Linux 终端操作命令(2)内部命令

Linux 终端操作命令
也称Shell命令,是用户与操作系统内核进行交互的命令解释器,它接收用户输入的命令并将其传递给操作系统进行执行,可分为内部命令和外部命令。内部命令是Shell程序的一部分,而外部命令是独立于Shell的可执行程序。
内部命令
内部命令,实际上是shell程序的一部分,由shell程序识别并在shell程序内部完成运行,通常在Linux系统加载运行时shell就被加载并驻留在系统内存中。内部命令是写在bash源码里面的,因为解析内部命令shell不需要创建子进程,其执行速度比外部命令快。比如:alias, break, cd, echo, exit, pwd 等。
外部命令
外部命令是bash shell之外的程序,也并不是shell的一部分。外部命令位于/bin,/sbin, /usr/bin 或 /usr/sbin 等系统目录中。外部命令是Linux系统中的实用程序部分,因为实用程序的功能通常都比较强大,所以其包含的程序量也会很大,在系统加载时并不随系统一起被加载到内存中,而是在需要时才将其调用内存。通常外部命令的实体并不包含在shell中,但是其命令执行过程是由shell程序控制的。比如: awk, grep, ping,tar, vi 等。 除Linux系统自带的外部命令,通常需要安装对应的程序包才能使用,内部命令之外的所有可执行程序都可以被认作为外部命令。
内外部命令区别
内部命令在系统启动时就调入内存,是常驻内存的,所以执行效率高。
外部命令是系统的软件功能,用户需要时才从硬盘中读入内存,执行速度比内部命令慢。
内部命令列表
help命令可以列出所有内部命令:
hann@HannYang:~$ help
GNU bash, version 5.0.17(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
These shell commands are defined internally. Type `help' to see this list.
Type `help name' to find out more about the function `name'.
Use `info bash' to find out more about the shell in general.
Use `man -k' or `info' to find out more about commands not in this list.
A star (*) next to a name means that the command is disabled.
job_spec [&] history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or history -anrw [filename]>
(( expression )) if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif COMMANDS; then COMMAN>
. filename [arguments] jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs -x command [args]
: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigspec] pid | jobspec .>
[ arg... ] let arg [arg ...]
[[ expression ]] local [option] name[=value] ...
alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ] logout [n]
bg [job_spec ...] mapfile [-d delim] [-n count] [-O origin] [-s count] [-t>
bind [-lpsvPSVX] [-m keymap] [-f filename] [-q name] [-u > popd [-n] [+N | -N]
break [n] printf [-v var] format [arguments]
builtin [shell-builtin [arg ...]] pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir]
caller [expr] pwd [-LP]
case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...) COMMANDS ;;]... esa> read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [-i text] [-n nchars] >
cd [-L|[-P [-e]] [-@]] [dir] readarray [-d delim] [-n count] [-O origin] [-s count] [>
command [-pVv] command [arg ...] readonly [-aAf] [name[=value] ...] or readonly -p
compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] [-A action] [-G globp> return [n]
complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DEI] [-o option] [-A act> select NAME [in WORDS ... ;] do COMMANDS; done
compopt [-o|+o option] [-DEI] [name ...] set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option-name] [--] [arg ...]
continue [n] shift [n]
coproc [NAME] command [redirections] shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname ...]
declare [-aAfFgilnrtux] [-p] [name[=value] ...] source filename [arguments]
dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N] suspend [-f]
disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec ... | pid ...] test [expr]
echo [-neE] [arg ...] time [-p] pipeline
enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [name ...] times
eval [arg ...] trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec ...]
exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [arguments ...]] [redirecti> true
exit [n] type [-afptP] name [name ...]
export [-fn] [name[=value] ...] or export -p typeset [-aAfFgilnrtux] [-p] name[=value] ...
false ulimit [-SHabcdefiklmnpqrstuvxPT] [limit]
fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] or fc -s [pat=rep] [c> umask [-p] [-S] [mode]
fg [job_spec] unalias [-a] name [name ...]
for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMANDS; done unset [-f] [-v] [-n] [name ...]
for (( exp1; exp2; exp3 )); do COMMANDS; done until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
function name { COMMANDS ; } or name () { COMMANDS ; } variables - Names and meanings of some shell variables
getopts optstring name [arg] wait [-fn] [id ...]
hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name ...] while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
help [-dms] [pattern ...] { COMMANDS ; }
通过整理以上内容,得到 68 个命令、函数、变量以及控制指令:
| 1 | alias | alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ] |
| 2 | bg | bg [job_spec ...] |
| 3 | bind | bind [-lpsvPSVX] [-m keymap] [-f filename] [-q name] [-u > |
| 4 | break | break [n] |
| 5 | builtin | builtin [shell-builtin [arg ...]] |
| 6 | caller | caller [expr] |
| 7 | case | case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...) COMMANDS ;;]... esa> |
| 8 | cd | cd [-L|[-P [-e]] [-@]] [dir] |
| 9 | command | command [-pVv] command [arg ...] |
| 10 | compgen | compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] [-A action] [-G globp> |
| 11 | complete | complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DEI] [-o option] [-A act> |
| 12 | compopt | compopt [-o|+o option] [-DEI] [name ...] |
| 13 | continue | continue [n] |
| 14 | coproc | coproc [NAME] command [redirections] |
| 15 | declare | declare [-aAfFgilnrtux] [-p] [name[=value] ...] |
| 16 | dirs | dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N] |
| 17 | disown | disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec ... | pid ...] |
| 18 | echo | echo [-neE] [arg ...] |
| 19 | enable | enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [name ...] |
| 20 | eval | eval [arg ...] |
| 21 | exec | exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [arguments ...]] [redirecti> |
| 22 | exit | exit [n] |
| 23 | export | export [-fn] [name[=value] ...] or export -p |
| 24 | false | false |
| 25 | fc | fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] or fc -s [pat=rep] [c> |
| 26 | fg | fg [job_spec] |
| 27 | for | for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMANDS; done for (( exp1; exp2; exp3 )); do COMMANDS; done |
| 28 | function | function name { COMMANDS ; } or name () { COMMANDS ; } |
