme() {if (mTheme == null) {mTheme = mResources.newTheme();}mTheme.applyStyle(mThemeResource, true);}// 其他方法的实现省略...
}
在ContextImpl,我们重点关注一下Resource及Theme的相关实现,ContextImpl中提供了getResources/setResources方法,用于获取Resources以及设置Resources,以提供资源的访问。
在getTheme/setTheme用于获取Theme以及设置Theme,以提供对主题的访问.
重点看一下getTheme()方法,该方法,会首先获取mThemeResource,这里直接选择的系统默认主题,系统会根据不同的sdk版本选择不同的默认主题。
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static int selectDefaultTheme(int curTheme, int targetSdkVersion) {return selectSystemTheme(curTheme, targetSdkVersion,com.android.internal.R.style.Theme,com.android.internal.R.style.Theme_Holo,com.android.internal.R.style.Theme_DeviceDefault,com.android.internal.R.style.Theme_DeviceDefault_Light_DarkActionBar);
}/** @hide */
public static int selectSystemTheme(int curTheme, int targetSdkVersion, int orig, int holo,int dark, int deviceDefault) {if (curTheme != ID_NULL) {return curTheme;}if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {return orig;}if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {return holo;}if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {return dark;}return deviceDefault;
}
通过ContextImpl的实例,应用程序可以获取到Resources对象和Theme对象,从而实现对资源和主题的访问和处理。需要注意的是,这是一个简化的,实际的ContextImpl源码非常复杂,还涉及到处理上下文的生命周期、系统服务的获取等方面的逻辑。
ContextWrapper
ContextWrapper是一个包装类,内部包含一个mBase成员变量,所有的实现都是调用mBase的方法。
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {@UnsupportedAppUsageContext mBase;public ContextWrapper(Context base) {mBase = base;}@Overridepublic void setTheme(int resid) {mBase.setTheme(resid);}/** @hide */@Override@UnsupportedAppUsagepublic int getThemeResId() {return mBase.getThemeResId();}@Overridepublic Resources.Theme getTheme() {return mBase.getTheme();}@Overridepublic ClassLoader getClassLoader() {return mBase.getClassLoader();}@Overridepublic String getPackageName() {return mBase.getPackageName();}}
ContextThemeWrapper
ContextThemeWrapper继承自ContextWrapper,从名字中可以看出,该类主要是跟主题相关的包装类:
public class ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper {...@Overridepublic Resources getResources() {return getResourcesInternal();}private Resources getResourcesInternal() {if (mResources == null) {if (mOverrideConfiguration == null) {mResources = super.getResources();} else {final Context resContext = createConfigurationContext(mOverrideConfiguration);mResources = resContext.getResources();}}return mResources;}@Overridepublic void setTheme(int resid) {if (mThemeResource != resid) {mThemeResource = resid;initializeTheme();}}@Overridepublic Resources.Theme getTheme() {if (mTheme != null) {return mTheme;}mThemeResource = Resources.selectDefaultTheme(mThemeResource,getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion);initializeTheme();return mTheme;}@UnsupportedAppUsageprivate void initializeTheme() {final boolean first = mTheme == null;if (first) {mTheme = getResources().newTheme();final Resources.Theme theme = getBaseContext().getTheme();if (theme != null) {mTheme.setTo(theme);}}onApplyThemeResource(mTheme, mThemeResource, first);}...}
和ContextImpl相比较,ContextThemeWrapper中获取资源以及主题的代码有所不同,多了一个Configuration,其他行为大致一致。
另外在AppCompat中,默认的主题为Theme_AppCompat_Light,
package androidx.appcompat.view;public class ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper {... @Overridepublic Resources.Theme getTheme() {if (mTheme != null) {return mTheme;}if (mThemeResource == 0) {mThemeResource = R.style.Theme_AppCompat_Light;}initializeTheme();return mTheme;}
}
App中不同Context对象的Theme
我们在开发中,经常会用到各种Context,常用的有activity/application/applicationContext/baseContext,为了测试不同Context中Theme对象,我们编写如下代码:
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)printLog("baseContext is ${baseContext.themeResId} baseContext is $baseContext")printLog("application is ${application.themeResId} application is $application")printLog("applicationContext is ${applicationContext.themeResId} applicationContext is $applicationContext")printLog("activity is ${this.themeResId}")}private fun printLog(msg: String) {println("MainActivity themeResId in $msg")}
}
我们分别获取每个Context对应的themeResId,即每个Context中Theme对应的resId:

对代码运行结果我们有如下结论:
getApplication和getApplicationContext得到的是同一个Application实例对象;Application对象中的themeResId为0 ,Application其实也有主题的应用,毕竟主题样式都是针对UI元素的;- **
Activity中的主题和getBaseContext**中的主题是不一样的,具体对应什么主题下文将进行探究 getBaseContext中得到的是ContextThemeWrapper,这点让我有点意外,之前的理解都是Activity启动时,会新建一个ContextImpl对象,在attachBaseContext中赋予Activity中的mBase,于是仔细研究一下发现,其实是AppCompatActivity做了替换:
//androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
// AppCompatActivity重写了Activity中的attachBaseContext方法
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {super.attachBaseContext(getDelegate().attachBaseContext2(newBase));
}
我们看一下代理类AppCompatDelegateImpl中attachBaseContext2的实现:
//androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatDelegateImpl@NonNull
@Override
@CallSuper
public Context attachBaseContext2(@NonNull final Context baseContext) {mBaseContextAttached = true;final int modeToApply = mapNightMode(baseContext, calculateNightMode());// If the base context is a ContextThemeWrapper (thus not an Application context)// and nobody's touched its Resources yet, we can shortcut and directly apply our// override configuration.if (sCanApplyOverrideConfiguration&& baseContext instanceof android.view.ContextThemeWrapper) {final Configuration config = createOverrideConfigurationForDayNight(baseContext, modeToApply, null);ContextThemeWrapperCompatApi17Impl.applyOverrideConfiguration((android.view.ContextThemeWrapper) baseContext, config);return baseContext;}// Again, but using the AppCompat version of ContextThemeWrapper.if (baseContext instanceof ContextThemeWrapper) {final Configuration config = createOverrideConfigurationForDayNight(baseContext, modeToApply, null);((ContextThemeWrapper) baseContext).applyOverrideConfiguration(config);return baseContext;}// We can't apply the configuration directly to the existing base context, so we need to// wrap it. We can't create a new configuration context since the app may rely on method// overrides or a specific theme -- neither of which are preserved when creating a// configuration context. Instead, we'll make a best-effort at wrapping the context and// rebasing the original theme.if (!sCanReturnDifferentContext) {return super.attachBaseContext2(baseContext);}Configuration configOverlay = null;final Configuration config = createOverrideConfigurationForDayNight(baseContext, modeToApply, configOverlay);//重点1:新建ContextThemeWrapper对象将传入的baseContext赋值给ContextWrapper中的mBase,// 并且ContextThemeWrapper中的主题为Theme_AppCompat_Empty// Next, we'll wrap the base context to ensure any method overrides or themes are left// intact. Since ThemeOverlay.AppCompat theme is empty, we'll get the base context's theme.final ContextThemeWrapper wrappedContext = new ContextThemeWrapper(baseContext,R.style.Theme_AppCompat_Empty);wrappedContext.applyOverrideConfiguration(config);// Check whether the base context has an explicit theme or is able to obtain one// from its outer context. If it throws an NPE because we're at an invalid point in app// initialization, we don't need to worry about rebasing under the new configuration.boolean needsThemeRebase;try {needsThemeRebase = baseContext.getTheme() != null;} catch (NullPointerException e) {needsThemeRebase = false;}if (needsThemeRebase) {// Attempt to rebase the old theme within the new configuration. This will only// work on SDK 23 and up, but it's unlikely that we're keeping the base theme// anyway so maybe nobody will notice. Note that calling getTheme() will clone// the base context's theme into the wrapped context's theme.ResourcesCompat.ThemeCompat.rebase(wrappedContext.getTheme());}return super.attachBaseContext2(wrappedContext);
}//androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatDelegate
@NonNull
@CallSuper
public Context attachBaseContext2(@NonNull Context context) {
// 重点2,将上一步包装了baseContext的ContextThemeWrapper对象进一步赋值给Activity的mBaseattachBaseContext(context);return context;
}
最终AppCompatActivity中的mBase是包装了ContextImpl的ContextThemeWrapper对象,并且其主题为Theme_AppCompat_Empty
关于第三点,getBaseActivity和Activity中的主题到底是哪一个,我们可以根据resId和resources索引表resource.arsc(直接将apk文件拖到AndroidStudio中就可以看到该文件)找到:
2131755410和2131755474对应16进制为0x7f100192与0x7f1001d2