| 29 | getopts | getopts optstring name [arg] |
| 30 | hash | hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name ...] |
| 31 | help | help [-dms] [pattern ...] |
| 32 | history | history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or history -anrw [filename]> |
| 33 | if | if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif COMMANDS; then COMMAN> |
| 34 | jobs | jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs -x command [args] |
| 35 | kill | kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigspec] pid | jobspec .> |
| 36 | let | let arg [arg ...] |
| 37 | local | local [option] name[=value] ... |
| 38 | logout | logout [n] |
| 39 | mapfile | mapfile [-d delim] [-n count] [-O origin] [-s count] [-t> |
| 40 | popd | popd [-n] [+N | -N] |
| 41 | printf | printf [-v var] format [arguments] |
| 42 | pushd | pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir] |
| 43 | pwd | pwd [-LP] |
| 44 | read | read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [-i text] [-n nchars] > |
| 45 | readarray | readarray [-d delim] [-n count] [-O origin] [-s count] [> |
| 46 | readonly | readonly [-aAf] [name[=value] ...] or readonly -p |
| 47 | return | return [n] |
| 48 | select | select NAME [in WORDS ... ;] do COMMANDS; done |
| 49 | set | set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option-name] [--] [arg ...] |
| 50 | shift | shift [n] |
| 51 | shopt | shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname ...] |
| 52 | source | source filename [arguments] |
| 53 | suspend | suspend [-f] |
| 54 | test | test [expr] |
| 55 | time | time [-p] pipeline |
| 56 | times | times |
| 57 | trap | trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec ...] |
| 58 | true | true |
| 59 | type | type [-afptP] name [name ...] |
| 60 | typeset | typeset [-aAfFgilnrtux] [-p] name[=value] ... |
| 61 | ulimit | ulimit [-SHabcdefiklmnpqrstuvxPT] [limit] |
| 62 | umask | umask [-p] [-S] [mode] |
| 63 | unalias | unalias [-a] name [name ...] |
| 64 | unset | unset [-f] [-v] [-n] [name ...] |
| 65 | until | until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done |
| 66 | variables | variables - Names and meanings of some shell variables |
| 67 | wait | wait [-fn] [id ...] |
| 68 | while | while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done |
注意,有些命令格式比较长的都被截短了,如bind, case 等命令最后显示的是 > 字符。
要想个办法,做一个比较完整的内部命令列表:
1. 把上表第2列,写入一个文本文件,比如 list.txt
2. 用vi编写一段shell代码,如 lists.sh
hann@HannYang:~$ cat lists.sh
#!/bin/bash# 指定文本文件路径
file_path="list.txt"# 打开文本文件并遍历每一行
while IFS= read -r line; do# 获取帮助信息并输出help -s "$line" >> commands.txt
done < "$file_path"echo "done!"3. 执行,遍历list.txt列出完整命令格式,写入列表文件 commands.txt
hann@HannYang:~$ bash lists.sh
4. 列出所有命令格式
hann@HannYang:~$ cat -n commands.txt
1 alias: alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ]
2 bg: bg [job_spec ...]
3 bind: bind [-lpsvPSVX] [-m keymap] [-f filename] [-q name] [-u name] [-r keyseq] [-x keyseq:shell-command] [keyseq:readline-function or readline-command]
4 break: break [n]
5 builtin: builtin [shell-builtin [arg ...]]
6 caller: caller [expr]
7 case: case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...) COMMANDS ;;]... esac
8 cd: cd [-L|[-P [-e]] [-@]] [dir]
9 command: command [-pVv] command [arg ...]
10 compgen: compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] [-A action] [-G globpat] [-W wordlist] [-F function] [-C command] [-X filterpat] [-P prefix] [-S suffix] [word]
11 complete: complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DEI] [-o option] [-A action] [-G globpat] [-W wordlist] [-F function] [-C command] [-X filterpat] [-P prefix] [-S suffix] [name ...]
12 compopt: compopt [-o|+o option] [-DEI] [name ...]
13 continue: continue [n]
14 coproc: coproc [NAME] command [redirections]
15 declare: declare [-aAfFgilnrtux] [-p] [name[=value] ...]
16 dirs: dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N]
17 disown: disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec ... | pid ...]
18 echo: echo [-neE] [arg ...]
19 enable: enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [name ...]
20 eval: eval [arg ...]
21 exec: exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [arguments ...]] [redirection ...]
22 exit: exit [n]
23 export: export [-fn] [name[=value] ...] or export -p
24 false: false
25 fc: fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] or fc -s [pat=rep] [command]
26 fg: fg [job_spec]
27 for: for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMANDS; done
28 function: function name { COMMANDS ; } or name () { COMMANDS ; }
29 getopts: getopts optstring name [arg]
30 hash: hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name ...]
31 help: help [-dms] [pattern ...]
32 history: history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or history -anrw [filename] or history -ps arg [arg...]
33 if: if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; ]... [ else COMMANDS; ] fi
34 jobs: jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs -x command [args]
35 kill: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigspec] pid | jobspec ... or kill -l [sigspec]
36 let: let arg [arg ...]
37 local: local [option] name[=value] ...
38 logout: logout [n]
39 mapfile: mapfile [-d delim] [-n count] [-O origin] [-s count] [-t] [-u fd] [-C callback] [-c quantum] [array]
40 popd: popd [-n] [+N | -N]
41 printf: printf [-v var] format [arguments]
42 pushd: pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir]
43 pwd: pwd [-LP]
44 read: read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [-i text] [-n nchars] [-N nchars] [-p prompt] [-t timeout] [-u fd] [name ...]
45 readarray: readarray [-d delim] [-n count] [-O origin] [-s count] [-t] [-u fd] [-C callback] [-c quantum] [array]
46 readonly: readonly [-aAf] [name[=value] ...] or readonly -p
47 return: return [n]
48 select: select NAME [in WORDS ... ;] do COMMANDS; done
49 set: set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option-name] [--] [arg ...]
50 shift: shift [n]
51 shopt: shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname ...]
52 source: source filename [arguments]
53 suspend: suspend [-f]
54 test: test [expr]
55 time: time [-p] pipeline
56 times: times
57 trap: trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec ...]
58 true: true
59 type: type [-afptP] name [name ...]
60 typeset: typeset [-aAfFgilnrtux] [-p] name[=value] ...
61 ulimit: ulimit [-SHabcdefiklmnpqrstuvxPT] [limit]
62 umask: umask [-p] [-S] [mode]
63 unalias: unalias [-a] name [name ...]
64 unset: unset [-f] [-v] [-n] [name ...]
65 until: until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
66 variables: variables - Names and meanings of some shell variables
67 wait: wait [-fn] [id ...]
68 while: while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
同样,代码中help的参数换成-d 就能得到命令的功能简介。
hann@HannYang:~$ cat lists.sh
#!/bin/bash# 指定文本文件路径
file_path="list.txt"rm commands.txt# 打开文本文件并遍历每一行
while IFS= read -r line; do# 获取帮助信息并输出help -d "$line" >> commands.txt
done < "$file_path"echo "done!"5. 列出所有命令简介
hann@HannYang:~$ cat -n commands.txt
1 alias - Define or display aliases.
2 bg - Move jobs to the background.
3 bind - Set Readline key bindings and variables.
4 break - Exit for, while, or until loops.
5 builtin - Execute shell builtins.
6 caller - Return the context of the current subroutine call.
7 case - Execute commands based on pattern matching.
8 cd - Change the shell working directory.
9 command - Execute a simple command or display information about commands.
10 compgen - Display possible completions depending on the options.
11 complete - Specify how arguments are to be completed by Readline.
12 compopt - Modify or display completion options.
13 continue - Resume for, while, or until loops.
14 coproc - Create a coprocess named NAME.
15 declare - Set variable values and attributes.
16 dirs - Display directory stack.
17 disown - Remove jobs from current shell.
18 echo - Write arguments to the standard output.
19 enable - Enable and disable shell builtins.
20 eval - Execute arguments as a shell command.
21 exec - Replace the shell with the given command.
22 exit - Exit the shell.
23 export - Set export attribute for shell variables.
24 false - Return an unsuccessful result.
25 fc - Display or execute commands from the history list.
26 fg - Move job to the foreground.
27 for - Execute commands for each member in a list.
28 function - Define shell function.
29 getopts - Parse option arguments.
30 hash - Remember or display program locations.
31 help - Display information about builtin commands.
32 history - Display or manipulate the history list.
33 if - Execute commands based on conditional.
34 jobs - Display status of jobs.
35 kill - Send a signal to a job.
36 let - Evaluate arithmetic expressions.
37 local - Define local variables.
38 logout - Exit a login shell.
39 mapfile - Read lines from the standard input into an indexed array variable.
40 popd - Remove directories from stack.
41 printf - Formats and prints ARGUMENTS under control of the FORMAT.
42 pushd - Add directories to stack.
43 pwd - Print the name of the current working directory.
44 read - Read a line from the standard input and split it into fields.
45 readarray - Read lines from a file into an array variable.
46 readonly - Mark shell variables as unchangeable.
47 return - Return from a shell function.
48 select - Select words from a list and execute commands.
49 set - Set or unset values of shell options and positional parameters.
50 shift - Shift positional parameters.
51 shopt - Set and unset shell options.
52 source - Execute commands from a file in the current shell.
53 suspend - Suspend shell execution.
54 test - Evaluate conditional expression.
55 time - Report time consumed by pipeline's execution.
56 times - Display process times.
57 trap - Trap signals and other events.
58 true - Return a successful result.
59 type - Display information about command type.
60 typeset - Set variable values and attributes.
61 ulimit - Modify shell resource limits.
62 umask - Display or set file mode mask.
63 unalias - Remove each NAME from the list of defined aliases.
64 unset - Unset values and attributes of shell variables and functions.
65 until - Execute commands as long as a test does not succeed.
66 variables - Common shell variable names and usage.
67 wait - Wait for job completion and return exit status.
68 while - Execute commands as long as a test succeeds.
简单翻译:
1 alias-定义或显示别名。
2 bg-将作业移到后台。
3 bind-设置Readline键绑定和变量。
4 break-退出循环、while或直到循环。
5 builtin-执行shell内建。
6 caller-返回当前子例程调用的上下文。
7 case-基于模式匹配执行命令。
8 cd-更改shell工作目录。
9 command-执行一个简单的命令或显示有关命令的信息。
10 compgen-根据选项显示可能的完成情况。
11 complete-指定Readline如何完成参数。
12 compopt-修改或显示完成选项。
13 continue-继续循环、while或直到循环。
14 coproc-创建一个名为NAME的协处理器。
15 declare-设置变量值和属性。
16 dirs-显示目录堆栈。
17 disown-从当前shell中删除作业。
18 echo-将参数写入标准输出。
19 enable-启用和禁用shell内置。
20 eval-将参数作为shell命令执行。
21 exec-用给定的命令替换shell。
22 exit-退出外壳。
23 export-为shell变量设置导出属性。
24 false-返回不成功的结果。
25 fc-显示或执行历史列表中的命令。
26 fg-将作业移到前台。
27 for-为列表中的每个成员执行命令。
28 function-定义外壳函数。
29 getopts-分析选项参数。
30 hash-记住或显示程序位置。
31 help-显示有关内置命令的信息。
32 history-显示或操作历史记录列表。
33 if-根据条件执行命令。
34 jobs-显示作业的状态。
35 kill-向工作发出信号。
36 let-评估算术表达式。
37 local-定义局部变量。
38 logout-退出登录shell。
39 mapfile-将标准输入中的行读取到索引数组变量中。
40 popd-从堆栈中删除目录。
41 printf-在FORMAT的控制下格式化和打印参数。
42 pushd-将目录添加到堆栈。
43 pwd-打印当前工作目录的名称。
44 read-从标准输入中读取一行,并将其拆分为字段。
45 readarray-将文件中的行读取到数组变量中。
46 readonly-将shell变量标记为不可更改。
47 return-从shell函数返回。
48 select-从列表中选择单词并执行命令。
49 set-设置或取消设置外壳选项和位置参数的值。
50 shift-移位位置参数。
51 shopt-设置和取消设置外壳选项。
52 source-从当前shell中的文件执行命令。
53 suspend-挂起shell执行。
54 test-评估条件表达式。
55 time-报告管道执行所消耗的时间。
56 times-显示处理时间。
57 trap-陷阱信号和其他事件。
58 true-返回成功的结果。
59 type-显示有关命令类型的信息。
60 typeset-设置变量值和属性。
61 ulimit-修改shell资源限制。
62 umask-显示或设置文件模式掩码。
63 unalias-从定义的别名列表中删除别名。
64 unset-取消设置shell变量和函数的值和属性。
65 until-只要测试不成功,就执行命令。
66 variables-常见的shell变量名称和用法。
67 wait-等待作业完成并返回退出状态。
68 while-循环结构,只要测试为真就执行命令。
完
相关文章:

Linux 终端操作命令(2)内部命令
Linux 终端操作命令 也称Shell命令,是用户与操作系统内核进行交互的命令解释器,它接收用户输入的命令并将其传递给操作系统进行执行,可分为内部命令和外部命令。内部命令是Shell程序的一部分,而外部命令是独立于Shell的可执行程序…...
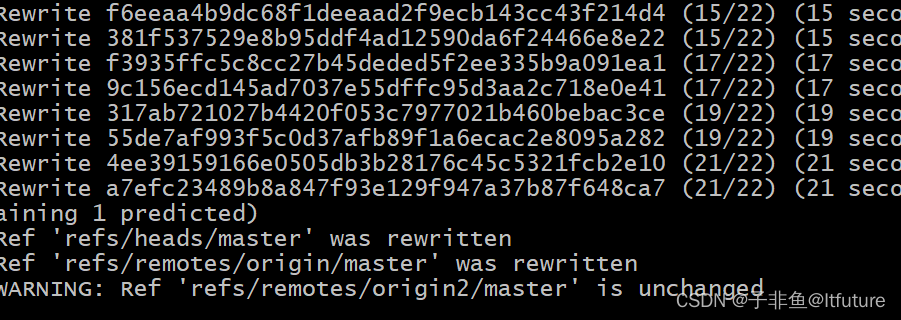
【Git】大大大问题之syntax error near unexpected token `(‘ 的错误解决办法
话不多说,先上图: 如图,因为在linux环境里,文件路径中含有括号(),因此报错! 解决办法 等同于 :linux下解决bash: syntax error near unexpected token (’ 的错误&am…...
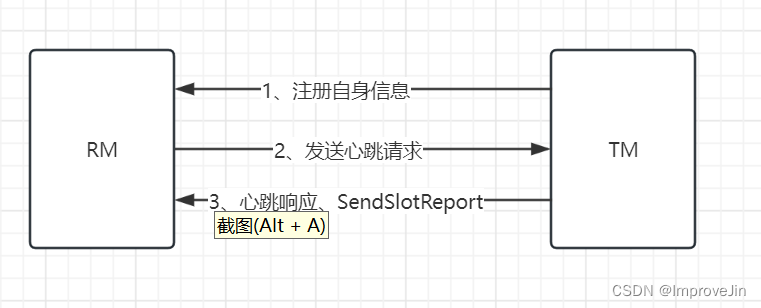
Flink源码之TaskManager启动流程
从启动命令flink-daemon.sh可以看出TaskManger入口类为org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskManagerRunner TaskManagerRunner::main TaskManagerRunner::runTaskManagerProcessSecurely TaskManagerRunner::runTaskManager //构造TaskManagerRunner并调用start()方法 …...