可以看到,getBaseActivity和Activity中的主题分别对应Theme_AppCompat_Empty 与我们在AndroidManifest.xml中设置的应用主题Theme.ThemeTest
总结
Context是Android应用程序与系统环境进行交互的桥梁,主要实现类是ContextImpl, 可以访问应用程序资源/启动组件/访问系统服务/访问应用程序的文件等,而Context可以分为三种:ContextImpl/ContextWrapper/ContextThemeWrapper,不同ContextImpl 是Context的主要实现类,ContextWrapper是简单的包装类,所有的实现都由其内部的mBase成员完成,ContextThemeWrapper继承自ContextWrapper ,它的主要继承者是Activity,和其他两个Context不同的是,他内部对应用资源和主题有不同的行为,在应用中使用跟主题相关的Context时,最好使用activity,而不要使用getBaseContext或者applictaion.
Android 学习笔录
Android 性能优化篇:https://qr18.cn/FVlo89
Android 车载篇:https://qr18.cn/F05ZCM
Android 逆向安全学习笔记:https://qr18.cn/CQ5TcL
Android Framework底层原理篇:https://qr18.cn/AQpN4J
Android 音视频篇:https://qr18.cn/Ei3VPD
Jetpack全家桶篇(内含Compose):https://qr18.cn/A0gajp
Kotlin 篇:https://qr18.cn/CdjtAF
Gradle 篇:https://qr18.cn/DzrmMB
OkHttp 源码解析笔记:https://qr18.cn/Cw0pBD
Flutter 篇:https://qr18.cn/DIvKma
Android 八大知识体:https://qr18.cn/CyxarU
Android 核心笔记:https://qr21.cn/CaZQLo
Android 往年面试题锦:https://qr18.cn/CKV8OZ
2023年最新Android 面试题集:https://qr18.cn/CgxrRy
Android 车载开发岗位面试习题:https://qr18.cn/FTlyCJ
音视频面试题锦:https://qr18.cn/AcV6Ap
相关文章:

理解Android中不同的Context
作者:两日的blog Context是什么,有什么用 在Android开发中,Context是一个抽象类,它是Android应用程序环境的一部分。它提供了访问应用程序资源和执行各种操作的接口。可以说,Context是Android应用程序与系统环境进行交…...

linux判断端口是否占用(好用)
netstat 一般的话使用 netstat -tunlp | grep xxx参数作用-t指明显示TCP端口-u指明显示UDP端口-l仅显示监听套接字(所谓套接字就是使应用程序能够读写与收发通讯协议(protocol)与资料的程序)-p显示进程标识符和程序名称,每一个套接字/端口都属于一个程序。-n不进行…...

springboot 自定义注解 ,实现接口限流(计数器限流)【强行喂饭版】
思路:通过AOP拦截注解标记的方法,在Redis中维护一个计数器来记录接口访问的频率, 并根据限流策略来判断是否允许继续处理请求。 另一篇:springboot 自定义注解 ,aop切面Around; 为接口实现日志插入【强行喂…...

istio安装部署总结
istio安装部署总结 大纲 istio基础概念版本选择安装istio核心主件卸载istiokiali安装 istio基础概念 https://istio.io/latest/zh/docs/ 中文文档 istio是一个服务治理平台,治理服务间的访问,(例如流量控制,安全策略…...