加入微软MCPP有什么优势?
目录 专业认可 技术支持 销售和市场推广支持 培训和认证 业务机会和合作伙伴网络...

leetcode做题笔记78子集
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。 解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。 思路一:回溯 void backtracking(int* nums, int numsSize, int** res, int* ret…...

Skywalking-9.6.0系列之本地源码编译并启动
Skywalking相信有很多人使用过,通过容器或者下载安装包进行安装的,今天从源代码角度,拉取、构建、启动。 官方文档步骤简洁明了,我这边会结合自己遇到的一些问题做出总结。 当前构建资源版本: MAC 10.15.7IDEA 2021.…...
proteus结合keil-arm编译器构建STM32单片机项目进行仿真
proteus是可以直接创建设计图和源码的,但是源码编译它需要借助keil-arm编译器,也就是我们安装keil-mdk之后自带的编译器。 下面给出一个完整的示例,主要是做一个LED灯闪烁的效果。 新建工程指定路径,Schematic,PCB layout都选择默…...

第五十三天
●剪辑——Pr 剪辑(Film editing),即将影片制作中所拍摄的大量素材,经过选择、取舍、分解与组接,最终完成一个连贯流畅、含义明确、主题鲜明并有艺术感染力的作品。 •线性编辑 将素材按时间顺序连接成新的连续画面的技术 •非线性编辑 …...

gorm基本操作
一、gorm安装 1.下载gorm go get -u gorm.io/gorm //gorm框架 go get -u gorm.io/driver/mysql //驱动2.mysql准备工作 mysql> create database godb; mysql> grant all on *.* to admin% identified by golang123!; mysql> flush privileges;3.导入gorm框架 impo…...
)
华为OD机试 - 排队游戏(Java JS Python)
题目描述 新来的老师给班里的同学排一个队。 每个学生有一个影力值。 一些学生是刺头,不会听老师的话,自己选位置,非刺头同学在剩下的位置按照能力值从小到大排。 对于非刺头同学,如果发现他前面有能力值比自己高的同学,他不满程度就增加,增加的数量等于前面能力值比…...

滚动条样式更改
::-webkit-scrollbar 滚动条整体部分,可以设置宽度啥的 ::-webkit-scrollbar-button 滚动条两端的按钮 ::-webkit-scrollbar-track 外层轨道 ::-webkit-scrollbar-track-piece 内层滚动槽 ::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb 滚动的滑块 ::-webkit-scrollbar…...
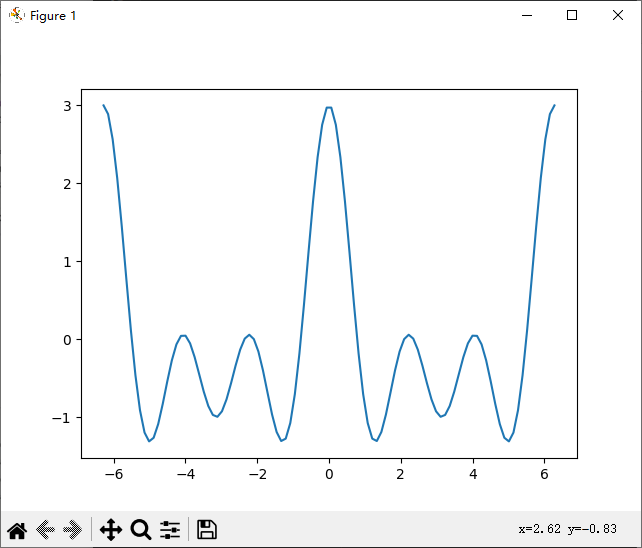
掌握Python的X篇_33_MATLAB的替代组合NumPy+SciPy+Matplotlib
numPy 通常与 SciPy( Scientific Python )和 Matplotlib (绘图库)一起使用,这种组合广泛用于替代 MatLab,是一个强大的科学计算环境,有助于我们通过 Python 学习数据科学或者机器学习。 文章目录 1. numpy1.1 numpy简介1.2 矩阵类型的nparra…...

Python解决-力扣002-两数相加
两数相加:链表表示的逆序整数求和 在这篇技术博客中,我们将讨论一个力扣(LeetCode)上的编程题目:两数相加。这个问题要求我们处理两个非空链表,它们表示两个非负整数。每个链表中的数字都是逆序存储的&…...
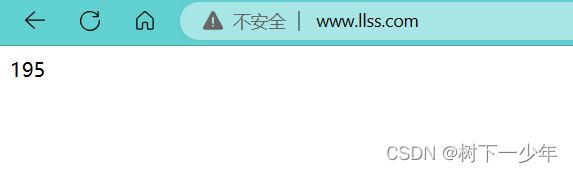
nginx基于源码安装的方式对静态页面、虚拟主机(IP、端口、域名)和日志文件进行配置
一.静态页面 1.更改页面内容 2.更改配置文件 3.测试 二.虚拟主机配置 1.基于IP (1)在html目录下新建目录存放测试文件 (2)修改nginx.conf文件,在htttp模块中配置两个server模块分别对应两个IP (3&am…...
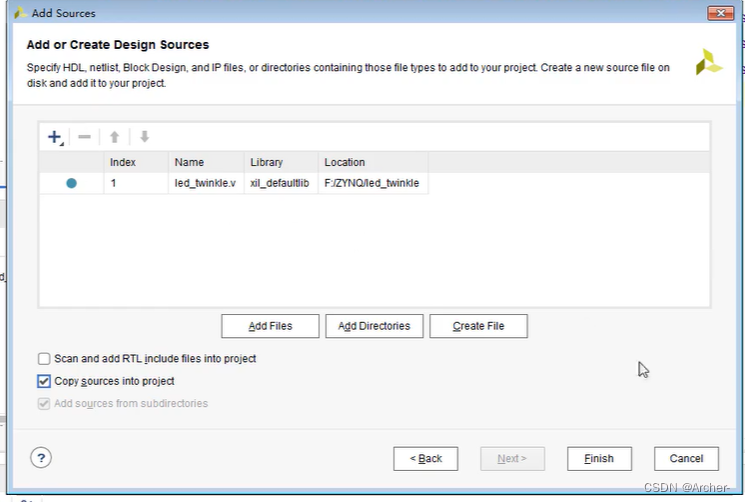
[FPAG开发]使用Vivado创建第一个程序
1 打开Vivado软件,新建项目 选择一个纯英文路径 选择合适的型号 产品型号ZYNQ-7010xc7z010clg400-1ZYNQ-7020xc7z010clg400-2 如果型号选错,可以单击这里重新选择 2 创建工程源文件 可以看到文件创建成功 双击文件打开,插入代码 modul…...
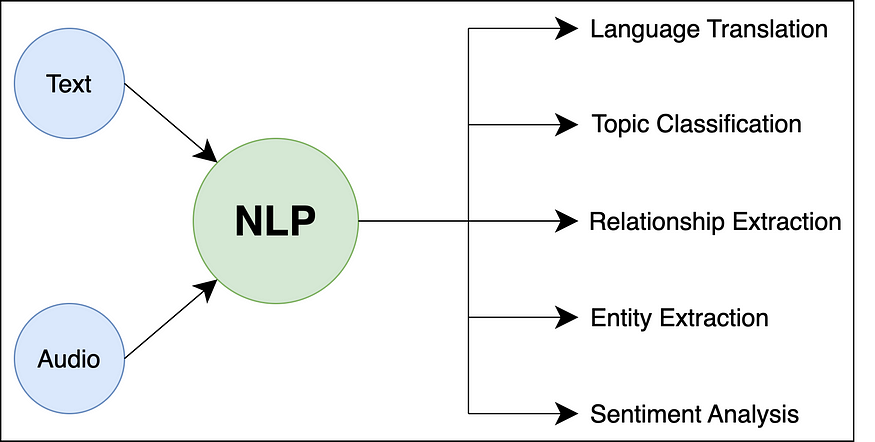
使用 Python 在 NLP 中进行文本预处理
一、说明 自然语言处理 (NLP) 是人工智能 (AI) 和计算语言学的一个子领域,专注于使计算机能够理解、解释和生成人类语言。它涉及计算机和自然语言之间的交互,允许机器以对人类有意义和有用的方式处理、分析…...
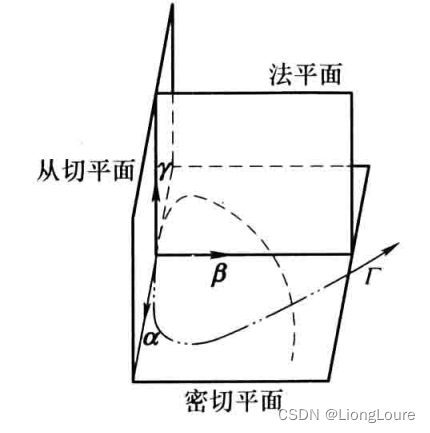
[足式机器人]Part3机构运动微分几何学分析与综合Ch03-1 空间约束曲线与约束曲面微分几何学——【读书笔记】
本文仅供学习使用 本文参考: 《机构运动微分几何学分析与综合》-王德伦、汪伟 《微分几何》吴大任 Ch01-4 平面运动微分几何学 3.1 空间曲线微分几何学概述3.1.1 矢量表示3.1.2 Frenet标架 连杆机构中的连杆与连架杆构成运动副,该运动副元素的特征点或特…...

pytest框架快速进阶篇-pytest前置和pytest后置,skipif跳过用例
一、Pytest的前置和后置方法 1.Pytest可以集成unittest实现前置和后置 importunittestimportpytestclassTestCase(unittest.TestCase):defsetUp(self)->None:print(unittest每个用例前置)deftearDown(self)->None:print(unittest每个用例后置)classmethoddefsetUpClass…...

Python 基础语法 | 常量表达式,变量,注释,输入输出
常量和表达式 我们可以把 Python 当成一个计算器,来进行一些算术运算 print(1 2 - 3) # 0 print(1 2 * 3) # 7 print(1 2 / 3) # 1.6666666666666665注意: print 是一个 Python 内置的 函数可以使用 - * / () 等运算符进行算术运算,先…...
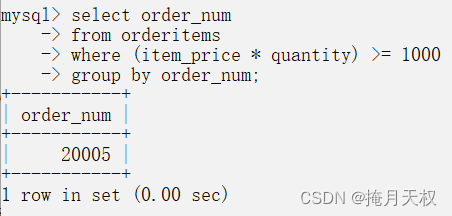
SQL | 分组数据
10-分组数据 两个新的select子句:group by子句和having子句。 10.1-数据分组 上面我们学到了,使用SQL中的聚集函数可以汇总数据,这样,我们就能够对行进行计数,计算和,计算平均数。 目前为止,…...