Linux操作系统~必考面试题⑨
1、rpm 命令 Linux rpm 命令用于管理套件。 rpm(redhat package manager) 原本是 Red Hat Linux 发行版专门用来管理Linux 各项套件的程序,由于它遵循 GPL 规则且功能强大方便,因而广受欢迎。逐渐受到其他发行版的采用。 RPM 套件管理方式的出现&…...
国标GB28181协议视频平台EasyCVR修改录像计划等待时间较长的原因排查与解决
音视频流媒体视频平台EasyCVR拓展性强,视频能力丰富,具体可实现视频监控直播、视频轮播、视频录像、云存储、回放与检索、智能告警、服务器集群、语音对讲、云台控制、电子地图、H.265自动转码H.264、平台级联等。为了便于用户二次开发、调用与集成&…...

线性代数(主题篇):第三章:向量组 、第四章:方程组
文章目录 第3章 n维向量1.概念(1)n维单位列向量 2.向量、向量组的的线性关系(线性相关性)(1)线性表示 :AXβ(2)线性相关、线性无关: AX0①线性相关②线性无关③线性相关性7大定理 3.极大线性无关组、等价向量组、向量组的秩1.极大线性无关组2.等价向量组…...

大数据课程C4——ZooKeeper结构运行机制
文章作者邮箱:yugongshiyesina.cn 地址:广东惠州 ▲ 本章节目的 ⚪ 了解Zookeeper的特点和节点信息; ⚪ 掌握Zookeeper的完全分布式安装 ⚪ 掌握Zookeeper的选举机制、ZAB协议、AVRO; 一、Zookeeper-简介 1. 特点…...

解决伪类元素‘after‘或者‘before‘遮挡父元素,导致鼠标移入或点击等事件不生效的问题
第一种调整css的index值 如果对显示没有影响的话,可以这么做 第二种设置css属性:pointer-event:none 原理是: 对一个元素设置 pointer-events: none,能让浏览器在处理鼠标操作时,忽视掉这个元素的存在&a…...

电动汽车市场的减速,正在让小鹏汽车付出代价
来源:猛兽财经 作者:猛兽财经 总结: (1)由于价格压力上升、竞争加剧和需求减弱,小鹏汽车的交付量出现了明显下滑,6月份的交付量已经同比下降了43%。 (2)小鹏汽车对2023年…...

Yarn上Streaming流自动调节资源设计
Streaming流自动调节资源 自动资源调节简单来说就是根据数据的输入速率和数据的消费速率来判断是否应该调节资源。如果输入速率大于消费速率,并且在输入速率还在攀升,则将该Job停止并调高Job的资源等级然后重启。如果消费速率大于输入速率,并…...

微信小程序的个人博客--【小程序花园】
微信目录集链接在此: 详细解析黑马微信小程序视频–【思维导图知识范围】难度★✰✰✰✰ 不会导入/打开小程序的看这里:参考 让别人的小程序长成自己的样子-更换window上下颜色–【浅入深出系列001】 文章目录 本系列校训啥是个人博客项目里的理论知识…...

智慧园区楼宇合集 | 图扑数字孪生管控系统
智慧园区是指将物联网、大数据、人工智能等技术应用于传统建筑和基础设施,以实现对园区的全面监控、管理和服务的一种建筑形态。通过将园区内设备、设施和系统联网,实现数据的传输、共享和响应,提高园区的管理效率和运营效益,为居…...
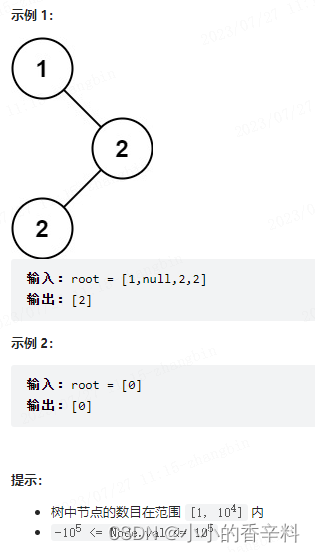
【代码随想录day21】二叉搜索树中的众数
题目 给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数(即,出现频率最高的元素)。 如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。 假定 BST 满足如下定义&am…...
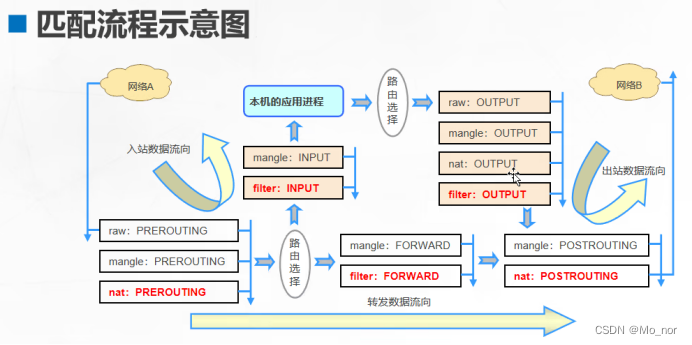
【防火墙】iptables防火墙(一)
防火墙具有隔离功能 主要部署在网络边缘或者主机边缘,防火墙的主要作用是决定哪些数据可以被外网访问,哪些数据可以进入内网访问 网络层(路由器):数据的转发 安全技术 1.入侵监测系统:在检测到威胁&…...