ssc377d修改flash分区大小
1、flash的分区默认分配16M、 / # df -h Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/root 1.9M 1.9M 0 100% / /dev/mtdblock4 3.0M...
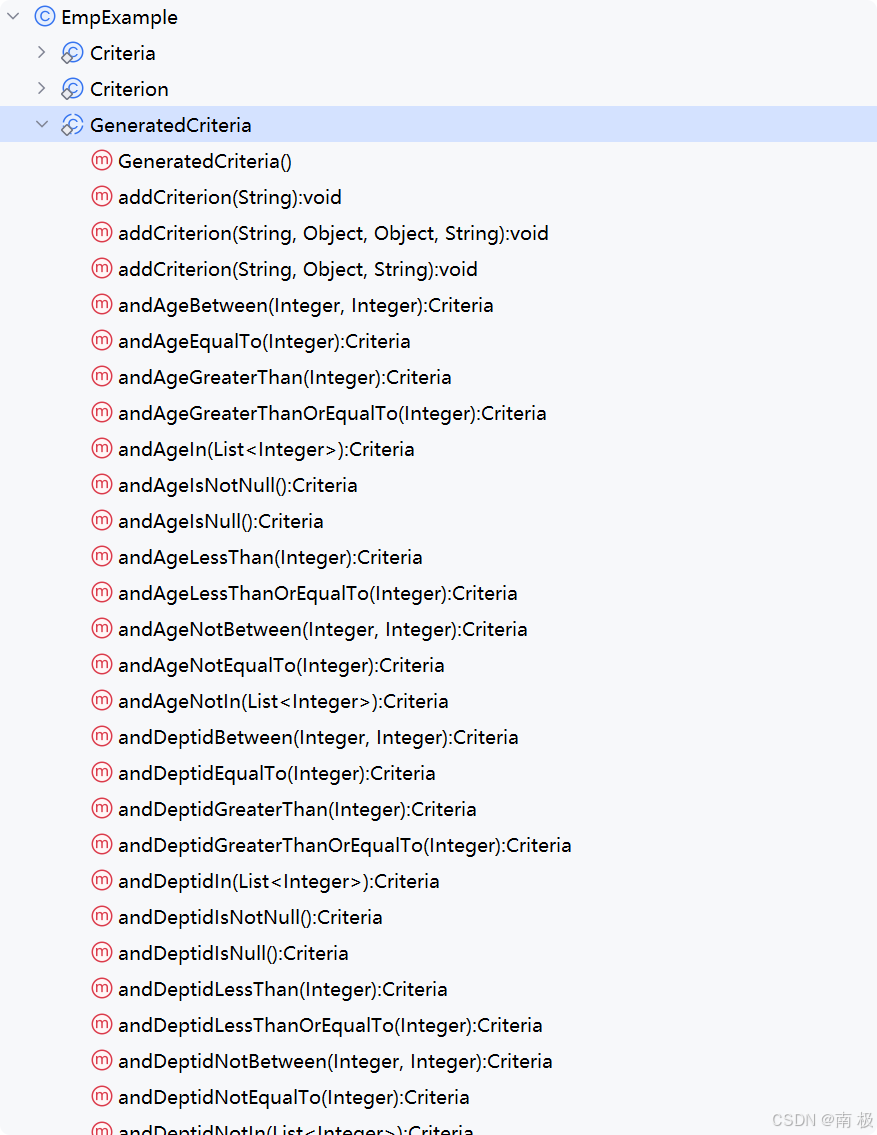
Mybatis逆向工程,动态创建实体类、条件扩展类、Mapper接口、Mapper.xml映射文件
今天呢,博主的学习进度也是步入了Java Mybatis 框架,目前正在逐步杨帆旗航。 那么接下来就给大家出一期有关 Mybatis 逆向工程的教学,希望能对大家有所帮助,也特别欢迎大家指点不足之处,小生很乐意接受正确的建议&…...

渲染学进阶内容——模型
最近在写模组的时候发现渲染器里面离不开模型的定义,在渲染的第二篇文章中简单的讲解了一下关于模型部分的内容,其实不管是方块还是方块实体,都离不开模型的内容 🧱 一、CubeListBuilder 功能解析 CubeListBuilder 是 Minecraft Java 版模型系统的核心构建器,用于动态创…...

对WWDC 2025 Keynote 内容的预测
借助我们以往对苹果公司发展路径的深入研究经验,以及大语言模型的分析能力,我们系统梳理了多年来苹果 WWDC 主题演讲的规律。在 WWDC 2025 即将揭幕之际,我们让 ChatGPT 对今年的 Keynote 内容进行了一个初步预测,聊作存档。等到明…...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...