微信小程序之富文本特殊处理
文章目录 前言一、video的处理二、img的处理总结 前言 小程序中使用富文本编辑器,由于rich-text受限 部分富文本内容无法渲染或排版错乱。以img和video为例,处理起来让人头疼。网上各种长篇大论,实际上没有任何帮助。接下来我们就一起聊聊im…...
react-draft-wysiwyg富文本编辑器
在React项目中使用 yarn add react-draft-wysiwyg draft-js or npm i react-draft-wysiwyg draft-js推荐在项目中单独创建一个富文本编辑器组件 import { Editor } from "react-draft-wysiwyg"; import { EditorState, convertToRaw, ContentState } from draft-js…...

P5721 【深基4.例6】数字直角三角形
【深基4.例6】数字直角三角形 题目描述 给出 n n n,请输出一个直角边长度是 n n n 的数字直角三角形。所有数字都是 2 2 2 位组成的,如果没有 2 2 2 位则加上前导 0 0 0。 输入格式 输入一个正整数 n n n。 输出格式 输出如题目要求的数字直…...

【电子设计大赛】2023 年全国大学生电子设计竞赛 仪器和主要元器件清单
2023 年全国大学生电子设计竞赛仪器设备和主要元器件及器材清单 [本科组] 1. 仪器设备清单 直流稳压电源(具有恒流/恒压模式自动切换功能,0~30V/3A,双路) 数字示波器(100MHz, 双通道) 函数发…...
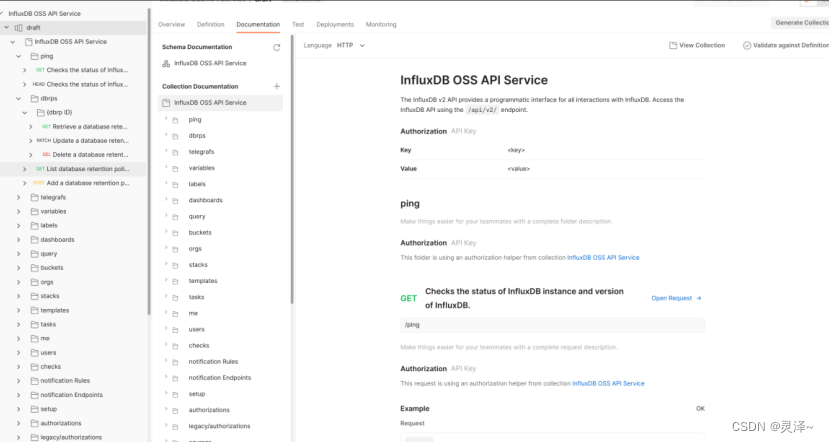
(八九)如何与InfluxDB交互InfluxDB HTTP API
以下内容来自 尚硅谷,写这一系列的文章,主要是为了方便后续自己的查看,不用带着个PDF找来找去的,太麻烦! 第 8 章 前言:如何与InfluxDB交互 1、InfluxDB启动后,会向外提供一套HTTP API。外部程…...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...
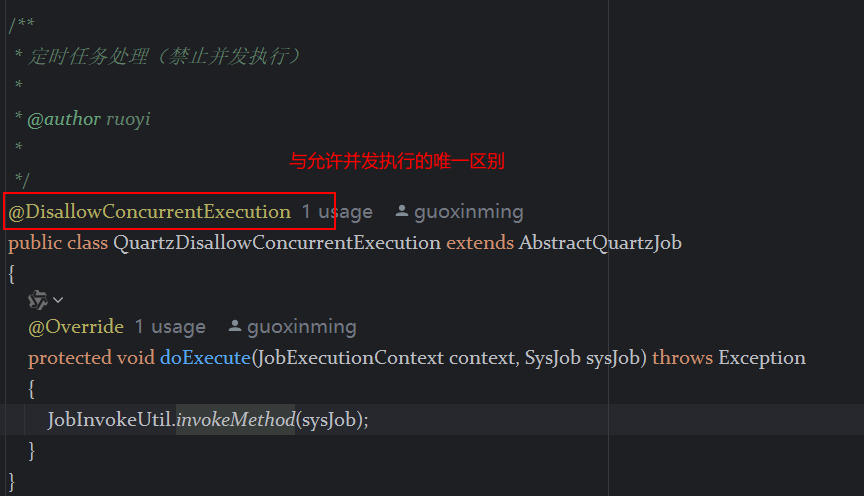
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...