【Zephyr 系列 10】实战项目:打造一个蓝牙传感器终端 + 网关系统(完整架构与全栈实现)
🧠关键词:Zephyr、BLE、终端、网关、广播、连接、传感器、数据采集、低功耗、系统集成 📌目标读者:希望基于 Zephyr 构建 BLE 系统架构、实现终端与网关协作、具备产品交付能力的开发者 📊篇幅字数:约 5200 字 ✨ 项目总览 在物联网实际项目中,**“终端 + 网关”**是…...
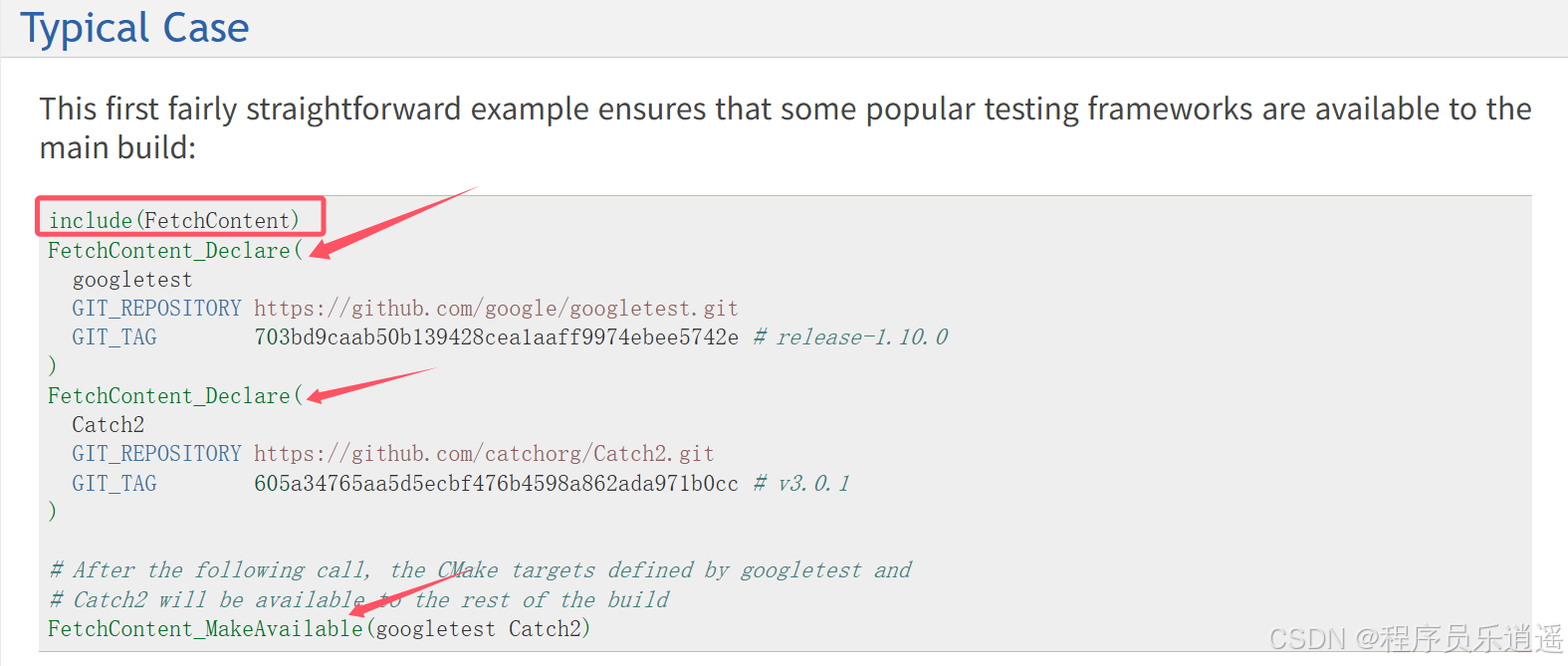
CMake 从 GitHub 下载第三方库并使用
有时我们希望直接使用 GitHub 上的开源库,而不想手动下载、编译和安装。 可以利用 CMake 提供的 FetchContent 模块来实现自动下载、构建和链接第三方库。 FetchContent 命令官方文档✅ 示例代码 我们将以 fmt 这个流行的格式化库为例,演示如何: 使用 FetchContent 从 GitH…...

A2A JS SDK 完整教程:快速入门指南
目录 什么是 A2A JS SDK?A2A JS 安装与设置A2A JS 核心概念创建你的第一个 A2A JS 代理A2A JS 服务端开发A2A JS 客户端使用A2A JS 高级特性A2A JS 最佳实践A2A JS 故障排除 什么是 A2A JS SDK? A2A JS SDK 是一个专为 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者设计的强大库ÿ…...
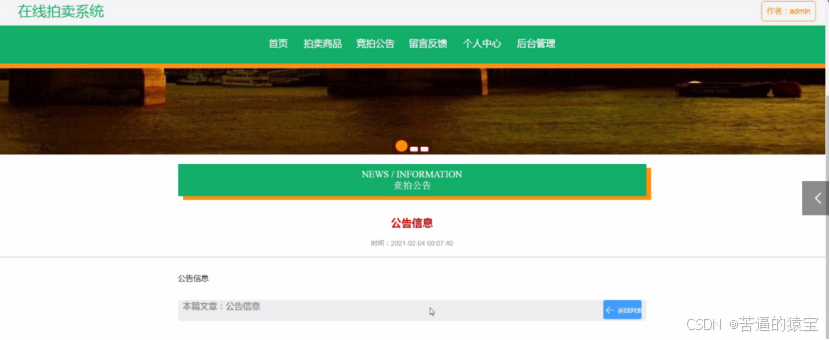
基于SpringBoot在线拍卖系统的设计和实现
摘 要 随着社会的发展,社会的各行各业都在利用信息化时代的优势。计算机的优势和普及使得各种信息系统的开发成为必需。 在线拍卖系统,主要的模块包括管理员;首页、个人中心、用户管理、商品类型管理、拍卖商品管理、历史竞拍管理、竞拍订单…...

JS手写代码篇----使用Promise封装AJAX请求
15、使用Promise封装AJAX请求 promise就有reject和resolve了,就不必写成功和失败的回调函数了 const BASEURL ./手写ajax/test.jsonfunction promiseAjax() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) > {const xhr new XMLHttpRequest();xhr.open("get&quo…...