MVC 数据库
MVC 数据库 引言 在软件开发领域,Model-View-Controller(MVC)是一种流行的软件架构模式,它将应用程序分为三个核心组件:模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)。这种模式有助于提高代码的可维护性和可扩展性。本文将深入探讨MVC架构与数据库之间的关系,以…...
【开发技术】.Net使用FFmpeg视频特定帧上绘制内容
目录 一、目的 二、解决方案 2.1 什么是FFmpeg 2.2 FFmpeg主要功能 2.3 使用Xabe.FFmpeg调用FFmpeg功能 2.4 使用 FFmpeg 的 drawbox 滤镜来绘制 ROI 三、总结 一、目的 当前市场上有很多目标检测智能识别的相关算法,当前调用一个医疗行业的AI识别算法后返回…...
基于 TAPD 进行项目管理
起因 自己写了个小工具,仓库用的Github。之前在用markdown进行需求管理,现在随着功能的增加,感觉有点难以管理了,所以用TAPD这个工具进行需求、Bug管理。 操作流程 注册 TAPD,需要提供一个企业名新建一个项目&#…...

动态 Web 开发技术入门篇
一、HTTP 协议核心 1.1 HTTP 基础 协议全称 :HyperText Transfer Protocol(超文本传输协议) 默认端口 :HTTP 使用 80 端口,HTTPS 使用 443 端口。 请求方法 : GET :用于获取资源,…...

人工智能--安全大模型训练计划:基于Fine-tuning + LLM Agent
安全大模型训练计划:基于Fine-tuning LLM Agent 1. 构建高质量安全数据集 目标:为安全大模型创建高质量、去偏、符合伦理的训练数据集,涵盖安全相关任务(如有害内容检测、隐私保护、道德推理等)。 1.1 数据收集 描…...

苹果AI眼镜:从“工具”到“社交姿态”的范式革命——重新定义AI交互入口的未来机会
在2025年的AI硬件浪潮中,苹果AI眼镜(Apple Glasses)正在引发一场关于“人机交互形态”的深度思考。它并非简单地替代AirPods或Apple Watch,而是开辟了一个全新的、日常可接受的AI入口。其核心价值不在于功能的堆叠,而在于如何通过形态设计打破社交壁垒,成为用户“全天佩戴…...

前端中slice和splic的区别
1. slice slice 用于从数组中提取一部分元素,返回一个新的数组。 特点: 不修改原数组:slice 不会改变原数组,而是返回一个新的数组。提取数组的部分:slice 会根据指定的开始索引和结束索引提取数组的一部分。不包含…...

实战设计模式之模板方法模式
概述 模板方法模式定义了一个操作中的算法骨架,并将某些步骤延迟到子类中实现。模板方法使得子类可以在不改变算法结构的前提下,重新定义算法中的某些步骤。简单来说,就是在一个方法中定义了要执行的步骤顺序或算法框架,但允许子类…...
